Investigating the Relationship between Air Pollutants and Meteorological Parameters Using Satellite Data over Bangladesh
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
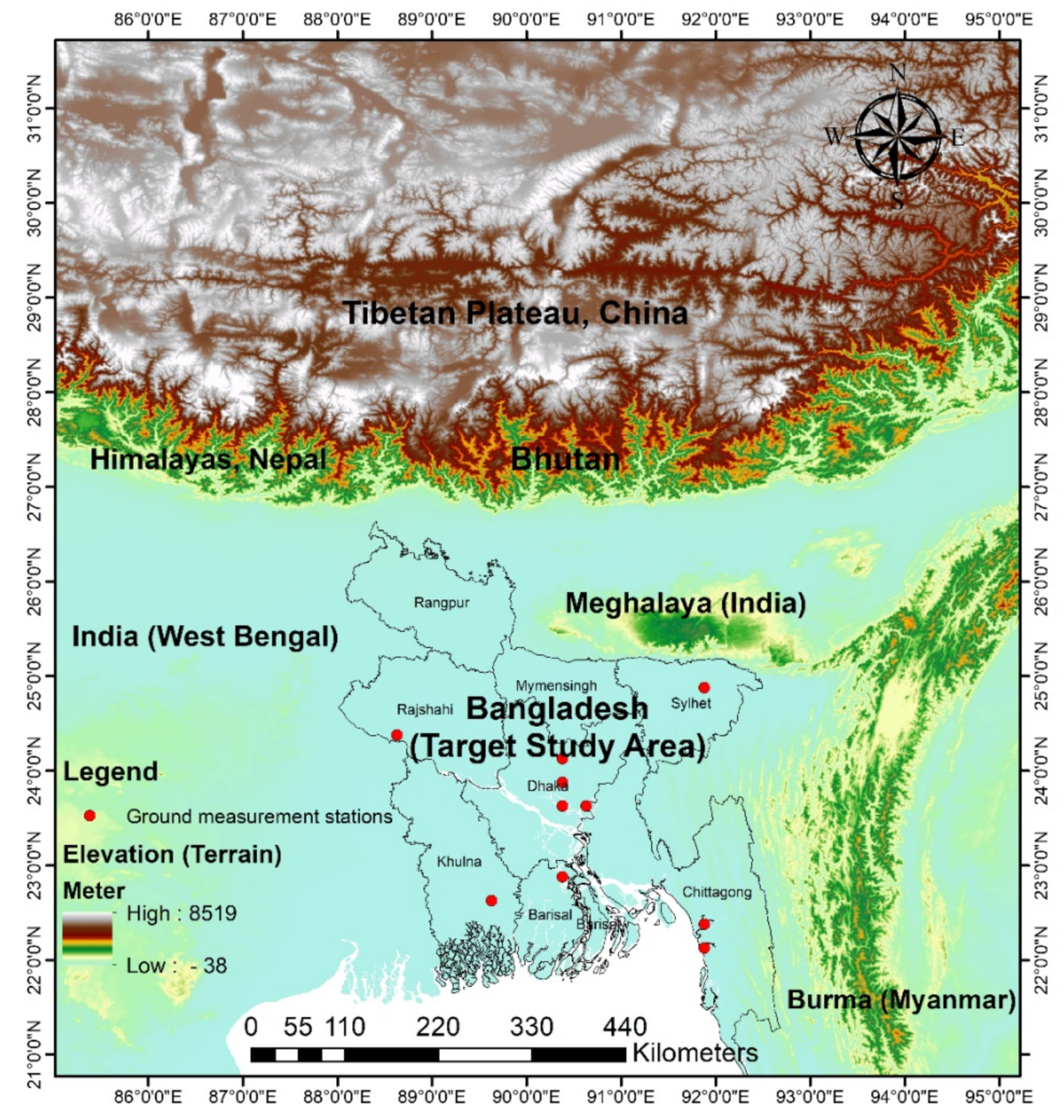
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Description
2.3. Methods
3. Results
3.1. Average Seaonal Variation in Air Pollutants
3.2. Trend Analysis of Air Pollutants
3.3. Trend Analysis of Meteorological Parameters
3.4. Relationship between Air Pollutants and Meteorological Parameters
3.4.1. Spatial Relationship between NO2 and Meteorological Variables
3.4.2. Spatial Relationship between O3 and Meteorological Variables
3.4.3. Spatial Relationship between SO2 and Meteorological Variables
3.4.4. Spatial Relationship between CO and Meteorological Variables
3.4.5. Average Coefficient Values between Air Pollutants and Meteorological Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kampa, M.; Castanas, E. Human health effects of air pollution. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 151, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Wang, W.; Wang, W.; Jiang, X.; Yu, T.; Ciren, P. Spatial assessment of health economic losses from exposure to ambient pollutants in China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guan, W.J.; Zheng, X.Y.; Chung, K.F.; Zhong, N.S. Impact of air pollution on the burden of chronic respiratory diseases in China: Time for urgent action. Lancet 2016, 388, 1939–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chen, R.; Sera, F.; Vicedo-Cabrera, A.M.; Guo, Y.; Tong, S.; Coelho, M.S.Z.S.; Saldiva, P.H.N.; Lavigne, E.; Matus, P.; et al. Ambient Particulate Air Pollution and Daily Mortality in 652 Cities. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vineis, P.; Forastiere, F.; Hoek, G.; Lipsett, M. Outdoor air pollution and lung cancer: Recent epidemiologic evidence. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 111, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoek, G.; Krishnan, R.M.; Beelen, R.; Peters, A.; Ostro, B.; Brunekreef, B.; Kaufman, J.D. Long-term air pollution exposure and cardio-respiratory mortality: A review. Environ. Health A Glob. Access Sci. Source 2013, 12, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lelieveld, J.; Evans, J.S.; Fnais, M.; Giannadaki, D.; Pozzer, A. The contribution of outdoor air pollution sources to premature mortality on a global scale. Nature 2015, 525, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buoli, M.; Grassi, S.; Caldiroli, A.; Carnevali, G.S.; Mucci, F.; Iodice, S.; Cantone, L.; Pergoli, L.; Bollati, V. Is there a link between air pollution and mental disorders? Environ. Int. 2018, 118, 154–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, B.N.; Prados, A.I.; Lamsal, L.N.; Liu, Y.; Streets, D.G.; Gupta, P.; Hilsenrath, E.; Kahn, R.A.; Nielsen, J.E.; Beyersdorf, A.J.; et al. Satellite data of atmospheric pollution for U.S. air quality applications: Examples of applications, summary of data end-user resources, answers to FAQs, and common mistakes to avoid. