Optimal Order of Time-Domain Adaptive Filter for Anti-Jamming Navigation Receiver
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Mathematics Model
2.1. Navigation Receiver Model
2.2. Time Domain Adaptive Anti-Jamming Filter Model
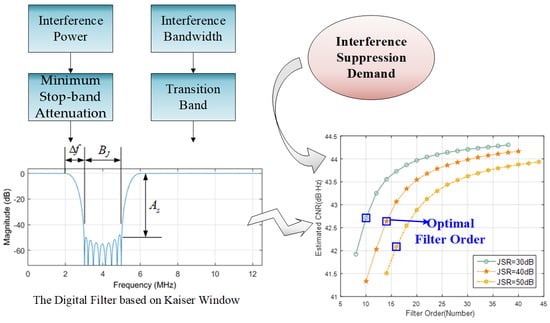
3. Analysis of Filter Order
4. Optimal Filter Order
4.1. Demand Analysis of Anti-Jamming Filter
4.2. Design of Optimal Filter
5. Experimental and Analysis
5.1. Simulation and Analysis
5.2. Measured Data Analysis
- Scene 1.
- Set interference bandwidth to 2 MHz, and JSR to approximately 50 dB.
- Scene 2.
- Set interference bandwidth to 2 MHz, and JSR to approximately 40 dB.
- Scene 3.
- Set interference bandwidth to 1 MHz, and JSR to approximately 50 dB.
- Scene 4.
- Set interference bandwidth to 1 MHz, and JSR to approximately 40 dB.
- Scene 5.
- Set interference to be single-frequency interference, and JSR to approximately 50 dB.
- Scene 6.
- Set interference to be single-frequency interference, and JSR to approximately 40 dB.
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- A higher power interference scenery requires a larger optimal filter order to meet the time-domain adaptive anti-jamming requirements.
- (2)
- A more expansive bandwidth interference scenery requires a larger optimal filter order to meet the time-domain adaptive anti-jamming requirements.
- (3)
- The time-domain adaptive filter can meet navigation receivers’ 3 dB·Hz anti-jamming requirement in simulations and 8 dB·Hz requirement in practical tests with the optimal filter order.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Y.-H.; Juang, J.-C.; Seo, J.; Lo, S.; Akos, D.M.; De Lorenzo, D.S.; Enge, P. Design and Implementation of Real-Time Software Radio for Anti-Interference GPS/WAAS Sensors. Sensors 2012, 12, 13417–13440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Cui, X.; Xu, H.; Lu, M. A Two-Stage Interference Suppression Scheme Based on Antenna Array for GNSS Jamming and Spoofing. Sensors 2019, 19, 3870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, Z.; Nie, J.; Wan, Y.; Ou, G. Optimal reference element for interference suppression in GNSS antenna arrays under channel mismatch. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2017, 11, 1161–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Tu, R.; Zhang, R.; Gao, Y.; Cai, H. Combining GPS, BeiDou, and Galileo Satellite Systems for Time and Frequency Transfer Based on Carrier Phase Observations. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loh-Ming, L.; Milstein, L. Rejection of Narrow-Band Interference in PN Spread-Spectrum Systems Using Transversal Filters. IEEE Trans. Commun. 1982, 30, 925–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Jia, Y.; Fu, S.; Cao, Z.; Chen, P. Adaptive Narrowband Antijam Method for Satellite Navigation. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Electromagnetics in Advanced Applications (ICEAA), Cartagena De Indias, Colombia, 10–14 September 2018; pp. 687–690. [Google Scholar]
- Chia-Lung, C.; Fan-Ren, C.; Kun-Yuan, T. Highly accurate real-time GPS carrier phase-disciplined oscillator. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2005, 54, 819–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kubo, N.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, H. Initial Positioning Assessment of BDS New Satellites and New Signals. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.; Zhou, B.; Wang, L.; Wei, Q.; Ji, F.; Zhang, R. Performance and Evaluation of GNSS Receiver Vector Tracking Loop Based on Adaptive Cascade Filter. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Cowan, C.F.N. A novel variable tap-length algorithm for linear adaptive filters. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Montreal, QC, Canada, 17–21 May 2004; p. ii-825. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z.; Chen, F.; Xie, Y.; Liu, Z. Impact on Anti-jamming Performance of GNSS Signal Bandwidth under Channel Mismatch Used Antenna Arrays. In Proceedings of the 2020 5th International Conference on Computer and Communication Systems (ICCCS), Shanghai, China, 15–18 May 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Xing, W.; Fang, C.; Huang, P.; Tan, W.; Gao, Z. RFI Suppression for SAR Systems Based on Removed Spectrum Iterative Adaptive Approach. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Zheng, H.; Wu, X.; Yue, X.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Q. Fractional Fourier Transform-Based Radio Frequency Interference Suppression for High-Frequency Surface Wave Radar. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, H.; Hu, Y.; Sun, H.; Feng, W. A BDS Interference Suppression Technique Based on Linear Phase Adaptive IIR Notch Filters. Sensors 2018, 18, 1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Widrow, B.; McCool, J.M.; Larimore, M.G.; Johnson, C.R. Stationary and nonstationary learning characteristics of the LMS adaptive filter. Proc. IEEE 1976, 64, 1151–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chern, S.; Sun, C. Linearly constrained RLS algorithm with variable forgetting factor for DS-CDMA system. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Symposium on Intelligent Signal Processing and Communication Systems (ISPACS), Kuching, Sarawak, Malaysia, 1–4 December 2014; pp. 261–264. [Google Scholar]
- Lee-Min, L.; Hsiao-Chuan, W. An extended Levinson-Durbin algorithm for the analysis of noisy autoregressive process. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 1996, 3, 13–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burg, J.P. Maximum Entropy Spectral Analysis; Stanford University: Stanford, CA, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Vijayan, R.; Poor, H.V. Nonlinear techniques for interference suppression in spread-spectrum systems. IEEE Trans. Commun. 1990, 38, 1060–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, Z.; He, H.; Haisong, J.; Qingliang, C.; Qing, G.; Feng, L.; Li, S. Research on Anti-jamming algorithm and performance of array antenna. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE CSAA Guidance, Navigation and Control Conference (CGNCC), Nanjing, China, 10–12 August 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Yuantao, G.; Kun, T.; Huijuan, C. LMS algorithm with gradient descent filter length. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2004, 11, 305–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riera-Palou, F.; Noras, J.M.; Cruickshank, D.G.M. Linear equalisers with dynamic and automatic length selection. Electron. Lett. 2001, 37, 1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Cowan, C.F.N. An LMS style variable tap-length algorithm for structure adaptation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2005, 53, 2400–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, Y.; Yan, Z. Variable Tap-Length LMS Algorithm with Adaptive Step Size. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2017, 36, 2815–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.T.; Ahmed, S. A robust normalized variable tap-length normalized fractional LMS algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 59th International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (MWSCAS), Monterey, CA, USA, 16–19 October 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Nie, J.; Li, B.; Wang, F. Distortionless space-time adaptive processor for global navigation satellite system receiver. Electron. Lett. 2015, 51, 2138–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Fang, R.; Geng, T.; Wang, G.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, J. Characterization of GNSS Signals Tracked by the iGMAS Network Considering Recent BDS-3 Satellites. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, Z.; Nie, J.; Chen, F.; Chen, H.; Ou, G. Adaptive Time Taps of STAP Under Channel Mismatch for GNSS Antenna Arrays. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2017, 66, 2813–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamalis, P.D.; Kanatas, A.G.; Constantinou, P. A Genetic Algorithm Applied for Optimization of Antenna Arrays Used in Mobile Radio Channel Characterization Devices. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2009, 58, 2475–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Lu, X.; Wang, R. Novel narrowband jamming suppression algorithm in communication system. In Proceedings of the 2017 7th IEEE International Conference on Electronics Information and Emergency Communication (ICEIEC), Barcelona, Spain, 21–23 July 2017; pp. 95–100. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Liu, Y.; Guo, J.; Song, W.; Zhang, P.; Wu, J.; Zhang, D. Precise Orbit Determination of BeiDou Satellites with Contributions from Chinese National Continuous Operating Reference Stations. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, Z.; Chen, H.; Chen, F.; Nie, J.; Ou, G. Blind adaptive channel mismatch equalisation method for GNSS antenna arrays. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2018, 12, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Chen, F.; Xie, Y.; Sun, Y.; Cai, H. High Precision Pseudo-Range Measurement in GNSS Anti-jamming Antenna Array Processing. Electronics 2020, 9, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shanmugam, Y.; Subbiya, A.; Sudhakar, M.; Harsha Visali, D. Design of FIR Filter Using Adaptive LMS Algorithm for Energy Efficient Application. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1916, 012067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saramaki, T. A class of window functions with nearly minimum sidelobe energy for designing FIR filters. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Monterey, CA, USA, 8–11 May 1989; Volume 351, pp. 359–362. [Google Scholar]
- Andria, G.; Savino, M.; Trotta, A. Windows and interpolation algorithms to improve electrical measurement accuracy. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 1989, 38, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, J. Nonrecursive digital filter design using the I-sinh window function. Proc. IEEE 1977, 1, 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser, J.; Schafer, R. On the use of the I0-sinh window for spectrum analysis. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1980, 28, 105–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, N.A.; Maybeck, P.S.; DeVilbiss, S.L. Detection of interference/jamming and spoofing in a DGPS-aided inertial system. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1998, 34, 1208–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Zhao, Z.; Tang, J.; He, F.; Li, Y.; Xiao, H. Performance Analysis and Optimal Design of the Adaptive Interference Cancellation System. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2013, 55, 1068–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, N.I.; Lee, S.U. On the adaptive lattice notch filter for the detection of sinusoids. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Analog Digit. Signal Process. 1993, 40, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Yu, B.; Elhajj, M.; Ochieng, W.Y.; Zhang, T.; Yang, J. A Novel GNSS Interference Detection Method Based on Smoothed Pseudo-Wigner–Hough Transform. Sensors 2021, 21, 4306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Zhang, T. A New GNSS Interference Detection Method Based on Rearranged Wavelet–Hough Transform. Sensors 2021, 21, 1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]











| Interference Suppression | JSR (dB) | Optimal Filter Order | CNR loss (dB·Hz) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-frequency | 40 | 31 | 2.907 |
| 50 | 41 | 3.503 | |
| 1 MHz | 40 | 35 | 2.726 |
| 50 | 47 | 4.839 | |
| 2 MHz | 40 | 45 | 3.571 |
| 50 | 59 | 6.198 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, J.; Lu, Z.; Xiao, Z.; Li, B.; Sun, G. Optimal Order of Time-Domain Adaptive Filter for Anti-Jamming Navigation Receiver. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14010048
Song J, Lu Z, Xiao Z, Li B, Sun G. Optimal Order of Time-Domain Adaptive Filter for Anti-Jamming Navigation Receiver. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(1):48. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14010048
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Jie, Zukun Lu, Zhibin Xiao, Baiyu Li, and Guangfu Sun. 2022. "Optimal Order of Time-Domain Adaptive Filter for Anti-Jamming Navigation Receiver" Remote Sensing 14, no. 1: 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14010048
APA StyleSong, J., Lu, Z., Xiao, Z., Li, B., & Sun, G. (2022). Optimal Order of Time-Domain Adaptive Filter for Anti-Jamming Navigation Receiver. Remote Sensing, 14(1), 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14010048