Evaluating the Latest IMERG Products in a Subtropical Climate: The Case of Paraná State, Brazil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
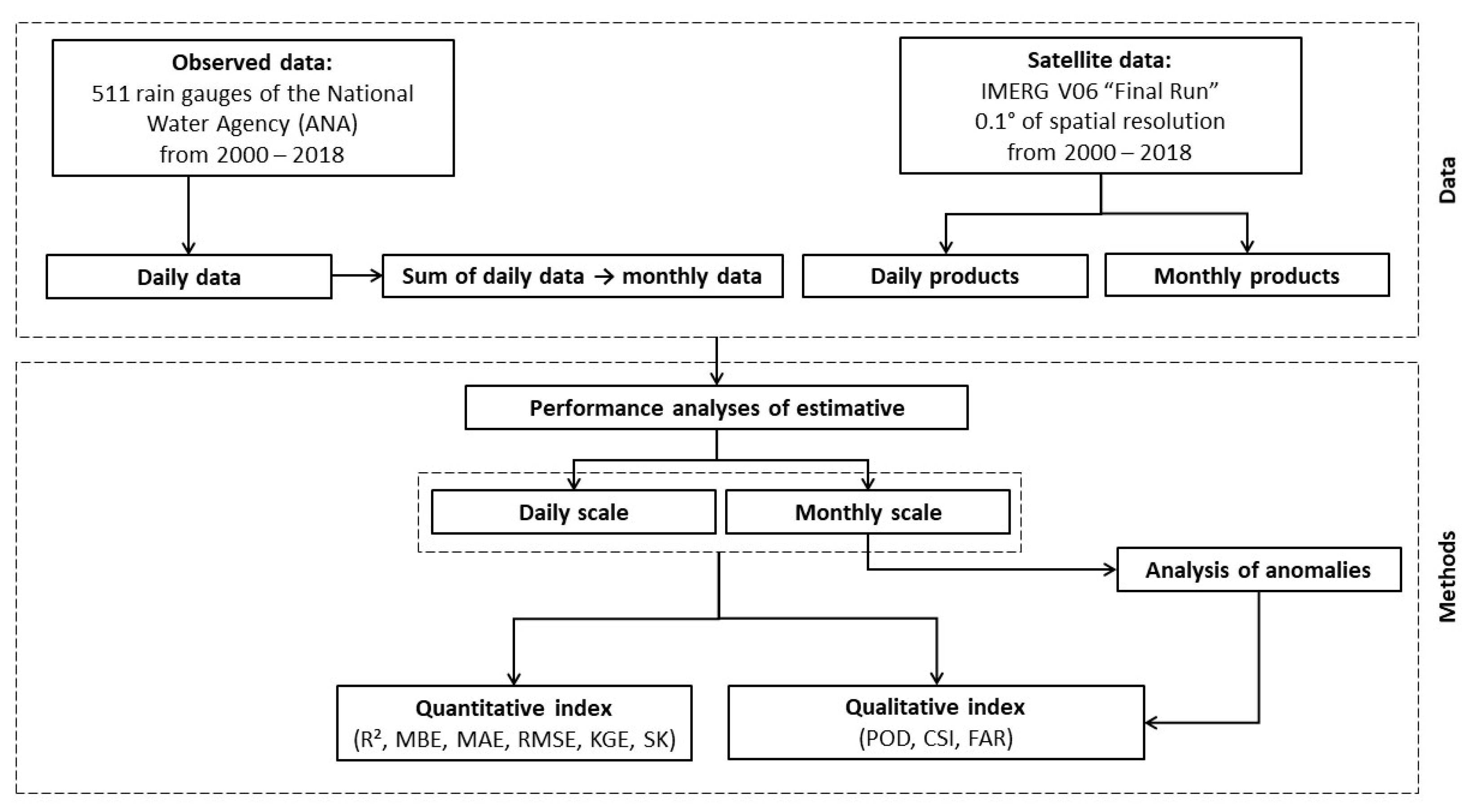
2. Material and Methods
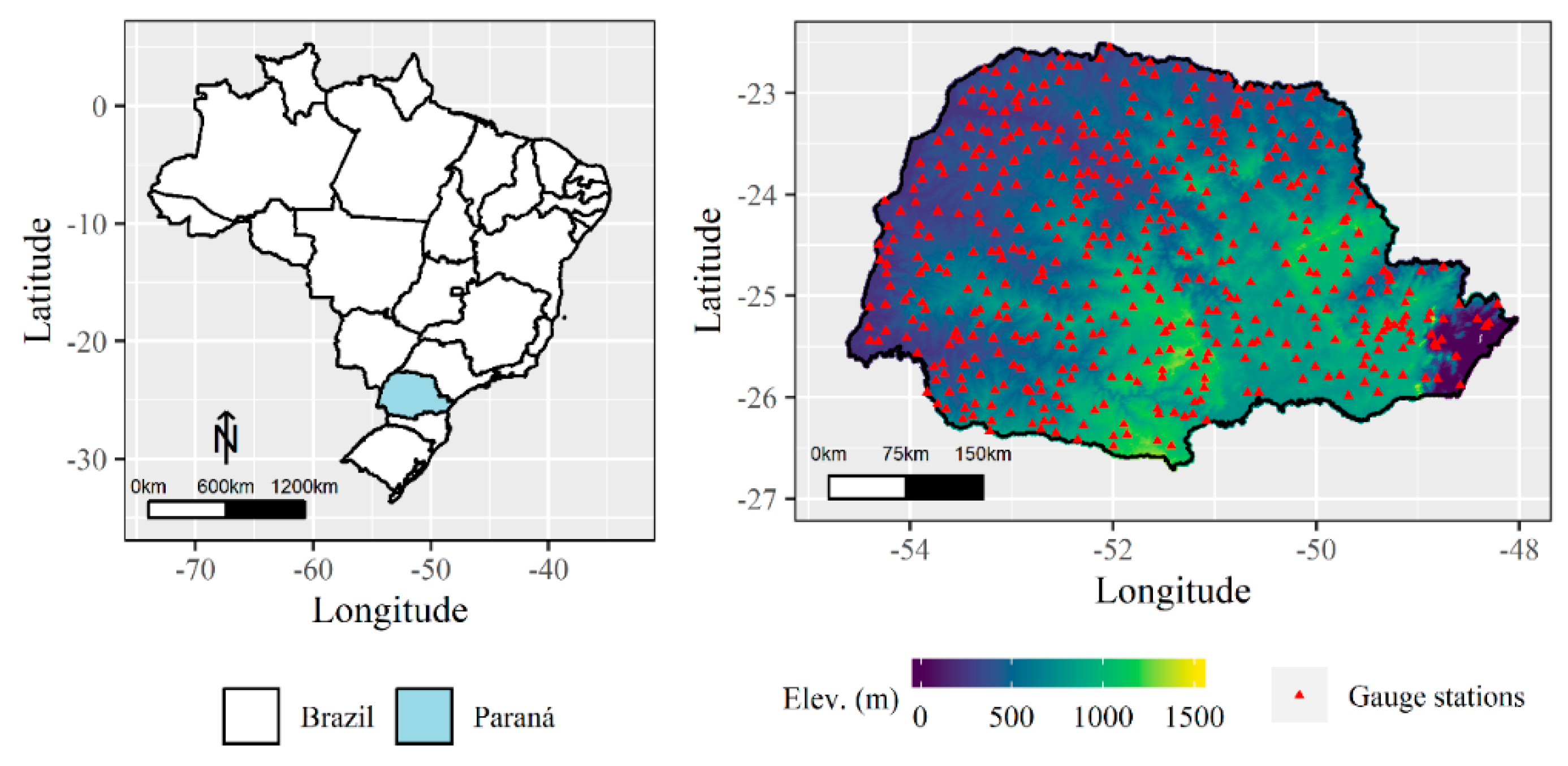
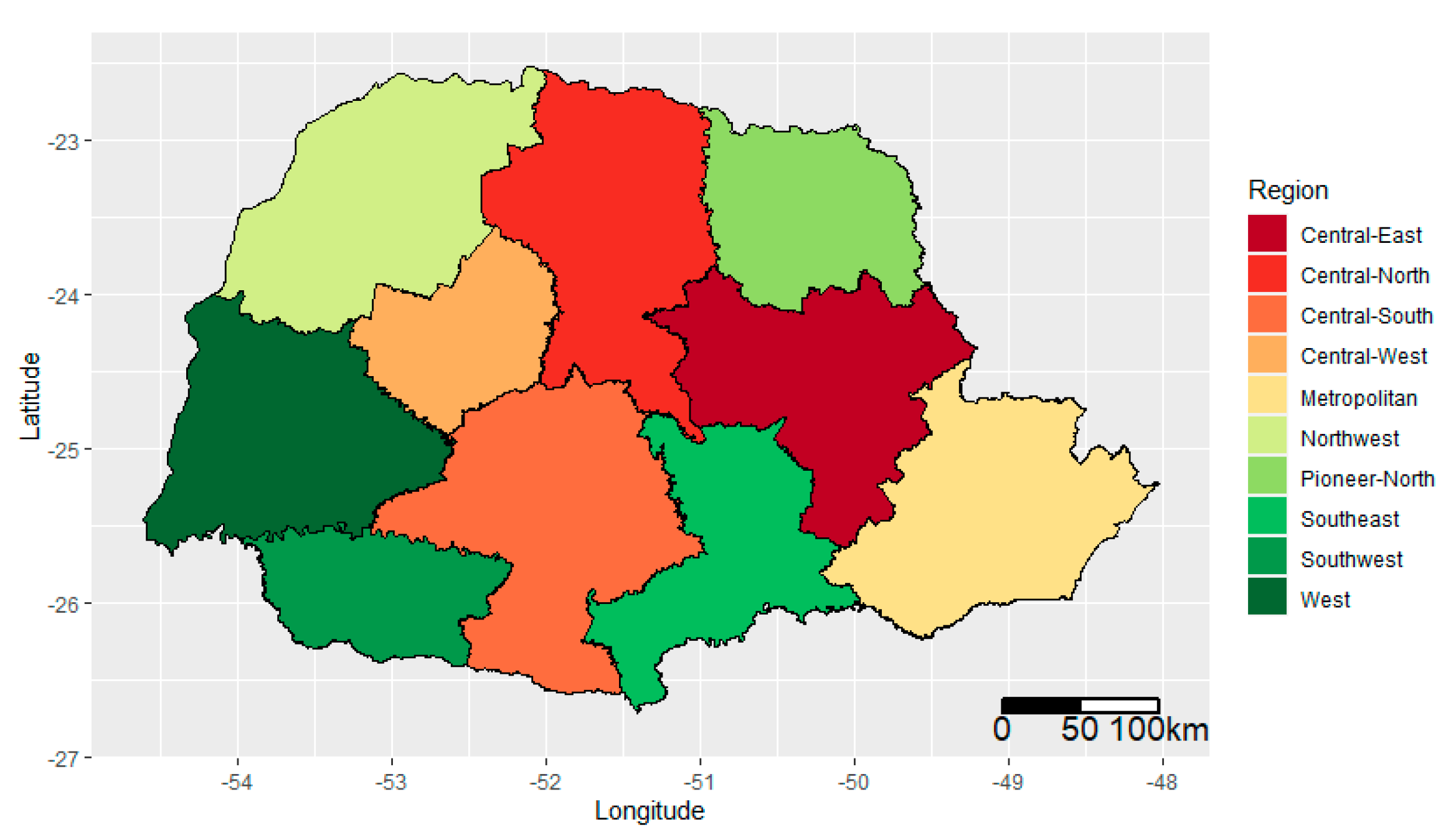
2.1. Study Region
2.2. Data
2.2.1. Observed Data: Ground Gauge
