Twentieth and Twenty-First Century Water Storage Changes in the Nile River Basin from GRACE/GRACE-FO and Modeling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
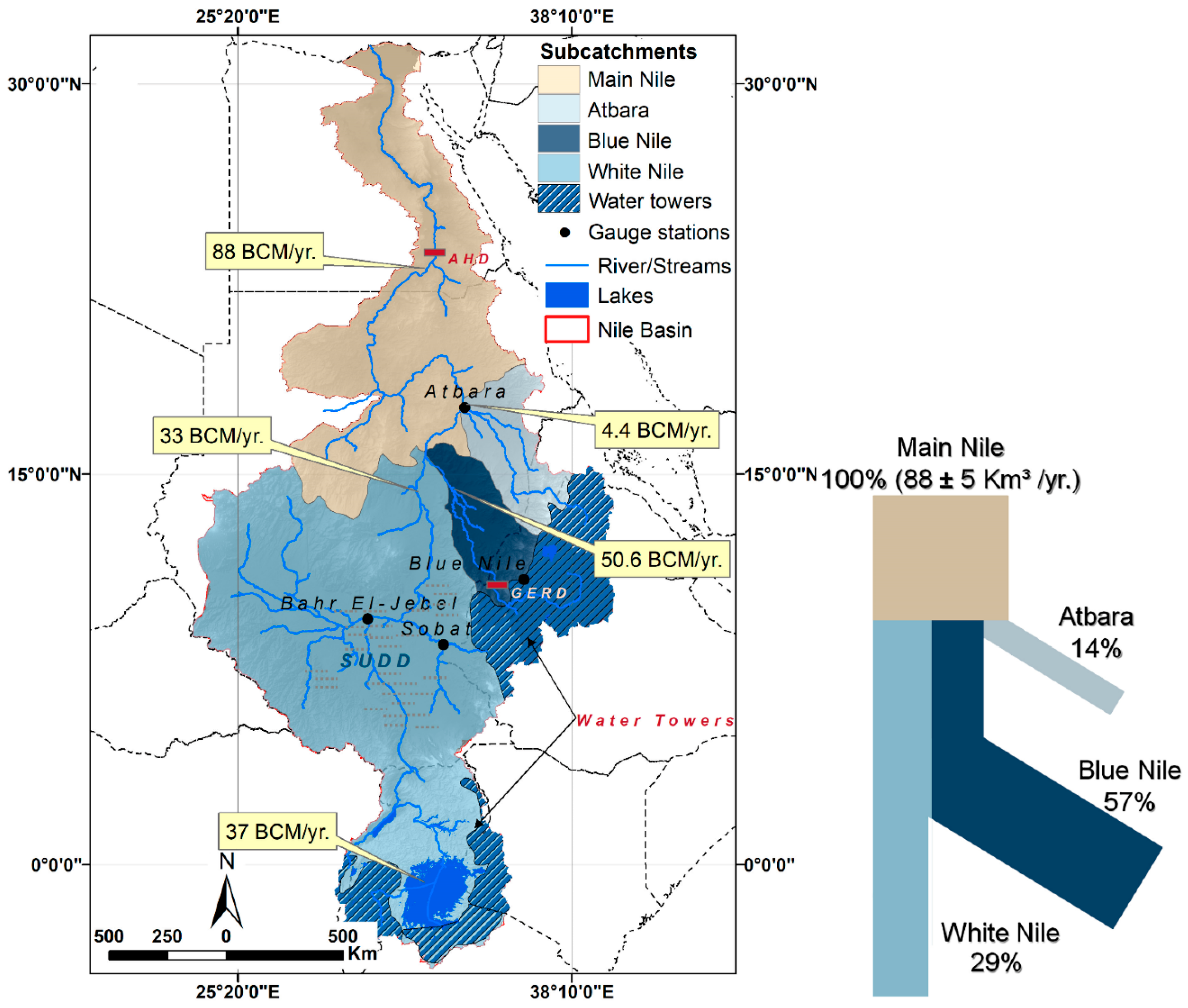
2. The Nile River Basin (NRB)
3. Data and Methods
3.1. GRACE TWS Observations
3.2. LSM Datasets
3.3. GPCC and CRU Datasets
3.4. ClimGen Data
3.5. Drought Indicators
3.6. GAMLSS Model
3.7. ARIMA Model
