Using Remotely Sensed Sea Surface Salinity and Colored Detrital Matter to Characterize Freshened Surface Layers in the Kara and Laptev Seas during the Ice-Free Season
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data
3. Methods
3.1. Data Fusion
3.2. FSL Characterization
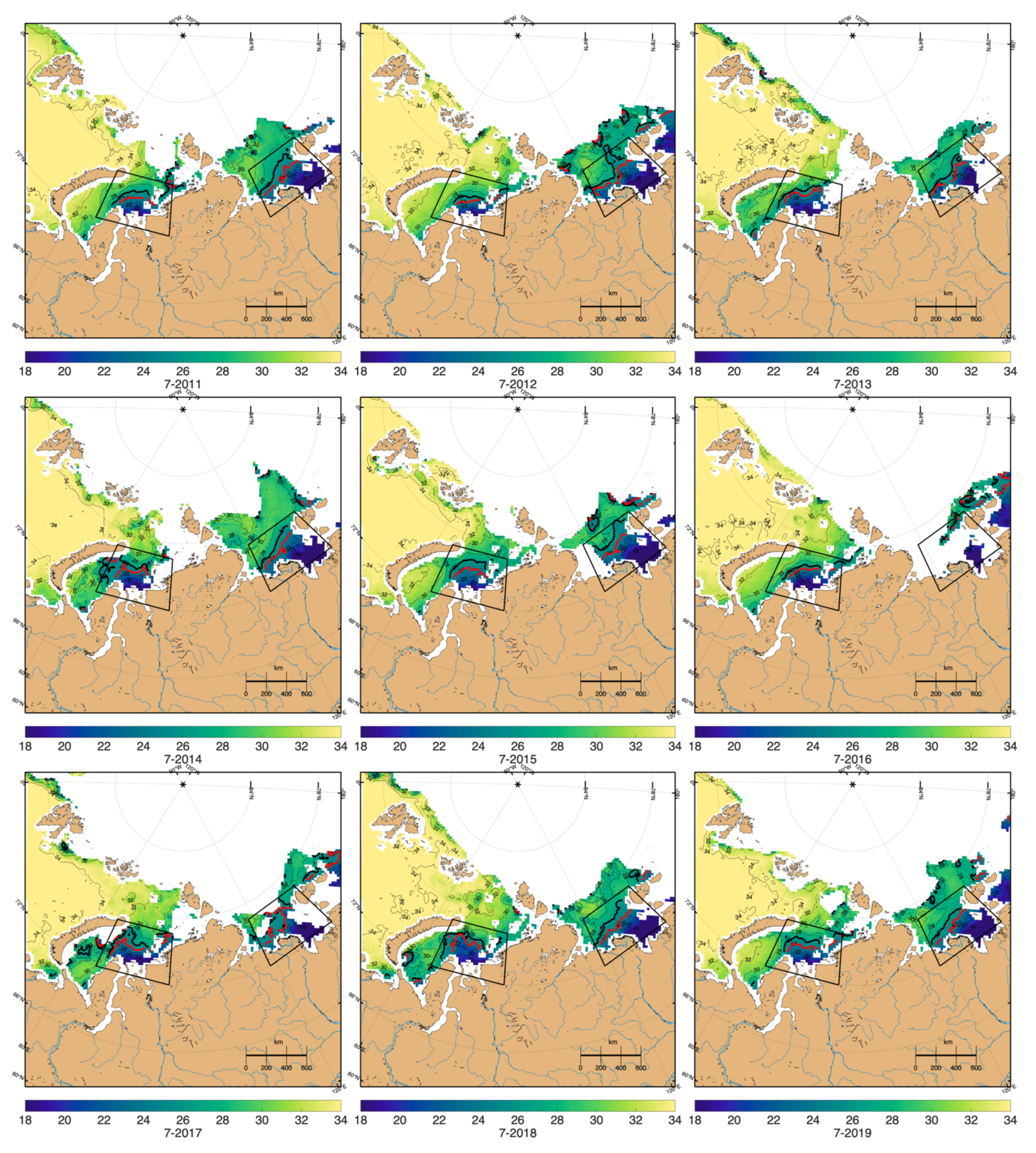
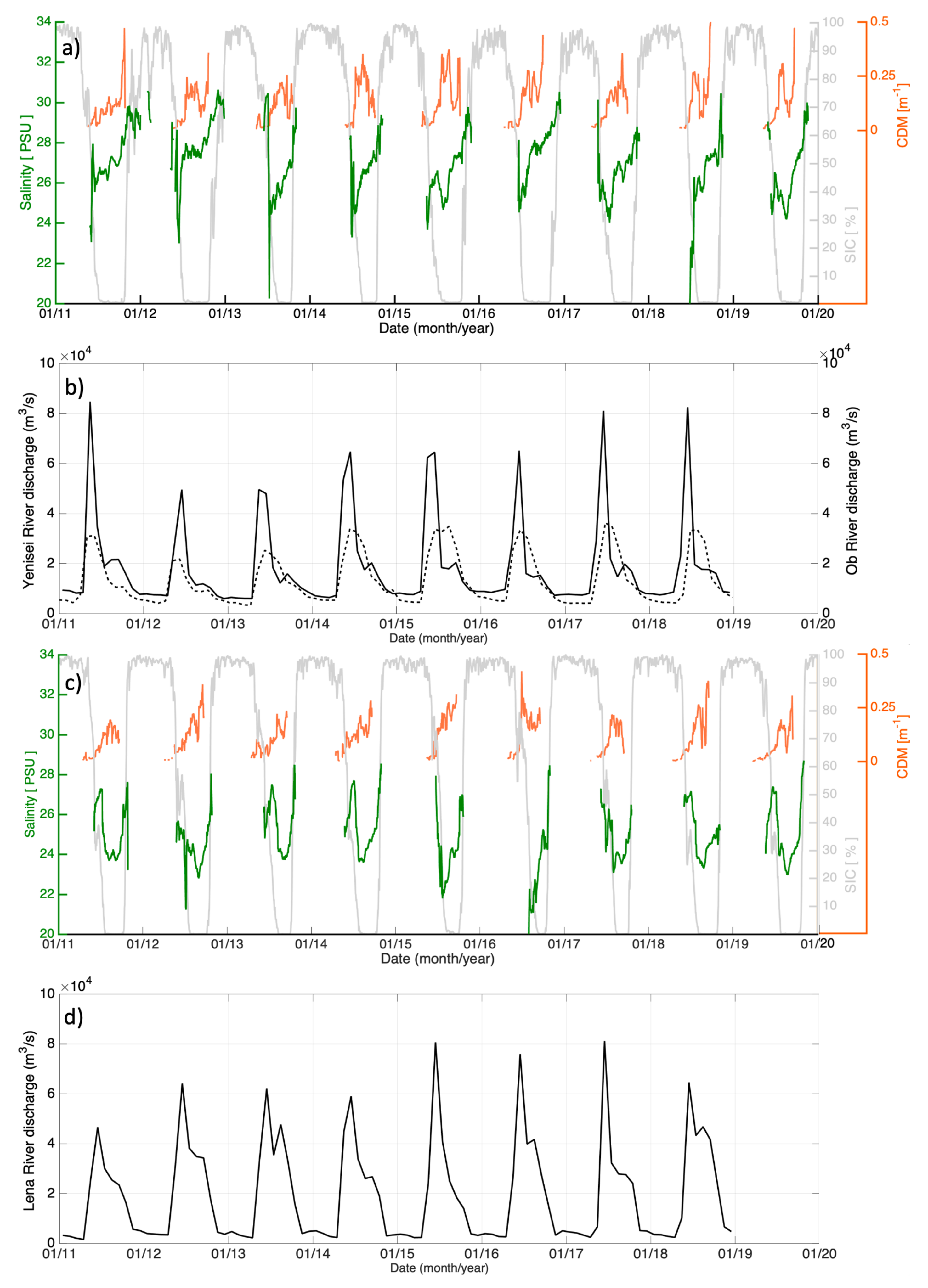
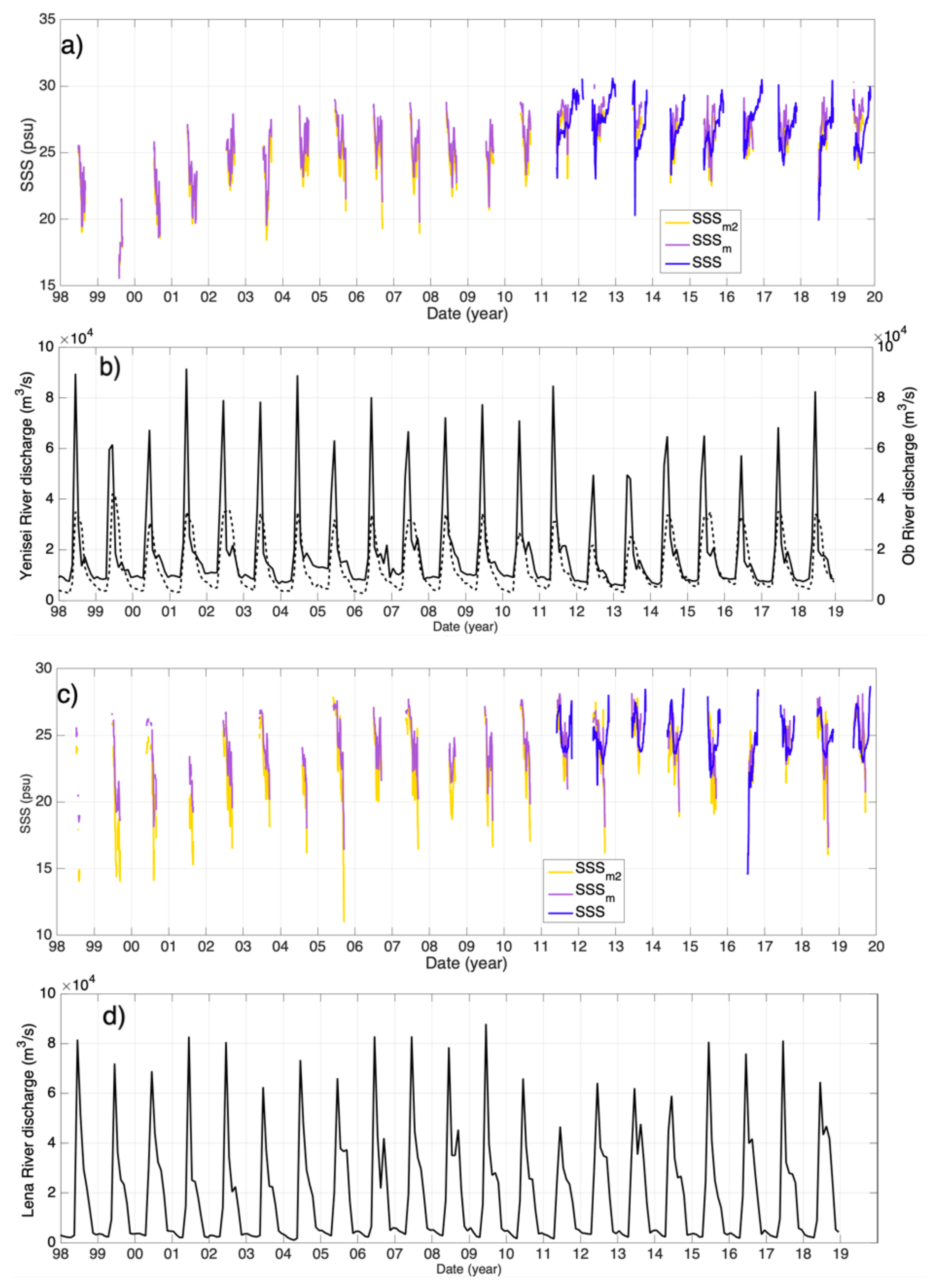
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Correlation between Sea Surface Salinity and Colored Detrital Matter
4.2. SSS Reconstruction Using Data Fusion
4.3. FSL Extension and Fresh Water Content
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Additional Figures





References
- Poloczanska, E.; Mintenbeck, K.; Portner, H.O.; Roberts, D.; Levin, L.A. The IPCC special report on the ocean and cryosphere in a changing climate. In Proceedings of the 2018 Ocean Sciences Meeting, Portland, OR, USA, 11–16 February 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Thoman, R.L.; Bhatt, U.S.; Bieniek, P.A.; Brettschneider, B.R.; Brubaker, M.; Danielson, S.; Labe, Z.; Lader, R.; Meier, W.N.; Sheffield, G.; et al. The Record Low Bering Sea Ice Extent in 2018: Context, Impacts, and an Assessment of the Role of Anthropogenic Climate Change. 2020. Available online: https://journals.ametsoc.org/view/journals/bams/101/1/bams-d-19-0175.1.xml?tab_body=previewPdf-43621 (accessed on 31 July 2021).
- National Snow and Ice Data Center. Available online: https://nsidc.org/arcticseaicenews/2020/ (accessed on 31 July 2021).
