Urban Water Quality Assessment Based on Remote Sensing Reflectance Optical Classification
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. In Situ Data Collection
2.2.1. Determination of Remote Sensing Reflection
2.2.2. Measurement of Water Quality Parameters
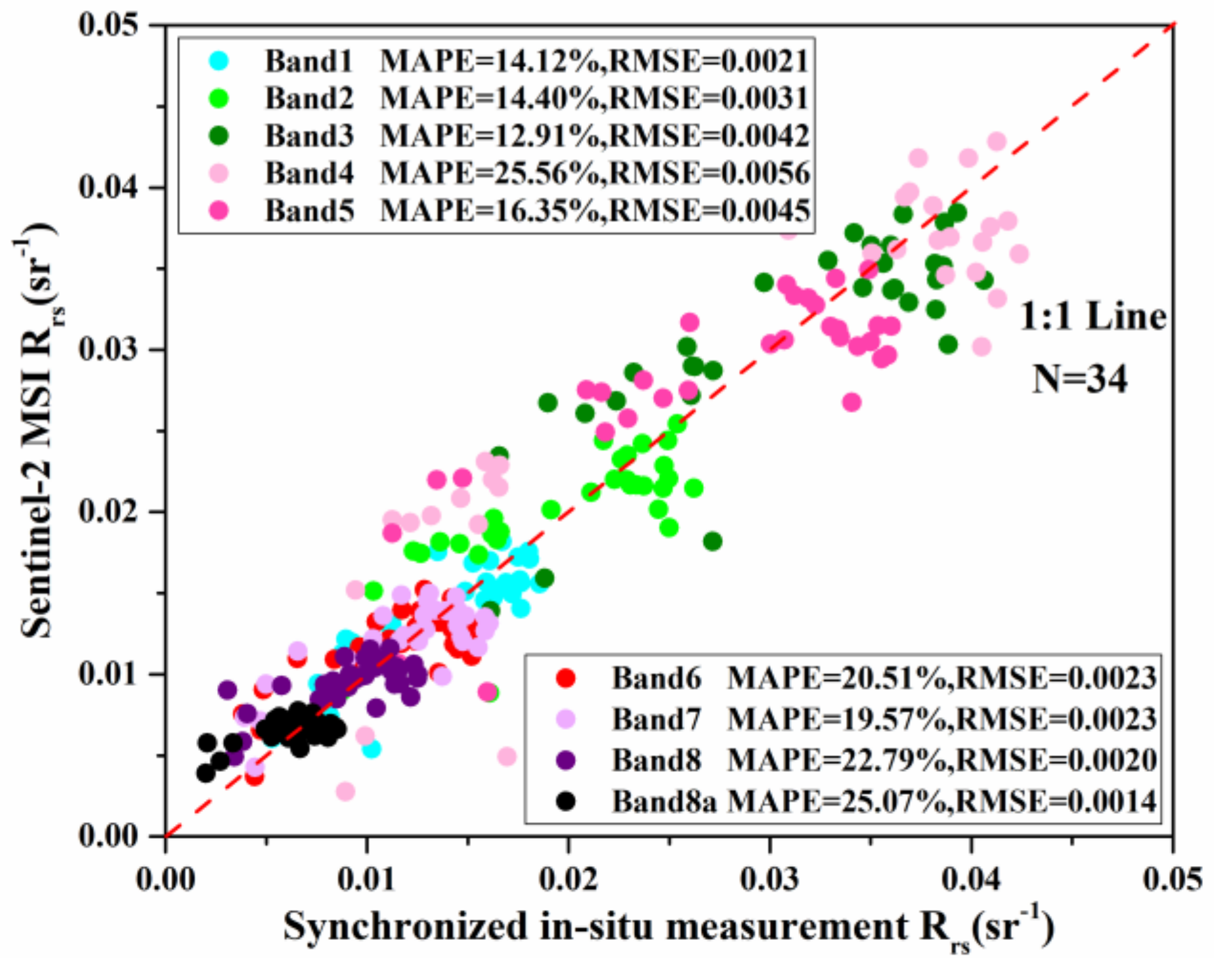
2.3. Sentinel-2 MSI Data Acquisition and Preprocessing
2.4. Urban Water Quality Assessment Method Based on Optical Classification
2.4.1. Construction of the OWT Library
2.4.2. Establishment of the Comprehensive Scoring Rules of Urban Water Quality
3. Results and Analysis
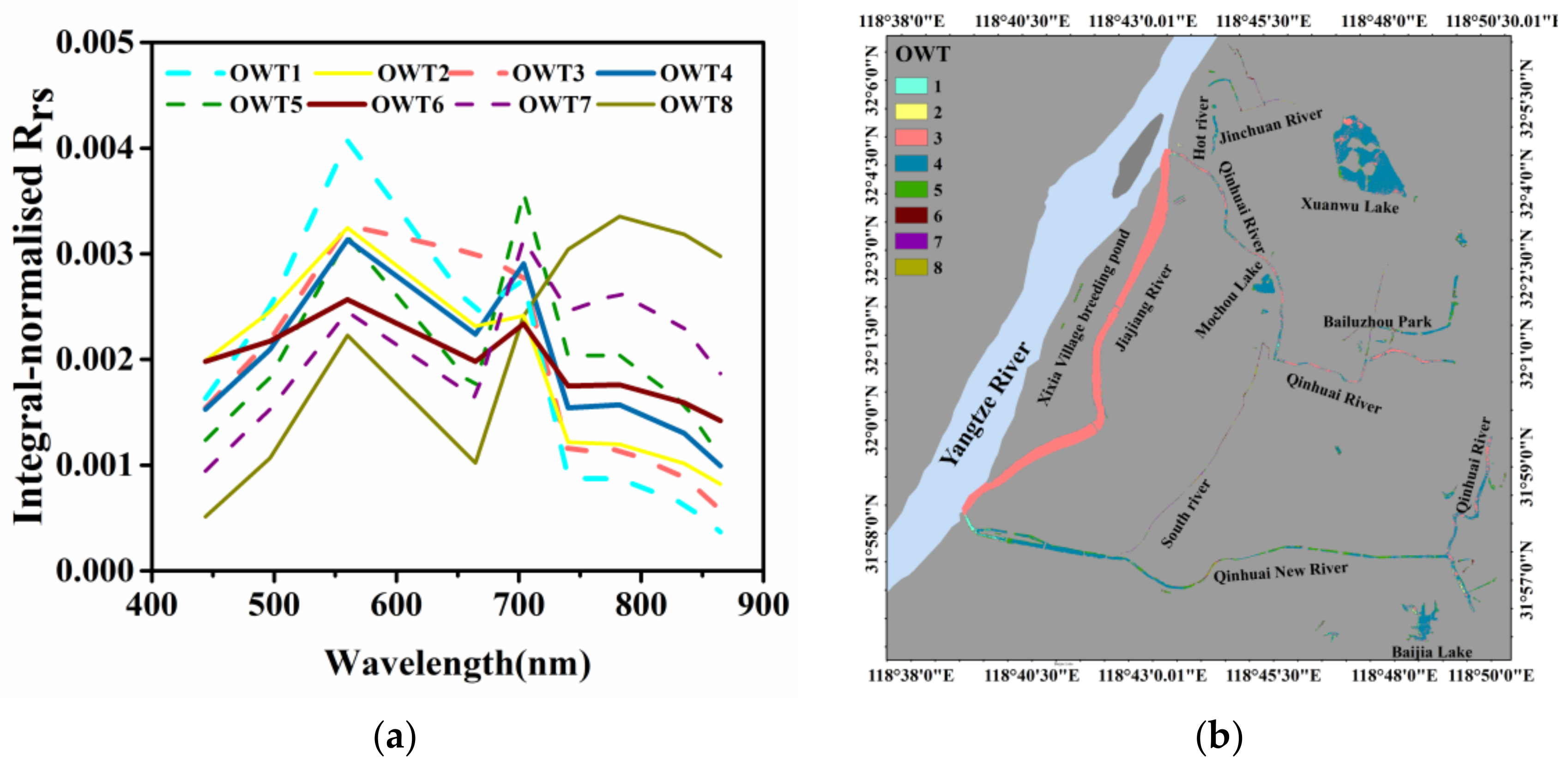
3.1. Optical Water Types of Urban Waterbodies
3.1.1. OWTs Classified by Rrs Measured In Situ
3.1.2. OWTs in the Urban Built-Up Area of Nanjing Based on Sentinel-2 MSI Images
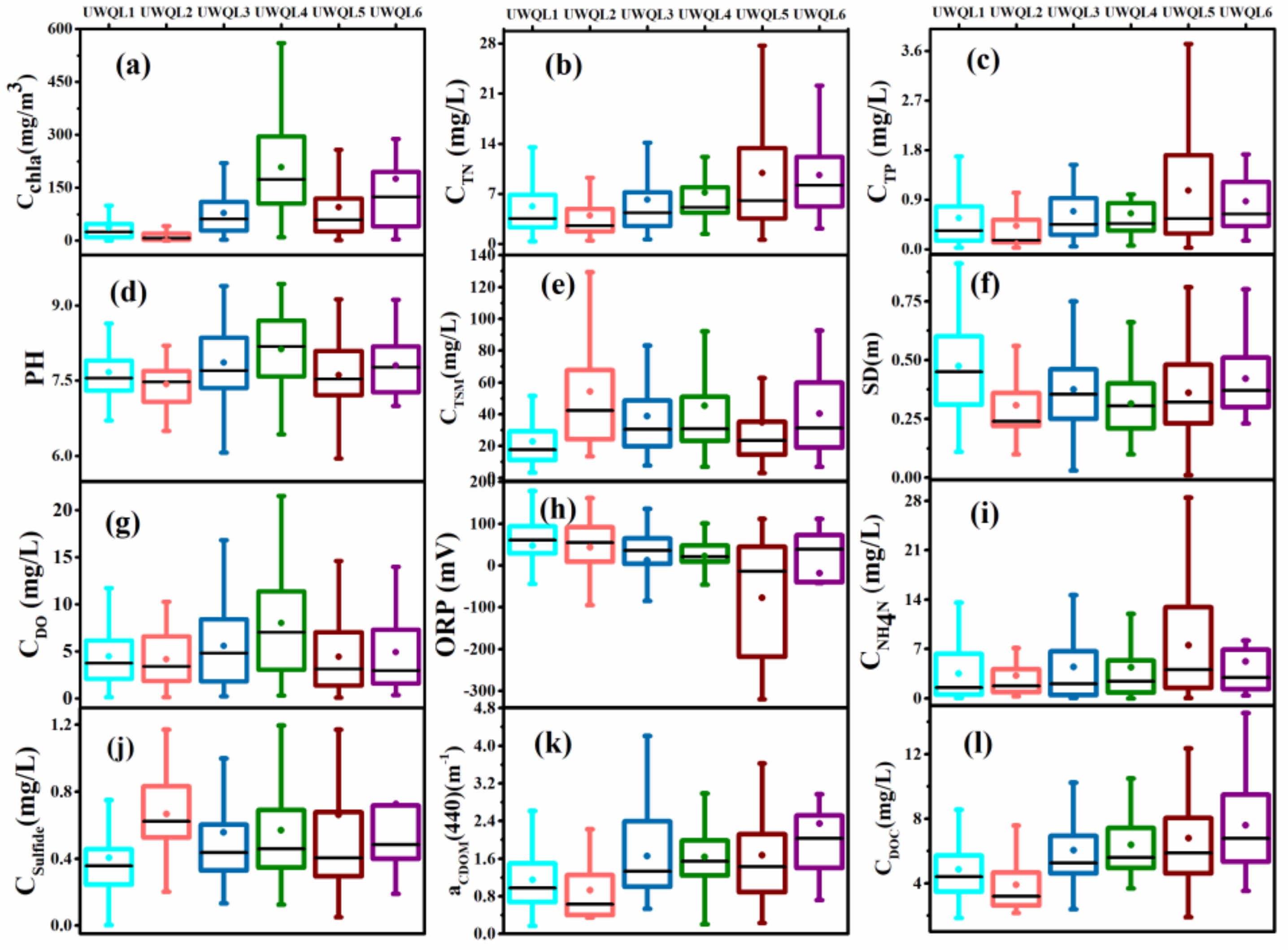
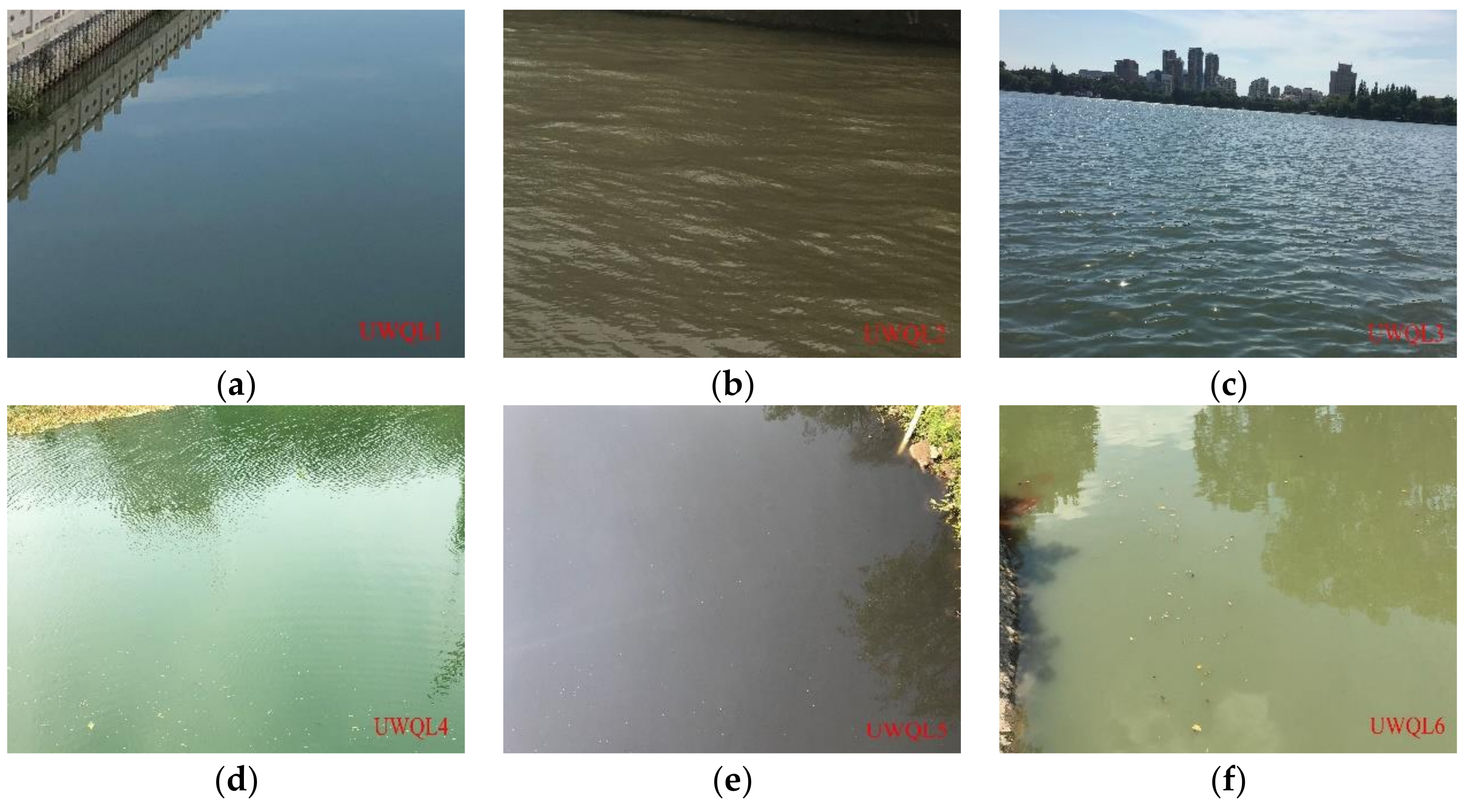
3.2. Urban Water Quality Grading Evaluation Based on OWTs
3.2.1. Grading Evaluation of OWTs Using the Comprehensive Scoring Rules Based on In Situ Data
3.2.2. Spatial Distribution of Water Quality Types in the Built-Up Area of Nanjing Using MSI Images
4. Discussion
4.1. Influence of the Concerned Water Quality Parameters on Rrs
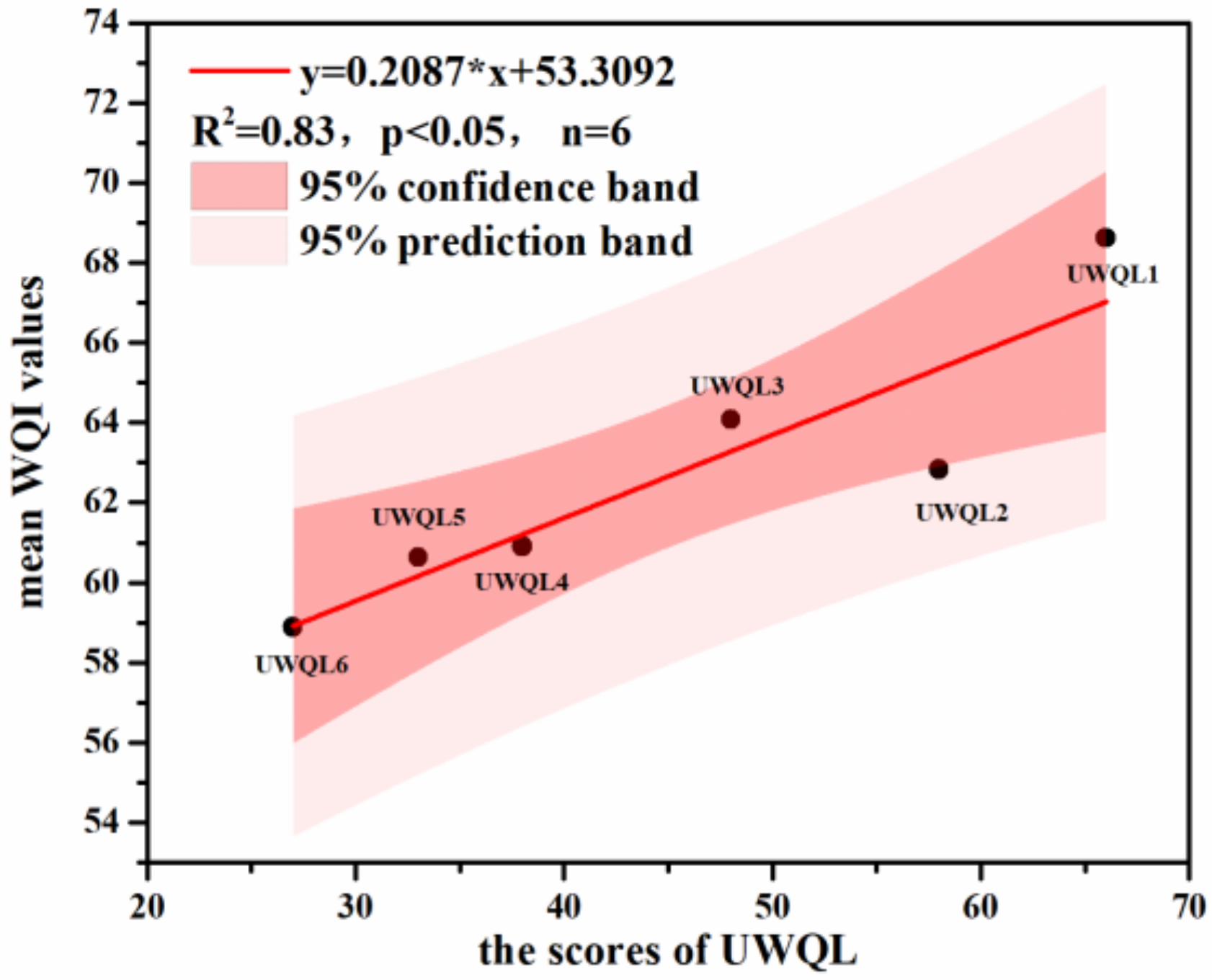
4.2. Relationship between UWQLs and the WQI
4.3. Effectiveness of the Data Processing Methods
4.4. Advantages, Limitations, and Prospects of the Proposed Method
4.4.1. Advantages
4.4.2. Limitations and Prospects
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jacobs, C.; Klok, L.; Bruse, M.; Cortesão, J.; Lenzholzer, S.; Kluck, J. Are urban water bodies really cooling? Urban Clim. 2020, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karn, S.K.; Harada, H. Surface water pollution in three urban territories of Nepal, India, and Bangladesh. Environ. Manag. 2001, 28, 483–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Peng, Y.; Wu, C.; Lv, Y.; Xiao, K.; Zhao, J.; Qian, G. Impact of rapid urbanization on the threshold effect in the relationship between impervious surfaces and water quality in shanghai, China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatica, E.A.; Almeida, C.A.; Mallea, M.A.; Del Corigliano, M.C.; Gonzalez, P. Water quality assessment, by statistical analysis, on rural and urban areas of Chocancharava River (Rio Cuarto), Cordoba, Argentina. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 7257–7274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruley, J.E. An assessment of long-term post-restoration water quality trends in a shallow, subtropical, urban hypereutrophic lake. Ecol. Eng. 2002, 19, 265–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girija, T.R.; Mahanta, C.; Chandramouli, V. Water quality assessment of an untreated effluent impacted urban stream: The Bharalu tributary of the Brahmaputra River, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 130, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Praus, P. Urban water quality evaluation using multivariate analysis. Acta Montan. Slovaca 2007, 12, 150–158. [Google Scholar]
- Sekabira, K.; Origa, H.O.; Basamba, T.A.; Mutumba, G.; Kakudidi, E. Heavy metal assessment and water quality values in urban stream and rain water. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 7, 759–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phiri, O.; Mumba, P.; Moyo, B.H.Z.; Kadewa, W. Assessment of the impact of industrial effluents on water quality of receiving rivers in urban areas of Malawi. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 2, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akoteyon, I.S. Determination of Water Quality Index and Suitability of Urban River for Municipal Water Supply in Lagos-Nigeria. Eur. J. Sci. Res. 2011, 54, 263–271. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, N.; Luo, L.; Wang, X.C.; Song, J.; Han, J.; Ao, D. A novel index for assessing the water quality of urban landscape lakes based on water transparency. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 735, 139351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.; Zhao, N.; Ni, Y.; Yi, J.; Wilson, J.P.; He, L.; Du, Y.; Pei, T.; Zhou, C.; Song, C.; et al. China’s improving inland surface water quality since 2003. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaau3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gebrehiwet Reta, X.D.; Li, Z.; Bo, H.; Yu, D.; Wan, H.; Su, B. Application of Single Factor and Multi-Factor Pollution Indices Assessment for Human-Impacted River Basins Water Quality Classification and Pollution Indicators. Nat. Environ. Pollut. Technol. 2019, 18, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar]
- The Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China. Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water (GB 3838–2002); The Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2002.
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, L.; Ren, H.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Dong, J. Mapping Water Quality Parameters in Urban Rivers from Hyperspectral Images Using a New Self-Adapting Selection of Multiple Artificial Neural Networks. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Jiang, Y.; Deng, X.; Zheng, Y.; Yue, Z. Temporal and Spatial Variations of Chlorophyll a Concentration and Eutrophication Assessment (1987–2018) of Donghu Lake in Wuhan Using Landsat Images. Water 2020, 12, 2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markogianni, V.; Dimitriou, E.; Karaouzas, I. Water quality monitoring and assessment of an urban Mediterranean lake facilitated by remote sensing applications. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 5009–5026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavery, P. Water Quality Monitoring in Estuarine Waters Using the Landsat Thematic Mapper. Remote Sens. Environ. 1993, 46, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Huang, L.; Sun, N.; Chen, J.; Pang, S. Landsat 8-observed water quality and its coupled environmental factors for urban scenery lakes: A case study of West Lake. Water Environ. Res. 2020, 92, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Xie, J.; Li, C.; Qiao, C.; Zhang, J.; Huo, A. Multispectral remote sensing inversion for city landscape water eutrophication based on Genetic Algorithm-Support Vector Machine. Water Qual. Res. J. 2014, 49, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neil, C.; Spyrakos, E.; Hunter, P.D.; Tyler, A.N. A global approach for chlorophyll-a retrieval across optically complex inland waters based on optical water types. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 229, 159–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazeer, M.; Nichol, J.E. Improved water quality retrieval by identifying optically unique water classes. J. Hydrol. 2016, 541, 1119–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, K.; Ma, R.; Wang, D.; Shen, M. Optical Classification of the Remote Sensing Reflectance and Its Application in Deriving the Specific Phytoplankton Absorption in Optically Complex Lakes. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, D.; Matsushita, B.; Pahlevan, N.; Gurlin, D.; Lehmann, M.K.; Fichot, C.G.; Schalles, J.; Loisel, H.; Binding, C.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Remotely estimating total suspended solids concentration in clear to extremely turbid waters using a novel semi-analytical method. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 258, 112386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.Q.; Liu, H.Q.; Lü, H.; Li, Y.M.; Zhu, L.; Zhou, Y.M.; Li, L.L.; Bi, S. Comprehensive Classification Method of Urban Water by Remote Sensing Based on High-Resolution Images. Environ. Sci. 2021, 42, 2213–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Yao, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, F.; Wang, S.; Wu, Y.; Ye, H.; Zhang, B. A CIE Color Purity Algorithm to Detect Black and Odorous Water in Urban Rivers Using High-Resolution Multispectral Remote Sensing Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 6577–6590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.L.; Li, Y.M.; Xu, J.; Yang, Z.Q.; Bi, S.; Xu, J.F. Remote Sensing Classification of Urban Black-odor Water Based on Decision Tree. Environ. Sci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mélin, F.; Vantrepotte, V. How optically diverse is the coastal ocean? Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 160, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trochta, J.T.; Mouw, C.B.; Moore, T.S. Remote sensing of physical cycles in Lake Superior using a spatio-temporal analysis of optical water typologies. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 171, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eleveld, M.; Ruescas, A.; Hommersom, A.; Moore, T.; Peters, S.; Brockmann, C. An Optical Classification Tool for Global Lake Waters. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, Y.; Shen, J.; Wang, H. Calculation of Water Resource Value in Nanjing Based on a Fuzzy Mathematical Model. Water 2018, 10, 920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bu, J.; Li, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z. Assessment and prediction of the water ecological carrying capacity in Changzhou city, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, S.; Lyu, H.; Xu, J.; Bi, S.; Guo, H.; Mu, M.; Lei, S.; Zeng, S.; Liu, H. Characteristics of the chromophoric dissolved organic matter of urban black-odor rivers using fluorescence and UV-visible spectroscopy. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, X.; Du, C.; Xu, P.; Zeng, G.; Huang, D.; Yin, L.; Yin, Q.; Hu, L.; Wan, J.; Zhang, J.; et al. Microplastic pollution in surface sediments of urban water areas in Changsha, China: Abundance, composition, surface textures. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 136, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morel, A.; Mueller, J.L. Normalized water-leaving radiance and remote sensing reflectance: Bidirectional reflectance and other factors. Ocean Opt. Protoc. Satell. Ocean Color Sens. Valid. Revis. 2002, 3, 183–210. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.W.; Tian, G.L.; Wang, X.Y.; Wang, X.M.; Song, Q.J. The methods of water spectra measurement and analysis I: Above-water method. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 8, 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Tyler, J.E. The secchi disc. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1968, 13, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Pan, D.; Bai, Y.; He, X.; Wang, D.; Wei, J.-A.; Zhang, L. Remote Sensing Observation of Particulate Organic Carbon in the Pearl River Estuary. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 8683–8704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jespersen, A.M.; Christoffersen, K. Mearsurements of chlorphyll-a from phytoplankton using ethanol as extraction solvent. Arch. Hydrobiol. 1987, 109, 445–454. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Xia, X.H.; Yang, Z.F.; Wang, F. Assessment of water quality in Baiyangdian Lake using multivariate statistical techniques. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2012, 13, 1213–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, J.H.; Lee, C.W.; Bong, C.W.; Affendi, Y.A.; Hii, Y.S.; Kudo, I. Distributions of particulate and dissolved phosphorus in aquatic habitats of Peninsular Malaysia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 128, 415–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bricaud, A. Absorption by dissolved organic matter of the sea (yellow substance) in the UV and visible domains. Limnol. Oceanogr 1981, 26, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Li, Y.; Guo, Y.; Xu, Y.; Liu, G.; Du, C. Landsat-Based Long-Term Monitoring of Total Suspended Matter Concentration Pattern Change in the Wet Season for Dongting Lake, China. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 13975–13999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Zhu, W.; Tian, Y.Q.; Yu, Q. Monitoring dissolved organic carbon by combining Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 satellites: Case study in Saginaw River estuary, Lake Huron. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 718, 137374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.; Choi, M. Assessment of water quality based on Landsat 8 operational land imager associated with human activities in Korea. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toming, K.; Kutser, T.; Laas, A.; Sepp, M.; Paavel, B.; Nõges, T. First Experiences in Mapping Lake Water Quality Parameters with Sentinel-2 MSI Imagery. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bi, S.; Li, Y.; Xu, J.; Liu, G.; Song, K.; Mu, M.; Lyu, H.; Miao, S.; Xu, J. Optical classification of inland waters based on an improved Fuzzy C-Means method. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 34838–34856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, S.E.; Jones, C.T.; Li, W.K.W.; Lazin, G.; Horne, E.; Caverhill, C.; Cullen, J.J. Deriving optical metrics of coastal phytoplankton biomass from ocean colour. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 119, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, T.; Sathyendranath, S.; Mélin, F. An improved optical classification scheme for the Ocean Colour Essential Climate Variable and its applications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 203, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, Y.-H.; Bricaud, A.; Morel, A. Light backscattering efficiency and related properties of some phytoplankters. Deep Sea Res. Part A Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 1992, 39, 1835–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutser, T. Quantitative detection of chlorophyll in cyanobacterial blooms by satellite remote sensing. Limnol. Oceanogr 2004, 49, 2179–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gower, J.; King, S.; Borstad, G.; Brown, L. Detection of intense plankton blooms using the 709 nm band of the MERIS imaging spectrometer. Int. J. Remote. Sens. 2007, 26, 2005–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilerson, A.; Zhou, J.; Hlaing, S.; Ioannou, I.; Schalles, J.; Gross, B.; Moshary, F.; Ahmed, S. Fluorescence component in the reflectance spectra from coastal waters. Dependence on water composition. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 15702–15721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimba, P.; Gitelson, A. Remote estimation of chlorophyll concentration in hyper-eutrophic aquatic systems: Model tuning and accuracy optimization. Aquaculture 2006, 256, 272–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, S.; Wu, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Huang, C.; Liu, G.; Zheng, Z.; Du, C.; Mu, M.; Xu, J.; et al. Remote sensing monitoring of the suspended particle size in Hongze Lake based on GF-1 data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 40, 3179–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, B.; Sillanpää, M.