FSRSS-Net: High-Resolution Mapping of Buildings from Middle-Resolution Satellite Images Using a Super-Resolution Semantic Segmentation Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work on Super Resolution
2.1. Super-Resolution Semantic Segmentation
2.2. Image Super-Resolution Based on Deep Learning
2.3. Feature Deconvolution
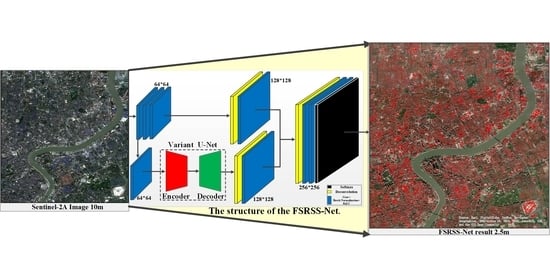
3. The Proposed Method for Super-Resolution Semantic Segmentation
3.1. The Structure of FSRSS-Net
3.2. A Variant of the U-Net Used in This Paper
4. Experimental Data
4.1. Data Source and Preprocessing
4.2. Dataset
4.3. Training Samples
5. Experiment and Discussion
5.1. Training Model
5.1.1. Experimental Setting
5.1.2. Training Accuracy and Loss
5.2. Quantitative Accuracy Evaluation and Comparison
5.3. Qualitative Analysis of the Generalization Ability
5.4. Discussion
5.4.1. Comparison between the 2.5 m Results of FSRSS-Net and the 2 m Recognition Results from GF2 Image
5.4.2. Comparison between FSRSS-Net and U-Net+2SR
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, X.; Cao, X.; Liao, A.; Chen, L.; Peng, S.; Lu, M.; Chen, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, H.; Han, G.; et al. Global mapping of artificial surfaces at 30-m resolution. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2016, 59, 2295–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momeni, R.; Aplin, P.; Boyd, D.S. Mapping Complex Urban Land Cover from Spaceborne Imagery: The Influence of Spatial Resolution, Spectral Band Set and Classification Approach. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martino, P.; Daniele, E.; Stefano, F.; Aneta, F.; Manuel, C.F.S.; Stamatia, H.; Maria, J.A.; Thomas, K.; Pierre, S.; Vasileios, S. Operating procedure for the production of the Global Human Settlement Layer from Landsat data of the epochs 1975, 1990, 2000, and 2014. JRC Tech. Rep. EUR 27741 EN. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshehhi, R.; Marpu, P.R.; Woon, W.L.; Mura, M.D. Simultaneous extraction of roads and buildings in remote sensing imagery with convolutional neural networks. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 130, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; He, C.; Fang, J.; Fu, H. Semantic Segmentation Based Building Extraction Method Using Multi-source GIS Map Datasets and Satellite Imagery. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW 2018), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 238–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hu, G.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, X.; Li, S.; Pei, F.; Wang, S. High-resolution multi-temporal mapping of global urban land using Landsat images based on the Google Earth Engine Platform. Remote Sens. Env. 2018, 209, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Liu, H.; Zhang, M.; Li, C.; Wang, J.; Huang, H.; Clinton, N.; Ji, L.; Bai, Y.; Chen, B.; et al. Stable classification with limited sample: Transferring a 30-m resolution sample set collected in 2015 to mapping 10-m resolution global land cover in 2017. Sci. Bull. 2019, 6, 370–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesaresi, M.; Ouzounis, G.K.; Gueguen, L. A new compact representation of morphological profiles: Report on first massive VHR image processing at the JRC. In Proc. SPIE 8390, Algorithms and Technologies for Multispectral, Hyperspectral, and Ultraspectral Imagery XVIII; SPIE: Baltimore, MD, USA, 24 May 2012; p. 839025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Wang, J.; Yu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, L.; Niu, Z.; Huang, X.; Fu, H.; Liu, S.; et al. Finer Resolution Observation and Monitoring of Global Land Cover: First Mapping Results with Landsat TM and ETM+ Data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 2607–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, Y.; Gong, P.; Giri, C. Global land cover mapping using earth observation satellite data: Recent progresses and challenges. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 103, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Li, C.; Zhao, Y.; Gong, P. A multi-resolution global land cover dataset through multisource data aggregation. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2014, 57, 2317–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, H.A.; Shao, X.A.; Iwao, K.; Shibasaki, R. Global urban area mapping in high resolution using aster satellite images. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2010, 38, 847–852. [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki, H.A.; Shao, X.; Iwao, K.; Shibasaki, R. An automated method for global urban area mapping by integrating aster satellite images and gis data. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. IEEE J. 2013, 6, 1004–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esch, T.; Heldens, W.; Hirner, A.; Keil, M.; Marconcini, M.; Roth, A.; Zeidler, J.; Dech, S.; Strano, E. Breaking New Ground in Mapping Human Settlements from Space-The Global Urban Footprint. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 134, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbane, C.; Pesaresi, M.; Politis, P.; Syrris, V.; Florczyk, A.J.; Soille, P.; Maffenini, L.; Burger, A.; Vasilev, V.; Rodriguez, D. Big earth data analytics on sentinel-1 and landsat imagery in support to global human settlements mapping. Big Earth Data 2017, 1, 118–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbane, C.; Pesaresi, M.; Kemper, T.; Politis, P.; Syrris, V.; Florczyk, A.J.; Soille, P.; Maffenini, L.; Burger, A.; Vasilev, V.; et al. Automated Global Delineation of Human Settlements from 40 Years of Landsat Satellite Data Archives. Big Earth Data 2019, 3, 140–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbane, C.; Sabo, F.; Syrris, V.; Kemper, T.; Politis, P.; Pesaresi, M.; Soille, P.; Osé, K. Application of the Symbolic Machine Learning to Copernicus VHR Imagery: The European Settlement Map. Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 17, 1153–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bing Maps Team. Microsoft Releases 125 million Building Footprints in the US as Open Data. Bing Blog. 28 June 2018. Available online: https://blogs.bing.com/maps/2018-06/microsoft-releases-125-million-building-footprints-in-the-us-as-open-data (accessed on 9 June 2021).
- Bonafilia, D.; Yang, D.; Gill, J.; Basu, S. Building High Resolution Maps for Humanitarian Aid and Development with Weakly- and Semi-Supervised Learning. Computer Vision for Global Challenges Workshop at CVPR. 2019. Available online: https://research.fb.com/publications/building-high-resolution-maps-for-humanitarian-aid-and-development-with-weakly-and-semi-supervised-learning/ (accessed on 9 June 2021).
- Pesaresi, M.; Syrris, V.; Julea, A. A New Method for Earth Observation Data Analytics Based on Symbolic Machine Learning. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesaresi, M.; Guo, H.; Blaes, X.; Ehrlich, D.; Ferri, S.; Gueguen, L.; Halkia, M.; Kauffmann, M.; Kemper, T.; Lu, L.; et al. A Global Human Settlement Layer From Optical HR/VHR RS Data: Concept and First Results. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. IEEE J. 2013, 6, 2102–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Xia, G.; Lu, Q.; Shen, H.; Li, S.; You, S.; Zhang, L. Land-cover classification with high-resolution remote sensing images using transferable deep models. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 237, 111322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, K. Super-Resolution via Deep Learning. Digit. Signal Process. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Hoi, S. Deep Learning for Image Super-resolution: A Survey. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1902.06068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Loy, C.C.; He, K.; Tang, X. Learning a Deep Convolutional Network for Image Super-Resolution. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 184–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Loy, C.C.; Tang, X. Accelerating the super-resolution convolutional neural network. Comput. Sci.-CVPR 2016, 391–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Caballero, J.; Huszár, F.; Totz, J.; Wang, Z. Real-time single image and video super-resolution using an efficient sub-pixel convolutional neural network. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1609.05158. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. IEEE CVPR 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, K.J.; Lee, M.K. Accurate Image Super-Resolution Using Very Deep Convolutional Networks. 2016 IEEE CVPR 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledig, C.; Theis, L.; Huszar, F.; Caballero, J.; Cunningham, A.; Acosta, A.; Aitken, A.; Tejani, A.; Totz, J.; Wang, Z.H.; et al. Photo-realistic single image super-resolution using a generative adversarial network. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1609.04802. [Google Scholar]
- Pathak, H.N.; Li, X.; Minaee, S.; Cowan, B. Efficient Super Resolution for Large-Scale Images Using Attentional GAN. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1812.04821. [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa, A.; Khan, S.H.; Hayat, M.; Shen, J.B.; Shao, L. Image Super-Resolution as a Defense Against Adversarial Attacks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1901.01677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargiulo, M. Advances on CNN-based super-resolution of Sentinel-2 images. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1902.02513. [Google Scholar]
- Castelluccio, M.; Poggi, G.; Sansone, C.; Verdoliva, L. Land Use Classification in Remote Sensing Images by Convolutional Neural Networks. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 28, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luc, P.; Couprie, C.; Chintala, S.; Verbeek, J. Semantic Segmentation using Adversarial Networks. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1611.08408. [Google Scholar]
