State of the Vietnamese Coast—Assessing Three Decades (1986 to 2021) of Coastline Dynamics Using the Landsat Archive
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.2.1. Landsat Archive
2.2.2. Validation Data
2.2.3. Sea Level Data
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Country-Scale Processing of Annual Water Index Images
2.3.2. Sub-Pixel Coastline Extraction
2.3.3. Shore-Normal Transect Generation
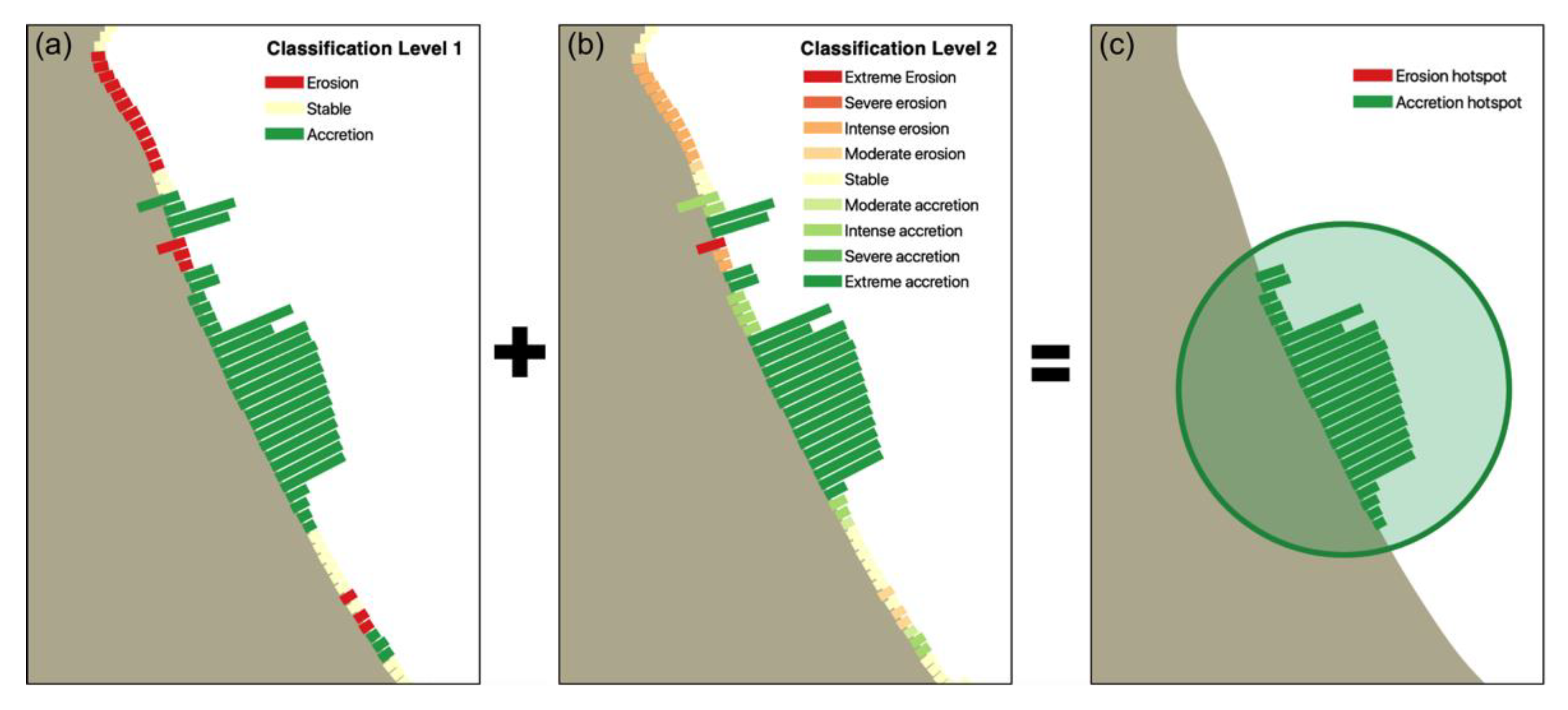
2.3.4. Coastline Change Quantification
2.3.5. Validation
3. Results
3.1. Coastline Detection
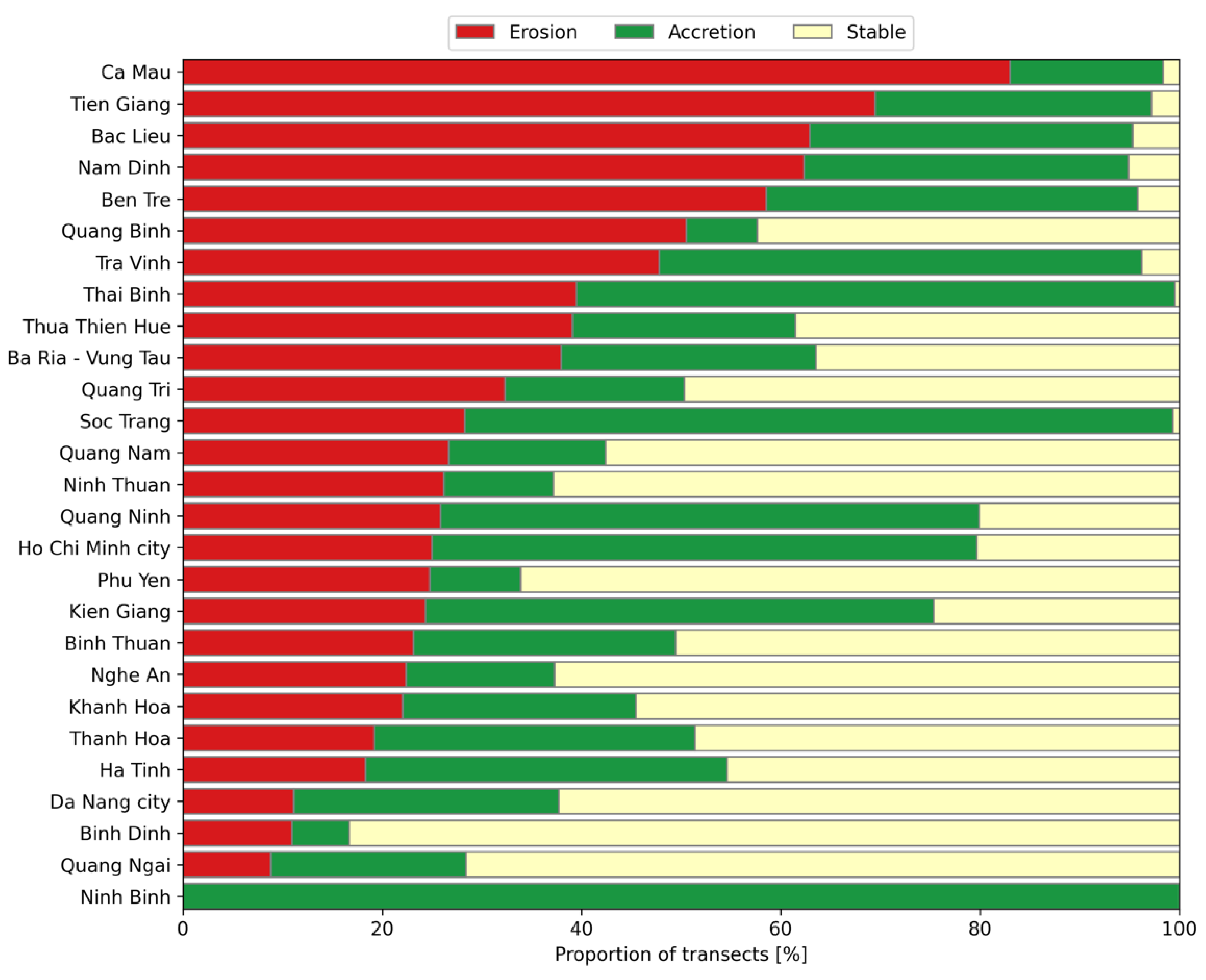
3.2. Spatio-Temporal Patterns of Coastline Change in Vietnam
3.3. Validation
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations of the Landsat-based Coastline Detection Method
4.2. Limitations of the Coastline Change Quantification
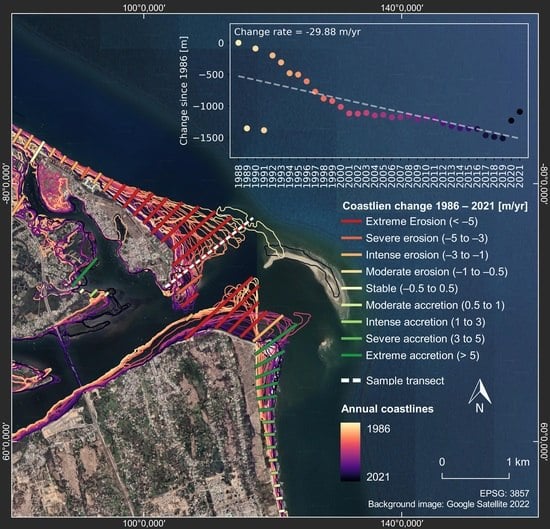
4.3. Potential Drivers of Coastline Change at Selected Hotspots
4.3.1. Erosion Hotspot in the Mekong Delta
4.3.2. Erosion Hotspot in the Red River Delta
4.3.3. Accretion Hotspot in Haiphong City
4.3.4. Accretion Hotspot at Haiphong Port
4.3.5. Stable Coastline in Da Nang
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barbier, E.B.; Hacker, S.D.; Kennedy, C.; Koch, E.W.; Stier, A.C.; Silliman, B.R. The Value of Estuarine and Coastal Ecosystem Services. Ecol. Monogr. 2011, 81, 169–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. UN Ocean Fact Sheet. In Proceedings of the Ocean Conference, New York, NY, USA, 5–7 June 2017; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wolanski, E.; Day, J.W.; Elliott, M.; Ramachandran, R. Coasts and Estuaries: The Future; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; ISBN 978-0-12-814003-1. [Google Scholar]