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 94, 647–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheehan, P.; Cheng, E.; English, A.; Sun, F. China’s response to the air pollution shock. Nat. Clim. Change 2014, 4, 306–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Tian, H.; Cheng, K.; Lu, L.; Zheng, M.; Wang, S.; Hao, J.; Wang, K.; Hua, S.; Zhu, C.; et al. The variation of chemical characteristics of PM 2.5 and PM 10 and formation causes during two haze pollution events in urban Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 107, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Mauzerall, D.L.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Song, Y.; Peng, W.; Klimont, Z.; Qiu, X.; Zhang, S.; Hu, M.; et al. Air pollutant emissions from Chinese households: A major and underappreciated ambient pollution source. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 7756–7761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Editorial Cleaner air for China. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 497. [CrossRef]
- Tilt, B. China’s air pollution crisis: Science and policy perspectives. Environ. Sci. Policy 2019, 92, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Gong, S.; Yu, Y.; Yu, L.; Wu, L.; Mao, H.; Song, C.; Zhao, S.; Liu, H.; Li, X.; et al. Air pollution characteristics and their relation to meteorological conditions during 2014–2015 in major Chinese cities. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, B.A.; Hopke, P.K.; Markwitz, A. Air pollution by fine particulate matter in Bangladesh. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2013, 4, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muntaseer Billah Ibn Azkar, M.A.; Chatani, S.; Sudo, K. Simulation of urban and regional air pollution in Bangladesh. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, 16509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ul-Haq, Z.; Tariq, S.; Ali, M. Tropospheric NO2 trends over south Asia during the last decade (2004–2014) using OMI Data. Adv. Meteorol. 2015, 2015, 959284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pavel, M.R.S.; Zaman, S.U.; Jeba, F.; Islam, M.S.; Salam, A. Long-Term (2003–2019) Air Quality, Climate Variables, and Human Health Consequences in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Front. Sustain. Cities 2021, 3, 681759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elminir, H.K. Dependence of urban air pollutants on meteorology. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 350, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Gao, H.; Liao, H.; Tian, X. Spatiotemporal variations and uncertainty in crop residue burning emissions over North China plain: Implication for atmospheric co2 simulation. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, Z.; Cui, L.; Fu, H.; Zhang, L.; Kong, L.; Chen, W.; Chen, J. Air pollution characteristics in China during 2015–2016: Spatiotemporal variations and key meteorological factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 902–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Yu, Y.; Gu, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, M.; Yue, H.; Gao, J.; Lei, R.; Ge, X. Characteristics of air pollution and their relationship with meteorological parameters: Northern versus southern cities of China. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, W.; Li, K.; Liao, H.; Wang, H.; Wu, L. Weather conditions conducive to Beijing severe haze more frequent under climate change. Nat. Clim. Change 2017, 7, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turalioglu, S.O. Relationship Between Air Pollutants and Some Meteorological Parameters in Erzurum, Turkey. In Global Warming, Green Energy and Technology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; Volume 31, ISBN 9781441910165. [Google Scholar]
