Vertical Structure of Dust Aerosols Observed by a Ground-Based Raman Lidar with Polarization Capabilities in the Center of the Taklimakan Desert
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Lidar Systems and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Dust Optical Properties from MODIS and Ground-Based Sun Photometer Observations
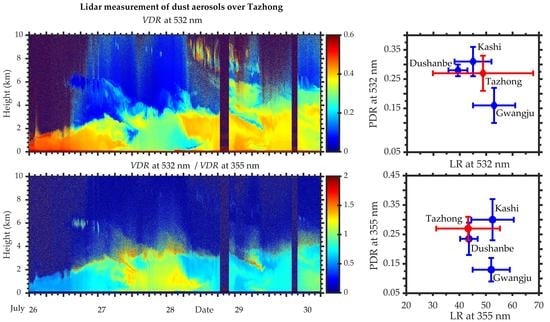
3.2. Vertical Structure of Dust Aerosols in the Center of the Taklimakan Desert
4. Discussion
| LR (sr) | PDR | Location | Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 532 nm | 355 nm | 532 nm | 355 nm | ||
| 49 ± 19 | 43 ± 12 | 0.32 ± 0.06 | 0.27 ± 0.04 | Current study | - |
| - | - | 0.34 ± 0.04 | 0.25 ± 0.003 | Ruoqiang | [50] |
| 45 ± 7 | 51–56 ± 8 | 0.36 ± 0.05 | 0.28–0.32 ± 0.07 | Kashi | [11] |
| 47 ± 4 | - | - | - | Wuhan | [80] |
| 53 ± 8 | 52 ± 7 | 0.21 ± 0.06 | 0.13 ± 0.04 | Gwangju | [81] |
| - | 52 ± 9 | - | 0.13 ± 0.05 | Beijing | [82] |
| 47.7 ± 2.8 | 63 ± 4.5 | - | - | Yinchuan | [83] |
| 54 ± 9 | 50 ± 7 | - | - | Fukuoka | [84] |
| 35.7−42.9 | 40.3−46.9 | 0.31−0.35 | 0.18−0.29 | Dushanbe | [85] |
| 32.6 | 66.9 | - | - | Deajoen | [86] |
| 43 | 49 | - | - | Tokyo | [87] |
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kok, J.F.; Ridley, D.A.; Zhou, Q.; Miller, R.L.; Zhao, C.; Heald, C.L.; Ward, D.S.; Albani, S.; Haustein, K. Smaller Desert Dust Cooling Effect Estimated from Analysis of Dust Size and Abundance. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 274–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofer, J.; Ansmann, A.; Althausen, D.; Engelmann, R.; Baars, H.; Abdullaev, S.F.; Makhmudov, A.N. Long-Term Profiling of Aerosol Light Extinction, Particle Mass, Cloud Condensation Nuclei, and Ice-Nucleating Particle Concentration over Dushanbe, Tajikistan, in Central Asia. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 4695–4711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Müller, D.; Wandinger, U.; Althausen, D.; Fiebig, M. Comprehensive Particle Characterization from Three-Wavelength Raman-Lidar Observations: Case Study. Appl. Opt. 2001, 40, 4863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, S.; Chen, J.; Qiang, M.; Liu, B.; Xu, Q.; Xia, D.; Chen, F. Holocene Dust Storm Variations over Northern China: Transition from a Natural Forcing to an Anthropogenic Forcing. Sci. Bull. 2021, 66, 2516–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginoux, P.; Prospero, J.M.; Gill, T.E.; Hsu, N.C.; Zhao, M. Global-Scale Attribution of Anthropogenic and Natural Dust Sources and Their Emission Rates Based on MODIS Deep Blue Aerosol Products. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.Y.; Chiba, M. A Numerical Study of the Contributions of Dust Source Regions to the Global Dust Budget. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2006, 52, 88–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Liu, T. The Age of the Taklimakan Desert. Science 2006, 312, 1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Z.; Nee, J.-B.; Chiang, C.-W.; Zhang, S.; Jin, H.; Wang, W.; Zhou, T. Real-Time Observations of Dust--Cloud Interactions Based on Polarization and Raman Lidar Measurements. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, D.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Winker, D.; Trepte, C. A Height Resolved Global View of Dust Aerosols from the First Year CALIPSO Lidar Measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Fang, Z.; Cao, Y.; Xie, C.; Zhou, T.; Wang, B.; Xing, K.; Lolli, S. Impacts of Transboundary Dust Transport on Aerosol Pollution in the Western Yangtze River Delta Region, China: Insights Gained From Ground-Based Lidar and Satellite Observations. Earth Sp. Sci. 2021, 8, e2020EA001533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Wang, H.; Goloub, P.; Li, Z.; Veselovskii, I.; Podvin, T.; Li, K.; Korenskiy, M. The Characterization of Taklamakan Dust Properties Using a Multiwavelength Raman Polarization Lidar in Kashi, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 13817–13834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottle, P.; Mueeller, D.; Shin, D.