Research on Instrument Visibility of Ozone Wind Imaging Interferometer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Principle
2.1. Principles of Atmospheric Wind Field Detection
2.2. Principle of Ozone Concentration Inversion
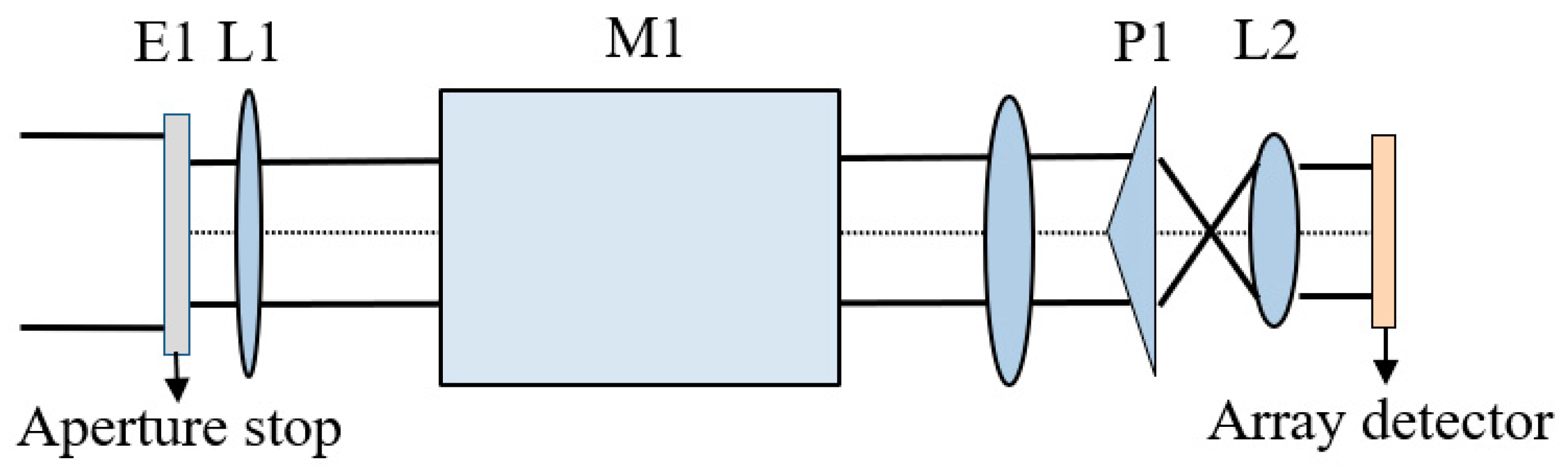
2.3. Principle of Ozone Wind Imaging Interferometer