- Jayamurugan, R.; Kumaravel, B.; Palanivelraja, S.; Chockalingam, M.P. Influence of Temperature, Relative Humidity and Seasonal Variability on Ambient Air Quality in a Coastal Urban Area. Int. J. Atmos. Sci. 2013, 2013, 264046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Lu, J. Exploring the relationship between air pollution and meteorological conditions in China under environmental governance. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, Y.H.; Li, R.R. Correlation analysis of AQI characteristics and meteorological conditions in heating season. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 242, 022067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, K.; Xu, X. Evaluation of the influence between local meteorology and air quality in Beijing using generalized additive models. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foody, G.M. Geographical weighting as a further refinement to regression modelling: An example focused on the NDVI-rainfall relationship. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 88, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, S.R. Handbook on Atmospheric Diffusion Models; U.S. Department of Energy: Washington, DC, USA, 1981; Volume 11223, ISBN 0870791273.
- Barua, D.K. The active delta of the ganges-brahmaputra rivers: Dynamics of its present formations. Mar. Geod. 1997, 20, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Ghosh, T.; Salehin, M.; Ghosh, A.; Haque, A.; Hossain, M.A.; Das, S.; Hazra, S.; Islam, N.; Sarker, M.H.; et al. Ganges-Brahmaputra-Meghna Delta, Bangladesh and India: A Transnational Mega-Delta. In Deltas in the Anthropocene; Palgrave Macmillan: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 23–51. ISBN 9783030235161. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, M.; Papa, F.; Karpytchev, M.; Delebecque, C.; Krien, Y.; Khan, J.U.; Ballu, V.; Durand, F.; Le Cozannet, G.; Islam, A.K.M.S.; et al. Water level changes, subsidence, and sea level rise in the Ganges-Brahmaputra-Meghna delta. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 1867–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bari, S.H.; Hussain, M.M.; Husna, N.E.A. Rainfall variability and seasonality in northern Bangladesh. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2017, 129, 995–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harzallah, A.; Sadourny, R. Observed lead-lag relationships between Indian summer monsoon and some meteorological variables. Clim. Dyn. 1997, 13, 635–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickolay, A.; Krotkov, L.N.; Lamsal, S.; Marchenko, V.; Celarier, A.E.; Bucsela, E.J.; William, H.; Swartz, J.J.; OMI Core Team. OMI/Aura NO2 Cloud-Screened Total and Tropospheric Column L3 Global Gridded 0.25 Degree × 0.25 Degree V3; NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Goddard Earth Sciences Data and Information Services Center (GES DISC): Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2019.
