Assessing within-Field Corn and Soybean Yield Variability from WorldView-3, Planet, Sentinel-2, and Landsat 8 Satellite Imagery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Q1: How does the spatial resolution affect our ability to explain crop yields at field scale?
- Q2: To what degree can crop yield variability at field scale be explained by using space-borne multi-spectral sensors only?
- Q3: What is the optimal timing of satellite image acquisitions and optimal spectral bands for explaining within-field variability?
2. Materials and Methods
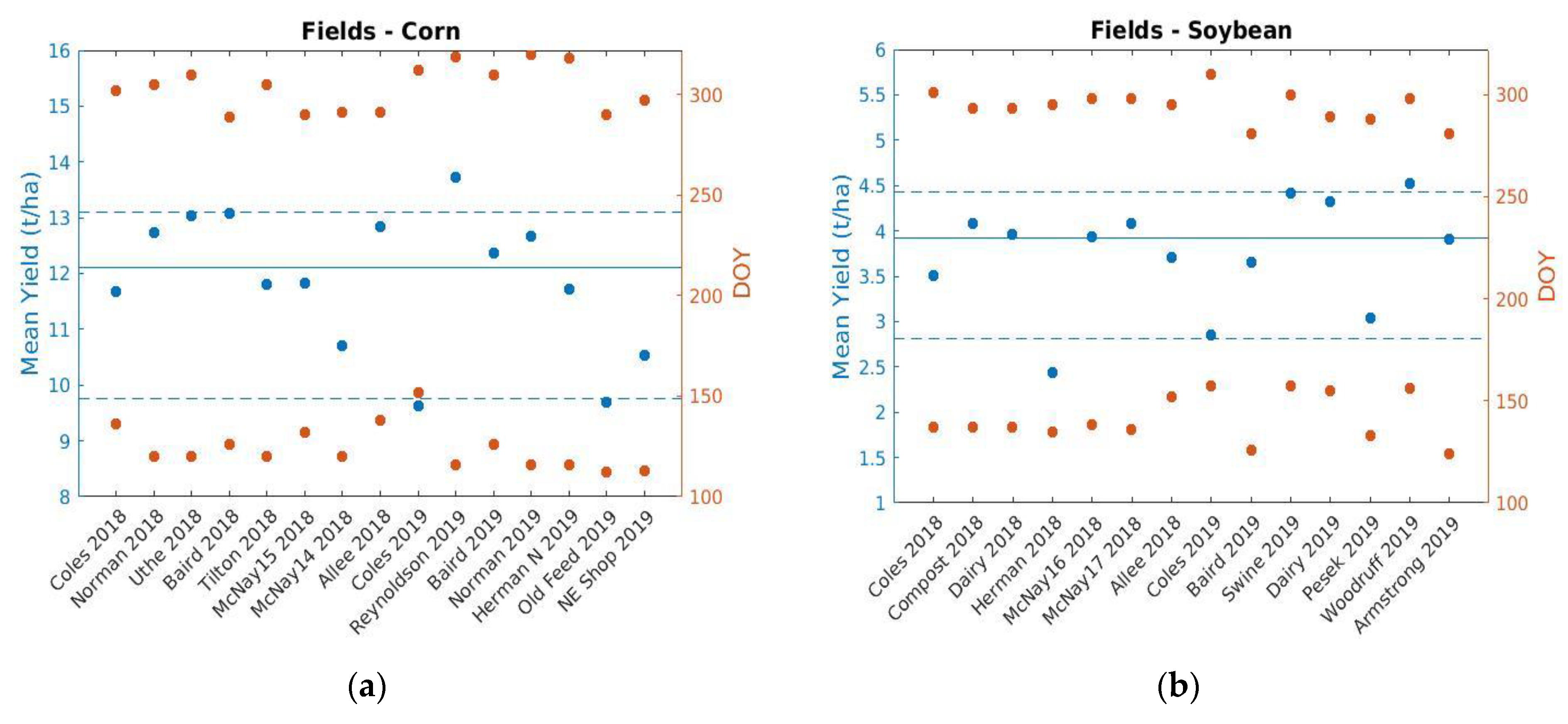
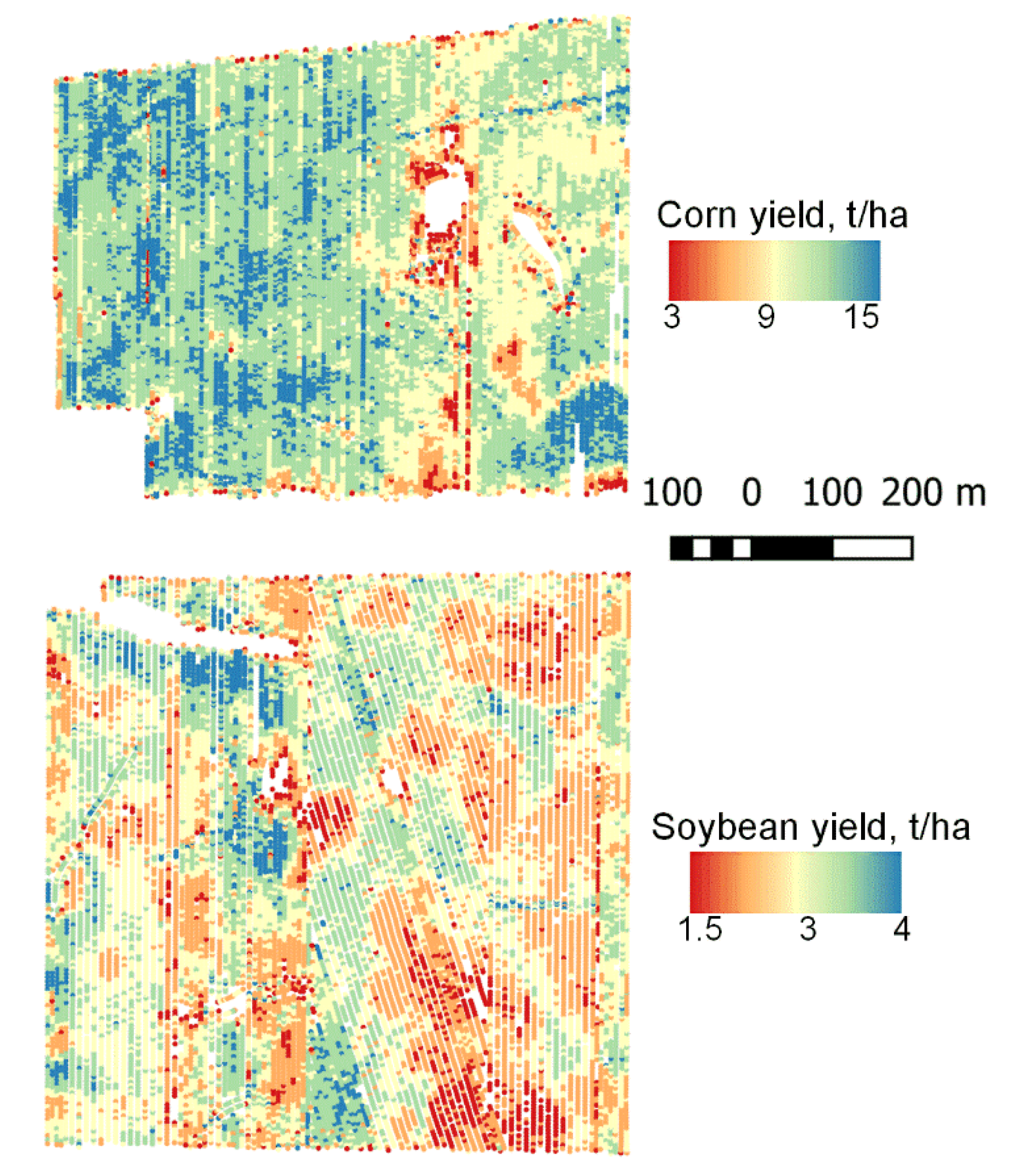
2.1. Study Area and Reference Yield Data
2.2. Satellite Data
2.2.1. Satellite Data at Very High Spatial Resolution (VHR): WorldView-3 and Planet
2.2.2. Satellite Data at Moderate Spatial Resolution: Landsat 8 and Sentinel-2
2.3. Methods
3. Results
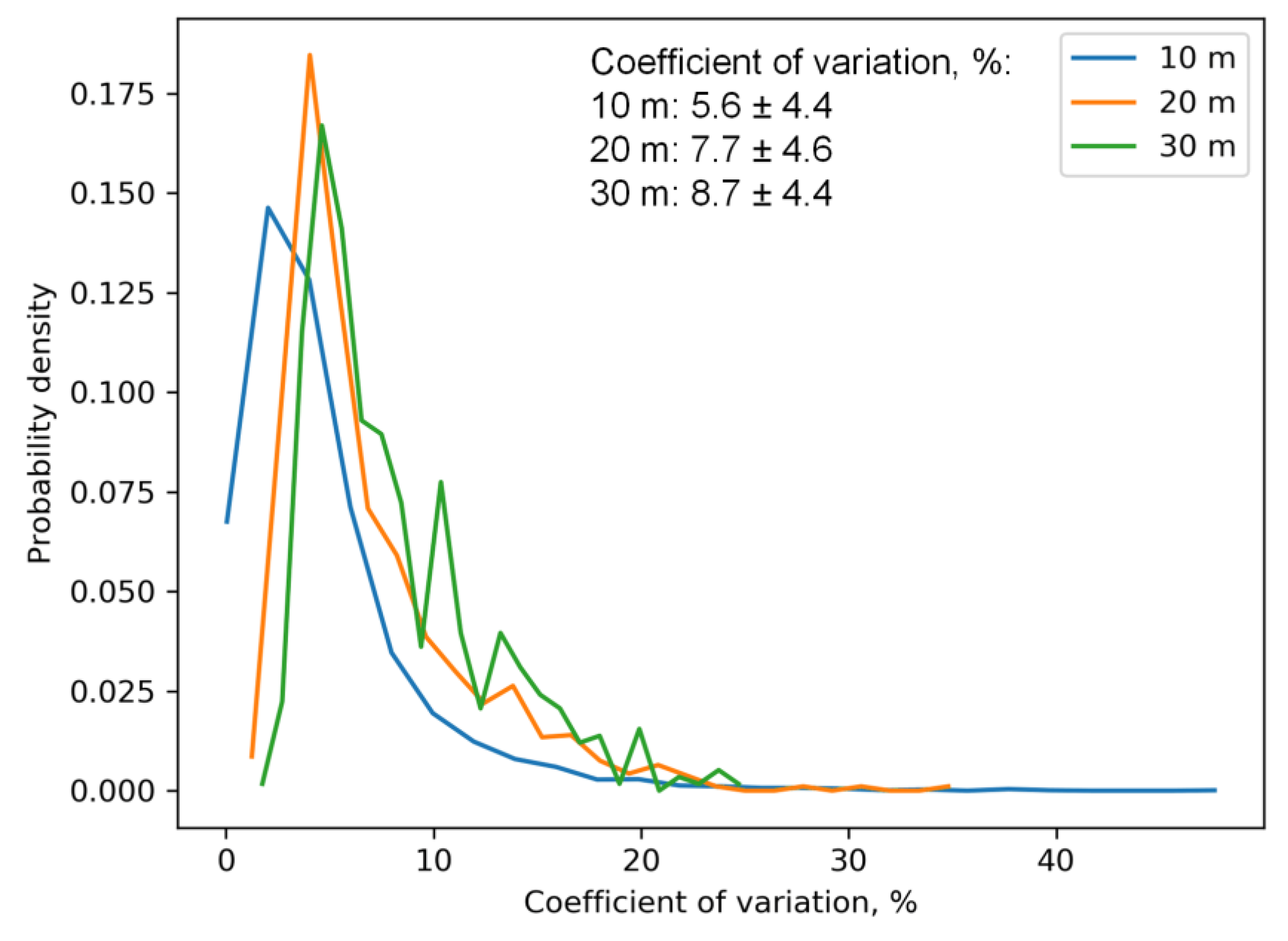
3.1. Effect of Spatial Resolution on Capturing Field Scale Yield Variability
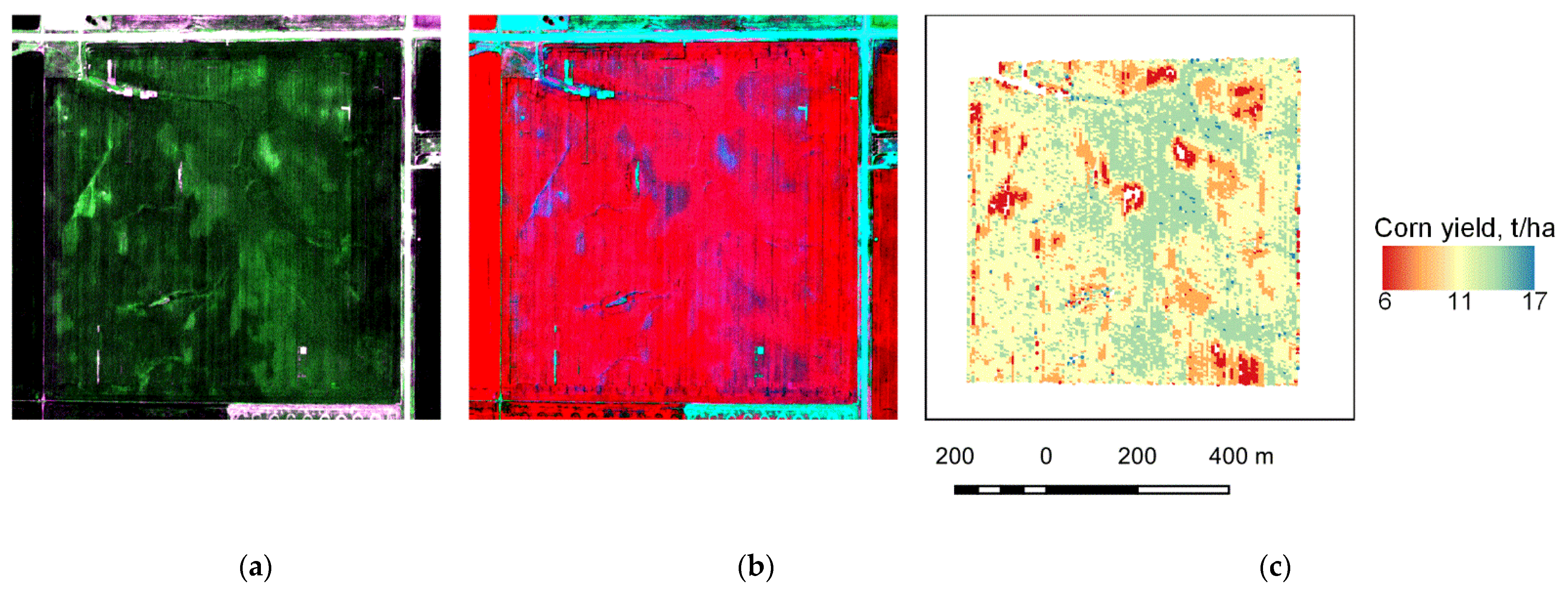
3.2. Analysis of Corn and Soybean Yield Varibility with WV-3 Data
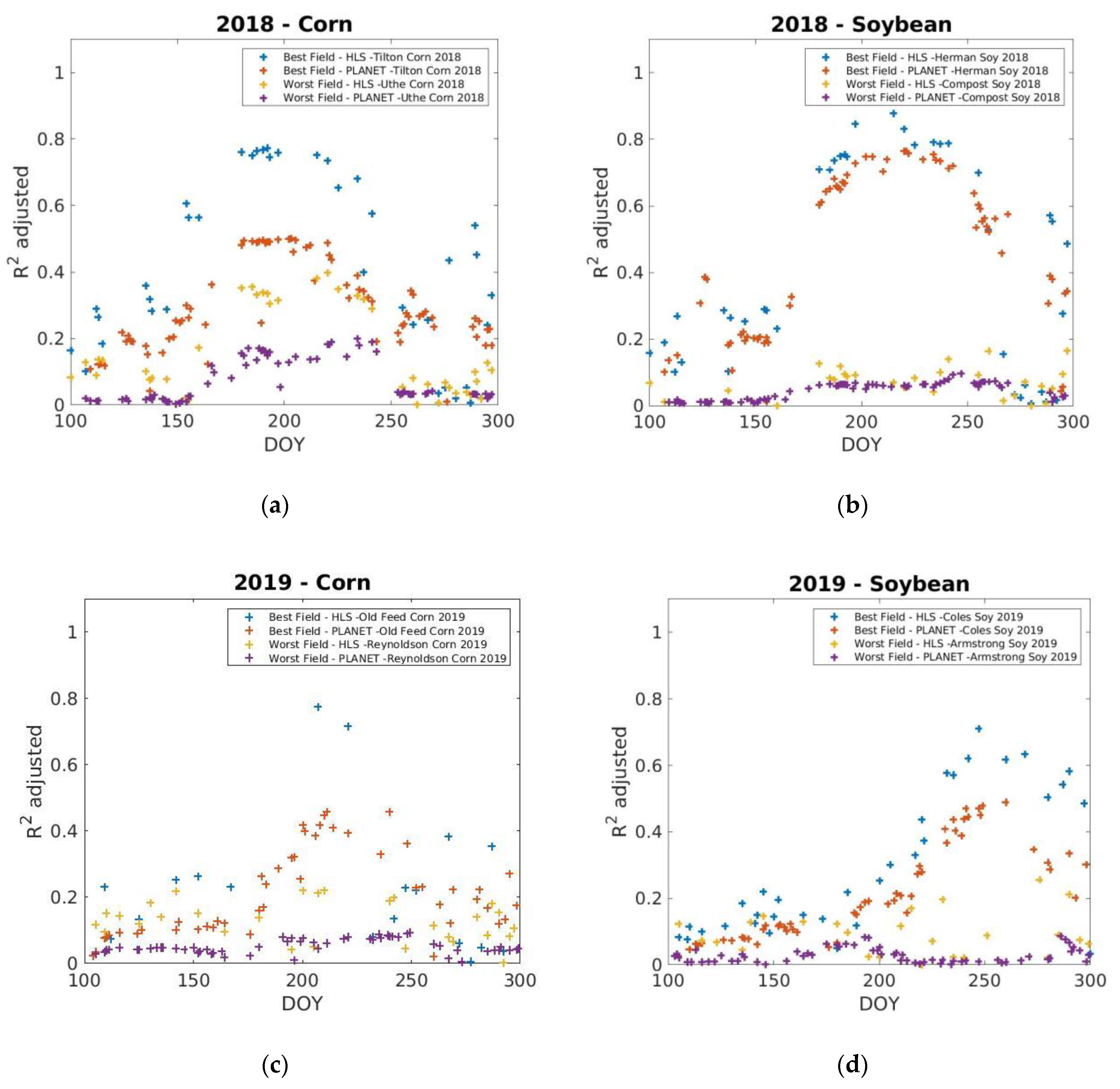
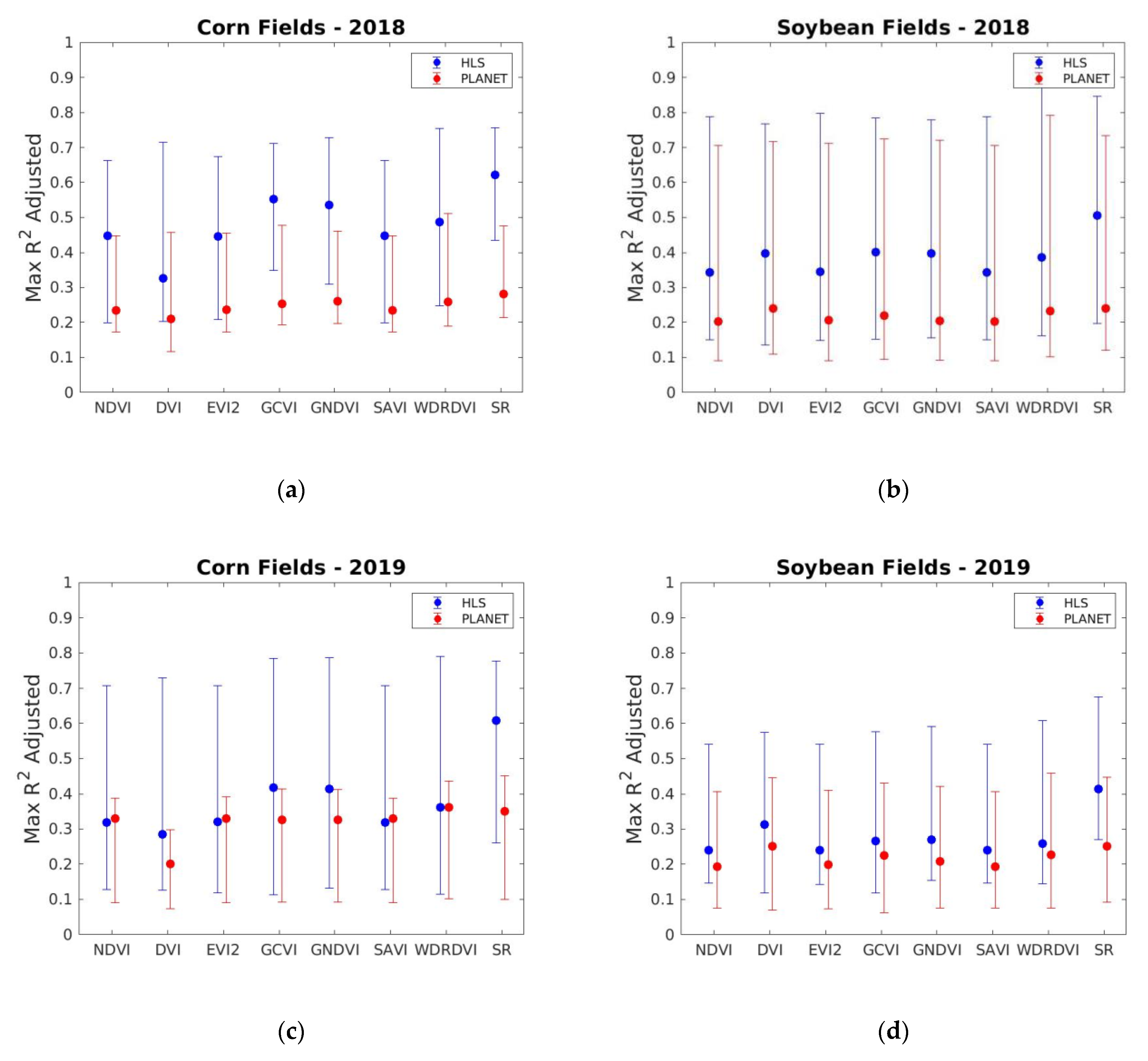
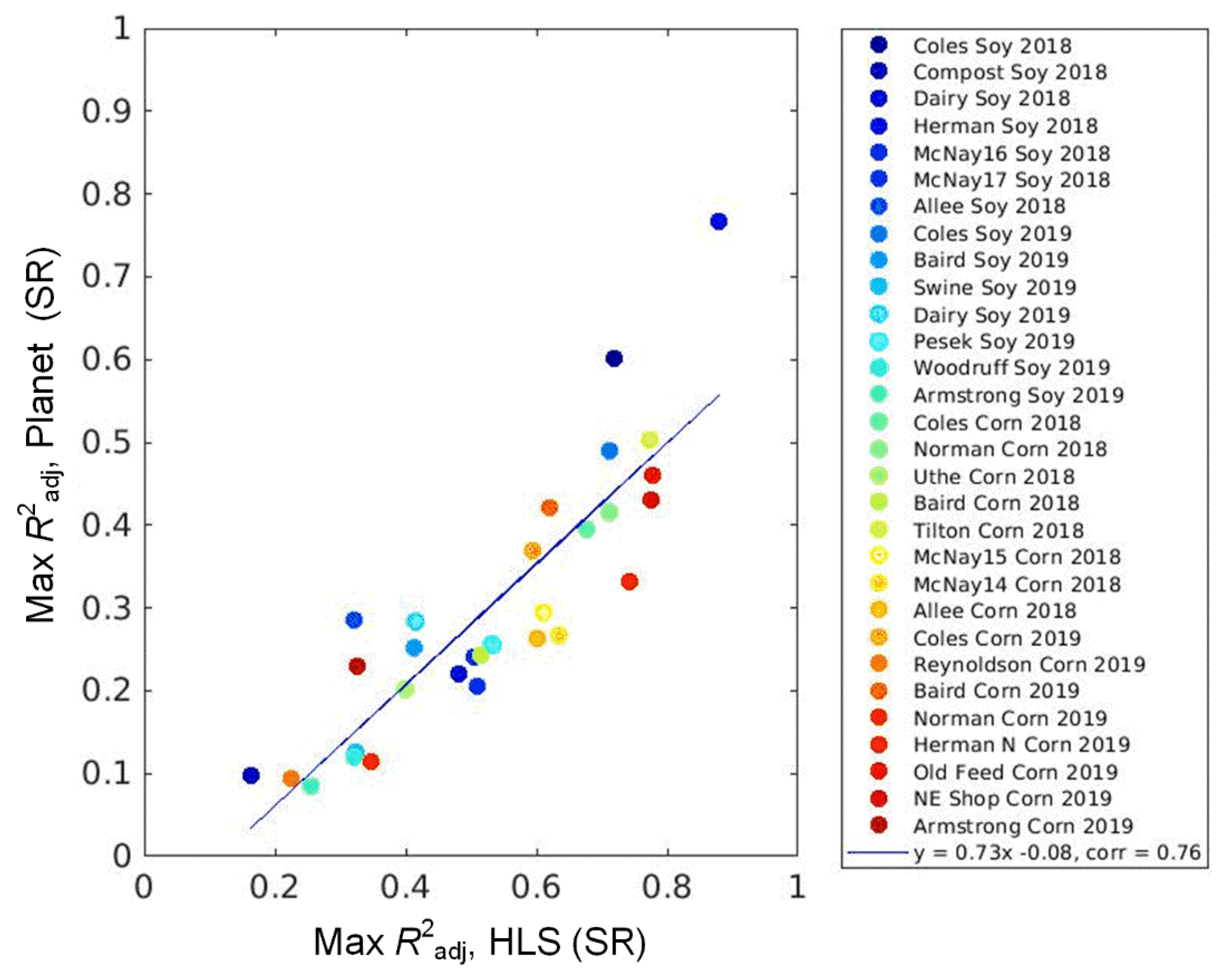
3.3. Analysis of Corn and Soybean Yield Varibility with Planet and HLS Data
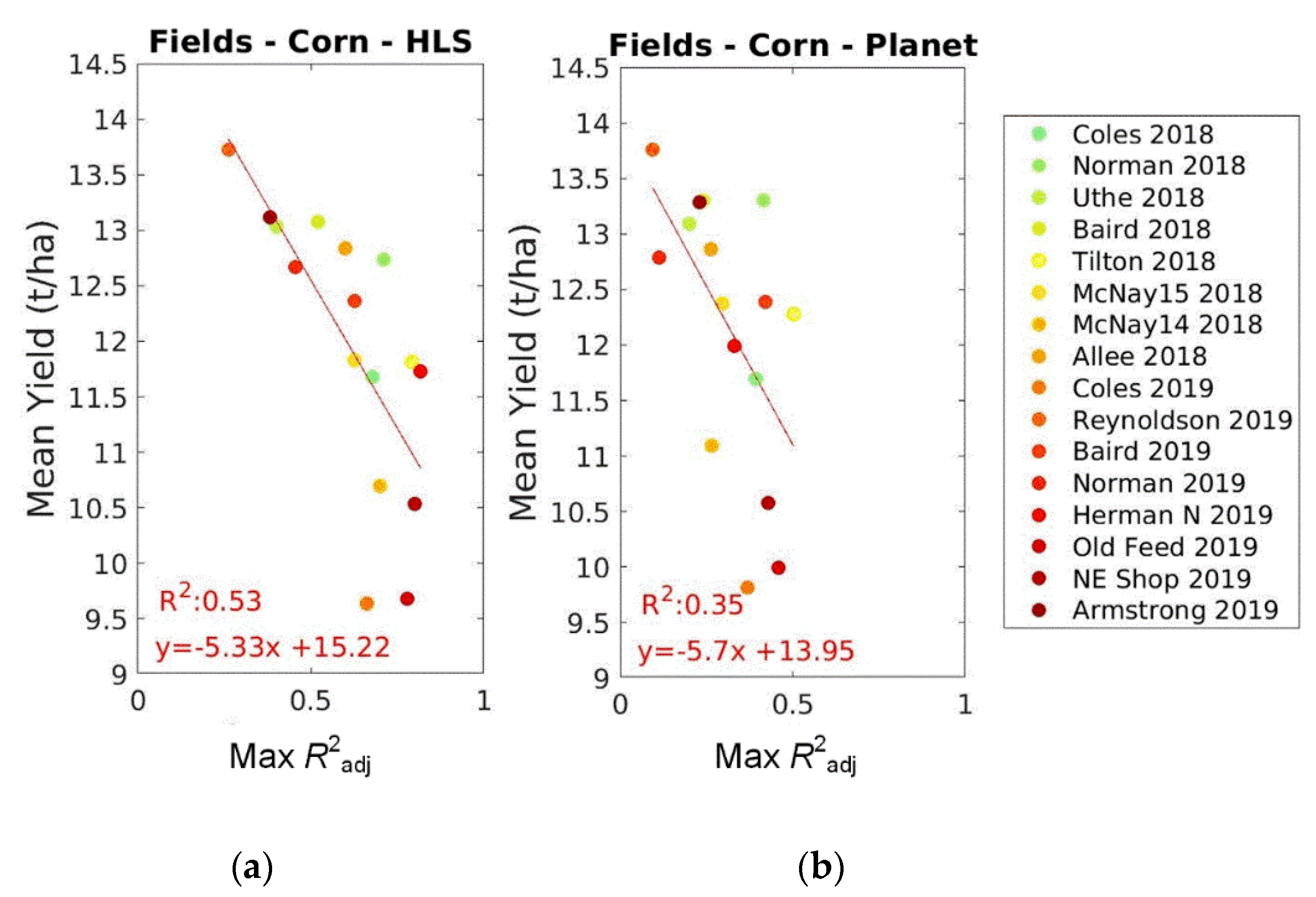
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Field Id | County in Iowa | Latitude, Longitude | Crop | Year | Yield, t/ha | Planting/ Harvesting DOY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baird | Jasper | 41.632, −93.305 | Corn | 2018 | 13.1 ± 1.2 | 126/289 |