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, J.; Wahed, M.S.M.A.; Kang, S. Water chemistry of the headwaters of the Yangtze River. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 6443–6458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olguin, E.J.; Sanchez-Galvan, G.; Melo, F.J.; Hernandez, V.J.; Gonzalez-Portela, R.E. Long-term assessment at field scale of Floating Treatment Wetlands for improvement of water quality and provision of ecosystem services in a eutrophic urban pond. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584–585, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, S.; Lyu, H.; Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Du, C.; Mu, M.; Zeng, S.; Miao, S.; Bi, S.; Wang, Q. Remote Monitoring of PSD Slope Under the Influence of Sand Dredging Activities in Lake Hongze Based on Landsat-8/OLI Data and VIIRS/DNB Night-Time Light Composite Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 4198–4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, A.; Sournia, A. Light and photosynthesis in aquatic ecosystems (J. T. O. Kirk). Limnol. Oceanogr. 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, W.; Feng, M.; Yu, R. A rule of hydrological regulating on nutritional status of Poyang Lake, since the operation of the Three Gorges Dam. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 104, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Lin, C.; Ma, R.; Cao, Z. Remote Sensing Estimation of Lake Total Phosphorus Concentration Based on MODIS: A Case Study of Lake Hongze. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yao, X.; Shi, K.; Jeppesen, E.; Yu, Q.; Zhu, W. Chromophoric dissolved organic matter in inland waters: Present knowledge and future challenges. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 759, 143550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Wang, S.; Pang, Y.; Chang Wu, F. Phosphorus fractions and the effect of pH on the phosphorus release of the sediments from different trophic areas in Taihu Lake, China. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 139, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.; Tzortziou, M.; Hu, C.; Mannino, A.; Fichot, C.G.; Del Vecchio, R.; Najjar, R.G.; Novak, M. Remote sensing retrievals of colored dissolved organic matter and dissolved organic carbon dynamics in North American estuaries and their margins. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 205, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Sun, Q.; Zhao, D.; Xu, M.; Shen, Q.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Ding, S. A critical review of the appearance of black-odorous waterbodies in China and treatment methods. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 385, 121511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Zheng, Z.; Li, Y.; Lv, G.; Wang, Q.; Lyu, H.; Huang, C.; Liu, G.; Du, C.; Mu, M.; et al. Remote observation of water clarity patterns in Three Gorges Reservoir and Dongting Lake of China and their probable linkage to the Three Gorges Dam based on Landsat 8 imagery. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 625, 1554–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinese Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development. Working Guidelines for the Treatment of Urban Black-odorous Water; Chinese Ministry of Housing and Urban-rural Development: Beijing, China, 2015.
