A Comprehensive Evaluation for the Tunnel Conditions with Ground Penetrating Radar Measurements
Abstract
:1. Introduction
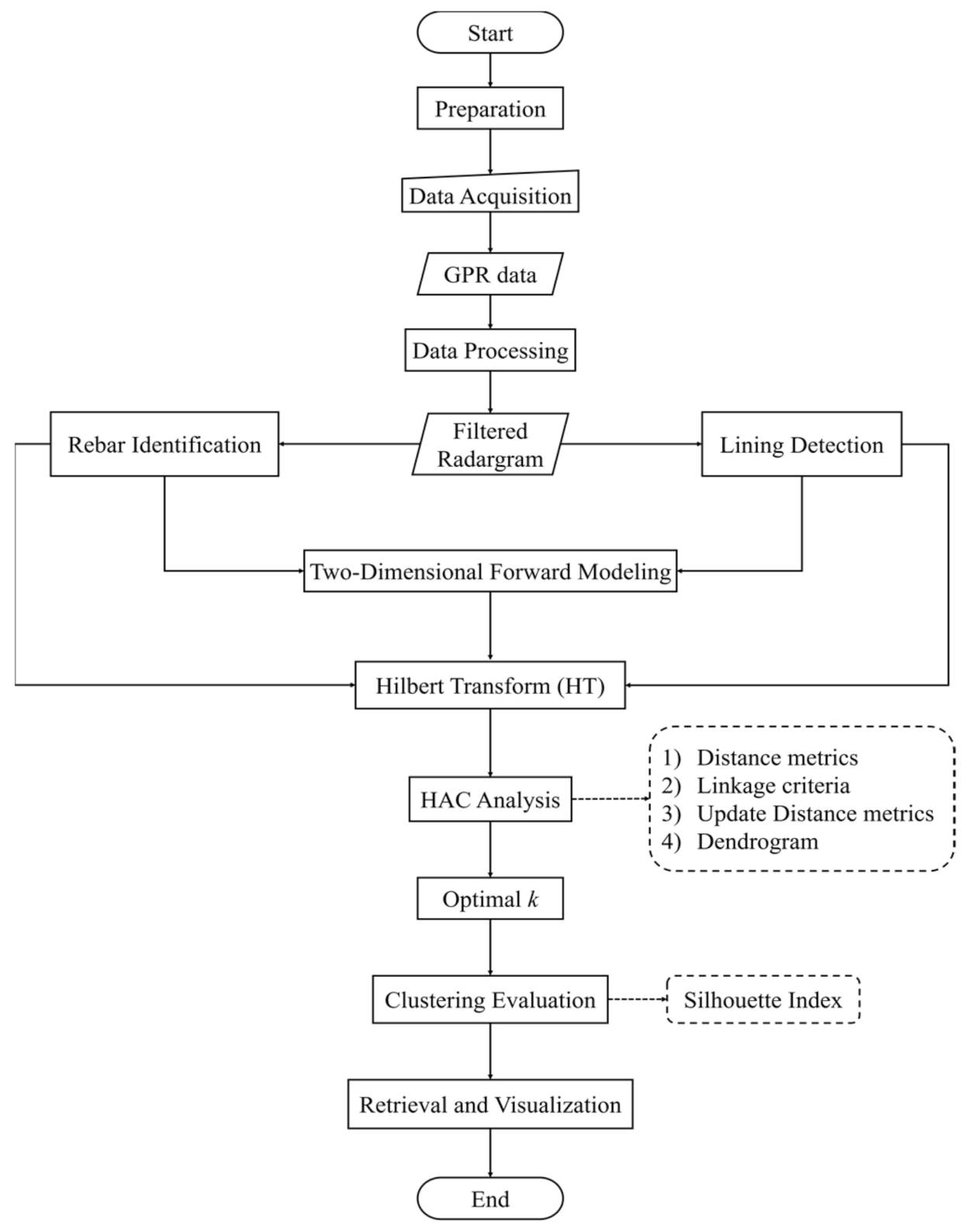
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Site Description and the GPR Measurements
2.2. The Processing of GPR Data
2.3. The Tunnel Lining Detection Method
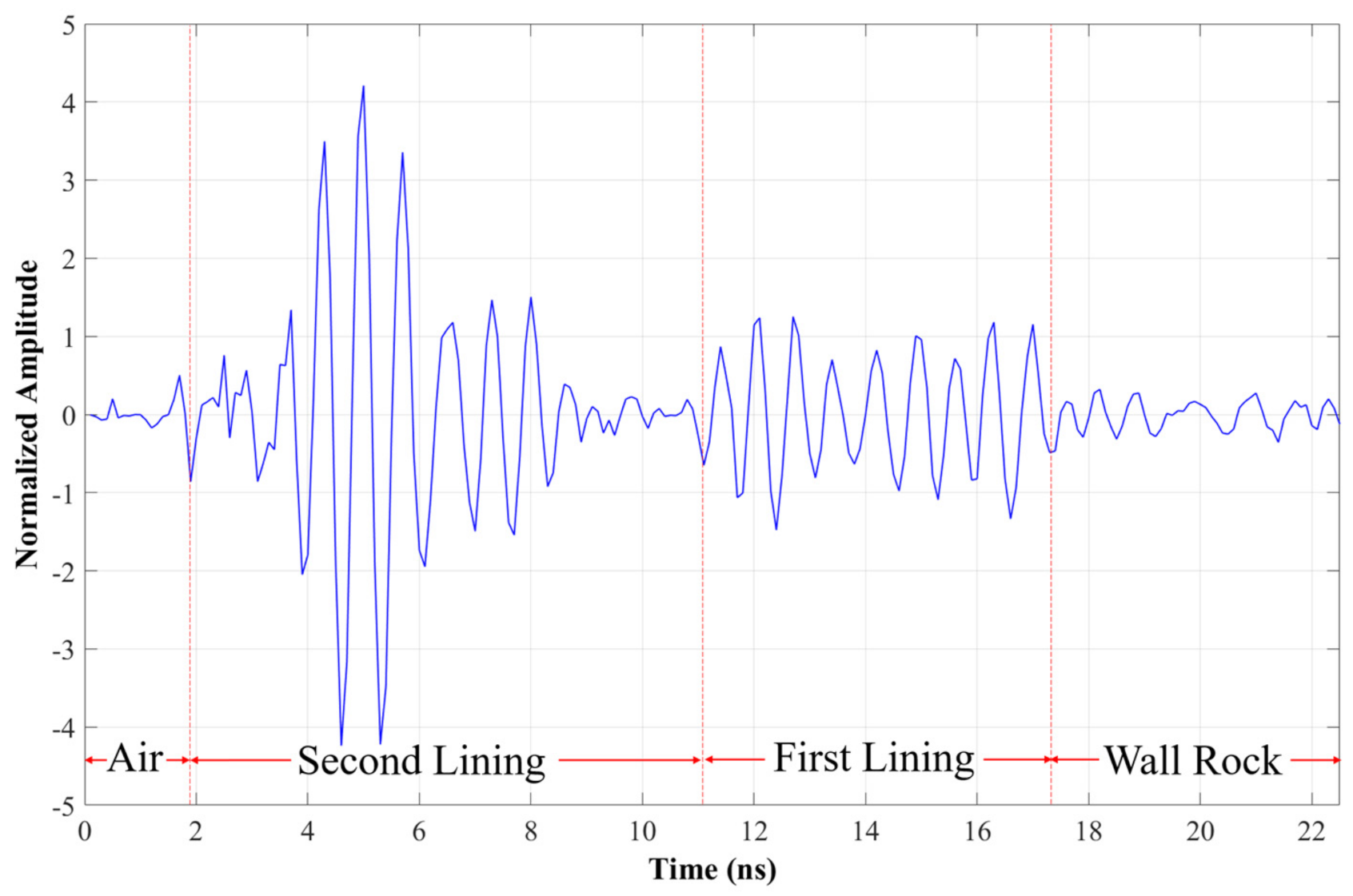
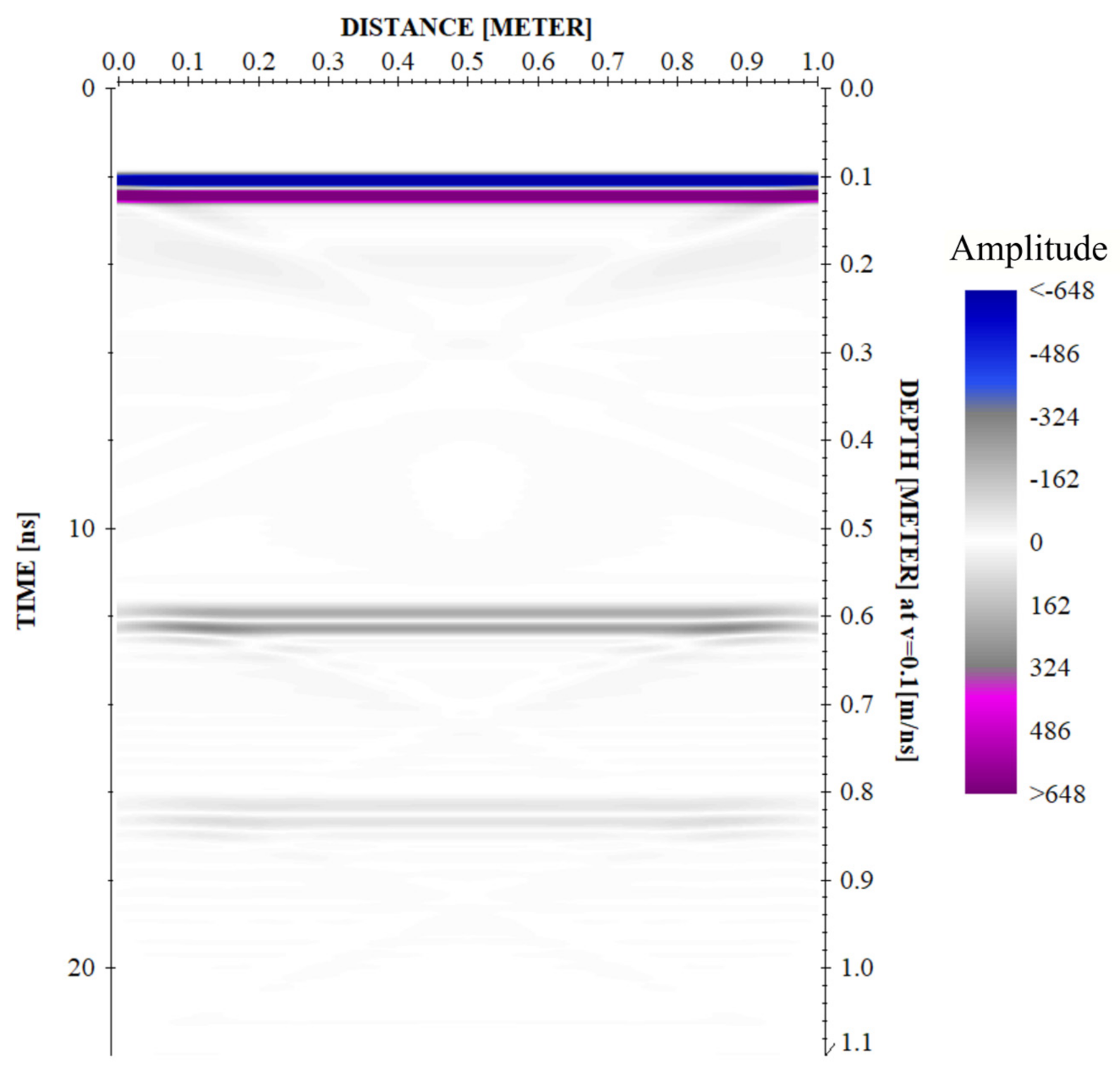
2.3.1. The Lining Detection in A-Scan
- The Boundary Between the Air Layer to the Second Lining
- The Boundary Between the Second Lining to the First Lining
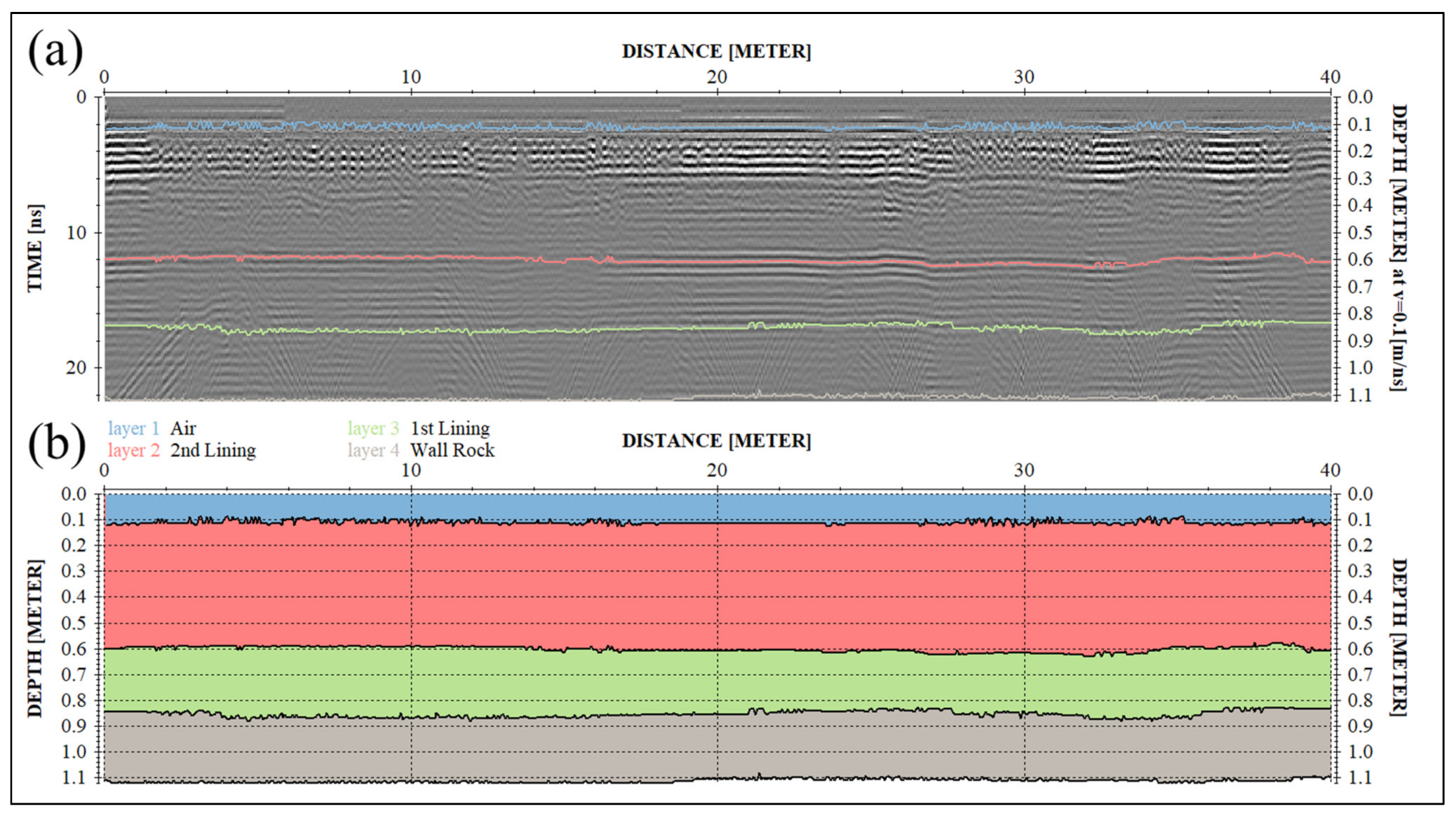
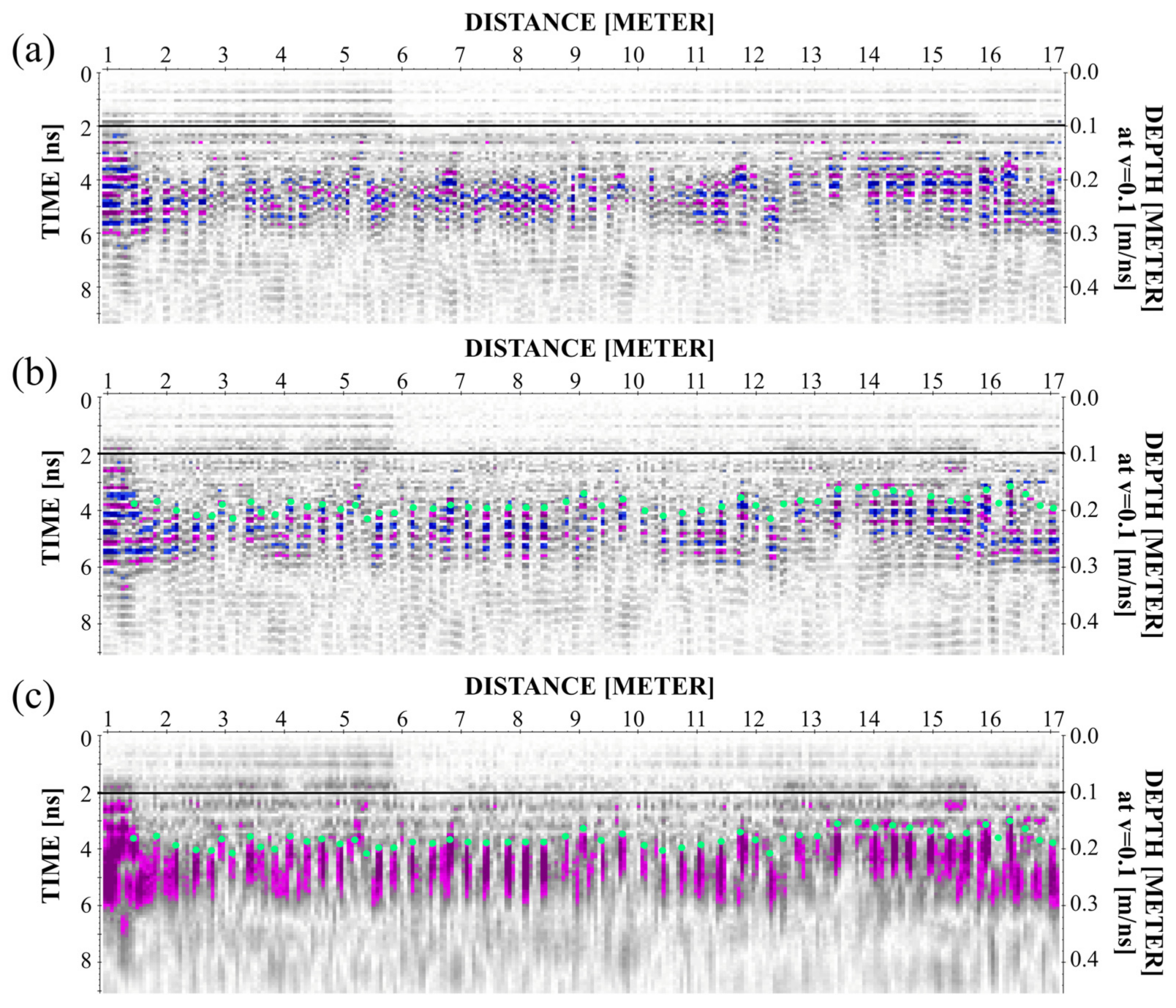
2.3.2. The Lining Detection in B-Scan
2.4. The Semi-Automatic Rebar Identification
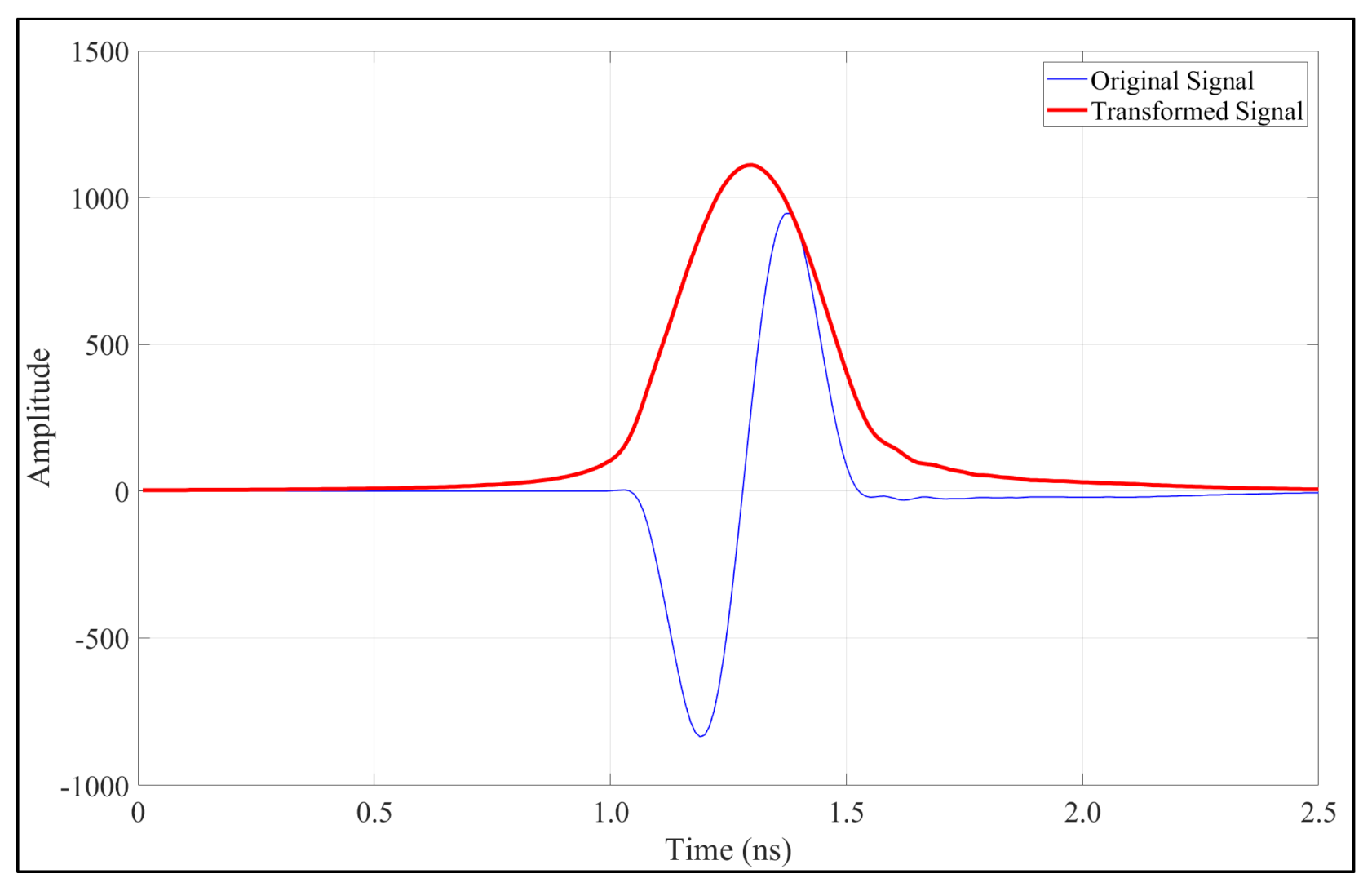
2.4.1. The Hilbert Transform (HT)
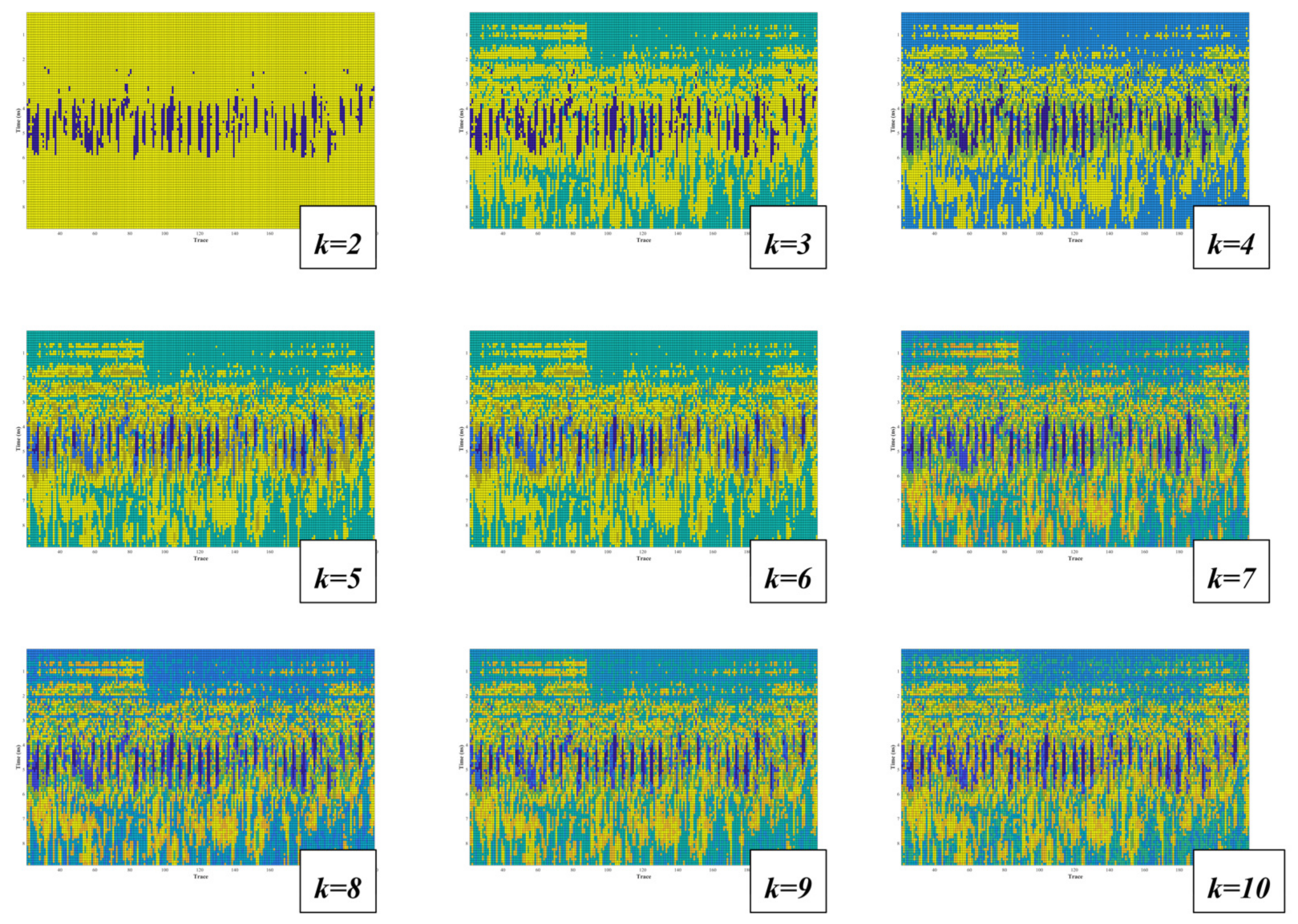
2.4.2. The Application of the Hierarchical Agglomerative Clustering (HAC)
