Spectral Temporal Information for Missing Data Reconstruction (STIMDR) of Landsat Reflectance Time Series
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Spatial-Based Methods
2.2. Temporal-Based Methods
2.3. Hybrid Methods
3. Materials and Methods
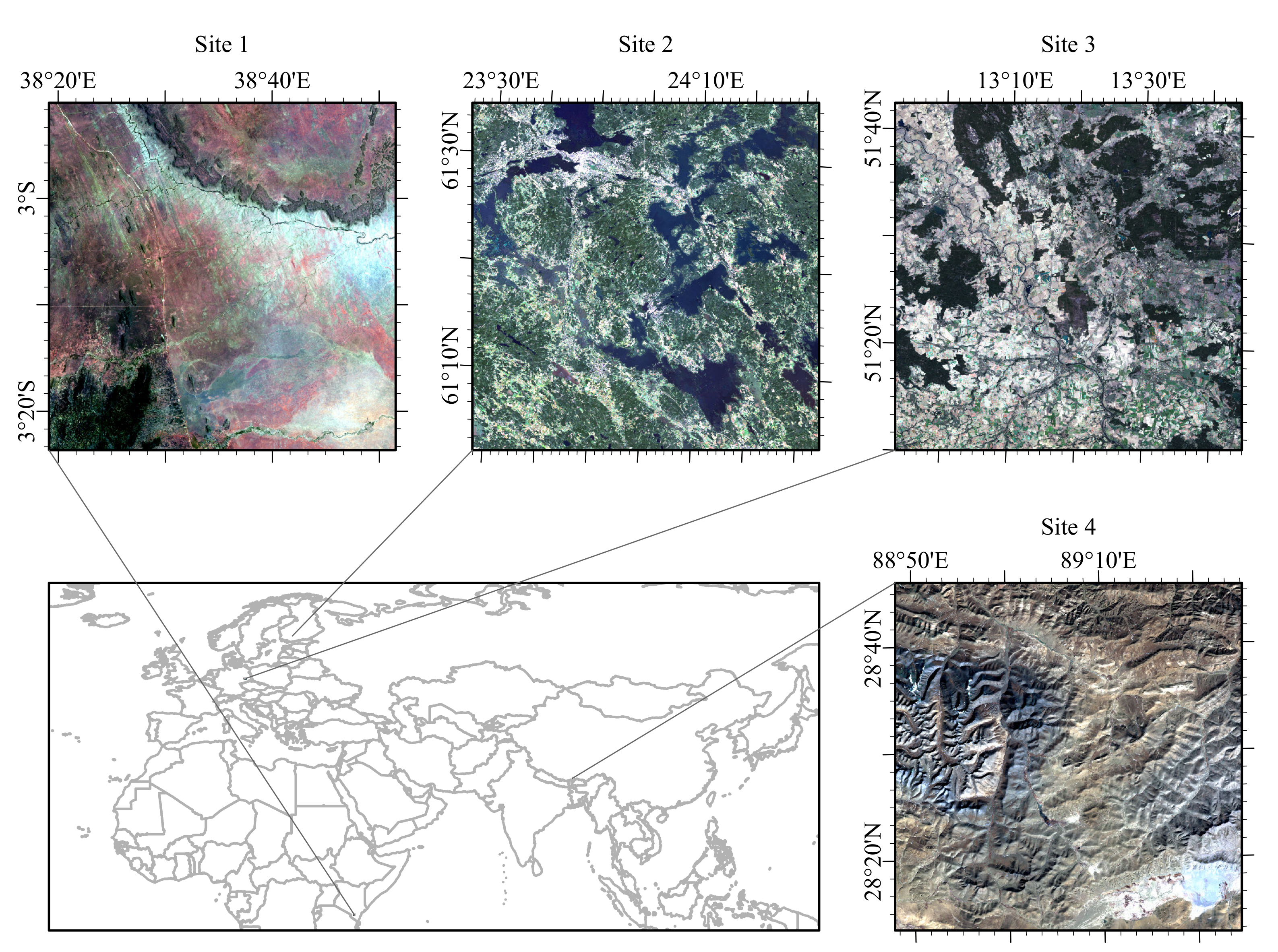
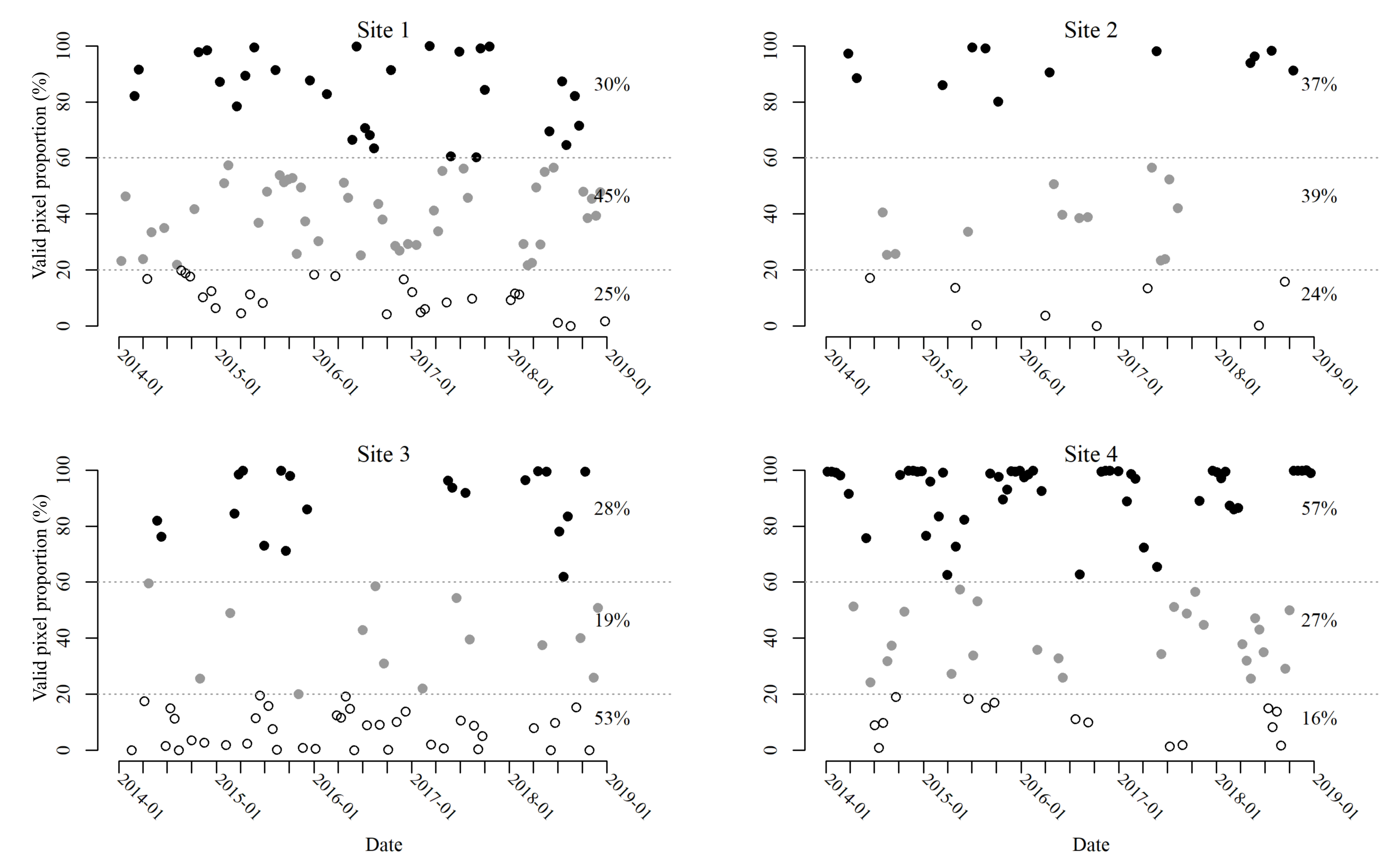
3.1. Study Area
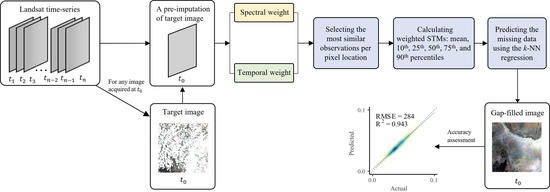
3.2. STIMDR Algorithm
3.2.1. Landsat Time Series and Preprocessing
3.2.2. Spectral and Temporal Information
3.2.3. Selection of the Most Similar Observations Per Pixel Location
3.2.4. Calculation of Weighted STMs
3.2.5. k-NN Regression and Variable Importance
3.3. Accuracy Assessment
3.3.1. Evaluation Metrics
3.3.2. Performance Comparison with Existing Methods
3.3.3. Experiments of Filling Single-Date Images
3.3.4. Experiments of Filling Images in Time Series
3.3.5. Experiments of Gap-Filled Images for LULC Classification Applications
4. Results
4.1. Optimization of the k Value and Importance of Variables
4.2. Results for Filling Single-Date Images
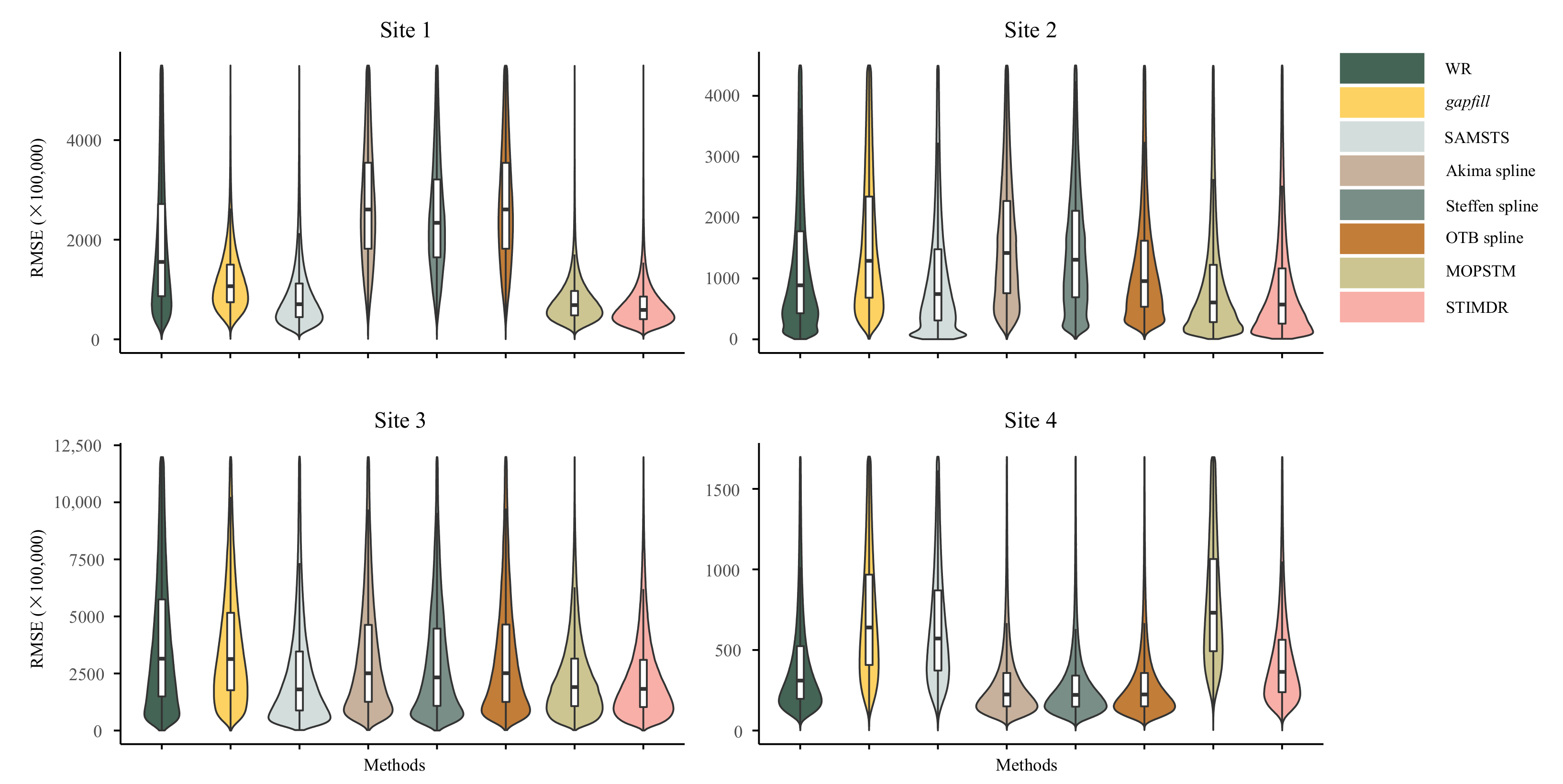
4.2.1. Overall Accuracy
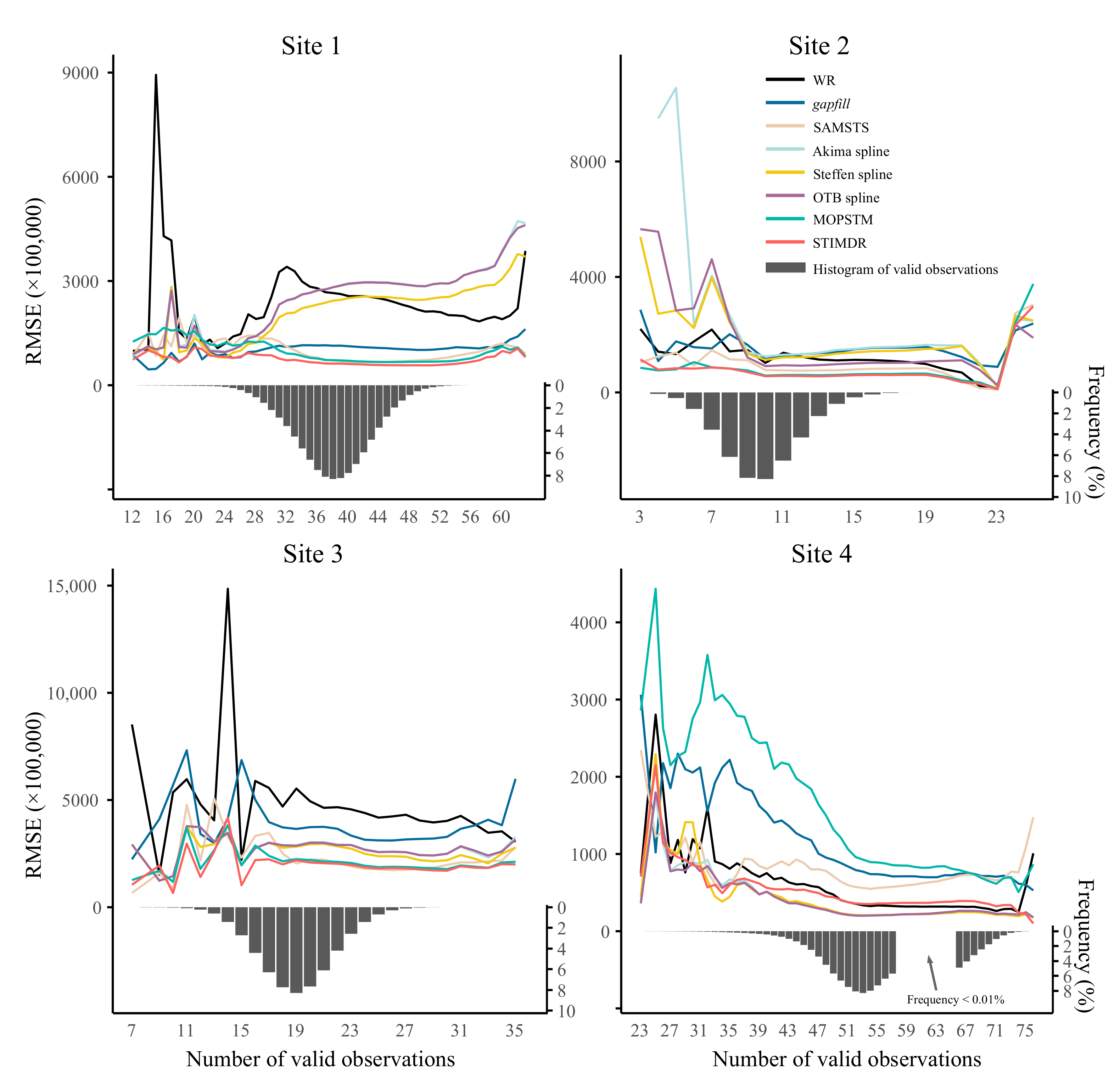
4.2.2. Dependence of the Number of the Observations
4.2.3. Results for Spectral Bands
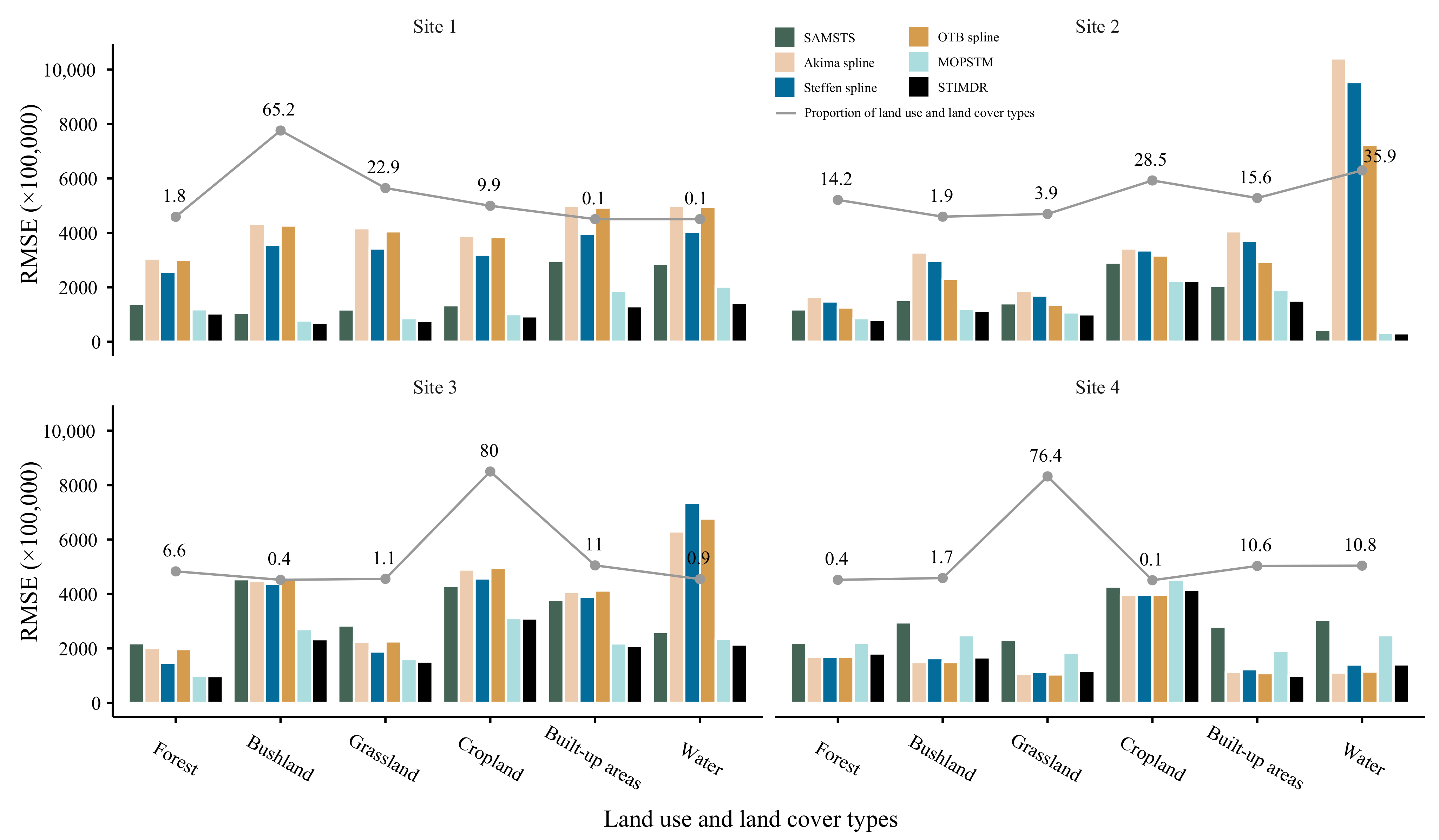
4.2.4. Results for LULC Types
4.3. Results for Filling Images in Time Series
4.4. Results of Gap-Filled Images for LULC Classification Applications
5. Discussion
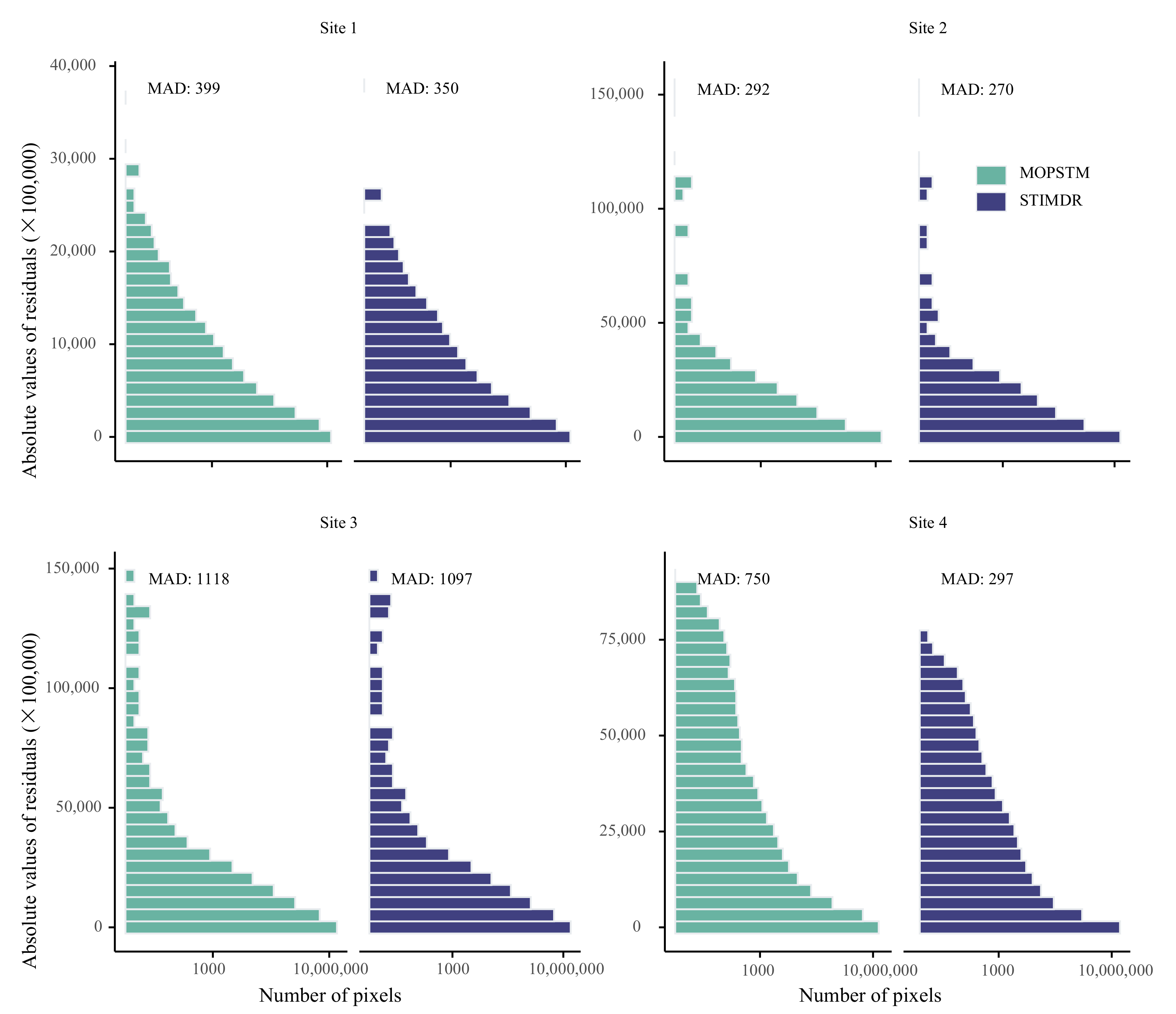
5.1. Comparisons with the Other Gap-Filling Methods
5.2. Computational Efficiency
5.3. Optimizing the User-Defined Parameters in a Global Implementation
5.4. Limitations and Future Work
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Woodcock, C.E.; Loveland, T.R.; Herold, M.; Bauer, M.E. Transitioning from change detection to monitoring with remote sensing: A paradigm shift. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 238, 111558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulder, M.A.; Coops, N.C.; Roy, D.P.; White, J.C.; Hermosilla, T. Land cover 2.0. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 4254–4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, X.; Liu, D.; Chen, J. A new geostatistical approach for filling gaps in Landsat ETM+ SLC-off images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Wulder, M.A.; Roy, D.P.; Woodcock, C.E.; Hansen, M.C.; Radeloff, V.C.; Healey, S.P.; Schaaf, C.; Hostert, P.; Strobl, P.; et al. Benefits of the free and open Landsat data policy. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 224, 382–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Woodcock, C.E.; Seto, K.C.; Lenney, M.P.; Macomber, S.A. Classification and Change Detection Using Landsat TM Data: When and How to Correct Atmospheric Effects? Remote Sens. Environ. 2001, 75, 230–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Woodcock, C.E. Continuous change detection and classification of land cover using all available Landsat data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 144, 152–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Heiskanen, J.; Maeda, E.E.; Pellikka, P.K.E. Burned area detection based on Landsat time series in savannas of southern Burkina Faso. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 64, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clevers, J.G.P.W.; van Leeuwen, H.J.C. Combined use of optical and microwave remote sensing data for crop growth monitoring. Remote Sens. Environ. 1996, 56, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolton, D.K.; Gray, J.M.; Melaas, E.K.; Moon, M.; Eklundh, L.; Friedl, M.A. Continental-scale land surface phenology from harmonized Landsat 8 and Sentinel-2 imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 240, 111685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Roy, D.P. Large-area gap filling of Landsat reflectance time series by spectral-angle-mapper based spatio-temporal similarity (SAMSTS). Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Egorov, A.V.; Roy, D.P.; Zhang, H.K.; Li, Z.; Yan, L.; Huang, H. Landsat 4, 5 and 7 (1982 to 2017) Analysis Ready Data (ARD) observation coverage over the conterminous United States and implications for terrestrial monitoring. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hilker, T.; Lyapustin, A.I.; Tucker, C.J.; Sellers, P.J.; Hall, F.G.; Wang, Y. Remote sensing of tropical ecosystems: Atmospheric correction and cloud masking matter. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 127, 370–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Zhu, X.; Vogelmann, J.E.; Gao, F.; Jin, S. A simple and effective method for filling gaps in Landsat ETM+ SLC-off images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1053–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, E.B.; Wynne, R.H.; Thomas, V.A. Using window regression to gap-fill Landsat ETM+ post SLC-Off data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, C.; Shen, H.; Zhang, L. Recovering missing pixels for Landsat ETM+ SLC-off imagery using multi-temporal regression analysis and a regularization method. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 131, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Gu, Y. Multitemporal Landsat missing data recovery based on tempo-spectral angle model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 3656–3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Li, X.; Cheng, Q.; Zeng, C.; Yang, G.; Li, H.; Zhang, L. Missing Information Reconstruction of Remote Sensing Data: A Technical Review. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2015, 3, 61–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Adhikari, H.; Pellikka, P.K.E.; Heiskanen, J. A method for predicting large-area missing observations in Landsat time series using spectral-temporal metrics. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 99, 102319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballester, C.; Bertalmio, M.; Caselles, V.; Sapiro, G.; Verdera, J. Filling-in by joint interpolation of vector fields and gray levels. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2001, 10, 1200–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, H.; Zhang, L. A MAP-based algorithm for destriping and inpainting of remotely sensed images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 47, 1492–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, W.; Travis, D. Gaps-fill of SLC-off Landsat ETM+ satellite image using a geostatistical approach. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 5103–5122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostopoulou, E. Applicability of ordinary Kriging modeling techniques for filling satellite data gaps in support of coastal management. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2021, 7, 1145–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, M.K.P.; Yuan, Q.; Yan, L.; Sun, J. An adaptive weighted tensor completion method for the recovery of remote sensing images with missing data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 3367–3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yuan, Q.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; Shen, H.; Zhang, L. Thick cloud and cloud shadow removal in multitemporal imagery using progressively spatio-temporal patch group deep learning. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 162, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akima, H. A method of bivariate interpolation and smooth surface fitting for irregularly distributed data points. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. (TOMS) 1978, 4, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akima, H. A new method of interpolation and smooth curve fitting based on local procedures. J. ACM (JACM) 1970, 17, 589–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evenden, G.I. Review of Three Cubic Spline Methods in Graphics Applications; US Department of the Interior, Geological Survey: Washington, DC, USA, 1989.