2.2.2. Satellite Data: IMERG
2.2.3. Performance Analyses
2.2.4. Analysis of Anomalies
3. Results
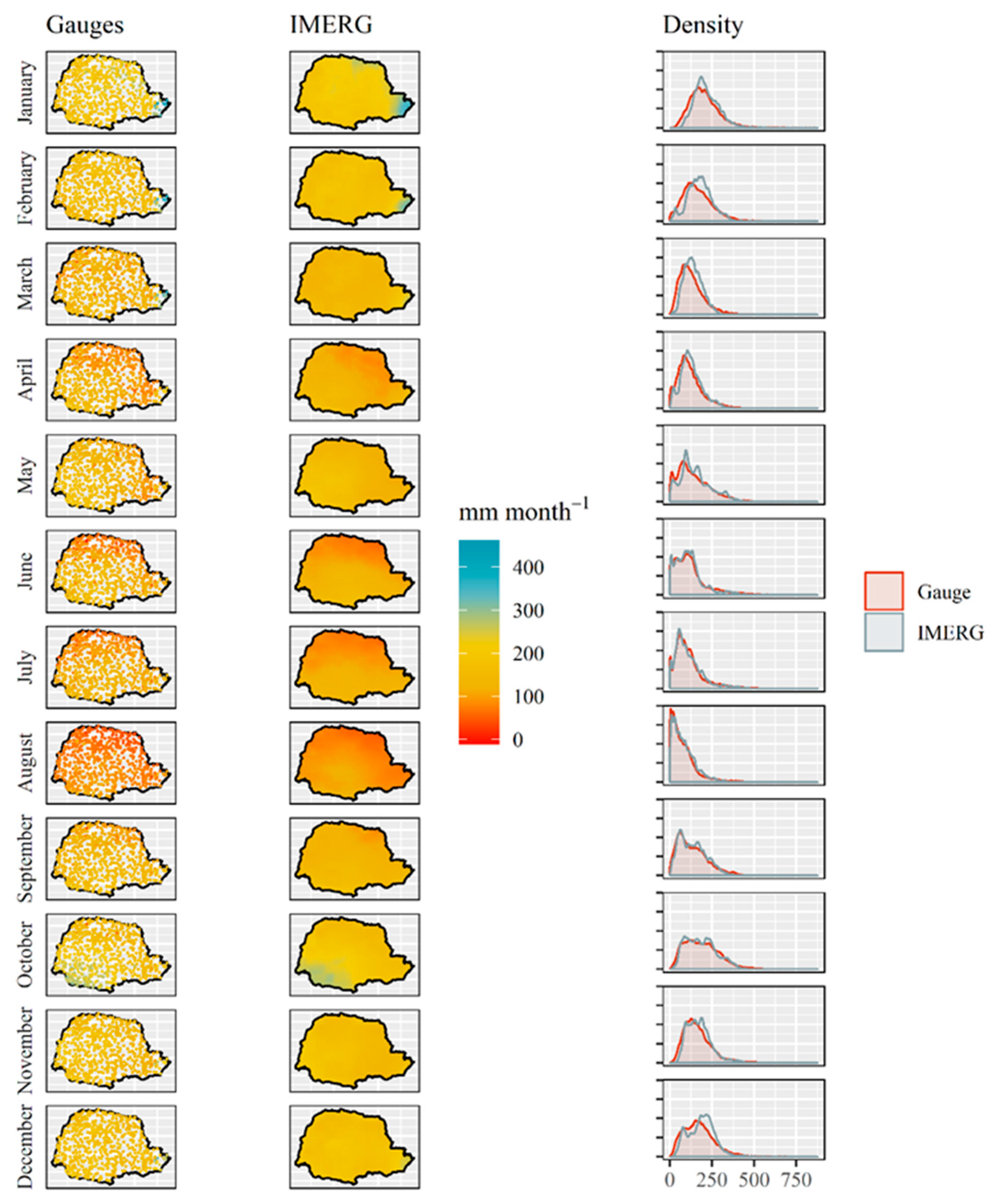
3.1. Temporal and Spatial Distribution of Precipitation
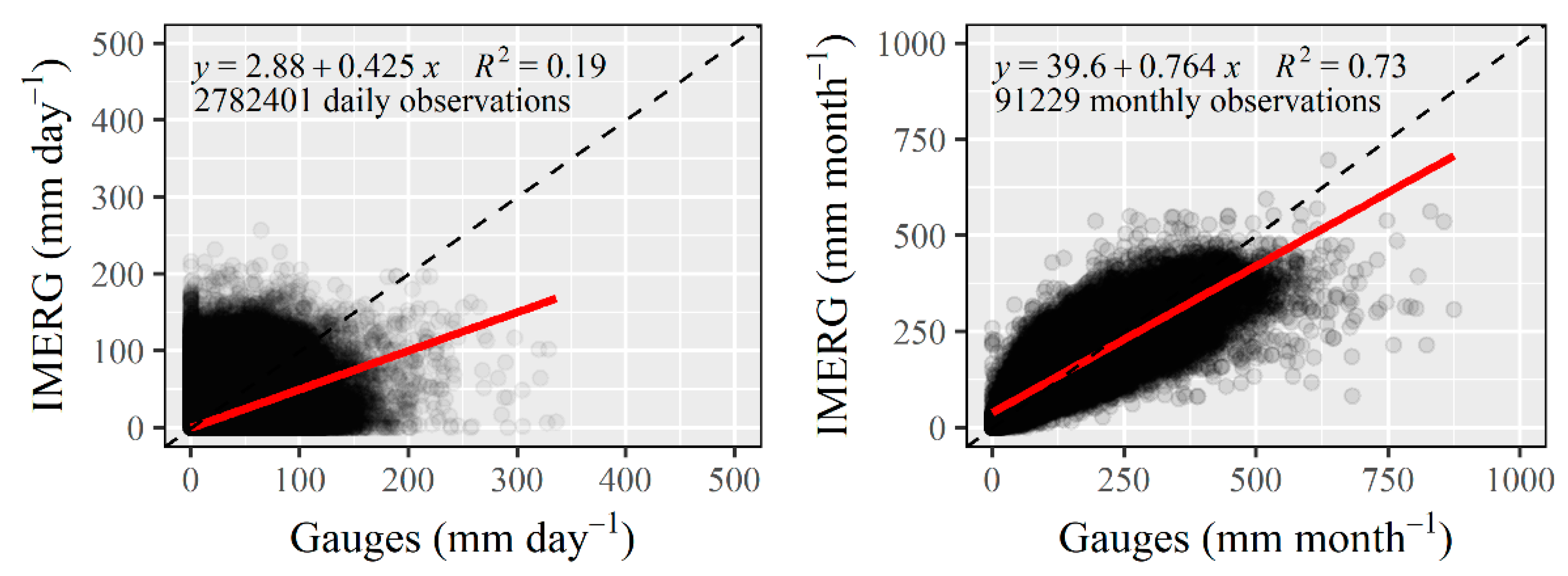
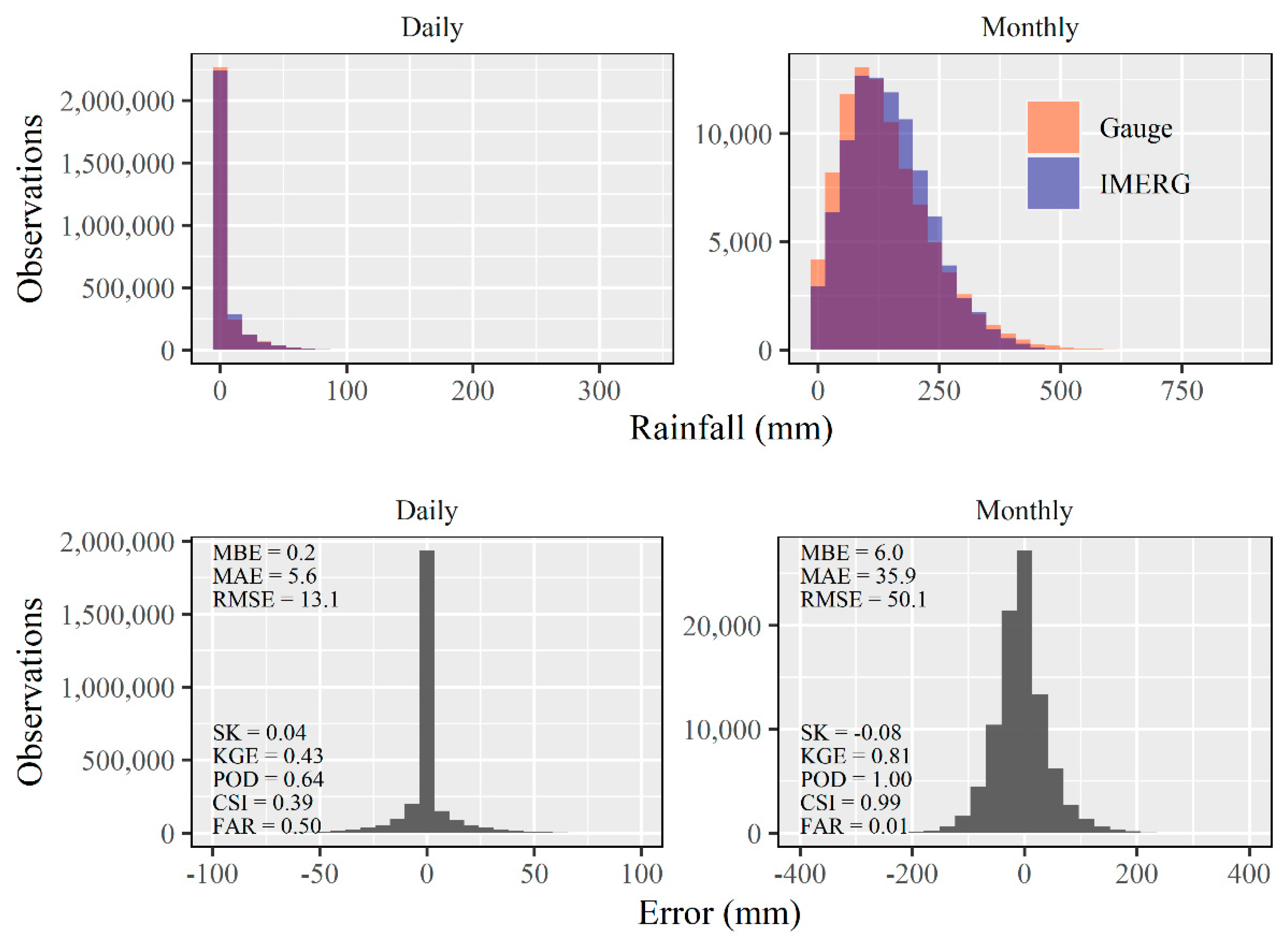
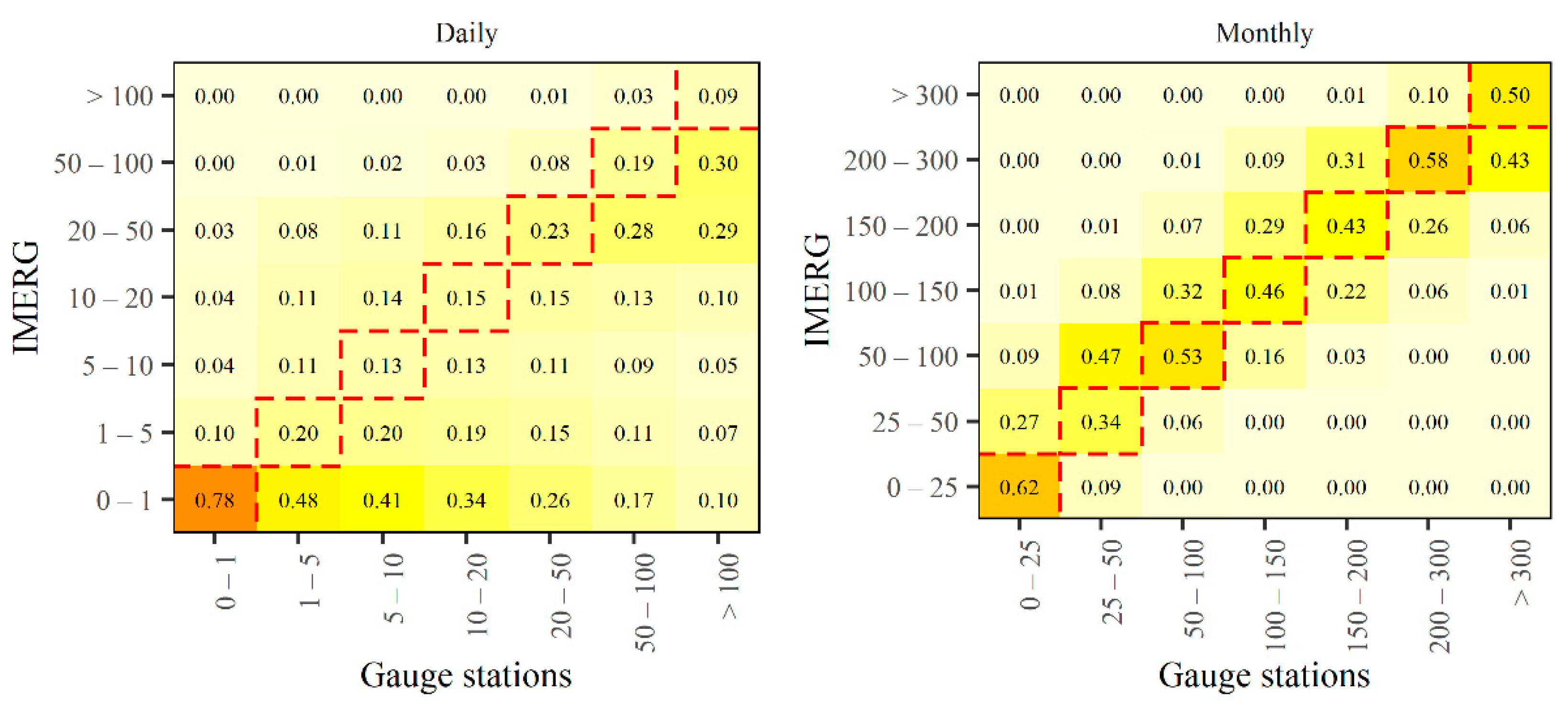
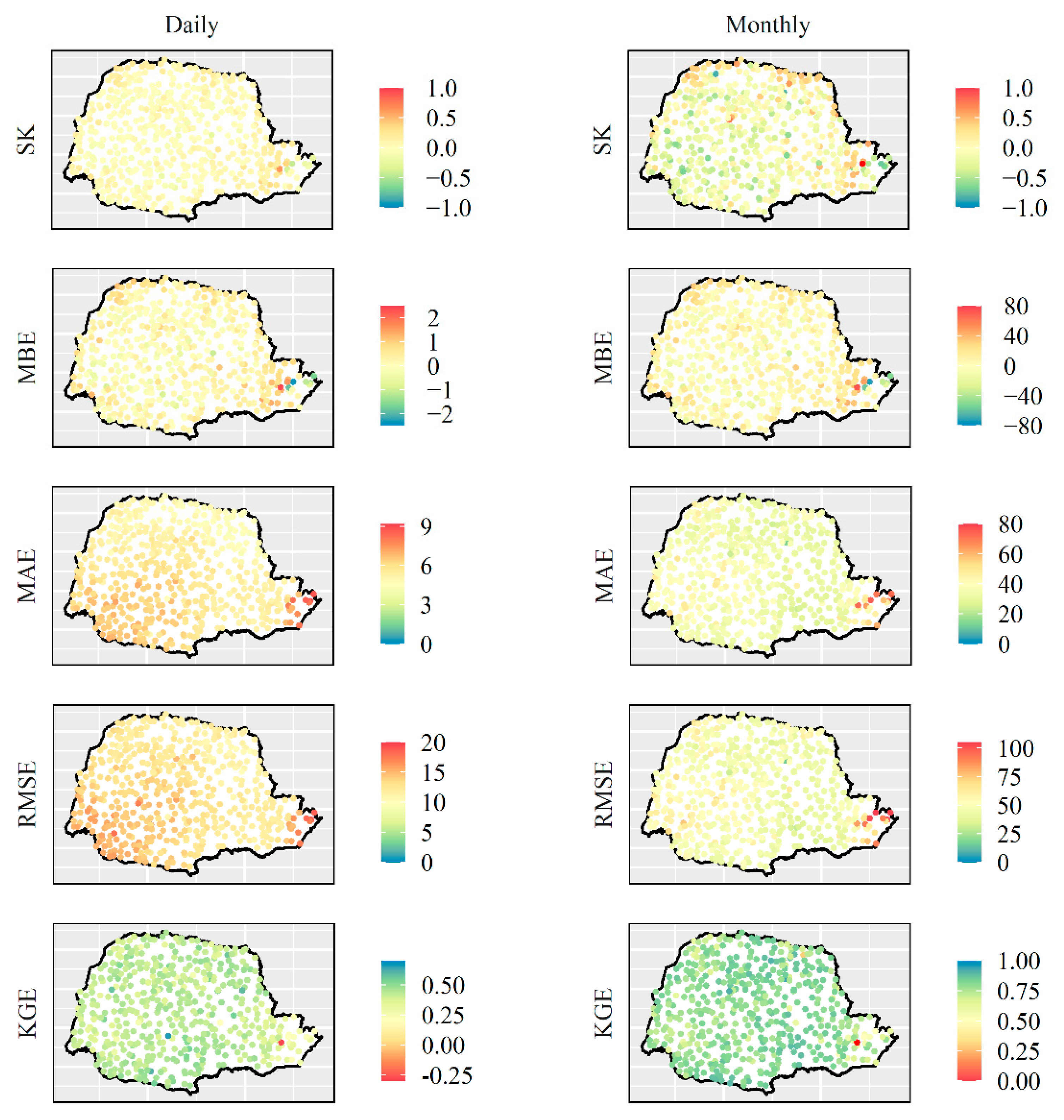
