A Continental-Scale Assessment of Density, Size, Distribution and Historical Trends of Farm Dams Using Deep Learning Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mapping Farm Dams in Australia
2.2. Quantifying Uncertainty
2.2.1. Water Detection Using Deep Learning Convolutional Neural Networks
2.2.2. Correcting for False Positives
2.2.3. Correcting for False Negatives
2.2.4. Compounding Multiple Uncertainties
2.3. Historical Trends
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Reported Farm Dams
3.2. Data Verification
3.3. Undetected Farm Dams
3.4. Total Farm Dams in Australia
3.5. Total Water Stored in Dams
3.6. Historical Trends
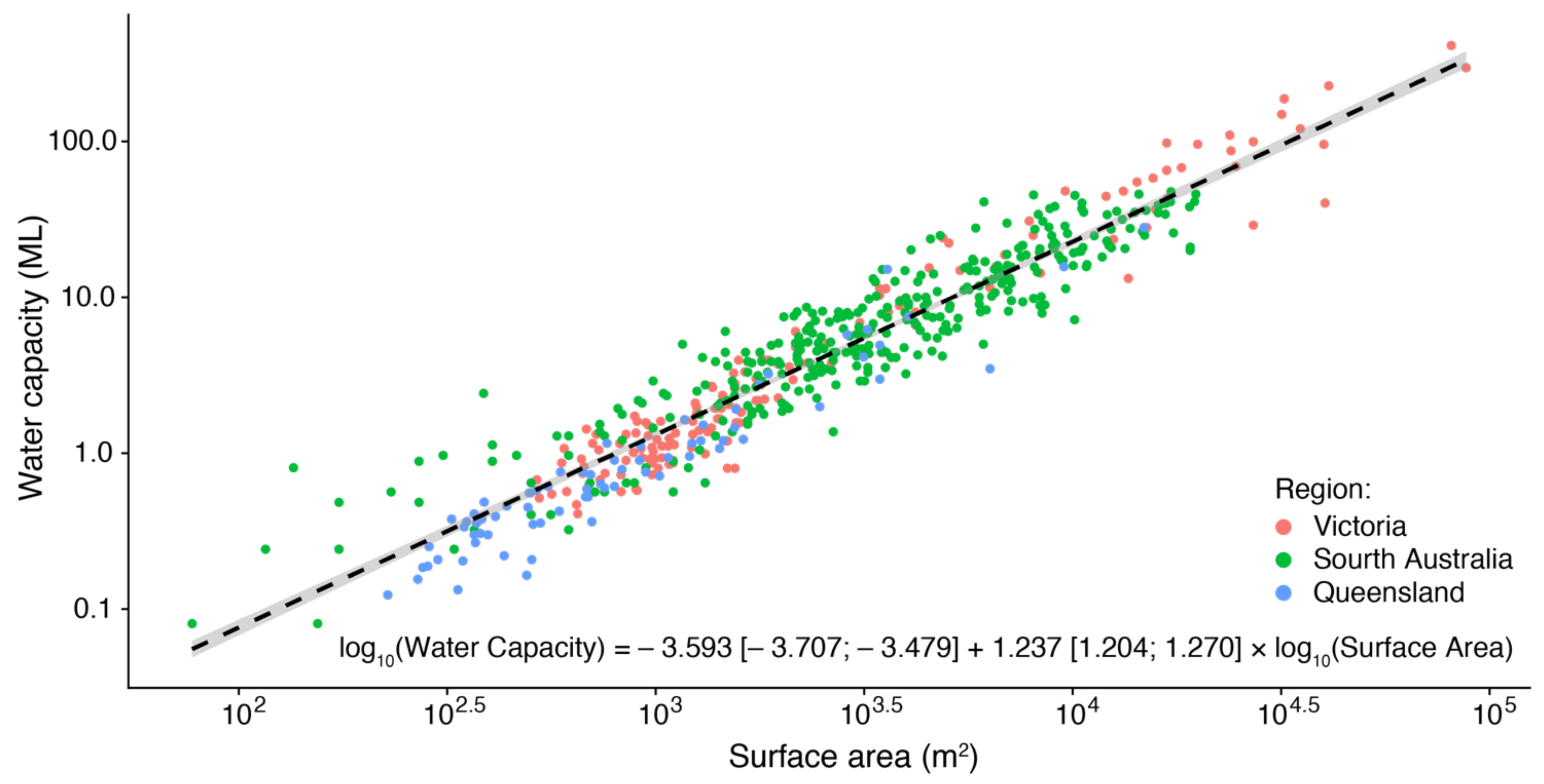
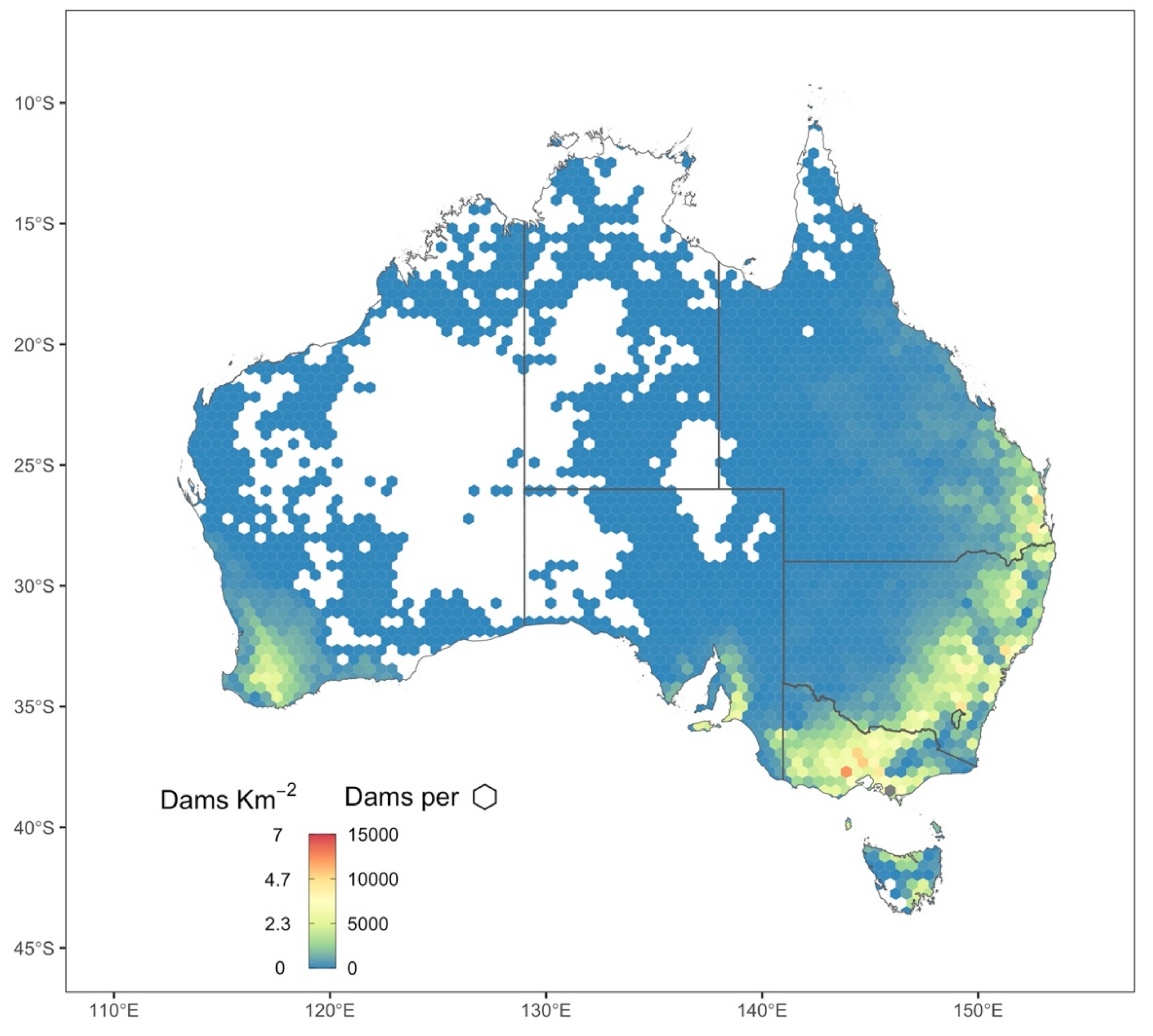
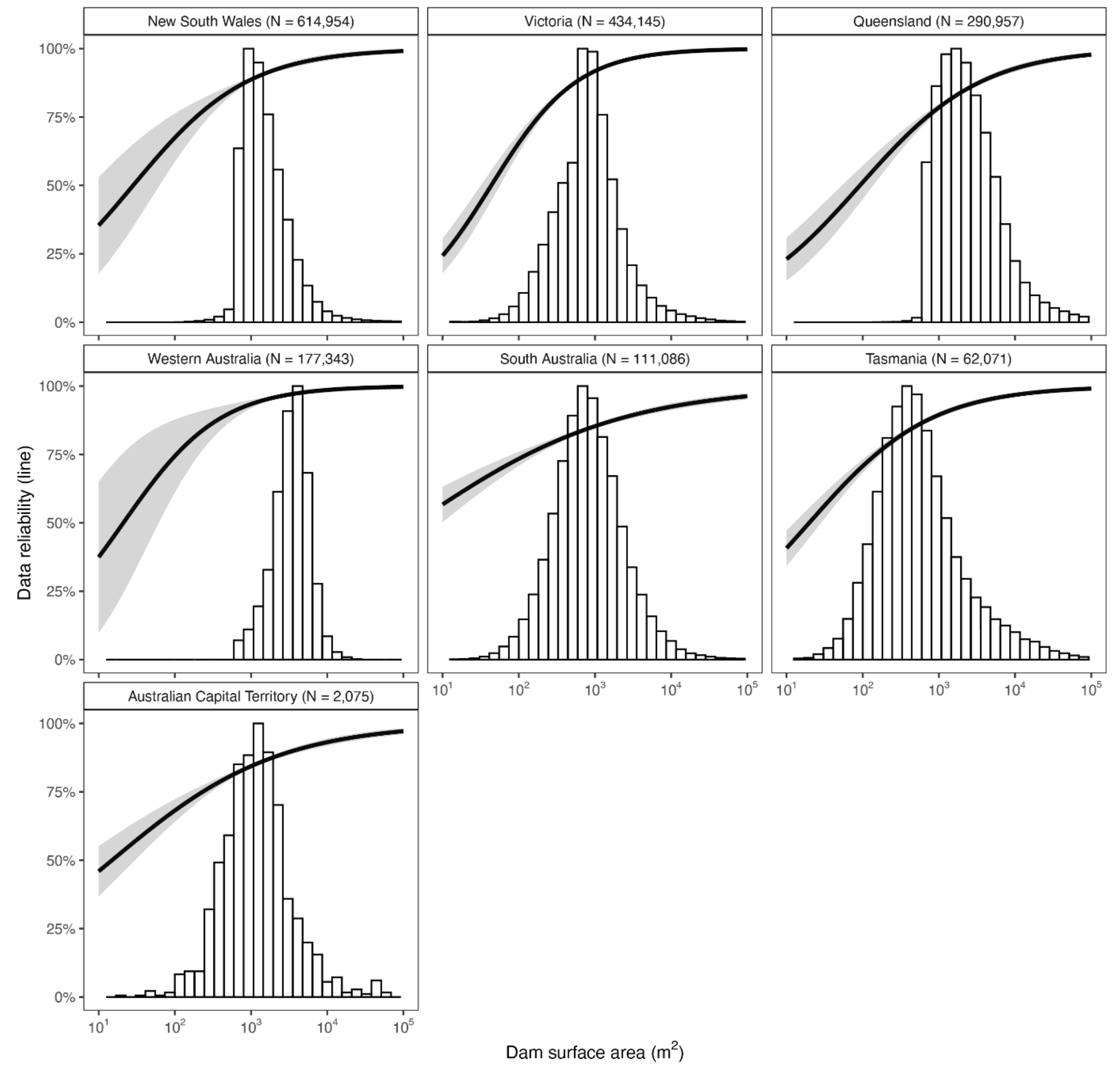



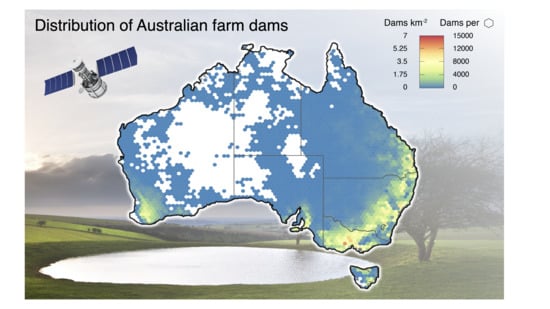
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tisdell, J.; Ward, J.R. The Development of Water Reform in Australia; Cooperative Research Centre for Catchment Hydrology: Clayton, VIC, Australia, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Clifford, C.; Heffernan, J.B. Artificial Aquatic Ecosystems. Water 2018, 10, 1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Downing, J.A. Emerging Global Role of Small Lakes and Ponds: Little Things Mean a Lot. Limnetica 2010, 29, 0009–0024. [Google Scholar]