3.8. Uncertainty Analysis and Model Performance
3.9. NRB Water Storage
3.10. GRACE Total Water Storage Deficit (TWSD)
4. Results
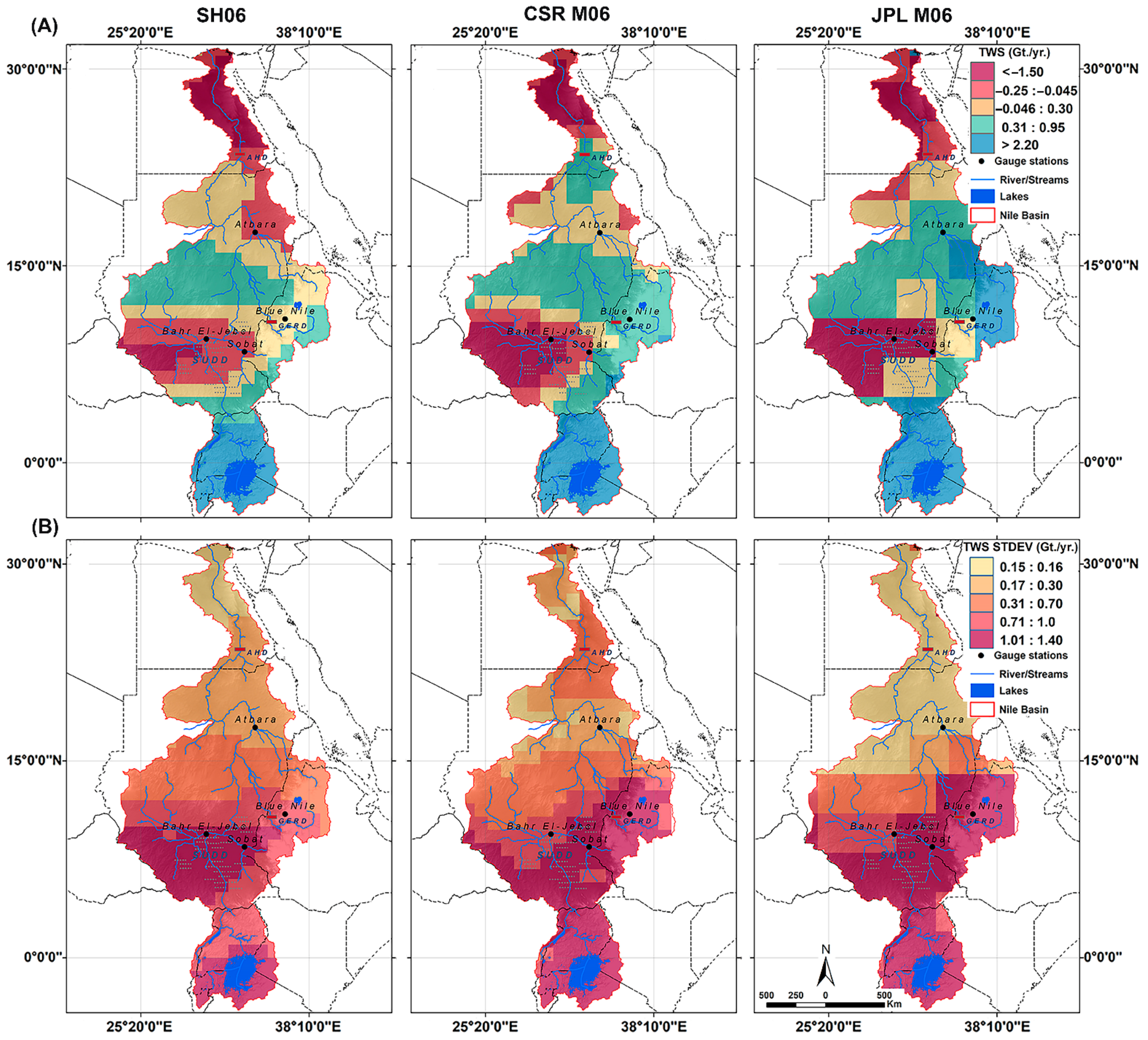
4.1. Uncertainty Analysis and Model Performance
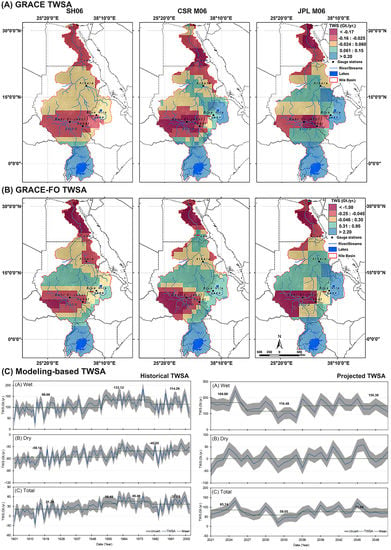
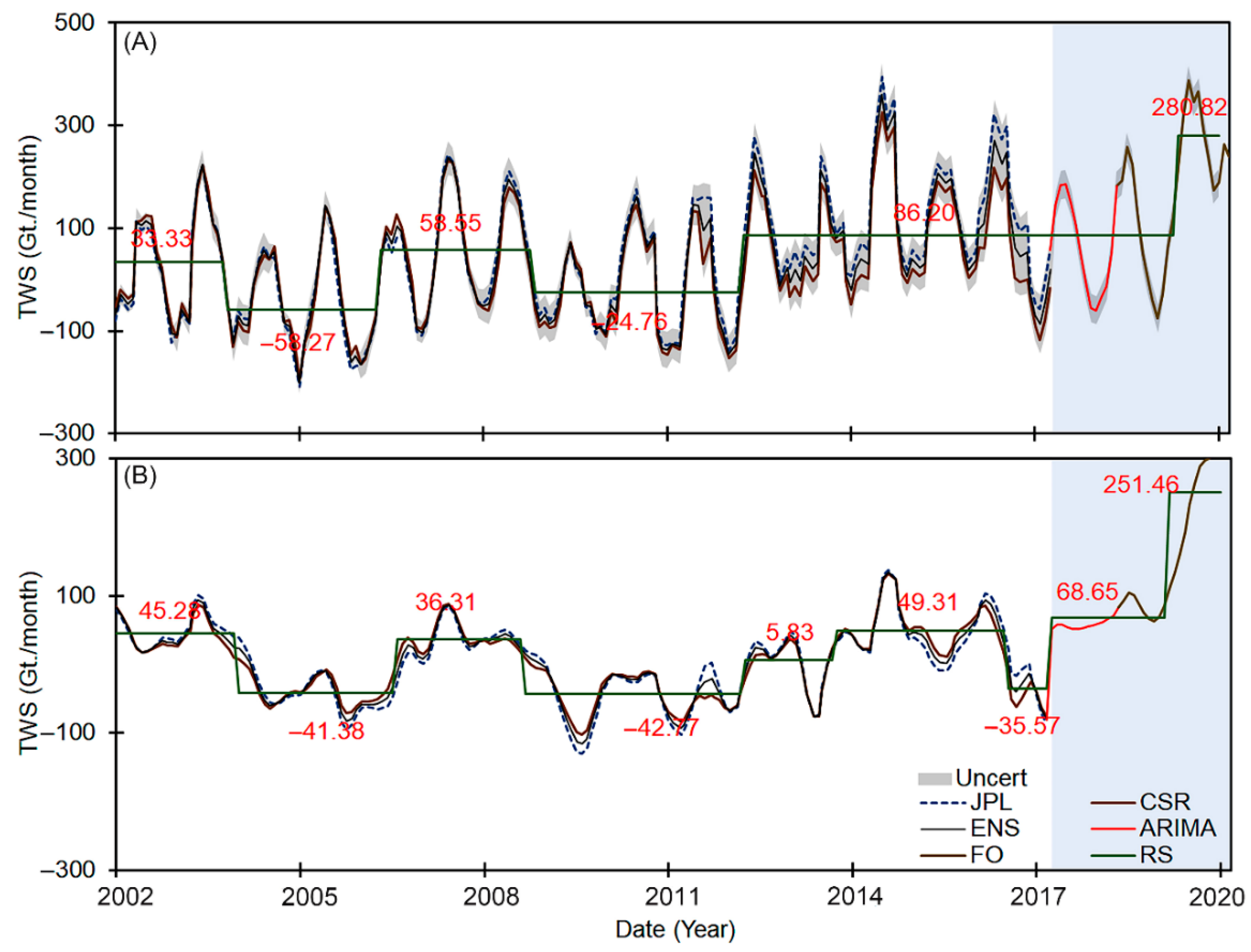
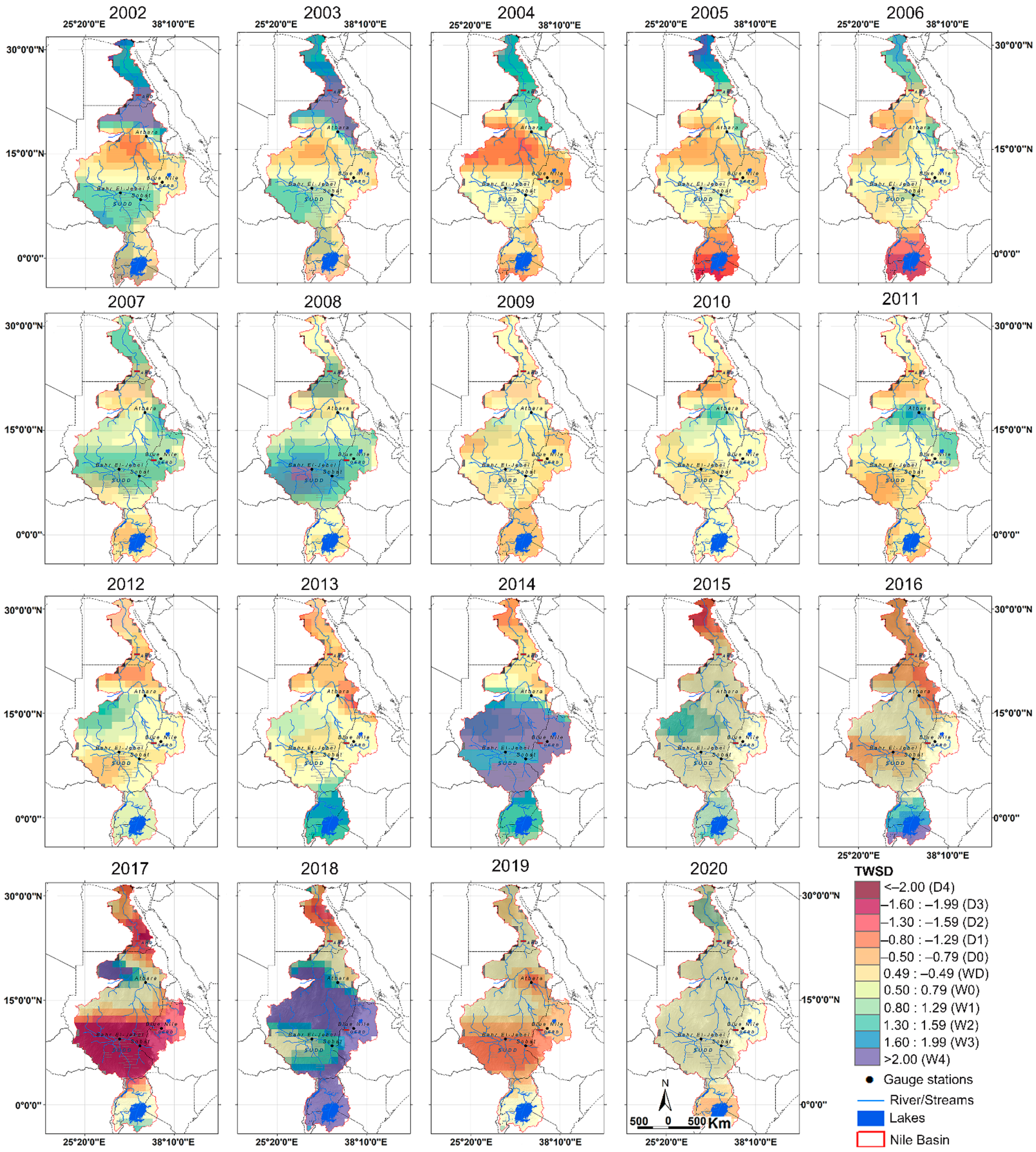
4.2. Present TWS Changes in NRB (2002 to 2020)