3.2. Daily and Monthly Evaluation of IMERG Products
3.3. Rainfall Anomalies between 2000 and 2018
4. Discussion
4.1. Temporal and Spatial Distribution of Precipitation
4.2. Daily and Monthly Evaluation of IMERG Products
4.3. Rainfall Anomalies between 2000 and 2018
5. Conclusions
- The volume and spatial distribution of observed and estimated rainfall are consistent across all months of the year in the monthly products of IMERG version 6, with similar rainfall distribution density curves.
- IMERG version 6 has a good relationship between precipitation estimates and those observed by gauges on the monthly time scale, with high correlation and accuracy, and low errors in statistical metrics. However, a lower performance was observed in estimating rainfall in regions with abrupt changes in topography along the coast, related to the lower accuracy when estimating orographic affected rainfall.
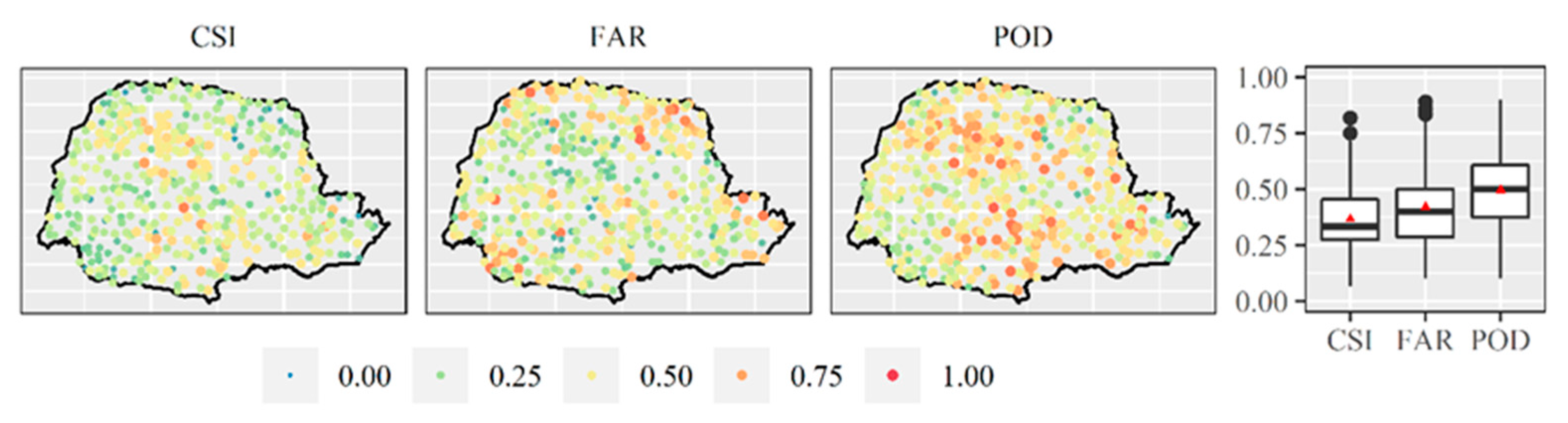
- The monthly products of IMERG version 6 performed very close to perfect considering qualitative assessments for the detection of rainfall events in this time scale throughout the study area.