- Evo, I.; Avramovi, A. Convolutional neural network based automatic object detection on aerial images. IEEE Geoence Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 740–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. PAMI 2014, 39, 640–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, H.; Hong, S.; Han, B. Learning Deconvolution Network for Semantic Segmentation. ICCV 2015, arXiv:1505.04366. [Google Scholar]
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. Segnet: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. PAMI 2017, 39, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE Trans. PAMI 2018, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1505.04597. [Google Scholar]
- Zeiler, M.D.; Fergus, R. Visualizing and Understanding Convolutional Networks. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1311.2901. [Google Scholar]
- Zeiler, M.D.; Krishnan, D.; Taylor, G.W.; Fergus, R. Deconvolutional networks. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zeiler, M.D.; Taylor, G.W.; Fergus, R. Adaptive deconvolutional networks for mid and high level feature learning. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, 6–13 November 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, Y.; Vladlen, K. Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1511.07122. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Tang, H. Evaluating the generalization ability of convolutional neural networks for built-up area extraction in different cities of china. Optoelectron. Lett. 2020, 16, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Tang, H. A Comprehensive Evaluation of Approaches for Built-Up Area Extraction from Landsat OLI Images Using Massive Samples. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
























| Prediction | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ground Truth | Background | Building | Sum | |
| Background | True Negative (TN) | False Positive (FP) | Actual Background (TN+FP) | |
| Building | False Negative (FN) | True Positive (TP) | Actual building (FN+TP) | |
| Sum | Predicted Background (TN+FN) | Predicted building (FP+TP) | TN+ TP+ FN+ FP | |
| Evaluation Regions | OA | Rec | Pre | F1 | IOU | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chongqing (236 samples, 17.22% building pixels) | U-Net 10 m result | 82.26 | 42.50 | 44.09 | 43.28 | 27.93 |
| U-Net 10 m result interpolation up-sampling to 2.5 m | 81.77 | 41.09 | 42.67 | 41.87 | 26.80 | |
| FSRSS-Net 2.5 m result | 82.80 | 39.63 | 44.80 | 42.06 | 26.94 | |
| Qingdao (206 samples, 20.21% building pixels) | U-Net 10 m result | 79.02 | 37.18 | 43.46 | 40.07 | 25.63 |
| U-Net 10 m result interpolation up-sampling to 2.5 m | 78.95 | 36.62 | 42.98 | 39.54 | 25.15 | |
| FSRSS-Net 2.5 m result | 80.48 | 39.15 | 47.55 | 42.94 | 27.80 | |
| Shanghai (225 samples, 21.71% building pixels) | U-Net 10 m result | 80.83 | 53.31 | 53.08 | 53.20 | 36.35 |
| U-Net 10 m result interpolation up-sampling to 2.5 m | 79.79 | 50.75 | 50.53 | 50.64 | 34.09 | |
| FSRSS-Net 2.5 m result | 81.91 | 51.56 | 55.95 | 53.67 | 36.70 | |
| Wuhan (99 samples, 22.40% building pixels) | U-Net 10 m result | 76.61 | 41.46 | 45.01 | 43.16 | 27.72 |
| U-Net 10 m result interpolation up-sampling to 2.5 m | 76.08 | 40.20 | 43.74 | 41.90 | 26.72 | |
| FSRSS-Net 2.5 m result | 77.04 | 39.07 | 45.54 | 42.06 | 26.88 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, T.; Tang, H.; Ding, Y.; Li, P.; Ji, C.; Xu, P. FSRSS-Net: High-Resolution Mapping of Buildings from Middle-Resolution Satellite Images Using a Super-Resolution Semantic Segmentation Network. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2290. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13122290
Zhang T, Tang H, Ding Y, Li P, Ji C, Xu P. FSRSS-Net: High-Resolution Mapping of Buildings from Middle-Resolution Satellite Images Using a Super-Resolution Semantic Segmentation Network. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(12):2290. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13122290
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Tao, Hong Tang, Yi Ding, Penglong Li, Chao Ji, and Penglei Xu. 2021. "FSRSS-Net: High-Resolution Mapping of Buildings from Middle-Resolution Satellite Images Using a Super-Resolution Semantic Segmentation Network" Remote Sensing 13, no. 12: 2290. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13122290
APA StyleZhang, T., Tang, H., Ding, Y., Li, P., Ji, C., & Xu, P. (2021). FSRSS-Net: High-Resolution Mapping of Buildings from Middle-Resolution Satellite Images Using a Super-Resolution Semantic Segmentation Network. Remote Sensing, 13(12), 2290. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13122290