- Li, C.; Nickolay, A.; Krotkov, P.L. OMI/Aura Sulfur Dioxide (SO2) Total Column L3 1 Day Best Pixel in 0.25 Degree × 0.25 Degree V3; Goddard Earth Sciences Data and Information Services Center (GES DISC): Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Veefkind, P. OMI/Aura Ozone (O3) DOAS Total Column L3 1 Day 0.25 degree × 0.25 Degree V3; Goddard Earth Sciences Data and Information Services Center (GES DISC): Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- MOPITT Team. MOPITT Measurement of Pollution in the Troposphere; MOPITT Team: Boulder, CO, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Barret, B.; De Mazière, M.; Mahieu, E. Ground-based FTIR measurements of CO from the Jungfraujoch: Characterisation and comparison with in situ surface and MOPITT data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2003, 3, 2217–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodell, M.; Houser, P.R.; Jambor, U.; Gottschalck, J.; Mitchell, K.; Meng, C.J.; Arsenault, K.; Cosgrove, B.; Radakovich, J.; Bosilovich, M.; et al. The Global Land Data Assimilation System. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2004, 85, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beaudoing, H.; Rodell, N. GLDAS Noah Land Surface Model L4 Monthly 0.25 × 0.25 degree V2.1. Goddard Earth Sciences Data and Information Services Center (GES DISC): Greenbelt, Maryland, USA. Available online: https://disc.gsfc.nasa.gov/datasets/GLDAS_NOAH025_3H_2.1/summary (accessed on 20 November 2021).
- Li, B.; Beaudoing, H.; Rodell, N.M. GLDAS Catchment Land Surface Model L4 Daily 0.25 × 0.25 Degree V2.0; Goddard Earth Sciences Data and Information Services Center (GES DISC): Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J. TRMM (TMPA) Precipitation L3 1 Day 0.25 Degree × 0.25 Degree V7; Savtchenko, A., Ed.; Goddard Earth Sciences Data and Information Services Center (GES DISC): Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, K.; Qin, J.; Zhao, L.; Tang, W.; Han, M. Evaluation of AMSR-E retrievals and GLDAS simulations against observations of a soil moisture network on the central Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 4466–4475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakaya, T.; Fotheringham, A.S.; Charlton, M.; Brunsdon, C. Semiparametric geographically weighted generalised linear modelling in GWR 4.0. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on GeoComputation, University of New South Wales, Sydney, Australia, 30 November–2 December 2009; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Nakaya, T. Windows Application for Geographically Weighted Regression Modelling; Department of Geography, Ritsumeikan University: Kyoto, Japan, 2016; Available online: https://gwr.maynoothuniversity.ie/gwr4-software/ (accessed on 28 October 2021).
