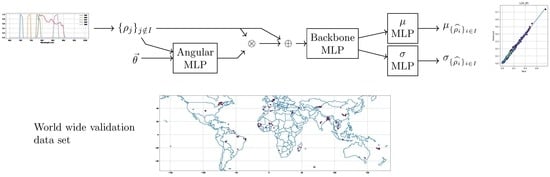
Assessment of the Usefulness of Spectral Bands for the Next Generation of Sentinel-2 Satellites by Reconstruction of Missing Bands
Abstract
Share and Cite
Inglada, J.; Michel, J.; Hagolle, O. Assessment of the Usefulness of Spectral Bands for the Next Generation of Sentinel-2 Satellites by Reconstruction of Missing Bands. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2503. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14102503
Inglada J, Michel J, Hagolle O. Assessment of the Usefulness of Spectral Bands for the Next Generation of Sentinel-2 Satellites by Reconstruction of Missing Bands. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(10):2503. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14102503
Chicago/Turabian StyleInglada, Jordi, Julien Michel, and Olivier Hagolle. 2022. "Assessment of the Usefulness of Spectral Bands for the Next Generation of Sentinel-2 Satellites by Reconstruction of Missing Bands" Remote Sensing 14, no. 10: 2503. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14102503
APA StyleInglada, J., Michel, J., & Hagolle, O. (2022). Assessment of the Usefulness of Spectral Bands for the Next Generation of Sentinel-2 Satellites by Reconstruction of Missing Bands. Remote Sensing, 14(10), 2503. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14102503