Validation of Satellite-Based Precipitation Products from TRMM to GPM
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data
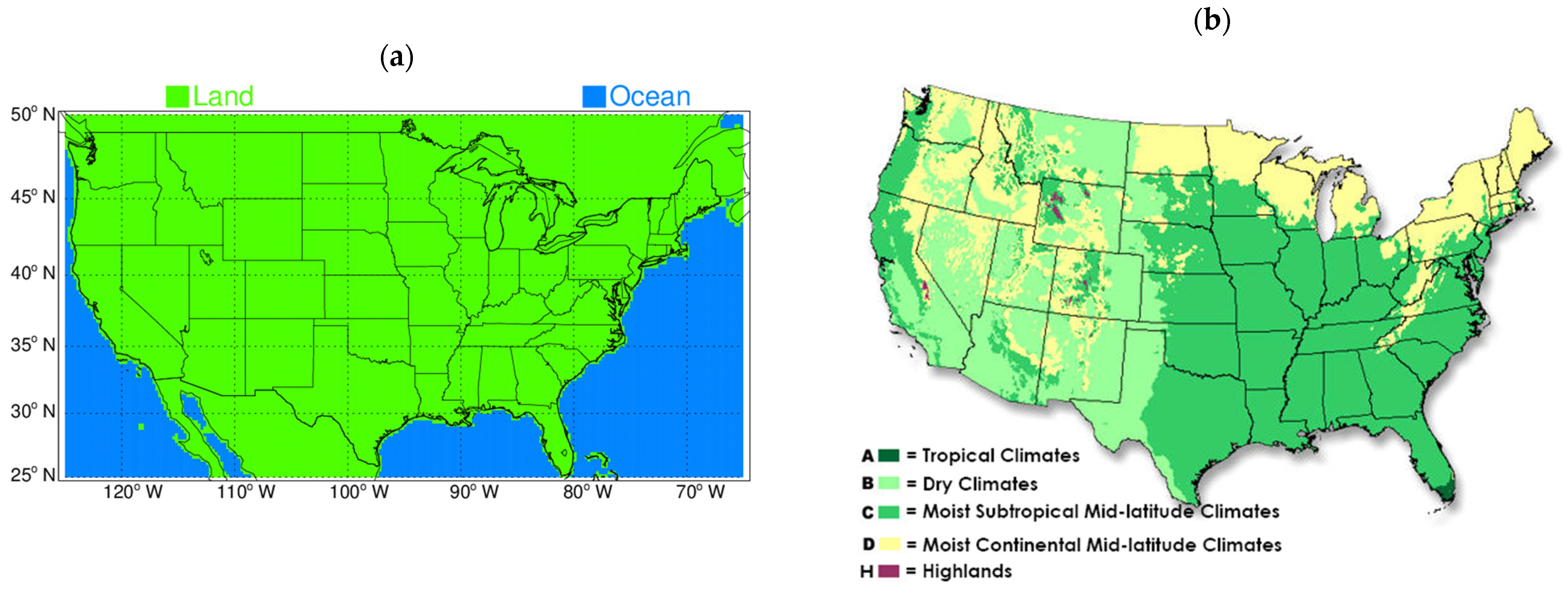
2.1. Study Domain
2.2. TRMM 3B42
2.3. GPM IMERG
2.4. Ground MRMS
2.5. Montly GPCC
3. Methodology and Evaluation Metrics
4. Results and Analysis
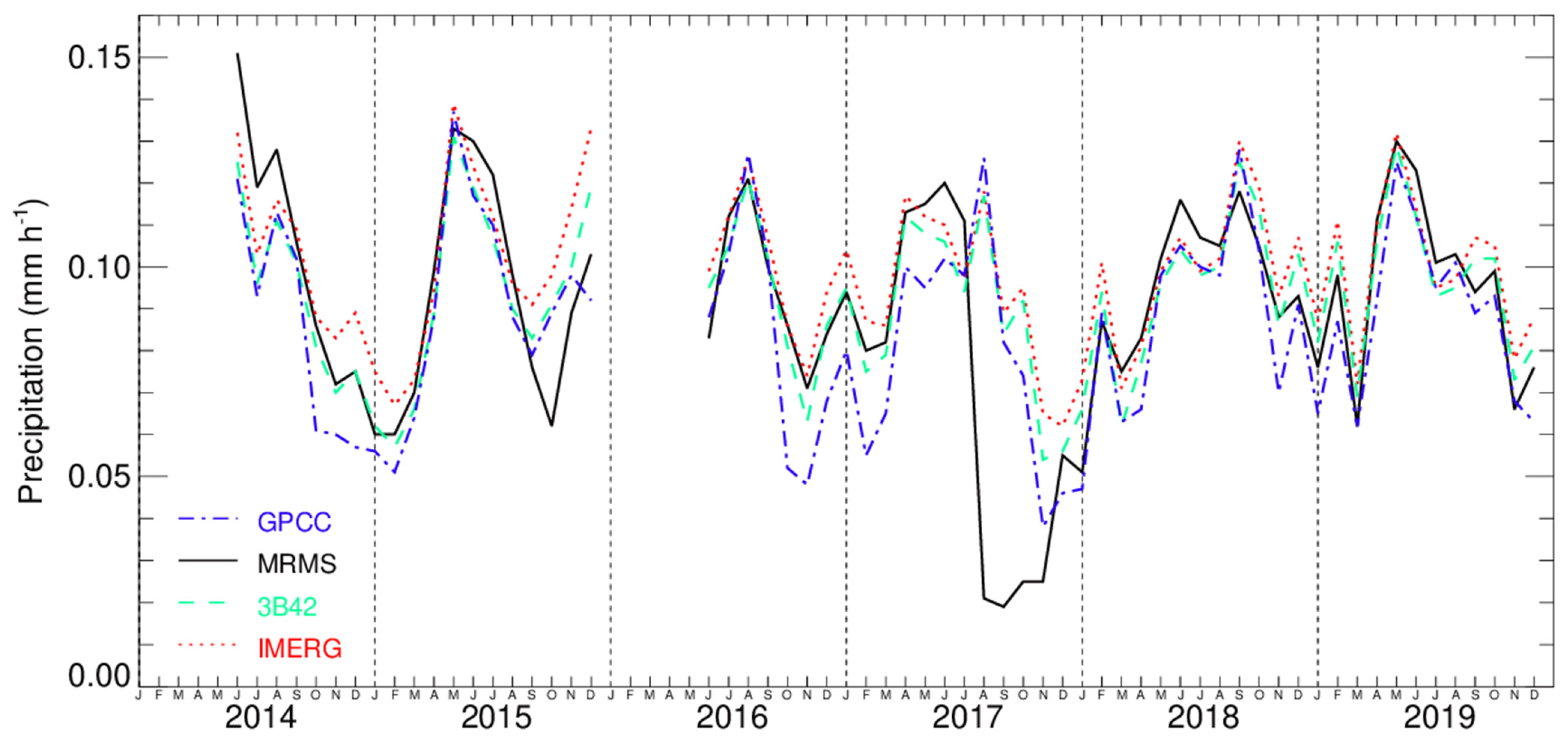
4.1. Time Series of Spatially Averaged Monthly Precipitation
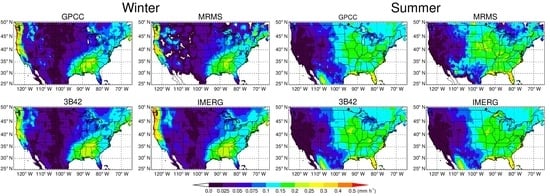
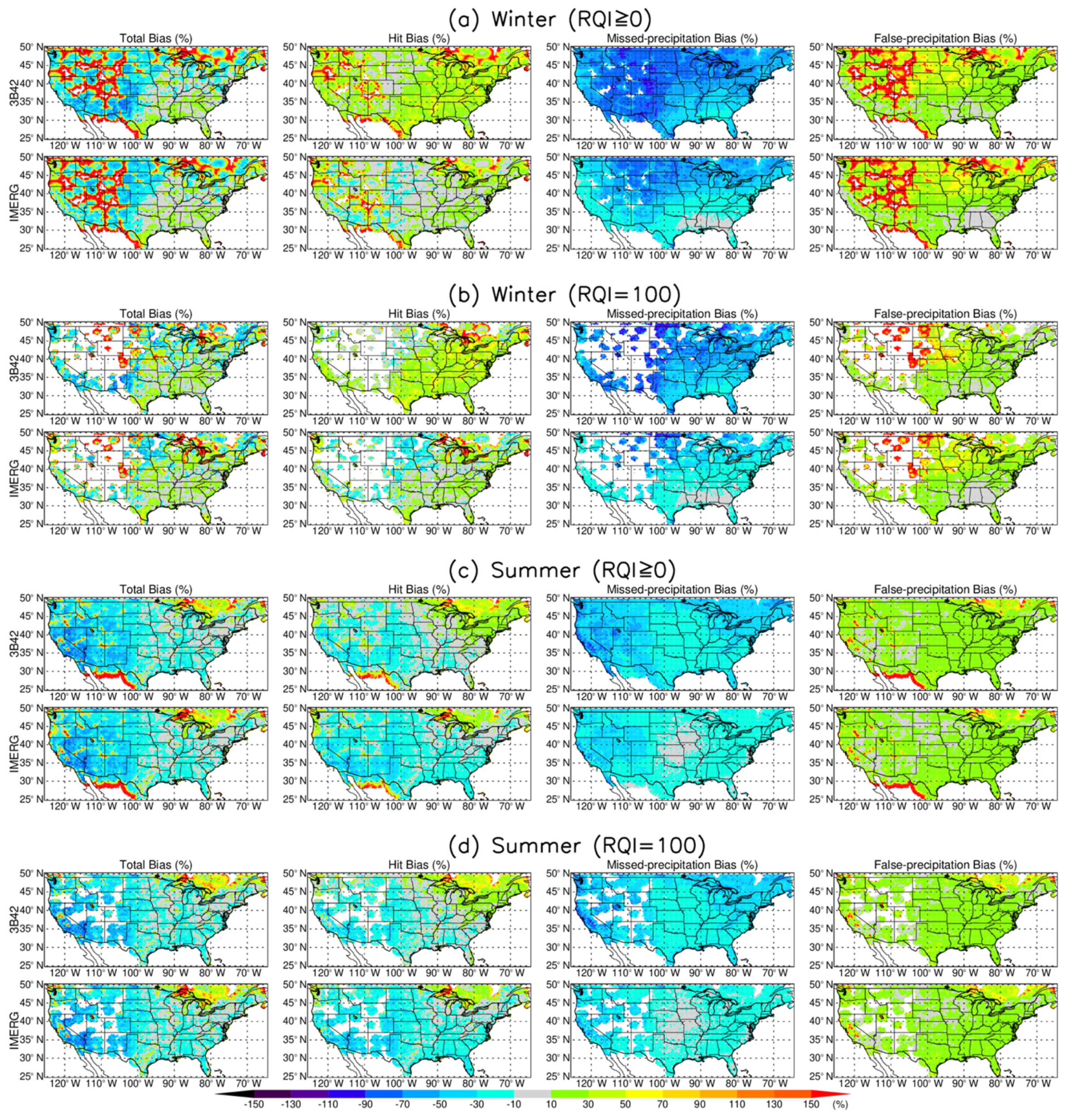
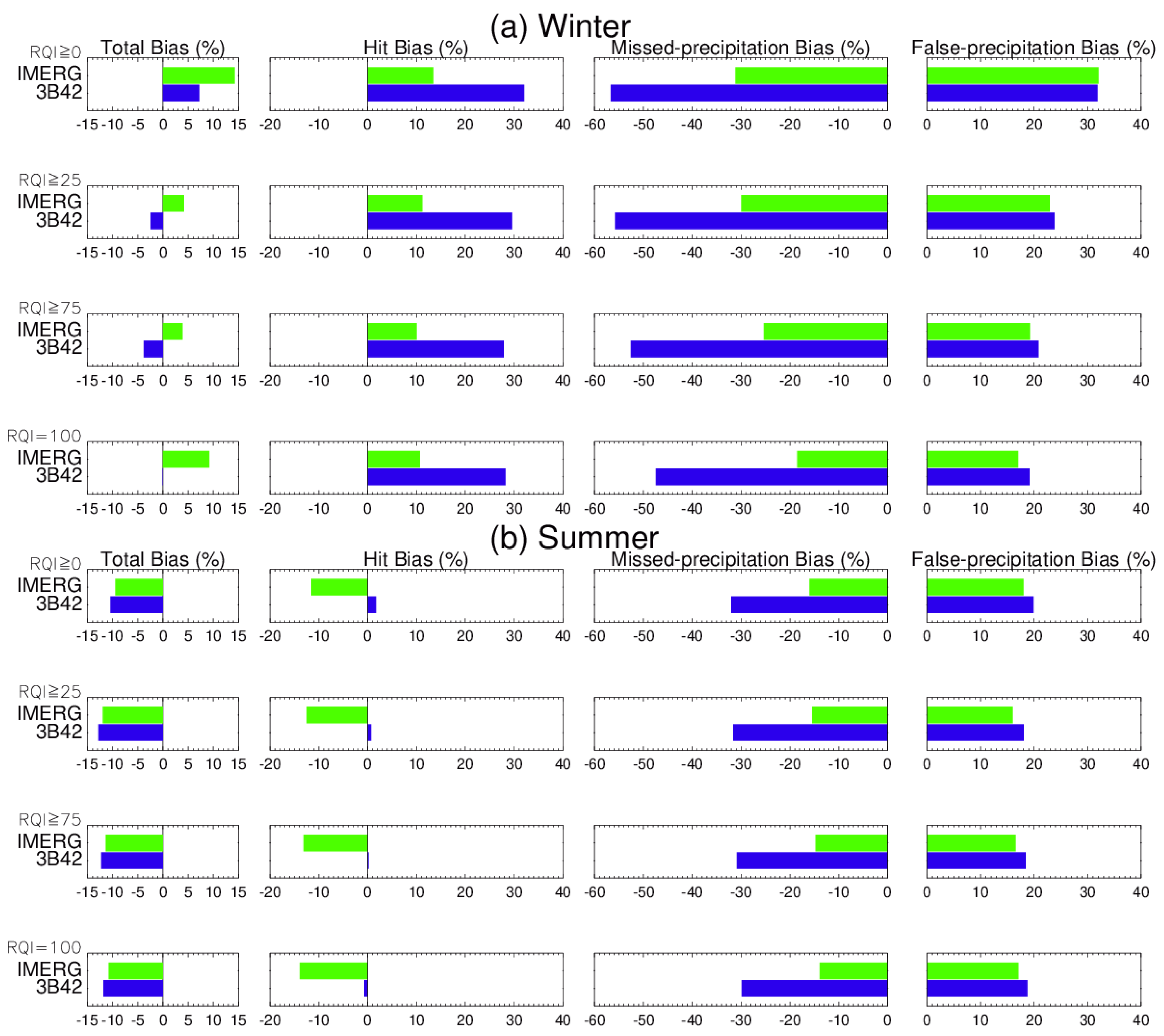
4.2. Spatial Distribution of Mean Monthly Precipitation and Error Decomposition Analysis
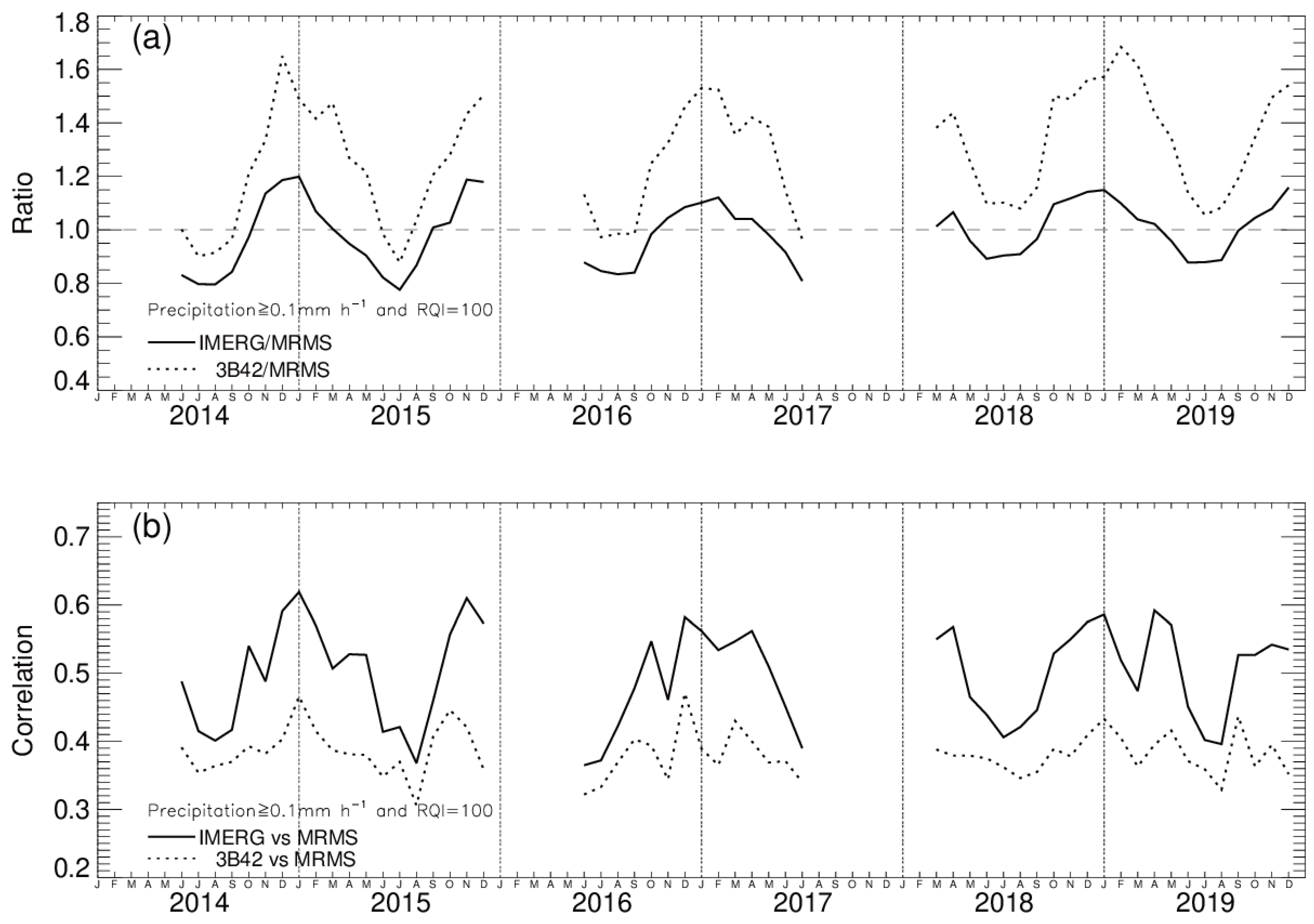
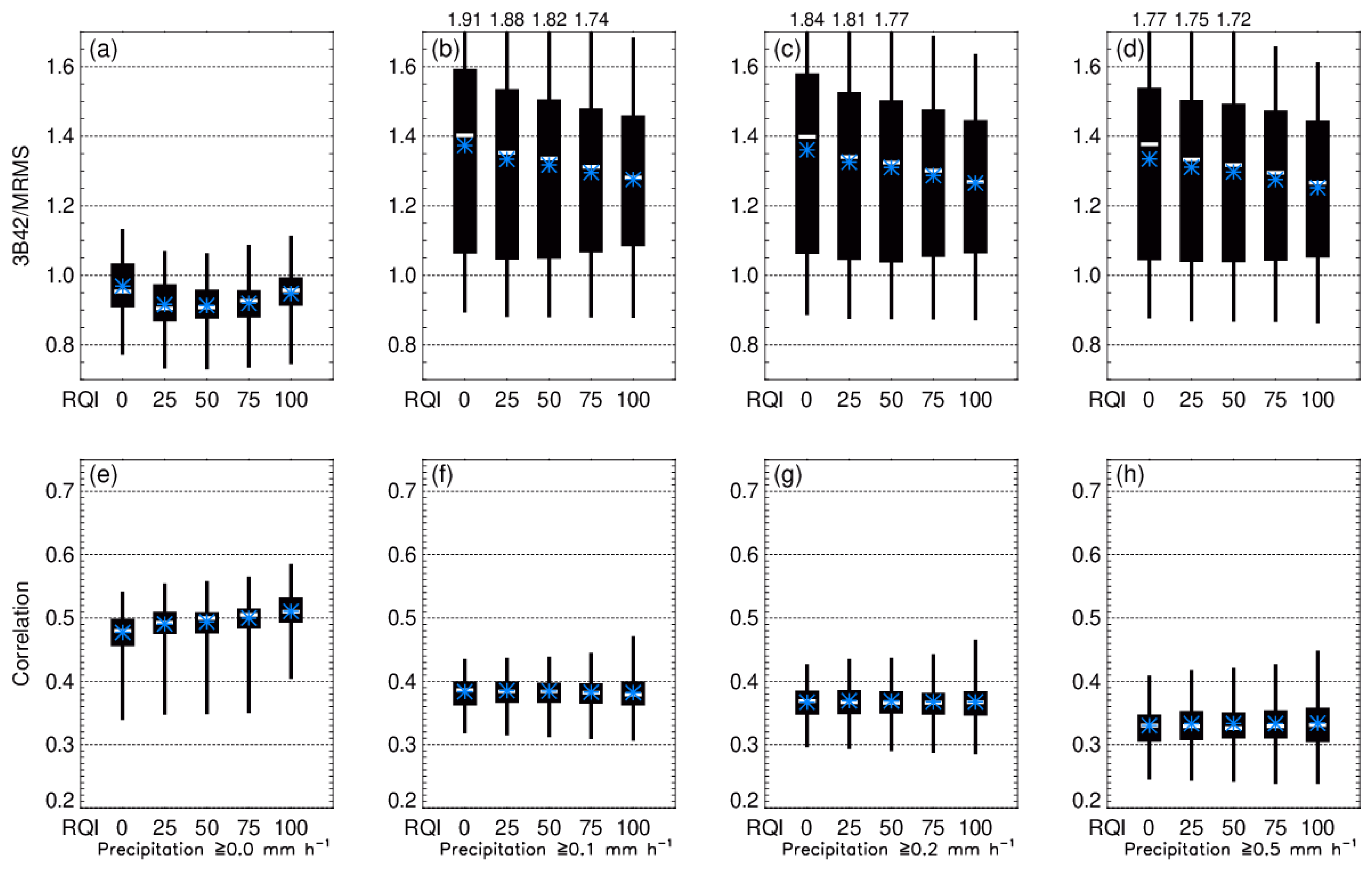
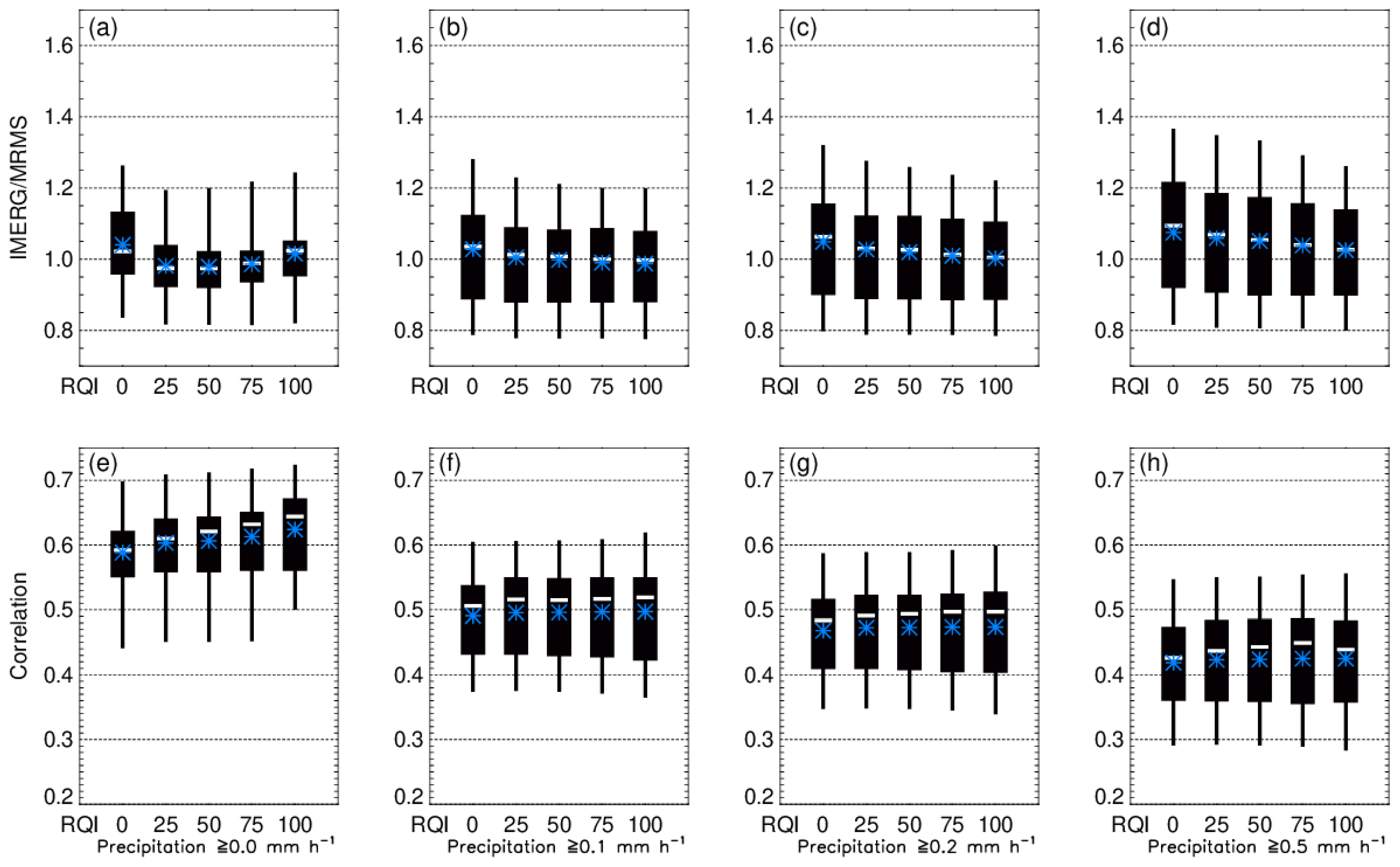