- Nakaya, T.; Fotheringham, A.S.; Brunsdon, C.; Charlton, M. Geographically weighted Poisson regression for disease association mapping. Stat. Med. 2005, 24, 2695–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calvert, J.G. Glossary of atmospheric chemistry terms. Pure Appl. Chem. 1990, 62, 2167–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dobson Unit—Wikipedia. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dobson_unit (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Dobson Unit. Available online: https://www.temis.nl/general/dobsonunit.php (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Rahman, M.M.; Mahamud, S.; Thurston, G.D. Recent spatial gradients and time trends in Dhaka, Bangladesh, air pollution and their human health implications. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2019, 69, 478–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, K.; Gope, K.; Chowdhury, S.M.R. Possible Causes & Solutions of Traffic Jam and Their Impact on the Economy of Dhaka City. J. Manag. Sustain. 2012, 2, 112–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Ge, X. Nitrogen Oxide Emission, Economic Growth and Urbanization in China: A Spatial Econometric Analysis. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 301, 012126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Liu, Y.; Gyilbag, A. Assessment of Meteorological Variables and Air Pollution Affecting COVID-19 Cases in Urban Agglomerations: Evidence from China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilić, P.; Popović, Z.; Nešković Markić, D. Assessment of Meteorological Effects and Ozone Variation in Urban Area. Ecol. Chem. Eng. 2020, 27, 373–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khiem, M.; Ooka, R.; Huang, H.; Hayami, H.; Yoshikado, H.; Kawamoto, Y. Analysis of the Relationship between Changes in Meteorological Conditions and the Variation in Summer Ozone Levels over the Central Kanto Area. Adv. Meteorol. 2010, 2010, 349248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, L.; Shen, L. Meteorology and Climate Influences on Tropospheric Ozone: A Review of Natural Sources, Chemistry, and Transport Patterns. Curr. Pollut. Reports 2019, 5, 238–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nurjanah, A.; Arifin, M.; Hayashi, T. Ozone Depletion and its Impacts on Life of Asian Countries; Gifu University: Gifu, Japan, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Okoro, E.C.; Okeke, F.N.; Omeje, L.C. Investigating Contributions of Total Column Ozone Variation on Some Meteorological Parameters in Nigeria. Atmos. Clim. Sci. 2022, 12, 132–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Automobile Air Conditioners and Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs). Available online: https://p2infohouse.org/ref/01/00038.htm (accessed on 18 January 2022).
- Ozone-Depleting Substances|US EPA. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/ozone-layer-protection/ozone-depleting-substances (accessed on 18 January 2022).
- Lin, C.A.; Chen, Y.C.; Liu, C.Y.; Chen, W.T.; Seinfeld, J.H.; Chou, C.C.K. Satellite-derived correlation of SO2, NO2, and aerosol optical depth with meteorological conditions over East Asia from 2005 to 2015. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khoder, M.I. Atmospheric conversion of sulfur dioxide to particulate sulfate and nitrogen dioxide to particulate nitrate and gaseous nitric acid in an urban area. Chemosphere 2002, 49, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Photodissociation—Wikipedia. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Photodissociation (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Environmental effects of ozone depletion and its interactions with climate change: 2002 assessment. Executive summary. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2003, 2, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.; Yin, H.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, B.; Notholt, J.; Lu, X.; Liu, C.; Tian, Y.; Liu, J. Quantifying variability, source, and transport of CO in the urban areas over the Himalayas and Tibetan Plateau. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 9201–9222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, S.; Klingmyr, D.; Tagesson, T. Global-scale patterns and trends in tropospheric no2 concentrations, 2005–2018. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Zhu, X.; Zhong, Q.; Yun, X.; Meng, W.; Li, B.; Ma, J.; Zeng, E.Y.; Tao, S. Spatial and Temporal Trends in Global Emissions of Nitrogen Oxides from 1960 to 2014. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 7992–8000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beevers, S.D.; Westmoreland, E.; de Jong, M.C.; Williams, M.L.; Carslaw, D.C. Trends in NOx and NO2 emissions from road traffic in Great Britain. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 54, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, J.A. Nitrogen Oxides in the Troposphere’ Global and Regional Budget. J. Geophys. Res. 1983, 88, 10785–10807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, C.; Ghude, S.D.; Pfister, G.G.; Chate, D.M.; Kumar, R.; Beig, G.; Surendran, D.E.; Fadnavis, S.; Lal, D.M. Influence of springtime biomass burning in South Asia on regional ozone (O3): A model based case study. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 100, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICIMOD. FACT SHEET-Brick Sector in Bangladesh; International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD): Kathmandu, Nepal, 2019; Available online: https://lib.icimod.org/record/34681 (accessed on 20 December 2021).
