Urban Sprawl and Changes in Land-Use Efficiency in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Region, China from 2000 to 2020: A Spatiotemporal Analysis Using Earth Observation Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Datasets
2.1. Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Region
2.2. Datasets
2.2.1. Landsat Imagery
2.2.2. Built-Up Area Products
2.2.3. Population Data
2.2.4. Ancillary Datasets
3. Methodology
3.1. Built-Up Area Extraction
3.2. Accuracy Assessment
3.3. Urban Growth Analysis
3.3.1. Functional City Boundary
3.3.2. Change in Urban Built-Up Area
3.3.3. Change in Urban Form
3.4. Derivation of LCR, PGR and LCRPGR
4. Results
4.1. Accuracy Assessment
4.2. Urban Growth Analysis
4.2.1. Changes in Urban Built-Up Area
4.2.2. Changes in Urban Form
4.3. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of SDG 11.3.1
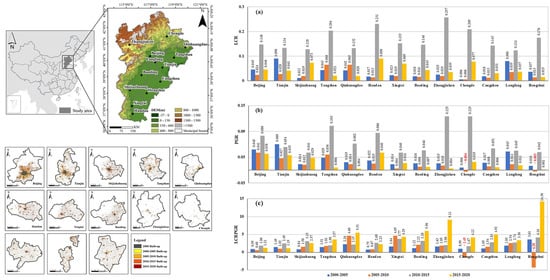
4.3.1. Variations in LCR, PGR and LCRPGR
4.3.2. Differences in LCRPGR by City Type
5. Discussion
5.1. Urban Growth Analysis
5.2. Uncertainties and Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs. World Urbanization Prospects: The 2018 Revision (ST/ESA/SER.A/420). In Population Division; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Grimm, N.B.; Faeth, S.H.; Golubiewski, N.E.; Redman, C.L.; Wu, J.; Bai, X.; Briggs, J.M. Global Change and the Ecology of Cities. Science 2008, 319, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaeger, J.A.G.; Bertiller, R.; Schwick, C.; Cavens, D.; Kienast, F. Urban permeation of landscapes and sprawl per capita: New measures of urban sprawl. Ecol. Indic. 2010, 10, 427–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitti, M.; Ferrara, C.; Perini, L.; Carlucci, M.; Salvati, L. Long-Term Urban Growth and Land Use Efficiency in Southern Europe: Implications for Sustainable Land Management. Sustainability 2015, 7, 3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hasse, J.E.; Lathrop, R.G. Land resource impact indicators of urban sprawl. Appl. Geogr. 2003, 23, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assembly, U.N.G. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development A/RES/70/1; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- UN-Habitat. SDG Indicator 11.3.1 Training Module: Land Use Efficiency; UN-Habitat: Nairobi, Kenya, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Haas, J.; Ban, Y. Urban growth and environmental impacts in Jing-Jin-Ji, the Yangtze, River Delta and the Pearl River Delta. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 30, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhao, S. Spatiotemporal dynamics of urban expansion in 13 cities across the Jing-Jin-Ji Urban Agglomeration from 1978 to 2015. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 87, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN-Habitat. Metadata on SDGs Indicator 11.3.1; UN-Habitat: Nairobi, Kenya, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Melchiorri, M.; Pesaresi, M.; Florczyk, A.J.; Corbane, C.; Kemper, T. Principles and Applications of the Global Human Settlement Layer as Baseline for the Land Use Efficiency Indicator—SDG 11.3.1. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, K.; Ryan, B.; Sonntag, W.; Kavvada, A.; Friedl, L. Earth observation in service of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. Geo Spat. Inf. Sci. 2017, 20, 77–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Tian, F.; Zhang, M.; Zeng, H.; Zeng, Y. Cloud services with big data provide a solution for monitoring and tracking sustainable development goals. Geogr. Sustain. 2020, 1, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; El-Askary, H.; Lakshmi, V.; Piechota, T.; Struppa, D. Earth Observation and Cloud Computing in Support of Two Sustainable Development Goals for the River Nile Watershed Countries. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q. Remote sensing of impervious surfaces in the urban areas: Requirements, methods, and trends. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 34–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Lu, L.; Weng, Q.; Xie, Y.; Guo, H. Monitoring Urban Dynamics in the Southeast U.S.A. Using Time-Series DMSP/OLS Nightlight Imagery. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, L.; Guo, H.; Corbane, C.; Li, Q. Urban sprawl in provincial capital cities in China: Evidence from multi-temporal urban land products using Landsat data. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 955–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pesaresi, M.; Huadong, G.; Blaes, X.; Ehrlich, D.; Ferri, S.; Gueguen, L.; Halkia, M.; Kauffmann, M.; Kemper, T.; Lu, L.; et al. A Global Human Settlement Layer From Optical HR/VHR RS Data: Concept and First Results. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 2102–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.C.; Huang, C.L.; Feng, Y.Y.; Zhao, M.Y.; Gu, J. Using Earth Observation for Monitoring SDG 11.3.1-Ratio of Land Consumption Rate to Population Growth Rate in Mainland China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mudau, N.; Mwaniki, D.; Tsoeleng, L.; Mashalane, M.; Beguy, D.; Ndugwa, R. Assessment of SDG Indicator 11.3.1 and Urban Growth Trends of Major and Small Cities in South Africa. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazaryan, G.; Rienow, A.; Oldenburg, C.; Thonfeld, F.; Trampnau, B.; Sticksel, S.; Jürgens, C. Monitoring of Urban Sprawl and Densification Processes in Western Germany in the Light of SDG Indicator 11.3.1 Based on an Automated Retrospective Classification Approach. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koroso, N.H.; Zevenbergen, J.A.; Lengoiboni, M. Urban land use efficiency in Ethiopia: An assessment of urban land use sustainability in Addis Ababa. Land Use Policy 2020, 99, 105081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. Statistical Communiqué of the People’s Republic of China on the 2019 National Economic and Social Development; National Bureau of Statistics of China: Beijing, China, 2020.
