Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.X. and H.S.; methodology, Y.X.; software, Y.X.; validation, H.S., J.C. and L.L.; formal analysis, H.S. and J.C.; investigation, K.J.; resources, L.L. and G.K.; data curation, Y.X.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.X.; writing—review and editing, Y.X. and H.S.; visualization, Y.X.; supervision, H.S.; project administration, G.K.; funding acquisition, H.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Figure 1.
Illustration of adversarial attacks on DNN models for SAR target recognition. The perturbations are amplified ten times for ease of observation.
Figure 1.
Illustration of adversarial attacks on DNN models for SAR target recognition. The perturbations are amplified ten times for ease of observation.
Figure 2.
With 11 evaluation methods in total, our comprehensive robustness evaluation framework focuses on data and model, which are the key factors in an adversarial setting.
Figure 2.
With 11 evaluation methods in total, our comprehensive robustness evaluation framework focuses on data and model, which are the key factors in an adversarial setting.
Figure 3.
Illustration of workflow comparison: (a) AT; (b) RoCL; (c) ACL(DS). Note that RoCL and ACL(DS) share all weights; however, adversarial and standard encoders use independent BN parameters.
Figure 3.
Illustration of workflow comparison: (a) AT; (b) RoCL; (c) ACL(DS). Note that RoCL and ACL(DS) share all weights; however, adversarial and standard encoders use independent BN parameters.
Figure 4.
Illustration of UACL’s architecture. We minimize the similarity loss between the features of augmented data and the corresponding unsupervised adversarial examples to optimize the Siamese network. EMA means exponential moving average. At the end of training, everything but the robust encoder, i.e., the ResNet18, is discarded.
Figure 4.
Illustration of UACL’s architecture. We minimize the similarity loss between the features of augmented data and the corresponding unsupervised adversarial examples to optimize the Siamese network. EMA means exponential moving average. At the end of training, everything but the robust encoder, i.e., the ResNet18, is discarded.
Figure 5.
Example images from the MSTAR dataset.
Figure 5.
Example images from the MSTAR dataset.
Figure 6.
Example images from the FUSAR-Ship dataset.
Figure 6.
Example images from the FUSAR-Ship dataset.
Figure 7.
Robust accuracy of MSTAR models trained with adversarial defense methods against adversarial attacks ( PGD) with different strengths (/255).
Figure 7.
Robust accuracy of MSTAR models trained with adversarial defense methods against adversarial attacks ( PGD) with different strengths (/255).
Figure 8.
Robust accuracy of FUSAR-Ship models trained with adversarial defense methods against adversarial attacks ( PGD) with different strengths (/255).
Figure 8.
Robust accuracy of FUSAR-Ship models trained with adversarial defense methods against adversarial attacks ( PGD) with different strengths (/255).
Figure 9.
Guided backpropagation images of MSTAR model in the classification of clean data.
Figure 9.
Guided backpropagation images of MSTAR model in the classification of clean data.
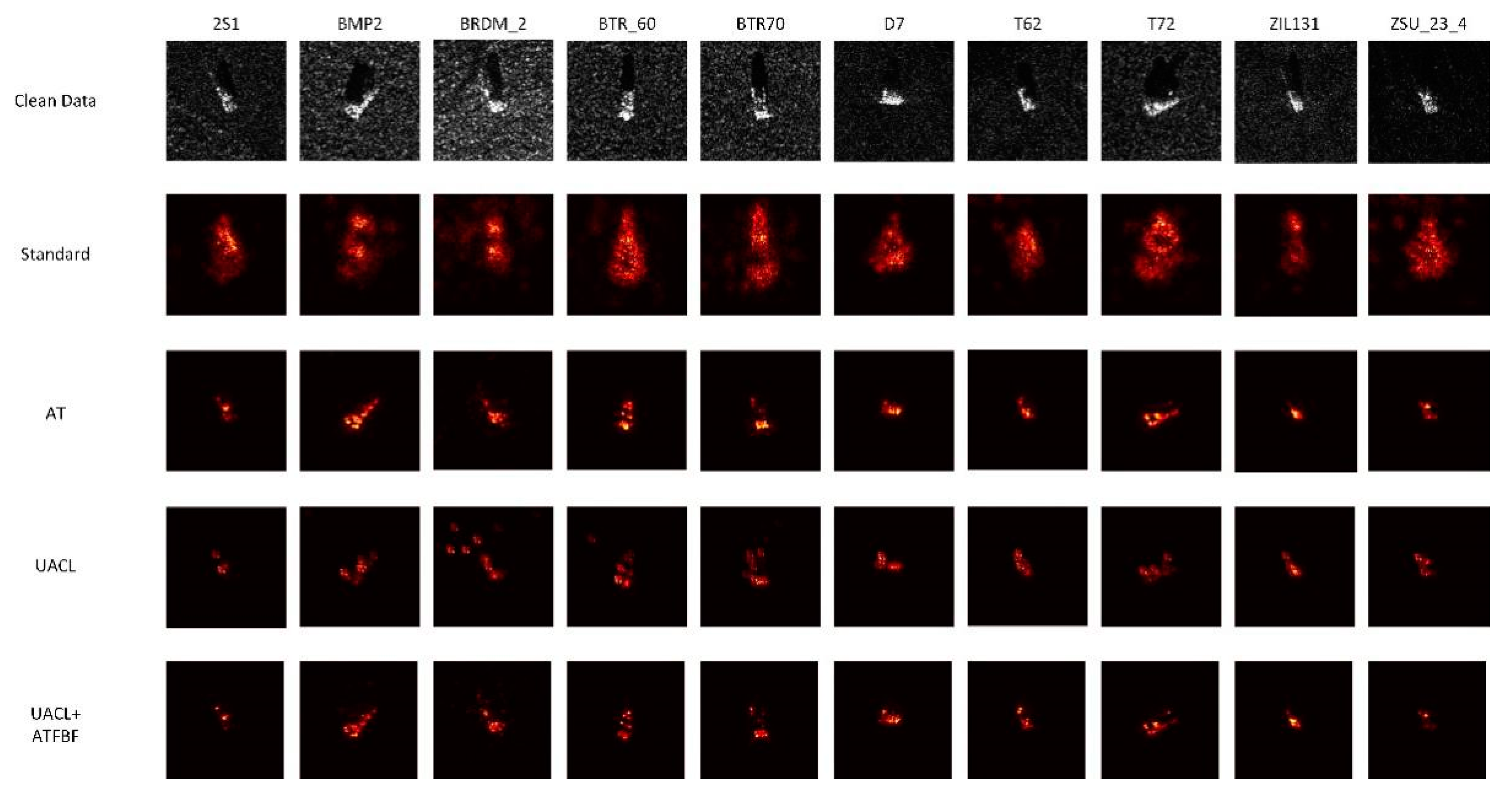
Figure 10.