- Guttikunda, S.K.; Begum, B.A.; Wadud, Z. Particulate pollution from brick kiln clusters in the Greater Dhaka region, Bangladesh. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2013, 6, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, H. Brick Kilns Top Polluter. Available online: https://www.thedailystar.net/frontpage/news/brick-kilns-top-polluter-1701871 (accessed on 25 December 2021).
- Wu, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhai, J.; Cong, L.; Wang, Y.; Ma, W.; Zhang, Z.; Li, C. Comparison of dry and wet deposition of particulate matter in near-surface waters during summer. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.J.; Noll, K.E.; Holsen, T.M. Dry deposition velocities as a function of particle size in the ambient atmosphere. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 1994, 20, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wałaszek, K.; Kryza, M.; Dore, A.J. The impact of precipitation on wet deposition of sulphur and nitrogen compounds. Ecol. Chem. Eng. S 2013, 20, 733–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zannetti, P. Dry and Wet Deposition. In Air Pollution Modeling; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1990; pp. 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleniacz, R.; Bogacki, M.; Szulecka, A.; Rzeszutek, M.; Mazur, M. Assessing the Impact of Wind Speed and Mixing-Layer Height on Air Quality in Krakow (Poland) in the Years 2014–2015. J. Civ. Eng. Environ. Archit. 2016, 63, 315–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lubiński, P. Analysis of extremely low signal-to-noise ratio data from INTEGRAL/PICsIT. Astron. Astrophys. 2009, 496, 557–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Han, H.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, H.; Meng, L.; Li, Y.C.; Liu, Y. Satellite-observed variations and trends in carbon monoxide over Asia and their sensitivities to biomass burning. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, B.; Chevallier, F.; Ciais, P.; Yin, Y.; Deeter, M.N.; Worden, H.M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; He, K. Rapid decline in carbon monoxide emissions and export from East Asia between years 2005 and 2016. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 044007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhuyan, M.D.I.; Islam, M.M.; Bhuiyan, M.E.K. A Trend Analysis of Temperature and Rainfall to Predict Climate Change for Northwestern Region of Bangladesh. Am. J. Clim. Change 2018, 7, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saimi, F.M.; Hamzah, F.M.; Toriman, M.E.; Jaafar, O.; Tajudin, H. Trend and linearity analysis of meteorological parameters in peninsular Malaysia. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Zhang, W.; Wang, K. Assessment on surface energy imbalance and energy partitioning using ground and satellite data over a semi-arid agricultural region in north China. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 213, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bei, N.; Li, G.; Huang, R.J.; Cao, J.; Meng, N.; Feng, T.; Liu, S.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Molina, L.T. Typical synoptic situations and their impacts on the wintertime air pollution in the Guanzhong basin, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 7373–7387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ning, G.; Wang, S.; Yim, S.H.L.; Li, J.; Hu, Y.; Shang, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, J. Impact of low-pressure systems on winter heavy air pollution in the northwest Sichuan Basin, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 13601–13615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schäfer, K.; Emeis, S.; Hoffmann, H.; Jahn, C. Influence of mixing layer height upon air pollution in urban and sub-urban areas. Meteorol. Z. 2006, 15, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]