- Haine, T.W.; Curry, B.; Gerdes, R.; Hansen, E.; Karcher, M.; Lee, C.; Rudels, B.; Spreen, G.; de Steur, L.; Stewart, K.D.; et al. Arctic freshwater export: Status, mechanisms, and prospects. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2015, 125, 13–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Proshutinsky, A.; Krishfield, R.; Toole, J.; Timmermans, M.L.; Williams, W.; Zimmermann, S.; Yamamoto-Kawai, M.; Armitage, T.; Dukhovskoy, D.; Golubeva, E.; et al. Analysis of the Beaufort Gyre freshwater content in 2003–2018. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2019, 124, 9658–9689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Solomon, A.; Heuzé, C.; Rabe, B.; Bacon, S.; Bertino, L.; Heimbach, P.; Inoue, J.; Iovino, D.; Mottram, R.; Zhang, X.; et al. Freshwater in the Arctic Ocean 2010–2019. Ocean Sci. 2021, 17, 1081–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, C.; Pfaffling, A.; Hendricks, S.; Rabenstein, L.; Etienne, J.L.; Rigor, I. Reduced ice thickness in Arctic Transpolar Drift favors rapid ice retreat. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carmack, E.; Polyakov, I.; Padman, L.; Fer, I.; Hunke, E.; Hutchings, J.; Jackson, J.; Kelley, D.; Kwok, R.; Layton, C.; et al. Toward quantifying the increasing role of oceanic heat in sea ice loss in the new Arctic. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 2079–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wekerle, C.; Danilov, S.; Sidorenko, D.; Koldunov, N.; Sein, D.; Rabe, B.; Jung, T. Recent sea ice decline did not significantly increase the total liquid freshwater content of the Arctic Ocean. J. Clim. 2019, 32, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Timmermans, M.L.; Marshall, J. Understanding Arctic Ocean circulation: A review of ocean dynamics in a changing climate. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2020, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savelieva, N.; Semiletov, I.; Vasilevskaya, L.; Pugach, S. A climate shift in seasonal values of meteorological and hydrological parameters for Northeastern Asia. Prog. Oceanogr. 2000, 47, 279–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammers, R.B.; Shiklomanov, A.I.; Vörösmarty, C.J.; Fekete, B.M.; Peterson, B.J. Assessment of contemporary Arctic river runoff based on observational discharge records. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 3321–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, B.J.; Holmes, R.M.; McClelland, J.W.; Vörösmarty, C.J.; Lammers, R.B.; Shiklomanov, A.I.; Shiklomanov, I.A.; Rahmstorf, S. Increasing river discharge to the Arctic Ocean. Science 2002, 298, 2171–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peterson, B.J.; McClelland, J.; Curry, R.; Holmes, R.M.; Walsh, J.E.; Aagaard, K. Trajectory shifts in the Arctic and subarctic freshwater cycle. Science 2006, 313, 1061–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rennermalm, A.K.; Wood, E.F.; Déry, S.J.; Weaver, A.J.; Eby, M. Sensitivity of the thermohaline circulation to Arctic Ocean runoff. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soppa, M.A.; Pefanis, V.; Hellmann, S.; Losa, S.N.; Hölemann, J.; Martynov, F.; Heim, B.; Janout, M.A.; Dinter, T.; Rozanov, V.; et al. Assessing the influence of water constituents on the radiative heating of Laptev Sea shelf waters. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, S.; Lee, T.; Wang, X.; Armitage, T.W.; Wang, O.; Fukumori, I.; Kwok, R. Sea surface salinity as a proxy for Arctic Ocean freshwater changes. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2020, 125, e2020JC016110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supply, A.; Boutin, J.; Vergely, J.L.; Kolodziejczyk, N.; Reverdin, G.; Reul, N.; Tarasenko, A. New insights into SMOS sea surface salinity retrievals in the Arctic Ocean. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 249, 112027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, Y.; Waldteufel, P.; Wigneron, J.; Delwart, S.; Cabot, F.; Boutin, J.; Escorihuela, M.; Font, J.; Reul, N.; Gruhier, C.; et al. The SMOS Mission: New Tool for Monitoring Key Elements of the Global Water Cycle. Proc. IEEE 2010, 98, 666–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mecklenburg, S.; Drusch, M.; Kerr, Y.H.; Font, J.; Martin-Neira, M.; Delwart, S.; Buenadicha, G.; Reul, N.; Daganzo-Eusebio, E.; Oliva, R.; et al. ESA’s soil moisture and ocean salinity mission: Mission performance and operations. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 1354–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reul, N.; Grodsky, S.; Arias, M.; Boutin, J.; Catany, R.; Chapron, B.; d’Amico, F.; Dinnat, E.; Donlon, C.; Fore, A.; et al. Sea surface salinity estimates from spaceborne L-band radiometers: An overview of the first decade of observation (2010–2019). Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 242, 111769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmedo, E.; Gabarró, C.; González-Gambau, V.; Martínez, J.; Ballabrera-Poy, J.; Turiel, A.; Portabella, M.; Fournier, S.; Lee, T. Seven years of SMOS sea surface salinity at high latitudes: Variability in Arctic and Sub-Arctic regions. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez, J. Arctic+ Salinity: Algorithm Theoretical Baseline Document; Technical Report; Argans LTD: Plymouth, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, J.; Gabarró, C.; Turiel, A. Arctic Sea Surface Salinity L2 orbits and L3 maps (V.3.1) [Dataset]. Technical Report. 2020. Available online: https://digital.csic.es/handle/10261/219679 (accessed on 31 July 2021). [CrossRef]