| Uthe | Boone | 41.931, −93.754 | Corn | 2018 | 13.0 ± 1.9 | 120/310 |
| Allee | Buena Vista | 42.586, −95.00 | Corn | 2018 | 12.8 ± 0.6 | 138/291 |
| Norman | Story | 41.952, −93.689 | Corn | 2018 | 12.7 ± 3.0 | 120/305 |
| McNay | Lucas | 40.956, −93434 | Corn | 2018 | 11.8 ± 2.2 | 132/290 |
| Tilton | Story | 41.954, −93.675 | Corn | 2018 | 11.8 ± 3.1 | 120/305 |
| Coles | Hamilton | 42.481, −93.523 | Corn | 2018 | 11.7 ± 1.2 | 136/302 |
| McNay | Lucas | 40.975, −93.432 | Corn | 2018 | 10.7 ± 2.2 | 120/291 |
| Compost | Story | 41.977, −93.656 | Soybean | 2018 | 4.1 ± 0.9 | 137/293 |
| McNay | Lucas | 40.979, −93.417 | Soybean | 2018 | 4.1 ± 0.6 | 136/298 |
| Dairy | Story | 41.974, −93.648 | Soybean | 2018 | 3.9 ± 0.7 | 137/293 |
| McNay | Lucas | 40.972, −93.32 | Soybean | 2018 | 3.9 ± 0.6 | 138/298 |
| Allee | Buena Vista | 42.584, −95.00 | Soybean | 2018 | 3.7 ± 0.3 | 152/295 |
| Coles | Hamilton | 42.488, −93.523 | Soybean | 2018 | 3.5 ± 0.5 | 157/310 |
| Herman | Boone | 41.909, −93.739 | Soybean | 2018 | 2.4 ± 0.6 | 135/295 |
| Reynoldson | Boone | 41.925, −93.761 | Corn | 2019 | 13.7 ± 1.3 | 116/319 |
| Armstrong | Pottawatomie | 41.329, −95.181 | Corn | 2019 | 13.1 ± 2.3 | 115/293 |
| Norman | Lucas | 41.952, −93.689 | Corn | 2019 | 12.7 ± 1.6 | 116/320 |
| Baird | Jasper | 41.639, −93.312 | Corn | 2019 | 12.4 ± 1.3 | 126/310 |
| Herman | Boone | 41.909, −93.739 | Corn | 2019 | 11.7 ± 1.6 | 116/318 |
| NE Shop | Lucas | 40.979, −93.417 | Corn | 2019 | 10.5 ± 1.5 | 113/297 |
| Old Feed | Lucas | 40.975, −93.432 | Corn | 2019 | 9.7 ± 2.4 | 112/290 |