- The daily estimates of IMERG version 6 were limited in representing the rainfall observed by the gauges, with little correlation between the data and low values of rain event detection rates. Although the gauges are direct observations and considered references, it is known there is great spatial variability in daily data, which is the probable cause of the low performance.
- The detection of anomalies by the monthly products of IMERG version 6 showed limited performance over the years analyzed and the study area, probably due to the topography and rainfall regime in the northeast, coast, and southeast.
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shen, Y.; Xiong, A. Validation and comparison of a new gauge-based precipitation analysis over mainland China. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 252–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Chen, S.; Bao, A.; Behrangi, A.; Hong, Y.; Ndayisaba, F.; Hu, J.; Stepanian, P.M. Early assessment of Integrated Multi-satellite Retrievals for Global Precipitation Measurement over China. Atmos. Res. 2016, 176, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucera, P.A.; Ebert, E.E.; Turk, F.J.; Levizzani, V.; Kirschbaum, D.B.; Tapiador, F.J.; Loew, A.; Borsche, M. Precipitation from Space: Advancing Earth System Science. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 94, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapiador, F.J.; Turk, F.; Petersen, W.; Hou, A.Y.; García-Ortega, E.; Machado, L.A.; Angelis, C.F.; Salio, P.; Kidd, C.; Huffman, G.J.; et al. Global precipitation measurement: Methods, datasets and applications. Atmos. Res. 2012, 104, 70–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, A.Y.; Kakar, R.K.; Neeck, S.; Azarbarzin, A.A.; Kummerow, C.D.; Kojima, M.; Oki, R.; Nakamura, K.; Iguchi, T. The Global Precipitation Measurement Mission. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 95, 701–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobouchian, M.P.; Salio, P.; Skabar, Y.G.; Vila, D.; Garreaud, R. Assessment of satellite precipitation estimates over the slopes of the subtropical Andes. Atmos. Res. 2017, 190, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salio, P.; Hobouchian, M.P.; Skabar, Y.G.; Vila, D. Evaluation of high-resolution satellite precipitation estimates over southern South America using a dense rain gauge network. Atmos. Res. 2015, 163, 146–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falck, A.; Maggioni, V.; Tomasella, J.; Diniz, F.; Mei, Y.; Beneti, C.; Herdies, D.; Neundorf, R.; Caram, R.; Rodriguez, D. Improving the use of ground-based radar rainfall data for monitoring and predicting floods in the Iguaçu river basin. J. Hydrol. 2018, 567, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummerow, C.; Barnes, W.; Kozu, T.; Shiue, J.; Simpson, J. The tropical rainfall measuring mission (TRMM) sensor pack-age. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1998, 15, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, R.J.; Janowiak, J.E.; Arkin, P.A.; Xie, P. CMORPH: A method that produces global precipitation estimates from passive microwave and infrared data at high spatial and temporal resolution. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mega, T.; Ushio, T.; Takahiro, M.; Kubota, T.; Kachi, M.; Oki, R. Gauge-Adjusted Global Satellite Mapping of Precipitation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 57, 1928–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, C.; Peterson, P.; Landsfeld, M.; Pedreros, D.; Verdin, J.; Shukla, S.; Husak, G.; Rowland, J.; Harrison, L.; Hoell, A.; et al. The climate hazards infrared precipitation with stations—A new environmental record for monitoring extremes. Sci. Data 2015, 2, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beck, H.E.; Van Dijk, A.I.J.M.; Levizzani, V.; Schellekens, J.; Miralles, D.G.; Martens, B.; De Roo, A. MSWEP: 3-hourly 0.25° global gridded precipitation (1979–2015) by merging gauge, satellite, and reanalysis data. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 589–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J.; Wolff, D.B.; Adler, R.F.; Gu, G.; Hong, Y.; Bowman, K.P.; Stocker, E.F. The TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA): Quasi-Global, Multiyear, Combined-Sensor Precipitation Estimates at Fine Scales. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Tang, G.; Han, Z.; Guo, X.; Hong, Y. Global intercomparison and regional evaluation of GPM IMERG Version-03, Version-04 and its latest Version-05 precipitation products: Similarity, difference and improvements. J. Hydrol. 2018, 564, 342–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J. Integrated Multi-SatellitE Retrievals for GPM (IMERG) Technical Documentation. NASA/GSFC Code. Available online: http://pmm.nasa.gov/sites/default/files/document_files/IMERG_doc.pdf (accessed on 2 February 2020).