- Dias, L.A.V.; Nery, C.E. Comparison Between Akima and Beta-Spline Interpolators for Digital Elevation Models. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 1993, 29, 925. [Google Scholar]
- Fassnacht, F.E.; Latifi, H.; Hartig, F. Using synthetic data to evaluate the benefits of large field plots for forest biomass estimation with LiDAR. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 213, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessel, P.; Smith, W.H.F. Free software helps map and display data. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1991, 72, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffen, M. A simple method for monotonic interpolation in one dimension. Astron. Astrophys. 1990, 239, 443. [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann, C.M.; Eon, R.S.; Ambeau, B.; Harms, J.; Badura, G.; Griffo, C. Modeling and intercomparison of field and laboratory hyperspectral goniometer measurements with G-LiHT imagery of the Algodones Dunes. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2017, 12, 012005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, J.D.; Bakos, G.Á. VARTOOLS: A program for analyzing astronomical time-series data. Astron. Comput. 2016, 17, 1–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kempeneers, P. PKTOOLS-Processing Kernel for Geospatial Data; Version 2.6.7.6; Open Source Geospatial Foundation: Beaverton, OR, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- McInerney, D.; Kempeneers, P. Open Source Geospatial Tools—Applications in Earth Observation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Grizonnet, M.; Michel, J.; Poughon, V.; Inglada, J.; Savinaud, M.; Cresson, R. Orfeo ToolBox: Open source processing of remote sensing images. Open Geospat. Data Softw. Stand. 2017, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inglada, J.; Christophe, E. The Orfeo Toolbox remote sensing image processing software. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Cape Town, South Africa, 12–17 July 2009; Volume 4, pp. IV–733. [Google Scholar]
- Inglada, J.; Vincent, A.; Arias, M.; Tardy, B.; Morin, D.; Rodes, I. Operational high resolution land cover map production at the country scale using satellite image time series. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inglada, J. OTB Gapfilling, a Temporal Gapfilling for Image Time Series Library. 2016. Available online: http://tully.ups-tlse.fr/jordi/temporalgapfilling (accessed on 4 February 2016).