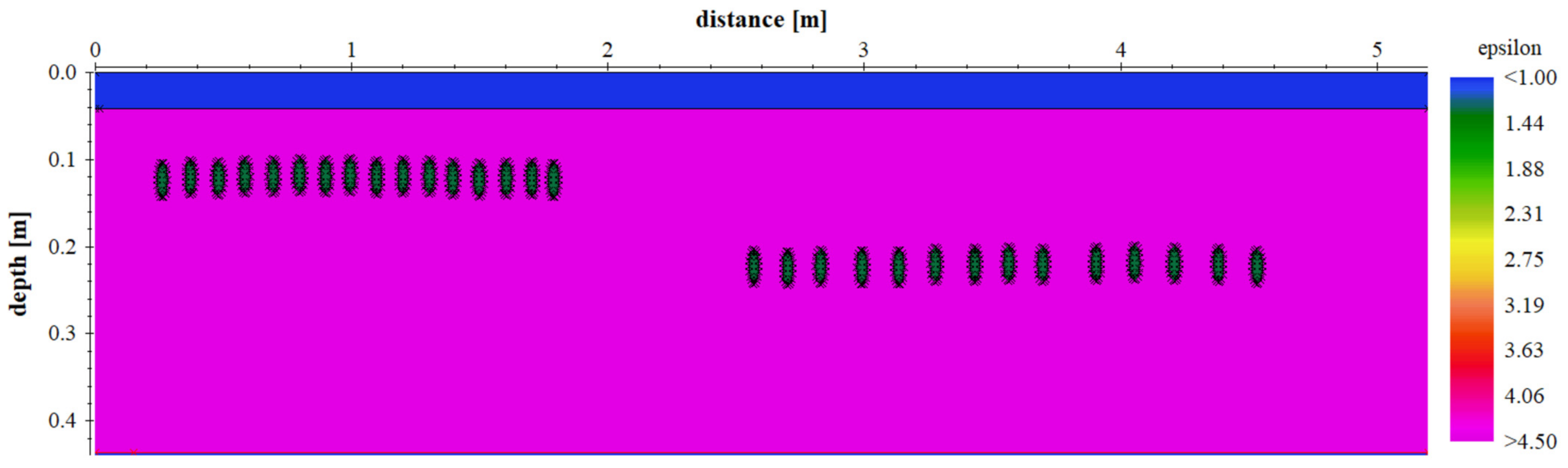
2.5. The Two-Dimensional Forward Modeling (TDFM)
3. Results
3.1. The Lining of The Tunnel
3.2. The Rebar Inside the Second Lining
3.3. The Result of TDFM
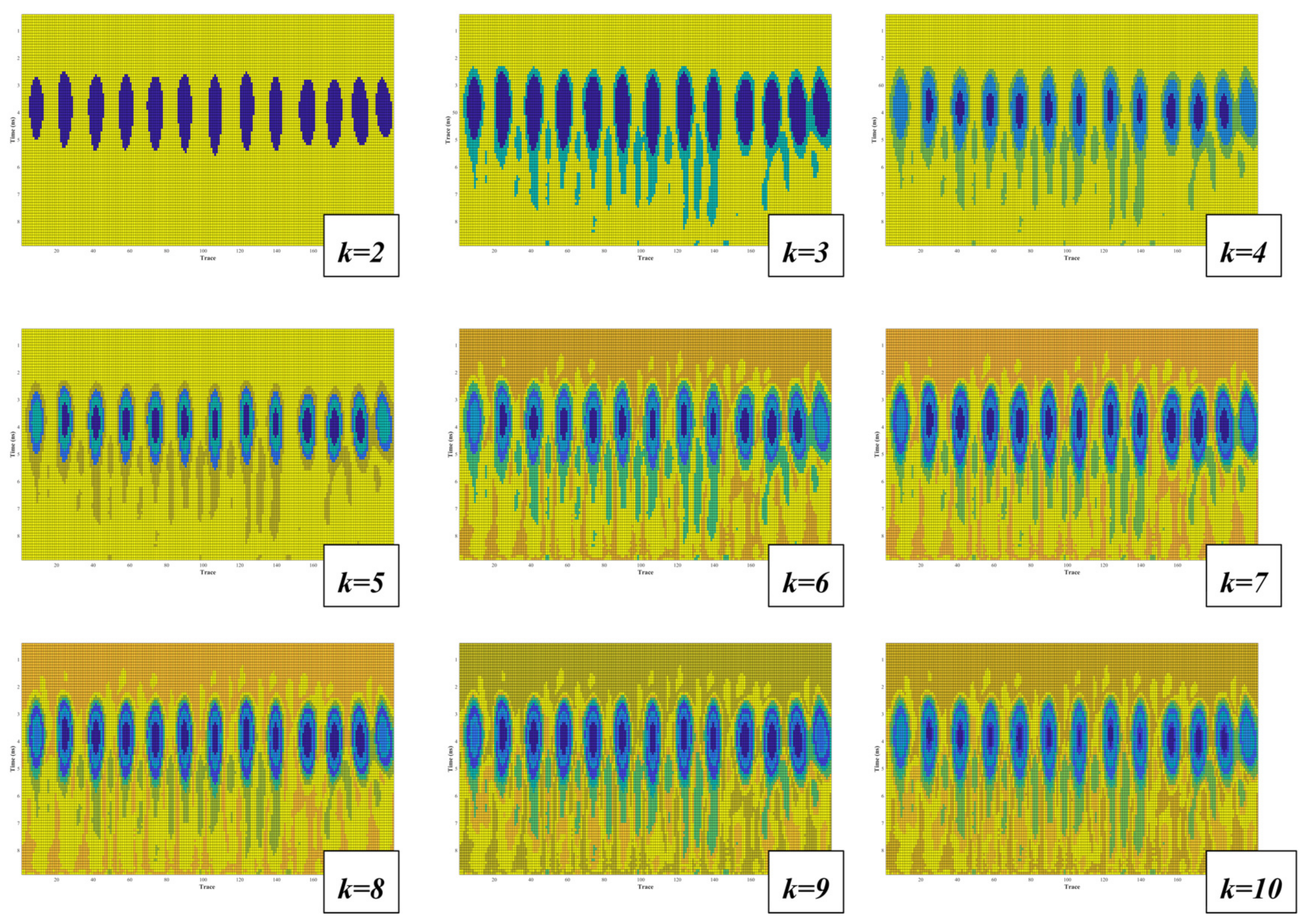
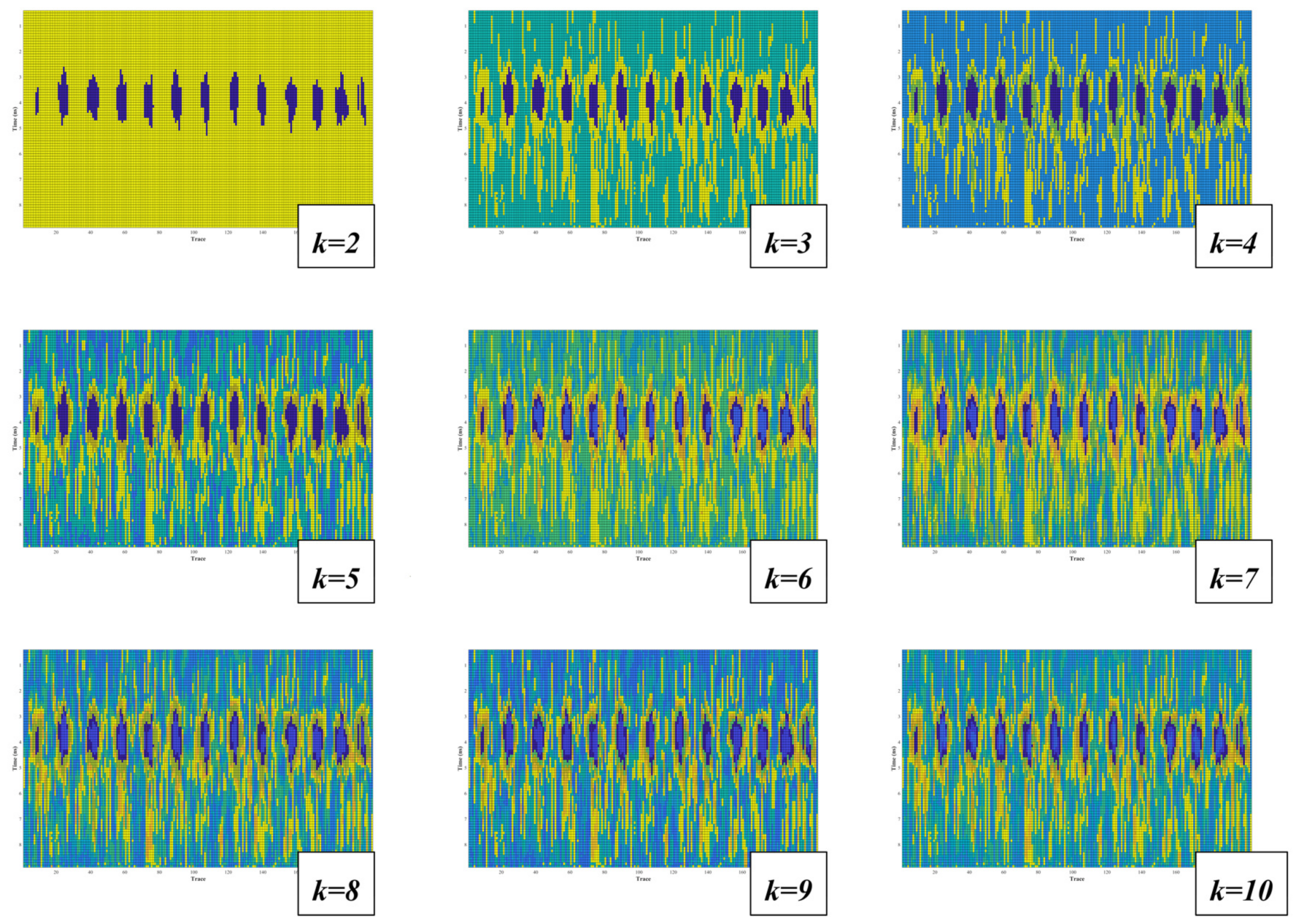
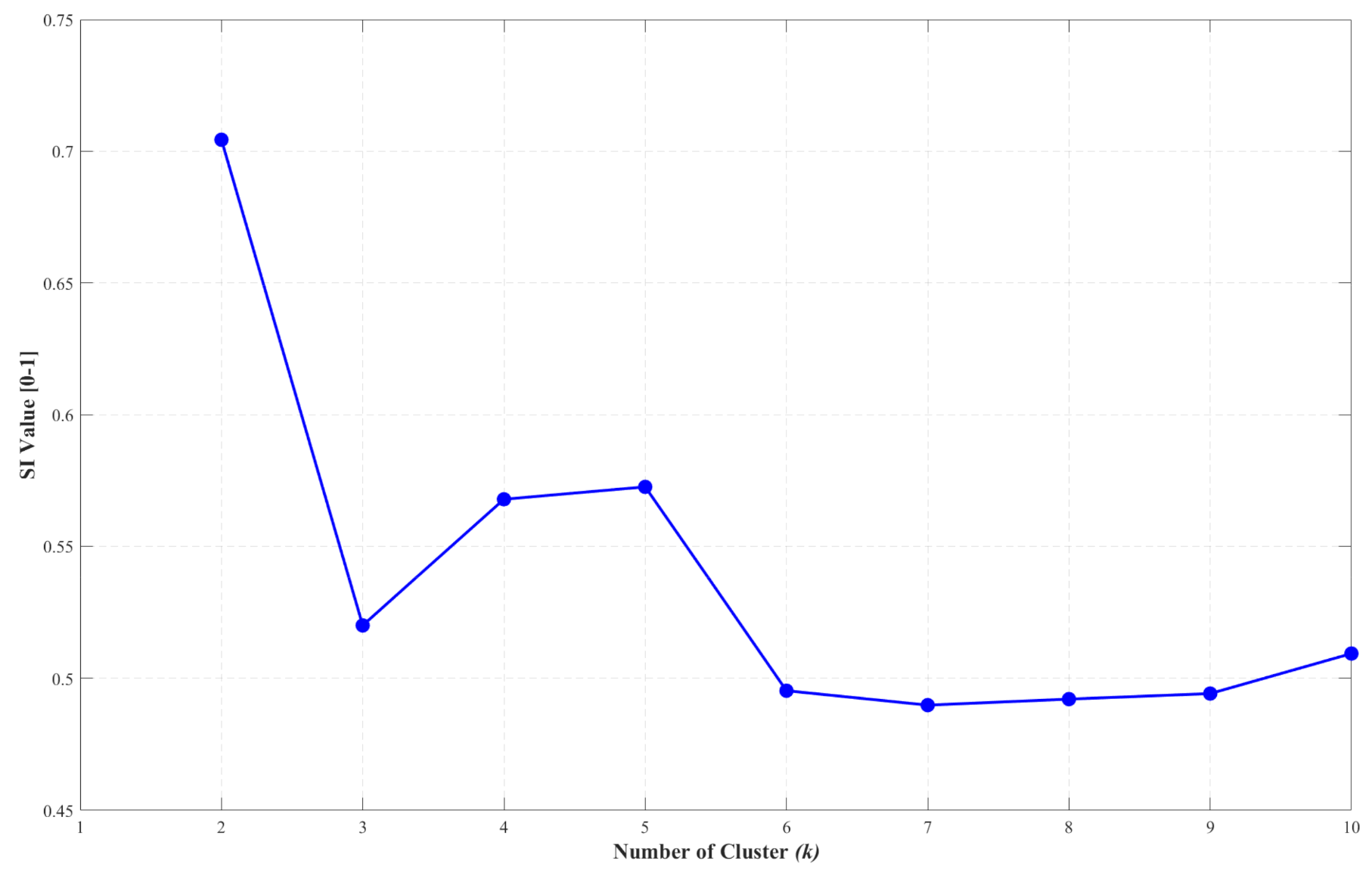
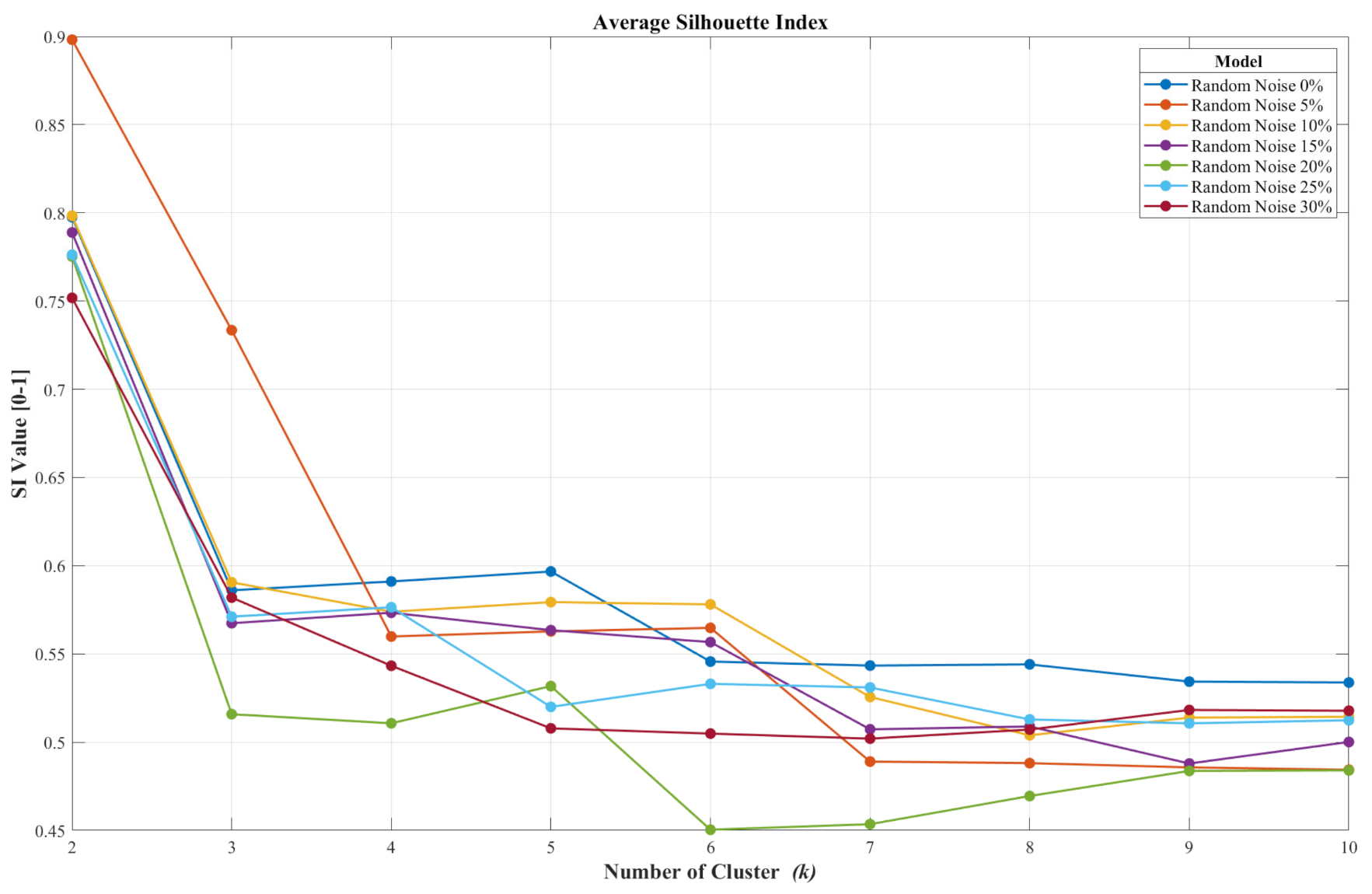
3.4. The Result of the HAC
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.T.; Chang, P.; Lee, Y.; Lee, M. Safety inspection and reinforcement of South-link line railway tunnels. In Proceedings of the 16th Asian Regional Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Taipei, Taiwan, 14–18 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.H.; Wang, T.T. Rock tunnel maintenance in Taiwan. In Proceedings of the 6th Asian Young Geotechnical Engineers Conference-2008, Bangalore, India, 20–21 December 2008; pp. 205–217. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, C.-H.; Tsao, T.-C.; Huang, C.-M.; Lee, C.-F.; Lee, Y.-T. Using Remote Sensing Techniques to Identify the Landslide Hazard Prone Sections along the South Link Railway in Taiwan. Procedia Eng. 2016, 143, 708–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- TRA (Taiwan Railways Administration). Available online: https://www.railway.gov.tw/en/ (accessed on 29 June 2021).
- Chen, C.H. Geological Map of Taiwan; Central Geological Survey: Taipei, Taiwan, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Chandra, S.; Agarwal, M.M. Railway Tunnelling. In Railway Engineering, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2013; pp. 543–561. [Google Scholar]
- Bickel, J.O.; Kuesel, T.R.; King, E.H. Tunnel Engineering Handbook, 2nd ed.; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkinson, G.; Ékes, C. Ground penetrating radar evaluation of concrete tunnel linings. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Ground Penetrating Radar, Birmingham, UK, 15–19 June 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Li, M.-J.; Zhao, Y.-G.; Liu, H.; Wan, Z.; Xu, J.-C.; Xu, X.-P.; Chen, Y.; Wang, B. Layer recognition and thickness evaluation of tunnel lining based on ground penetrating radar measurements. J. Appl. Geophys. 2011, 73, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Zhou, H.-l.; Shu, Z.; Tan, S.-h.; Liang, G.-q.; Zhu, J. GPR evaluation of the Damaoshan highway tunnel: A case study. NDT E Int. 2013, 59, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zan, Y.; Li, Z.; Su, G.; Zhang, X. An innovative vehicle-mounted GPR technique for fast and efficient monitoring of tunnel lining structural conditions. Case Stud. Nondestruct. Test. Eval. 2016, 6, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alani, A.M.; Tosti, F. GPR applications in structural detailing of a major tunnel using different frequency antenna systems. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 158, 1111–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, K.; Zayed, T.; Moufti, S.; Shami, A.; Jabri, A.; Abouhamad, M.; Dawood, T. Clustering-Based Threshold Model for Condition Assessment of Concrete Bridge Decks with Ground-Penetrating Radar. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2015, 2522, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, K.; Gucunski, N.; Duong, T.H. An algorithm for automatic localization and detection of rebars from GPR data of concrete bridge decks. Autom. Constr. 2018, 89, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Q.; Wei, L.; Magee, D.R.; Cohn, A.G. Real-Time Hyperbola Recognition and Fitting in GPR Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2017, 55, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, H.; Xing, L.; Lin, J. Application and Algorithm of Ground-Penetrating Radar for Plant Root Detection: A Review. Sensors 2020, 20, 2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic, G.; Eren, L. Neural network based inspection of voids and karst conduits in hydro–electric power station tunnels using GPR. J. Appl. Geophys. 2018, 151, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkaya, U.; Melgani, F.; Belete Bejiga, M.; Seyfi, L.; Donelli, M. GPR B scan image analysis with deep learning methods. Measurement 2020, 165, 107770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Duan, Y. Wavelet Scattering Network-Based Machine Learning for Ground Penetrating Radar Imaging: Application in Pipeline Identification. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Quan, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Liu, X.; Chen, J.; Cao, X.; Guo, L. GPR-Based Automatic Identification of Root Zones of Influence Using HDBSCAN. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.Y.; Lin, D.J.; Puntu, J.M. Antenna Holder Device for Ground Penetrating Radar. In H01Q-001/00(2006.01); Intellectual Property Office MOEA R.O.C: Taipei, Taiwan, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, F. Introduction to HPC with MPI for Data Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shyu, J.B.H. Neotectonic architecture of Taiwan and its implications for future large earthquakes. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ho, C.S. An Introduction to the Geology of Taiwan, Explanatory Text of the Geologic Map of Taiwan, 2nd ed.; Central Geological Survey Taiwan, Ministry of Economy Affairs: Taipei, Taiwan, 1988; p. 192.