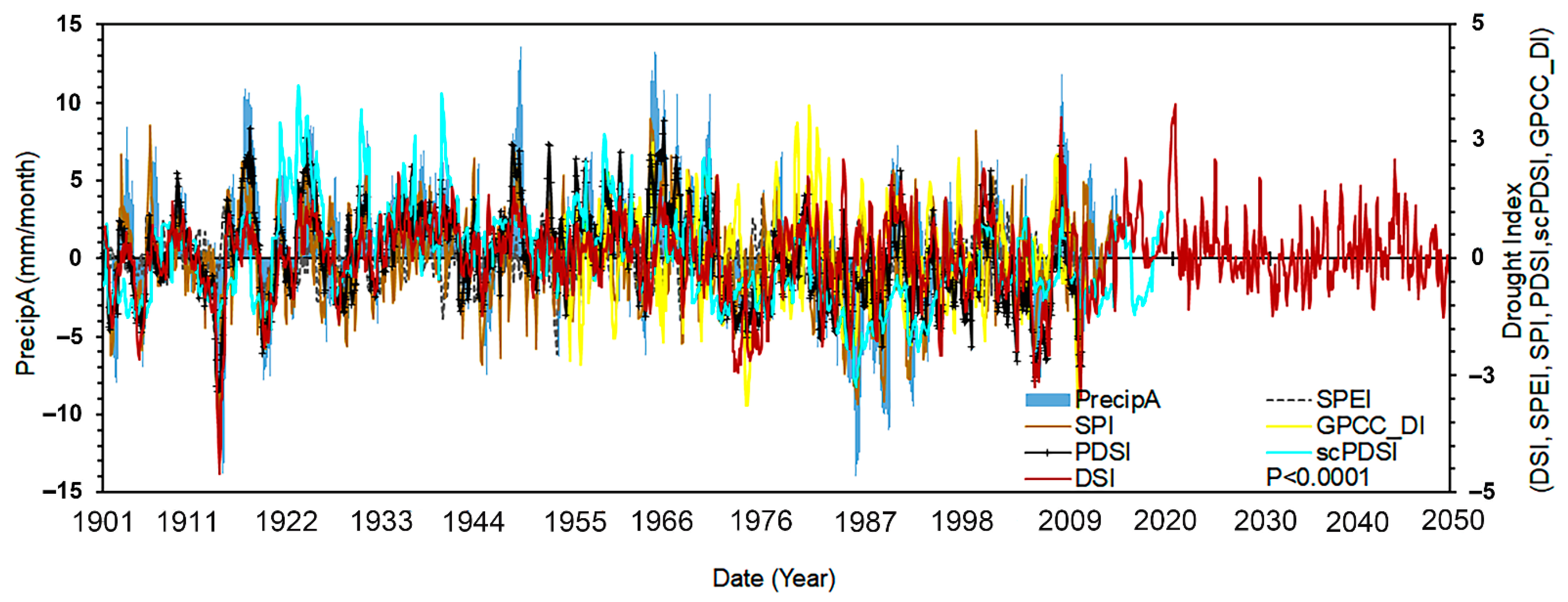
4.3. Past TWS Changes in the NRB (1901–2002)
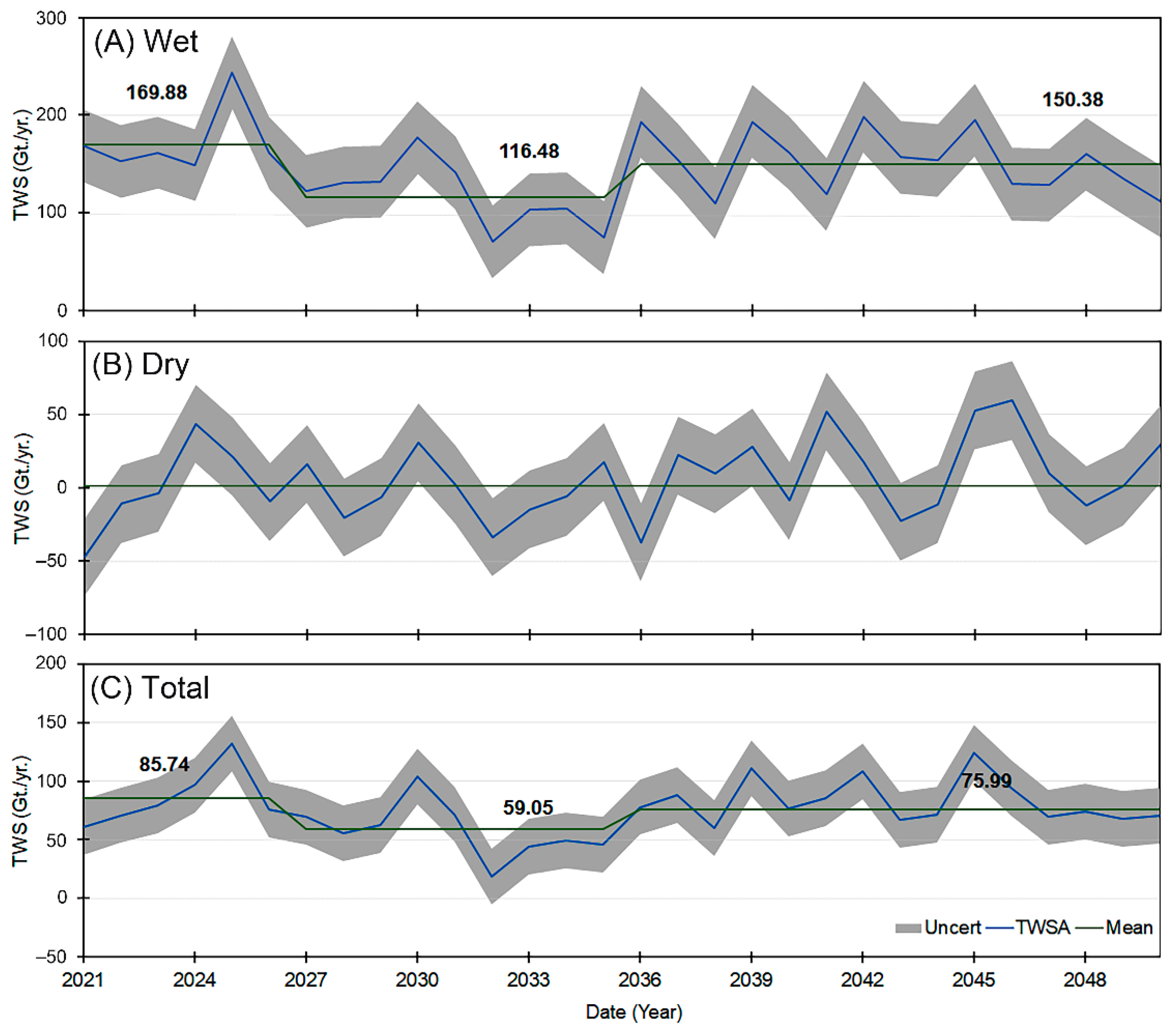
4.4. Future TWS Scenarios in NRB (2021 to 2050)
4.5. Drought and Flooding in the NRB
4.5.1. GRACE-Based TWSD between 2002 to 2020
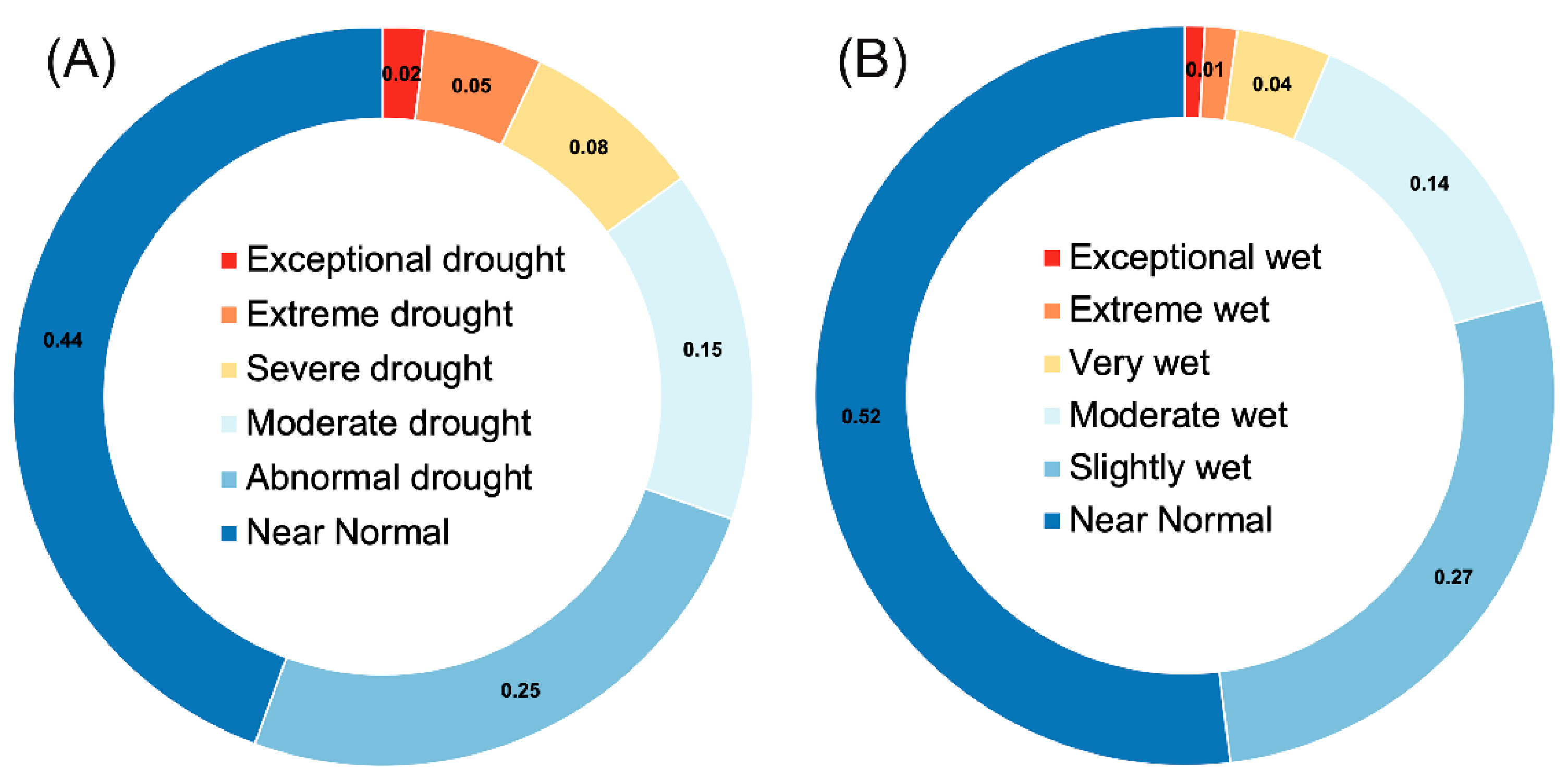
4.5.2. NRB Drought and Flooding Records (1901 to 2050)
5. Discussion
5.1. Water Storage in the NRB
