Seasonal and Interannual Variability of Sea Surface Salinity Near Major River Mouths of the World Ocean Inferred from Gridded Satellite and In-Situ Salinity Products
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. Method
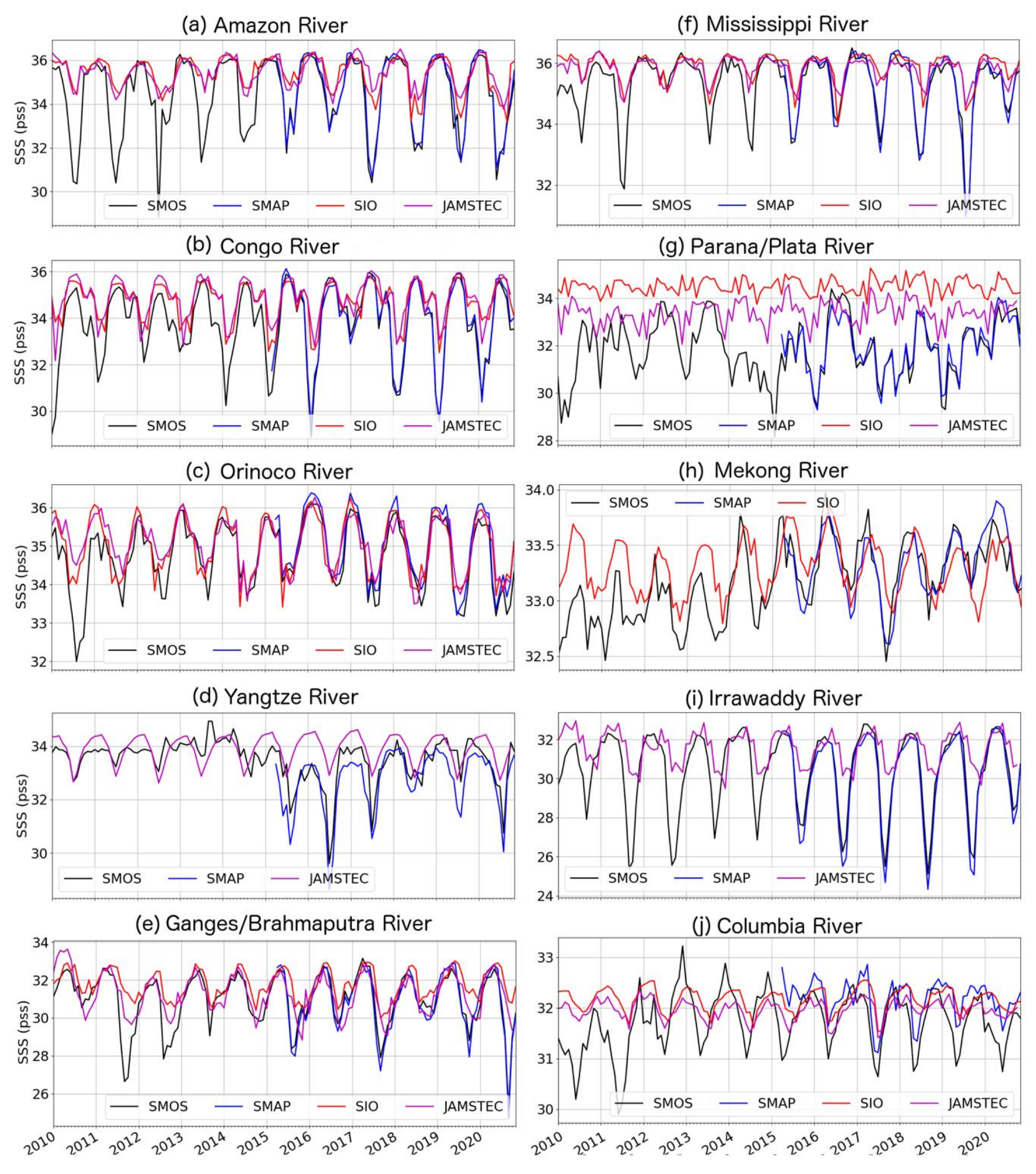
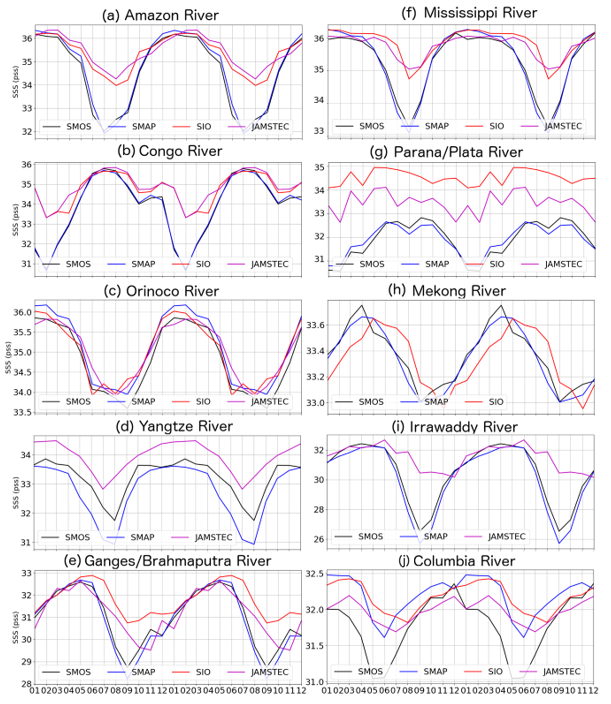
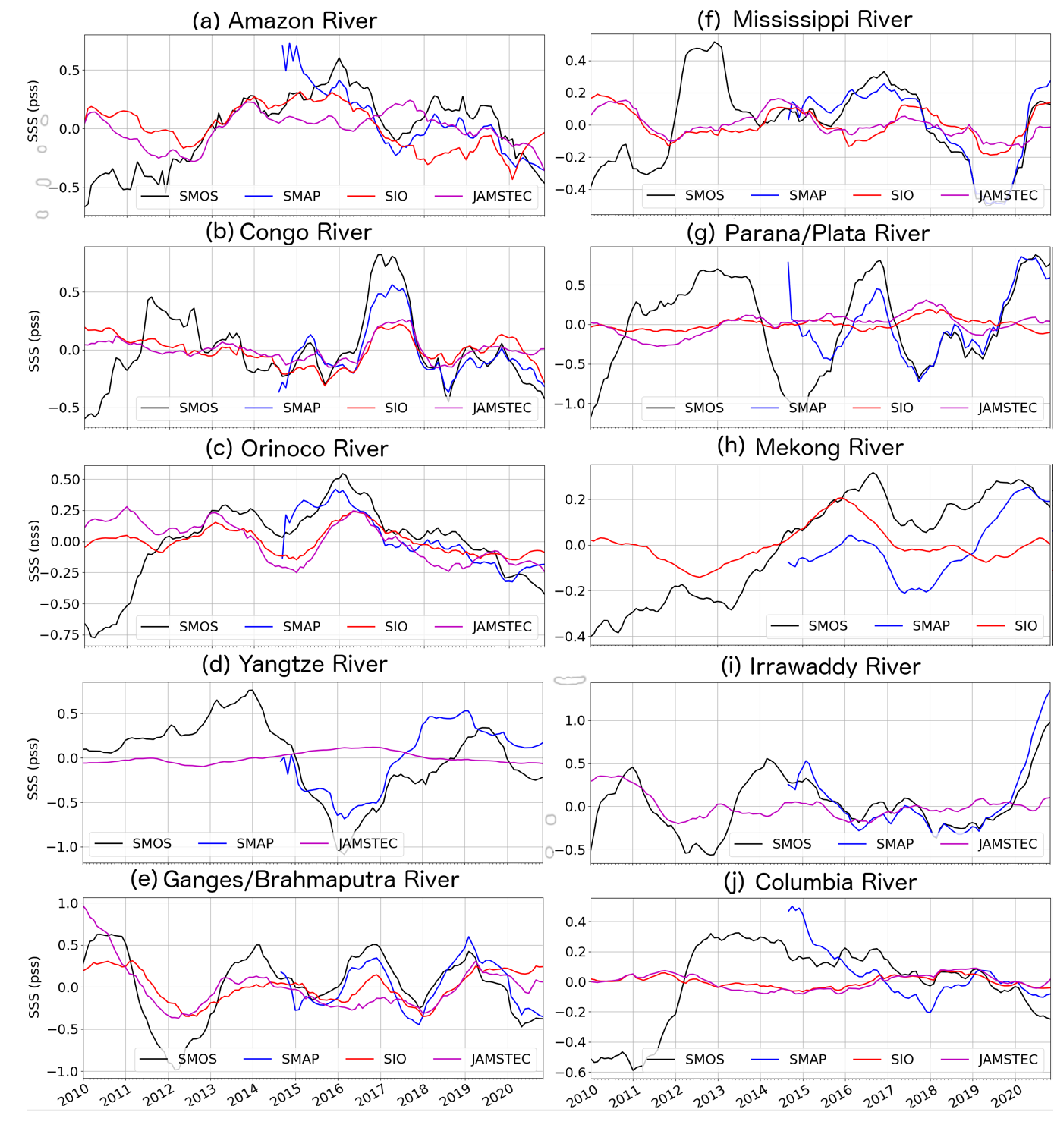
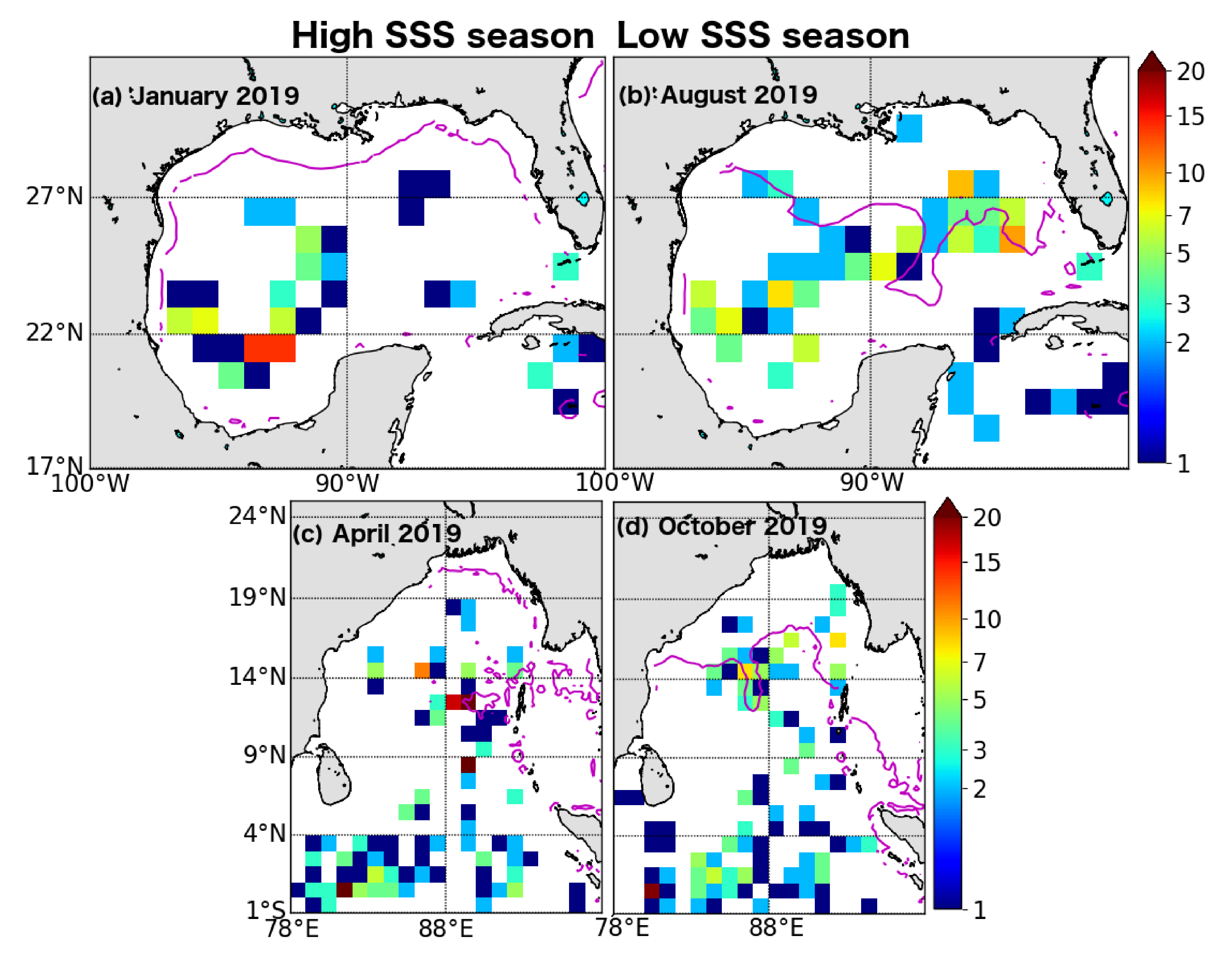
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trenberth, K.E.; Smith, L.; Qian, T.; Dai, A.; Fasullo, J. Estimates of the global water budget and its annual cycle using observational and model data. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 758–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pailler, K.; Bourlès, B.; Gouriou, Y. The barrier layer in the western tropical Atlantic Ocean. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1999, 26, 2069–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson, S.; Delecluse, P. Influence of the Amazon River runoff on the tropical atlantic. Phys. Chem. Earth Part B Hydrol. Ocean. Atmos. 