3. Analysis and Calculation of Instrument Visibility
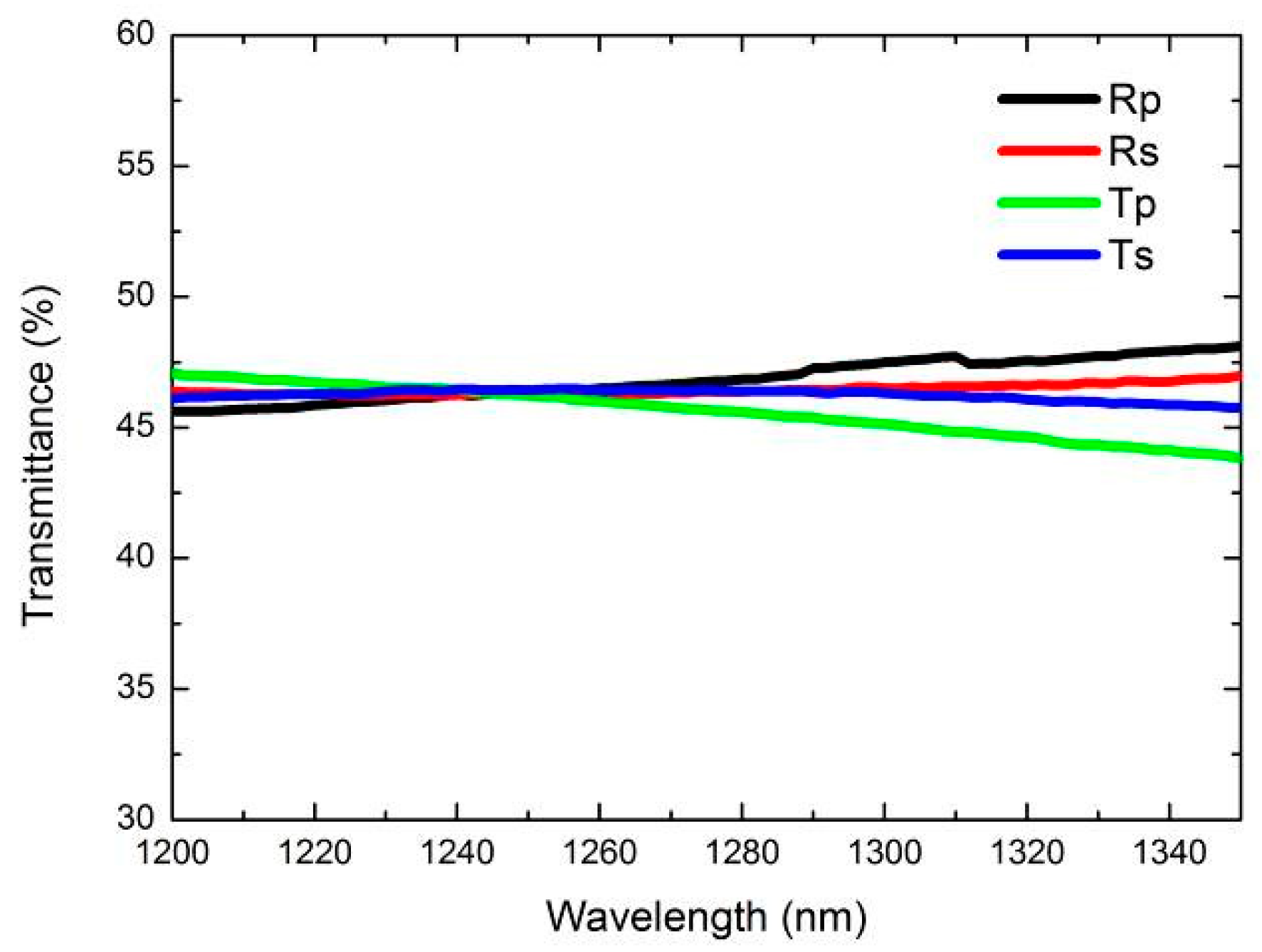
3.1. The Influence of Transmittance on Instrument Visibility
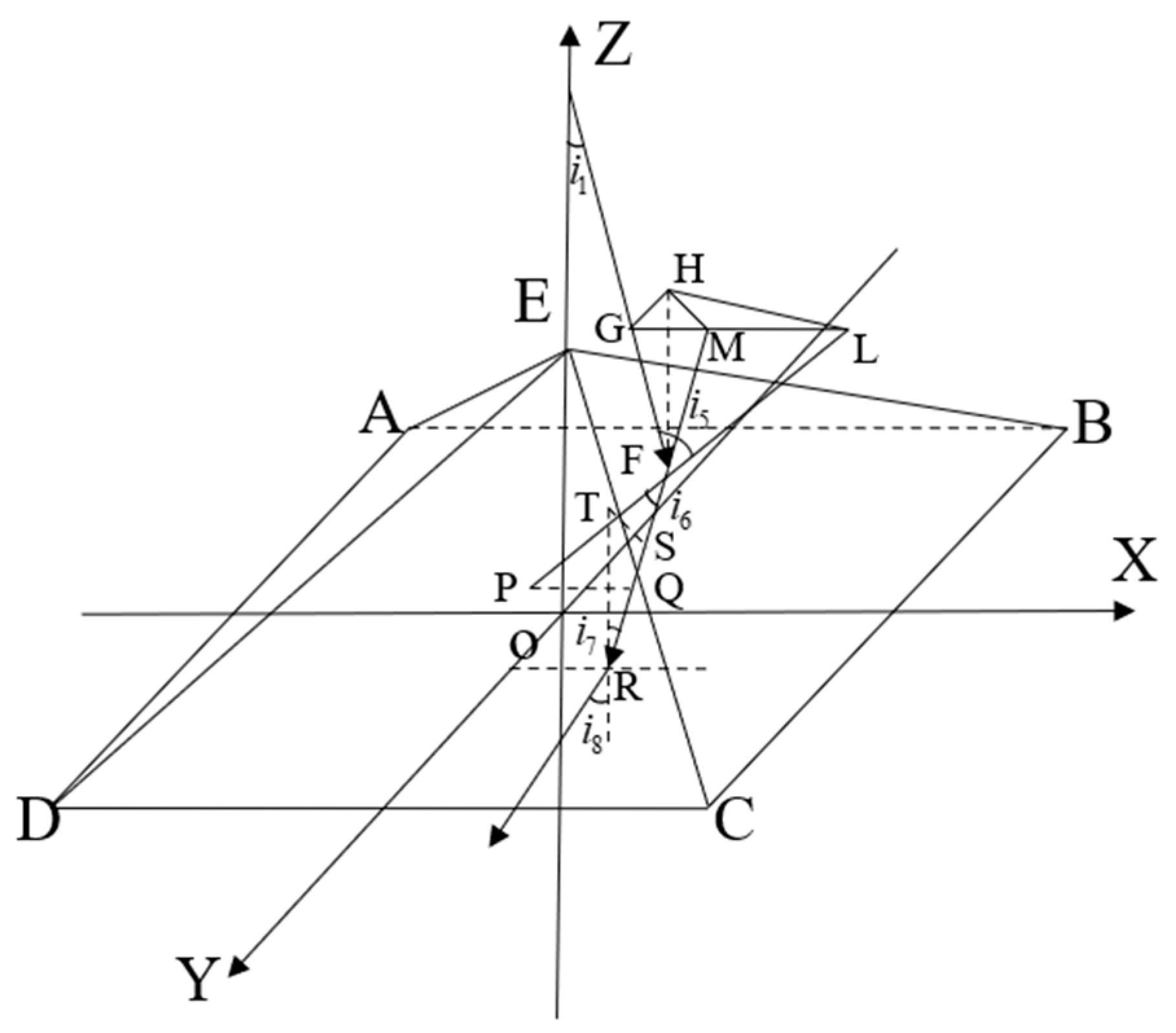
3.2. The Influence of Compensation Glass Surface Tilt on Instrument Visibility
3.3. The Influence of Mirror Surface Accuracy on Instrument Visibility