5.2. Hydrological Extremes in the NRB
5.3. Call for Further Water Resources Planning
6. Conclusions
- -
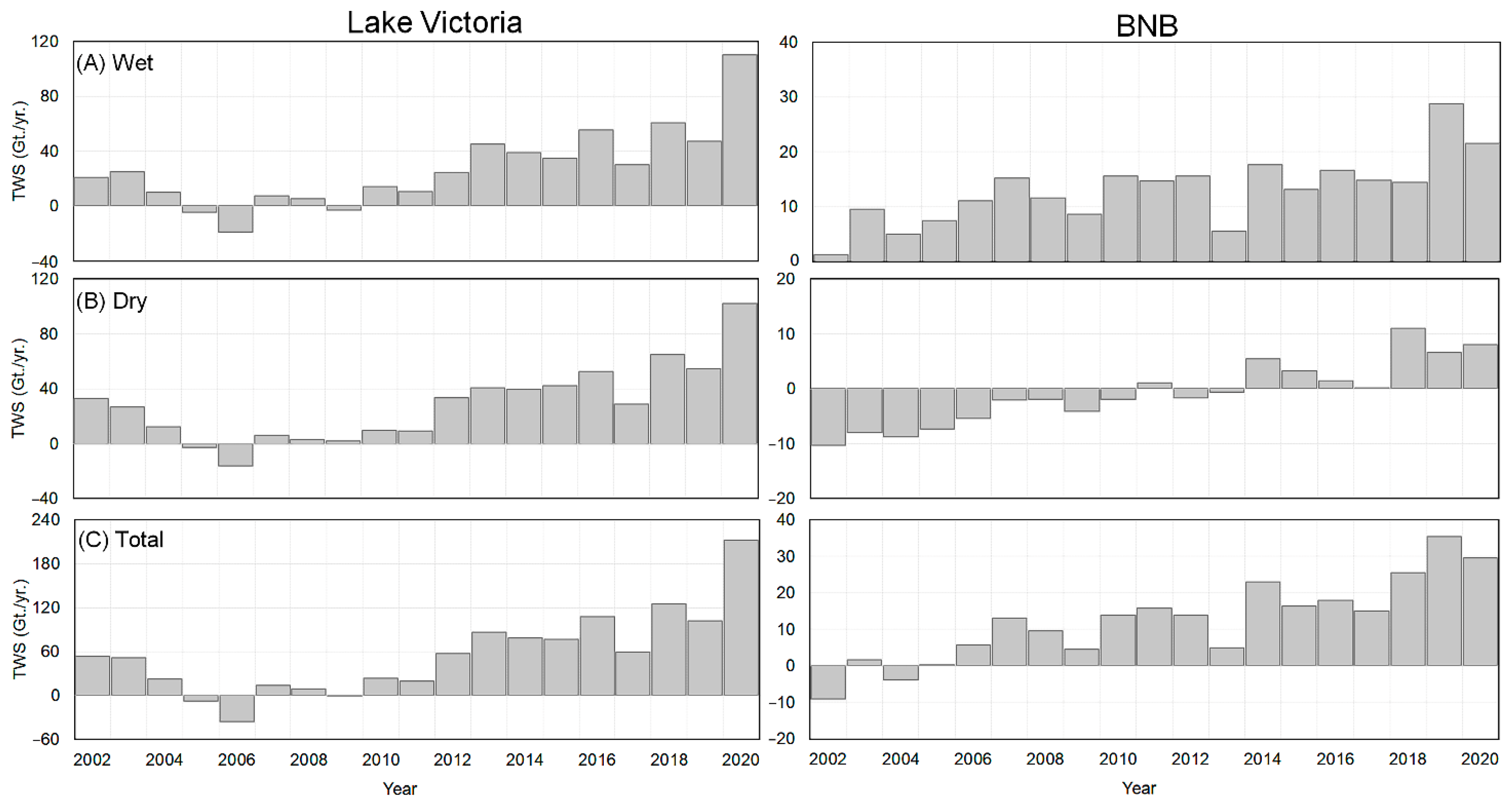
- The present TWS changes in NRB (2002 to 2020) indicated that the basin is experiencing a generally humid phase. In recent years, the NRB has received more water storage. Furthermore, the TWSA exhibited more wet cycles compared to the dry cycles in the region.