| Data Source/Platform | Parameter | Default Units * | Spatial Resolution | Temporal Resolution | Web Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI)/Aura | Nitrogen dioxide (NO2) | Molecules/cm2 | 0.25° × 0.25° | Daily ** | https://giovanni.gsfc.nasa.gov/giovanni (accessed on 25 October 2021) |
| Ozone (O3) | Dobson Units (DU) | 0.25° × 0.25° | Daily ** | ||
| Sulfur dioxide (SO2) | Dobson Units (DU) | 0.25° × 0.25° | Daily ** | ||
| Measurement of Pollution in the Troposphere (MOPITT)/Terra | Carbon monoxide (CO) | Molecules/cm2 | 1.0° × 1.0° | Monthly | |
| Global Land Data Assimilation System (GLDAS)/Noah ** | Temperature (T) | Kelvin | 0.25° × 0.25° | Monthly | |
| Pressure (P) | Pascal (Pa) | 0.25° × 0.25° | Monthly | ||
| Specific humidity (SH) | kg/kg | 0.25° × 0.25° | Monthly | ||
| Wind speed (WS) | m/s | 0.25° × 0.25° | Monthly | ||
| Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) | Rainfall (Rf) | Mm | 0.25° × 0.25° | Monthly | |
| Global Land Data Assimilation System/Noah *** | Net solar radiation (Rs) | W/m2 | 0.25° × 0.25° | Monthly | |
| Latent heat flux (LE) | W/m2 | 0.25° × 0.25° | Monthly |
| Air Pollutant | Conversion Factor | Molecular Weight |
|---|---|---|
| Ozone (O3) | 1 ppb * = 1.96 µg/m3 | 48.00 g/mol |
| Nitrogen dioxide (NO2) | 1 ppb = 1.88 µg/m3 | 46.01 g/mol |
| Sulfur dioxide (SO2) | 1 ppb = 2.62 µg/m3 | 64.07 g/mol |
| Carbon monoxide (CO) | 1 ppb = 1.15 µg/m3 | 2.01 g/mol |
| Variable Names (Units) | NO2 (DU *) | O3 (DU) | SO2 (DU) | CO (DU *) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature (K) | 0.95 | −132.30 | −1.30 | 0.26 |
| Pressure (Pa) | −0.19 | −2.50 | −0.11 | −0.02 |
| Specific Humidity (g/g) | −0.06 | −3.21 | −0.08 | 0.01 |
| Wind Speed (m/s) | 0.01 | 1.13 | 0.01 | 0.002 |
| Rainfall (mm) | −0.01 | −0.53 | −0.002 | −0.002 |
| Solar Radiation (W/m2) | 0.02 | −1.42 | −0.01 | −0.003 |
| Latent Heat Flux (W/m2) | −0.01 | −0.52 | −0.003 | 0.0003 |
| R2 | 0.90 | 0.93 | 0.76 | 0.94 |
| Variable Names (Units) | NO2 (DU *) | O3 (DU) | SO2 (DU) | CO (DU *) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature (K) | 0.12 | −29.02 | 0.182 | 31.09 |
| Pressure (Pa) | 0.43 | 7.21 | 0.002 | 34.67 |
| Specific Humidity (g/g) | −0.04 | −1.09 | −0.001 | 5.93 |
| Wind Speed (m/s) | 0.02 | 0.57 | −0.002 | −0.85 |
| Rainfall (mm) | −0.01 | −0.82 | −0.018 | −1.79 |
| Solar Radiation (W/m2) | −0.02 | −0.62 | −0.012 | 0.62 |
| Latent Heat Flux (W/m2) | −0.01 | −0.15 | −0.002 | 1.12 |
| R2 | 0.90 | 0.93 | 0.76 | 0.94 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rahman, M.M.; Shuo, W.; Zhao, W.; Xu, X.; Zhang, W.; Arshad, A. Investigating the Relationship between Air Pollutants and Meteorological Parameters Using Satellite Data over Bangladesh. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2757. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14122757
Rahman MM, Shuo W, Zhao W, Xu X, Zhang W, Arshad A. Investigating the Relationship between Air Pollutants and Meteorological Parameters Using Satellite Data over Bangladesh. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(12):2757. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14122757
Chicago/Turabian StyleRahman, Md Masudur, Wang Shuo, Weixiong Zhao, Xuezhe Xu, Weijun Zhang, and Arfan Arshad. 2022. "Investigating the Relationship between Air Pollutants and Meteorological Parameters Using Satellite Data over Bangladesh" Remote Sensing 14, no. 12: 2757. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14122757
APA StyleRahman, M. M., Shuo, W., Zhao, W., Xu, X., Zhang, W., & Arshad, A. (2022). Investigating the Relationship between Air Pollutants and Meteorological Parameters Using Satellite Data over Bangladesh. Remote Sensing, 14(12), 2757. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14122757