4.3. Statistical Metrics and Categorical Skill Score
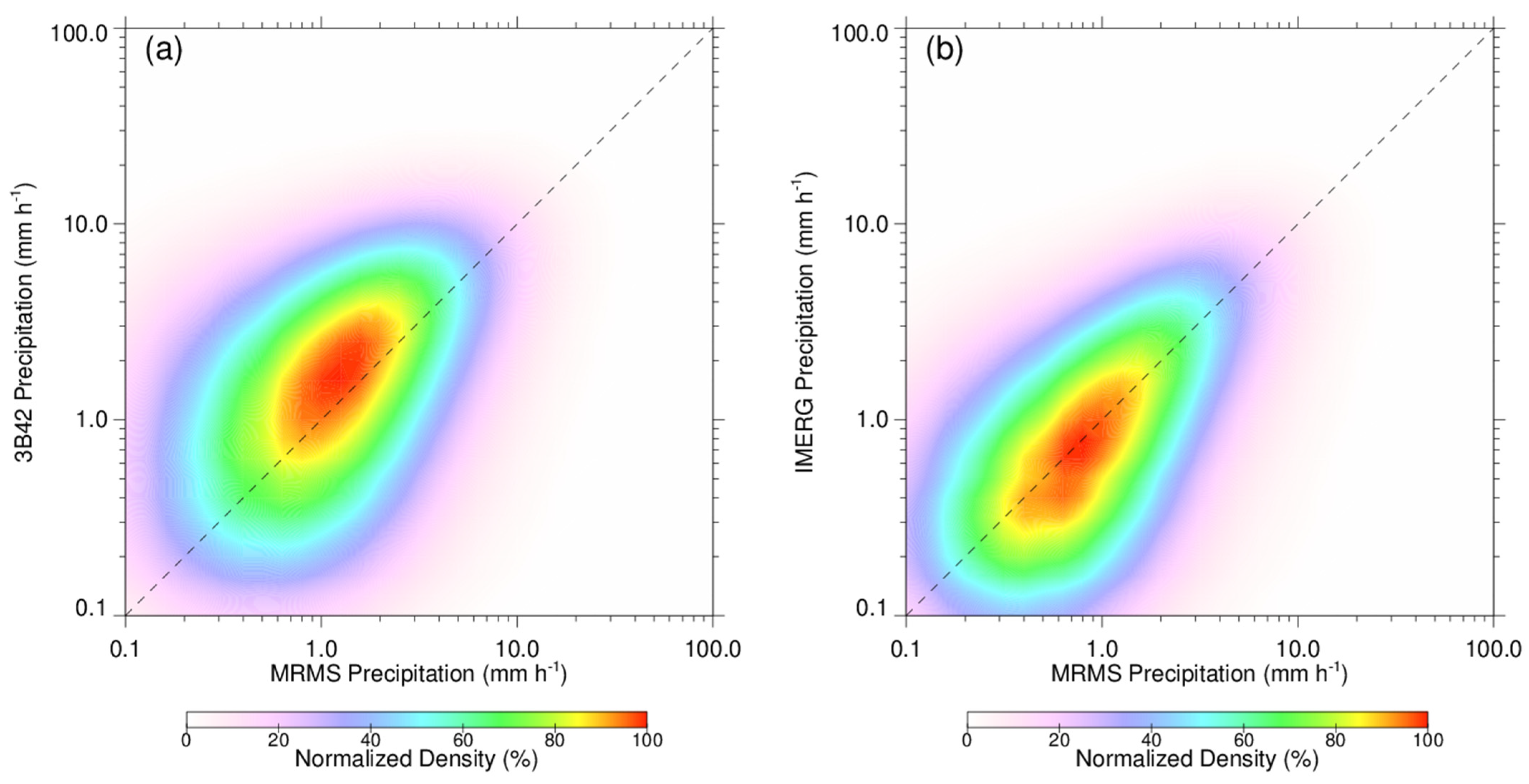
4.4. Probability Distribution Analysis
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- All products display a high degree of consistency in spatial distribution patterns though some differences are visually discernable.
- (2)
- The IMERG shows substantial improvements in terms of nearly all statistical metrics, compared to its predecessor 3B42.
- (3)
- For winter, the improvement in IMERG was primarily from significantly reduced missed-precipitation bias, and from largely reduced positive hit bias. For summer, the improvement was mainly from notably reduced missed-precipitation bias and marginally reduced false-precipitation bias but at the expense of worse hit bias.
- (4)
