Land Subsidence Monitoring and Dynamic Prediction of Reclaimed Islands with Multi-Temporal InSAR Techniques in Xiamen and Zhangzhou Cities, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
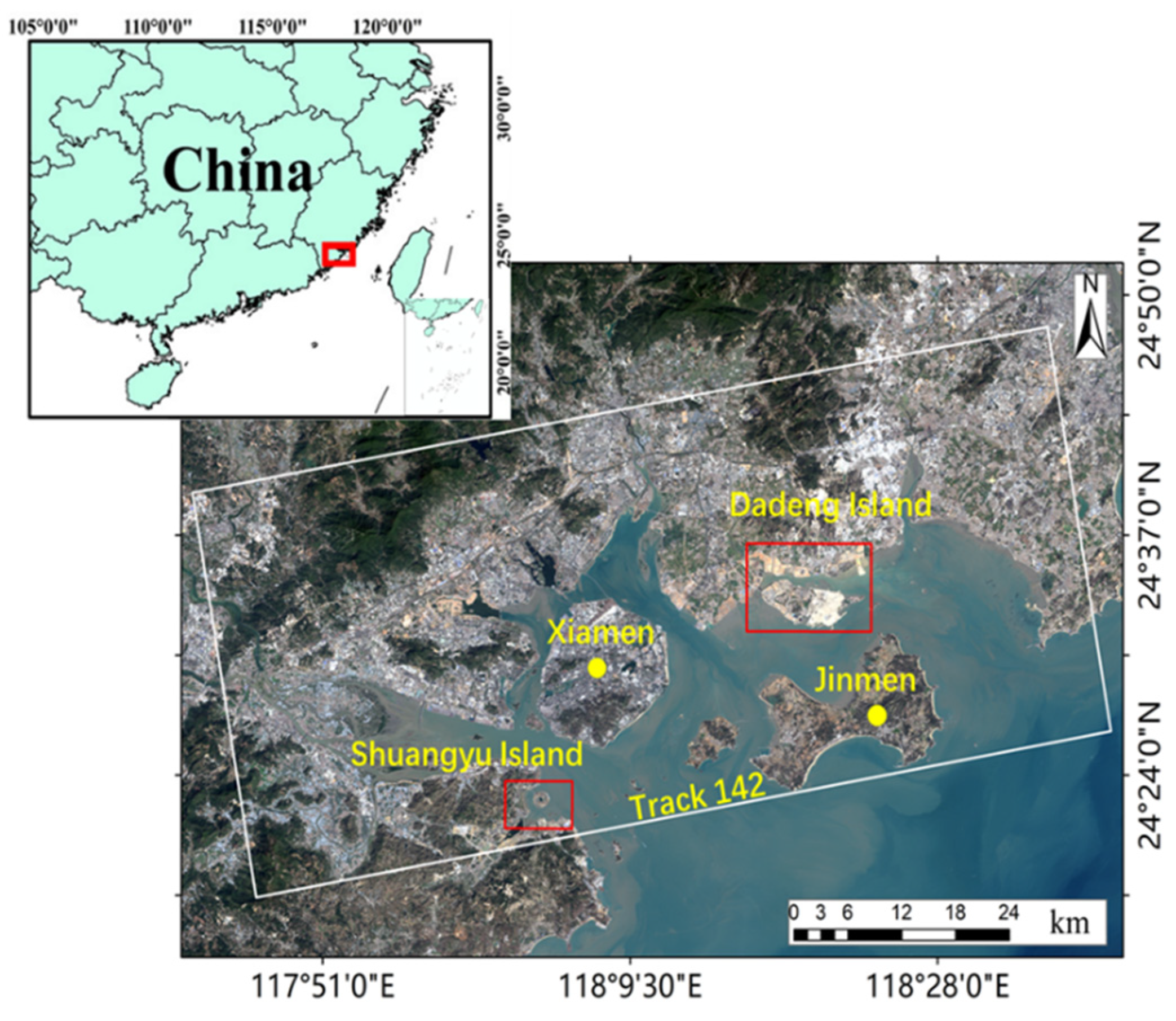
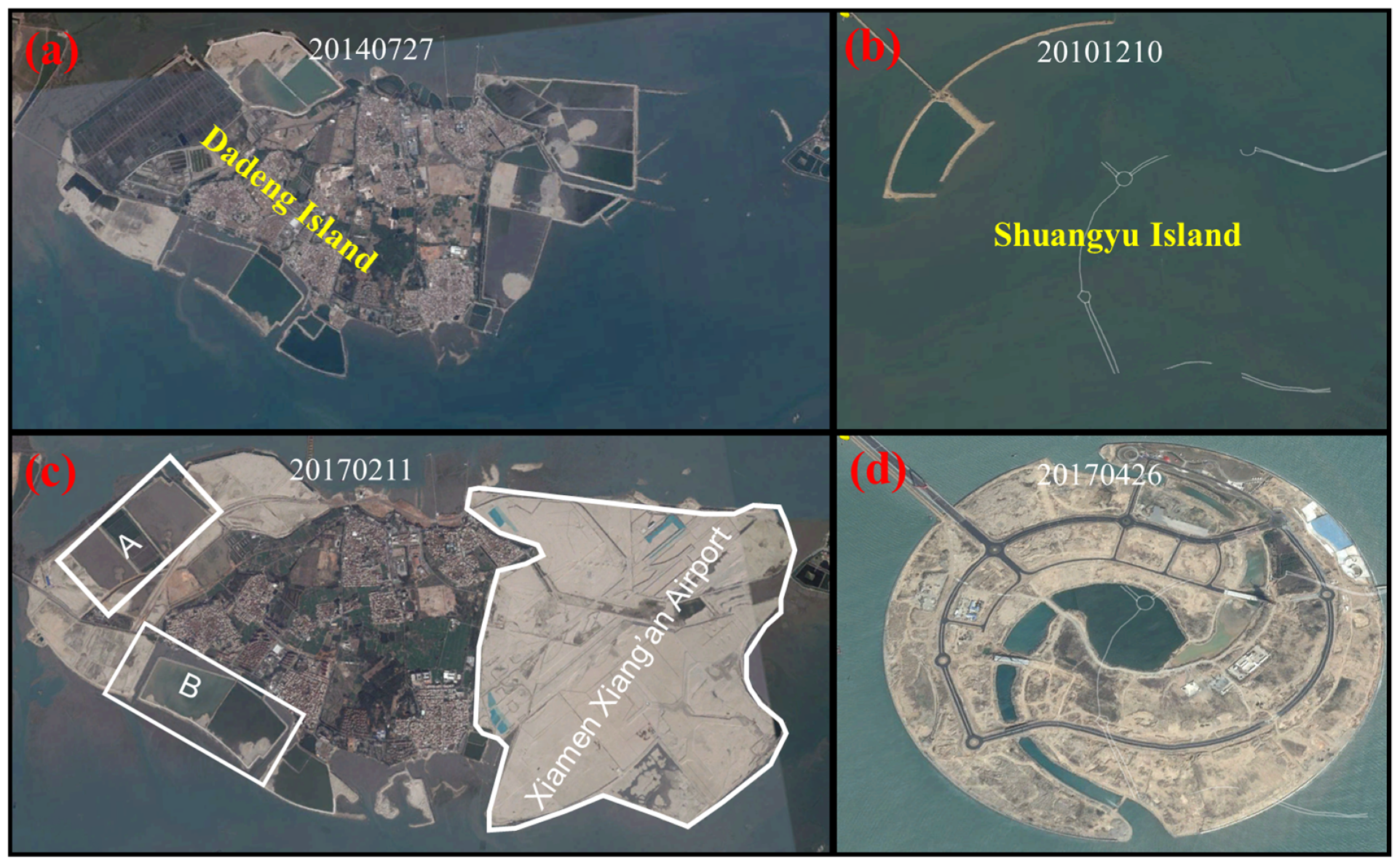
2.1. Study Area
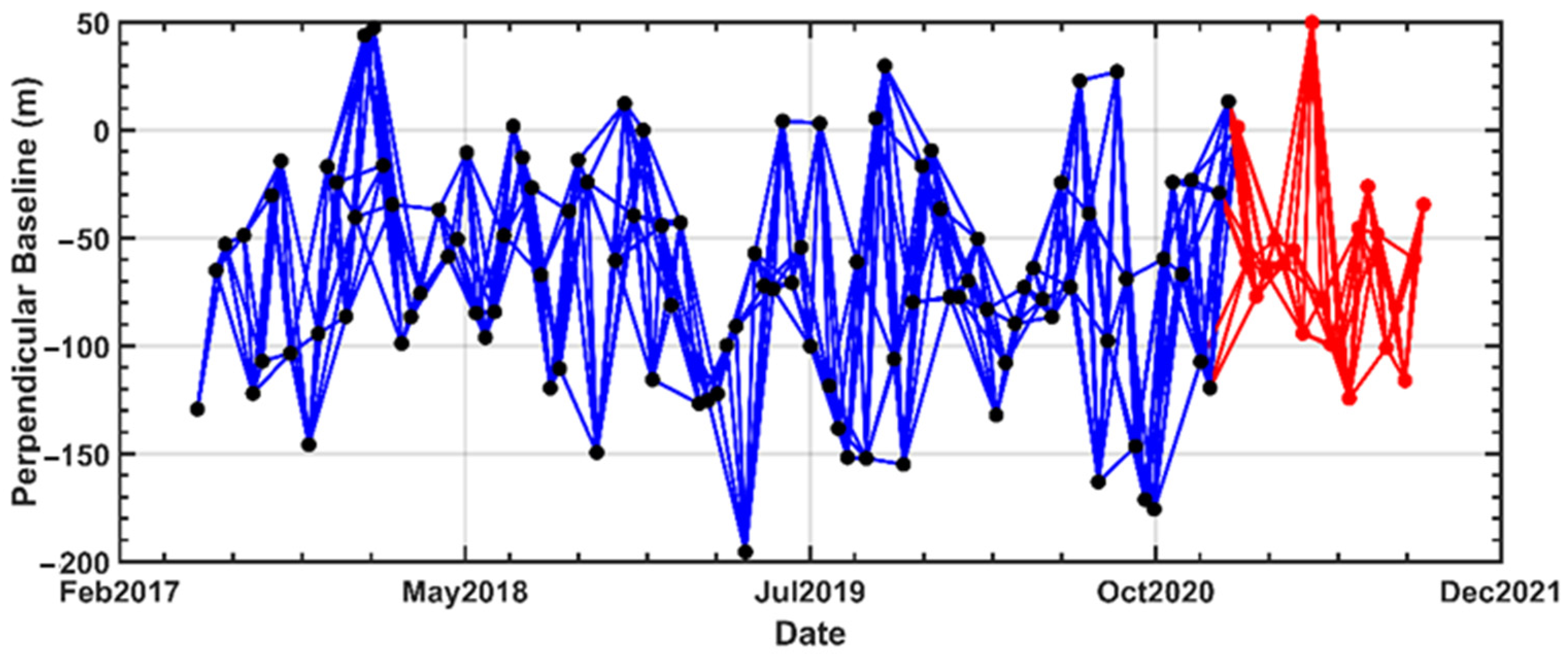
2.2. Data
3. Method
4. Results
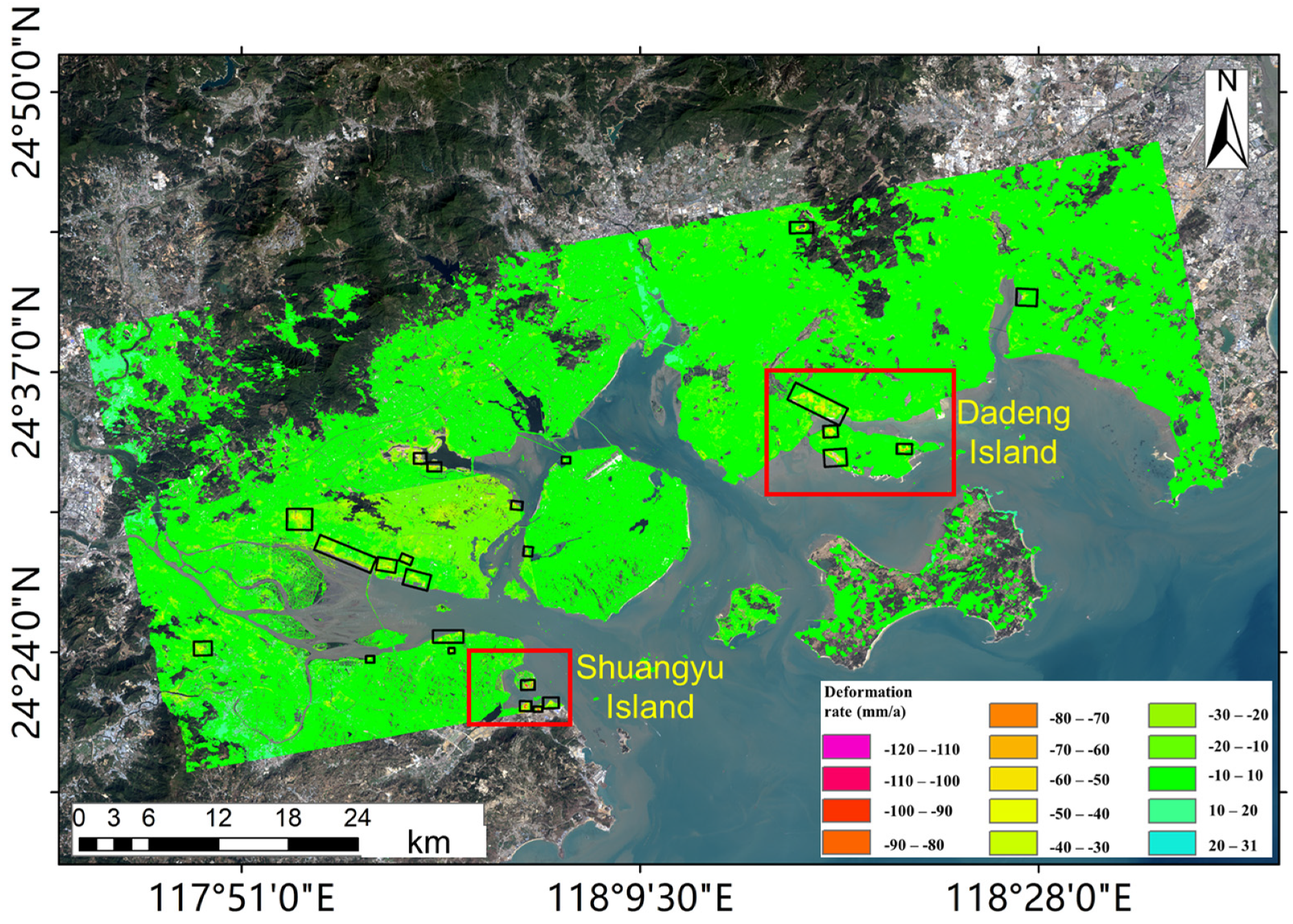
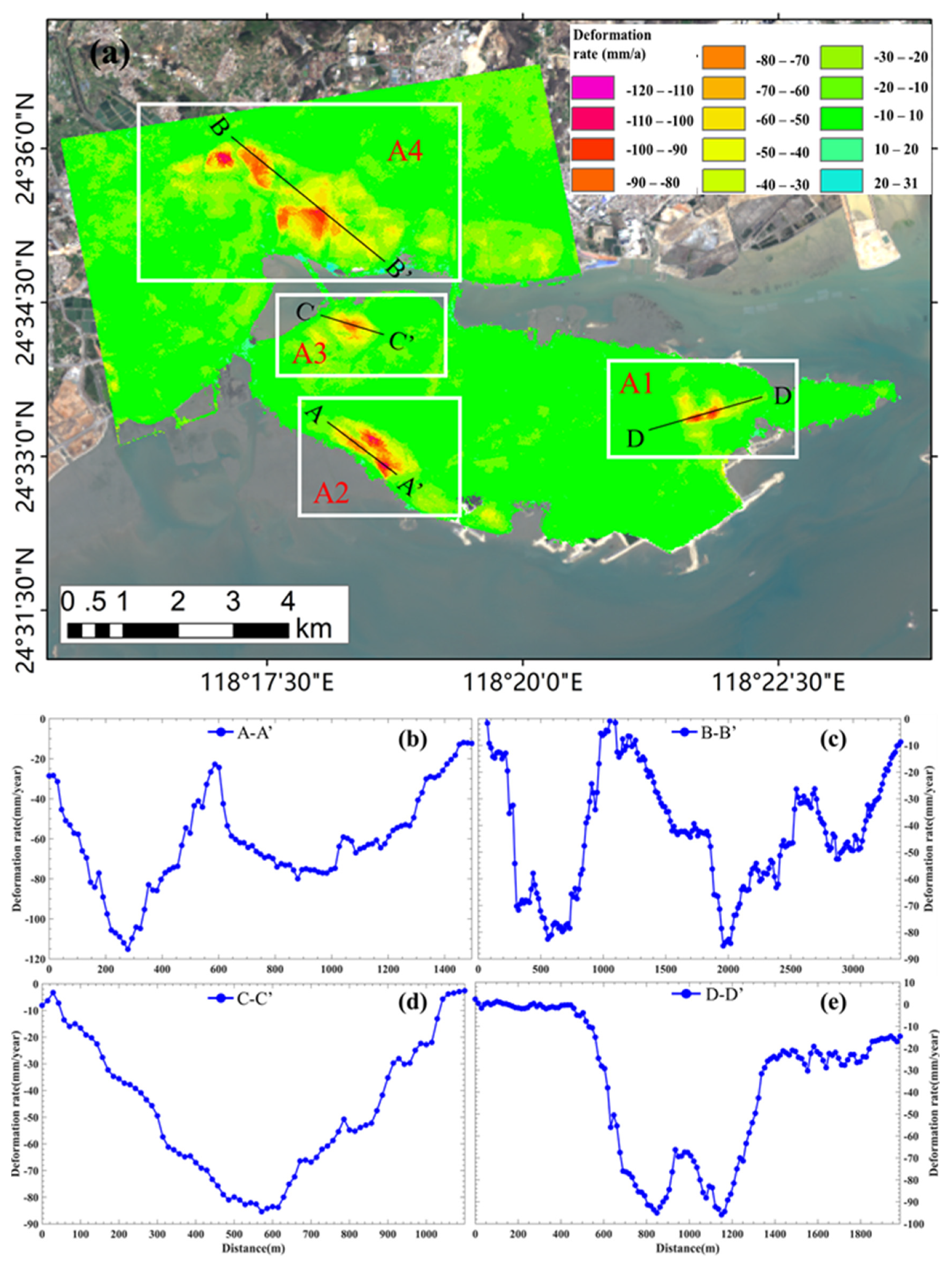
4.1. Large Area Identification of Land Subsidence
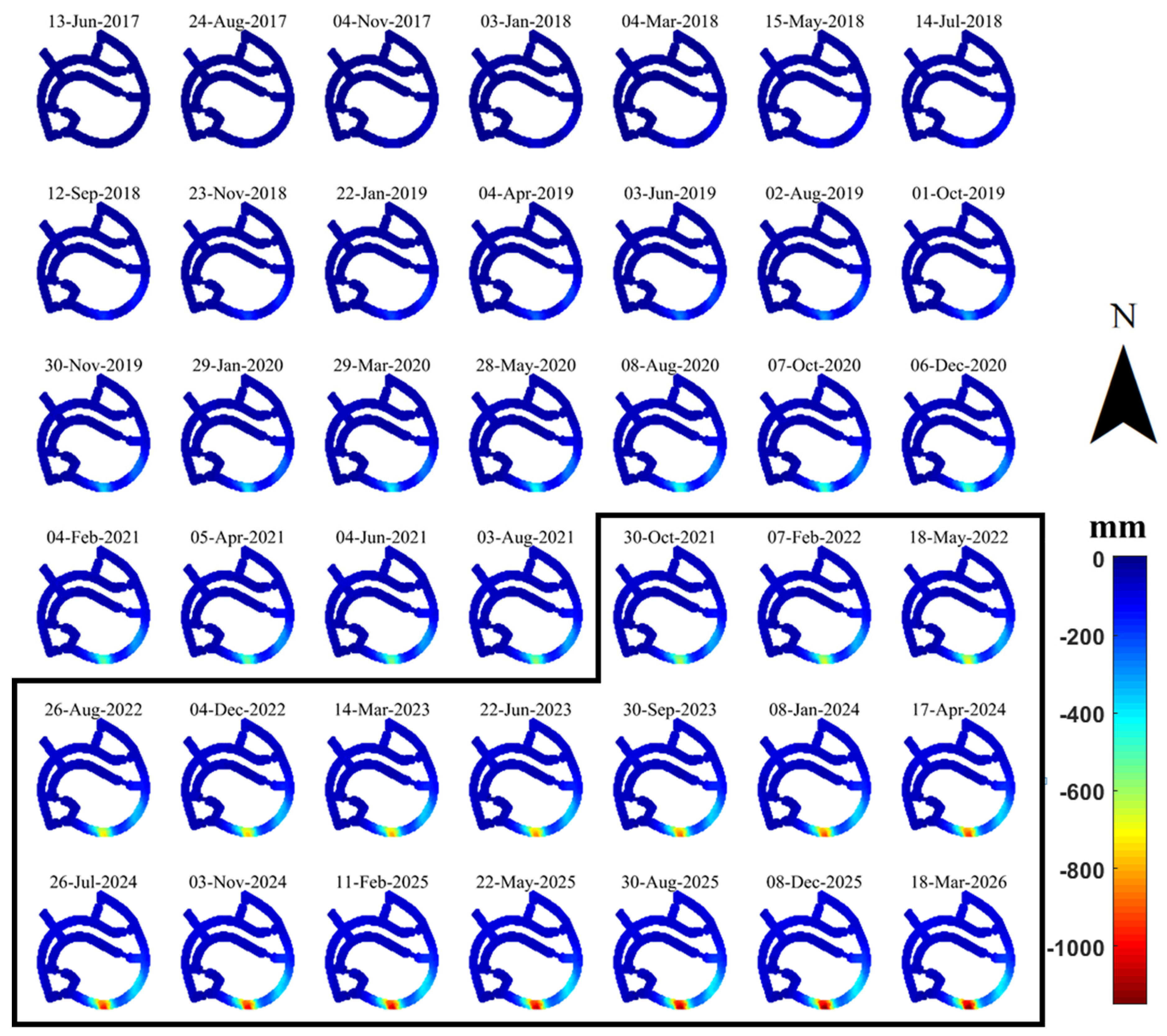
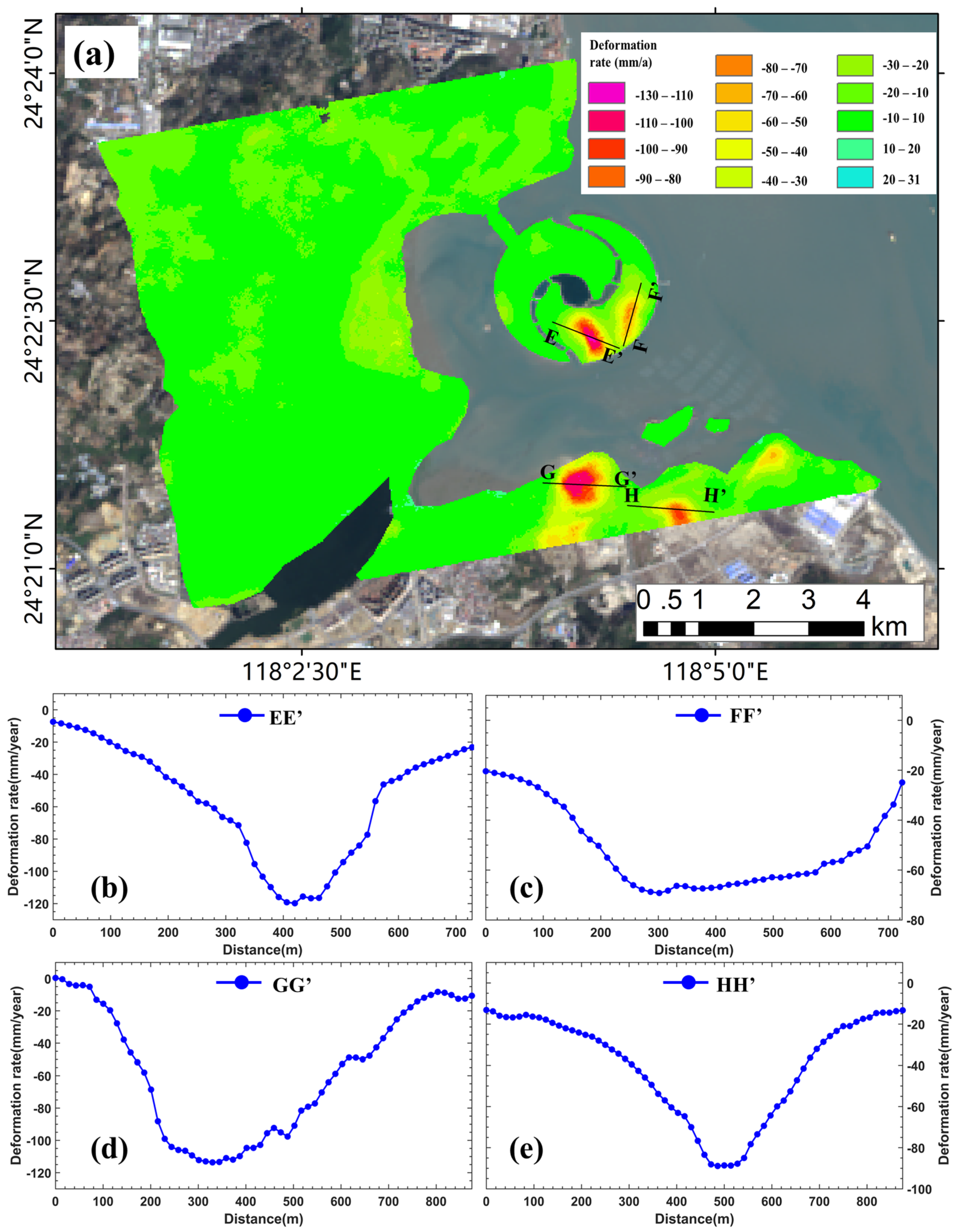
4.2. DS-InSAR Results for Two Artificial ISLANDS
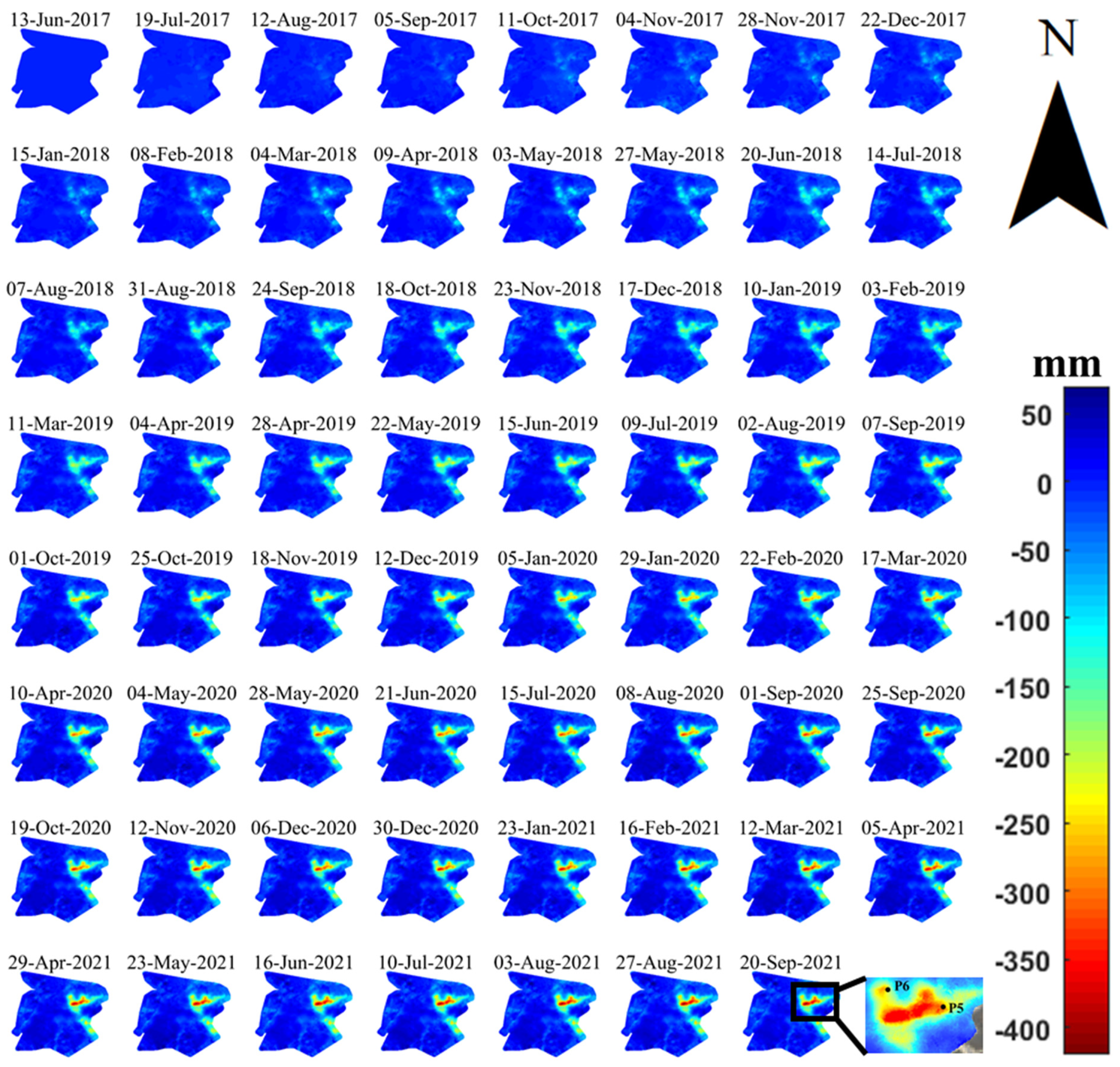
4.2.1. Dadeng Island
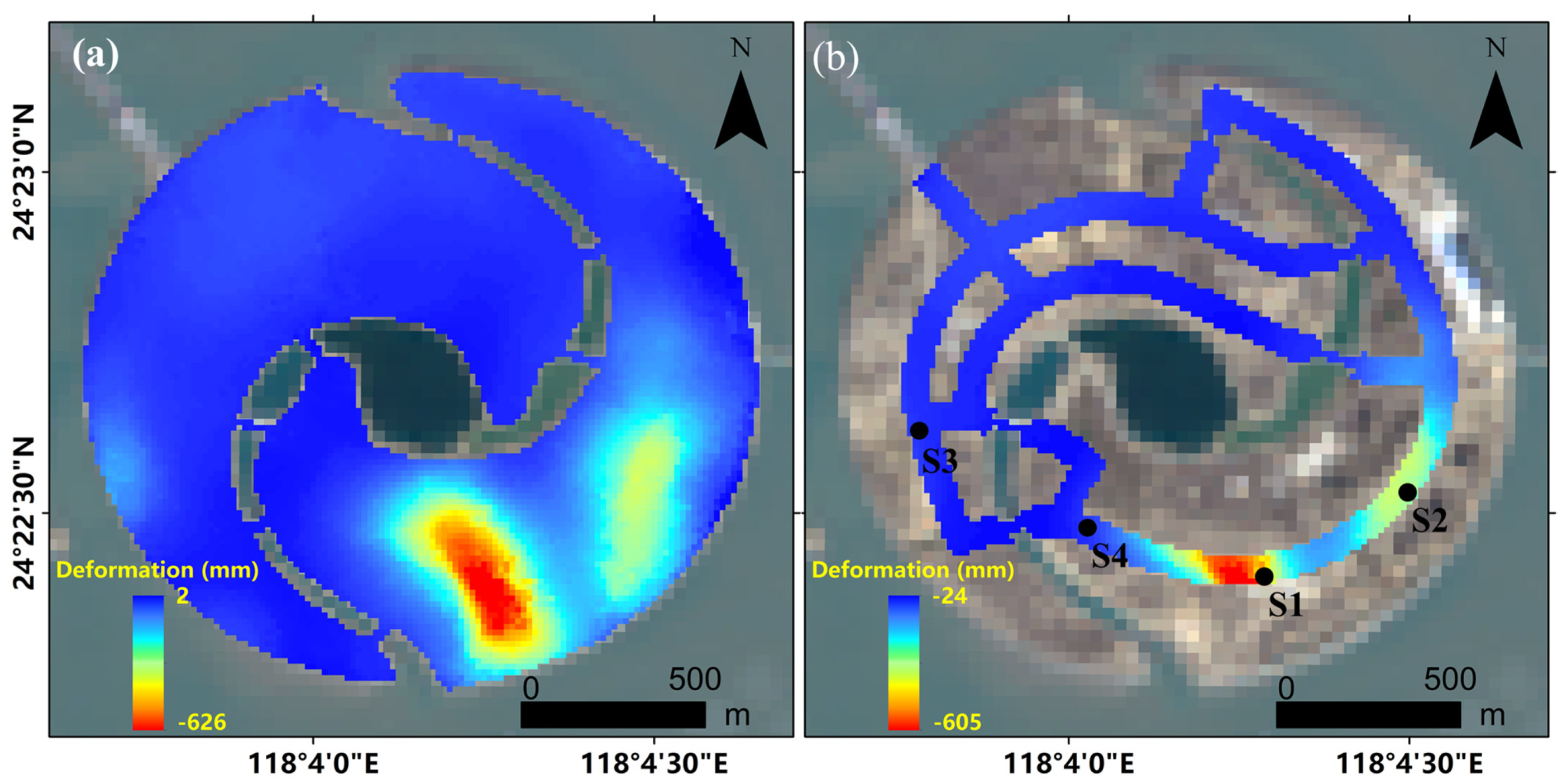
4.2.2. Shuangyu Island
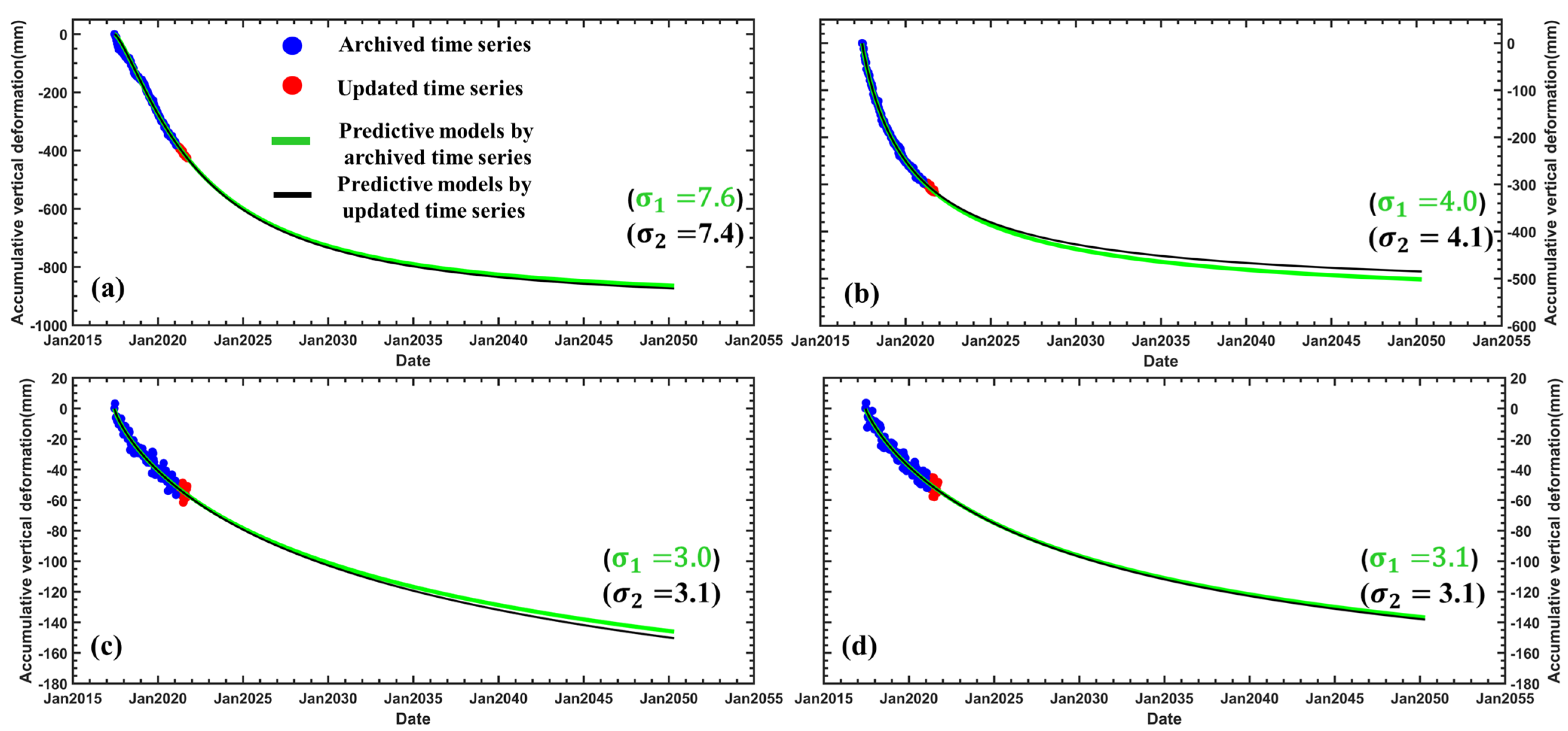
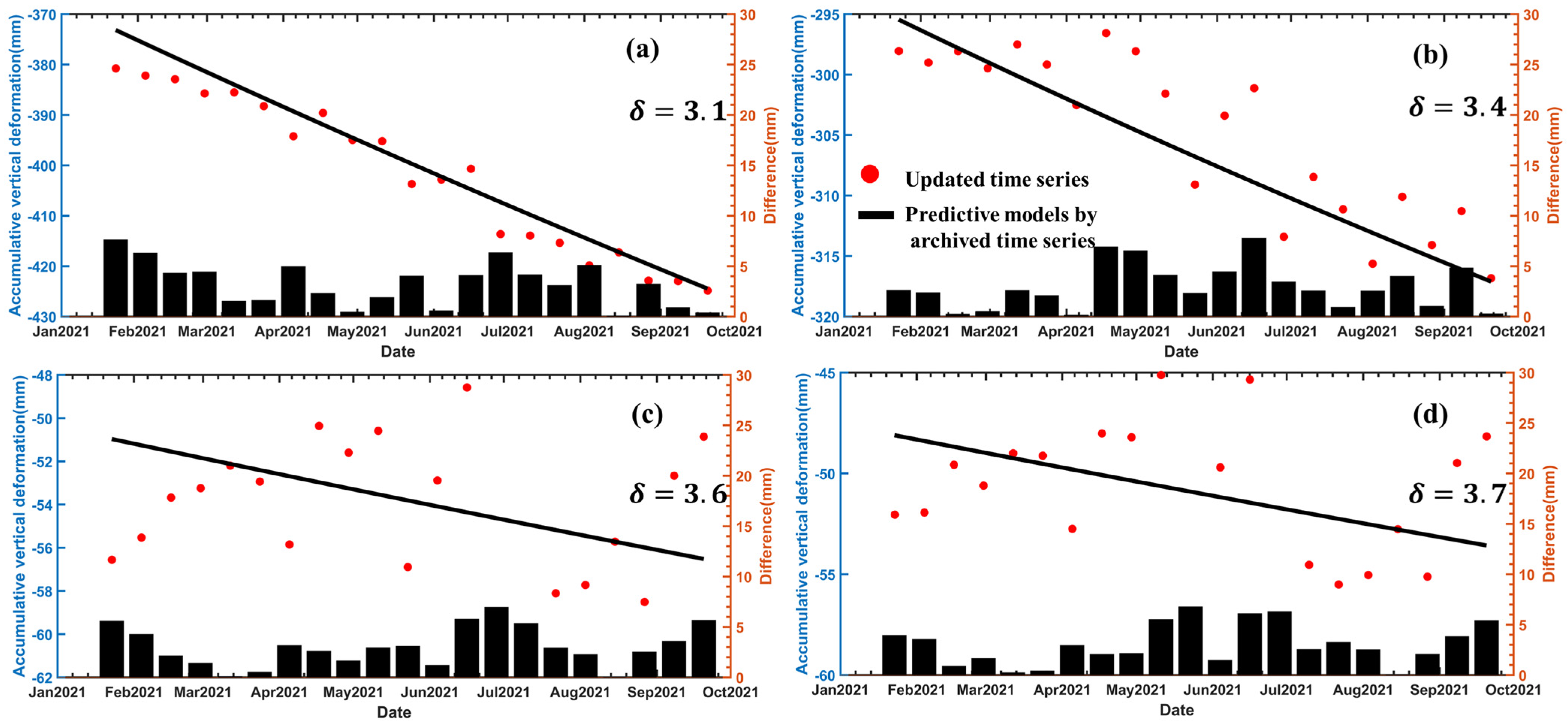
4.3. Deformation Prediction of Land Subsidence at Shuangyu Island
5. Discussion and Analysis
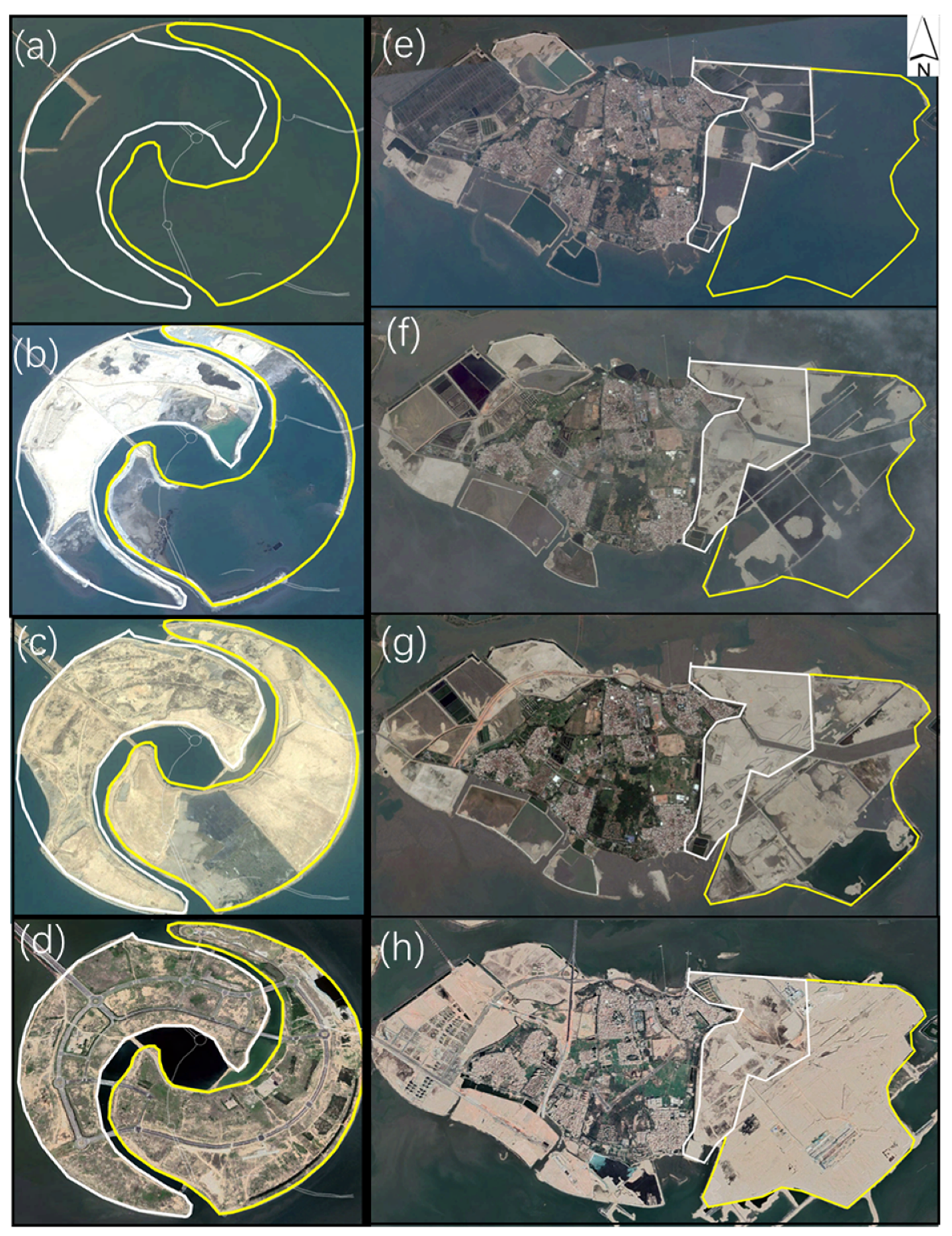
5.1. Spatial Evolution of Artificial Islands
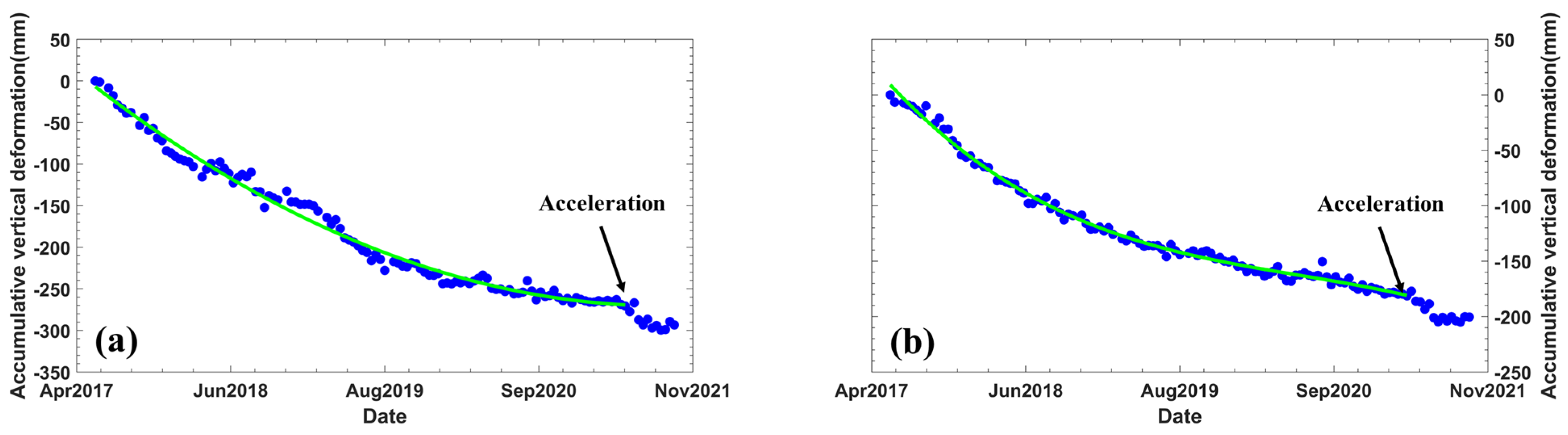
5.2. Secondary Landfill and Land Subsidence
5.3. Analysis of the Causes of Uneven Subsidence on Reclaimed Land