- Garioud, A.; Valero, S.; Giordano, S.; Mallet, C. Recurrent-based regression of Sentinel time series for continuous vegetation monitoring. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 263, 112419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, C.; Valero, S.; Inglada, J.; Champion, N.; Dedieu, G. Assessing the robustness of Random Forests to map land cover with high resolution satellite image time series over large areas. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 187, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amatulli, G.; Casalegno, S.; D’Annunzio, R.; Haapanen, R.; Kempeneers, P.; Lindquist, E.; Pekkarinen, A.; Wilson, A.M.; Zurita-Milla, R. Teaching spatiotemporal analysis and efficient data processing in open source environment. In Proceedings of the 3rd Open Source Geospatial Research & Education Symposium, Helsinki, Finland, 10–13 June 2014; p. 13. [Google Scholar]
- Siabi, N.; Sanaeinejad, S.H.; Ghahraman, B. Comprehensive evaluation of a spatio-temporal gap filling algorithm: Using remotely sensed precipitation, LST and ET data. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 261, 110228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarafanov, M.; Kazakov, E.; Nikitin, N.O.; Kalyuzhnaya, A.V. A Machine Learning Approach for Remote Sensing Data Gap-Filling with Open-Source Implementation: An Example Regarding Land Surface Temperature, Surface Albedo and NDVI. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, J.C.; Epiphanio, J.C.N.; Rennó, C.D. Window regression: A spatial-temporal analysis to estimate pixels classified as low-quality in MODIS NDVI time series. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 3123–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mondal, S.; Jeganathan, C.; Amarnath, G.; Pani, P. Time-series cloud noise mapping and reduction algorithm for improved vegetation and drought monitoring. GISci. Remote Sens. 2017, 54, 202–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, F.; de Jong, R.; Schaepman, M.E.; Schaepman-Strub, G.; Furrer, R. Predicting missing values in spatio-temporal remote sensing data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 2841–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Asrar, G.R.; Zhu, Z. Creating a seamless 1 km resolution daily land surface temperature dataset for urban and surrounding areas in the conterminous United States. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 206, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Roy, D.P. Spatially and temporally complete Landsat reflectance time series modelling: The fill-and-fit approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 241, 111718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Adhikari, H.; Pellikka, P.K.; Heiskanen, J. Producing a Gap-free Landsat Time Series for the Taita Hills, Southeastern Kenya. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2020-2020 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 26 September–2 October 2020; pp. 1319–1322. [Google Scholar]
- Das, M.; Ghosh, S.K. A deep-learning-based forecasting ensemble to predict missing data for remote sensing analysis. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 5228–5236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yuan, Q.; Zeng, C.; Li, X.; Wei, Y. Missing data reconstruction in remote sensing image with a unified spatial–temporal–spectral deep convolutional neural network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 4274–4288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foga, S.; Scaramuzza, P.L.; Guo, S.; Zhu, Z.; Dilley, R.D., Jr.; Beckmann, T.; Schmidt, G.L.; Dwyer, J.L.; Hughes, M.J.; Laue, B. Cloud detection algorithm comparison and validation for operational Landsat data products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 194, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiu, S.; Lin, Y.; Shang, R.; Zhang, J.; Ma, L.; Zhu, Z. Making Landsat time series consistent: Evaluating and improving Landsat analysis ready data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atto, A.; Bovolo, F.; Bruzzone, L. Change Detection and Image Time-Series Analysis 2: Supervised Methods; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Shen, H.; Cheng, Q.; Liu, Y.; You, S.; He, Z. Deep learning based cloud detection for medium and high resolution remote sensing images of different sensors. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 150, 197–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Irish, R.R. Landsat 7 automatic cloud cover assessment. Algorithms for Multispectral, Hyperspectral, and Ultraspectral Imagery VI. In Proceedings of the International Society for Optics and Photonics, Orlando, FL, USA, 24–26 April 2000; Volume 4049, pp. 348–355. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.; Woodcock, C.E. Automated cloud, cloud shadow, and snow detection in multitemporal Landsat data: An algorithm designed specifically for monitoring land cover change. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 152, 217–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navruz, G.; Özdemir, A.F. A new quantile estimator with weights based on a subsampling approach. Br. J. Math. Stat. Psychol. 2020, 73, 506–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höhle, J.; Höhle, M. Accuracy assessment of digital elevation models by means of robust statistical methods. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2009, 64, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hyndman, R.J.; Fan, Y. Sample quantiles in statistical packages. Am. Stat. 1996, 50, 361–365. [Google Scholar]
- Beygelzimer, A.; Kakadet, S.; Langford, J.; Arya, S.; Mount, D.; Li, S.; Li, M.S. Package ‘FNN’. 2015, Volume 1. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/FNN/FNN.pdf (accessed on 16 February 2019).
- Team, R.C. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing: R Foundation for Statistical Computing. 2013. Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 25 September 2013).
- Kuhn, M. A Short Introduction to the caret Package: R Foundation for Statistical Computing. 2015, Volume 1. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/caret/vignettes/caret.html (accessed on 6 August 2015).
- Yan, L.; Roy, D.P. SAMSTS Satellite Time Series Gap Filling Source Codes-Landsat; South Dakota State University: Brookings, SD, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Rousseeuw, P.J.; Croux, C. Alternatives to the median absolute deviation. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1993, 88, 1273–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leys, C.; Ley, C.; Klein, O.; Bernard, P.; Licata, L. Detecting outliers: Do not use standard deviation around the mean, use absolute deviation around the median. J. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 2013, 49, 764–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosner, B.; Glynn, R.J.; Ting Lee, M.L. Incorporation of clustering effects for the Wilcoxon rank sum test: A large-sample approach. Biometrics 2003, 59, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridge, P.D.; Sawilowsky, S.S. Increasing physicians’ awareness of the impact of statistics on research outcomes: Comparative power of the t-test and Wilcoxon rank-sum test in small samples applied research. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1999, 52, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, M. Random forest classifier for remote sensing classification. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgiu, M.; Drăguţ, L. Random forest in remote sensing: A review of applications and future directions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 114, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congalton, R.G. A review of assessing the accuracy of classifications of remotely sensed data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1991, 37, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.; Mariethoz, G.; McCabe, M.F. Gap-filling of landsat 7 imagery using the direct sampling method. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pipia, L.; Amin, E.; Belda, S.; Salinero-Delgado, M.; Verrelst, J. Green LAI Mapping and Cloud Gap-Filling Using Gaussian Process Regression in Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhu, X.; Li, N.; Pan, Y. Gap-Filling of a MODIS Normalized Difference Snow Index Product Based on the Similar Pixel Selecting Algorithm: A Case Study on the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kandasamy, S.; Baret, F.; Verger, A.; Neveux, P.; Weiss, M. A comparison of methods for smoothing and gap filling time series of remote sensing observations; application to MODIS LAI products. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 4055–4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moreno-Martínez, Á.; Izquierdo-Verdiguier, E.; Maneta, M.P.; Camps-Valls, G.; Robinson, N.; Muñoz-Marí, J.; Sedano, F.; Clinton, N.; Running, S.W. Multispectral high resolution sensor fusion for smoothing and gap-filling in the cloud. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 247, 111901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, D.M. The problem of overfitting. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2004, 44, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Liang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Du, B. Spectral-Spatial Weighted Kernel Manifold Embedded Distribution Alignment for Remote Sensing Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2020, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.G. Smoothing Filter-based Intensity Modulation: A spectral preserve image fusion technique for improving spatial details. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2000, 21, 3461–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foody, G.M. Geographical weighting as a further refinement to regression modelling: An example focused on the NDVI–rainfall relationship. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 88, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J. An Improved Adaptive Intensity–Hue–Saturation Method for the Fusion of Remote Sensing Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 985–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.G.; Tang, P. Improving time series anomaly detection based on exponentially weighted moving average (EWMA) of season-trend model residuals. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Beijing, China, 10–15 July 2016; pp. 3414–3417. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Qu, J.; Dong, W.; Zheng, Y. Hyperspectral pansharpening via improved PCA approach and optimal weighted fusion strategy. Neurocomputing 2018, 315, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witten, I.H.; Frank, E.; Hall, M.A.; Pal, C.; DATA, M. Practical machine learning tools and techniques. Data Min. 2005, 2, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Hechenbichler, K.; Schliep, K. Weighted k-nearest-neighbor techniques and ordinal classification. Int. J. Chem. Mol. Eng. 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schliep, K.; Hechenbichler, K.; Schliep, M.K. Package ‘kknn’. 2016. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/kknn/kknn.pdf (accessed on 29 August 2016).