- The precipitation intensity distribution shows a significant improvement of IMERG algorithm in comparison with 3B42, which obviously overestimated heavy precipitation but underestimated light precipitation.
- (5)
- Missed-precipitation bias over mountainous regions, especially over frozen surfaces in winter, is still a challenging problem in satellite-based precipitation retrieval algorithms. The bias correction is of particular importance in mountainous regions such as Serra Nevada Mountains in California and Rocky Mountains in Colorado.
- (6)
- All the statistical metrics and the error decomposition approach work together were effective in evaluation of the performances for the satellite-based precipitation products.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kidd, C.; Huffman, G.J. Global precipitation measurement. Meteorol. Appl. 2011, 18, 334–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wolff, D.B. Evaluation of TRMM Ground-Validation Radar-Rain Errors Using Rain Gauge Measurements. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2010, 49, 310–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Wolff, D.B. Evaluation of TRMM Rain Estimates Using Ground Measurements over Central Florida. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2012, 51, 926–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Petersen, W.A.; Kirchengast, G.; Goodrich, D.C.; Wolff, D.B. Evaluation of Global Precipitation Measurement Rainfall Estimates against Three Dense Gauge Networks. J. Hydrometeorol. 2018, 19, 517–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, D.B.; Marks, D.A.; Amitai, E.; Silberstein, D.S.; Fisher, B.L.; Tokay, A.; Wang, J.; Pippitt, J.L. Ground Validation for the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM). J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2005, 22, 365–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringi, V.N.; Chandrasekar, V. Polarimetric Doppler Weather Radar: Principles and Applications; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2001; p. 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifelli, R.; Chandrasekar, V.; Lim, S.; Kennedy, P.C.; Wang, Y.; Rutledge, S.A. A New Dual-Polarization Radar Rainfall Algorithm: Application in Colorado Precipitation Events. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2011, 28, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kidd, C.; Levizzani, V. Status of satellite precipitation retrievals. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J.; Wolff, D.B.; Adler, R.F.; Gu, G.; Hong, Y.; Bowman, K.P.; Stocker, E.F. The TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA): Quasi-Global, Multiyear, Combined-Sensor Precipitation Estimates at Fine Scales. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J. NASA Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Integrated Multi-Satellite Retrievals for GPM (IMERG). NASA Algorithm Theoretical Basis Doc., Version 06; p. 39. Available online: https://gpm.nasa.gov/sites/default/files/2020-05/IMERG_ATBD_V06.3.pdf (accessed on 29 April 2021).