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, W.; Wang, D.; Huang, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, L.; Wei, X.; Sang, M.; Wang, F.; Liu, J.; Hu, B. Monitoring and analysis of coastal reclamation from 1995–2015 in Tianjin Binhai New Area, China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Xu, N.; Li, Z.; Huang, C. Satellite derived coastal reclamation expansion in China since the 21st century. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 30, e01797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wali, M.K. Practices and Problems of Land Reclamation in Western North America; University of North Dakota Press: Forks, ND, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.; Ma, G.; Wang, Q.; Yang, T.; Liu, M.; Gao, W.; Falabella, F.; Mastro, P.; Pepe, A. Generation of long-term InSAR ground displacement time-series through a novel multi-sensor data merging technique: The case study of the Shanghai coastal area. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 154, 10–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepe, A.; Bonano, M.; Zhao, Q.; Yang, T.; Wang, H. The use of C-/X-band time-gapped SAR data and geotechnical models for the study of Shanghai’s ocean-reclaimed lands through the SBAS-DInSAR technique. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Douglas, I.; Lawson, N. Airport construction: Materials use and geomorphic change. J. Air Transp. Manag. 2003, 9, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Yang, Z.; Ding, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, L.; Lu, Z. Two decades of settlement of Hong Kong International Airport measured with multi-temporal InSAR. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 248, 111976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Yang, T.; Zhang, L.; Lin, J.; Qin, X.; Liao, M. Spatio-temporal characterization of a reclamation settlement in the Shanghai coastal area with time series analyses of X-, C-, and L-band SAR datasets. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baek, W.K.; Jung, H.S.; Jo, M.J.; Lee, W.J.; Zhang, L. Ground subsidence observation of solid waste landfill park using multi-temporal radar interferometry. Int. J. Urban Sci. 2019, 23, 406–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, A.K.; Goldstein, R.M.; Zebker, H.A. Mapping small elevation changes over large areas: Differential radar interferometry. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1989, 94, 9183–9191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lanari, R.; Mora, O.; Manunta, M.; Mallorquí, J.J.; Berardino, P.; Sansosti, E. A small-baseline approach for investigating deformations on full-resolution differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 1377–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ding, X.; Lu, Z. Ground