- Michie, D.; Spiegelhalter, D.J.; Taylor, C.C. Machine Learning, Neural and Statistical Classification; Ellis Horwood: Chichester, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Pyle, D. Data Preparation for Data Mining; Morgan Kaufmann: Burlington, MA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]


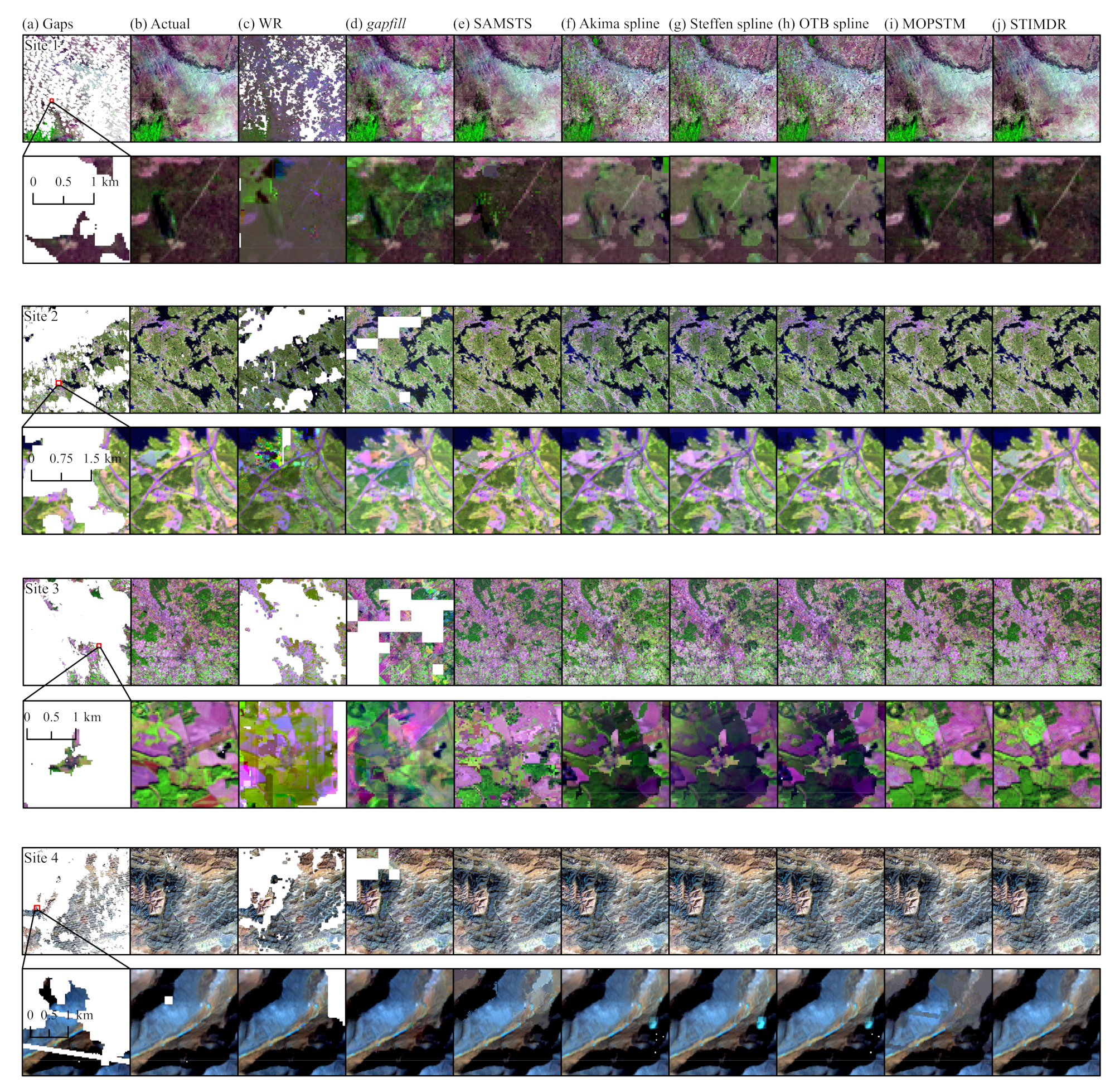

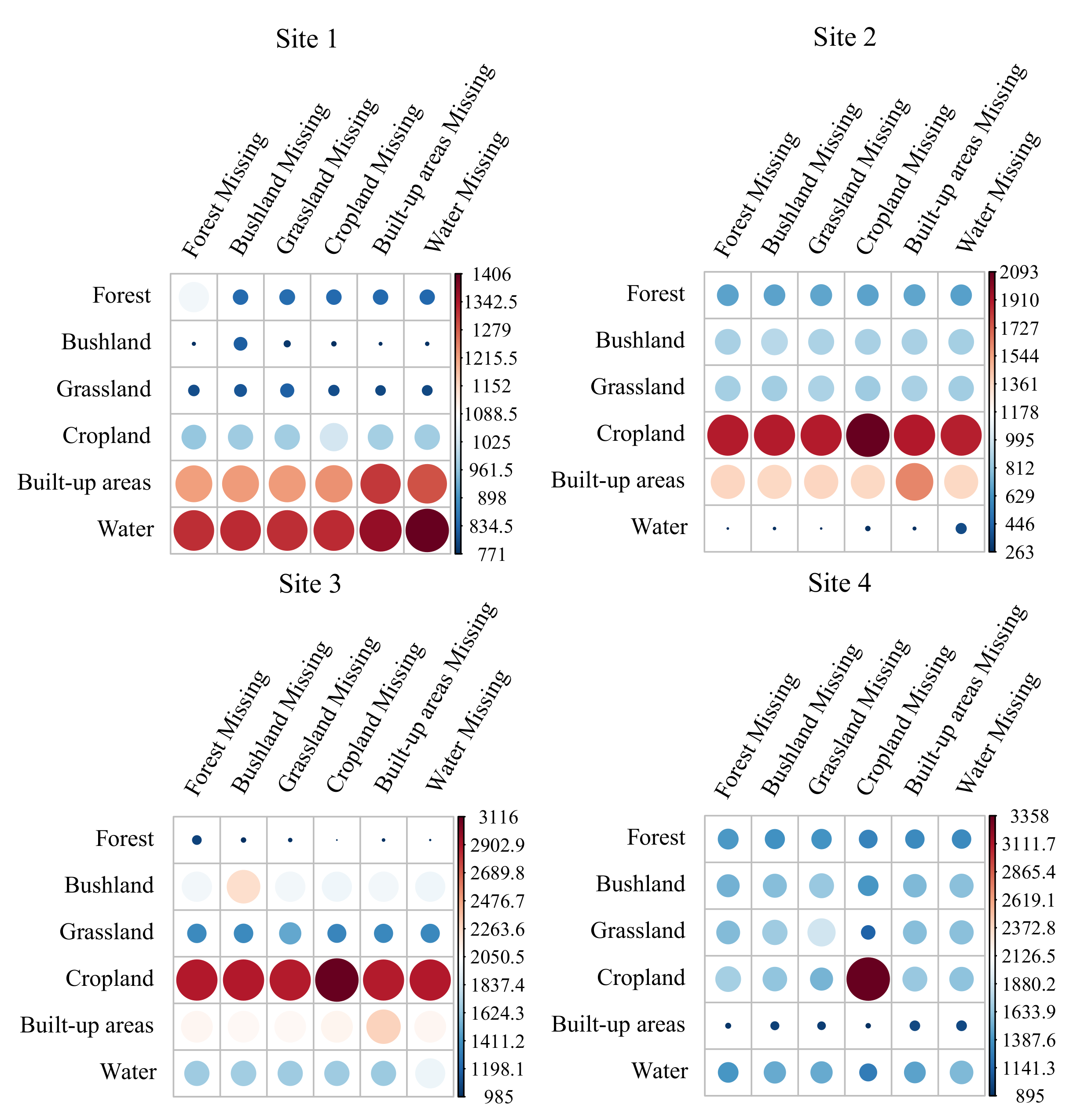
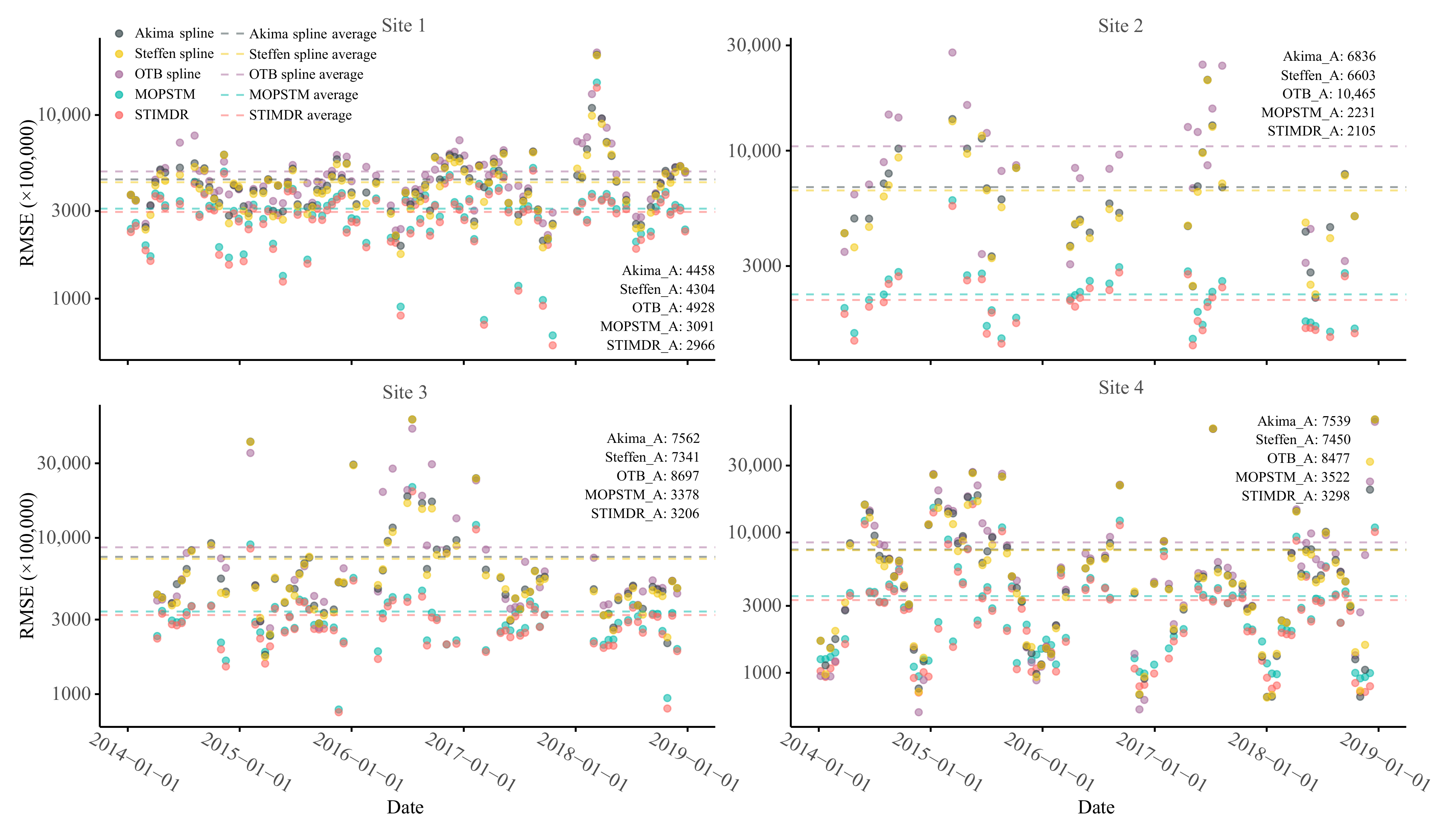
| Method | Type | Details | Limitation | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Akima spline | Temporal | Spline models | Single noise-like (e.g., cloud-contaminated pixels) observations can result in large changes in the interpolation curve [31]. | [25] |
| Steffen spline | Temporal | Spline models | Steffen spline may have issues recovering peak and trough values by interpolating monotonic curves between each interval. | [31] |
| OTB spline | Temporal | Linear and spline models in Orfeo Toolbox | OTB spline has the same limitations that Akima spline method has. | [36,39] |
| WR | Hybrid | Window regression | WR has difficulties in recovering pixels that have heterogeneous land cover in the neighborhood, especially for coarser spatial resolution analysis [46]. In addition, it is inefficient to reconstruct large-area gaps. | [14,45] |
| gapfill | Hybrid | Quantitle regression fitted to spatio-temporal subsets | gapfill may recover large-area gaps, but its efficiency decreases as the number of gap-filling routine repeats increases due to the large size of gaps [48]. | [47] |
| SAMSTS | Hybrid | Spectral-Angle-Mapper based Spatio-Temporal Similarity | The segmentation process involved in SAMSTS can produce unwanted values [18]. | [10] |
| MOPSTM | Hybrid | Missing Observation Prediction based on Spectral-Temporal Metrics | MOPSTM may be sensitive to the time period due to the lack of mechanics that exclude dissimilar data in time series (e.g., different phenology or changes in land cover). | [18] |
| Site | Location | Path and Row | Sensor | Number of Bands | Area (km) | Spatial Resolution (m) | Number of Images Collected |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 2 3 4 | Taita Taveta, Kenya Pirkanmaa, Finland Brandenburg, Germany Tibet, China | 167, 62 189, 17 193, 24 139, 40 | OLI | 8 | 3600 | 30 | 99 33 72 92 |
| Site 1 | Site 2 | Site 3 | Site 4 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full | Partial | Full | Partial | Full | Partial | Full | Partial | ||
| Filled pixel proportion (%) | 62.7 | 41.4 | 60.7 | 22.4 | 84.7 | 13.4 | 73.6 | 34.8 | |
| RMSE (×100,000) | WR | 77,816 | 11,105 | 106,531 | 1177 | ||||
| gapfill | 1325 | 1204 | 2364 | 4949 | 1355 | ||||
| SAMSTS | 1135 | 1081 | 1715 | 1715 | 3830 | 3395 | 2349 | 1390 | |
| Akima spline | 4231 | 4231 | 5685 | 4769 | 4343 | 4342 | 1114 | 625 | |
| Steffen spline | 3477 | 3534 | 5182 | 4379 | 4053 | 3945 | 1247 | 700 | |
| OTB spline | 4182 | 4206 | 4107 | 3530 | 4367 | 4357 | 1115 | 625 | |