Guided backpropagation images of MSTAR model in the classification of adversarial examples.
Figure 10.
Guided backpropagation images of MSTAR model in the classification of adversarial examples.
Figure 11.
Guided backpropagation images of FUSAR-Ship model in the classification of clean data.
Figure 11.
Guided backpropagation images of FUSAR-Ship model in the classification of clean data.
Figure 12.
Guided backpropagation images of FUSAR-Ship model in the classification of adversarial examples.
Figure 12.
Guided backpropagation images of FUSAR-Ship model in the classification of adversarial examples.
Figure 13.
Extremal perturbations images of MSTAR model in the classification of clean data.
Figure 13.
Extremal perturbations images of MSTAR model in the classification of clean data.
Figure 14.
Extremal perturbations images of MSTAR model in the classification of adversarial examples.
Figure 14.
Extremal perturbations images of MSTAR model in the classification of adversarial examples.
Figure 15.
Extremal perturbations images of FUSAR-Ship model in the classification of clean data.
Figure 15.
Extremal perturbations images of FUSAR-Ship model in the classification of clean data.
Figure 16.
Extremal perturbations images of FUSAR-Ship model in the classification of adversarial examples.
Figure 16.
Extremal perturbations images of FUSAR-Ship model in the classification of adversarial examples.
Table 1.
Details of MSTAR, including target class and data number.
Table 1.
Details of MSTAR, including target class and data number.
| Target Class | Training Number | Testing Number |
|---|
| 2S1 | 299 | 274 |
| BMP2 | 233 | 296 |
| BRDM2 | 298 | 274 |
| BTR60 | 256 | 195 |
| BTR70 | 233 | 196 |
| D7 | 299 | 274 |
| T62 | 299 | 273 |
| T72 | 232 | 196 |
| ZIL131 | 299 | 274 |
| ZSU234 | 299 | 274 |
Table 2.
Details of FURSAR-Ship, including target class and data number.
Table 2.
Details of FURSAR-Ship, including target class and data number.
| Target Class | Training Number | Testing Number |
|---|
| BulkCarrier | 97 | 25 |
| CargoShip | 126 | 32 |
| Fishing | 75 | 19 |
| Tanker | 36 | 10 |
Table 3.
Classification accuracy of MSTAR models against standard adversarial attack (PGD). The adversarial examples can be divided into norm, norm, and norm limited attacks.
Table 3.
Classification accuracy of MSTAR models against standard adversarial attack (PGD). The adversarial examples can be divided into norm, norm, and norm limited attacks.
| | Clean Data | Adversarial Examples |
|---|
| | | | |
|---|
| | 8/255 | 16/255 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 7.84 | 12 |
|---|
| ResNet18 | 97.65 ± 0.28 | 2.02 ± 0.08 | 1.86 ± 0.04 | 62.60 ± 0.85 | 17.53 ± 0.47 | 86.23 ± 1.33 | 76.87 ± 1.47 |
| ResNet50 | 97.86 ± 0.12 | 1.73 ± 0.07 | 1.65 ± 0.07 | 56.41 ± 0.87 | 19.51 ± 0.68 | 75.18 ± 1.58 | 59.01 ± 1.21 |
| ResNet101 | 98.68 ± 0.25 | 1.53 ± 0.11 | 1.36 ± 0.12 | 56.25 ± 1.16 | 15.13 ± 0.97 | 72.49 ± 1.02 | 57.73 ± 0.93 |
| DenseNet121 | 98.56 ± 0.13 | 0.82 ± 0.08 | 0.37 ± 0.13 | 47.67 ± 2.07 | 6.02 ± 1.28 | 86.35 ± 2.47 | 69.44 ± 1.84 |
| DenseNet201 | 98.68 ± 0.07 | 0.66 ± 0.09 | 0.08 ± 0.15 | 52.82 ± 2.12 | 7.46 ± 1.67 | 84.45 ± 3.11 | 69.94 ± 2.03 |
| MobileNet | 98.23 ± 0.17 | 2.31 ± 0.06 | 1.32 ± 0.07 | 10.31 ± 2.15 | 3.46 ± 1.35 | 67.09 ± 1.09 | 35.09 ± 1.04 |
| ShuffleNet | 95.01 ± 0.78 | 1.48 ± 0.06 | 1.32 ± 0.09 | 9.24 ± 1.45 | 3.09 ± 1.22 | 74.64 ± 1.38 | 23.92 ± 0.79 |
| A-ConvNet | 99.79 ± 0.84 | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 71.84 ± 2.46 | 17.73 ± 0.38 | 94.39 ± 2.46 | 83.55 ± 2.34 |
| A-ConvNet-M | 98.14 ± 0.33 | 1.98 ± 0.03 | 1.69 ± 0.07 | 68.78 ± 2.73 | 21.85 ± 1.52 | 87.05 ± 1.10 | 73.15 ± 1.22 |
Table 4.