- Small, C.; Nicholls, R.J. A Global Analysis of Human Settlement in Coastal Zones. J. Coast. Res. 2003, 19, 584–599. [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer, M.; Glavovic, B.C.; Hinkel, J.; van de Wal, R.; Magnan, A.K.; Abd-Elgawad, A.; Cai, R.; Cifuentes-Jara, M.; DeConto, R.M.; Ghosh, T.; et al. Sea Level Rise and Implications for Low-Lying Islands, Coasts and Communities. In IPCC Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate; Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ranasinghe, R. Assessing Climate Change Impacts on Open Sandy Coasts: A Review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2016, 160, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicholls, R.J.; Woodroffe, C.; Burkett, V. Coastline Degradation as an Indicator of Global Change. In Climate Change; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 309–324. ISBN 978-0-444-63524-2. [Google Scholar]
- Boak, E.H.; Turner, I.L. Shoreline Definition and Detection: A Review. J. Coast. Res. 2005, 214, 688–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kien, P.H.; Cong, L.V.; Thanh, V.T. Vietnam Coastal Erosion—Cause and Challenges. Presentation Slides. Hanoi. 2018. Available online: http://sciencedocbox.com/Geology/116703635-Vietnam-coastal-erosion-cause-and-challenges.html (accessed on 18 May 2022).
- Toure, S.; Diop, O.; Kpalma, K.; Maiga, A. Shoreline Detection Using Optical Remote Sensing: A Review. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Viaña-Borja, S.P.; Ortega-Sánchez, M. Automatic Methodology to Detect the Coastline from Landsat Images with a New Water Index Assessed on Three Different Spanish Mediterranean Deltas. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohan, R.K.; Short, A.D.; Cambers, G.; MacLeod, M.; Cooper, J.A.G.; Hopley, D.; May, V.; Mörner, N.-A.; Otvos, E.G.; West, N.; et al. Coasts, Coastlines, Shores, and Shorelines. In Encyclopedia of Coastal Science; Schwartz, M.L., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 323–327. ISBN 978-1-4020-1903-6. [Google Scholar]
- Marchesiello, P.; Nguyen, N.M.; Gratiot, N.; Loisel, H.; Anthony, E.J.; Dinh, C.S.; Nguyen, T.; Almar, R.; Kestenare, E. Erosion of the Coastal Mekong Delta: Assessing Natural against Man Induced Processes. Cont. Shelf Res. 2019, 181, 72–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangor Definitions of Coastal Terms. Coastalwiki. 2021. Available online: http://www.coastalwiki.org/wiki/Definitions_of_coastal_terms (accessed on 2 May 2021).