- -
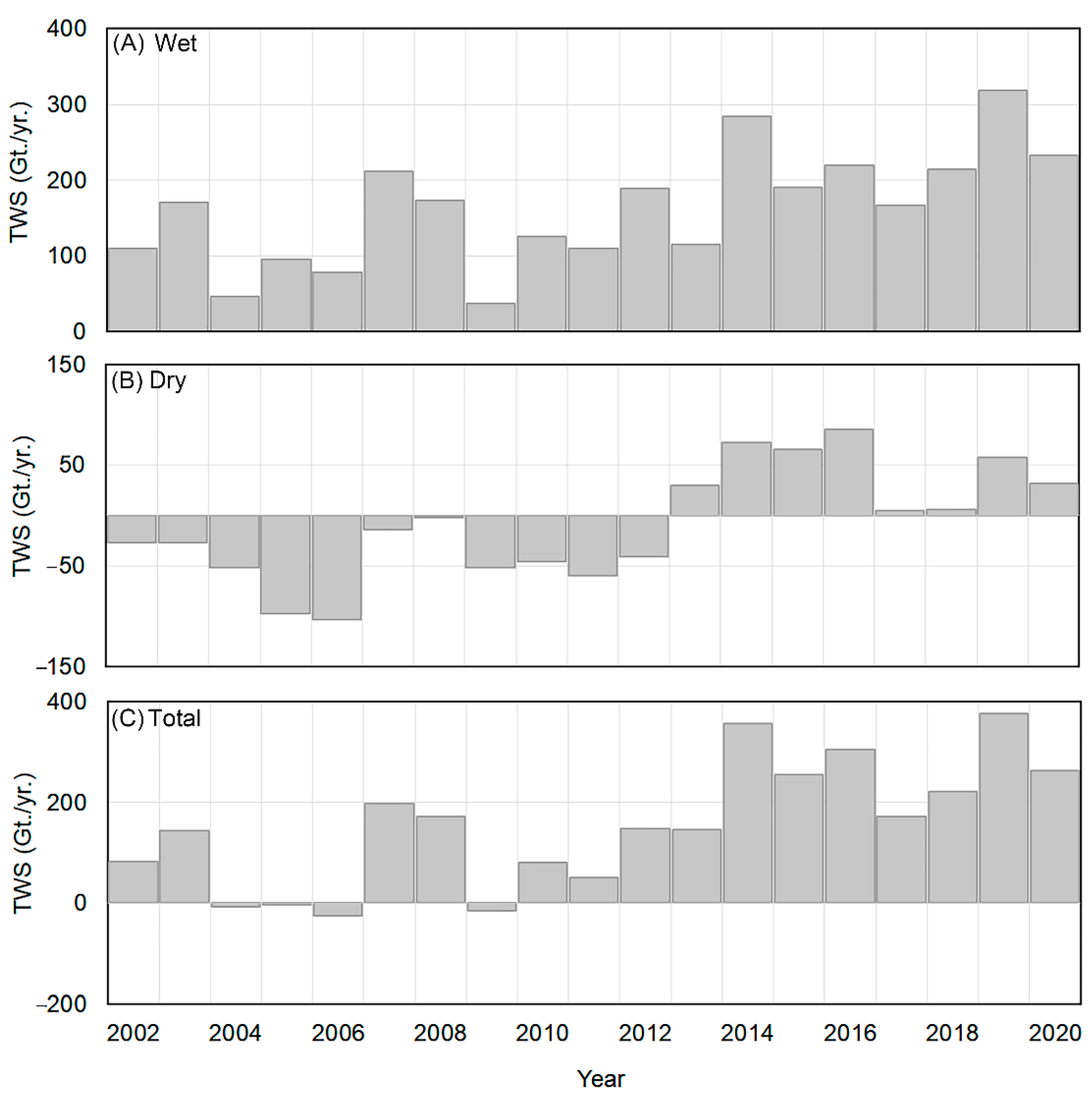
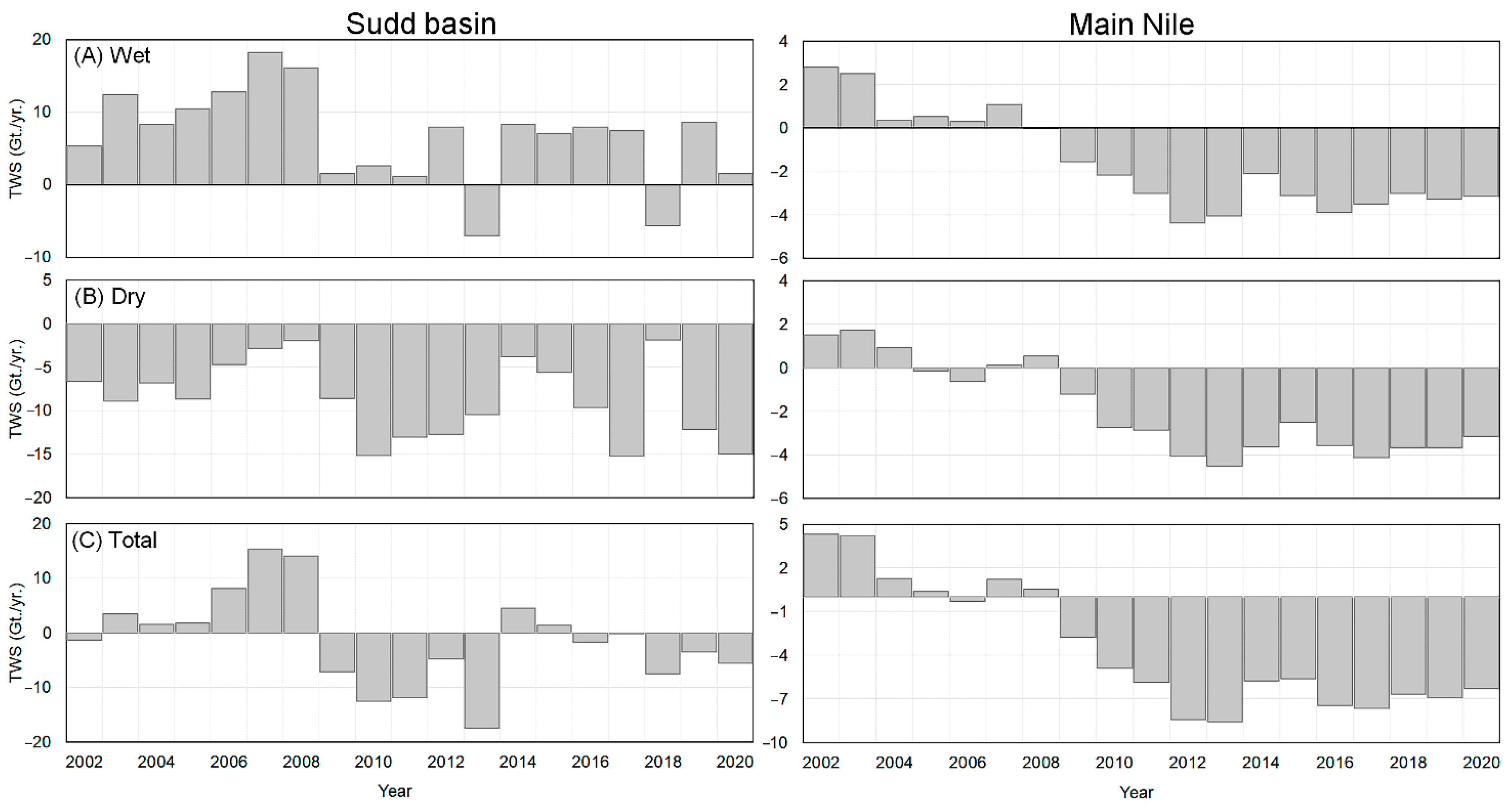
- Temporally, the net changes in TWAS were assessed during the wet, dry seasons across the NRB, two main water source regions (Lake Victoria and BNB), and two main water sink areas (Sudd and Main Nile regions).
- -
- TWS basin-wide water storage records indicated that the basin has received ~50 Gt./yr. to ~310 Gt./yr. during the wet season, and lost ~30 Gt./yr. to ~70 Gt./yr. during the dry season.
- -
- While the BNB contributes between 57 to ~60% of the surface runoff in the Nile River, the Lake Victoria region (Equatorial Lake area) holds at least twice as much water storage during the wet season compared to BNB.
- -
- The Sudd Basin, on the other hand, loses twice the amount of water storage compared to that of the Main Nile region.
- -
- Spatially, GRACE-based TWSA displayed positive changes at the Lake Victoria and BNB regions, with strong temporal variability. While in the area to the north, the TWS degrades negatively with less temporal variability.
- -
- The basin-wide TWSA from GRACE shows significantly higher storage amounts compared to the reported water storage volume from surface water flow (i.e., 200 BCM vs. 100 BCM). The discrepancy in the TWSA estimates is likely due to the fact that the GRACE satellite detects all forms of available storage, including the deep groundwater component, as well as the anthropogenic influence on different water stocks.