3.4. Wind Speed and Temperature Measurement Accuracy
4. Computer Simulation and Analysis
4.1. Influence of Beam Splitting Ratio on Instrument Visibility

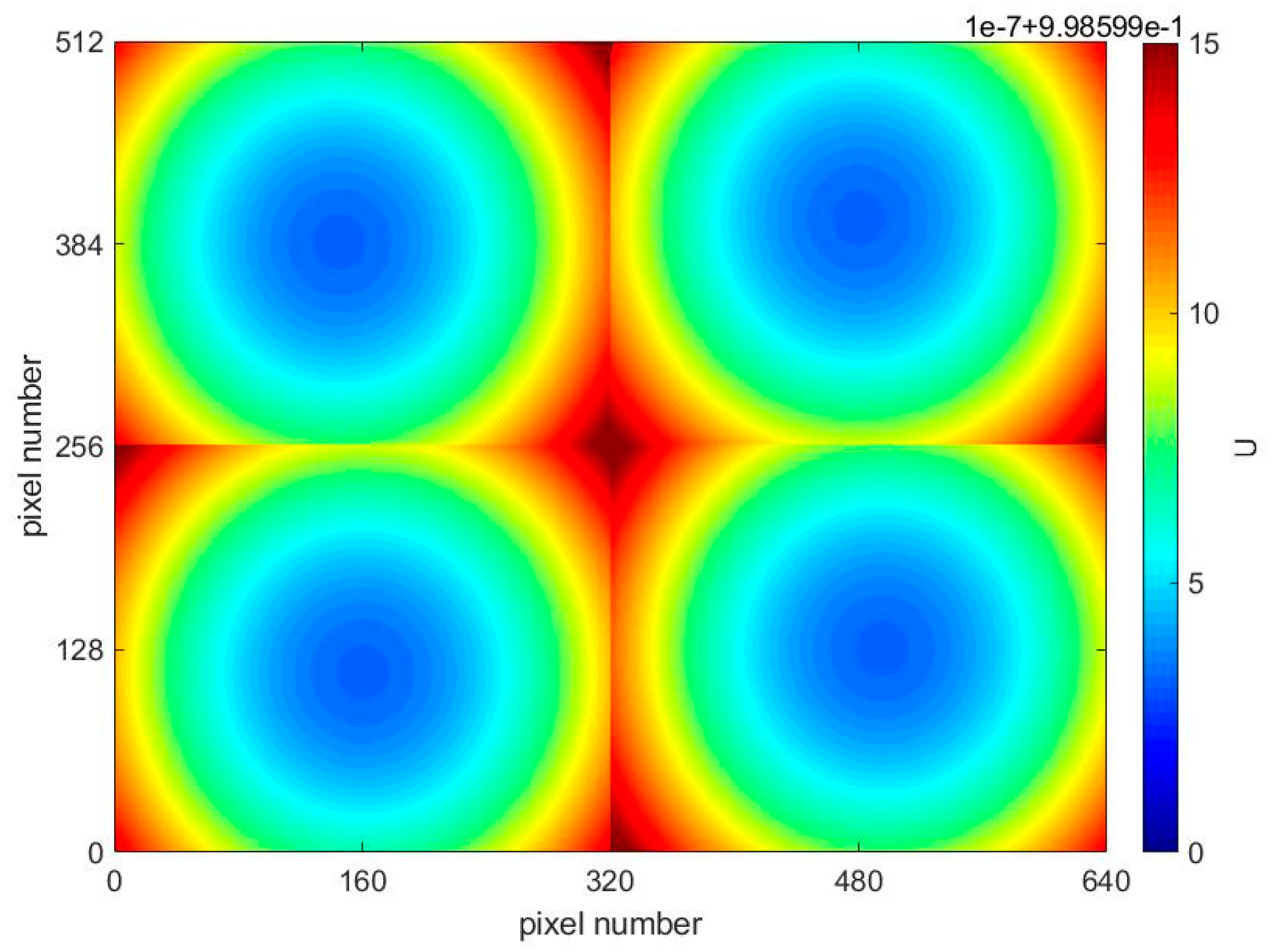
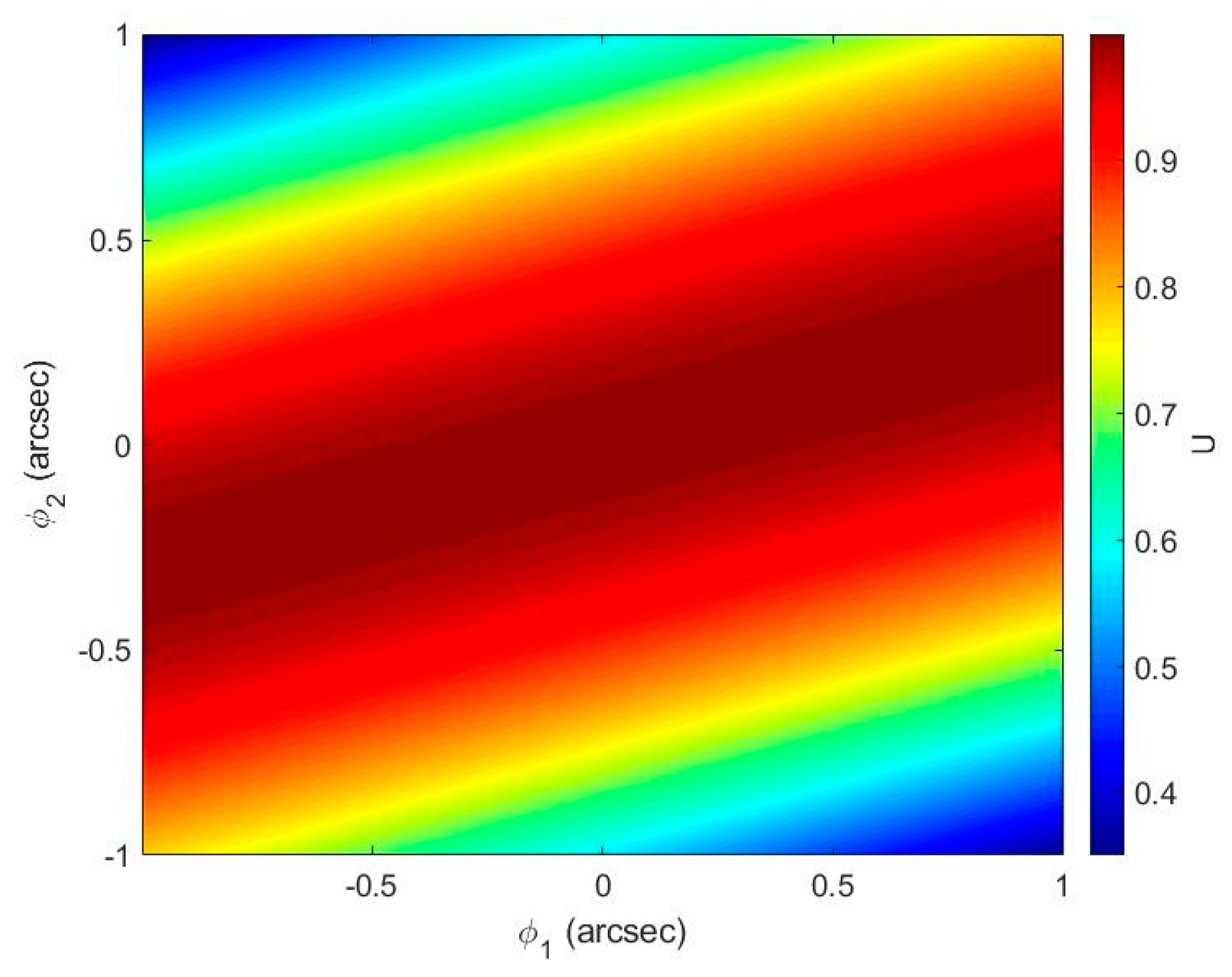
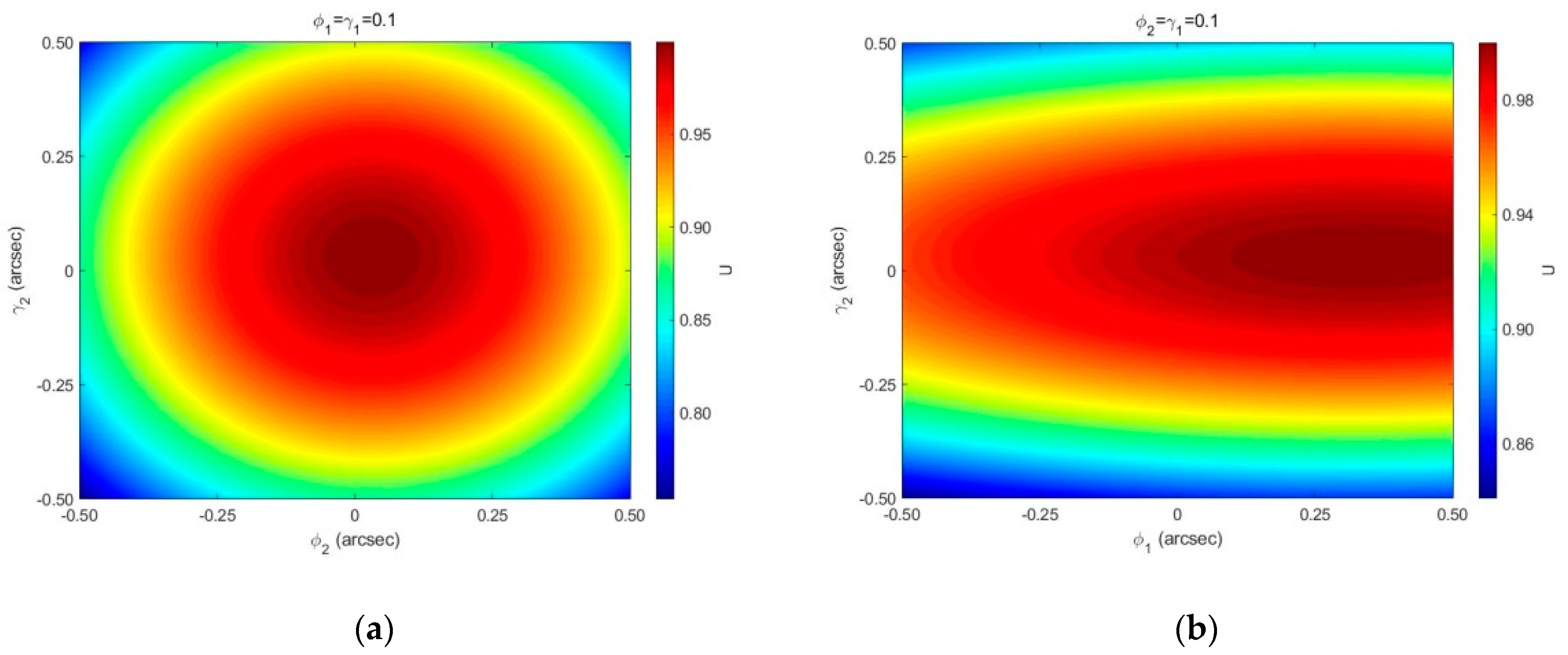
4.2. The Influence of Compensation Glass Surface Tilt on Instrument Visibility