Classification accuracy of FUSAR-Ship models against standard adversarial attack (PGD).
Table 4.
Classification accuracy of FUSAR-Ship models against standard adversarial attack (PGD).
| | Clean Data | Adversarial Examples |
|---|
| | | | |
|---|
| | 8/255 | 16/255 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 7.84 | 12 |
|---|
| ResNet18 | 69.77 ± 2.32 | 8.14 ± 2.32 | 8.14 ± 2.32 | 16.28 ± 2.32 | 13.95 ± 2.32 | 53.49 ± 3.49 | 37.21 ± 3.49 |
| ResNet50 | 68.60 ± 3.49 | 4.65 ± 1.16 | 4.65 ± 1.16 | 13.95 ± 2.32 | 12.79 ± 1.16 | 50.00 ± 2.32 | 37.21 ± 2.32 |
| ResNet101 | 70.93 ± 4.65 | 29.07 ± 2.32 | 29.07 ± 2.32 | 25.58 ± 3.49 | 20.93 ± 2.32 | 53.49 ± 3.49 | 45.35 ± 2.32 |
| DenseNet121 | 66.28 ± 4.65 | 24.42 ± 2.32 | 24.42 ± 2.32 | 11.63 ± 2.32 | 6.98 ± 1.16 | 59.30 ± 3.49 | 41.86 ± 3.49 |
| DenseNet201 | 68.60 ± 4.65 | 29.06 ± 3.49 | 29.07 ± 2.32 | 30.23 ± 3.49 | 24.42 ± 2.32 | 68.60 ± 2.32 | 55.81 ± 3.49 |
| MobileNet | 63.95 ± 4.65 | 29.07 ± 4.65 | 29.07 ± 2.32 | 20.93 ± 1.16 | 20.93 ± 1.16 | 22.09 ± 1.16 | 23.26 ± 2.32 |
| ShuffleNet | 45.35 ± 5.81 | 26.74 ± 3.49 | 26.74 ± 2.32 | 29.07 ± 2.32 | 29.07 ± 3.49 | 38.37 ± 2.32 | 36.05 ± 2.32 |
| A-ConvNet | 81.34 ± 3.49 | 5.81 ± 2.32 | 5.81 ± 2.32 | 48.83 ± 3.49 | 26.74 ± 2.32 | 63.95 ± 2.32 | 56.98 ± 3.49 |
| A-ConvNet-M | 70.93 ± 2.32 | 25.58 ± 4.65 | 25.58 ± 2.32 | 31.39 ± 2.32 | 26.74 ± 3.49 | 43.02 ± 3.49 | 36.05 ± 2.32 |
Table 5.
Classification accuracy of MSTAR models against different kinds of adversarial attack.
Table 5.
Classification accuracy of MSTAR models against different kinds of adversarial attack.
| Method | Clean Data | PGD | FGSM | APGD | Deep Fool | CW | Sparse-RS | Sparse Fool | Square Attack | Hop Skip Jump |
|---|
| ResNet18 | 97.65 ± 0.28 | 2.02 ± 0.08 | 3.01 ± 0.57 | 2.02 ± 0.05 | 2.10 ± 0.06 | 14.85 ± 0.79 | 63.59 ± 0.84 | 51.76 ± 0.86 | 70.47 ± 2.44 | 13.81 ± 0.76 |
| ResNet50 | 97.86 ± 0.12 | 1.73 ± 0.07 | 9.61 ± 0.66 | 1.32 ± 0.05 | 1.94 ± 0.13 | 12.29 ± 0.47 | 62.93 ± 0.92 | 50.98 ± 0.69 | 58.68 ± 1.76 | 9.36 ± 0.55 |
| ResNet101 | 98.68 ± 0.25 | 1.53 ± 0.11 | 12.33 ± 0.93 | 1.36 ± 0.07 | 1.73 ± 0.26 | 10.56 ± 0.77 | 61.94 ± 0.95 | 48.98 ± 0.93 | 60.66 ± 1.57 | 14.72 ± 0.87 |
| DenseNet121 | 98.56 ± 0.13 | 0.82 ± 0.08 | 6.14 ± 1.64 | 0.82 ± 0.09 | 1.32 ± 0.14 | 18.68 ± 1.56 | 60.70 ± 1.21 | 50.32 ± 0.98 | 57.24 ± 1.22 | 8.74 ± 0.58 |
| DenseNet201 | 98.68 ± 0.07 | 0.66 ± 0.09 | 6.02 ± 1.06 | 0.62 ± 0.09 | 1.03 ± 0.25 | 16.29 ± 1.36 | 60.82 ± 1.09 | 51.30 ± 0.90 | 48.00 ± 0.74 | 16.33 ± 0.80 |
| MobileNet | 98.23 ± 0.17 | 2.31 ± 0.06 | 4.58 ± 0.60 | 2.10 ± 0.05 | 3.38 ± 0.20 | 31.30 ± 2.32 | 45.61 ± 0.83 | 41.26 ± 0.84 | 47.96 ± 0.49 | 9.40 ± 0.48 |
| ShuffleNet | 95.01 ± 0.78 | 1.48 ± 0.06 | 2.10 ± 0.49 | 1.32 ± 0.06 | 1.73 ± 0.08 | 29.69 ± 2.14 | 42.64 ± 0.42 | 41.09 ± 0.68 | 48.16 ± 0.83 | 9.07 ± 0.74 |
| A-ConvNet | 99.79 ± 0.84 | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 0.16 ± 0.01 | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 0.16 ± 0.01 | 16.41 ± 0.92 | 71.05 ± 1.24 | 69.03 ± 1.22 | 39.59 ± 0.66 | 3.79 ± 0.32 |
| A-ConvNet-M | 98.14 ± 0.03 | 1.98 ± 0.03 | 8.78 ± 0.87 | 1.94 ± 0.07 | 3.75 ± 0.14 | 83.34 ± 2.56 | 67.84 ± 1.07 | 68.11 ± 1.01 | 17.36 ± 0.82 | 10.47 ± 0.54 |
Table 6.