- -
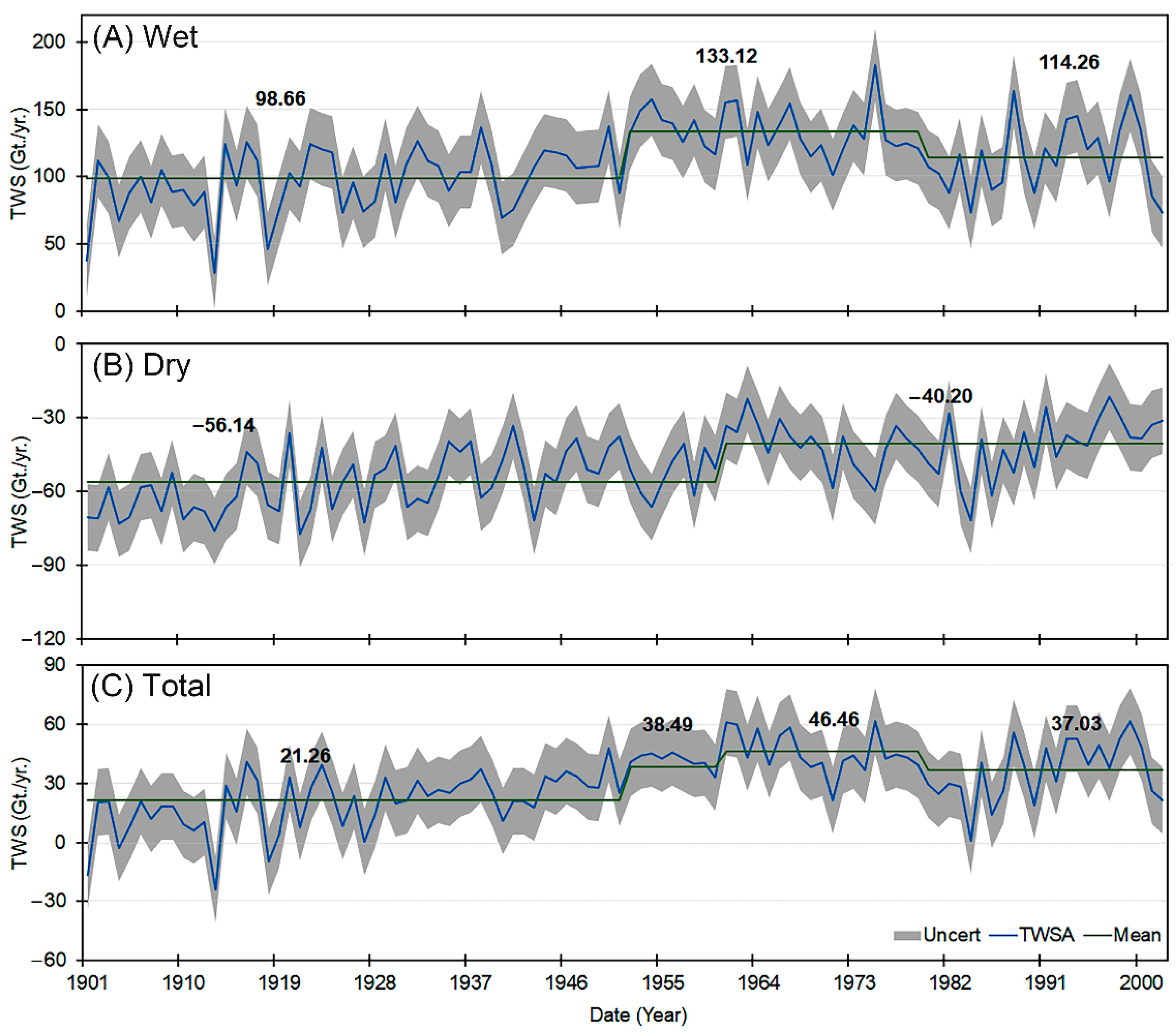
- The past and future TWS changes in the NRB between 1901 to 2002 and 2021 to 2050, respectively, were evaluated using standard evaluation criteria. Overall, the model performance showed satisfactory results. The uncertainty bounds for the extended (past and future) TWS records were illustrated using standard deviation.
- -
- The Past TWS records indicated that NRB has witnessed a positive increase in TWS of ~17% during the rainy season. While, the TWS has recovered by ~28 during the dry periods.
- -
- The future TWS scenarios suggest slight positive changes in the TWSA mean during the dry period across the basin. However, TWS in the NRB is subjected to decrease by 10 to 30% from 2021 to 2050.
- -
- The flooding and drought analysis using the reconstructed (inclusive), present, and projected (exclusive) TWSD records between 1901 to 2050 showed that the NRB has more wet periods, 86-years, compared to 64-years of dry record.
- -
- The recurrence analysis of the drought and flooding records in the NRB between 1901 to 2050 revealed short drought and flooding intervals of ~6 years recurrence intervals.
- -
- The exceedance probability analysis for the extreme hydrological events in the basin indicates that the near-normal conditions occupy a higher percentage of 44 and 52% relative to the extreme events.
- -
- The future projections of TWSA indicate an insignificant increase in the TWS during the wet and dry seasons of the projected TWSA compared to the overall mean average. The reason for this is likely related to the projected increase in the precipitation amount in the region.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shahin, M. Hydrology of the Nile Basin; Elsevier Science Publishing Company Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe, J.V.; Parks, Y.P. The Hydrology of the Nile; IAHS Special Publication no. 5; The International Water Management Institute: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, R. The Nile; Yale University Press: New Haven, CT, USA; London, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Said, R. The Geological Evolution of the River Nile; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Swain, A. Challenges for water sharing in the Nile basin: Changing geo-politics and changing climate. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2011, 56, 687–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karyabwite, D.R. Water Sharing in the Nile River Valley; UNEP/DEWA/GRID: Geneva, Switzerland, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Oestigaard, T. Nile Issues, Small Streams from the Nile Basin Research Programme; Fountain Publishers: Kampala, Uganda, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Arsano, Y. Ethiopia and the Nile; Center for Security Studies (CSS): ETH Zurich, Switzerland, 2007; p. 324. [Google Scholar]
- NBI. Nile Basin Water Resources Atlas; Seid, A.H., Mbuliro, M., Alarabawy, M., Eds.; Nile Basin Initiative (NBI): Entebbe, Uganda, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Haub, C.; Kaneda, T. 2013 World Population Data Sheet: Population Reference Bureau (PRB). 2013. Available online: https://www.prb.org/2013-world-population-data-sheet/ (accessed on 1 March 2019).
- Abu-Zeid, M. The river Nile: Main water transfer projects in Egypt and impacts on Egyptian agriculture. In Long-Distance Water Transfer; Tycooly International Publishing Ltd.: Dublin, Ireland, 1983; pp. 6–34. [Google Scholar]
- Basheer, M.; Wheeler, K.G.; Ribbe, L.; Majdalawi, M.; Abdo, G.; Zagona, E.A. Quantifying and evaluating the impacts of cooperation in transboundary river basins on the Water-Energy-Food nexus: The Blue Nile Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 630, 1309–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oestigaard, T. Water Scarcity and Food Security Along the Nile Politics, Population Increase and Climate Change; Nordiska Afrikainstitutet: Uppsala, Sweden, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Turhan, Y. The hydro-political dilemma in Africa water geopolitics: The case of the Nile river basin. Afr. Secur. Rev. 2020, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, A. Who owns the Nile? Egypt, Sudan, and Ethiopia’s history-changing dam. Origins 2013, 6, 2–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ayele, H.; Li, M.-H.; Tung, C.-P.; Liu, T.-M. Impact of Climate Change on Runoff in the Gilgel Abbay Watershed, the Upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Water 2016, 8, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conway, D. Water resources: Future Nile river flows. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2017, 7, 319–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dessie, M.; Verhoest, N.E.C.; Pauwels, V.R.N.; Admasu, T.; Poesen, J.; Adgo, E.; Deckers, J.; Nyssen, J. Analyzing runoff processes through conceptual hydrological modeling in the Upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 5149–5167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gleick, P.H. The vulnerability of runoff in the Nile basin to climatic changes. Environ. Prof. 1991, 13, 66–73. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, E.; Tarhule, A.; Kirstetter, P.-E.; Clark, R.; Hong, Y. Runoff sensitivity to climate change in the Nile River Basin. J. Hydrol. 2018, 561, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurni, H.; Tato, K.; Zeleke, G. The Implications of Changes in Population, Land Use, and Land Management for Surface Runoff in the Upper Nile Basin Area of Ethiopia. Mt. Res. Dev. 2005, 25, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kebede, S.; Travi, Y.; Alemayehu, T.; Marc, V. Water balance of Lake Tana and its sensitivity to fluctuations in rainfall, Blue Nile basin, Ethiopia. J. Hydrol. 2006, 316, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swenson, S.; Wahr, J. Monitoring the water balance of Lake Victoria, East Africa, from space. J. Hydrol. 2009, 370, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awange, J.L.; Forootan, E.; Kuhn, M.; Kusche, J.; Heck, B. Water storage changes and climate variability within the Nile Basin between 2002 and 2011. Adv. Water Resour 2014, 73, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khaki, M.; Awange, J. Improved remotely sensed satellite products for studying Lake Victoria’s water storage changes. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 915–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonsor, H.C.; Mansour, M.M.; MacDonald, A.M.; Hughes, A.G.; Hipkin, R.G.; Bedada, T. Interpretation of GRACE data of the Nile Basin using a groundwater recharge model. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2010, 7, 4501–4533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shamsudduha, M.; Taylor, R.G.; Longuevergne, L. Monitoring groundwater storage changes in the highly seasonal humid tropics: Validation of GRACE measurements in the Bengal Basin. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conway, D. From headwater tributaries to international river: Observing and adapting to climate variability and change in the Nile basin. Global Environ. Chang. 2005, 15, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, D.; Hulme, M. The Impacts of Climate Variability and Future Climate Change in the Nile Basin on Water Resources in Egypt. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 1996, 12, 277–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, E.; Tarhule, A. GRACE: Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment long-term trend investigation over the Nile River Basin: Spatial variability drivers. J. Hydrol. 2020, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, E.; Tarhule, A.; Zume, J.T.; Kirstetter, P.E. +50 Years of Terrestrial Hydroclimatic Variability in Africa’s Transboundary Waters. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hassan, A.; Jin, S. Water storage changes and balances in Africa observed by GRACE and hydrologic models. Geod. Geodyn. 2016, 7, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anyah, R.O.; Forootan, E.; Awange, J.L.; Khaki, M. Understanding linkages between global climate indices and terrestrial water storage changes over Africa using GRACE products. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 1405–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khaki, M.; Awange, J.; Forootan, E.; Kuhn, M. Understanding the association between climate variability and the Nile’s water level fluctuations and water storage changes during 1992–2016. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 1509–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hasan, E.; Khan, S.I.; Hong, Y. Investigation of potential sea level rise impact on the Nile Delta, Egypt using digital elevation models. Environ. Monit Assess. 2015, 187, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swenson, S.; Famiglietti, J.; Basara, J.; Wahr, J. Estimating profile soil moisture and groundwater variations using GRACE and Oklahoma Mesonet soil moisture data. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swenson, S.; Wahr, J. Estimating Large-Scale Precipitation Minus Evapotranspiration from GRACE Satellite Gravity Measurements. J. Hydrometeorol. 2006, 7, 252–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tapley, B.D.; Bettadpur, S.; Ries, J.C.; Thompson, P.F.; Watkins, M.M. GRACE Measurements of Mass Variability in the Earth System. Science 2004, 305, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tapley, B.D.; Watkins, M.M.; Flechtner, F.; Reigber, C.; Bettadpur, S.; Rodell, M.; Sasgen, I.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Landerer, F.W.; Chambers, D.P.; et al. Contributions of GRACE to understanding climate change. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2019, 9, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, B.R.; Zhang, Z.; Rateb, A.; Sun, A.; Wiese, D.; Save, H.; Beaudoing, H.; Lo, M.H.; Müller-Schmied, H.; Döll, P.; et al. Tracking Seasonal Fluctuations in Land Water Storage Using Global Models and GRACE Satellites. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, B.R.; Zhang, Z.; Save, H.; Sun, A.Y.; Muller Schmied, H.; van Beek, L.P.H.; Wiese, D.N.; Wada, Y.; Long, D.; Reedy, R.C.; et al. Global models underestimate large decadal declining and rising water storage trends relative to GRACE satellite data. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E1080–E1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alemu, H.; Senay, G.; Kaptue, A.; Kovalskyy, V. Evapotranspiration Variability and Its Association with Vegetation Dynamics in the Nile Basin, 2002–2011. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 5885–5908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coffel, E.D.; Keith, B.; Lesk, C.; Horton, R.M.; Bower, E.; Lee, J.; Mankin, J.S. Future Hot and Dry Years Worsen Nile Basin Water Scarcity Despite Projected Precipitation Increases. Earth’s Future 2019, 7, 967–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tesemma, Z.K.; Mohamed, Y.A.; Steenhuis, T.S. Trends in Rainfall and Runoff in the Blue Nile Basin: 1964–2003. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 3747–3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elshamy, M.E.; Seierstad, I.A.; Sorteberg, A. Impacts of climate change on Blue Nile flows using bias-corrected GCM scenarios. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 551–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siam, M.S.; Eltahir, E.A.B. Climate change enhances interannual variability of the Nile river flow. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2017, 7, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allam, M.M.; Jain Figueroa, A.; McLaughlin, D.B.; Eltahir, E.A.B. Estimation of evaporation over the upper Blue Nile basin by combining observations from satellites and river flow gauges. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 644–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Digna, R.F.; Mohamed, Y.A.; van der Zaag, P.; Uhlenbrook, S.; Corzo, G.A. Nile River Basin modelling for water resources management—A literature review. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2016, 15, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dile, Y.T.; Berndtsson, R.; Setegn, S.G. Hydrological response to climate change for Gilgel Abay River, in the Lake Tana Basin -Upper Blue Nile Basin of Ethiopia. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Senay, G.B.; Velpuri, N.M.; Bohms, S.; Demissie, Y.; Gebremichael, M. Understanding the hydrologic sources and sinks in the Nile Basin using multisource climate and remote sensing data sets. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 8625–8650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayehu, G.; Tadesse, T.; Gessesse, B. Monitoring Residual Soil Moisture and Its Association to the Long-Term Variability of Rainfall over the Upper Blue Nile Basin in Ethiopia. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebelo, L.M.; Senay, G.B.; McCartney, M.P. Flood Pulsing in the Sudd Wetland: Analysis of Seasonal Variations in Inundation and Evaporation in South Sudan. Earth Interact. 2012, 16, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelwares, M.; Lelieveld, J.; Zittis, G.; Haggag, M.; Wagdy, A. A comparison of gridded datasets of precipitation and temperature over the Eastern Nile Basin region. Euro-Mediterr. J. Environ. Integr. 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belete, M.; Deng, J.; Wang, K.; Zhou, M.; Zhu, E.; Shifaw, E.; Bayissa, Y. Evaluation of satellite rainfall products for modeling water yield over the source region of Blue Nile Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 134834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koukoula, M.; Nikolopoulos, E.I.; Dokou, Z.; Anagnostou, E.N. Evaluation of Global Water Resources Reanalysis Products in the Upper Blue Nile River Basin. J. Hydrometeorol. 2020, 21, 935–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yitayew, M.; Melesse, A.M. Critical Water Resources Issues in the Nile River Basin. In Nile River Basin; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 401–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degefu, D.M.; He, W. Water bankruptcy in the mighty Nile river basin. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 2, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shamsudduha, M.; Taylor, R.G.; Jones, D.; Longuevergne, L.; Owor, M.; Tindimugaya, C. Recent changes in terrestrial water storage in the Upper Nile Basin: An evaluation of commonly used gridded GRACE products. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 4533–4549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lakew, H.B.; Moges, S.A.; Asfaw, D.H. Hydrological performance evaluation of multiple satellite precipitation products in the upper Blue Nile basin, Ethiopia. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2020, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayissa, Y.; Maskey, S.; Tadesse, T.; van Andel, S.; Moges, S.; van Griensven, A.; Solomatine, D. Comparison of the Performance of Six Drought Indices in Characterizing Historical Drought for the Upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Geosciences 2018, 8, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Longuevergne, L.; Wilson, C.R.; Scanlon, B.R.; Crétaux, J.F. GRACE water storage estimates for the Middle East and other regions with significant reservoir and lake storage. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 4817–4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nie, N.; Zhang, W.; Chen, H.; Guo, H. A Global Hydrological Drought Index Dataset Based on Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) Data. Water Resour. Manag. 2017, 32, 1275–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, J.; Welsby, D.; Macklin, M. The Holocene fluvial sedimentary record and alluvial geoarchaeology in the Nile Valley of northern Sudan. In River Basin Sediment Systems—Archives of Environmental Change; Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sutcliffe, J.; Brown, E. Water losses from the Sudd. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2018, 63, 527–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, E.; Tarhule, A.; Hong, Y.; Moore, B. Assessment of Physical Water Scarcity in Africa Using GRACE and TRMM Satellite Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moges, S.A.; Gebremichael, M. Climate Change Impacts and Development-Based Adaptation Pathway to the Nile River Basi; Melesse, A., Abtew, W., Setegn, S.G., Eds.; Springer International Publishing Switzerland: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Abu-Zeid, M.; Shiklomanov, I.A. Water Resources as a Challenge of the Twenty-First Century; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Camberlin, P. Nile Basin Climates. In The Nile: Origin, Environments, Limnology and Human Use; Dumont, H.J., Ed.; Springer, Monographiae Biologicae: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 307–333. [Google Scholar]