- Gebremichael, M.; Hossain, F. Satellite Rainfall Applications for Surface Hydrology; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 1–327. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, W.A.; Kirstetter, P.E.; Wang, J.; Wolff, D.B.; Tokay, A. The GPM Ground Validation Program. In Satellite Precipitation Measurement, Chapter 26; Levizzani, V., Kidd, C., Kirschbaum, D.B., Kummerow, C., Nakamura, K., Turk, F.J., Eds.; Springer-Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Chen, S.; Bao, A.; Behrangi, A.; Hong, Y.; Ndayisaba, F.; Hu, J.; Stepanian, P.M. Early assessment of Integrated Multi-satellite Retrievals for Global Precipitation Measurement over China. Atmos. Res. 2016, 176, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Lü, H.; Ryu, D.; Zhu, Y. The Assessment and Comparison of TMPA and IMERG Products over the Major Basins of Mainland China. Earth Space Sci. 2019, 6, 2461–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Petersen, W.A.; Tokay, A. A Novel Approach to Identify Sources of Errors in IMERG for GPM Ground Validation. J. Hydrometeorol. 2016, 17, 2477–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Petersen, W.A.; Wolff, D.B.; Bolvin, D.T.; Kirstetter, P.-E. Validation of satellite precipitation products using NMQ over the CONUS. In Proceedings of the 8th European Conference on Radar in Meteorology and Hydrology, Garmisch-Partenkirchen, Germany, 1–5 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gebregiorgis, A.S.; Kirstetter, P.; Hong, Y.E.; Gourley, J.J.; Huffman, G.J.; Petersen, W.A.; Xue, X.; Schwaller, M.R. To What Extent is the Day 1 GPM IMERG Satellite Precipitation Estimate Improved as Compared to TRMM TMPA-RT? J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 1694–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Ma, Y.; Long, D.; Zhong, L.; Hong, Y. Evaluation of GPM Day-1 IMERG and TMPA Version-7 legacy products over Mainland China at multiple spatiotemporal scales. J. Hydrol. 2016, 533, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Tian, F.; Yang, L.; Hu, H.; Lu, H.; Hou, A. Ground validation of GPM IMERG and TRMM 3B42V7 rainfall products over southern Tibetan Plateau based on a high-density rain gauge network. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 910–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.; Lü, H.; Crow, W.T.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, J.; Su, J. Evaluation of Satellite-Based Precipitation Products from IMERG V04A and V03D, CMORPH and TMPA with Gauged Rainfall in Three Climatologic Zones in China. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, Q.; Li, Y.; Feng, H.; Yu, Q.; Zou, Y.; Liu, F.; Pulatov, B. Performance evaluation and correction of precipitation data using the 20-year IMERG and TMPA precipitation products in diverse subregions of China. Atmos. Res. 2021, 249, 105304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Li, X. Evaluation of IMERG and TRMM 3B43 Monthly Precipitation Products over Mainland China. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krishna, U.V.M.; Das, S.K.; Deshpande, S.M.; Doiphode, S.L.; Pandithurai, G. The assessment of Global Precipitation Measurement estimates over the Indian subcontinent. Earth Space Sci. 2017, 4, 540–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A. Statistical comparison of satellite-retrieved precipitation products with rain gauge observations over Bangladesh. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 2906–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moazam, S.; Najafi, M.R. A comprehensive evaluation of GPM-IMERG V06 and MRMS with hourly ground-based precipitation observations across Canada. J. Hydrol. 2020, 549, 125929. [Google Scholar]
- Anjum, M.N.; Ahmad, I.; Ding, Y.; Shangguan, D.; Zaman, M.; Ijaz, M.W.; Sarwar, K.; Han, H.; Yang, M. Assessment of IMERG-V06 Precipitation Product over Different Hydro-Climatic Regimes in the Tianshan Mountains, North-Western China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huffman, G.J. The Transition in Multi-Satellite Products from TRMM to GPM (TMPA to IMERG). Available online: https://gpm.nasa.gov/sites/default/files/2020-10/TMPA-to-IMERG_transition_201002.pdf (accessed on 29 April 2021).
- Bolvin, D.T.; Huffman, G.J. Transition of 3B42/3B43 Research Product from Monthly to Climatological Calibra-Tion/Adjustment. 2015 NASA TRMM Doc.; p. 11. Available online: https://pmm.nasa.gov/sites/default/files/document_files/3B42_3B43_TMPA_restart.pdf (accessed on 29 April 2021).