Classification accuracy of FUSAR-Ship models against different kinds of adversarial attack.
Table 6.
Classification accuracy of FUSAR-Ship models against different kinds of adversarial attack.
| Method | Clean Data | PGD | FGSM | APGD | Deep Fool | CW | Sparse-RS | Sparse Fool | Square Attack | Hop Skip Jump |
|---|
| ResNet18 | 69.77 ± 2.32 | 8.14 ± 2.32 | 29.07 ± 2.32 | 8.14 ± 1.16 | 22.09 ± 1.16 | 19.77 ± 2.32 | 12.79 ± 1.16 | 33.72 ± 2.32 | 69.77 ± 2.32 | 24.42 ± 2.32 |
| ResNet50 | 68.60 ± 3.49 | 4.65 ± 1.16 | 29.07 ± 2.32 | 5.81 ± 1.16 | 20.93 ± 2.32 | 26.74 ± 2.32 | 13.95 ± 1.16 | 33.72 ± 2.32 | 68.60 ± 3.49 | 4.65 ± 1.16 |
| ResNet101 | 70.93 ± 4.65 | 29.07 ± 2.32 | 44.19 ± 2.32 | 26.74 ± 2.32 | 23.26 ± 2.32 | 32.56 ± 1.16 | 40.70 ± 2.32 | 38.37 ± 3.49 | 70.93 ± 4.65 | 29.07 ± 2.32 |
| DenseNet121 | 66.28 ± 4.65 | 24.42 ± 2.32 | 17.44 ± 1.16 | 8.14 ± 2.32 | 20.93 ± 1.16 | 24.42 ± 2.32 | 30.23 ± 2.32 | 50.00 ± 3.49 | 66.28 ± 4.65 | 24.42 ± 2.32 |
| DenseNet201 | 68.60 ± 4.65 | 29.06 ± 3.49 | 29.07 ± 2.32 | 5.81 ± 1.16 | 20.93 ± 1.16 | 27.91 ± 3.16 | 19.77 ± 2.32 | 43.03 ± 2.32 | 68.60 ± 4.65 | 29.06 ± 3.49 |
| MobileNet | 63.95 ± 4.65 | 29.07 ± 4.65 | 29.07 ± 2.32 | 16.28 ± 2.32 | 47.67 ± 3.49 | 25.58 ± 1.16 | 22.09 ± 1.16 | 33.72 ± 2.32 | 63.95 ± 4.65 | 29.07 ± 4.65 |
| ShuffleNet | 45.35 ± 5.81 | 26.74 ± 3.49 | 19.77 ± 2.32 | 15.12 ± 2.32 | 38.37 ± 1.16 | 37.21 ± 3.16 | 30.23 ± 2.32 | 38.37 ± 3.49 | 45.35 ± 5.81 | 26.74 ± 3.49 |
| A-ConvNet | 81.34 ± 3.49 | 5.81 ± 2.32 | 40.70 ± 3.49 | 9.30 ± 2.32 | 36.04 ± 2.32 | 8.14 ± 1.16 | 36.05 ± 1.16 | 12.79 ± 2.32 | 81.34 ± 3.49 | 5.81 ± 2.32 |
| A-ConvNet-M | 70.93 ± 2.32 | 25.58 ± 4.65 | 26.74 ± 2.32 | 23.26 ± 2.32 | 23.26 ± 1.16 | 41.86 ± 4.65 | 48.84 ± 2.32 | 13.95 ± 3.49 | 70.93 ± 2.32 | 25.58 ± 4.65 |
Table 7.
Comprehensive evaluation of different DNN models against PGD attack (attack strength is 8/255 in norm) in MSTAR dataset.
Table 7.
Comprehensive evaluation of different DNN models against PGD attack (attack strength is 8/255 in norm) in MSTAR dataset.