-H.; Zhang, X.X.; Feng, G.; McKendry, I.; Strawbridge, K. Studying Taklamakan Aerosol Properties with Lidar (STAPL). In Lidar Technologies, Techniques, and Measurements for Atmospheric Remote Sensing IX; Singh, U.N., Pappalardo, G., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2013; Volume 8894, ISBN 978-0-8194-9762-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Huang, J.; Zhao, C.; Jin, Q.; Ma, Y.; Yang, B. Modeling Dust Sources, Transport, and Radiative Effects at Different Altitudes over the Tibetan Plateau. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 1507–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, D.D.; Crawford, J.; Stelcer, E.; Vuong Thu, B. Long Range Transport of Fine Particle Windblown Soils and Coal Fired Power Station Emissions into Hanoi between 2001 to 2008. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 3761–3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, N.; Shimizu, A.; Nishizawa, T.; Jin, Y.; Yumimoto, K. Long-Range-Transported Mineral Dust From Africa and Middle East to East Asia Observed with the Asian Dust and Aerosol Lidar Observation Network (AD-Net). EPJ Web Conf. 2020, 237, 05009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Huang, J.; Hayasaka, T.; Wang, S.; Zhou, T.; Jin, H. Short-Cut Transport Path for Asian Dust Directly to the Arctic: A Case Study. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 114018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kröpelin, S.; Verschuren, D.; Lézine, A.M.; Eggermont, H.; Cocquyt, C.; Francus, P.; Cazet, J.P.; Fagot, M.; Rumes, B.; Russell, J.M.; et al. Climate-Driven Ecosystem Succession in the Sahara: The Past 6000 Years. Science 2008, 320, 765–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uno, I.; Eguchi, K.; Yumimoto, K.; Takemura, T.; Shimizu, A.; Uematsu, M.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Hara, Y.; Sugimoto, N. Asian Dust Transported One Full Circuit around the Globe. Nat. Geosci. 2009, 2, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahowald, N. Aerosol Indirect Effect on Biogeochemical Cycles and Climate. Science 2011, 334, 794–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.; Huang, Z.; Huang, J.; Maki, T.; Zhang, S.; Ma, X.; Shi, J.; Bi, J.; Zhou, T.; Wang, G.; et al. Characterization of Atmospheric Bioaerosols along the Transport Pathway of Asian Dust during the Dust-Bioaerosol 2016 Campaign. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 18, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Hua, S.; Alam, K.; Dai, T.; Cheng, Y. Tibetan Plateau Driven Impact of Taklimakan Dust on Northern Rainfall. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 234, 117583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Lin, B.; Minnis, P.; Wang, T.; Wang, X.; Hu, Y.; Yi, Y.; Ayers, J.K. Satellite-Based Assessment of Possible Dust Aerosols Semi-Direct Effect on Cloud Water Path over East Asia. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, J.; Wang, T.; Wang, W.; Li, Z.; Yan, H. Climate Effects of Dust Aerosols over East Asian Arid and Semiarid Regions. J. Geophys. Res. 2014, 119, 11398–11416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, J.T.; Chuang, C.C.; Wexler, A.S. Influence of Dust Composition on Cloud Droplet Formation. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 2904–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoose, C.; Lohmann, U.; Erdin, R.; Tegen, I. The Global Influence of Dust Mineralogical Composition on Heterogeneous Ice Nucleation in Mixed-Phase Clouds. Environ. Res. Lett. 2008, 3, 25003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhou, W.; Wenig, M.; Yang, L. Impact of Long-Range Desert Dust Transport on Hydrometeor Formation over Coastal East Asia. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2017, 34, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, F.; Luo, G.; Fan, J.; Liu, S. Impacts of Long-Range-Transported Mineral Dust on Summertime Convective Cloud and Precipitation: A Case Study over the Taiwan Region. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 17433–17451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karyampudi, V.M.; Palm, S.P.; Reagan, J.A.; Fang, H.; Melfi, S.H. Validation of the Saharan Dust Plume Conceptual Model Using Lidar, Meteosat, and ECMWF Data. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1967, 80, 1045–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gardner, C.S.; Sechrist, C.F., Jr.; Shelton, J.D. Lidar Observations of the Mount St. Helens Dust Layers over Urbana, Illinois. Appl. Opt. 1980, 19, A192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, N.; Huang, Z.; Nishizawa, T.; Matsui, I.; Tatarov, B. Fluorescence from Atmospheric Aerosols Observed with a Multi-Channel Lidar Spectrometer. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 20800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, N.; Huang, Z. Lidar Methods for Observing Mineral Dust. J. Meteorol. Res. 2014, 28, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lolli, S.; Khor, W.Y.; Matjafri, M.Z.; Lim, H.S. Monsoon Season Quantitative Assessment of Biomass Burning Clear-Sky Aerosol Radiative Effect at Surface by Ground-Based Lidar Observations in Pulau Pinang, Malaysia in 2014. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, B.; Yin, B.; Wu, S. Small Angle Scattering Intensity Measurement by an Improved Ocean Scheimpflug Lidar System. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobbi, G.P.; Barnaba, F.; Blumthaler, M.; Labow, G.; Herman, J.R. Observed Effects of Particles Nonsphericity on the Retrieval of Marine and Desert Dust Aerosol Optical Depth by Lidar. Atmos. Res. 2002, 61, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattis, I.; Ansmann, A.; Muller, D.; Wandinger, U.; Althausen, D. Dual-Wavelength Raman Lidar Observations of the Extinction-to-Backscatter Ratio of Saharan Dust. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 20-1–20-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Huang, J.; Bi, J.; Wang, G.; Wang, W.; Fu, Q.; Li, Z.; Tsay, S.-C.; Shi, J. Dust Aerosol Vertical Structure Measurements Using Three MPL Lidars during 2008 China-U.S. Joint Dust Field Experiment. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, S.; Huang, Z.; Ma, X.; Huang, J.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, S.; Dong, Q.; Bi, J.; Shi, J. Classification of Atmospheric Aerosols and Clouds by Use of Dual-Polarization Lidar Measurements. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 23461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamouri, R.E.; Ansmann, A. Fine and Coarse Dust Separation with Polarization Lidar. Atmos. Meas. Technol. 2014, 7, 3717–3735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Sugimoto, N.; Murayama, T. Extinction-to-Backscatter Ratio of Asian Dust Observed with High-Spectral-Resolution Lidar and Raman Lidar. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 2760–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Gong, W.; Mao, F.; Pan, Z. Physical Constraint Method to Determine Optimal Overlap Factor of Raman Lidar. J. Opt. 2017, 47, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, L.; Ma, T.; Zhang, Z.; Fei, R.; Liu, K.; Gong, Z.; Li, H. Experimental Calibration of the Overlap Factor for the Pulsed Atmospheric Lidar by Employing a Collocated Scheimpflug Lidar. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pietruczuk, A.; Podgorski, J. The Lidar Ratio Derived from Sun-Photometer Measurements at Belsk Geophysical Observatory. Acta Geophys. 2009, 57, 476–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-H.; Kim, S.-W.; Omar, A.H. Dust Lidar Ratios Retrieved from the CALIOP Measurements Using the MODIS AOD as a Constraint. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuzmanoski, M.; Box, M.A.; Schmid, B.; Box, G.P.; Wang, J.; Russell, P.B.; Bates, D.; Jonsson, H.H.; Welton, E.J.; Seinfeld, J.H. Aerosol Properties Computed from Aircraft-Based Observations during the ACE-Asia Campaign: 2. A Case Study of Lidar Ratio Closure. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ansmann, A.; Riebesell, M.; Wandinger, U.; Weitkamp, C.; Voss, E.; Lahmann, W.; Michaelis, W. Combined Raman Elastic-Backscatter LIDAR for Vertical Profiling of Moisture, Aerosol Extinction, Backscatter, and LIDAR Ratio. Appl. Phys. B 1992, 55, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hostetler, C.A.; Liu, Z.; Reagan, J.; Vaughan, M.; Winker, D.; Osborn, M.; Hunt, W.H.; Powell, K.A.; Trepte, C. CALIOP Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document, Calibration and Level 1 Data Products. Available online: https://www-calipso.larc.nasa.gov/resources/pdfs/PC-SCI-201v1.0.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2022).
