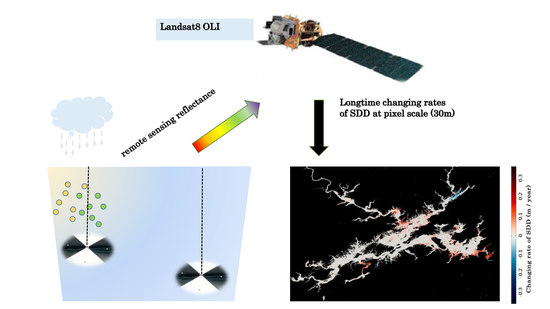
Monitoring Changes in the Transparency of the Largest Reservoir in Eastern China in the Past Decade, 2013–2020
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Used in Research
2.1.1. In Situ Data
2.1.2. Satellite Data
2.2. Analysis Method
2.2.1. The Matchup Method between Satellite and In Situ Data
2.2.2. SDD Algorithms Construction Approaches
2.2.3. Statistical Parameters
3. Results
3.1. Algorithm Construction and Validation
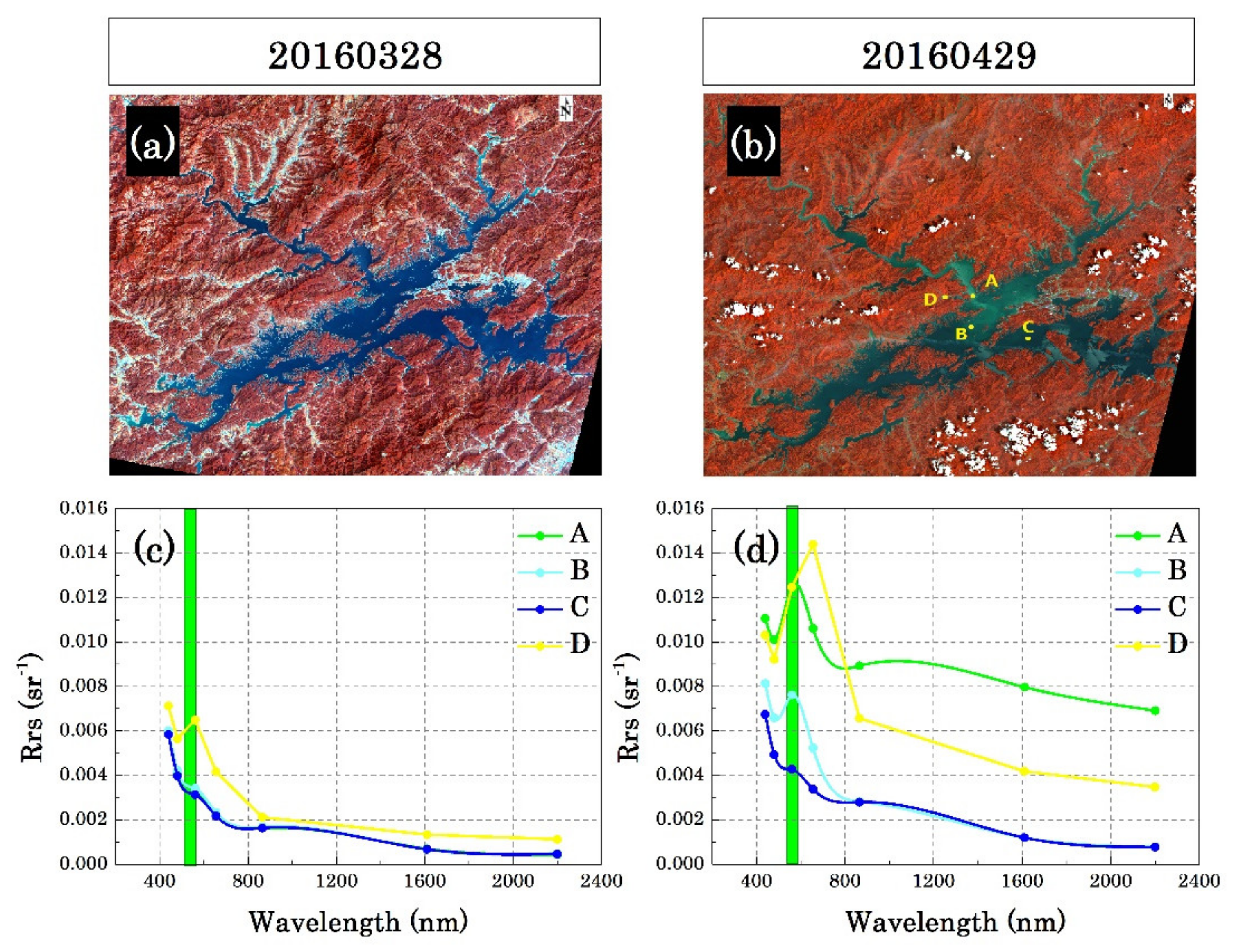
3.1.1. Spectral Feature Analysis
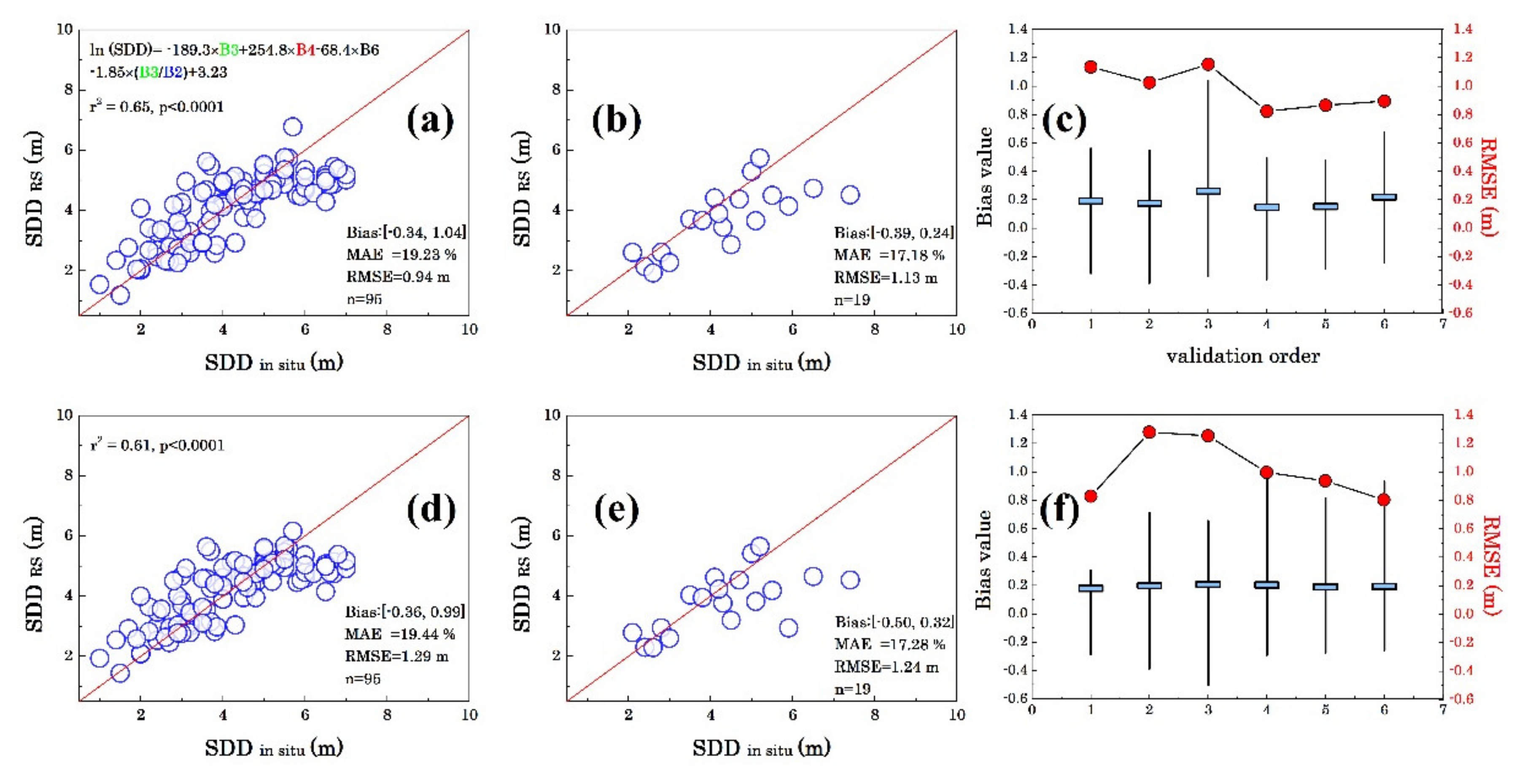
3.1.2. Algorithm Evaluation
3.2. Spatiotemporal Variation of SDD in the Qiandao Lake
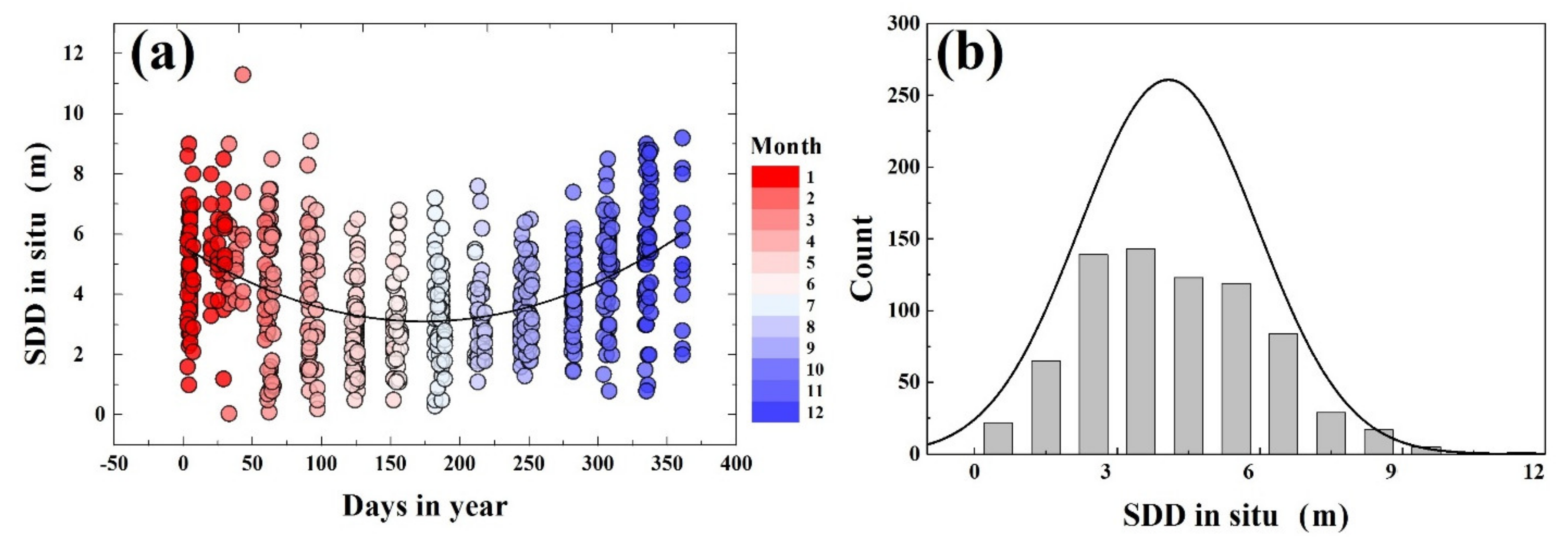
3.2.1. Intra-Annual Variability
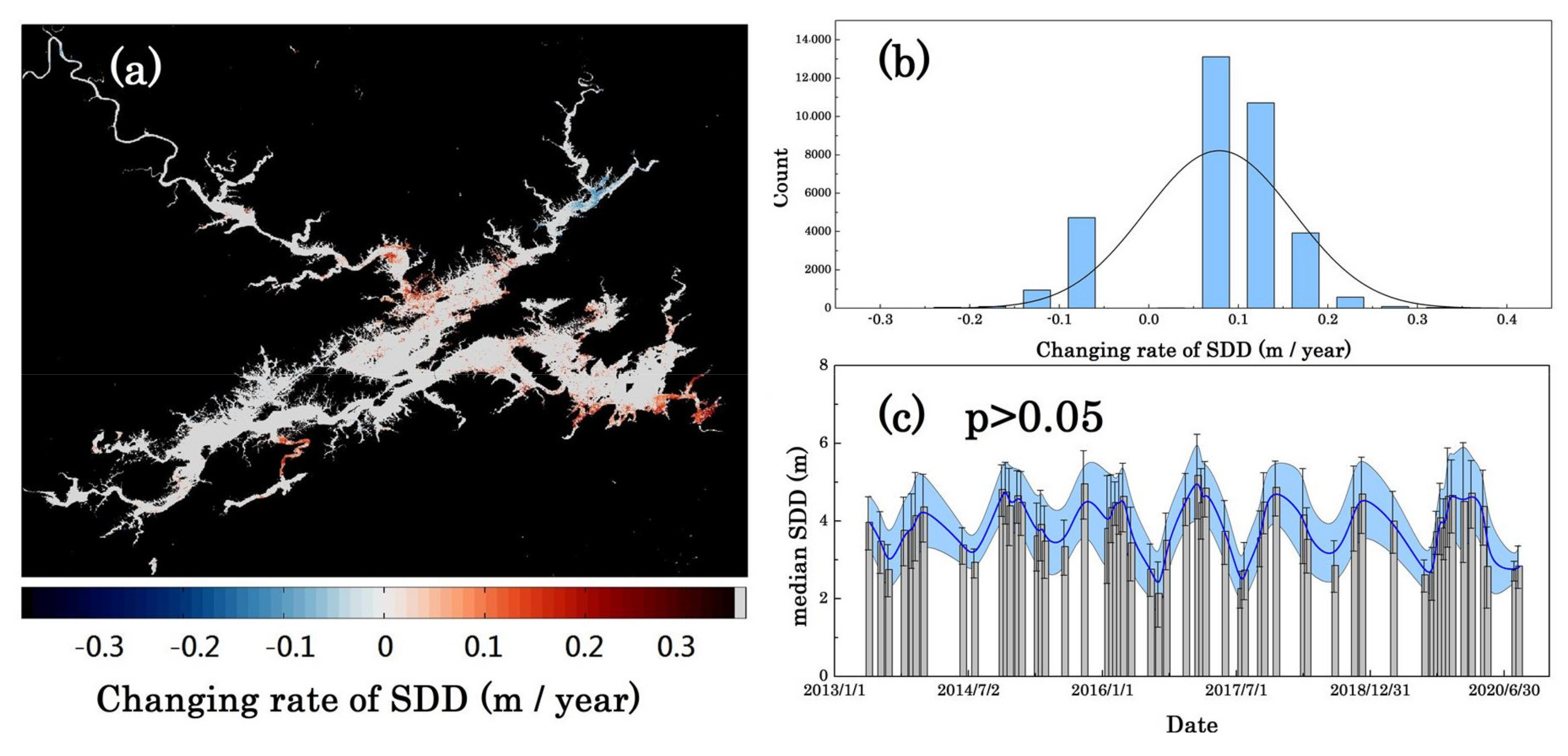
3.2.2. Inter-Annual Variability
3.3. SDD Changes under Heavy Rainfall Event in 2020
4. Discussion
4.1. Algorithm Uncertainty
4.2. Long-Term SDD Changes
4.3. Impact of Heavy Rainfall on SDD Changes in the Qiandao Lake
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Assessment, M.E. Ecosystems and Human Well-Being: Synthesis, 1st ed.; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; pp. 40–150. [Google Scholar]
- Williamson, C.E.; Saros, J.E. What Do Lakes and Reservoirs Tell Us About Climate Change?: Proceedings of the Chapman Conference on Lakes as Sentinels, Integrators, and Regulators of Climate Change, Incline Village, Nevada, USA, 8–10 September 2008. EOS Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2008, 89, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tranvik, L.J.; Downing, J.A.; Cotner, J.B.; Loiselle, S.A.; Striegl, R.G.; Ballatore, T.J.; Dillon, P.; Finlay, K.; Fortino, K.; Knoll, L.B.; et al. Lakes and Reservoirs as Regulators of Carbon Cycling and Climate. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 2298–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blenckner, T. Climate Change Effects on Lakes. In Encyclopedia of Lakes and Reservoirs; Bengtsson, L., Herschy, R.W., Fairbridge, R.W., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 165–167. [Google Scholar]
- Williamson, C.E.; Saros, J.E.; Vincent, W.F.; Smol, J.P. Lakes and Reservoirs as Sentinels, Integrators, and Regulators of Climate Change. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 2273–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolway, R.I.; Weyhenmeyer, G.A.; Schmid, M.; Dokulil, M.T.; de Eyto, E.; Maberly, S.C.; May, L.; Merchant, C.J. Substantial Increase in Minimum Lake Surface Temperatures under Climate Change. Clim. Chang. 2019, 155, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schneider, P.; Hook, S.J.; Radocinski, R.G.; Corlett, G.K.; Hulley, G.C.; Schladow, S.G.; Steissberg, T.E. Satellite Observations Indicate Rapid Warming Trend for Lakes in California and Nevada. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, J.A.; Colman, S.M. Lake Superior Summer Water Temperatures are Increasing more Rapidly than Regional Air Temperatures: A positive Ice-albedo Feedback. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhu, G.; Qin, B.; Gao, G. Long-Term MODIS Observations of Cyanobacterial Dynamics in Lake Taihu: Responses to Nutrient Enrichment and Meteorological Factors. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, G.; Qin, B.; Pan, D. Deteriorating Water Clarity in Shallow Waters: Evidence from Long Term MODIS and In-situ Observations. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 68, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jeppesen, E.; Liu, X.; Qin, B.; Shi, K.; Zhou, Y.; Thomaz, S.M.; Deng, J. Global Loss of Aquatic Vegetation in Lakes. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2017, 173, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzel, R.G. 5-LIGHT IN INLAND WATERS. In Limnology, 3rd ed.; Wetzel, R.G., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2001; pp. 49–69. [Google Scholar]
- Mobley, C.D.; Preisendorfer, R.W. Light and Water: Radiative Transfer in Natural Waters; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Z.; Shang, S.; Hu, C.; Du, K.; Weidemann, A.; Hou, W.; Lin, J.; Lin, G. Secchi Disk Depth: A new Theory and Mechanistic Model for Underwater Visibility. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 169, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, D.; Duan, H.; Loiselle, S.; Hu, C.; Zhang, G.; Li, J.; Yang, H.; Thompson, J.R.; Cao, Z.; Shen, M.; et al. Observations of Water Transparency in China’s Lakes from Space. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2020, 92, 102187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, M.R.; Kuring, N.; Yentsch, C. Global Patterns of Ocean Transparency: Implications for the New Production of the Open Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1988, 93, 6847–6856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Pan, D.; Bai, Y.; Wang, T.; Chen, C.-T.A.; Zhu, Q.; Hao, Z.; Gong, F. Recent Changes of Global Ocean Transparency Observed by SeaWiFS. Cont. Shelf Res. 2017, 143, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, J.E. The Secchi Disc. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1968, 13, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernand, M.R. On the History of the Secchi Disc. J. Eur. Opt. Soc. Rapid Publ. 2010, 5, 10013s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pitarch, J. A Review of Secchi’s Contribution to Marine Optics and the Foundation of Secchi Disk Science. Oceanography 2020, 33, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erlandsson, C.P.; Stigebrandt, A. Increased Utility of the Secchi Disk to Assess Eutrophication in Coastal Waters with Freshwater Run-off. J. Mar. Syst. 2006, 60, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyce, D.G.; Lewis, M.; Worm, B. Integrating Global Chlorophyll Data from 1890 to 2010. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2012, 10, 840–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, B.; Lee, Z.; Spyrakos, E.; Feng, L.; Liu, C.; Zhao, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, L.; et al. Changes of Water Clarity in Large Lakes and Reservoirs across China Observed from Long-term MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 247, 111949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Liu, G.; Wang, Q.; Wen, Z.; Lyu, L.; Du, Y.; Sha, L.; Fang, C. Quantification of Lake Clarity in China using Landsat OLI Imagery data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 243, 111800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, M.; Shi, K.; Yu, Z. Seasonal-Spatial Distribution and Long-Term Variation of Transparency in Xin’anjiang Reservoir: Implications for Reservoir Management. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 9492–9507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Feng, Q.; Gong, J.; Hu, Z.; Hu, M. Inversion of Chlorophyll-a Concentration Based on Satellite Remote Sensing in Qiandao Lake. Acta Laser Biol. Sin. 2015, 24, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Hu, Z.; Liu, Q.; Ren, L.; Chen, L.; Li, P. Evaluation of Water Quality by Two Trophic State Indices in Lake Qiandaohu during 2007–2011. J. Shanghai Ocean Univ. 2013, 22, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Mao, F.; Jin, P.; Cheng, Q. Spatial-temporal Variations of Chlorophyll-a in Qiandao Lake using GF1_WFV Data. China Environ. Sci. 2020, 40, 4580–4588. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zha, Y.; Shi, K.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, M. Remote Sensing Estimation of Total Suspended Matter Concentration in Xin’anjiang Reservoir Using Landsat 8 Data. Environ. Sci. 2015, 36, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, R.E. A Trophic State Index for Lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1977, 22, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, M.; Zhu, G.; Wu, Z.; Liu, M. Effects of Rainfall on Thermal Stratification and Dissolved Oxygen in a Deep Drinking Water Reservoir. Hydrol. Process. 2020, 34, 3387–3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, K.; Zhang, Y.; Moreno-Madriñán, M.J.; Zhu, G.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y. River Plume Monitoring in a Deep Valley Reservoir using HJ-1 A/B Images. J. Hydrol. 2020, 587, 125031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Liu, M.; He, J.; Shi, K.; Wang, M.; Yu, Z. Thermal Structure and Response to Long-term Climatic Changes in Lake Qiandaohu, a Deep Subtropical Reservoir in China. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2014, 59, 1193–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, K.; Zhou, Y.; Li, N. Remote Sensing Estimation of Water Clarity for Various Lakes in China. Water Res. 2021, 192, 116844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, J.L.; Fargion, G.S.; McClain, C.R.; Pegau, S.; Zanefeld, J.; Mitchell, B.G.; Kahru, M.; Wieland, J.; Stramska, M. Inherent Optical Properties: Instruments, Characterizations, Field Measurements and Data Analysis Protocols. In Ocean Optics Protocols for Satellite Ocean Color Sensor Validation; NASA, Ed.; Goddard Space Flight Space Center: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2003; Volume IV, pp. 1–84. [Google Scholar]