2001, 26, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thadathil, P.; Suresh, I.; Gautham, S.; Kumar, S.P.; Lengaigne, M.; Rao, R.R.; Neetu, S.; Hegde, A. Surface layer temperature inversion in the Bay of Bengal: Main characteristics and related mechanisms. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2016, 121, 5682–5696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, B.; Aller, R.; Allison, M.; Bianchi, T.; Kineke, G. Transport and transformation of dissolved and particulate materials on continental margins influenced by major rivers: Benthic boundary layer and seabed processes. Cont. Shelf Res. 2004, 24, 899–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, B.M.; Kudela, R.M.; Nash, J.D.; Bruland, K.W.; Peterson, W.T.; MacCready, P.; Lessard, E.J.; Jay, D.A.; Banas, N.S.; Baptista, A.M.; et al. River Influences on Shelf Ecosystems: Introduction and synthesis. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2010, 115, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentz, S.J. Seasonal variations in the horizontal structure of the Amazon Plume inferred from historical hydrographic data. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1995, 100, 2391–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, J.; Lucas, M.; Dufau, C.; Sutton, M.; Stum, J.; Lauret, O.; Channelliere, C. Detection and variability of the Congo River plume from satellite derived sea surface temperature, salinity, ocean colour and sea level. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 139, 365–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, S.; Chapron, B.; Salisbury, J.E.; VanDeMark, D.; Reul, N. Comparison of spaceborne measurements of sea surface salinity and colored detrital matter in the Amazon plume. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2015, 120, 3177–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fournier, S.; Lee, T.; Gierach, M.M. Seasonal and interannual variations of sea surface salinity associated with the Mississippi River plume observed by SMOS and Aquarius. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 180, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, S.; Reager, J.T.; Lee, T.; Vazquez-Cuervo, J.; David, C.H.; Gierach, M.M. SMAP observes flooding from land to sea: The Texas event of 2015. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 10–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, S.; Vandemark, D.; Gaultier, L.; Lee, T.; Jonsson, B.; Gierach, M.M. Interannual variation in offshore advection of Amazon-Orinoco plume waters: Observations, forcing mechanisms, and impacts. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2017, 122, 8966–8982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, S.; Vialard, J.; Lengaigne, M.; Lee, T.; Gierach, M.M.; Chaitanya, A.V.S. Modulation of the Ganges-Brahmaputra River Plume by the Indian Ocean Dipole and Eddies Inferred From Satellite Observations. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2017, 122, 9591–9604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, D.; Su, X.; Qiu, Z.; Wang, S.; Mao, Z.; He, Y. Remote Sensing Estimation of Sea Surface Salinity from GOCI Measurements in the Southern Yellow Sea. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boutin, J.; Vergely, J.L.; Khvorostyanov, D. SMOS SSS L3 Maps Generated by CATDS CEC LOCEAN Debias V5.0. Available online: https://www.seanoe.org/data/00417/52804/ (accessed on 20 January 2021).