- Brainwood, M.; Burgin, S. Hotspots of Biodiversity or Homogeneous Landscapes? Farm Dams as Biodiversity Reserves in Australia. Biodivers. Conserv. 2009, 18, 3043–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazell, D.; Cunnningham, R.; Lindenmayer, D.; Mackey, B.; Osborne, W. Use of Farm Dams as Frog Habitat in an Australian Agricultural Landscape: Factors Affecting Species Richness and Distribution. Biol. Conserv. 2001, 102, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, M.L.; Whiles, M.R.; Webber, J.A.; Williard, K.W.; Reeve, J.D. Macroinvertebrate Communities in Agri-Culturally Impacted Southern Illinois Streams: Patterns with Riparian Vegetation, Water Quality, and In-Stream Habitat Quality. J. Environ. Qual. 2005, 34, 907–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenberg, L.; Tuukkanen, T.; Finér, L.; Ronkanen, A.-K.; Piirainen, S.; Kløve, B.; Koivusalo, H. Ditch Erosion Processes and Sediment Transport in a Drained Peatland Forest. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 75, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowley, D.E.; Wissmar, R.C.; Sallenave, R. Fish Assemblages and Seasonal Movements of Fish in Irrigation Canals and River Reaches of the Middle Rio Grande, New Mexico (USA). Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2007, 16, 548–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinham, A.; Albert, S.; Deering, N.; Dunbabin, M.; Bastviken, D.; Sherman, B.; Lovelock, C.E.; Evans, C.D. The Importance of Small Artificial Water Bodies as Sources of Methane Emissions in Queensland, Australia. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 5281–5298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ollivier, Q.R.; Maher, D.T.; Pitfield, C.; Macreadie, P.I. Punching above Their Weight: Large Release of Green-House Gases from Small Agricultural Dams. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2019, 25, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoate, C.; Báldi, A.; Beja, P.; Boatman, N.; Herzon, I.; Van Doorn, A.; De Snoo, G.; Rakosy, L.; Ramwell, C. Ecological Impacts of Early 21st Century Agricultural Change in Europe—A Review. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 91, 22–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isikdogan, F.; Bovik, A.C.; Passalacqua, P. Surface Water Mapping by Deep Learning. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 4909–4918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Fan, R.; Yang, X.; Wang, J.; Latif, A. Extraction of Urban Water Bodies from High-Resolution Remote-Sensing Imagery Using Deep Learning. Water 2018, 10, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, L.; Wang, Z.; Tian, S.; Ye, F.; Ding, J.; Kong, J. Convolutional Neural Networks for Water Body Extraction from Landsat Imagery. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Appl. 2017, 16, 1750001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Wang, C.; Chen, X.; Wan, W.; Li, H.; Zhu, S.; Fang, Y.; Liu, B.; Hong, Y. Recognizing Global Reservoirs From Landsat 8 Images: A Deep Learning Approach. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote. Sens. 2019, 12, 3168–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogilvie, A.; Belaud, G.; Massuel, S.; Mulligan, M.; Le Goulven, P.; Calvez, R. Surface Water Monitoring in Small Water Bodies: Potential and Limits of Multi-Sensor Landsat Time Series. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 4349–4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Yan, Z.; Shen, Q.; Cheng, G.; Gao, L.; Zhang, B. Water Body Extraction from Very High Spatial Resolution Remote Sensing Data Based on Fully Convolutional Networks. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lehane, S. Australia’s Water Security Part 1: Water Resources. Available online: https://www.futuredirections.org.au/publication/australia-s-water-security-part-1-water-resources/ (accessed on 18 January 2021).
