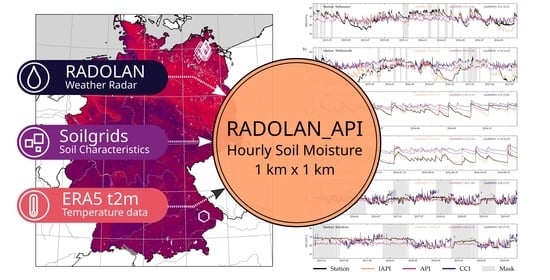
RADOLAN_API: An Hourly Soil Moisture Data Set Based on Weather Radar, Soil Properties and Reanalysis Temperature Data
Abstract
Share and Cite
Ramsauer, T.; Weiß, T.; Löw, A.; Marzahn, P. RADOLAN_API: An Hourly Soil Moisture Data Set Based on Weather Radar, Soil Properties and Reanalysis Temperature Data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1712. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13091712
Ramsauer T, Weiß T, Löw A, Marzahn P. RADOLAN_API: An Hourly Soil Moisture Data Set Based on Weather Radar, Soil Properties and Reanalysis Temperature Data. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(9):1712. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13091712
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamsauer, Thomas, Thomas Weiß, Alexander Löw, and Philip Marzahn. 2021. "RADOLAN_API: An Hourly Soil Moisture Data Set Based on Weather Radar, Soil Properties and Reanalysis Temperature Data" Remote Sensing 13, no. 9: 1712. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13091712
APA StyleRamsauer, T., Weiß, T., Löw, A., & Marzahn, P. (2021). RADOLAN_API: An Hourly Soil Moisture Data Set Based on Weather Radar, Soil Properties and Reanalysis Temperature Data. Remote Sensing, 13(9), 1712. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13091712