- El Kenawy, A.M.; Lopez-Moreno, J.I.; McCabe, M.F.; Vicente-Serrano, S.M. Evaluation of the TMPA-3B42 precipitation product using a high-density rain gauge network over complex terrain in northeastern Iberia. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2015, 133, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Melo, D.D.C.D.; Xavier, A.C.; Bianchi, T.; Oliveira, P.T.S.; Scanlon, B.R.; Lucas, M.C.; Wendland, E. Performance evaluation of rainfall estimates by TRMM Multi-satellite Precipitation Analysis 3B42V6 and V7 over Brazil. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 9426–9436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, J.; Yang, W.; Luan, Y.; Du, J.; Lin, A.; Zhao, L. Evaluation of the TRMM 3B42 and GPM IMERG products for extreme precipitation analysis over China. Atmos. Res. 2019, 223, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadelha, A.N.; Coelho, V.H.R.; Xavier, A.C.; Barbosa, L.R.; Melo, D.C.; Xuan, Y.; Huffman, G.J.; Petersen, W.A.; Almeida, C.D.N. Grid box-level evaluation of IMERG over Brazil at various space and time scales. Atmos. Res. 2019, 218, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, F.; Li, X. Evaluation of IMERG and TRMM 3B43 Monthly Precipitation Products over Mainland China. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krishna, U.V.M.; Das, S.K.; Deshpande, S.M.; Doiphode, S.L.; Pandithurai, G. The assessment of Global Precipitation Measurement estimates over the Indian subcontinent. Earth Space Sci. 2017, 4, 540–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moazami, S.; Najafi, M. A comprehensive evaluation of GPM-IMERG V06 and MRMS with hourly ground-based precipitation observations across Canada. J. Hydrol. 2021, 594, 125929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A. Statistical comparison of satellite-retrieved precipitation products with rain gauge observations over Bangladesh. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 2906–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhuiyan, A.E.; Yang, F.; Biswas, N.K.; Rahat, S.H.; Neelam, T.J. Machine Learning-Based Error Modeling to Improve GPM IMERG Precipitation Product over the Brahmaputra River Basin. Forecasting 2020, 2, 248–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R.; Maggioni, V.; Vila, D.; Porcacchia, L. Using Satellite Error Modeling to Improve GPM-Level 3 Rainfall Estimates over the Central Amazon Region. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z. Comparison of Integrated Multisatellite Retrievals for GPM (IMERG) and TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA) Monthly Precipitation Products: Initial Results. J. Hydrometeorol. 2016, 17, 777–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozante, J.R.; Vila, D.A.; Barboza Chiquetto, J.; Fernandes, A.D.A.; Souza Alvim, D. Evaluation of TRMM/GPM blended daily products over Brazil. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Yong, B.; Shen, Y.; Liu, J.; Hong, Y.; Zhang, J. Comparison analysis of six purely satellite-derived global precipitation estimates. J. Hydrol. 2020, 581, 124376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Clark, M.P.; Papalexiou, S.M.; Ma, Z.; Hong, Y. Have satellite precipitation products improved over last two decades? A comprehensive comparison of GPM IMERG with nine satellite and reanalysis datasets. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 240, 111697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J.; Tan, J. Integrated Multi-Satellite Retrievals for GPM (IMERG) Technical Documentation. Available online: https://docserver.gesdisc.eosdis.nasa.gov/public/project/GPM/IMERG_doc.06.pdf (accessed on 2 February 2020).
- Zandonadi, L.; Acquaotta, F.; Fratianni, S.; Zavattini, J.A. Changes in precipitation extremes in Brazil (Paraná River Basin). Theor. Appl. Clim. 2016, 123, 741–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ANA. Conjuntura dos Recursos Hídricos no Brasil 2017. Relatório Pleno/Agência Nacional de Águas. Brasília. Available online: http//www.ana.gov.br (accessed on 18 March 2020).
- IBGE-Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística. Sinopse do Censo Demográfico Rio de Janeiro. Available online: https://www.in.gov.br/en/web/dou/-/resolucao-n-3-de-26-de-agosto-de-2019-212912380 (accessed on 8 May 2020).
- Alvares, C.A.; Stape, J.L.; Sentelhas, P.C.; Gonçalves, J.L.D.M.; Sparovek, G. Köppen’s climate classification map for Brazil. Meteorol. Z. 2013, 22, 711–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.J.C.; Oka-Fiori, C.; Canali, N.E.; Fiori, A.P.; Da Silveira, C.T.; Da Silva, J.M.F.; Ross, J.L.S. Mapeamento Geomorfológico do Estado do Paraná. Rev. Bras. Geomorfol. 2006, 7, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grimm, A.M.; Pal, J.S.; Giorgi, F. Connection between Spring Conditions and Peak Summer Monsoon Rainfall in South America: Role of Soil Moisture, Surface Temperature, and Topography in Eastern Brazil. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 5929–5945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grimm, A.M. Interannual climate variability in South America: Impacts on seasonal precipitation, extreme events, and possible effects of climate change. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2010, 25, 537–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Lü, H.; Zhu, Y.; Cui, Y.; Wang, X. Evaluating the hydrological utility of latest IMERG products over the Upper Huaihe River Basin, China. Atmos. Res. 2019, 225, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Ma, Y.; Long, D.; Zhong, L.; Hong, Y. Evaluation of GPM Day-1 IMERG and TMPA Version-7 legacy products over Mainland China at multiple spatiotemporal scales. J. Hydrol. 2016, 533, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, Q.; Duan, Z.; Zhang, J.; Mo, K.; Li, Z.; Tang, G. Multiscale Comparative Evaluation of the GPM IMERG v5 and TRMM 3B42 v7 Precipitation Products from 2015 to 2017 over a Climate Transition Area of China. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, M.L.; Duan, Z. Assessment of GPM and TRMM Precipitation Products over Singapore. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, J.; Yuan, F.; Shi, C.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, L.; Ren, L.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, S.; Liu, Y. Statistical Evaluation of the Latest GPM-Era IMERG and GSMaP Satellite Precipitation Products in the Yellow River Source Region. Water 2020, 12, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aragão, L.E.O.C.; Malhi, Y.; Roman-Cuesta, R.M.; Saatchi, S.; Anderson, L.O.; Shimabukuro, Y.E. Spatial patterns and fire response of recent Amazonian droughts. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Junior, C.H.L.S.; Almeida, C.T.; Santos, J.R.N.; Anderson, L.O.; Aragão, L.E.O.C.; Silva, F.B. Spatiotemporal rainfall trends in the Brazilian legal amazon between the years 1998 and 2015. Water 2018, 10, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, L.O.; Malhi, Y.; Aragão, L.E.O.C.; Ladle, R.; Arai, R.; Barbier, N.; Phillips, O. Remote sensing detection of droughts in Amazonian forest canopies. New Phytol. 