- Bird, E.C.F. Coastal Geomorphology: An Introduction, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Chichester, UK; Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; ISBN 978-0-470-51729-1. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, B.-L.; Li, X.-Y. Coastline Change of the Yellow River Estuary and Its Response to the Sediment and Runoff (1976–2005). Geomorphology 2011, 127, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhan, N.H.; Cao, N.B. Damming the Mekong: Impacts in Vietnam and Solutions. In Coasts and Estuaries; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 321–340. ISBN 978-0-12-814003-1. [Google Scholar]
- Warrick, J.A.; Stevens, A.W.; Miller, I.M.; Harrison, S.R.; Ritchie, A.C.; Gelfenbaum, G. World’s Largest Dam Removal Reverses Coastal Erosion. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bravard, J.-P.; Goichot, M.; Gaillot, S. Geography of Sand and Gravel Mining in the Lower Mekong River: First Survey and Impact Assessment. EchoGéo 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jordan, C.; Tiede, J.; Lojek, O.; Visscher, J.; Apel, H.; Nguyen, H.Q.; Quang, C.N.X.; Schlurmann, T. Sand Mining in the Mekong Delta Revisited—Current Scales of Local Sediment Deficits. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besset, M.; Gratiot, N.; Anthony, E.J.; Bouchette, F.; Goichot, M.; Marchesiello, P. Mangroves and Shoreline Erosion in the Mekong River Delta, Viet Nam. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 226, 106263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentaschi, L.; Vousdoukas, M.I.; Pekel, J.-F.; Voukouvalas, E.; Feyen, L. Global Long-Term Observations of Coastal Erosion and Accretion. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mangor Human Causes of Coastal Erosion. Coastalwiki. 2020. Available online: http://www.coastalwiki.org/wiki/Human_causes_of_coastal_erosion (accessed on 30 April 2021).