- Kannel, P.R.; Lee, S.; Lee, Y.S.; Kanel, S.R.; Khan, S.P. Application of water quality indices and dissolved oxygen as indicators for river water classification and urban impact assessment. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 132, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesce, S.F.; Wunderlin, D.A. Use of water quality indices to verify the impact of Córdoba City (Argentina) on Suquıía River. Water Res. 2000, 34, 2915–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yulong, G.; Yunmei, L.; Heng, L.; Shanshan, W.; Yongbo, W. Applicability analysis of the model for remotely estimating total suspended matter concentration based on principal component dimension reduction. J. Lake Sci. 2013, 25, 892–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spyrakos, E.; O’Donnell, R.; Hunter, P.D.; Miller, C.; Scott, M.; Simis, S.G.H.; Neil, C.; Barbosa, C.C.F.; Binding, C.E.; Bradt, S.; et al. Optical types of inland and coastal waters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2018, 63, 846–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vantrepotte, V.; Loisel, H.; Dessailly, D.; Mériaux, X. Optical classification of contrasted coastal waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 123, 306–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Luo, G.; Chen, X.; Yang, X.; Hall, M.H.; Guo, R.; Wang, H.; Cui, J.; et al. Heavy metal contamination of urban soil in an old industrial city (Shenyang) in Northeast China. Geoderma 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, R.; Cheng, M.; Yang, X.; Yang, Y.; Shi, M. Exposure levels and health damage assessment of dust in a coal mine of Shanxi Province, China. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 128, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksimovich, N.; Pyankov, S.; Khayrulina, E. Environmental assessment of closeded coal mine territory using GIS analysis. Mine Water Circ. Econ. 2017, 2017, 212–217. [Google Scholar]
- Colomina, I.; Molina, P. Unmanned aerial systems for photogrammetry and remote sensing: A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 92, 79–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guimarães, T.T.; Veronez, M.R.; Koste, E.C.; Souza, E.M.; Brum, D.; Gonzaga, L.; Mauad, F.F. Evaluation of Regression Analysis and Neural Networks to Predict Total Suspended Solids in Water Bodies from Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Images. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, L.; Huang, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, X.; Cao, L. Monitoring of Urban Black-Odor Water Based on Nemerow Index and Gradient Boosting Decision Tree Regression Using UAV-Borne Hyperspectral Imagery. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



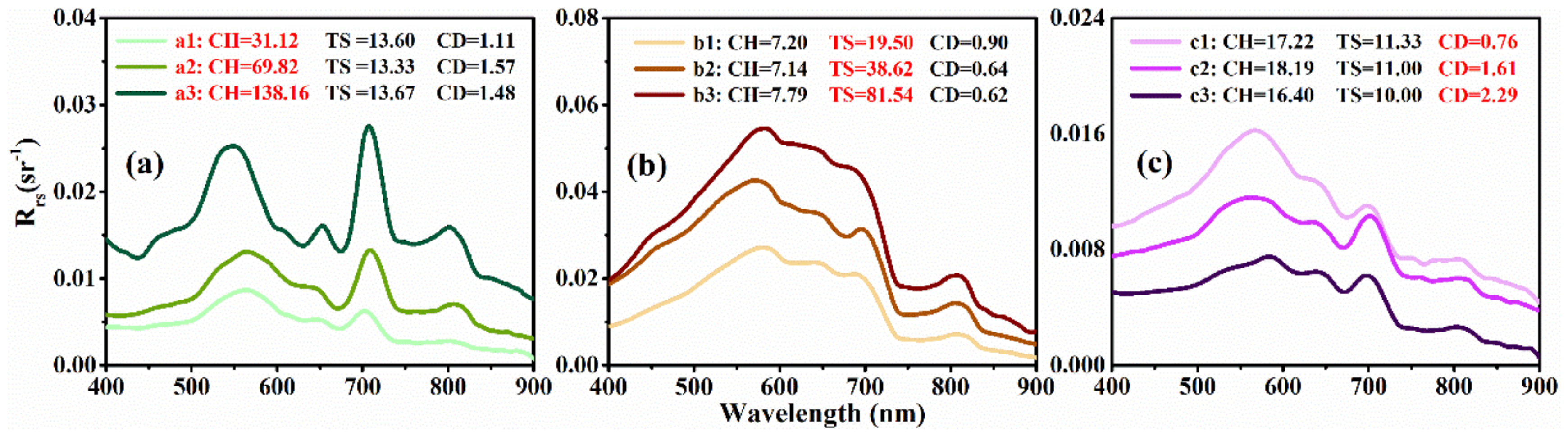
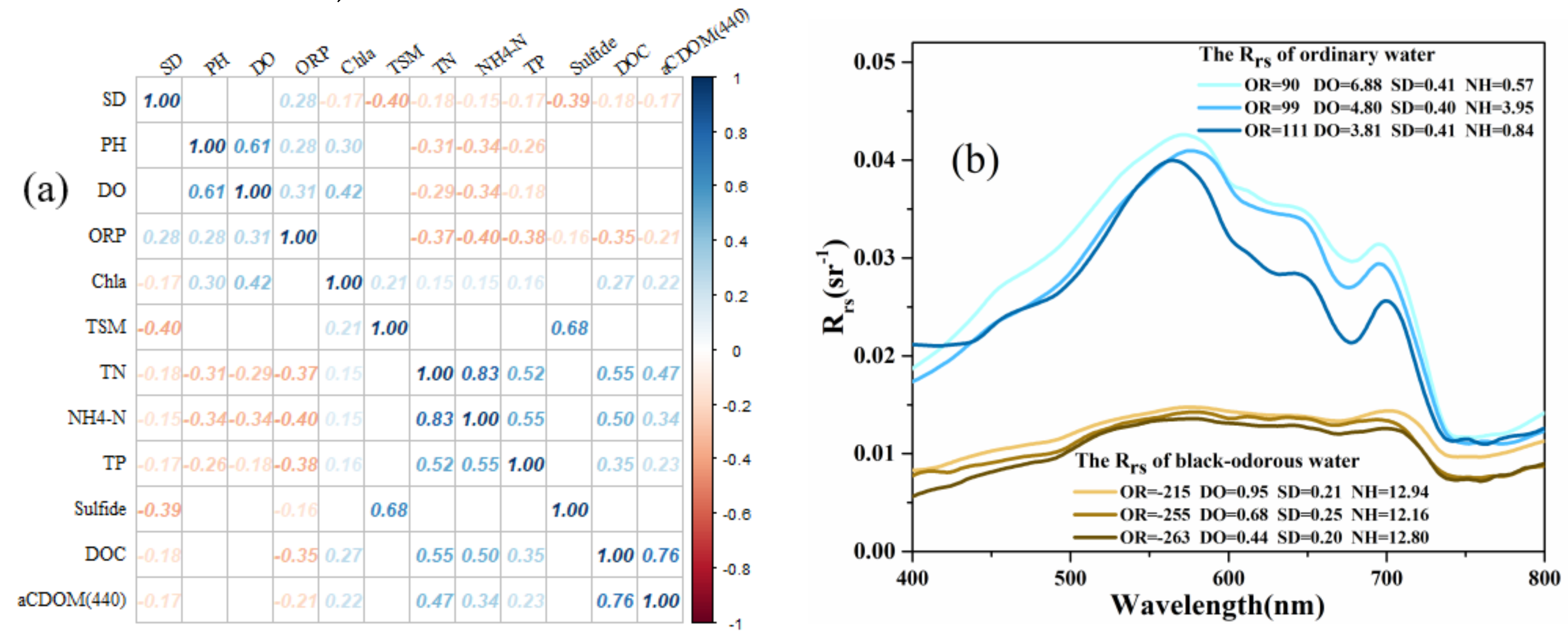
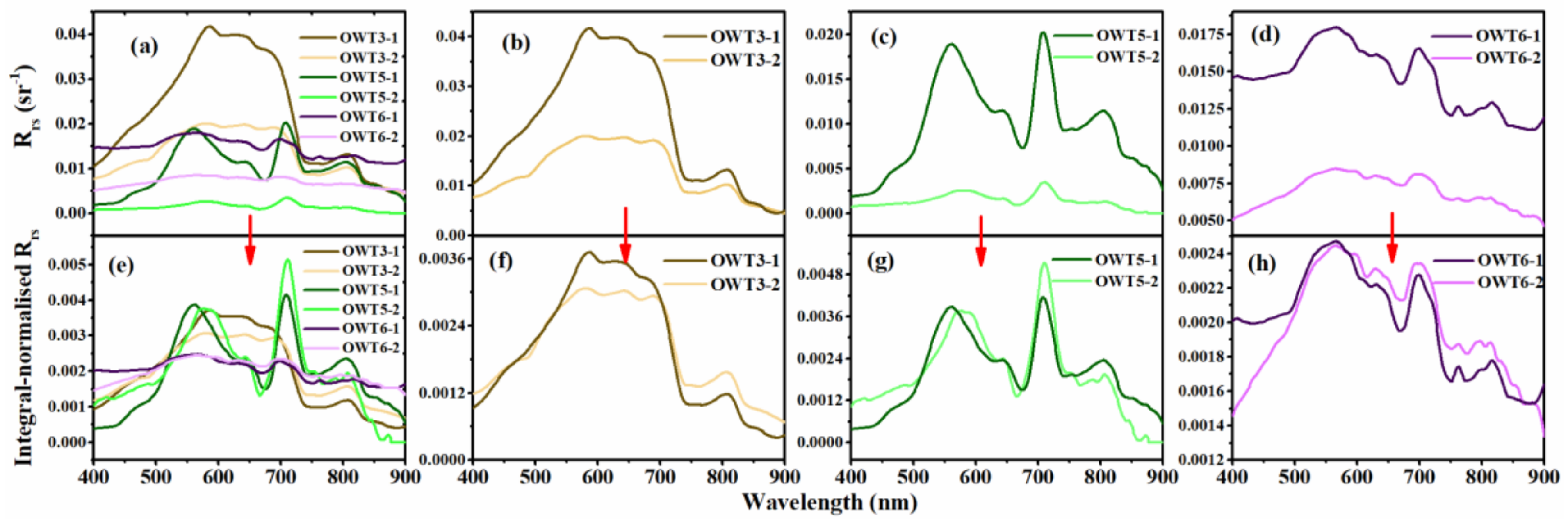
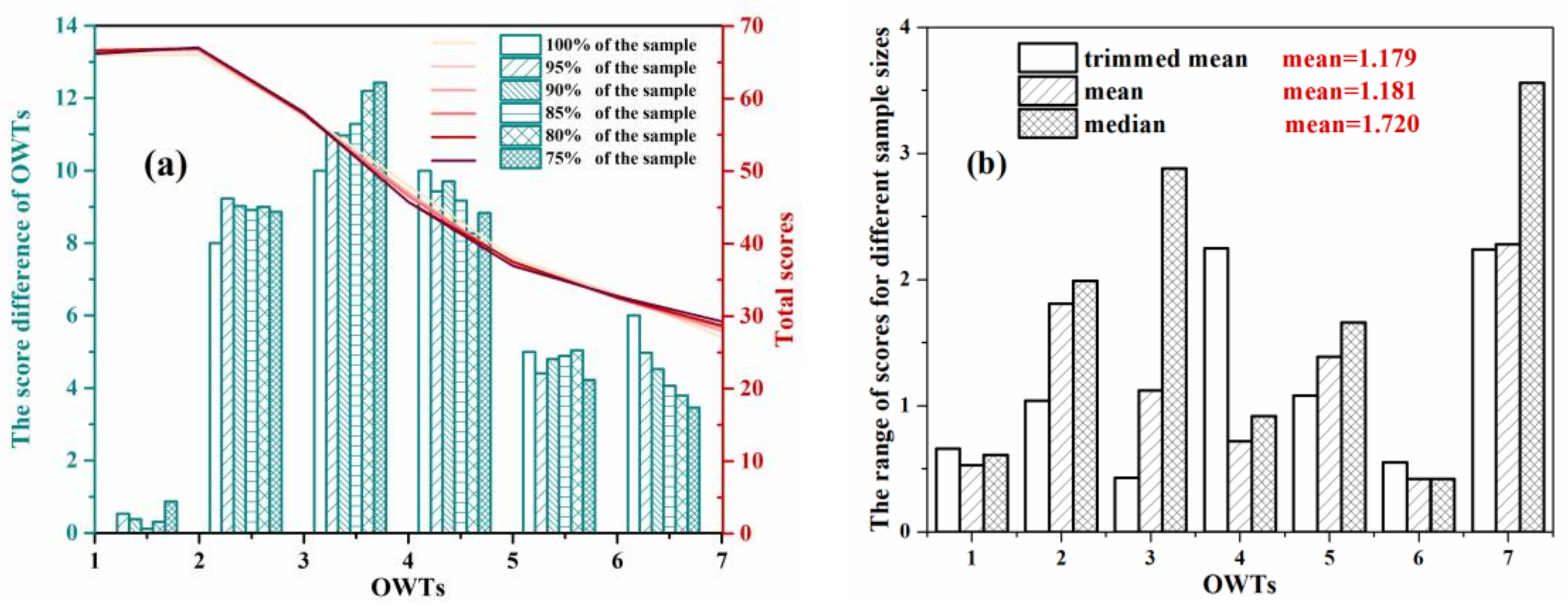
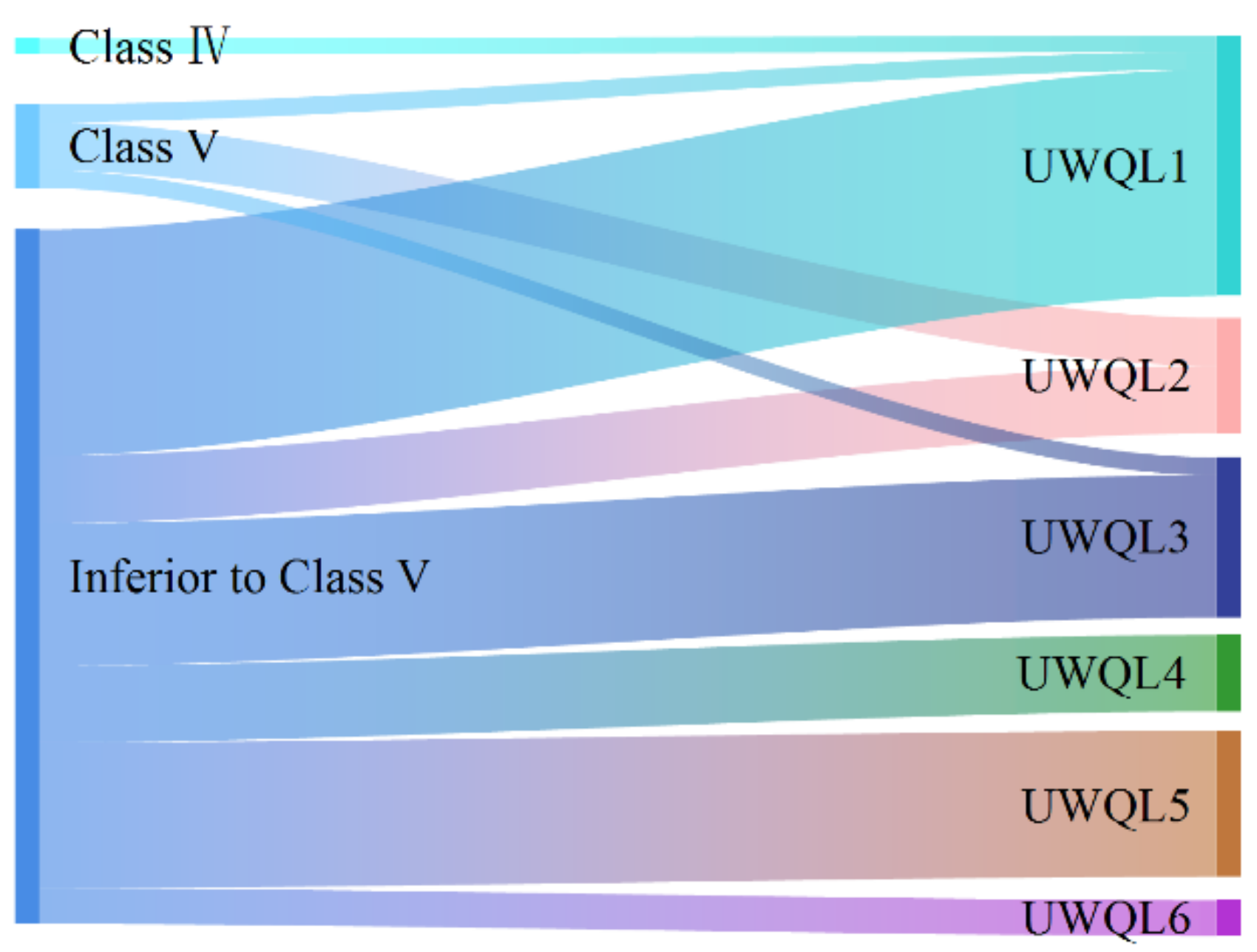
| Parameters | SD | PH | DO | ORP | Chla | TSM | TN | NH4-N | TP | Sulfide | DOC | aCDOM(440) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MEAN ± S.D. | 0.39 ± 0.19 | 7.72 ± 0.70 | 5.06 ± 4.17 | 15.34 ± 105.54 | 77.02 ± 101.27 | 35.61 ± 35.68 | 6.56 ± 6.39 | 4.70 ± 5.85 | 0.68 ± 0.74 | 0.54 ± 0.54 | 5.61 ± 2.81 | 1.43 ± 0.93 |