| | SA | RA | ACAC | RCAC | NTE | EBD | ALPp | ASS | PSD | TKNC |
|---|
| L0 | L2 | |
|---|
| ResNet18 | 97.65 | 2.02 | 0.99 | 685 | 0.99 | 1.66 | 0.97 | 685 | 8 | 0.83 | 423 | 0.11 |
| ResNet50 | 97.86 | 1.73 | 1.00 | inf | 1.00 | 1.55 | 0.97 | 917 | 8 | 0.84 | 415 | 0.03 |
| ResNet101 | 98.68 | 1.53 | 1.00 | inf | 1.00 | 1.66 | 0.97 | 914 | 8 | 0.84 | 414 | 0.03 |
| DenseNet121 | 98.56 | 0.82 | 0.99 | 1470 | 0.98 | 1.66 | 0.95 | 880 | 8 | 0.85 | 392 | 0.03 |
| DenseNet201 | 98.68 | 0.66 | 0.99 | 1668 | 0.98 | 1.66 | 0.96 | 897 | 8 | 0.84 | 402 | 0.02 |
| MobileNet | 98.23 | 2.31 | 0.99 | 1514 | 0.98 | 1.66 | 0.94 | 789 | 8 | 0.86 | 342 | 0.03 |
| ShuffleNet | 95.01 | 1.48 | 0.99 | 1474 | 0.98 | 1.52 | 0.95 | 830 | 8 | 0.84 | 364 | 0.06 |
| A-ConvNet | 99.79 | 0.12 | 1.0 | inf | 1.0 | 1.66 | 0.96 | 862 | 8 | 0.84 | 385 | 0.23 |
| A-ConvNet-M | 98.14 | 1.98 | 1.00 | inf | 1.0 | 1.66 | 0.94 | 819 | 8 | 0.84 | 385 | 0.18 |
Table 8.
Comprehensive evaluation of different DNN models against PGD attack (attack strength is 8/255 in norm) in FUSAR-Ship dataset.
Table 8.
Comprehensive evaluation of different DNN models against PGD attack (attack strength is 8/255 in norm) in FUSAR-Ship dataset.
| | SA | RA | ACAC | RCAC | NTE | EBD | ALPp | ASS | PSD | TKNC |
|---|
| L0 | L2 | |
|---|
| ResNet18 | 69.77 | 8.14 | 1.00 | inf | 1.00 | 1.30 | 0.92 | 2924 | 8.00 | 0.38 | 6153 | 0.07 |
| ResNet50 | 68.60 | 6.98 | 1.00 | inf | 1.00 | 1.30 | 0.97 | 3641 | 8.00 | 0.39 | 6834 | 0.04 |
| ResNet101 | 70.93 | 20.93 | 0.99 | inf | 1.00 | 1.85 | 0.96 | 3485 | 8.00 | 0.29 | 6445 | 0.01 |
| DenseNet121 | 66.28 | 24.42 | 1.00 | inf | 1.00 | 1.59 | 0.97 | 3667 | 8.00 | 0.35 | 6915 | 0.01 |
| DenseNet201 | 68.60 | 10.47 | 1.00 | inf | 1.00 | 1.85 | 0.97 | 3509 | 8.00 | 0.29 | 6515 | 0.01 |
| MobileNet | 63.95 | 29.07 | 1.00 | inf | 1.00 | 1.85 | 0.98 | 3821 | 8.00 | 0.35 | 7338 | 0.01 |
| ShuffleNet | 45.35 | 26.74 | 1.00 | inf | 1.00 | 1.79 | 0.98 | 3571 | 8.00 | 0.28 | 6675 | 0.02 |
| A-ConvNet | 81.34 | 5.81 | 1.00 | inf | 1.00 | 1.59 | 0.97 | 3762 | 8.00 | 0.35 | 6343 | 0.01 |
| A-ConvNet-M | 70.93 | 26.74 | 0.99 | inf | 1.00 | 1.85 | 0.94 | 3145 | 8.00 | 0.35 | 6934 | 0.01 |
Table 9.
Classification accuracy of models (ResNet18) with no-defense or defense methods against PGD adversarial attacks in MSTAR dataset.
Table 9.
Classification accuracy of models (ResNet18) with no-defense or defense methods against PGD adversarial attacks in MSTAR dataset.
| | | Clean Data | Adversarial Examples |
|---|
| | | | | |
|---|
| | | 8/255 | 16/255 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 7.84 | 12 |
|---|
| No Defense | Standard | 97.65 ± 0.28 | 2.02 ± 0.11 | 1.86 ± 0.08 | 62.60 ± 0.68 | 17.53 ± 0.77 | 86.23 ± 1.44 | 76.87 ± 1.11 |
| SimCLR | 99.38 ± 0.19 | 22.93 ± 0.74 | 2.27 ± 0.54 | 97.65 ± 0.92 | 93.15 ± 0.69 | 98.56 ± 1.20 | 98.35 ± 1.01 |
| BYOL | 99.51 ± 0.22 | 29.15 ± 0.66 | 4.99 ± 0.51 | 97.28 ± 0.99 | 93.24 ± 0.88 | 98.43 ± 1.23 | 97.94 ± 0.78 |
| Defense | AT | 86.23 ± 1.59 | 79.13 ± 0.74 | 69.98 ± 0.61 | 85.11 ± 1.24 | 84.33 ± 0.93 | 85.57 ± 0.97 | 85.36 ± 0.55 |
| TRADES | 90.85 ± 0.86 | 80.87 ± 0.83 | 66.02 ± 0.77 | 90.14 ± 1.09 | 88.45 ± 0.69 | 90.56 ± 1.54 | 80.87 ± 0.98 |
| ATFBF | 86.02 ± 0.58 | 84.41 ± 0.67 | 82.06 ± 0.53 | 84.29 ± 1.10 | 84.49 ± 0.79 | 83.75 ± 1.29 | 84.12 ± 0.69 |
| RoCL | 92.43 ± 0.95 | 80.73 ± 0.82 | 65.40 ± 0.76 | 88.16 ± 1.33 | 90.29 ± 0.90 | 89.65 ± 0.93 | 89.10 ± 0.69 |
| ACL | 95.34 ± 1.33 | 74.43 ± 0.44 | 51.88 ± 0.35 | 88.99 ± 2.22 | 83.59 ± 1.20 | 90.19 ± 1.49 | 90.43 ± 0.93 |
| UACL | 95.09 ± 0.90 | 80.92 ± 0.89 | 60.74 ± 0.54 | 94.10 ± 2.04 | 93.36 ± 0.80 | 94.31 ± 1.10 | 94.27 ± 0.90 |
| UACL+TRADES | 90.02 ± 0.48 | 87.88 ± 0.62 | 84.91 ± 0.44 | 89.73 ± 1.79 | 89.53 ± 0.77 | 89.98 ± 0.92 | 89.90 ± 0.53 |
| UACL+ ATFBF | 96.99 ± 0.29 | 95.38 ± 0.60 | 92.16 ± 0.38 | 96.86 ± 1.53 | 96.66 ± 0.74 | 97.03 ± 0.88 | 97.03 ± 0.47 |
Table 10.