- Sandmeier, K.J. Reflexw Version 9.0: Windows XP/7/8/10-Program for the Processing of Seismic, Acoustic or Electromagnetic, Reflection, Refraction and Transmission Data; Sandmeier Geophysical Research: Karlsruhe, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Jol, H.M. Ground Penetrating Radar Theory and Applications; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetto, A.; Tosti, F.; Ciampoli, L.B.; D’amico, F. An overview of ground-penetrating radar signal processing techniques for road inspections. Signal Process. 2017, 132, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobes, D.C. Geophysical surveys of burial sites: A case study of the Oaro urupa. Geophysics 1999, 64, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olhoeft, G.R. Maximizing the information return from ground penetrating radar. J. Appl. Geophys. 2000, 43, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Cho, S.-J.; Yi, M.-J. Removal of ringing noise in GPR data by signal processing. Geosci. J. 2007, 11, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruddani, B.; Sandi, E. The Development of Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) Data Processing. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Comput. 2019, 9, 768–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utsi, E.C. Ground Penetrating Radar: Theory and Practice; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, D.J. Ground Penetrating Radar, 2nd ed.; The Institution of Electrical Engineer: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ismail, M.; Abas, A.; Arifin, M.; Ismail, M.; Othman, N.; Setu, A.; Ahmad, M.; Shah, M.; Amin, S.; Sarah, T. Integrity inspection of main access tunnel using ground penetrating radar. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 271, 012088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neal, A. Ground-penetrating radar and its use in sedimentology: Principles, problems and progress. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2004, 66, 261–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.-T. Application of Ground Penetrating Radar to Locate Underground Pipes. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 1993, 4, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, T. Concrete Scanning with GPR Guidebook; Sensors & Software Inc.: Mississauga, ON, Canada, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Vasudeo, A.; Katpatal, Y.; Ingle, R. Uses of dielectric constant reflection coefficients for determination of groundwater using ground-penetrating radar. World Appl. Sci. J. 2009, 6, 1321–1325. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, F.; Chen, Z.; Liu, H.; Cui, J.; Spencer, B.F.; Fang, G. Simultaneous Estimation of Rebar Diameter and Cover Thickness by a GPR-EMI Dual Sensor. Sensors 2018, 18, 2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Everitt, B.S.; Landau, S.; Leese, M.; Stahl, D. Cluster Analysis, 5th ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ah-Pine, J. An Efficient and Effective Generic Agglomerative Hierarchical Clustering Approach. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2018, 19, 1615–1658. [Google Scholar]
- Batrakov, D.; Golovin, D.; Simachev, A.; Batrakova, A. Hilbert transform application to the impulse signal processing. In Proceedings of the 2010 5th International Confernce on Ultrawideband and Ultrashort Impulse Signals, Sevastopol, Ukraine, 6–10 September 2010; pp. 113–115. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Venkatachalam, A.S.; Xia, T.; Xie, Y.; Wang, G. Data analysis technique to leverage ground penetrating radar ballast inspection performance. IEEE Radar Conf. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delforge, D.; Watlet, A.; Kaufmann, O.; Van Camp, M.; Vanclooster, M. Time-series clustering approaches for subsurface zonation and hydrofacies detection using a real time-lapse electrical resistivity dataset. J. Appl. Geophys. 2020, 184, 104203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumont, M.; Reninger, P.A.; Pryet, A.; Martelet, G.; Aunay, B.; Join, J.L. Agglomerative hierarchical clustering of airborne electromagnetic data for multi-scale geological studies. J. Appl. Geophys. 2018, 157, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Sirieix, C.; Riss, J.; Malaurent, P. A clustering approach applied to time-lapse ERT interpretation—Case study of Lascaux cave. J. Appl. Geophys. 2017, 144, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genelle, F.; Sirieix, C.; Riss, J.; Naudet, V. Monitoring landfill cover by electrical resistivity tomography on an experimental site. Eng. Geol. 2012, 145–146, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Demsa, J.; Curk, T.; Erjavec, A.; Gorup, C.; Hocevar, T.; Milutinovic, M.; Mozina, M.; Polajnar, M.; Toplak, M.; Staric, A.; et al. Orange: Data Mining Toolbox in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2013, 14, 2349–2353. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, X.; Xu, Y.; Xiao, L.; Dang, Y.; Zhu, P.; Tang, C.P.; Zhang, X.; Liu, B.; Gou, S.; Yue, Z. Ground-penetrating radar measurements of subsurface structures of lacustrine sediments in the Qaidam Basin (NW China): Possible implications for future in-situ radar experiments on Mars. Icarus 2019, 338, 113576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinsunmade, A.; Karczewski, J.; Mazurkiewicz, E.; Tomecka-Suchoń, S. Finite-difference time domain (FDTD) modeling of ground penetrating radar pulse energy for locating burial sites. Acta Geophys. 2019, 67, 1945–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.; Zeng, Z.; Deng, L. FDTD simulations for ground penetrating radar in urban applications. J. Geophys. Eng. 2007, 4, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Tunnel Name | Start Point (Mileage) | End Point (Mileage) | Total Distance (m) | Average Thickness (m) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2nd Lining | 1st Lining | ||||
| Fangdian 1 (FD1) | 12k+764 | 12k+804 | 40 | 0.49 | 0.25 |
| Fangdian 2 (FD 2) | 12k+980 | 13k+065 | 85 | 0.49 | 0.26 |
| Fangshan 1 (FS1) | 13k+945 | 14k+245 | 300 | 0.50 | 0.23 |
| Fangshan 2 (FS2) | 14k+917 | 15k+502 | 585 | 0.48 | 0.22 |
| Fangshan 3 (FS3) | 15k+795 | 16k+483 | 688 | 0.49 | 0.19 |
| Fangshan 4 (FS4) | 17k+170 | 17k+326 | 156 | 0.42 | 0.19 |
| Fangshan 5 (FS5) | 17k+729 | 17k+934 | 205 | 0.46 | 0.23 |
| Fangye 1 (FY1) | 18k+218 | 20k+027 | 1809 | 0.46 | 0.22 |
| Fangye 2 (FY2) | 20k+777 | 21k+499 | 722 | 0.44 | 0.19 |
| Fangye 3 (FY3) | 22k+004 | 23k+364 | 1360 | 0.41 | 0.20 |
| Tunnel Name | Percentage (%) | Category |
|---|---|---|
| Fangdian 1 (FD1) | 0 | A |
| Fangdian 2 (FD 2) | 0 | A |
| Fangshan 1 (FS1) | 0.13 | A |
| Fangshan 2 (FS2) | 0.76 | A |
| Fangshan 3 (FS3) | 1.05 | A |
| Fangshan 4 (FS4) | 0.10 | A |
| Fangshan 5 (FS5) | 0 | A |
| Fangye 1 (FY1) | 19.39 | B |
| Fangye 2 (FY2) | 1.71 | A |
| Fangye 3 (FY3) | 0.07 | A |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Puntu, J.M.; Chang, P.-Y.; Lin, D.-J.; Amania, H.H.; Doyoro, Y.G. A Comprehensive Evaluation for the Tunnel Conditions with Ground Penetrating Radar Measurements. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4250. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13214250
Puntu JM, Chang P-Y, Lin D-J, Amania HH, Doyoro YG. A Comprehensive Evaluation for the Tunnel Conditions with Ground Penetrating Radar Measurements. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(21):4250. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13214250
Chicago/Turabian StylePuntu, Jordi Mahardika, Ping-Yu Chang, Ding-Jiun Lin, Haiyina Hasbia Amania, and Yonatan Garkebo Doyoro. 2021. "A Comprehensive Evaluation for the Tunnel Conditions with Ground Penetrating Radar Measurements" Remote Sensing 13, no. 21: 4250. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13214250
APA StylePuntu, J. M., Chang, P. -Y., Lin, D. -J., Amania, H. H., & Doyoro, Y. G. (2021). A Comprehensive Evaluation for the Tunnel Conditions with Ground Penetrating Radar Measurements. Remote Sensing, 13(21), 4250. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13214250