4.3. The Influence of Mirror Surface Accuracy on Instrument Visibility
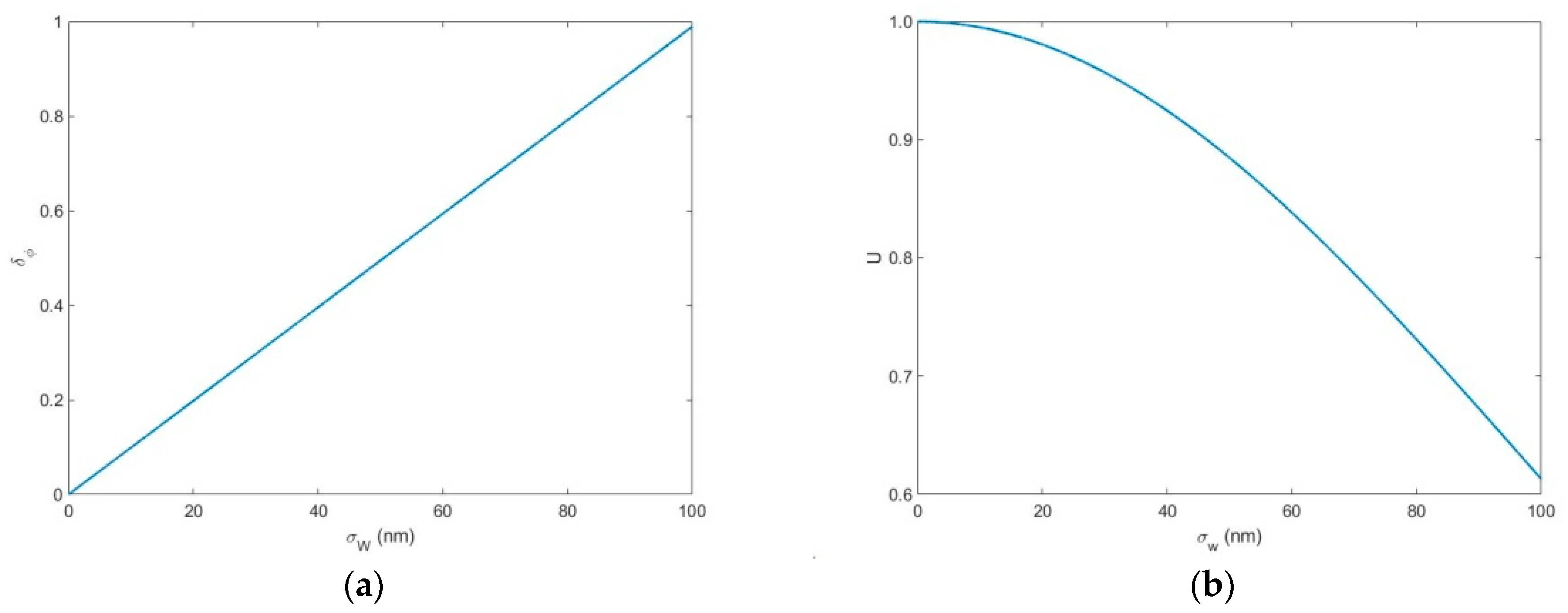
4.4. Wind Speed and Temperature Measurement Accuracy
5. Conclusions
- When the splitting ratio of the beam splitter reaches 1:1, the instrument visibility reaches the maximum value. The splitting ratio should satisfy when the incident angle is and . The splitting ratio of the beam splitter and the pyramid prism play an important role in the distribution of instrument visibility.
- The tilt angle of the compensation glass surface and have the same impact on the instrument visibility; for and , the influence of is greater than that of . When and are limited to , the instrument visibility . In practical applications, the tilt angle of the compensation glass surface should be controlled as much as possible to increase the instrument visibility.
- When considering the mirror surface error, should satisfy if the instrument visibility .