Classification accuracy of models (ResNet18) with no-defense or defense methods against PGD adversarial attacks in FUSAR-Ship dataset.
Table 10.
Classification accuracy of models (ResNet18) with no-defense or defense methods against PGD adversarial attacks in FUSAR-Ship dataset.
| | | Clean Data | Adversarial Examples |
|---|
| | | | | |
|---|
| | | 8/255 | 16/255 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 7.84 | 12 |
|---|
| No Defense | Standard | 69.77 ± 2.32 | 8.14 ± 2.32 | 8.14 ± 2.32 | 16.28 ± 2.32 | 13.95 ± 2.32 | 53.49 ± 3.49 | 37.21 ± 3.49 |
| SimCLR | 80.23 ± 5.81 | 37.21 ± 2.32 | 26.74 ± 2.32 | 47.67 ± 2.32 | 47.67 ± 3.49 | 40.70 ± 2.32 | 46.51 ± 3.49 |
| BYOL | 80.23 ± 5.81 | 51.16 ± 2.32 | 41.86 ± 3.49 | 59.30 ± 3.49 | 58.14 ± 3.49 | 59.30 ± 3.49 | 59.30 ± 4.65 |
| Defense | AT | 60.47 ± 2.32 | 60.47 ± 3.49 | 60.47 ± 2.32 | 60.47 ± 4.65 | 60.47 ± 4.65 | 60.47 ± 4.65 | 60.47 ± 3.49 |
| TRADES | 61.63 ± 3.49 | 61.63 ± 3.49 | 61.63 ± 3.49 | 61.63 ± 4.65 | 61.63 ± 4.65 | 61.63 ± 4.65 | 61.63 ± 3.49 |
| ATFBF | 59.30 ± 2.32 | 60.47 ± 4.65 | 60.47 ± 2.32 | 59.30 ± 3.49 | 59.30 ± 3.49 | 59.30 ± 4.65 | 59.30 ± 4.65 |
| RoCL | 62.79 ± 2.32 | 56.98 ± 3.49 | 37.21 ± 2.32 | 61.63 ± 5.81 | 61.63 ± 3.49 | 62.79 ± 5.81 | 62.79 ± 5.81 |
| ACL | 69.77 ± 3.49 | 56.98 ± 5.81 | 53.49 ± 2.32 | 72.09 ± 5.81 | 69.77 ± 5.81 | 70.93 ± 5.81 | 70.93 ± 5.81 |
| UACL | 68.60 ± 2.32 | 65.12 ± 3.49 | 55.81 ± 2.32 | 67.44 ± 3.49 | 67.44 ± 4.65 | 68.60 ± 3.49 | 68.60 ± 4.65 |
| UACL+TRADES | 69.77 ± 2.32 | 67.44 ± 4.65 | 68.60 ± 5.81 | 68.60 ± 4.65 | 68.60 ± 4.65 | 69.77 ± 5.81 | 69.77 ± 4.65 |
| UACL+ ATFBF | 66.28 ± 3.49 | 66.28 ± 4.65 | 67.44 ± 5.81 | 66.28 ± 4.65 | 66.28 ± 4.65 | 66.28 ± 4.65 | 66.28 ± 3.49 |
Table 11.
Classification accuracy of models (ResNet18) with no-defense or defense methods against different kinds of adversarial attack in MSTAR dataset.
Table 11.
Classification accuracy of models (ResNet18) with no-defense or defense methods against different kinds of adversarial attack in MSTAR dataset.