- Meissner, T.; Wentz, F.J.; Le Vine, D.M. The Salinity Retrieval Algorithms for the NASA Aquarius Version 5 and SMAP Version 3 Releases. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vazquez-Cuervo, J.; Fournier, S.; Dzwonkowski, B.; Reager, J. Intercomparison of In-Situ and Remote Sensing Salinity Products in the Gulf of Mexico, a River-Influenced System. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vazquez-Cuervo, J.; Gomez-Valdes, J.; Bouali, M.; Miranda, L.E.; Van Der Stocken, T.; Tang, W.; Gentemann, C. Using Saildrones to Validate Satellite-Derived Sea Surface Salinity and Sea Surface Temperature along the California/Baja Coast. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roemmich, D.; Gilson, J. The 2004–2008 mean and annual cycle of temperature, salinity, and steric height in the global ocean from the Argo Program. Prog. Oceanogr. 2009, 82, 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, S.; Reager, J.T.; Dzwonkowski, B.; Vazquez-Cuervo, J. Statistical Mapping of Freshwater Origin and Fate Signatures as Land/Ocean “Regions of Influence” in the Gulf of Mexico. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2019, 124, 4954–4973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoda, S.; Ohira, T.; Nakamura, T. A monthly mean dataset of global oceanic temperature and salinity derived from Argo float observations. JAMSTEC Rep. Res. Dev. 2008, 8, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, A.; Trenberth, K.E. Estimates of freshwater discharge from continents: Latitudinal and seasonal variations. J. Hydrometeorol. 2002, 3, 660–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, T. Consistency of Aquarius sea surface salinity with Argo products on various spatial and temporal scales. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 3857–3864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, L.; Bingham, F.M.; Lee, T.; Dinnat, E.; Fournier, S.; Melnichenko, O.V.; Tang, W. Revisiting the Global Patterns of Seasonal Cycle in Sea Surface Salinity. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2021. under review. [Google Scholar]
- Del Castillo, C.E.; Miller, R.L. On the use of ocean color remote sensing to measure the transport of dissolved organic carbon by the Mississippi River Plume. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Del Vecchio, R.; Subramaniam, A. Influence of the Amazon river on the surface optical properties of the western tropical north Atlantic ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Latitude Boundaries | Longitude Boundaries | |
|---|---|---|
| Amazon | [5.5°N, 8.5°N] | [51.5°W, 48.5°W] |
| Congo | [6°S, 9°S] | [10°E, 13°E] |
| Orinoco | [11.5°N, 14.5°N] | [62.5°W, 59.5°W] |
| Yangtze | [29.5°N, 32.5°N] | [124.5°E, 127.5°E] |
| Ganges/Brahmaputra | [17.5°N, 20.5°N] | [88.5°E, 91.5°E] |
| Mississippi | [26.5°N, 29.5°N] | [88.5°W, 85.5°W] |
| Parana/Plata | [38°S, 35°S] | [56°W, 53°W] |
| Mekong | [12.5°N, 15.5°N] | [109.5°W, 112.5°W] |
| Irrawaddy | [12.5°N, 15.5°N] | [94.5°E, 97.5°E] |
| Columbia | [44.5°N, 47.5°N] | [127.5°W, 124.5°W] |
| STD (psu) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMOS/SMAP | SIO/JAMSTEC | SMOS/SIO | SMOS/JAMSTEC | SMAP/SIO | SMAP/JAMSTEC | |
| Amazon | 0.32 | 0.45 | 1.08 | 1.22 | 1.05 | 1.19 |