- Organelli, E.; Bricaud, A.; Gentili, B.; Antoine, D.; Vellucci, V. Retrieval of Colored Detrital Matter (CDM) light absorption coefficients in the Mediterranean Sea using field and satellite ocean color radiometry: Evaluation of bio-optical inversion models. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 186, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowers, D.; Brett, H. The relationship between CDOM and salinity in estuaries: An analytical and graphical solution. J. Mar. Syst. 2008, 73, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakada, S.; Kobayashi, S.; Hayashi, M.; Ishizaka, J.; Akiyama, S.; Fuchi, M.; Nakajima, M. High-resolution surface salinity maps in coastal oceans based on geostationary ocean color images: Quantitative analysis of river plume dynamics. J. Oceanogr. 2018, 74, 287–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, G.; Dowell, M. CDOM absorption characteristics with relation to fluorescence and salinity in coastal areas of the southern Baltic Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1998, 47, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binding, C.; Bowers, D. Measuring the salinity of the Clyde Sea from remotely sensed ocean colour. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2003, 57, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urquhart, E.A.; Zaitchik, B.F.; Hoffman, M.J.; Guikema, S.D.; Geiger, E.F. Remotely sensed estimates of surface salinity in the Chesapeake Bay: A statistical approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 123, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korosov, A.; Counillon, F.; Johannessen, J.A. Monitoring the spreading of the A mazon freshwater plume by MODIS, SMOS, A quarius, and TOPAZ. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2015, 120, 268–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, S.; Chapron, B.; Salisbury, J.; Vandemark, D.; Reul, N. Comparison of spaceborne measurements of sea surface salinity and colored detrital matter in the Amazon plume. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2015, 120, 3177–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, C.; Muller-Karger, F.E.; Biggs, D.C.; Carder, K.L.; Nababan, B.; Nadeau, D.; Vanderbloemen, J. Comparison of ship and satellite bio-optical measurements on the continental margin of the NE Gulf of Mexico. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 2597–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Hu, C. Estimating sea surface salinity in the northern Gulf of Mexico from satellite ocean color measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 201, 115–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Castillo, C.E.; Miller, R.L. On the use of ocean color remote sensing to measure the transport of dissolved organic carbon by the Mississippi River Plume. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bai, Y.; Pan, D.; Cai, W.J.; He, X.; Wang, D.; Tao, B.; Zhu, Q. Remote sensing of salinity from satellite-derived CDOM in the Changjiang River dominated East China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2013, 118, 227–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granskog, M.A.; Macdonald, R.W.; Mundy, C.J.; Barber, D.G. Distribution, characteristics and potential impacts of chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM) in Hudson Strait and Hudson Bay, Canada. Cont. Shelf Res. 2007, 27, 2032–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves-Araujo, R.; Stedmon, C.A.; Heim, B.; Dubinenkov, I.; Kraberg, A.; Moiseev, D.; Bracher, A. From fresh to marine waters: Characterization and fate of dissolved organic matter in the Lena River Delta Region, Siberia. Front. Mar. Sci. 2015, 2, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alling, V.; Sanchez-Garcia, L.; Porcelli, D.; Pugach, S.; Vonk, J.E.; Van Dongen, B.; Mörth, C.M.; Anderson, L.G.; Sokolov, A.; Andersson, P.; et al. Nonconservative behavior of dissolved organic carbon across the Laptev and East Siberian seas. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2010, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hölemann, J.A.; Juhls, B.; Bauch, D.; Janout, M.; Koch, B.P.; Heim, B. The impact of the freeze–melt cycle of land-fast ice on the distribution of dissolved organic matter in the Laptev and East Siberian seas (Siberian Arctic). Biogeosciences 2021, 18, 3637–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drozdova, A.N.; Nedospasov, A.A.; Lobus, N.V.; Patsaeva, S.V.; Shchuka, S.A. CDOM Optical Properties and DOC Content in the Largest Mixing Zones of the Siberian Shelf Seas. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhls, B.; Overduin, P.P.; Hölemann, J.; Hieronymi, M.; Matsuoka, A.; Heim, B.; Fischer, J. Dissolved organic matter at the fluvial–marine transition in the Laptev Sea using in situ data and ocean colour remote sensing. Biogeosciences 2019, 16, 2693–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glukhovets, D.I.; Goldin, Y.A. Surface desalinated layer distribution in the Kara Sea determined by shipboard and satellite data. Oceanologia 2020, 62, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, R.M.; McClelland, J.W.; Peterson, B.J.; Tank, S.E.; Bulygina, E.; Eglinton, T.I.; Gordeev, V.V.; Gurtovaya, T.Y.; Raymond, P.A.; Repeta, D.J.; et al. Seasonal and annual fluxes of nutrients and organic matter from large rivers to the Arctic Ocean and surrounding seas. Estuaries Coasts 2012, 35, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiklomanov, A.; Déry, S.; Tretiakov, M.; Yang, D.; Magritsky, D.; Georgiadi, A.; Tang, W. River Freshwater Flux to the Arctic Ocean. In Arctic Hydrology, Permafrost and Ecosystems; Yang, D., Kane, D.L., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 703–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aagaard, K.; Carmack, E.C. The role of sea ice and other fresh water in the Arctic circulation. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1989, 94, 14485–14498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harms, I.; Karcher, M. Kara Sea freshwater dispersion and export in the late 1990s. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Osadchiev, A.; Frey, D.; Shchuka, S.; Tilinina, N.; Morozov, E.; Zavialov, P. Structure of the freshened surface layer in the Kara Sea during ice-free periods. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2021, 126, e2020JC016486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demidov, A.; Gagarin, V.; Vorobieva, O.; Makkaveev, P.; Artemiev, V.; Khrapko, A.; Grigoriev, A.; Sheberstov, S. Spatial and vertical variability of primary production in the Kara Sea in July and August 2016: The influence of the river plume and subsurface chlorophyll maxima. Polar Biol. 2018, 41, 563–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavergne, T.; Sørensen, A.M.; Kern, S.; Tonboe, R.; Notz, D.; Aaboe, S.; Bell, L.; Dybkjær, G.; Eastwood, S.; Gabarro, C.; et al. Version 2 of the EUMETSAT OSI SAF and ESA CCI sea-ice concentration climate data records. Cryosphere 2019, 13, 49–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- EUMETSAT Ocean and Sea Ice Satellite Application Facility. Global Sea Ice Concentration Climate Data Record 1979–2015 (v2.0, 2017); Norwegian and Danish Meteorological Institutes: Darmstadt, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUMETSAT Ocean and Sea Ice Satellite Application Facility. Global Sea Ice Concentration Interim Climate Data Record 2016 Onwards (v2.0, 2019); Norwegian and Danish Meteorological Institutes: Darmstadt, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Shiklomanov, A.I.; Holmes, R.M.; McClelland, J.W.; Tank, S.E.; Spencer, R.G.M. Arctic Great Rivers Observatory. Discharge Dataset, Version 20180527. Technical Report. 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Nieves, V.; Llebot, C.; Turiel, A.; Solé, J.; García-Ladona, E.; Estrada, M.; Blasco, D. Common turbulent signature in sea surface temperature and chlorophyll maps. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L23602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Polyakova, Y.I.; Kryukova, I.; Martynov, F.; Novikhin, A.; Abramova, E.; Kassens, H.; Hölemann, J. Community structure and spatial distribution of phytoplankton in relation to hydrography in the Laptev Sea and the East Siberian Sea (autumn 2008). Polar Biol. 2021, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zatsepin, A.; Kremenetskiy, V.; Kubryakov, A.; Stanichny, S.; Soloviev, D. Propagation and transformation of waters of the surface desalinated layer in the Kara Sea. Oceanology 2015, 55, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubryakov, A.; Stanichny, S.; Zatsepin, A. River plume dynamics in the Kara Sea from altimetry-based lagrangian model, satellite salinity and chlorophyll data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 176, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paclov, V.; Timokhov, L.; Baskakov, G.; Kulakov, M.Y.; Kurazhov, V. Hydrometeorological Regime of the Kara, Laptev, and East-Siberian Seas; Technical Report; Washington Univ Seattle Applied Physics Lab: Seattle, WA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Conrad, S.; Ingri, J.; Gelting, J.; Nordblad, F.; Engström, E.; Rodushkin, I.; Andersson, P.S.; Porcelli, D.; Gustafsson, Ö.; Semiletov, I.; et al. Distribution of Fe isotopes in particles and colloids in the salinity gradient along the Lena River plume, Laptev Sea. Biogeosciences 2019, 16, 1305–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janout, M.; Hölemann, J.; Laukert, G.; Smirnov, A.; Krumpen, T.; Bauch, D.; Timokhov, L. On the variability of stratification in the freshwater-influenced Laptev Sea region. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osadchiev, A.; Pisareva, M.; Spivak, E.; Shchuka, S.; Semiletov, I. Freshwater transport between the Kara, Laptev, and East-Siberian seas. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 113041. [Google Scholar]
- Heim, B.; Juhls, B.; Abramova, E.; Bracher, A.; Doerffer, R.; Gonçalves-Araujo, R.; Hellman, S.; Kraberg, A.; Martynov, F.; Overduin, P. Ocean colour remote sensing in the Laptev Sea. In Remote Sensing of the Asian Seas; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 123–138. [Google Scholar]
- Gonçalves-Araujo, R.; Juhls, B. Dissolved Organic Matter in the Lena River Delta Region, Siberia, Russia. 2019. Available online: https://repository.geologyscience.ru/handle/123456789/8007 (accessed on 31 July 2021). [CrossRef]