- when the instrument visibility , in the detection range, the random deviation of wind speed is within 1.1 , and the random deviation of temperature within 5.7 .
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, X.; Yee, J.-H.; Talaat, E.R. Diagnosis of Dynamics and Energy Balance in the Mesosphere and Lower Thermosphere. J. Atmos. Sci. 2001, 58, 2441–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.-W.; Wu, K.-J.; Wang, S.-N. Observation technology of wind and temperature by on board imaging interferometer with 1.27 μm air glow. Opt. Optoelectron. Technol. 2019, 17, 72–74. [Google Scholar]
- Shangguan, M.; Xia, H.; Wang, C.; Qiu, J.; Shentu, G.; Zhang, Q.; Dou, X.; Pan, J.W. All-fiber up conversion high spectral resolution wind lidar using a Fabry-Perot interferometer. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 19322–19336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Yi, F. Lidar-measured atmospheric N_2 vibrational-rotational Raman spectra and consequent temperature retrieval. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 27833–27844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao-Hua, J.; Chun-Min, Z.; Bao-Chang, Z. A new method for spectrum reproduction and interferogram processing. Acta Phys. Sin. 2007, 56, 824–829. [Google Scholar]
- Zhi-Lin, Y.; Chun-Min, Z.; Bao-Chang, Z. Study of SNR of a novel polarization interference imaging spectrometer. Acta Phys. Sin. 2007, 56, 6413–6419. [Google Scholar]
- Zhi-Hong, P.; Chun-Min, Z.; Bao-Chang, Z.; Ying-Cai, L.; Fu-Quan, W. The transmittance of Savart polariscope in polarization interference imaging spectrometer. Acta Phys. Sin. 2006, 55, 6374–6381. [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd, G.G.; Gault, W.A.; Miller, D.W.; Pasturczyk, Z.; Johnston, S.F.; Kosteniuk, P.R.; Haslett, J.W.; Kendall, D.J.W.; Wimperis, J.R. WAMDII: Wide-angle Michelson Doppler imaging interferometer for Spacelab. Appl. Opt. 1985, 24, 1571–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chunmin, Z. Interference image spectroscopy for upper atmospheric wind field measurement. Acta Opt. Sin. 2000, 20, 234–239. [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd, G.G.; Thuillier, G.; Gault, W.A.; Solheim, B.H.; Hersom, C.; Alunni, J.M.; Brun, J.-F.; Brune, S.; Charlot, P.; Cogger, L.L.; et al. WINDII, the wind imaging interferometer on the Upper Atmosphere Research Satellite. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1993, 98, 10725–10750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gault, W.A.; Sargoytchev, S.I.; Shepherd, G.G. Divided-Mirror Scanning Technique for a Small Michelson Interferometer. In Optical Spectroscopic Techniques and Instrumentation for Atmospheric and Space Research II; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1996; Volume 2830, pp. 15–18. [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd, G.G.; Thuillier, G.; Cho, Y.M.; Duboin, M.L.; Evans, W.F.; Gault, W.A.; Hersom, C.; Kendall, D.J.W.; Lathuillere, C.; Lowe, R.P.; et al. The Wind Imaging Interferometer (WINDII) on the Upper Atmosphere Research Satellite: A 20 year perspective. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50, RG2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, W.E.; Gault, W.A.; Shepherd, G.G.; Rowlands, N. Research om theory and application of the interferogram of vogit profile. Proc. SPIE 2001, 4540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhang, C.M.; Zhang, Q.G. Research om theory and application of the interferogram of vogit profile. Acta Phys. Sin. 2007, 27, 423–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crutzen, P.J.; Jones, I.T.N.; Wayne, R.P. Calculation of [O2(a1Δg)] in the atmosphere using new laboratory data. J. Geophys. Res. 1971, 76, 1490–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Fu, D.; Feng, Y.; Li, J.; Hao, X.; Li, F. Simulation and application of the emission line O19P18 of O-2(a(1)Delta(g)) dayglow near 1.27 μm for wind observations from limb-viewing satellites. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 16984–16999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, W.F.J.; Hunten, D.M.; Llewellyn, E.J.; Jones, A.V. Altitude profile of the infrared atmospheric system of oxygen in the dayglow. J. Geophys. Res. 1968, 73, 2885–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlynczak, M.G.; Morgan, F.; Yee, J.H.; Espy, P.; Murtagh, D.; Marshall, B.; Schmidlin, F. Simultaneous measurements of the O2(1Δ) and O2(1∑) Airglows and ozone in the daytime mesosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 999–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.J.; Barth, C.A.; Rusch, D.W.; Sanders, R.W. Solar Mesosphere Explorer Near-Infrared Spectrometer: Measurements of 1.27 μm radiances and the inference of mesospheric ozone. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1984, 89, 9569–9580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llewellyn, E.J.; Lloyd, N.D.; Degenstein, D.A.; Gattinger, R.L.; Petelina, S.V.; Bourassa, A.E.; Wiensz, J.T.; Ivanov, E.V.; McDade, I.C.; Solheim, B.H.; et al. The OSIRIS instrument on the Odin spacecraft. Can. J. Phys. 2004, 82, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlynczak, M.G.; Marshall, B.T.; Martin-Torres, F.J.; Russell, J.M., III; Thompson, R.E.; Remsberg, E.E.; Gordley, L.L. Sounding of the Atmosphere using Broad band Emission Radiometry observations of daytime mesospheric O2(1Δ) 1.27 μm emission and derivation of ozone, atomic oxygen, and solar and chemical energy deposition rates. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, D15306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahnama, P.; Rochon, Y.J.; McDade, I.C.; Shepherd, G.G.; Gault, W.A.; Scott, A. Satellite measurement of stratospheric winds and ozone using Doppler Michelson interferometry. Part I: Instrument model and measurement simulation. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2006, 23, 753–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Chun-Min, Z.; Xiao-Hua, J. Passive detection of upper atmospheric wind field based on the Lorentzian line shape profile. Acta Phys. Sin. 2010, 59, 899–906. [Google Scholar]
- Rahanma, P. Simulation and Analysis Studies of SWIFT Measurements. Master’s Thesis, York University, Toronto, ON, Canada, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd, G.G. Spectral Imaging of the Atmosphere; Academic Press: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2002; p. 82. [Google Scholar]
- Piao, R. Middle Atmospheric Temperature Variation and Near-Infrared Static Wind Imaging Interferometry. Ph.D. Thesis, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Shaanxi, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, W.F.J.; McDade, I.C.; Yuen, J.; Llewellyn, E.J. A rocket measurement of the O2 Infrared Atmospheric (0–0) band emission in the dayglow and a determination of the mesospheric ozone and atomic oxygen densities. Can. J. Phys. 1988, 66, 941–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, G.G.; McDade, I.C.; Gault, W.A.; Rochon, Y.J.; Scott, A.; Rowlands, N.; Buttner, G. The Stratospheric Wind Interferometer for Transport studies (SWIFT). In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE International Geoscience Remote Sensing Symposium, Sydney, Australia, 9–13 July 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Rochon, Y.J. The retrieval of winds, Doppler temperatures, and emission rates for the WINDII experiment. Ph.D. Thesis, York University, Toronto, ON, Canada, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Rahnama, P.; Rochon, Y.J.; McDade, I.C.; Shepherd, G.G.; Gault, W.A.; Scott, A. Satellite Measurement of Stratospheric Winds and Ozone Using Doppler Michelson Interferometry. Part II: Retrieval Method and Expected Performance. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2006, 23, 770–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katti, P.K.; Singh, K. A Note on the Surface Accuracy and Alignment of the End Mirrors in a Michelson Interferometer. Appl. Opt. 1966, 5, 1962–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, W.E. The Design and Implementation of the Wide-Angle Michelson Interferometer to Observe Thermospheric Winds. Ph.D. Thesis, York University, Toronto, ON, Canada, 1988. [Google Scholar]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, C.; Du, X.; Yan, T.; Li, G. Research on Instrument Visibility of Ozone Wind Imaging Interferometer. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13061062
Zhang C, Du X, Yan T, Li G. Research on Instrument Visibility of Ozone Wind Imaging Interferometer. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(6):1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13061062
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Chunmin, Xiao Du, Tingyu Yan, and Guixiu Li. 2021. "Research on Instrument Visibility of Ozone Wind Imaging Interferometer" Remote Sensing 13, no. 6: 1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13061062
APA StyleZhang, C., Du, X., Yan, T., & Li, G. (2021). Research on Instrument Visibility of Ozone Wind Imaging Interferometer. Remote Sensing, 13(6), 1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13061062