| Coles | Hamilton | 42.488, −93.523 | Corn | 2019 | 9.6 ± 1.4 | 153/312 |
| Woodruff | Story | 41.992, −93.694 | Soybean | 2019 | 4.5 ± 1.3 | 156/298 |
| Swine | Boone | 42.048, −93.701 | Soybean | 2019 | 4.4 ± 1.1 | 157/300 |
| Dairy | Story | 41.975, −93.649 | Soybean | 2019 | 4.3 ± 0.6 | 155/289 |
| Armstrong | Pottawatomie | 41.305, −95.180 | Soybean | 2019 | 3.9 ± 0.6 | 124/281 |
| Baird | Jasper | 41.632, −93.305 | Soybean | 2019 | 3.6 ± 0.6 | 126/281 |
| Coles | Hamilton | 42.481, −93.523 | Soybean | 2019 | 2.8 ± 0.5 | 157/310 |
| Pesek | Boone | 42.043, −93.701 | Soybean | 2019 | 3.0 ± 0.4 | 133/288 |
References
- Whitcraft, A.K.; Becker-Reshef, I.; Justice, C.O.; Gifford, L.; Kavvada, A.; Jarvis, I. No pixel left behind: Toward integrating Earth Observations for agriculture into the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals framework. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 235, 111470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker-Reshef, I.; Barker, B.; Humber, M.; Puricelli, E.; Sanchez, A.; Sahajpal, R.; McGaughey, K.; Justice, C.; Baruth, B.; Wu, B.; et al. The GEOGLAM crop monitor for AMIS: Assessing crop conditions in the context of global markets. Glob. Food Secur. 2019, 23, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birrell, S.J.; Sudduth, K.A.; Borgelt, S.C. Comparison of sensors and techniques for crop yield mapping. Comput. Electron. Agric. 