| MIN | 0.01 | 5.50 | 0.09 | −320.00 | 0.02 | 3.00 | 0.37 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.003 | 1.85 | 0.17 |
| MAX | 1.21 | 10.10 | 23.89 | 235.00 | 660.09 | 337.00 | 37.21 | 48.5 | 5.53 | 6.27 | 23.98 | 8.00 |
| OWTs | OWT1 | OWT2 | OWT3 | OWT4 | OWT5 | OWT6 | OWT7 | OWT8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCORE | 66 | 66 | 58 | 48 | 38 | 33 | 27 | - |
| UWQLs | UWQL1 | UWQL1 | UWQL2 | UWQL3 | UWQL4 | UWQL5 | UWQL6 | UWQLM |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, X.; Li, Y.; Bi, S.; Lei, S.; Xu, J.; Wang, H.; Dong, X.; Li, J.; Zeng, S.; Lyu, H. Urban Water Quality Assessment Based on Remote Sensing Reflectance Optical Classification. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4047. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13204047
Cai X, Li Y, Bi S, Lei S, Xu J, Wang H, Dong X, Li J, Zeng S, Lyu H. Urban Water Quality Assessment Based on Remote Sensing Reflectance Optical Classification. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(20):4047. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13204047
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Xiaolan, Yunmei Li, Shun Bi, Shaohua Lei, Jie Xu, Huaijing Wang, Xianzhang Dong, Junda Li, Shuai Zeng, and Heng Lyu. 2021. "Urban Water Quality Assessment Based on Remote Sensing Reflectance Optical Classification" Remote Sensing 13, no. 20: 4047. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13204047
APA StyleCai, X., Li, Y., Bi, S., Lei, S., Xu, J., Wang, H., Dong, X., Li, J., Zeng, S., & Lyu, H. (2021). Urban Water Quality Assessment Based on Remote Sensing Reflectance Optical Classification. Remote Sensing, 13(20), 4047. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13204047