| | | PGD | FGSM | APGD | DeepFool | CW | Sparse-RS | Sparsefool | SquareAttack | HopSkipJump |
|---|
| No Defense | Standard | 2.02 ± 0.11 | 3.01 ± 0.34 | 2.02 ± 0.09 | 2.10 ± 0.09 | 14.85 ± 1.29 | 63.59 ± 1.08 | 51.76 ± 1.46 | 70.47 ± 0.86 | 13.81 ± 0.32 |
| SimCLR | 22.93 ± 0.74 | 47.22 ± 0.59 | 19.34 ± 0.50 | 36.70 ± 0.09 | 93.57 ± 0.53 | 74.89 ± 1.22 | 60.33 ± 1.46 | 55.96 ± 0.53 | 46.35 ± 0.89 |
| BYOL | 29.15 ± 0.66 | 58.10 ± 0.56 | 26.93 ± 0.33 | 30.19 ± 0.09 | 97.20 ± 1.16 | 76.16 ± 1.40 | 61.09 ± 1.46 | 71.22 ± 0.76 | 67.88 ± 0.96 |
| Defense | AT | 79.13 ± 0.74 | 81.53 ± 0.98 | 79.84 ± 0.42 | 74.14 ± 0.09 | 84.91 ± 1.29 | 84.91 ± 1.31 | 81.93 ± 1.46 | 85.32 ± 0.92 | 86.10 ± 0.94 |
| TRADES | 80.87 ± 0.83 | 85.03 ± 1.20 | 81.98 ± 0.54 | 75.01 ± 0.09 | 89.24 ± 1.79 | 89.11 ± 1.57 | 85.31 ± 1.46 | 89.81 ± 0.98 | 90.35 ± 1.02 |
| ATFBF | 84.41 ± 0.67 | 83.59 ± 0.97 | 83.26 ± 0.47 | 81.07 ± 0.09 | 83.67 ± 1.60 | 84.08 ± 1.30 | 84.24 ± 1.46 | 83.30 ± 0.67 | 83.55 ± 0.89 |
| RoCL | 80.73 ± 0.82 | 86.02 ± 0.84 | 76.29 ± 0.70 | 81.07 ± 0.09 | 90.38 ± 1.57 | 90.55 ± 1.69 | 88.49 ± 1.46 | 84.08 ± 1.24 | 91.90 ± 1.23 |
| ACL | 74.43 ± 0.44 | 79.53 ± 0.68 | 59.98 ± 0.31 | 68.60 ± 0.09 | 80.62 ± 1.01 | 87.42 ± 1.64 | 82.10 ± 1.46 | 82.14 ± 1.08 | 86.52 ± 1.20 |
| UACL | 80.92 ± 0.89 | 85.20 ± 1.14 | 76.33 ± 0.66 | 81.53 ± 0.09 | 93.20 ± 1.32 | 93.07 ± 1.89 | 93.07 ± 1.46 | 85.15 ± 1.33 | 92.33 ± 1.08 |
| UACL+TRADES | 87.88 ± 0.62 | 88.66 ± 0.92 | 87.92 ± 0.68 | 86.47 ± 0.09 | 89.65 ± 1.05 | 89.40 ± 1.02 | 89.67 ± 1.46 | 89.53 ± 1.03 | 89.65 ± 1.01 |
| UACL+ ATFBF | 95.38 ± 0.60 | 95.92 ± 0.77 | 95.55 ± 0.53 | 88.29 ± 0.09 | 96.82 ± 1.10 | 95.22 ± 0.77 | 95.18 ± 1.46 | 96.91 ± 0.93 | 96.99 ± 0.92 |
Table 12.
Classification accuracy of models (ResNet18) with no-defense or defense methods against different kinds of adversarial attack in FUSAR-Ship dataset.
Table 12.
Classification accuracy of models (ResNet18) with no-defense or defense methods against different kinds of adversarial attack in FUSAR-Ship dataset.
| | | PGD | FGSM | APGD | DeepFool | CW | Sparse-RS | Sparsefool | SquareAttack | HopSkipJump |
|---|
| No Defense | Standard | 8.14 ± 2.32 | 19.77 ± 2.32 | 8.14 ± 1.16 | 29.07 ± 2.32 | 19.77 ± 2.32 | 38.49 ± 2.32 | 36.90 ± 3.49 | 12.79 ± 2.32 | 34.88 ± 2.32 |
| SimCLR | 37.21 ± 2.32 | 46.51 ± 2.32 | 53.49 ± 3.49 | 47.67 ± 2.32 | 47.67 ± 3.49 | 53.49 ± 3.49 | 46.51 ± 4.65 | 17.44 ± 2.32 | 53.49 ± 4.65 |
| BYOL | 51.16 ± 2.32 | 40.70 ± 2.32 | 48.84 ± 2.32 | 58.14 ± 3.49 | 55.81 ± 4.65 | 46.51 ± 2.32 | 40.70 ± 3.49 | 46.51 ± 4.65 | 48.84 ± 4.65 |
| Defense | AT | 60.47 ± 3.49 | 60.47 ± 2.32 | 60.47 ± 3.49 | 60.47 ± 3.49 | 60.47 ± 4.65 | 60.47 ± 3.49 | 60.47 ± 5.81 | 60.47 ± 3.49 | 60.47 ± 2.32 |
| TRADES | 61.63 ± 3.49 | 61.63 ± 3.49 | 61.63 ± 3.49 | 61.63 ± 4.65 | 61.63 ± 4.65 | 61.63 ± 3.49 | 61.63 ± 4.65 | 62.79 ± 3.49 | 61.63 ± 3.49 |
| ATFBF | 60.47 ± 4.65 | 60.47 ± 3.49 | 60.47 ± 2.32 | 59.30 ± 3.49 | 59.30 ± 3.49 | 59.30 ± 2.32 | 59.30 ± 4.65 | 60.47 ± 3.49 | 60.47 ± 2.32 |
| RoCL | 56.98 ± 3.49 | 46.51 ± 4.65 | 54.65 ± 3.49 | 62.79 ± 3.49 | 62.79 ± 4.65 | 59.30 ± 4.65 | 55.81 ± 5.81 | 58.14 ± 5.81 | 56.98 ± 5.81 |
| ACL | 56.98 ± 5.81 | 26.74 ± 4.65 | 33.72 ± 4.65 | 70.93 ± 5.81 | 70.93 ± 4.65 | 61.63 ± 4.65 | 59.30 ± 5.81 | 30.23 ± 5.81 | 55.81 ± 5.81 |
| UACL | 65.12 ± 3.49 | 62.79 ± 3.49 | 63.95 ± 3.49 | 68.60 ± 4.65 | 69.77 ± 3.49 | 68.60 ± 3.49 | 68.60 ± 4.65 | 56.98 ± 3.49 | 55.81 ± 4.65 |
| UACL+TRADES | 67.44 ± 4.65 | 67.44 ± 4.65 | 67.44 ± 3.49 | 69.77 ± 4.65 | 69.77 ± 4.65 | 69.77 ± 3.49 | 69.77 ± 4.65 | 68.60 ± 4.65 | 70.93 ± 3.49 |
| UACL+ ATFBF | 66.28 ± 4.65 | 66.28 ± 4.65 | 67.44 ± 2.32 | 66.28 ± 3.49 | 66.28 ± 3.49 | 66.28 ± 2.32 | 66.28 ± 4.65 | 67.44 ± 3.49 | 67.44 ± 3.49 |
Table 13.