2010, 187, 733–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Wong, D.W.S. Statistical Analysis with ArcView GIS; John Wiley and Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Hirata, F.E.; Grimm, A.M. The role of synoptic and intraseasonal anomalies in the life cycle of summer rainfall ex-tremes over South America. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 46, 3041–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulanger, J.P.; Leloup, J.; Penalba, O.; Rusticucci, M.; Lafon, F.; Vargas, W. Observed precipitation in the Paraná-Plata hydrological basin: Long-term trends, extreme conditions, and ENSO teleconnections. Clim. Dyn. 2005, 24, 393–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, A.M.; Ferraz, S.E.; Gomes, J. Precipitation anomalies in southern Brazil associated with El Niño and La Niña events. J. Clim. 1998, 11, 2863–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Terassi, P.M.D.B.; Galvani, E. Identification of Homogeneous Rainfall Regions in the Eastern Watersheds of the State of Paraná, Brazil. Climate 2017, 5, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anjum, M.N.; Ding, Y.; Shangguan, D.; Ahmad, I.; Ijaz, M.W.; Farid, H.U.; Yagoub, Y.E.; Zaman, M.; Adnan, M. Performance evaluation of latest integrated multi-satellite retrievals for Global Precipitation Measurement (IMERG) over the northern highlands of Pakistan. Atmos. Res. 2018, 205, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitson, B.C.; Crane, R.G. Gridded Area-Averaged Daily Precipitation via Conditional Interpolation. J. Clim. 2005, 18, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schumacher, V.; Justino, F.; Fernández, A.; Meseguer-Ruiz, O.; Sarricolea, P.; Comin, A.; Venancio, L.P.; Althoff, D. Comparison between observations and gridded data sets over complex terrain in the Chilean Andes: Precipitation and temperature. Int. J. Clim. 2020, 40, 5266–5288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Wilson, A.M.; Barros, A.P. Scoping a field experiment: Error diagnostics of TRMM precipitation radar estimates in complex terrain as a basis for IPHEx. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 1501–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dinku, T.; Chidzambwa, S.; Ceccato, P.; Connor, S.J.; Ropelewski, C.F. Validation of high-resolution satellite rainfall products over complex terrain. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 4097–4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaseva, M.O.; Prakash, S.; Gairola, R.M. Validation of high-resolution TRMM-3B43 precipitation product using rain gauge measurements over Kyrgyzstan. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2011, 108, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, A.; García-Ortega, E.; Merino, A.; Sánchez, J.L.; Kummerow, C.; Tapiador, F.J. Assessment of IMERG Precipitation Estimates over Europe. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vanhoni, F.; Mendonça, F. O Clima Do Litoral Do Estado Do Paraná. Rev. Bras. de Clim. 2008, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, Y.; Peters-Lidard, C.D.; Eylander, J.B.; Joyce, R.J.; Huffman, G.J.; Adler, R.F.; Hsu, K.-L.; Turk, F.J.; Garcia, M.; Zeng, J. Component analysis of errors in satellite-based precipitation estimates. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2009, 114, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Navarro, A.; García-Ortega, E.; Merino, A.; Sánchez, J.L.; Tapiador, F.J. Orographic biases in IMERG precipitation estimates in the Ebro River basin (Spain): The effects of rain gauge density and altitude. Atmos. Res. 2020, 244, 105068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, H.E.; Lee, J.W.; Craven, J.P. The spatial distribution of severe thunderstorm and tornado environments from global reanalysis data. Atmos. Res. 2003, 67, 73–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, J.A.; Brand, V.S.; Capucim, M.N.; Felix, R.R.; Martins, L.D.; Freitas, E.D.; Gonçalves, F.L.; Hallak, R.; Dias, M.A.F.S.; Cecil, D.J. Climatology of destructive hailstorms in Brazil. Atmos. Res. 2017, 184, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beal, A.; Hallak, R.; Martins, L.D.; Martins, J.A.; Biz, G.; Rudke, A.P.; Tarley, C.R. Climatology of hail in the triple border Paraná, Santa Catarina (Brazil) and Argentina. Atmos. Res. 2020, 234, 104747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Index | Unit | Equation * | Best Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Determination coefficient (R2) | - | 1 | |
| Mean error (MBE) | mm | 0 | |
| Mean absolute error (MAE) | mm | 0 | |
| Root of the mean square error (RMSE) | mm | 0 | |
| Kling–Gupta Eficiency (KGE) | - | 1 | |
| Coefficient of skewness (SK) | - | 0 | |
| Probability of detection (POD) | - | 1 | |
| Critical success index (CSI) | - | 1 | |
| False alarm ratio (FAR) | - | 0 |
| RMSE | MAE | MBE | RMSE | MAE | MBE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Region | (mm day−1) | (mm month−1) | ||||
| Central-South | 13.70 | 6.19 | 0.02 | 48.50 | 36.30 | 0.83 |
| Central-West | 13.40 | 5.79 | 0.14 | 51.20 | 37.80 | 4.44 |
| Central-East | 11.90 | 5.24 | 0.18 | 43.20 | 31.90 | 5.52 |
| Metropolitan | 13.10 | 5.99 | 0.44 | 56.90 | 41.80 | 13.20 |
| Northwest | 12.40 | 5.14 | 0.31 | 50.50 | 36.90 | 9.37 |
| Central-North | 12.20 | 5.17 | 0.14 | 44.40 | 32.10 | 4.25 |
| Pioneer-North | 11.30 | 4.66 | 0.26 | 46.90 | 33.40 | 7.75 |
| West | 14.30 | 6.12 | 0.08 | 55.40 | 39.50 | 2.38 |
| Southeast | 12.60 | 5.58 | 0.31 | 41.60 | 31.10 | 9.41 |
| Southwest | 14.80 | 6.50 | 0.17 | 48.20 | 35.80 | 5.54 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
G. Nascimento, J.; Althoff, D.; C. Bazame, H.; M. U. Neale, C.; N. Duarte, S.; L. Ruhoff, A.; Z. Gonçalves, I. Evaluating the Latest IMERG Products in a Subtropical Climate: The Case of Paraná State, Brazil. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 906. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13050906
G. Nascimento J, Althoff D, C. Bazame H, M. U. Neale C, N. Duarte S, L. Ruhoff A, Z. Gonçalves I. Evaluating the Latest IMERG Products in a Subtropical Climate: The Case of Paraná State, Brazil. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(5):906. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13050906
Chicago/Turabian StyleG. Nascimento, Jéssica, Daniel Althoff, Helizani C. Bazame, Christopher M. U. Neale, Sergio N. Duarte, Anderson L. Ruhoff, and Ivo Z. Gonçalves. 2021. "Evaluating the Latest IMERG Products in a Subtropical Climate: The Case of Paraná State, Brazil" Remote Sensing 13, no. 5: 906. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13050906
APA StyleG. Nascimento, J., Althoff, D., C. Bazame, H., M. U. Neale, C., N. Duarte, S., L. Ruhoff, A., & Z. Gonçalves, I. (2021). Evaluating the Latest IMERG Products in a Subtropical Climate: The Case of Paraná State, Brazil. Remote Sensing, 13(5), 906. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13050906