- Cooley, T.; Anderson, G.; Felde, G.W.; Hoke, M.; Ratkowski, A.J.; Chetwynd, J.; Gardner, J.; Adler-Golden, S.; Matthew, M.; Berk, A.; et al. FLAASH, a MODTRAN4-based Atmospheric Correction Algorithm, its Application and Validation. IEEE Int. Geosci. Remote. Sens. Symp. 2002, 3, 1414–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, S.W.; Werdell, P.J. A Multi-sensor Approach for the On-orbit Validation of Ocean Color Satellite Data Products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 102, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khullar, S.; Singh, N. Machine Learning Techniques in River Water Quality Modelling: A Research Travelogue. Water Supply 2020, 21, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholizadeh, M.H.; Melesse, A.M.; Reddi, L. A Comprehensive Review on Water Quality Parameters Estimation Using Remote Sensing Techniques. Sensors 2016, 16, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, Z.; Carder, K.L.; Arnone, R.A. Deriving Inherent Optical Properties from Water Color: A Multiband Quasi-analytical Algorithm for Optically Deep Waters. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 5755–5772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werdell, P.J.; McKinna, L.I.W.; Boss, E.; Ackleson, S.G.; Craig, S.E.; Gregg, W.W.; Lee, Z.; Maritorena, S.; Roesler, C.S.; Rousseaux, C.S.; et al. An Overview of Approaches and Challenges for Retrieving Marine Inherent Optical Properties from Ocean Color Remote Sensing. Prog. Oceanogr. 2018, 160, 186–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doron, M.; Babin, M.; Hembise, O.; Mangin, A.; Garnesson, P. Ocean Transparency from Space: Validation of Algorithms Estimating Secchi Depth using MERIS, MODIS and SeaWiFS Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2986–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloiber, S.M.; Brezonik, P.L.; Olmanson, L.G.; Bauer, M.E. A Procedure for Regional Lake Water Clarity Assessment using Landsat Multispectral Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 82, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutsch, E.S.; Cardille, J.A.; Koll-Egyed, T.; Fortin, M.-J. Landsat 8 Lake Water Clarity Empirical Algorithms: Large-Scale Calibration and Validation Using Government and Citizen Science Data from across Canada. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmanson, L.G.; Bauer, M.E.; Brezonik, P.L. A 20-year Landsat Water Clarity Census of Minnesota’s 10,000 lakes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 4086–4097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niroumand-Jadidi, M.; Bovolo, F.; Bruzzone, L. Novel Spectra-Derived Features for Empirical Retrieval of Water Quality Parameters: Demonstrations for OLI, MSI, and OLCI Sensors. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote 2019, 57, 10285–10300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, H.J.; Lutz, D.A.; Steele, B.G.; Cottingham, K.L.; Weathers, K.C.; Ducey, M.J.; Palace, M.; Johnson, K.M.; Chipman, J.W. Remote Sensing of Lake Water Clarity: Performance and Transferability of Both Historical Algorithms and Machine Learning. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.; Shang, S.; Du, K.; Wei, J. Resolving the Long-standing Puzzles about the Observed Secchi Depth Relationships. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2018, 63, 2321–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alikas, K.; Kratzer, S. Improved Retrieval of Secchi Depth for Optically-complex Waters using Remote Sensing Data. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 77, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, N.; Haque, M.O.; Leigh, L.; Aaron, D.; Helder, D.; Markham, B. Radiometric Cross Calibration of Landsat 8 Operational Land Imager (OLI) and Landsat 7 Enhanced Thematic Mapper Plus (ETM+). Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 12619–12638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Feng, L.; Zhao, D.; Lu, J. Assessment of Landsat Atmospheric Correction Methods for Water Color Applications using Global AERONET-OC Data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2020, 93, 102192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Ma, R.; Xue, K.; Loiselle, S. The Assessment of Landsat-8 OLI Atmospheric Correction Algorithms for Inland Waters. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, X.; Bai, Y.; Pan, D.; Tang, J.; Wang, D. Atmospheric Correction of Satellite Ocean Color Imagery using the Ultraviolet Wavelength for Highly Turbid Waters. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 20754–20770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Duan, H.; Yu, S.; Shen, M.; Xue, K. Human-induced Eutrophication Dominates the Bio-optical Compositions of Suspended Particles in Shallow Lakes: Implications for Remote Sensing. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 667, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachauri, R.K.; Allen, M.R.; Barros, V.R.; Broome, J.; Cramer, W.; Christ, R.; Church, J.A.; Clarke, L.; Dahe, Q.D.; Dasqupta, P.; et al. Climate Change 2014 Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II, and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, G.; Gong, Z.; Deng, J.; Hamilton, D.P.; Gao, G.; Shi, K.; Zhou, J.; Shao, K.; et al. Are Nitrogen-to-phosphorus Ratios of Chinese Lakes Actually Increasing? Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 21000–21002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Qin, B.; Shi, K.