- Fang, C. Important progress and future direction of studies on China’s urban agglomerations. J. Geogr. Sci. 2015, 25, 1003–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, C.; Yu, D. Urban agglomeration: An evolving concept of an emerging phenomenon. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 162, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, R.; Hansen, M. Google Earth Engine: A new cloud-computing platform for global-scale earth observation data and analysis. AGU Fall Meet. Abstr. 2011, 2011, IN43C-02. [Google Scholar]
- Gorelick, N.; Hancher, M.; Dixon, M.; Ilyushchenko, S.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Google Earth Engine: Planetary-scale geospatial analysis for everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Bai, Y.; Chen, B.; Hu, T.; Liu, X.; Xu, B.; Yang, J.; Zhang, W.; et al. Annual maps of global artificial impervious area (GAIA) between 1985 and 2018. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martino, P.; Daniele, E.; Stefano, F.; Aneta, F.; Vasileios, S. Operating procedure for the production of the Global Human Settlement Layer from Landsat data of the epochs 1975, 1990, 2000, and 2014. Publ. Off. Eur. Union 2016, 1–62. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, L.; Chen, X.; Gao, Y.; Xie, S.; Mi, J. GLC_FCS30: Global land-cover productwith fine classification system at 30 m using time-series Landsat imagery. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 2753–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Liao, A.; Cao, X.; Chen, L.; Chen, X.; He, C.; Han, G.; Peng, S.; Lu, M.; et al. Global land cover mapping at 30 m resolution: A POK-based operational approach. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 103, 7–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lloyd, C.T.; Sorichetta, A.; Tatem, A.J. High resolution global gridded data for use in population studies. Sci. Data 2017, 4, 170001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Farr, T.G.; Kobrick, M. Shuttle radar topography mission produces a wealth of data. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2000, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Lu, L.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Sui, Y.; Guo, H. MODIS-Derived Spatiotemporal Changes of Major Lake Surface Areas in Arid Xinjiang, China, 2000–2014. Water 2015, 7, 5731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Kuenzer, C.; Wang, C.; Guo, H.; Li, Q. Evaluation of Three MODIS-Derived Vegetation Index Time Series for Dryland Vegetation Dynamics Monitoring. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 7597–7614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, L.; Weng, Q.; Xiao, D.; Guo, H.; Li, Q.; Hui, W. Spatiotemporal Variation of Surface Urban Heat Islands in Relation to Land Cover Composition and Configuration: A Multi-Scale Case Study of Xi’an, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wei, M.; Pu, D.; He, G.; Wang, G.; Long, T. Assessment of Annual Composite Images Obtained by Google Earth Engine for Urban Areas Mapping Using Random Forest. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olofsson, P.; Foody, G.M.; Herold, M.; Stehman, S.V.; Woodcock, C.E.; Wulder, M.A. Good practices for estimating area and assessing accuracy of land change. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 148, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foody, G.M. Status of land cover classification accuracy assessment. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 80, 185–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundel, H.L.; Polansky, M. Measurement of Observer Agreement. Radiology 2003, 228, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, J.; Stehman, S.V.; Gass, L.; Dewitz, J.A.; Sorenson, D.G.; Granneman, B.J.; Poss, R.V.; Baer, L.A. Thematic accuracy assessment of the 2011 National Land Cover Database (NLCD). Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 191, 328–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, R. Exploring the optimal integration levels between SAR and optical data for better urban land cover mapping in the Pearl River Delta. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 64, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smits, P.C. Multiple classifier systems for supervised remote sensing image classification based on dynamic classifier selection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 801–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Weng, Q. Annual dynamics of impervious surface in the Pearl River Delta, China, from 1988 to 2013, using time series Landsat imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 113, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Wang, Z.; Sui, L.; Yang, X.; Ma, Y.; Wang, J. Consistency Analysis of Remote Sensing Land Cover Products in the Tropical Rainforest Climate Region: A Case Study of Indonesia. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xiao, P.; Feng, X.; Li, H. Accuracy assessment of seven global land cover datasets over China. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 125, 156–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Mi, J.; Xie, S. Consistency Analysis and Accuracy Assessment of Three Global 30-m Land-Cover Products over the European Union using the LUCAS Dataset. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabo, F.; Corbane, C.; Florczyk, A.J.; Ferri, S.; Pesaresi, M.; Kemper, T. Comparison of built-up area maps produced within the global human settlement framework. Trans. GIS 2018, 22, 1406–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, Z.X.; Shi, L.F.; Zhao, X.L.; Xu, J.Y.; Yi, L.; Liu, B.; Wen, Q.K.; Hu, S.G.; Wang, X.; et al. Urban expansion in China and its spatial-temporal differences over the past four decades. J. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 1477–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Qi, W.; Fu, B.; Wang, K. Geographical transformations of urban sprawl: Exploring the spatial heterogeneity across cities in China 1992–2015. Cities 2020, 105, 102415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Zhang, B. Operational Built-Up Areas Extraction for Cities in China Using Sentinel-1 SAR Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Huang, X.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, H.; Tang, X.; Gong, J. Automatic extraction of built-up area from ZY3 multi-view satellite imagery: Analysis of 45 global cities. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 226, 51–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiß, C.; Schrade, H.; Aravena Pelizari, P.; Taubenböck, H. Multistrategy ensemble regression for mapping of built-up density and height with Sentinel-2 data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 170, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Product | Data Source | Classification Method | Publisher | Time Coverage | Spatial Resolution (m) | Geographic Projection |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GAIA | Landsat TM, ETM+, OLI, VIIRS NTL, Sentinel-1 SAR | Exclusion–inclusion algorithm and temporal consistency check | Tsinghua University http://data.ess.tsinghua.edu.cn (10 March 2021) | 1985–2018 | 30 | WGS 1984 |
| GHS-Built | Landsat MSS, TM, ETM+ | Symbolic machine learning | Joint Research Centre, European Commission https://ghsl.jrc.ec.europa.eu/ (20 November 2020) | 1975; 1990; 2000; 2015 | 30 | WGS 1984; WGS 1984 Web Mercator Auxiliary Sphere |
| GLC_FCS-2020 | Landsat 8 surface reflectance, Sentinel-1 SAR | Random forest classifier | Chinese Academy of Sciences https://zenodo.org/record/4280923#.YHamCjim02w (10 October 2020) | 2020 | 30 | WGS 1984 |
| GlobeLand30 | Landsat TM, ETM+, OLI, HJ-1 | POK (based on pixels, objects, and knowledge) | National Geomatics Center of China http://www.globallandcover.com (10 January 2021) | 2000; 2010; 2020 | 30 | WGS 1984; UTM |
| DATA | 1: Non-Built-Up | 2: Built-Up |
|---|---|---|
| GAIA | 2000:0 Non-impervious, 1–18 impervious | 2000:19–34 impervious |
| 2010:0 Non-impervious, 1–8 impervious | 2010:9–34 impervious | |
| 2018:0 Non-impervious | 2018:1–34 impervious | |
| GHS-Built | 1: Water surface, 2: Land not built-up in any epoch, 3: Built-up from 2000 to 2014 | 4: Built-up from 1990 to 2000, 5: Built-up from 1975 to 1990, 6: Built-up until 1975 |