- Nordstrom, K.F. Living with Shore Protection Structures: A Review. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2014, 150, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hapke, C.J.; Kratzmann, M.G.; Himmelstoss, E.A. Geomorphic and Human Influence on Large-Scale Coastal Change. Geomorphology 2013, 199, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rentschler, J.; de Vries Robbé, S.; Braese, J.; Nguyen, D.H.; van Ledden, M.; Pozueta Mayo, B. Resilient Shores: Vietnam’s Coastal Development between Opportunity and Disaster Risk; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kelletat, D. Physische Geographie Der Meere Und Küsten: Eine Einführung; Studienbücher der Geographie; 3., neu bearb. und erw. Aufl.; Borntraeger: Stuttgart, Germany, 2013; ISBN 978-3-443-07150-9. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, B.; Wu, W.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, Y. Drivers, Trends, and Potential Impacts of Long-Term Coastal Reclamation in China from 1985 to 2010. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 170, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luijendijk, A.; Hagenaars, G.; Ranasinghe, R.; Baart, F.; Donchyts, G.; Aarninkhof, S. The State of the World’s Beaches. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayre, R.; Noble, S.; Hamann, S.; Smith, R.; Wright, D.; Breyer, S.; Butler, K.; Van Graafeiland, K.; Frye, C.; Karagulle, D.; et al. A New 30 Meter Resolution Global Shoreline Vector and Associated Global Islands Database for the Development of Standardized Ecological Coastal Units. J. Oper. Oceanogr. 2019, 12, S47–S56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sabour, S.; Brown, S.; Nicholls, R.J.; Haigh, I.D.; Luijendijk, A.P. Multi-Decadal Shoreline Change in Coastal Natural World Heritage Sites—A Global Assessment. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 104047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFeeters, S.K. The Use of the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) in the Delineation of Open Water Features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop-Taylor, R.; Sagar, S.; Lymburner, L.; Alam, I.; Sixsmith, J. Sub-Pixel Waterline Extraction: Characterising Accuracy and Sensitivity to Indices and Spectra. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cipolletti, M.P.; Delrieux, C.A.; Perillo, G.M.E.; Cintia Piccolo, M. Superresolution Border Segmentation and Measurement in Remote Sensing Images. Comput. Geosci. 2012, 40, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Liu, F.; Ling, F.; Yue, L. Automatic Semi-Global Artificial Shoreline Subpixel Localization Algorithm for Landsat Imagery. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pardo-Pascual, J.; Sánchez-García, E.; Almonacid-Caballer, J.; Palomar-Vázquez, J.; Priego de los Santos, E.; Fernández-Sarría, A.; Balaguer-Beser, Á. Assessing the Accuracy of Automatically Extracted Shorelines on Microtidal Beaches from Landsat 7, Landsat 8 and Sentinel-2 Imagery. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.-W.; Chang, H.-K. Estimation of Shoreline Position and Change from Satellite Images Considering Tidal Variation. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2009, 84, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ashmawy, N. Automatic Determination of Shoreline at Maximum Retreating. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2019, 22, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop-Taylor, R.; Nanson, R.; Sagar, S.; Lymburner, L. Mapping Australia’s Dynamic Coastline at Mean Sea Level Using Three Decades of Landsat Imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 267, 112734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelick, N.; Hancher, M.; Dixon, M.; Ilyushchenko, S.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Google Earth Engine: Planetary-Scale Geospatial Analysis for Everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.-H.; McAlpine, C.; Pullar, D.; Leisz, S.J.; Galina, G. Drivers of Coastal Shoreline Change: Case Study of Hon Dat Coast, Kien Giang, Vietnam. Environ. Manage. 2015, 55, 1093–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, N.T.; Duc, D.M.; Quynh, D.T.; Cuong, V.D. Nearshore Topographical Changes and Coastal Stability in Nam Dinh Province, Vietnam. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duc, D.M.; Nhuan, M.T.; Ngoi, C.V. An Analysis of Coastal Erosion in the Tropical Rapid Accretion Delta of the Red River, Vietnam. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2012, 43, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hue, N.H.; Thanh, N.H. Assessing the Impact of Massive Development of Beach Resorts on Current Status of Coastal Erosion Along the Central Coast of Vietnam; Trung Viet, N., Xiping, D., Thanh Tung, T., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 551–556. [Google Scholar]
- Quang Tuan, N.; Cong Tin, H.; Quang Doc, L.; Anh Tuan, T. Historical Monitoring of Shoreline Changes in the Cua Dai Estuary, Central Vietnam Using Multi-Temporal Remote Sensing Data. Geosciences 2017, 7, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wyatt, A.B.; Thanh, N.T.P.; Gian, T.P. Viet Nam Situation Analysis; IUCN: Hanoi, Vietnam, 2012; p. 95. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, Q.H.; Takewaka, S. Land Subsidence and Its Effects on Coastal Erosion in the Nam Dinh Coast (Vietnam). Cont. Shelf Res. 2020, 207, 104227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN Viet Nam—Country Profile. UN Data. 2020. Available online: http://data.un.org/en/iso/vn.html (accessed on 25 June 2021).