- Taylor, K.S. What Does ‘Water Security’ Mean for Australia? A Review of Australian Policy. In Parliamentary Library’s Annual Summer Scholar Program; Parliament of Australia: Canberra, ACT, Australia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, H.H.; Recknagel, F.; Meyer, W.; Frizenschaf, J.; Shrestha, M.K. Modelling the Impacts of Altered Management Practices, Land Use and Climate Changes on the Water Quality of the Millbrook Catchment-Reservoir System in South Australia. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 202, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land & Water Australia. Farm Dam Management 2008. Available online: http://lwa.gov.au/node/2640 (accessed on 9 July 2020).
- Rajendra, P.; Qureshi, M.E.; Shi, T. A Comparison of Water Policies for Sustainable Irrigation Management: The Case of India and Australia. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 1079–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, I.P. Loss of Storage Water through Evaporation with Particular Reference to Arid and Semi-Arid Zone Pasto-Ralism in Australia, DKCRC Working Paper 19, The WaterSmart™ Literature Reviews; Desert Knowledge CRC: Alice Springs, NT, Australia, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Mueller, N.; Lewis, A.C.A.; Roberts, D.; Ring, S.; Melrose, R.; Sixsmith, J.; Lymburner, L.; McIntyre, A.; Tan, P.; Curnow, S.; et al. Water Observations from Space: Mapping Surface Water from 25 Years of Landsat Imagery across Australia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 174, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crossman, S.; Li, O. Surface Hydrology Polygons (Regional); Geoscience Australia: Canberra, ACT, Australia, 2015.
- Crossman, S.; Li, O. Surface Hydrology Points (Regional); Geoscience Australia: Canberra, ACT, Australia, 2015.
- Lowe, L.; Nathan, R.; Morden, R. Assessing the Impact of Farm Dams on Streamflows, Part II: Regional Characterisation. Australas. J. Water Resour. 2005, 9, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair Knight Merz. Improved Assessment of the Impact of Stock and Domestic Farm Dams in Queensland; Sinclair Knight Merz: Sydney, NSW, Australia; Department of Environment and Resource Management: Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 2012.
- McMurray, D. Farm Dam Volume Estimations from Simple Geometric Relationships; Department of Water, Land and Biodiversity Conservation: Adelaide, SA, Australia, 2004.
- Howard, J.; Gugger, S. Fastai: A Layered API for Deep Learning. Information 2020, 11, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burnham, K.P.; Anderson, D.R. Multimodel Inference—Understanding Aic and Bic in Model Selection. Sociol. Method Res. 2004, 33, 261–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ALUM—The Australian Land Use and Management. The Australian Land Use and Management Classification (Version 8) 2016. Available online: https://www.agriculture.gov.au/abares/aclump/land-use/alum-classification (accessed on 18 January 2021).
- Efron, B.; Tibshirani, R. The Problem of Regions. Ann. Stat. 1998, 26, 1687–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Efron, B. Bootstrap Methods: Another Look at the Jackknife. In Breakthroughs in Statistics; Springer Series in Statistics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1992; pp. 569–593. [Google Scholar]
- Python Software Foundation. P.L.R. Version 2.7. Available online: http://www.python.org (accessed on 18 January 2021).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2018; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 10 November 2020).
- Pebesma, E. Simple Features for R: Standardized Support for Spatial Vector Data. R J. 2018, 10, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hijmans, R.J. Raster: Geographic Data Analysis and Modeling. R Package Version 2.5-8. 2016. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=raster (accessed on 18 January 2021).
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lamigueiro, O.P.; Hijmans, R. RasterVis. R Package Version 0.41. 2016. Available online: http://oscarperpinan.github.io/rastervis (accessed on 18 January 2021).
- Wilke, C.O. Cowplot: Streamlined Plot Theme and Plot Annotations for ‘Ggplot2’. R Package Version 0.7.0. 2016. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=cowplot (accessed on 18 January 2021).
- Chang, W.; Cheng, J.; Allaire, J.; Xie, Y.; McPherson, J. Shiny: Web Application Framework for R. R Package Version 1.4.0.2. 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=shiny (accessed on 18 January 2021).
- Cheng, J.; Karambelkar, B.; Xie, Y. Leaflet: Create Interactive Web Maps with the JavaScript ’Leaflet’ Library. R package version 2.0.3. 2019. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=leaflet (accessed on 18 January 2021).