- Schneider, U.; Becker, A.; Finger, P.; Rustemeier, E.; Ziese, M. GPCC Full Data Monthly Product Version 2020 at 0.25°: Monthly Land-Surface Precipitation from Rain-Gauges Built on GTS-based and Historical Data; Global Precipitation Climatology Centre at Deutscher Wetterdienst: Offenbach, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, R.J.; Xie, P. Kalman Filter–Based CMORPH. J. Hydrometeorol. 2011, 12, 1547–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Hsu, K.-L.; Sorooshian, S.; Gao, X. Precipitation Estimation from Remotely Sensed Imagery Using an Artificial Neural Network Cloud Classification System. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2004, 43, 1834–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, J.; Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J. IMERG V06: Changes to the Morphing Algorithm. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2019, 36, 2471–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Howard, K.W.; Langston, C.; Kaney, B.; Qi, Y.; Tang, L.; Grams, H.M.; Wang, Y.; Cocks, S.; Martinaitis, S.M.; et al. Multi-Radar Multi-Sensor (MRMS) Quantitative Precipitation Estimation: Initial Operating Capabilities. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 97, 621–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirstetter, P.-E.; Hong, Y.; Gourley, J.J.; Chen, S.; Flamig, Z.; Zhang, J.; Schwaller, M.; Petersen, W.; Amitai, E. Toward a Framework for Systematic Error Modeling of Spaceborne Precipitation Radar with NOAA/NSSL Ground Radar–Based National Mosaic QPE. J. Hydrometeorol. 2012, 13, 1285–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Qi, Y.; Langston, C.; Kaney, B. Radar quality index (RQI)—A combined measure for beam blockage and VPR effects in a national network. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Weather Radar and Hydrology, Exeter, UK, 18–21 April 2011; IAHS Publ.: Paris, France, 2011; Volume 351, pp. 388–393. [Google Scholar]
- Wilks, D.S. Statistical Methods in the Atmospheric Sciences, 3rd ed.; International Geophysics Series; Academic Press: Waltham, MA, USA, 2011; Volume 100, p. 704. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Peters-Lidard, C.D.; Eylander, J.B.; Joyce, R.J.; Huffman, G.J.; Adler, R.F.; Hsu, K.-L.; Turk, F.J.; Garcia, M.; Zeng, J. Component analysis of errors in satellite-based precipitation estimates. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2009, 114, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Habib, E.; Larson, B.F.; Graschel, J. Validation of NEXRAD multisensor precipitation estimates using an experimental dense rain gauge network in south Louisiana. J. Hydrol. 2009, 373, 463–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirstetter, P.-E.; Gourley, J.J.; Hong, Y.; Zhang, J.; Moazamigoodarzi, S.; Langston, C.; Arthur, A. Probabilistic precipitation rate estimates with ground-based radar networks. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 1422–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Tian, Y.; Yan, F.; Habib, E. An improved procedure for the validation of satellite-based precipitation estimates. Atmos. Res. 2015, 163, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shige, S.; Kida, S.; Ashiwake, H.; Kubota, T.; Aonashi, K. Improvement of TMI Rain Retrievals in Mountainous Areas. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2013, 52, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kummerow, C.; Brown, P. GPROF: Progress towards an improved orographic precipitation product. In Proceedings of the PMM Science Team Meeting 2020, Virtual (Microsoft Teams), 19–23 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ringerud, S.; Peters-Lidard, C.; Munchak, J.; You, Y. Applications of Dynamic Land Surface Information for Passive Microwave Precipitation Retrieval. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2021, 38, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Dong, X.; Xi, B.; Feng, Z.; Fan, J. Can the GPM IMERG Final Product Accurately Represent MCSs’ Precipitation Characteristics over the Central and Eastern United States? J. Hydrometeorol. 2020, 21, 39–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, H.V.; Kling, H.; Yilmaz, K.K.; Martinez, G.F. Decomposition of the mean squared error and NSE performance criteria: Implications for improving hydrological modelling. J. Hydrol. 2009, 377, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kling, H.; Fuchs, M.; Paulin, M. Runoff conditions in the upper Danube basin under an ensemble of climate change scenarios. J. Hydrol. 2012, 424, 264–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, A.Y.; Kakar, R.K.; Neeck, S.; Azarbarzin, A.A.; Kummerow, C.D.; Kojima, M.; Oki, R.; Nakamura, K.; Iguchi, T. The global precipitation measurement mission. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 95, 701–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skofronick-Jackson, G.; Kirschbaum, D.; Petersen, W.; Huffman, G.; Kidd, C.; Stocker, E.; Kakar, R. The Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) mission’s scientific achievements and societal contributions: Reviewing four years of advanced rain and snow observations. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 144, 27–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Yong, B.; Qi, W.; Wu, H.; Ren, L.; Hong, Y. Investigating the Evaluation Uncertainty for Satellite Precipitation Estimates Based on Two Different Ground Precipitation Observation Products. J. Hydrometeorol. 2020, 21, 2595–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Winter | Summer | 55 Months | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3B42 | IMERG | 3B42 | IMERG | 3B42 | IMERG | |
| RQI ≥ 0 | −0.193 | 0.372 | 0.359 | 0.362 | 0.286 | 0.465 |
| RQI = 100 | 0.026 | 0.466 | 0.338 | 0.335 | 0.330 | 0.449 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Petersen, W.A.; Wolff, D.B. Validation of Satellite-Based Precipitation Products from TRMM to GPM. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1745. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13091745
Wang J, Petersen WA, Wolff DB. Validation of Satellite-Based Precipitation Products from TRMM to GPM. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(9):1745. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13091745
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jianxin, Walter A. Petersen, and David B. Wolff. 2021. "Validation of Satellite-Based Precipitation Products from TRMM to GPM" Remote Sensing 13, no. 9: 1745. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13091745
APA StyleWang, J., Petersen, W. A., & Wolff, D. B. (2021). Validation of Satellite-Based Precipitation Products from TRMM to GPM. Remote Sensing, 13(9), 1745. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13091745