- Beck, H.E.; Zimmermann, N.E.; McVicar, T.R.; Vergopolan, N.; Berg, A.; Wood, E.F. Present and Future Köppen-Geiger Climate Classification Maps at 1-Km Resolution. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- WorldBank Vietnam—Climate Data: Historical. Climate Change Knowledge Portal—Development Practitioners and Policy Makers. 2020. Available online: https://climateknowledgeportal.worldbank.org/country/vietnam (accessed on 25 June 2021).
- WorldBank Vietnam. World Development Indicators. 2021. Available online: https://data.worldbank.org/country/vietnam (accessed on 25 June 2021).
- Eisma, D. Vietnam. In Encyclopedia of the World’s Coastal Landforms; Bird, E.C.F., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 1147–1150. ISBN 978-1-4020-8639-7. [Google Scholar]
- Trinh, T.T.; Pattiaratchi, C.; Bui, T. The Contribution of Forerunner to Storm Surges along the Vietnam Coast. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlasova, G.A.; Xuan, N.B.; Demenok, M.N.; Long, B.H.; Mau, L.D.; Dung, N.T.T. Tropical Cyclone in the North of the South China Sea as a Factor Affecting the Structure of the Vietnamese Current. Izv. Atmospheric Ocean. Phys. 2020, 56, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USGS Landsat Satellite Missions. USGS Science for a Changing World. 2021. Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/core-science-systems/nli/landsat/landsat-satellite-missions?qt-science_support_page_related_con=0#qt-science_support_page_related_con (accessed on 30 June 2021).
- Vermote, E.; Justice, C.; Claverie, M.; Franch, B. Preliminary Analysis of the Performance of the Landsat 8/OLI Land Surface Reflectance Product. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ESA RapidEye. Earth Online. 2021. Available online: https://earth.esa.int/eogateway/missions/rapideye (accessed on 1 July 2021).
- Planet RAPIDEYETM Imagery Product Specifications. 2016. Available online: https://www.planet.com/products/satellite-imagery/files/160625-RapidEye%20Image-Product-Specifications.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2021).
- Caldwell, P.C.; Merrifield, M.A.; Thompson, P.R. Sea Level Measured by Tide Gauges from Global Oceans as Part of the Joint Archive for Sea Level (JASL) Since 1846. 2010. Available online: https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/archive/accession/JIMAR-JASL (accessed on 2 July 2021).