- NBI. State of River Nile Basin 2012; Nile Basin Initiative (NBI): Entebbe, Uganda, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Landerer, F.W.; Swenson, S.C. Accuracy of scaled GRACE terrestrial water storage estimates. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Save, H. CSR GRACE RL06 Mascon Solutions, V1 ed.; Save, H., Ed.; Texas Data Repository Dataverse, University of Texas at Austin: Austin, TX, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Save, H.; Bettadpur, S.; Tapley, B.D. High-resolution CSR GRACE RL05 mascons. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2016, 121, 7547–7569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, M.M.; Wiese, D.N.; Yuan, D.-N.; Boening, C.; Landerer, F.W. Improved methods for observing Earth’s time variable mass distribution with GRACE using spherical cap mascons. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2015, 120, 2648–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodell, M.; Houser, P.; Jambor, U.E.A.; Gottschalck, J.; Mitchell, K.; Meng, J.; Arsenault, K.; Brian, C.; Radakovich, J.; Mg, B.; et al. The Global Land Data Assimilation System. Bams 2004, 85, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, B.; Rodell, M.; Kumar, S.; Beaudoing, H.K.; Getirana, A.; Zaitchik, B.F.; Goncalves, L.G.; Cossetin, C.; Bhanja, S.; Mukherjee, A.; et al. Global GRACE Data Assimilation for Groundwater and Drought Monitoring: Advances and Challenges. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 7564–7586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, B.; Beaudoing, H.; Rodell, M.; NASA/GSFC/HSL. GLDAS Catchment Land Surface Model L4 daily 0.25 × 0.25 Degree V2.0 [Dataset]; Goddard Earth Sciences Data and Information Services Center (GES DISC): Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Schneider, U.; Becker, A.; Meyer-Christoffer, A.; Ziese, M.; Rudolf, B. Global Precipitation Analysis Products of the GPCC; Deutscher Wetterdienst, Offenbach a. M.: Frankfurter, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, U.; Finger, P.; Meyer-Christoffer, A.; Rustemeier, E.; Ziese, M.; Becker, A. Evaluating the Hydrological Cycle over Land Using the Newly-Corrected Precipitation Climatology from the Global Precipitation Climatology Centre (GPCC). Atmosphere 2017, 8, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- CRU. Climate Research Unite Data; CRU[Dataset]; University of East Anglia: Norwich, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Osborn, T.J. A User Guide for ClimGen: A Flexible Tool for Generating Monthly Climate Data Sets and Scenarios; Climatic Research Unit (CRU), School of Environmental Sciences, University of East Anglia: Norwich, UK, 2009; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Osborn, T.J.; Wallace, C.J.; Harris, I.C.; Melvin, T.M. Pattern scaling using ClimGen: Monthly-resolution future climate scenarios including changes in the variability of precipitation. Clim. Chang. 2015, 134, 353–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watterson, I.G.; Whetton, P.H. Distributions of decadal means of temperature and precipitation change under global warming. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitchell, T.D. Pattern Scaling: An Examination of the Accuracy of the Technique for Describing Future Climates. Clim. Chang. 2003, 60, 217–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finger, P.; Ziese, M.; Meyer-Christoffer, A.; Schneider, U.; Becker, A. GPCC Interpolation Test Dataset at 1.0°; Global Precipitation Climatology Centre (GPCC) at Deutscher Wetterdienst: Frankfurter, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Beguería, S.; Vicente, S. SPEIbase v.2.6 [Dataset]: DIGITAL.CSIC. 2020. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10261/202305 (accessed on 1 April 2020).
- Zhong, R.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Lai, C.; Goddard, S.; Wells, N.; Hayes, M. scPDSI: Calculation of the Conventional and Self-Calibrating Palmer Drought Severity Index, v. 0.1.3: R package V. 0.1.3. 2018. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=scPDSI (accessed on 10 March 2019).
- Beguería, S.; Vicente, S. SPI Calculator: DIGITAL.CSIC. 2009. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10261/10006 (accessed on 14 July 2017).
- Rigby, R.A.; Stasinopoulos, D.M. Generalized additive models for location, scale and shape. J. R. Stat. Soc. 2005, 54, 507–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akantziliotou, C.; Rigby, R.; Stasinopoulos, D. The R implementation of generalized additive models for location, scale and shape. In Statistical Modelling in Society, Proceedings of the 17th International Workshop on Statistical Modelling, Chania, Crete, 8–12 July 2002; Statistical Modelling Society: Chania, Crete, 2002; pp. 75–83. [Google Scholar]
- Stasinopoulos, D.M.; Rigby, R.A. Generalized additive models for location scale and shape (GAMLSS) in R. J. Stat. Softw. 2007, 10, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stasinopoulos, M.; Rigby, B.; Voudouris, V.; Akantziliotou, C.; Enea, M.; Kiose, D. Gamlss: Generalised Additive Models for Location Scale and Shape: R package V 5.2-0. 2020. Available online: https://www.gamlss.com/ (accessed on 21 October 2020).
- Jing, W.; Di, L.; Zhao, X.; Yao, L.; Xia, X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhou, C. A data-driven approach to generate past GRACE-like terrestrial water storage solution by calibrating the land surface model simulations. Adv. Water Resour. 2020, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Sultan, M.; Elbayoumi, T.; Tissot, P. Forecasting GRACE Data over the African Watersheds Using Artificial Neural Networks. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richter, H.M.P.; Luck, C.; Klos, A.; Sideris, M.G.; Rangelova, E.; Kusche, J. Reconstructing GRACE-type time-variable gravity from the Swarm satellites. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyndman, R.J.; Athanasopoulos, G.; Bergmeir, C.; Caceres, G.; Chhay, L.; O’Hara-Wild, M.; Petropoulos, F.; Razbash, S.; Wang, E.; Yasmeen, F. Forecast: Forecasting Functions for Time Series and Linear Models: R package V. 8.3. 2020. Available online: https://cloud.r-project.org/web/packages/forecast/index.html (accessed on 30 October 2020).
- Scanlon, B.R.; Zhang, Z.; Save, H.; Wiese, D.N.; Landerer, F.W.; Long, D.; Longuevergne, L.; Chen, J. Global evaluation of new GRACE mascon products for hydrologic applications. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 9412–9429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, V.M.; Wahr, J.; Swenson, S. Dwindling groundwater resources in northern India, from satellite gravity observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodionov, S.N. Use of prewhitening in climate regime shift detection. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abd-Elbaky, M.; Jin, S. Hydrological mass variations in the Nile River Basin from GRACE and hydrological models. Geod. Geodyn. 2019, 10, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. AQUASTAT—FAO’s Information System on Water and Agriculture; Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO): Rome, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, M.; Meyssignac, B.; Xavier, L.; Cazenave, A.; Alkama, R.; Decharme, B. Past terrestrial water storage (1980–2008) in the Amazon Basin reconstructed from GRACE and in situ river gauging data. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nerem, S.R.; Talpe, M.; Pilinski, E.; Lemoine, F.G.; Chinn, D.S. Reconstruction of Greenland and Antarctica Mass Changes Prior to the GRACE Mission; EGU General Assembly: Vienna, Austria, 2013; p. 11285. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, N.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, H.; Ishwaran, N. Reconstructed Terrestrial Water Storage Change (ΔTWS) from 1948 to 2012 over the Amazon Basin with the Latest GRACE and GLDAS Products. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 30, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Wu, W.; Wu, Y. Variations in China’s terrestrial water storage over the past decade using GRACE data. Geod. Geodyn. 2015, 6, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taye, M.; Sahlu, D.; Zaitchik, B.F.; Neka, M. Evaluation of Satellite Rainfall Estimates for Meteorological Drought Analysis over the Upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Geosciences 2020, 10, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessema, R.S. Agricultural Drought Assessment for Upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia Using SWAT; UNESCO-IHE Institute for Water Education: Delft, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson, T. The Nile: A Journey Downriver through Egypt’s Past and Present; Knopf Doubleday Publishing Group: New York, NY, USA, 2014; p. 347. [Google Scholar]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hasan, E.; Tarhule, A.; Kirstetter, P.-E. Twentieth and Twenty-First Century Water Storage Changes in the Nile River Basin from GRACE/GRACE-FO and Modeling. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 953. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13050953
Hasan E, Tarhule A, Kirstetter P-E. Twentieth and Twenty-First Century Water Storage Changes in the Nile River Basin from GRACE/GRACE-FO and Modeling. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(5):953. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13050953
Chicago/Turabian StyleHasan, Emad, Aondover Tarhule, and Pierre-Emmanuel Kirstetter. 2021. "Twentieth and Twenty-First Century Water Storage Changes in the Nile River Basin from GRACE/GRACE-FO and Modeling" Remote Sensing 13, no. 5: 953. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13050953
APA StyleHasan, E., Tarhule, A., & Kirstetter, P.-E. (2021). Twentieth and Twenty-First Century Water Storage Changes in the Nile River Basin from GRACE/GRACE-FO and Modeling. Remote Sensing, 13(5), 953. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13050953