| MOPSTM | 838 | 831 | 1358 | 1381 | 2664 | 2687 | 1927 | 1395 | |
| STIMDR | 748 | 738 | 1275 | 1331 | 2655 | 2673 | 1203 | 715 | |
| (0.2) | (0.3) | (0.5) | (0.4) | (0.3) | (0.5) | (3.2) | (0.3) | ||
| WR | 0.003 | 0.086 | 0.003 | 0.946 | |||||
| gapfill | 0.836 | 0.863 | 0.614 | 0.361 | 0.938 | ||||
| SAMSTS | 0.851 | 0.868 | 0.753 | 0.741 | 0.557 | 0.628 | 0.827 | 0.935 | |
| Akima spline | 0.367 | 0.379 | 0.536 | 0.524 | 0.520 | 0.495 | 0.958 | 0.983 | |
| Steffen spline | 0.454 | 0.462 | 0.581 | 0.574 | 0.560 | 0.554 | 0.944 | 0.977 | |
| OTB spline | 0.370 | 0.381 | 0.611 | 0.594 | 0.518 | 0.494 | 0.958 | 0.983 | |
| MOPSTM | 0.920 | 0.923 | 0.829 | 0.815 | 0.760 | 0.749 | 0.888 | 0.936 | |
| STIMDR | 0.934 | 0.938 | 0.861 | 0.839 | 0.764 | 0.753 | 0.952 | 0.980 | |
| (<0.001) | (<0.001) | (<0.001) | (<0.001) | (<0.001) | (<0.001) | (<0.001) | (<0.001) | ||
| Producer’s Accuracy (%) | User’s Accuracy (%) | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site | Class | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) |
| forest | 25.6 | 20.2 | 22.5 | 20.3 | 20.2 | 21.5 | 26.7 | 43.2 | 48.3 | 49.4 | 48.2 | 54.2 | 55.1 | 49.9 | |
| bushland | 89.2 | 92.7 | 92.3 | 92.6 | 93.3 | 92.7 | 92.2 | 72.3 | 70.1 | 70.7 | 70.1 | 71.2 | 71.8 | 72.5 | |
| grassland | 22.2 | 13.9 | 15.7 | 14.1 | 17.2 | 19.2 | 21.7 | 41.8 | 39.2 | 40.5 | 38.9 | 42.2 | 43.6 | 46.0 | |
| 1 | cropland | 15.4 | 7.9 | 9.1 | 7.9 | 9.0 | 12.1 | 14.1 | 31.9 | 24.6 | 26.4 | 25.1 | 34.4 | 37.1 | 37.6 |
| built-up areas | 11.3 | 5.0 | 6.6 | 4.9 | 7.9 | 9.2 | 9.3 | 3.9 | 8.5 | 10.2 | 8.2 | 8.0 | 8.8 | 6.9 | |
| water | 15.5 | 19.9 | 21.2 | 19.1 | 17.3 | 19.4 | 21.9 | 8.1 | 11.9 | 11.5 | 11.5 | 13.5 | 12.2 | 11.5 | |
| Overall accuracy (%) | 66.4 | 66.1 | 66.4 | 66.1 | 67.4 | 67.7 | 68.2 | ||||||||
| forest | 87.9 | 87.5 | 87.7 | 87.6 | 89.6 | 90.1 | 88.6 | 73.0 | 72.8 | 73.9 | 73.7 | 73.8 | 73.8 | 73.9 | |
| bushland | 2.9 | 2.3 | 2.5 | 2.8 | 2.3 | 2.4 | 2.5 | 16.0 | 20.6 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 19.9 | 21.4 | 19.7 | |
| grassland | 2.3 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.0 | 0.3 | 0.6 | 1.2 | 19.6 | 16.6 | 17.9 | 17.8 | 15.8 | 17.4 | 18.4 | |
| 2 | cropland | 64.3 | 63.2 | 65.3 | 65.5 | 68.4 | 67.9 | 66.0 | 64.2 | 62.0 | 63.0 | 63.2 | 68.2 | 68.1 | 66.5 |
| built-up areas | 40.9 | 39.9 | 40.9 | 42.1 | 44.5 | 43.3 | 47.3 | 55.7 | 54.1 | 54.6 | 57.2 | 61.0 | 61.6 | 58.9 | |
| water | 93.0 | 93.7 | 94.3 | 94.2 | 94.1 | 94.3 | 93.7 | 90.5 | 90.6 | 90.3 | 90.2 | 90.5 | 90.4 | 91.3 | |
| Overall accuracy (%) | 72.8 | 72.4 | 73.1 | 73.2 | 74.9 | 74.9 | 74.3 | ||||||||
| forest | 85.2 | 85.7 | 87.2 | 85.6 | 88.8 | 90.0 | 89.8 | 84.4 | 83.8 | 85.1 | 83.9 | 85.4 | 85.5 | 87.0 | |
| bushland | 2.7 | 0.6 | 1.1 | 0.6 | 3.4 | 1.5 | 2.4 | 15.5 | 31.7 | 27.7 | 27.8 | 16.6 | 20.2 | 24.9 | |
| grassland | 13.5 | 9.4 | 11.4 | 8.9 | 17.6 | 16.0 | 14.9 | 38.9 | 56.1 | 55.9 | 53.3 | 39.8 | 47.5 | 49.8 | |