- McClelland, J.W.; Holmes, R.M.; Peterson, B.J.; Stieglitz, M. Increasing river discharge in the Eurasian Arctic: Consideration of dams, permafrost thaw, and fires as potential agents of change. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walker, S.A.; Amon, R.M.; Stedmon, C.A. Variations in high-latitude riverine fluorescent dissolved organic matter: A comparison of large Arctic rivers. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2013, 118, 1689–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polukhin, A. The role of river runoff in the Kara Sea surface layer acidification and carbonate system changes. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 105007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janout, M.; Hölemann, J.; Juhls, B.; Krumpen, T.; Rabe, B.; Bauch, D.; Wegner, C.; Kassens, H.; Timokhov, L. Episodic warming of near-bottom waters under the Arctic sea ice on the central Laptev Sea shelf. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janout, M.A.; Aksenov, Y.; Hölemann, J.A.; Rabe, B.; Schauer, U.; Polyakov, I.V.; Bacon, S.; Coward, A.C.; Karcher, M.; Lenn, Y.D.; et al. Kara S ea freshwater transport through V ilkitsky S trait: Variability, forcing, and further pathways toward the western A rctic O cean from a model and observations. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2015, 120, 4925–4944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathyendranath, S. Remote Sensing of Ocean Colour in Coastal, and Other Optically-Complex, Waters; International Ocean Colour Coordinating Group (IOCCG): Dartmouth, NS, Canada, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Salisbury, J.; Vandemark, D.; Campbell, J.; Hunt, C.; Wisser, D.; Reul, N.; Chapron, B. Spatial and temporal coherence between Amazon River discharge, salinity, and light absorption by colored organic carbon in western tropical Atlantic surface waters. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maritorena, S.; Siegel, D.A.; Peterson, A.R. Optimization of a semianalytical ocean color model for global-scale applications. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 2705–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janout, M.A.; Hölemann, J.; Waite, A.M.; Krumpen, T.; von Appen, W.J.; Martynov, F. Sea-ice retreat controls timing of summer plankton blooms in the Eastern Arctic Ocean. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 12–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsuoka, A.; Babin, M.; Devred, E.C. A new algorithm for discriminating water sources from space: A case study for the southern Beaufort Sea using MODIS ocean color and SMOS salinity data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 184, 124–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubinina, E.; Kossova, S.; Miroshnikov, A.Y.; Fyaizullina, R. Isotope parameters (δD, δ 18 O) and sources of freshwater input to Kara Sea. Oceanology 2017, 57, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubinina, E.; Kossova, S.; Miroshnikov, A.Y.; Kokryatskaya, N. Isotope (δD, δ 18 O) systematics in waters of the Russian Arctic seas. Geochem. Int. 2017, 55, 1022–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasenko, A.; Supply, A.; Kusse-Tiuz, N.; Ivanov, V.; Makhotin, M.; Tournadre, J.; Chapron, B.; Boutin, J.; Kolodziejczyk, N.; Reverdin, G. Properties of surface water masses in the Laptev and the East Siberian seas in summer 2018 from in situ and satellite data. Ocean Sci. 2021, 17, 221–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bintanja, R.; Selten, F. Future increases in Arctic precipitation linked to local evaporation and sea-ice retreat. Nature 2014, 509, 479–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmack, E.C.; Yamamoto-Kawai, M.; Haine, T.W.; Bacon, S.; Bluhm, B.A.; Lique, C.; Melling, H.; Polyakov, I.V.; Straneo, F.; Timmermans, M.L.; et al. Freshwater and its role in the Arctic Marine System: Sources, disposition, storage, export, and physical and biogeochemical consequences in the Arctic and global oceans. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2016, 121, 675–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umbert, M.; Hoareau, N.; Turiel, A.; Ballabrera-Poy, J. New blending algorithm to synergize ocean variables: The case of SMOS sea surface salinity maps. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 146, 172–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umbert, M.; Guimbard, S.; Lagerloef, G.; Thompson, L.; Portabella, M.; Ballabrera-Poy, J.; Turiel, A. Detecting the surface salinity signature of Gulf Stream cold-core rings in Aquarius synergistic products. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olmedo, E.; Martínez, J.; Umbert, M.; Hoareau, N.; Portabella, M.; Ballabrera-Poy, J.; Turiel, A. Improving time and space resolution of SMOS salinity maps using multifractal fusion. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 180, 246–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umbert, M.; Guimbard, S.; Ballabrera Poy, J.; Turiel, A. Synergy between Ocean Variables: Remotely Sensed Surface Temperature and Chlorophyll Concentration Coherence. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bricaud, A.; Morel, A.; Babin, M.; Allali, K.; Claustre, H. Variations of light absorption by suspended particles with chlorophyll a concentration in oceanic (case 1) waters: Analysis and implications for bio-optical models. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1998, 103, 31033–31044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves-Araujo, R.; Rabe, B.; Peeken, I.; Bracher, A. High colored dissolved organic matter (CDOM) absorption in surface waters of the central-eastern Arctic Ocean: Implications for biogeochemistry and ocean color algorithms. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodwell Climate Research Center. Arctic Great Rivers Observatory. Available online: https://arcticgreatrivers.org/rivers/ (accessed on 31 July 2021).