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, J.; Wild, M.; Li, L.; Zhou, Y.; Yao, X.; Liu, M.; et al. Radiation Dimming and Decreasing Water Clarity Fuel Underwater Darkening in Lakes. Sci. Bull. 2020, 65, 1675–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Song, C.; Wang, J.; Ke, L. China’s Inland Water Dynamics: The Significance of Water Body Types. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 13876–13878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Zhu, L.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Ju, J.; Qiao, B.; Ma, Q.; Wang, S. The Increasing Water Clarity of Tibetan Lakes over Last 20 Years according to MODIS Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 253, 112199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, W.; Cao, C.; Zhang, F.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, B. A Dataset of Remote-sensed Forel-Ule Index for Global Inland Waters during 2000–2018. Sci. Data 2021, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moges, M.A.; Schmitter, P.; Tilahun, S.A.; Ayana, E.K.; Ketema, A.A.; Nigussie, T.E.; Steenhuis, T.S. Water Quality Assessment by Measuring and Using Landsat 7 ETM+ Images for the Current and Previous Trend Perspective: Lake Tana Ethiopia. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2017, 9, 1564–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naumenko, M.A. Seasonality and Trends in the Secchi Disk Transparency of Lake Ladoga. Hydrobiologia 2008, 599, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Feng, L.; Duan, H.; Chen, X.; Sun, D.; Shi, K. Fifteen-year Monitoring of the Turbidity Dynamics in Large Lakes and Reservoirs in the Middle and Lower Basin of the Yangtze River, China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 190, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topp, S.N.; Pavelsky, T.M.; Stanley, E.H.; Yang, X.; Griffin, C.G.; Ross, M.R.V. Multi-decadal Improvement in US Lake Water Clarity. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 055025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Feng, L.; Hou, X.; Schurgers, G.; Zheng, Y.; Tang, J. Eutrophication Changes in Fifty Large Lakes on the Yangtze Plain of China Derived from MERIS and OLCI observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 246, 111890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, M.; Zhou, L.; Jang, K.-S.; Xu, H.; Shi, K.; Zhu, G.; Liu, M.; Deng, J.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Rainstorm Events Shift the Molecular Composition and Export of Dissolved Organic Matter in a Large Drinking Water Reservoir in China: High frequency buoys and field observations. Water Res. 2020, 187, 116471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Zhang, Y.; Song, K.; Liu, M.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhu, G.; Qin, B. A Semi-analytical Approach for Remote Sensing of Trophic State in Inland Waters: Bio-optical Mechanism and Application. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 232, 111349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Wu, S.; Sha, H.; Wu, X.; Yang, Q.; Lv, X.; Zhu, S.; Xue, W.; Wang, F.; Chen, D. Lacustrine Micro-ecosystem Responses to the Inflow Discharge Gradient of Water Diversion from Yangtze River to Lake Taihu. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 1021–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullough, I.M.; Loftin, C.S.; Sader, S.A. Landsat Imagery Reveals Declining Clarity of Maine’s Lakes during 1995–2010. Freshw. Sci. 2013, 32, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peckham, S.D.; Lillesand, T.M. Detection of Spatial and Temporal Trends in Wisconsin Lake Water Clarity Using Landsat-derived Estimates of Secchi Depth. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2006, 22, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Shi, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Liu, M.; Guo, Y.; Li, N. Analysis of Water Clarity Decrease in Xin’anjiang Reservoir, China, from 30-Year Landsat TM, ETM+, and OLI Observations. J. Hydrol. 2020, 590, 125476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.R.; Fulweiler, R.W.; Li, C.Y.; Bargu, S.; Walker, N.D.; Twilley, R.R.; Green, S.E. Mississippi River Flood of 2008: Observations of a Large Freshwater Diversion on Physical, Chemical, and Biological Characteristics of a Shallow Estuarine Lake. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 5599–5604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, M.; Zhai, W.; Cai, W.; Callahan, J.; Huang, B.; Shang, S.; Huang, T.; Li, X.; Lu, Z.; Chen, W. Effects of An Estuarine Plume-associated Bloom on the Carbonate System in the Lower Reaches of the Pearl River Estuary and the Coastal Zone of the Northern South China Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 2008, 28, 1416–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.; Pan, D.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Liu, D. The Analysis of Phytoplankton Blooms off the Yangtze River Estuary in the Spring of 2007. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2014, 17, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrenfeld, M.J.; Boss, E.S. Student’s Tutorial on Bloom Hypotheses in the Context of Phytoplankton Annual Cycles. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2018, 24, 55–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Pan, D.; Xianqiang, H.E.; Bai, Y.; Wang, D. Upper Ocean Responses to Category 5 Typhoon Megi in the Western North Pacific. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2012, 31, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Tang, D.; Wang, Y. Comparison of Phytoplankton Blooms Triggered by Two Typhoons with Different Intensities and Translation Speeds in the South China Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 365, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
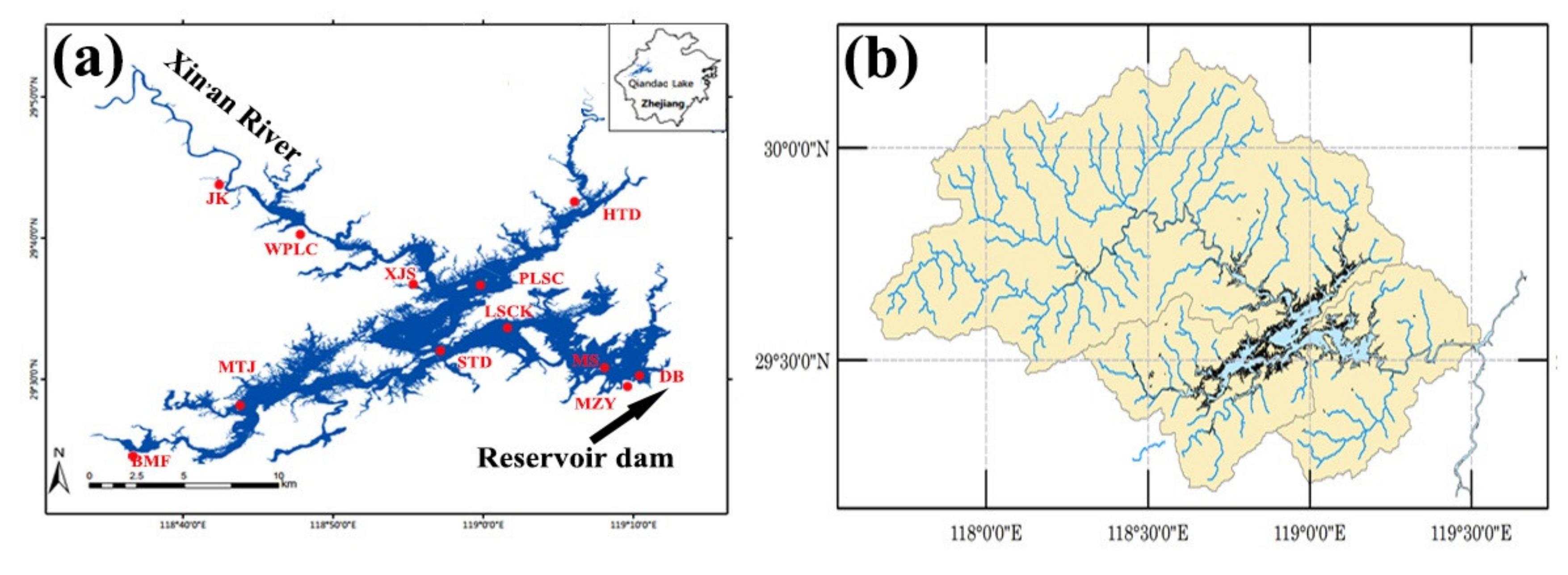




| Stations | Latitude | Longitude | Number of Measurements |
|---|---|---|---|
| JK | 29.72°N | 118.72°E | 81 |