| 3 | cropland | 93.6 | 94.2 | 94.8 | 94.3 | 93.6 | 94.0 | 94.6 | 87.4 | 85.8 | 86.5 | 85.7 | 89.8 | 89.8 | 90.0 |
| built-up areas | 26.7 | 13.8 | 15.2 | 12.7 | 37.1 | 35.9 | 36.3 | 50.3 | 47.6 | 52.1 | 47.1 | 55.2 | 58.2 | 57.3 | |
| water | 64.9 | 68.5 | 69.8 | 67.5 | 61.2 | 67.0 | 70.9 | 62.2 | 63.2 | 66.3 | 61.7 | 58.2 | 62.3 | 70.6 | |
| Overall accuracy (%) | 84.8 | 84.3 | 85.2 | 84.2 | 86.4 | 86.9 | 87.4 | ||||||||
| forest | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 17.1 | 7.7 | 7.0 | 9.2 | 17.1 | 2.3 | 16.8 | |
| bushland | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 6.9 | 7.3 | 8.5 | 6.7 | 6.9 | 8.2 | 8.5 | |
| grassland | 98.0 | 97.7 | 97.6 | 97.6 | 98.0 | 97.7 | 97.6 | 85.5 | 85.8 | 85.8 | 85.8 | 85.5 | 85.7 | 85.7 | |
| 4 | cropland | 4.1 | 2.1 | 3.8 | 3.8 | 4.1 | 2.1 | 3.6 | 4.9 | 6.0 | 6.2 | 5.0 | 4.9 | 6.0 | 5.4 |
| built-up areas | 23.1 | 24.8 | 25.3 | 25.4 | 23.1 | 24.8 | 24.8 | 44.4 | 43.0 | 43.1 | 42.9 | 44.4 | 42.0 | 42.7 | |
| water | 10.4 | 10.6 | 11.6 | 11.3 | 10.4 | 10.6 | 11.4 | 38.6 | 38.0 | 38.1 | 38.2 | 38.6 | 38.3 | 37.7 | |
| Overall accuracy (%) | 83.1 | 83.0 | 83.0 | 83.0 | 83.1 | 83.0 | 83.0 | ||||||||
| Method | Language | Size in Pixels | CPU Cores a | RAM Used per Core | Estimated Running Time per Core |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WR | R | 500 × 500 | 1344 | 1.2 GB | 10 h |
| gapfill | R, C++ | 200 × 200 | 8400 | 3 GB | 20 h (max 40 h) |
| SAMSTS | C | 2000 × 2000 | 1 | 15 GB | 8 h |
| Akima spline | C++ | 2000 × 2000 | 7 | 2.8 GB | 0.5 h |
| Steffen spline | C++ | 2000 × 2000 | 7 | 2.8 GB | 0.5 h |
| OTB spline | C++, Python | 2000 × 2000 | 6 | 2.5 GB | 0.6 h |
| MOPSTM | R | 2000 × 2000 | 7 | 40 GB | 1.8 h |
| STIMDR | R | 500 × 500 b | 112 | 12 GB | 0.2 h |
| 2000 × 2000 c | 7 | 40 GB | 1.8 h |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, Z.; Amatulli, G.; Pellikka, P.K.E.; Heiskanen, J. Spectral Temporal Information for Missing Data Reconstruction (STIMDR) of Landsat Reflectance Time Series. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14010172
Tang Z, Amatulli G, Pellikka PKE, Heiskanen J. Spectral Temporal Information for Missing Data Reconstruction (STIMDR) of Landsat Reflectance Time Series. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(1):172. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14010172
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Zhipeng, Giuseppe Amatulli, Petri K. E. Pellikka, and Janne Heiskanen. 2022. "Spectral Temporal Information for Missing Data Reconstruction (STIMDR) of Landsat Reflectance Time Series" Remote Sensing 14, no. 1: 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14010172
APA StyleTang, Z., Amatulli, G., Pellikka, P. K. E., & Heiskanen, J. (2022). Spectral Temporal Information for Missing Data Reconstruction (STIMDR) of Landsat Reflectance Time Series. Remote Sensing, 14(1), 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14010172