- He, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, F.; Yin, Z.; Yi, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Yi, F. Retrievals of Dust-Related Particle Mass and Ice-Nucleating Particle Concentration Profiles with Ground-Based Polarization Lidar and Sun Photometer over a Megacity in Central China. Atmos. Meas. Technol. 2021, 14, 5939–5954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; Herman, M.; Holdak, A.; Lapyonok, T.; Tanré, D.; Deuzé, J.L.; Ducos, F.; Sinyuk, A.; Lopatin, A. Statistically Optimized Inversion Algorithm for Enhanced Retrieval of Aerosol Properties from Spectral Multi-Angle Polarimetric Satellite Observations. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2011, 4, 975–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veselovskii, I.; Dubovik, O.; Kolgotin, A.; Korenskiy, M.; Whiteman, D.N.; Allakhverdiev, K.; Huseyinoglu, F. Linear Estimation of Particle Bulk Parameters from Multi-Wavelength Lidar Measurements. Atmos. Meas. Technol. 2012, 5, 1135–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, Q.; Huang, Z.; Li, W.; Li, Z.; Song, X.; Liu, W.; Wang, T.; Bi, J.; Shi, J. Polarization Lidar Measurements of Dust Optical Properties at the Junction of the Taklimakan Desert–Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Ma, Y.; Liu, J.; Gong, W.; Wang, W.; Zhang, M. Graphics Algorithm for Deriving Atmospheric Boundary Layer Heights from CALIPSO Data. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 5075–5085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.; Nehrir, A.R.; Ren, X.; Dickerson, R.R.; Huang, J.; Stratton, P.R.; Gronoff, G.; Kooi, S.A.; Collins, J.E.; Berkoff, T.A.; et al. Synergistic Aircraft and Ground Observations of Transported Wildfire Smoke and Its Impact on Air Quality in New York City during the Summer 2018 LISTOS Campaign. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 773, 145030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelemeijer, R.B.A.; Homan, C.D.; Matthijsen, J. Comparison of Spatial and Temporal Variations of Aerosol Optical Thickness and Particulate Matter over Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 5304–5315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Zhou, C.; Liao, Y. Dust Storms Evolution in Taklimakan Desert and Its Correlation with Climatic Parameters. J. Geogr. Sci. 2008, 18, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, R.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; Ren, F. Decadal Change of the Spring Dust Storm in Northwest China and the Associated Atmospheric Circulation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, B.; Braeuning, A.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, Z.; Esper, J. Dust Storm Frequency and Its Relation to Climate Changes in Northern China during the Past 1000 Years. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 9288–9299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulitza, S.; Heslop, R.; Pittauerova, R.; Fischer, R.W.; Meyer, R.; Stuut, R.B.; Zabel, M.; Mollenhauer, R.; Collins, R.A.; Kuhnert, R. Increase in African Dust Flux at the Onset of Commercial Agriculture in the Sahel Region. Nature 2010, 466, 226–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neff, J.C.; Ballantyne, A.P.; Farmer, G.L.; Mahowald, N.M.; Conroy, J.L.; Landry, C.C.; Overpeck, J.T.; Painter, T.H.; Lawrence, C.R.; Reynolds, R.L. Increasing Eolian Dust Deposition in the Western United States Linked to Human Activity. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamouri, R.-E.; Ansmann, A.; Nisantzi, A.; Solomos, S.; Kallos, G.; Hadjimitsis, D.G. Extreme Dust Storm over the Eastern Mediterranean in September 2015: Satellite, Lidar, and Surface Observations in the Cyprus Region. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 13711–13724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, C.; Liu, X.; Ruby Leung, L.; Hagos, S. Radiative Impact of Mineral Dust on Monsoon Precipitation Variability over West Africa. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 1879–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kabatas, B.; Unal, A.; Pierce, R.B.; Kindap, T.; Pozzoli, L. The Contribution of Saharan Dust in PM10 Concentration Levels in Anatolian Peninsula of Turkey. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 488–489, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgoulias, A.K.; Alexandri, G.; Kourtidis, K.A.; Lelieveld, J.; Zanis, P.; Pöschl, U.; Levy, R.; Amiridis, V.; Marinou, E.; Tsikerdekis, A. Spatiotemporal Variability and Contribution of Different Aerosol Types to the Aerosol Optical Depth over the Eastern Mediterranean. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 13853–13884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, X.; Huang, Z.; Qi, S.; Huang, J.; Zhang, S.; Dong, Q.; Wang, X. Ten-Year Global Particulate Mass Concentration Derived from Space-Borne CALIPSO Lidar Observations. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 721, 137699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theodosi, C.; Im, U.; Bougiatioti, A.; Zarmpas, P.; Yenigun, O.; Mihalopoulos, N. Aerosol Chemical Composition over Istanbul. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 2482–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, C.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shi, X.; Wu, X.; Chen, T.; Wu, F.; Qiu, Y. Analysis of Influential Factors for the Relationship between PM2.5 and AOD in Beijing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 13473–13489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yin, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, T. Chemical Characteristics and Source Apportionment of PM10 during Asian Dust Storm and Non-Dust Storm Days in Beijing. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 91, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Givehchi, R.; Arhami, M.; Tajrishy, M. Contribution of the Middle Eastern Dust Source Areas to PM10 Levels in Urban Receptors: Case Study of Tehran, Iran. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 75, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agacayak, T.; Kindap, T.; Unal, A.; Pozzoli, L.; Mallet, M.; Solmon, F. A Case Study for Saharan Dust Transport over Turkey via RegCM4. 1 Model. Atmos. Res. 2015, 153, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandler, K.; Schütz, L.; Jäckel, S.; Lieke, K.; Emmel, C.; Müller-Ebert, D.; Ebert, M.; Scheuvens, D.; Schladitz, A.; Šegvić, B.; et al. Ground-Based off-Line Aerosol Measurements at Praia, Cape Verde, during the Saharan Mineral Dust Experiment: Microphysical Properties and Mineralogy. Tellus Ser. B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2011, 63, 459–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; He, Q.; Mamtimin, A.; Huo, W.; Liu, X. Diurnal Variations of Saltation Activity at Tazhong: The Hinterland of Taklimakan Desert. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2013, 119, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Wei, W.; He, Q.; Yang, Y.; Fan, L.; Zhang, J. Summer Atmospheric Boundary Layer Structure in the Hinterland of Taklimakan Desert, China. J. Arid Land 2016, 8, 846–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Che, J.; Zhao, P. Characteristics of the Summer Atmospheric Boundary Layer Height over the Tibetan Plateau and Influential Factors. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 5253–5268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, B.; Han, G.; Zhang, T.; Liu, B. Characteristics of the Planetary Boundary Layer above Wuhan, China Based on CALIPSO. Atmos. Res. 2018, 214, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Che, H.; Xia, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, P.; Ma, Y.; Yang, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Multiyear Ground-Based Measurements of Aerosol Optical Properties and Direct Radiative Effect Over Different Surface Types in Northeastern China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 13887–13916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Lei, M.; Zhao, Y.; Jian, B.; Zhang, M.; Huang, J. Long-Term Variation of Boundary Layer Height and Possible Contribution Factors: A Global Analysis Science of the Total Environment Long-Term Variation of Boundary Layer Height and Possible Contribution Factors: A Global Analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 796, 148950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofer, J.; Ansmann, A.; Althausen, D.; Engelmann, R.; Baars, H.; Fomba, K.W.; Wandinger, U.; Abdullaev, S.F.; Makhmudov, A.N. Optical Properties of Central Asian Aerosol Relevant for Spaceborne Lidar Applications and Aerosol Typing at 355 and 532 Nm. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 9265–9280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Qi, S.; Zhou, T.; Dong, Q.; Ma, X.; Zhang, S.; Bi, J.; Shi, J. Investigation of Aerosol Absorption with Dual-Polarization Lidar Observations. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 7028–7035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansmann, A.; Mamouri, R.