1996, 14, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobell, D.B. The use of satellite data for crop yield gap analysis. Field Crop. Res. 2013, 143, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Ittersum, M.K.; Cassman, K.G.; Grassini, P.; Wolf, J.; Tittonell, P.; Hochman, Z. Yield gap analysis with local to global relevance—A review. Field Crop. Res. 2013, 143, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bokusheva, R.; Kogan, F.; Vitkovskaya, I.; Conradt, S.; Batyrbayeva, M. Satellite-based vegetation health indices as a criteria for insuring against drought-related yield losses. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2016, 220, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, D.M. A comprehensive assessment of the correlations between field crop yields and commonly used MODIS products. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 52, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franch, B.; Vermote, E.F.; Skakun, S.; Roger, J.-C.; Becker-Reshef, I.; Murphy, E.; Justice, C. Remote sensing based yield monitoring: Application to winter wheat in United States and Ukraine. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2019, 76, 112–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skakun, S.; Vermote, E.; Franch, B.; Roger, J.-C.; Kussul, N.; Ju, J.; Masek, J. Winter Wheat Yield Assessment from Landsat 8 and Sentinel-2 Data: Incorporating Surface Reflectance, Through Phenological Fitting, into Regression Yield Models. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kussul, N.; Lavreniuk, M.; Kolotii, A.; Skakun, S.; Rakoid, O.; Shumilo, L. A workflow for Sustainable Development Goals indicators assessment based on high-resolution satellite data. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2020, 13, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.P.; Wulder, M.A.; Loveland, T.R.; Woodcock, C.E.; Allen, R.G.; Anderson, M.C.; Helder, D.; Irons, J.R.; Johnson, D.M.; Kennedy, R.; et al. Landsat-8: Science and product vision for terrestrial global change research. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 145, 154–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drusch, M.; Del Bello, U.; Carlier, S.; Colin, O.; Fernandez, V.; Gascon, F.; Hoersch, B.; Isola, C.; Laberinti, P.; Martimort, P.; et al. Sentinel-2: ESA’s optical high-resolution mission for GMES operational services. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Everitt, J.H.; Du, Q.; Luo, B.; Chanussot, J. Using high-resolution airborne and satellite imagery to assess crop growth and yield variability for precision agriculture. Proc. IEEE 2013, 101, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.; Srivastava, A.K.; Joon, R.K.; McDonald, A.; Royal, K.; Lisaius, M.C.; Lobell, D.B. Mapping smallholder wheat yields and sowing dates using micro-satellite data. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sahajpal, R.; Becker-Reshef, I.; Coutu, S. Optimizing Crop Cut Collection for Determining Field-Scale Yields in an Insurance Context. Workshop Fragile Earth Data Sci. Sustain. Planet 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego, F.J. Remote sensing and land cover area estimation. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 3019–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olofsson, P.; Foody, G.M.; Herold, M.; Stehman, S.V.; Woodcock, C.E.; Wulder, M.A. Good practices for estimating area and assessing accuracy of land change. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 148, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morisette, J.T.; Baret, F.; Privette, J.L.; Myneni, R.B.; Nickeson, J.E.; Garrigues, S.; Shabanov, N.V.; Weiss, M.; Fernandes, R.A.; Leblanc, S.G.; et al. Validation of global moderate-resolution LAI products: A framework proposed within the CEOS land product validation subgroup. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 1804–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, J.; Clay, D.E.; Dalsted, K.; Clay, S.; O’Neill, M. Corn (Zea mays L.) yield prediction using multispectral and multidate reflectance. Agron. J. 2003, 95, 1447–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobermann, A.; Ping, J.L. Geostatistical integration of yield monitor data and remote sensing improves yield maps. Agron. J. 2004, 96, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Everitt, J.H.; Bradford, J.M. Evaluating high resolution SPOT 5 satellite imagery to estimate crop yield. Precis. Agric. 2009, 10, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, Y.; Ssegane, H.; Negri, M.C. Mapping intra-field yield variation using high resolution satellite imagery to integrate bioenergy and environmental stewardship in an agricultural watershed. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 9753–9768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peralta, N.R.; Assefa, Y.; Du, J.; Barden, C.J.; Ciampitti, I.A. Mid-season high-resolution satellite imagery for forecasting site-specific corn yield. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mulla, D.J. Twenty five years of remote sensing in precision agriculture: Key advances and remaining knowledge gaps. Biosyst. Eng. 2013, 114, 358–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharel, T.P.; Swink, S.N.; Maresma, A.; Youngerman, C.; Kharel, D.; Czymmek, K.J.; Ketterings, Q.M. Yield monitor data cleaning is essential for accurate corn grain and silage yield determination. Agron. J. 2019, 111, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Whelan, B.; McBratney, A.B.; Minasny, B. An integrated framework for software to provide yield data cleaning and estimation of an opportunity index for site-specific crop management. Precis. Agric. 2013, 14, 376–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neigh, C.S.; Masek, J.G.; Nickeson, J.E. High-resolution satellite data open for government research. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2013, 94, 121–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vermote, E.; Justice, C.; Claverie, M.; Franch, B. Preliminary analysis of the performance of the Landsat 8/OLI land surface reflectance product. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doxani, G.; Vermote, E.; Roger, J.-C.; Gascon, F.; Adriaensen, S.; Frantz, D.; Hagolle, O.; Hollstein, A.; Kirches, G.; Li, F.; et al. Atmospheric correction inter-comparison exercise. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- NASA. “Private Sector Small Constellation Satellite Data Product Pilot” Program. Available online: https://earthdata.nasa.gov/esds/small-satellite-data-buy-program/csdap-pilot-evaluation (accessed on 25 February 2021).