| Congo | 0.27 | 0.37 | 1.13 | 1.17 | 1.06 | 1.09 |
| Orinoco | 0.12 | 0.32 | 0.41 | 0.43 | 0.38 | 0.44 |
| Yangtze | 0.54 | N/A | N/A | 0.77 | N/A | 0.80 |
| Ganges/Brahmaputra | 0.38 | 0.59 | 1.00 | 1.03 | 1.16 | 1.16 |
| Mississippi | 0.22 | 0.26 | 0.78 | 0.80 | 0.88 | 0.91 |
| Parana/Plata | 0.40 | 0.27 | 1.21 | 1.28 | 1.19 | 1.25 |
| Mekong | 0.17 | N/A | 0.26 | N/A | 0.18 | N/A |
| Irrawaddy | 0.36 | N/A | N/A | 1.62 | N/A | 1.86 |
| Columbia | 0.34 | 0.12 | 0.41 | 0.39 | 0.30 | 0.32 |
| Correlation Coefficient | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMOS/SMAP | SIO/JAMSTEC | SMOS/SIO | SMOS/JAMSTEC | SMAP/SIO | SMAP/JAMSTEC | |
| Amazon | 1 | 0.95 | 0.97 | 0.91 | 0.97 | 0.93 |
| Congo | 1 | 0.95 | 0.86 | 0.90 | 0.86 | 0.90 |
| Orinoco | 1 | 0.94 | 0.96 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.97 |
| Yangtze | 0.97 | N/A | N/A | 0.91 | N/A | 0.96 |
| Ganges/Brahmaputra | 0.99 | 0.86 | 0.87 | 0.83 | 0.84 | 0.82 |
| Mississippi | 1 | 0.93 | 0.88 | 0.95 | 0.86 | 0.94 |
| Parana/Plata | 0.97 | 0.62 | 0.58 | 0.45 | 0.65 | 0.58 |
| Mekong | 0.97 | N/A | 0.71 | N/A | 0.76 | N/A |
| Irrawaddy | 1 | N/A | N/A | 0.72 | N/A | 0.70 |
| Columbia | 0.84 | 0.88 | 0.51 | 0.75 | 0.78 | 0.83 |
| Correlation Coefficient | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMOS/SMAP | SIO/JAMSTEC | SMOS/SIO | SMOS/JAMSTEC | SMAP/SIO | SMAP/JAMSTEC | |
| Amazon | 0.82 | 0.25 | 0.67 | 0.43 | 0.83 | 0.35 |
| Congo | 0.95 | 0.82 | 0.70 | 0.82 | 0.70 | 0.86 |
| Orinoco | 0.91 | 0.95 | 0.80 | 0.71 | 0.64 | 0.55 |
| Yangtze | 0.82 | N/A | N/A | −0.75 | N/A | −0.85 |
| Ganges/Brahmaputra | 0.81 | 0.83 | −0.02 | −0.03 | 0.41 | 0.44 |
| Mississippi | 0.97 | 0.71 | 0.57 | 0.65 | 0.65 | 0.63 |
| Parana/Plata | 0.73 | 0.62 | −0.64 | −0.18 | −0.70 | −0.35 |
| Mekong | 0.77 | N/A | 0.09 | N/A | −0.01 | N/A |
| Irrawaddy | 0.98 | N/A | N/A | 0.30 | N/A | 0.39 |
| Columbia | 0.54 | 0.93 | 0.09 | −0.16 | 0.39 | 0.25 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fournier, S.; Lee, T. Seasonal and Interannual Variability of Sea Surface Salinity Near Major River Mouths of the World Ocean Inferred from Gridded Satellite and In-Situ Salinity Products. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 728. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13040728
Fournier S, Lee T. Seasonal and Interannual Variability of Sea Surface Salinity Near Major River Mouths of the World Ocean Inferred from Gridded Satellite and In-Situ Salinity Products. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(4):728. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13040728
Chicago/Turabian StyleFournier, Severine, and Tong Lee. 2021. "Seasonal and Interannual Variability of Sea Surface Salinity Near Major River Mouths of the World Ocean Inferred from Gridded Satellite and In-Situ Salinity Products" Remote Sensing 13, no. 4: 728. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13040728
APA StyleFournier, S., & Lee, T. (2021). Seasonal and Interannual Variability of Sea Surface Salinity Near Major River Mouths of the World Ocean Inferred from Gridded Satellite and In-Situ Salinity Products. Remote Sensing, 13(4), 728. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13040728