Comprehensive evaluation of models (ResNet18) with no-defense or defense methods against PGD attacks (attack strength is 8/255 in norm) in MSTAR dataset.
Table 13.
Comprehensive evaluation of models (ResNet18) with no-defense or defense methods against PGD attacks (attack strength is 8/255 in norm) in MSTAR dataset.
| | | SA | RA | ACAC | RCAC | NTE | EBD | PSD | TKNC |
|---|
| No Defense | Standard | 97.65 | 2.02 | 0.998 | 685 | 0.996 | 1.66 | 423 | 0.11 |
| SimCLR | 99.38 | 22.93 | 0.916 | 27.6 | 0.841 | 1.66 | 427 | 0.49 |
| BYOL | 99.51 | 29.15 | 0.927 | 29.0 | 0.863 | 1.60 | 423 | 0.47 |
| Defense | AT | 86.23 | 79.13 | 0.491 | 1.4 | 0.142 | 1.67 | 422 | 0.41 |
| TRADES | 90.85 | 80.87 | 0.563 | 1.8 | 0.247 | 1.67 | 424 | 0.39 |
| ATFBF | 86.02 | 84.41 | 0.540 | 1.6 | 0.194 | 1.67 | 441 | 0.49 |
| RoCL | 92.43 | 80.73 | 0.691 | 41.4 | 0.855 | 1.66 | 423 | 0.51 |
| ACL | 95.34 | 34.43 | 0.629 | 13.6 | 0.698 | 1.67 | 422 | 0.57 |
| UACL | 95.09 | 80.92 | 0.661 | 9.8 | 0.742 | 1.64 | 433 | 0.56 |
| UACL+TRADES | 90.02 | 87.88 | 0.526 | 1.4 | 0.161 | 1.50 | 418 | 0.58 |
| UACL+ ATFBF | 96.99 | 95.38 | 0.787 | 3.8 | 0.579 | 1.67 | 403 | 0.43 |
Table 14.
Comprehensive evaluation of models (ResNet18) with no-defense or defense methods against PGD attacks (attack strength is 8/255 in norm) in FUSAR-Ship dataset. Because the robust accuracy of some models is not less than the standard accuracy, some parameters cannot be obtained.
Table 14.
Comprehensive evaluation of models (ResNet18) with no-defense or defense methods against PGD attacks (attack strength is 8/255 in norm) in FUSAR-Ship dataset. Because the robust accuracy of some models is not less than the standard accuracy, some parameters cannot be obtained.
| | | SA | RA | ACAC | RCAC | NTE | EBD | PSD | TKNC |
|---|
| No Defense | Standard | 69.77 | 8.14 | 1 | inf | 1 | 1.30 | 6153 | 0.07 |
| SimCLR | 80.23 | 37.21 | 0.84 | 9.10 | 0.70 | 1.21 | 5173 | 0.05 |
| BYOL | 80.23 | 51.16 | 0.81 | 10.4 | 0.77 | 1.14 | 5802 | 0.04 |
| Defense | AT | 60.47 | 60.47 | \ | \ | \ | 1.77 | \ | 0.02 |
| TRADES | 61.63 | 61.63 | \ | \ | \ | 1.80 | \ | 0.03 |
| ATFBF | 59.30 | 60.47 | \ | \ | \ | 1.74 | \ | 0.03 |
| RoCL | 62.79 | 56.98 | 0.65 | 3.56 | 0.35 | 1.59 | 4598 | 0.03 |
| ACL | 69.77 | 56.98 | 0.70 | 7.33 | 0.34 | 1.62 | 4794 | 0.03 |
| UACL | 68.60 | 65.12 | 0.61 | 2.02 | 0.31 | 1.68 | 4560 | 0.03 |
| UACL+TRADES | 69.77 | 67.44 | 0.50 | 1.01 | 0.01 | 1.74 | 4992 | 0.03 |
| UACL+ ATFBF | 66.28 | 66.28 | \ | \ | \ | 1.42 | \ | 0.03 |
Table 15.
Classification accuracy of models (ResNet18) with different defense methods trained with 10% labeled data against PGD adversarial attacks.
Table 15.
Classification accuracy of models (ResNet18) with different defense methods trained with 10% labeled data against PGD adversarial attacks.
| | Clean data | PGD(ε = 8/255) | PGD(ε = 16/255) |
|---|
| Standard | 77.15 | 2.02 | 2.02 |
| AT | 42.76 | 42.64 | 42.72 |
| TRADES | 40.87 | 37.77 | 37.90 |
| ATFTF | 41.24 | 40.99 | 41.03 |
| RoCL | 63.42 | 62.02 | 61.77 |
| ACL | 68.20 | 47.90 | 45.18 |
| UACL | 64.45 | 62.35 | 61.28 |
Table 16.
The training times of adversarial contrastive pretraining defenses.
Table 16.
The training times of adversarial contrastive pretraining defenses.
| | RoCL | ACL | UACL |
|---|
| MSTAR | 25:01:24 | 29:12:36 | 17:28:14 |
| FUSAR-Ship | 7:12:09 | 5:34:56 | 4:09:40 |