- Guay, C.K.; Falkner, K.K.; Muench, R.D.; Mensch, M.; Frank, M.; Bayer, R. Wind-driven transport pathways for Eurasian Arctic river discharge. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2001, 106, 11469–11480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordeev, V.; Martin, J.; Sidorov, I.; Sidorova, M. A reassessment of the Eurasian river input of water, sediment, major elements, and nutrients to the Arctic Ocean. Am. J. Sci. 1996, 296, 664–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| SSS–CDM | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ob–Yenisei | |||||||||
| Slope | −16.92 | −55.34 | −25.38 | −13.12 | −17.80 | −28.75 | −26.45 | −27.08 | −16.91 |
| Y-intercept | 27.68 | 32.12 | 28.49 | 27.85 | 29.08 | 30.93 | 29.53 | 28.83 | 27.57 |
| 0.09 | 0.76 | 0.44 | 0.20 | 0.27 | 0.68 | 0.42 | 0.35 | 0.20 | |
| R | −0.30 | −0.87 | −0.66 | −0.45 | −0.51 | −0.82 | −0.65 | −0.59 | −0.45 |
| Lena | |||||||||
| Slope | −46.23 | −39.60 | −37.36 | −47.63 | −41.48 | −43.38 | −27.42 | −43.19 | −41.59 |
| Y-intercept | 29.30 | 28.99 | 28.27 | 30.56 | 31.33 | 28.25 | 27.13 | 30.46 | 27.79 |
| 0.39 | 0.80 | 0.32 | 0.36 | 0.49 | 0.68 | 0.37 | 0.73 | 0.38 | |
| R | −0.63 | −0.90 | −0.57 | −0.60 | −0.70 | −0.83 | −0.61 | −0.86 | −0.62 |
| Ob–Yenisei | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | Mean |
| Mean | 1.57 | 0.09 | 1.58 | 0.67 | 0.20 | −0.44 | 0.70 | 1.15 | 1.26 | 0.75 |
| STD | 1.39 | 1.35 | 1.52 | 1.74 | 1.31 | 1.20 | 1.52 | 1.41 | 1.41 | 1.42 |
| R | 0.86 | 0.95 | 0.89 | 0.70 | 0.84 | 0.93 | 0.84 | 0.89 | 0.81 | 0.86 |
| Mean | 0.73 | −0.60 | 0.79 | −0.32 | −0.56 | −1.22 | −0.12 | 0.31 | 0.43 | −0.06 |
| STD | 2.42 | 2.22 | 2.51 | 2.50 | 1.98 | 2.07 | 2.26 | 2.33 | 2.40 | 2.30 |
| R | 0.20 | 0.84 | 0.63 | 0.35 | 0.54 | 0.79 | 0.56 | 0.56 | 0.31 | 0.53 |
| Lena | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | Mean |
| Mean | 0.40 | 0.69 | 0.81 | 0.07 | −0.48 | 1.31 | 1.00 | −0.21 | 1.16 | 0.53 |
| STD | 1.17 | 1.13 | 1.56 | 1.60 | 1.31 | 1.14 | 1.65 | 0.74 | 1.70 | 1.33 |
| R | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.94 | 0.96 | 0.94 | 0.96 | 0.92 | 0.98 | 0.93 | 0.95 |
| Mean | 0.48 | 0.05 | 0.42 | −0.92 | −2.37 | 2.26 | 0.64 | −1.48 | 0.88 | −0.00 |
| STD | 2.76 | 1.94 | 3.34 | 3.40 | 2.96 | 1.17 | 3.45 | 2.13 | 3.34 | 2.72 |
| R | 0.74 | 0.88 | 0.58 | 0.60 | 0.66 | 0.84 | 0.57 | 0.86 | 0.60 | 0.70 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Umbert, M.; Gabarro, C.; Olmedo, E.; Gonçalves-Araujo, R.; Guimbard, S.; Martinez, J. Using Remotely Sensed Sea Surface Salinity and Colored Detrital Matter to Characterize Freshened Surface Layers in the Kara and Laptev Seas during the Ice-Free Season. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3828. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13193828
Umbert M, Gabarro C, Olmedo E, Gonçalves-Araujo R, Guimbard S, Martinez J. Using Remotely Sensed Sea Surface Salinity and Colored Detrital Matter to Characterize Freshened Surface Layers in the Kara and Laptev Seas during the Ice-Free Season. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(19):3828. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13193828
Chicago/Turabian StyleUmbert, Marta, Carolina Gabarro, Estrella Olmedo, Rafael Gonçalves-Araujo, Sebastien Guimbard, and Justino Martinez. 2021. "Using Remotely Sensed Sea Surface Salinity and Colored Detrital Matter to Characterize Freshened Surface Layers in the Kara and Laptev Seas during the Ice-Free Season" Remote Sensing 13, no. 19: 3828. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13193828
APA StyleUmbert, M., Gabarro, C., Olmedo, E., Gonçalves-Araujo, R., Guimbard, S., & Martinez, J. (2021). Using Remotely Sensed Sea Surface Salinity and Colored Detrital Matter to Characterize Freshened Surface Layers in the Kara and Laptev Seas during the Ice-Free Season. Remote Sensing, 13(19), 3828. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13193828