| XJS | 29.62°N | 118.94°E | 82 |
| STD | 29.50°N | 118.97°E | 82 |
| DB | 29.51°N | 119.21°E | 82 |
| MTJ | 29.47°N | 118.75°E | 82 |
| HTD | 29.71°N | 119.12°E | 77 |
| WPLC | 29.67°N | 118.83°E | 40 |
| LSCK | 29.56°N | 119.05°E | 23 |
| MS | 29.51°N | 119.15°E | 23 |
| MZY | 29.50°N | 119.18°E | 23 |
| BMF | 29.42°N | 118.63°E | 51 |
| PLSC | 29.61°N | 119.03°E | 33 |
| Band ID | Band Type | Bandwidth (nm) | Main Uses in Watercolor Research |
|---|---|---|---|
| Band 1 | Coastal/Aerosol | 433–453 | Coastal water and aerosol monitoring |
| Band 2 | Blue | 450–515 | Suspended materials monitoring |
| Band 3 | Green | 525–600 | |
| Band 4 | Red | 630–680 | |
| Band 5 | Near-infrared | 845–885 | Atmospheric correction |
| Band 6 | Shortwave infrared | 1560–1660 | |
| Band 7 | Shortwave infrared | 2100–2300 | |
| Band 8 | Panchromatic | 500–680 | Water boundary recognition |
| Band 9 | Cirrus | 1360–1390 | Cirrus monitoring |
| Lake Location | SDD Changing Rates | References |
|---|---|---|
| Tibetan Plateau, China | 0.033 m/year between 2000 and 2019. | Liu, et al. [59] |
| Lake Ladoga, Europe | −0.02 m/year during 1905–2003. | Naumenko [62] |
| Minnesota, USA | Remained stable over the period 1985–2005. | Olmanson, et al. [45] |
| Maine, USA | −0.04 m/year during 1995–2010. | McCullough, et al. [69] |
| Wisconsin, USA | 0.04 m/year during 1980–2000. | Peckham and Lillesand [70] |
| USA | 0.005 m/year from 1984 to 2020. | Topp, et al. [64] |
| Qiandao Lake | −0.006 m/year during 1986–2016. | Li, et al. [71] |
| −0.08 m/year during 1988–2013. | Wu, et al. [25] | |
| 0.9% area changed −0.09 m/year 4.42% area changed 0.11 m/year during 2013–2020. | This research |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, T.; Zhu, B.; Cao, F.; Sun, H.; He, X.; Liu, M.; Gong, F.; Bai, Y. Monitoring Changes in the Transparency of the Largest Reservoir in Eastern China in the Past Decade, 2013–2020. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2570. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13132570
Li T, Zhu B, Cao F, Sun H, He X, Liu M, Gong F, Bai Y. Monitoring Changes in the Transparency of the Largest Reservoir in Eastern China in the Past Decade, 2013–2020. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(13):2570. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13132570
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Teng, Bozhong Zhu, Fei Cao, Hao Sun, Xianqiang He, Mingliang Liu, Fang Gong, and Yan Bai. 2021. "Monitoring Changes in the Transparency of the Largest Reservoir in Eastern China in the Past Decade, 2013–2020" Remote Sensing 13, no. 13: 2570. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13132570
APA StyleLi, T., Zhu, B., Cao, F., Sun, H., He, X., Liu, M., Gong, F., & Bai, Y. (2021). Monitoring Changes in the Transparency of the Largest Reservoir in Eastern China in the Past Decade, 2013–2020. Remote Sensing, 13(13), 2570. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13132570