- Foga, S.; Scaramuzza, P.L.; Guo, S.; Zhu, Z.; Dilley, R.D.; Beckmann, T.; Schmidt, G.L.; Dwyer, J.L.; Joseph Hughes, M.; Laue, B. Cloud Detection Algorithm Comparison and Validation for Operational Landsat Data Products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 194, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corbane, C.; Politis, P.; Kempeneers, P.; Simonetti, D.; Soille, P.; Burger, A.; Pesaresi, M.; Sabo, F.; Syrris, V.; Kemper, T. A Global Cloud Free Pixel- Based Image Composite from Sentinel-2 Data. Data Brief 2020, 31, 105737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. Modification of Normalised Difference Water Index (NDWI) to Enhance Open Water Features in Remotely Sensed Imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ling, F.; Wang, Q.; Li, W.; Li, X. Water Bodies’ Mapping from Sentinel-2 Imagery with Modified Normalized Difference Water Index at 10-m Spatial Resolution Produced by Sharpening the SWIR Band. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelly, J.T.; Gontz, A.M. Using GPS-Surveyed Intertidal Zones to Determine the Validity of Shorelines Automatically Mapped by Landsat Water Indices. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 65, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsu, N. A Threshold Selection Method from Gray-Level Histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1979, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vos, K.; Splinter, K.D.; Harley, M.D.; Simmons, J.A.; Turner, I.L. CoastSat: A Google Earth Engine-Enabled Python Toolkit to Extract Shorelines from Publicly Available Satellite Imagery. Environ. Model. Softw. 2019, 122, 104528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, H.-F.; Jargalsaikhan, D.; Tsai, H.-C.; Lin, C.-Y. An Improved Method for Image Thresholding Based on the Valley-Emphasis Method. In Proceedings of the 2013 Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference, Kaohsiung, Taiwan, 29 October–1 November 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- van der Walt, S.; Schönberger, J.L.; Nunez-Iglesias, J.; Boulogne, F.; Warner, J.D.; Yager, N.; Gouillart, E.; Yu, T. Scikit-Image: Image Processing in Python. PeerJ 2014, 2, e453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, T.; Vu, H.V.; Ho, H.; Dao, T.T.T.; Nguyen, H.T.H. Performance of Fish Farms in Vietnam–Does Financial Access Help Improve Their Cost Efficiency? Int. J. Financ. Stud. 2019, 7, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- GADM. Global Administrative Areas. 2020. Available online: https://gadm.org/data.html (accessed on 1 July 2021).
- Narayana, A.C. Shoreline Changes. In Encyclopedia of Estuaries; Kennish, M.J., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 590–602. ISBN 978-94-017-8800-7. [Google Scholar]
- Eckey, H.-F.; Kosfeld, R.; Türck, M. Deskriptive Statistik; Gabler: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2008; ISBN 978-3-8349-0859-9. [Google Scholar]
- Himmelstoss, E.A.; Henderson, R.E.; Kratzmann, M.G.; Farris, A.S. Digital Shoreline Analysis System (DSAS) Version 5.0 User Guide; Open-File Report; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2018. [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mullick, M.R.A.; Islam, K.M.A.; Tanim, A.H. Shoreline Change Assessment Using Geospatial Tools: A Study on the Ganges Deltaic Coast of Bangladesh. Earth Sci. Inform. 2020, 13, 299–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estevesf, L.S.; Finkl, C.; Raton, B. The Problem of Critically Eroded Areas (CEA): An Evaluation of Florida Beaches; Conference Paper. 1998. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/25736114 (accessed on 26 May 2021).
- Scheffler, D.; Hollstein, A.; Diedrich, H.; Segl, K.; Hostert, P. AROSICS: An Automated and Robust Open-Source Image Co-Registration Software for Multi-Sensor Satellite Data. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liem, N.V.; Bao, D.V.; Bac, D.K.; Cuong, N.C.; Nga, P.T.P.; Burkhard, B.; Chi, G.T.K. Assessment of Shoreline Changes for Setback Zone Establishment from Son Tra (Da Nang City) to Cua Dai (Hoi An City), Vietnam. Vietnam J. Earth Sci. 2020, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulder, M.A.; White, J.C.; Loveland, T.R.; Woodcock, C.E.; Belward, A.S.; Cohen, W.B.; Fosnight, E.A.; Shaw, J.; Masek, J.G.; Roy, D.P. The Global Landsat Archive: Status, Consolidation, and Direction. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- General Statistics Office of Vietnam. Results of the Census of Population and Housing at 0 O’clock April 1, 2019. Part III—Tabulated Tables; Statistical Publishing House: Hanoi, Vietnam, 2019; ISBN 978-604-75-1448-9.