| GLC_FCS-2020 | 10: Rainfed cropland, 11: Herbaceous cover, 12: Tree or shrub cover (orchard), 20: Irrigated cropland, 51: Open evergreen broadleaved forest, 52: Open evergreen broadleaved forest, 61: Open deciduous broadleaved forest (0.15 < fc < 0.4), 62: Closed evergreen needle-leaved forest (fc > 0.4), 71: Open evergreen needle-leaved forest (0.15 < fc < 0.4), 72: Closed evergreen needle-leaved forest (fc > 0.14), 81: Open deciduous needle-leaved forest (0.15 < fc < 0.4), 82: Closed deciduous needle-leaved forest (fc > 0.4), 91: Open mixed-leaf forest (broadleaved and needle-leaved), 92: Closed mixed-leaf forest (broadleaved and needle-leaved), 120: Shrubland, 121: Evergreen shrubland, 122: Deciduous shrubland, 130: Grassland, 140: Lichens and mosses, 150: Sparse vegetation (fc < 0.15), 152: Sparse shrubland (fc < 0.15), 153: Sparse herbaceous (fc < 0.15), 180: Wetlands, 200: Bare areas, 201: Consolidated bare areas, 202: Unconsolidated bare areas, 210: Water body, 220: Permanent ice and snow, 250: Filled value | 190: Impervious surfaces |
| Globeland30 | 10: Cultivated land, 20: Forest, 30: Grassland, 40: Shrubland, 50: Wetland, 60: Water bodies, 70: Tundra, 90: Bare Land, 100: Permanent snow and ice | 80: Artificial surfaces |
| LCRPGR Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
| LCRPGR < −1 | the rate of population decline is greater than the rate of built-up area expansion |
| −1 < LCRPGR < 0 | the rate of population decline is less than the rate of built-up area expansion |
| 0 < LCRPGR < 1 | the rate of population growth is greater than the rate of built-up area expansion |
| 1 < LCRPGR < 2 | the rate of built-up area expansion is 1–2 times the rate of population growth |
| LCRPGR > 2 | the rate of built-up area expansion is greater than 2 times the rate of population growth |
| Product | Year | OA | KAPPA | OE | CE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GAIA | 2000 | 0.82 | 0.64 | 0.07 | 0.31 |
| 2010 | 0.84 | 0.67 | 0.05 | 0.29 | |
| 2018 | 0.86 | 0.72 | 0.05 | 0.24 | |
| Average | 0.84 | 0.67 | 0.06 | 0.28 | |
| GHS-Built | 2000 | 0.87 | 0.75 | 0.04 | 0.22 |
| GLC_FCS | 2020 | 0.88 | 0.77 | 0.05 | 0.29 |
| Globeland30 | 2000 | 0.84 | 0.68 | 0.05 | 0.28 |
| 2010 | 0.85 | 0.7 | 0.05 | 0.26 | |
| 2020 | 0.86 | 0.72 | 0.04 | 0.25 | |
| Average | 0.85 | 0.7 | 0.05 | 0.26 | |
| BTH_BU | 2000 | 0.91 | 0.83 | 0.05 | 0.13 |
| 2005 | 0.91 | 0.83 | 0.04 | 0.14 | |
| 2010 | 0.94 | 0.87 | 0.05 | 0.08 | |
| 2015 | 0.93 | 0.86 | 0.04 | 0.10 | |
| 2020 | 0.94 | 0.89 | 0.04 | 0.07 | |
| Average | 0.93 | 0.85 | 0.04 | 0.11 |
| Time Period | LCR | PGR | LCRPGR |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2000–2005 | 0.045 | 0.039 | 1.142 |
| 2005–2010 | 0.027 | 0.028 | 0.946 |
| 2010–2015 | 0.154 | 0.069 | 2.232 |
| 2015–2020 | 0.048 | 0.031 | 1.538 |
| Type | Cities | Population |
|---|---|---|
| Megacities | Beijing, Tianjin | ≥10,000,000 |
| Large cities | Shijiazhuang | 5,000,000–10,000,000 |
| Medium cities | Tangshan, Qinhuangdao, Handan, Xingtai, Baoding, Zhangjiakou | 1,000,000–5,000,000 |
| Small cities | Canzhou, Langfang | 500,000–1,000,000 |
| Very small cities | Chengde, Hengshui | <500,000 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, M.; Lu, L.; Guo, H.; Weng, Q.; Cao, S.; Zhang, S.; Li, Q. Urban Sprawl and Changes in Land-Use Efficiency in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Region, China from 2000 to 2020: A Spatiotemporal Analysis Using Earth Observation Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2850. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13152850
Zhou M, Lu L, Guo H, Weng Q, Cao S, Zhang S, Li Q. Urban Sprawl and Changes in Land-Use Efficiency in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Region, China from 2000 to 2020: A Spatiotemporal Analysis Using Earth Observation Data. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(15):2850. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13152850
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Meiling, Linlin Lu, Huadong Guo, Qihao Weng, Shisong Cao, Shuangcheng Zhang, and Qingting Li. 2021. "Urban Sprawl and Changes in Land-Use Efficiency in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Region, China from 2000 to 2020: A Spatiotemporal Analysis Using Earth Observation Data" Remote Sensing 13, no. 15: 2850. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13152850
APA StyleZhou, M., Lu, L., Guo, H., Weng, Q., Cao, S., Zhang, S., & Li, Q. (2021). Urban Sprawl and Changes in Land-Use Efficiency in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Region, China from 2000 to 2020: A Spatiotemporal Analysis Using Earth Observation Data. Remote Sensing, 13(15), 2850. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13152850