-E.; Hofer, J.; Baars, H.; Althausen, D.; Abdullaev, S.F. Dust Mass, CCN, and INP Profiling with Polarization Lidar: Updated POLIPHON Conversion Factors from Global AERONET Analysis. Atmos. Meas. Technol. Discuss. 2019, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, D.R. Rayleigh-scattering by air. Planet. Space Sci. 1984, 32, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Yi, F.; Liu, F.; Yin, Z.; He, Y. Optical Properties of Aerosol and Cloud Particles Measured by a Single-Line-Extracted Pure Rotational Raman Lidar. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 21947–21964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.-K.; Müller, D.; Lee, C.; Lee, K.H.; Shin, D.; Kim, Y.J.; Noh, Y.M. Vertical Variation of Optical Properties of Mixed Asian Dust/Pollution Plumes According to Pathway of Air Mass Transport over East Asia. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 6707–6720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, C.; Dong, Y.; Hu, Q.; Liu, T.; Zhu, Y.; Xing, C. Profiling of Dust and Urban Haze Mass Concentrations during the 2019 National Day Parade in Beijing by Polarization Raman Lidar. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Hua, D.; Mao, J.; Zhou, C. Investigate the Relationship between Multiwavelength Lidar Ratios and Aerosol Size Distributions Using Aerodynamic Particle Sizer Spectrometer. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2017, 188, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, Y.; Nishizawa, T.; Sugimoto, N.; Matsui, I.; Pan, X.; Kobayashi, H.; Osada, K.; Uno, I. Optical Properties of Mixed Aerosol Layers over Japan Derived with Multi-Wavelength Mie–Raman Lidar System. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2017, 188, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofer, J.; Althausen, D.; Abdullaev, S.F.; Makhmudov, A.N.; Nazarov, B.I.; Schettler, G.; Engelmann, R.; Baars, H.; Fomba, K.W.; Müller, K.; et al. Long-Term Profiling of Mineral Dust and Pollution Aerosol with Multiwavelength Polarization Raman Lidar at the Central Asian Site of Dushanbe, Tajikistan: Case Studies. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 14559–14577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, I.; Kim, Y.; Baik, S.H.; Park, S.K.; Cha, H.; Choi, S.; Chung, C.M.; Kim, D. Measurement of Aerosol Parameters with Altitude by Using Two Wavelength Rotational Raman Signals. J. Opt. Soc. Korea 2010, 14, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murayama, T.; Mueller, D.; Sekiguchi, M. Study of Tropospheric Aerosols and Clouds with Raman Lidar Technique. In Proceedings of the 13th International School on Quantum Electronics: Laser Physics and Applications, Bourgas, Bulgaria, 20 September 2004; Volume 5830, pp. 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Mass Conc. | PM10 | TSP | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (μg m−3) | Hourly Mean | In Situ | Hourly Mean | In Situ |
| Max | 7618.2 | 7600 | 9994.6 | 9994.6 |
| Mean | 491.41 ± 6.43 | - | 4580.5 ± 19.87 | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Huang, Z.; Li, M.; Shen, X.; Wang, Y.; Dong, Q.; Bi, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Li, Z.; et al. Vertical Structure of Dust Aerosols Observed by a Ground-Based Raman Lidar with Polarization Capabilities in the Center of the Taklimakan Desert. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2461. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14102461
Zhang S, Huang Z, Li M, Shen X, Wang Y, Dong Q, Bi J, Zhang J, Li W, Li Z, et al. Vertical Structure of Dust Aerosols Observed by a Ground-Based Raman Lidar with Polarization Capabilities in the Center of the Taklimakan Desert. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(10):2461. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14102461
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shuang, Zhongwei Huang, Meishi Li, Xingtai Shen, Yongkai Wang, Qingqing Dong, Jianrong Bi, Jiantao Zhang, Wuren Li, Ze Li, and et al. 2022. "Vertical Structure of Dust Aerosols Observed by a Ground-Based Raman Lidar with Polarization Capabilities in the Center of the Taklimakan Desert" Remote Sensing 14, no. 10: 2461. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14102461
APA StyleZhang, S., Huang, Z., Li, M., Shen, X., Wang, Y., Dong, Q., Bi, J., Zhang, J., Li, W., Li, Z., & Song, X. (2022). Vertical Structure of Dust Aerosols Observed by a Ground-Based Raman Lidar with Polarization Capabilities in the Center of the Taklimakan Desert. Remote Sensing, 14(10), 2461. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14102461