- Minderhoud, P.S.J.; Erkens, G.; Pham, V.H.; Bui, V.T.; Erban, L.; Kooi, H.; Stouthamer, E. Impacts of 25 Years of Groundwater Extraction on Subsidence in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 064006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.; Tran, T.; Kervyn, M. Dynamics of Land Cover/Land Use Changes in the Mekong Delta, 1973–2011: A Remote Sensing Analysis of the Tran Van Thoi District, Ca Mau Province, Vietnam. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 2899–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hung, N.M.; Larson, M. Coastline and River Mouth Evolution in the Central Part of the Red River Delta. In Coastal Disasters and Climate Change in Vietnam; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 43–79. ISBN 978-0-12-800007-6. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, H.-H.; Tran, L.T.N.; Le, A.T.; Nghia, N.H.; Duong, L.V.K.; Nguyen, H.T.T.; Bohm, S.; Premnath, C.F.S. Monitoring Changes in Coastal Mangrove Extents Using Multi-Temporal Satellite Data in Selected Communes, Hai Phong City, Vietnam. For. Soc. 2020, 4, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.D.; Yoshino, K. Impacts of Mangrove Management Systems on Mangrove Changes in the Northern Coast of Vietnam. Tropics 2016, 24, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, H.-H.; McAlpine, C.; Pullar, D.; Johansen, K.; Duke, N.C. The Relationship of Spatial–Temporal Changes in Fringe Mangrove Extent and Adjacent Land-Use: Case Study of Kien Giang Coast, Vietnam. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2013, 76, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, S.; Xuan To, P.; Phuong, P.; Thuy, P.; Cuong, C.; Brown, S.; Robertson, S.; Vu, N.; McNally, R. Roots in the Water: Legal Frameworks for Mangrove PES in Vietnam; Forest Trends: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.Z.; Xuan Quynh, L.; Canters, F.; Corijn, E. SECOA 4—Environmental Conflicts in Coastal Urban Areas. Towards a Strategic Assessment Framework for Sustainable Development; Sapienza Università Editrice: Rome, Italy, 2013; 420p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DEEP-C Industrial Zones. Exploring Vietnam 2.0; Presentation Slides. 2020. Available online: https://www.oav.de/fileadmin/user_upload/2_Termine/Allgemein/OAV_ppt_20200702.pdf (accessed on 11 July 2021).











| Satellite | Tile ID | Date | Acquisition Time [UTC] | Cloud Cover [%] | Processing Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RE1 | 4946401 | 7 February 2017 | 03:51:05 | 0 | 3A |
| RE1 | 4946402 | 7 February 2017 | 03:51:04 | 0 | 3A |
| RE1 | 4946403 | 7 February 2017 | 03:51:03 | 1 | 3A |
| RE1 | 4946501 | 7 February 2017 | 03:51:02 | 0 | 3A |
| RE1 | 4946502 | 7 February 2017 | 03:51:01 | 0 | 3A |
| RE1 | 4946503 | 7 February 2017 | 03:51:00 | 0 | 3A |
| LC8 | 124049 | 7 February 2017 | 03:06:27 | 0 | T1 L2 |
| Class | Change Rates [m/Year] |
|---|---|
| Extreme accretion | >5 |
| Severe accretion | 5 to 3 |
| Intense accretion | 3 to 1 |
| Moderate accretion | 1 to 0.5 |
| Stable | 0.5 to −0.5 |
| Moderate erosion | −0.5 to −1 |
| Intense erosion | −1 to −3 |
| Severe erosion | −3 to −5 |
| Intense erosion | <−5 |
| Classification L1 [m/Year] | Proportion [%] | Classification L2 [m/Year] | Proportion [%] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stable (0.5 to −0.5) | 45.2 | ||
| Erosion (<−0.5) | 27.7 | Extreme erosion (<−5) | 39.2 |
| Severe erosion (−3 to −5) | 9.6 | ||
| Intense erosion (−3 to −1) | 22.0 | ||
| Moderate erosion (−1 to −0.5) | 29.3 | ||
| Accretion (>0.5) | 27.1 | Extreme accretion (>5) | 49.5 |
| Severe accretion (5 to 3) | 9.3 | ||
| Intense accretion (3 to 1) | 23.7 | ||
| Moderate accretion (1 to 0.5) | 17.5 |