- Sievert, C. Interactive Web-Based Data Visualization with R, Plotly, and Shiny; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Australian Bureau of Statistics (2018). Gross Value of Irrigated Agricultural Production, 2017–2018. Available online: https://www.abs.gov.au/AUSSTATS/abs@.nsf/0/63D842A33B16F4F6CA2581D4001234EB?Opendocument (accessed on 18 January 2021).
- Australian Bureau of Statistics (2018). Water Use on Australian Farms (2016–2017). Available online: https://www.abs.gov.au/ausstats/abs@.nsf/lookup/4618.0Media%20Release12016-17 (accessed on 18 January 2021).
- Habteyes, B.G.; Ward, F.A. Economics of Irrigation Water Conservation: Dynamic Optimization for Consumption and Investment. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 258, 110040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quiggin, J.; Adamson, D.; Chambers, S.; Schrobback, P. Climate Change, Uncertainty, and Adaptation: The Case of Irrigated Agriculture in the Murray-Darling Basin in Australia. Can. J. Agric. Econ. Can. D’agroeconomie 2010, 58, 531–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steffen, W.; Dean, A.; Rice, M. Weather Gone Wild: Climate Change-Fuelled Extreme Weather in 2018; Climate Council: Sydney, NSW, Australia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Scanlon, T.T.; Doncon, G. Rain, Rain, Gone Away: Decreased Growing-Season Rainfall for the Dryland Cropping Region of the South-West of Western Australia. Crop. Pasture Sci. 2020, 71, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, C.R.; Stewardson, M.J.; Finlayson, B.L.; Godden, L.C. Managing Cumulative Effects of Farm Dams in Southeastern Australia. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2019, 145, 05019003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollivier, Q.R.; Maher, D.T.; Pitfield, C.; Macreadie, P.I. Winter Emissions of CO2, CH4, and N2O from Temperate Agricultural Dams: Fluxes, Sources, and Processes. Ecosphere 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- IPCC. Refinement to the 2006 IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories.; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Letnic, M.; Webb, J.K.; Jessop, T.S.; Dempster, T. Restricting Access to Invasion Hubs Enables Sustained Control of an Invasive Vertebrate. J. Appl. Ecol. 2015, 52, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brainwood, M.; Burgin, S.; Maheshwari, B. Temporal Variations in Water Quality of Farm Dams: Impacts of Land Use and Water Sources. Agric. Water Manag. 2004, 70, 151–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolders, A.; Rolls, R.J.; Ryder, D.; Watkinson, A.; MacKenzie, M. Cattle-Derived Microbial Input to Source Water Catchments: An Experimental Assessment of Stream Crossing Modification. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 156, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garnier, J.; Billen, G.; Vilain, G.; Benoit, M.; Passy, P.; Tallec, G.; Tournebize, J.; Anglade, J.; Billy, C.; Mercier, B.; et al. Curative vs. Preventive Management of Nitrogen Transfers in Rural Areas: Lessons from the Case of the Orgeval Watershed (Seine River basin, France). J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 144, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verstraeten, G.; Prosser, I.P. Modelling the Impact of Land-Use Change and Farm Dam Construction on Hillslope Sediment Delivery to Rivers at the Regional Scale. Geomorphology 2008, 98, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callow, J.N.; Smettem, K.R.J. The Effect of Farm Dams and Constructed Banks on Hydrologic Connectivity and Runoff Estimation in Agricultural Landscapes. Environ. Model. Softw. 2009, 24, 959–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malerba, M.E.; Wright, N.; Macreadie, P.I. A Continental-Scale Assessment of Density, Size, Distribution and Historical Trends of Farm Dams Using Deep Learning Convolutional Neural Networks. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13020319
Malerba ME, Wright N, Macreadie PI. A Continental-Scale Assessment of Density, Size, Distribution and Historical Trends of Farm Dams Using Deep Learning Convolutional Neural Networks. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(2):319. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13020319
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalerba, Martino E., Nicholas Wright, and Peter I. Macreadie. 2021. "A Continental-Scale Assessment of Density, Size, Distribution and Historical Trends of Farm Dams Using Deep Learning Convolutional Neural Networks" Remote Sensing 13, no. 2: 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13020319
APA StyleMalerba, M. E., Wright, N., & Macreadie, P. I. (2021). A Continental-Scale Assessment of Density, Size, Distribution and Historical Trends of Farm Dams Using Deep Learning Convolutional Neural Networks. Remote Sensing, 13(2), 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13020319