- Planet Team. Planet Application Program Interface: In Space for Life on Earth. San Francisco, CA, USA. 2017. Available online: https://api.planet.com (accessed on 25 February 2021).
- Claverie, M.; Ju, J.; Masek, J.G.; Dungan, J.L.; Vermote, E.F.; Roger, J.-C.; Skakun, S.; Justice, C. The Harmonized Landsat and Sentinel-2 surface reflectance data set. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 219, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Roy, D.P. A global analysis of Sentinel-2A, Sentinel-2B and Landsat-8 data revisit intervals and implications for terrestrial monitoring. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 902. [Google Scholar]
- Gallego, F.J.; Kussul, N.; Skakun, S.; Kravchenko, O.; Shelestov, A.; Kussul, O. Efficiency assessment of using satellite data for crop area estimation in Ukraine. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 29, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strobl, C.; Boulesteix, A.L.; Kneib, T.; Augustin, T.; Zeileis, A. Conditional variable importance for random forests. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnson, D.M. An assessment of pre-and within-season remotely sensed variables for forecasting corn and soybean yields in the United States. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 141, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Anderson, M.; Daughtry, C.; Johnson, D. Assessing the variability of corn and soybean yields in central Iowa using high spatiotemporal resolution multi-satellite imagery. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mladenova, I.E.; Bolten, J.D.; Crow, W.T.; Anderson, M.C.; Hain, C.R.; Johnson, D.M.; Mueller, R. Intercomparison of soil moisture, evaporative stress, and vegetation indices for estimating corn and soybean yields over the US. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 1328–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Anderson, M.C.; Gao, F.; Wardlow, B.; Hain, C.R.; Otkin, J.A.; Alfieri, J.; Yang, Y.; Sun, L.; Dulaney, W. Field-scale mapping of evaporative stress indicators of crop yield: An application over Mead, NE, USA. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 210, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.C.; Yang, Y.; Xue, J.; Knipper, K.R.; Yang, Y.; Gao, F.; Hain, C.R.; Kustas, W.P.; Cawse-Nicholson, K.; Hulley, G.; et al. Interoperability of ECOSTRESS and Landsat for mapping evapotranspiration time series at sub-field scales. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 252, 112189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatfield, J.L.; Aflakpui, G. Spatial patterns of water and nitrogen response within corn production fields. In Agricultural Science; Aflakpui, G., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 73–96. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.; Gitelson, A.A. Remote estimation of gross primary productivity in soybean and maize based on total crop chlorophyll content. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Vegetation Index | Formula |
|---|---|
| Normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) | |
| Difference vegetation index (DVI) | |
| Enhanced vegetation index (EVI) | |
| Green NDVI (GNDVI) | |
| Green chlorophyll vegetation index (GCVI) | |
| Wide dynamic range vegetation index (WDRVI) | |
| Soil-adjusted vegetation index (SAVI) | |
| Red edge chlorophyll index (CIre) 1 |
| Crop | Acquisition Date | RMSE, t/ha | RRMSE, % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corn | 2 July 2018 | 0.35 | 1.23 | 10.5 |
| Corn | 21 July 2018 | 0.48 | 1.07 | 9.2 |
| Soybean | 2 July 2018 | 0.28 | 0.50 | 14.2 |
| Soybean | 21 July 2018 | 0.36 | 0.47 | 13.2 |
| Crop | Year | Harvest | HLS | Planet |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corn | 2018 | 298 ± 8 | 195 ± 19 | 206 ± 22 |
| Corn | 2019 | 307 ± 12 | 206 ± 22 | 216 ± 26 |
| Soybean | 2018 | 297 ± 6 | 209 ± 20 | 221 ± 16 |
| Soybean | 2019 | 292 ± 11 | 227 ± 24 | 223 ± 22 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Skakun, S.; Kalecinski, N.I.; Brown, M.G.L.; Johnson, D.M.; Vermote, E.F.; Roger, J.-C.; Franch, B. Assessing within-Field Corn and Soybean Yield Variability from WorldView-3, Planet, Sentinel-2, and Landsat 8 Satellite Imagery. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 872. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13050872
Skakun S, Kalecinski NI, Brown MGL, Johnson DM, Vermote EF, Roger J-C, Franch B. Assessing within-Field Corn and Soybean Yield Variability from WorldView-3, Planet, Sentinel-2, and Landsat 8 Satellite Imagery. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(5):872. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13050872
Chicago/Turabian StyleSkakun, Sergii, Natacha I. Kalecinski, Meredith G. L. Brown, David M. Johnson, Eric F. Vermote, Jean-Claude Roger, and Belen Franch. 2021. "Assessing within-Field Corn and Soybean Yield Variability from WorldView-3, Planet, Sentinel-2, and Landsat 8 Satellite Imagery" Remote Sensing 13, no. 5: 872. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13050872
APA StyleSkakun, S., Kalecinski, N. I., Brown, M. G. L., Johnson, D. M., Vermote, E. F., Roger, J.-C., & Franch, B. (2021). Assessing within-Field Corn and Soybean Yield Variability from WorldView-3, Planet, Sentinel-2, and Landsat 8 Satellite Imagery. Remote Sensing, 13(5), 872. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13050872