| No. | Length [m] | Mean Change Rate [m/year] | Mean Standard Error [m] | Province |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0b | 39,400 | 34.4 | 4.9 | Thai Binh/Hai Phong City |
| 1b | 32,000 | 22.6 | 3.3 | Soc Trang |
| 2b | 22,600 | 39.0 | 3.3 | Ca Mau |
| 3b | 20,400 | 23.5 | 1.9 | Soc Trang/Tra Vinh |
| 4b | 17,200 | 8.6 | 2.5 | Bac Lieu |
| 5b | 16,200 | 47.3 | 6.9 | Thanh Hoa/Ninh Binh |
| 6b | 15,800 | 36.8 | 3.2 | Quang Ninh |
| 7b | 14,600 | 11.4 | 1.6 | Kien Giang |
| 8b | 14,200 | 14.8 | 1.0 | Kien Giang |
| 9b | 12,600 | 25.3 | 2.5 | Quang Ninh |
| 10b | 12,000 | 15.2 | 1.7 | Quang Ninh |
| 11b | 11,800 | 10.2 | 1.8 | Tra Vinh |
| 12b | 11,400 | 21.1 | 2.5 | Quang Ninh |
| 13b | 9400 | 15.3 | 2.4 | Da Nang City |
| 14b | 9400 | 13.0 | 5.8 | Quang Ninh |
| 15b | 9400 | 5.1 | 0.5 | Kien Giang |
| 16b | 9400 | 11.5 | 3.7 | Nam Dinh |
| 17b | 8800 | 15.6 | 3.7 | Nam Dinh |
| 18b | 7600 | 7.9 | 2.2 | Quang Ninh |
| 19b | 7200 | 6.7 | 1.3 | Kien Gang |
| 20b | 6800 | 24.9 | 3.6 | Ben Tre |
| 21b | 6400 | 28.9 | 4.1 | Ben Tre |
| 22b | 6200 | 20.1 | 5.2 | Thai Binh |
| 23b | 6200 | 6.1 | 0.3 | Kien Giang |
| 24b | 6000 | 12.3 | 3.2 | Quang Ninh |
| 25b | 6000 | 51.5 | 13.9 | Hai Phong City/Quang Ninh |
| 26b | 6000 | 6.8 | 0.8 | Tra Vinh |
| 27b | 6000 | 11.0 | 4.8 | Quang Ninh |
| 28b | 6000 | 21.4 | 8.2 | Nam Dinh |
| 29b | 5800 | 6.5 | 0.9 | Quang Ninh |
| 30b | 5000 | 21.8 | 3.9 | Ha Tinh |
| 31b | 4800 | 8.8 | 1.2 | Hai Phong City |
| 32b | 4400 | 9.5 | 1.7 | Khanh Hoa |
| 33b | 4400 | 10.9 | 1.7 | Hai Phong City |
| 34b | 4400 | 25.1 | 2.8 | Kien Giang |
| 35b | 4200 | 19.2 | 2.0 | Tien Giang |
| 36b | 4200 | 6.1 | 1.0 | Binh Thuan |
| No. | Length [m] | Mean Change Rate [m/year] | Mean Standard Error [m] | Province |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0a | 101,600 | −25.1 | 1.0 | Ca Mau/Bac Lieu |
| 1a | 82,200 | −10.7 | 0.8 | Kien Giang/Ca Mau |
| 2a | 14,200 | −13.2 | 0.5 | Ben Tre |
| 3a | 13,600 | −7.7 | 0.4 | Tien Giang |
| 4a | 13,400 | −16.7 | 2.3 | Bac Lieu/Soc Trang |
| 5a | 12,600 | −7.8 | 1.6 | Bac Lieu/Soc Trang |
| 6a | 12,000 | −9.5 | 1.2 | Kien Giang |
| 7a | 12,000 | −5.7 | 0.6 | Tra Vinh |
| 8a | 10,800 | −5.3 | 1.0 | Nam Dinh |
| 9a | 9200 | −5.9 | 1.6 | Bac Lieu |
| 10a | 9000 | −6.2 | 1.5 | Quang Nam |
| 11a | 8800 | −10.9 | 0.5 | Soc Trang |
| 12a | 8400 | −18.5 | 1.2 | Tien Giang/Ben Tre |
| 13a | 7800 | −7.1 | 1.2 | Ba Ria/Vung Tau |
| 14a | 7200 | −9.5 | 4.4 | Quang Ninh |
| 15a | 6800 | −27.7 | 2.4 | Nam Dinh |
| 16a | 6600 | −22.3 | 2.3 | Nam Dinh |
| 17a | 6400 | −15.7 | 7.2 | Quang Ninh |
| 18a | 5400 | −8.4 | 0.8 | Nam Dinh |
| 19a | 5400 | −6.3 | 2.7 | Thai Binh |
| 20a | 4200 | −8.5 | 2.4 | Quang Ninh |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lappe, R.; Ullmann, T.; Bachofer, F. State of the Vietnamese Coast—Assessing Three Decades (1986 to 2021) of Coastline Dynamics Using the Landsat Archive. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2476. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14102476
Lappe R, Ullmann T, Bachofer F. State of the Vietnamese Coast—Assessing Three Decades (1986 to 2021) of Coastline Dynamics Using the Landsat Archive. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(10):2476. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14102476
Chicago/Turabian StyleLappe, Ronja, Tobias Ullmann, and Felix Bachofer. 2022. "State of the Vietnamese Coast—Assessing Three Decades (1986 to 2021) of Coastline Dynamics Using the Landsat Archive" Remote Sensing 14, no. 10: 2476. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14102476
APA StyleLappe, R., Ullmann, T., & Bachofer, F. (2022). State of the Vietnamese Coast—Assessing Three Decades (1986 to 2021) of Coastline Dynamics Using the Landsat Archive. Remote Sensing, 14(10), 2476. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14102476