settlement monitoring based on temporarily coherent points between two SAR acquisitions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2011, 66, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, C.; Wegmuller, U.; Strozzi, T.; Wiesmann, A. Interferometric point target analysis for deformation mapping. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2003. 2003 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. Proceedings (IEEE Cat. No. 03CH37477), Toulouse, France, 21–25 July 2003; pp. 4362–4364. [Google Scholar]
- Bateson, L.; Cigna, F.; Boon, D.; Sowter, A. The application of the Intermittent SBAS (ISBAS) InSAR method to the South Wales Coalfield, UK. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2015, 34, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferretti, A.; Fumagalli, A.; Novali, F.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F.; Rucci, A. A new algorithm for processing interferometric data-stacks: SqueeSAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 3460–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, C.; Zhang, J. Characterizing and monitoring ground settlement of marine reclamation land of Xiamen New Airport, China with Sentinel-1 SAR Datasets. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aslan, G.; Cakır, Z.; Ergintav, S.; Lasserre, C.; Renard, F. Analysis of secular ground motions in Istanbul from a long-term InSAR time-series (1992–2017). Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, X.; Chen, C.; Dai, K.; Deng, J.; Wen, N.; Yin, Y.; Dong, X. Monitoring and Predicting the Subsidence of Dalian Jinzhou Bay International Airport, China by Integrating InSAR Observation and Terzaghi Consolidation Theory. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, N.; Lee, H.; Jung, H.C. A phase-decomposition-based PSInSAR processing method. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 54, 1074–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Ding, X.; Hanssen, R.F.; Malhotra, R.; Chang, L. Fast statistically homogeneous pixel selection for covariance matrix estimation for multitemporal InSAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 53, 1213–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Miao, Z.; Gamba, P.; Yong, B. Application of multitemporal InSAR covariance and information fusion to robust road extraction. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 3611–3622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, B. SAR interferogram denoising based on robust covariance matrix decomposition. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2019, 48, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, C.; Pepe, A.; Niu, Y. Near Real-Time InSAR Deformation Time Series Estimation With Modified Kalman Filter and Sequential Least Squares. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 2437–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, Z.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y. Sequential estimation of dynamic deformation parameters for SBAS-InSAR. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 17, 1017–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, Z.; Pepe, A. Long-Term Continuously Updated Deformation Time Series From Multisensor InSAR in Xi’an, China From 2007 to 2021. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 7297–7309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, Q.; Peng, M. Sequential InSAR Time Series Deformation Monitoring of Land Subsidence and Rebound in Xi’an, China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, P.; Tang, Y.; Zhou, N.; Wang, J. Consolidation settlement of Shanghai dredger fill under self-weight using centrifuge modeling test. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 2008, 39, 862–866. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.; Pepe, A.; Gao, W.; Lu, Z.; Bonano, M.; He, M.L.; Wang, J.; Tang, X. A DInSAR Investigation of the Ground Settlement Time Evolution of Ocean-Reclaimed Lands in Shanghai. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 1763–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiamen Xiang’an International Airport. Available online: https://baike.so.com/doc/6377062-6590710.html (accessed on 24 May 2022).
- Zhuo, G.; Dai, K.; Huang, H.; Li, S.; Shi, X.; Feng, Y.; Li, T.; Dong, X.; Deng, J. Evaluating potential ground subsidence geo-hazard of Xiamen Xiang’an new airport on reclaimed land by SAR interferometry. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei-Qing, P.U.; Zhou, J.H.; Jin, H. Design features of Shuangyu Artificial Island. Port Waterw. Eng. 2018, 6, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.H.; Pu, W.-Q.; Jun, M.A. Analysis of elements for land elevation design of Shuangyu Artificial Island. Port Waterw. Eng. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuangyu Island-Operating Sea Use Project in Zhangzhou City, Fujian Province. Available online: https://baike.so.com/doc/2577786-24421466.html (accessed on 13 June 2022).
- Wang, B.H.; Zhao, C.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, L.-Q.; Chen, H.-Y. Update two-dimensional SAR offset tracking deformation time series with complex sequential least squares estimation. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 12, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzaghi, K.; Peck, R.B.; Mesri, G. Soil Mechanics in Engineering Practice; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Plant, G.W.; Covil, C.S.; Hughes, R.A. Site Preparation for the New Hong Kong International Airport; Thomas Telford: London, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Lambe, T.; Whitman, R. Soil Mechanics; John Wiley & Sons Inc: New York, NY, USA, 1969; Volume 553. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, J.C.; Shen, S.L.; Zhu, H.H.; Zhang, X.L. 1D analysis of land subsidence in Shanghai. Lowl. Technol. Int. 2005, 7, 33–41. [Google Scholar]
- Stamatopoulos, C.; Petridis, P.; Parcharidis, I.; Foumelis, M. A method predicting pumping-induced ground settlement using back-analysis and its application in the Karla region of Greece. Nat. Hazards 2018, 92, 1733–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Lin, H. Integrated analysis of SAR interferometric and geological data for investigating long-term reclamation settlement of Chek Lap Kok Airport, Hong Kong. Eng. Geol. 2010, 110, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Study Area | Time Intervals | Techniques |
|---|---|---|
| Large area | 13 June 2017–20 September 2021 | SBAS-InSAR |
| Dadeng Island | 13 June 2017–20 September 2021 | DS-InSAR |
| Shuangyu Island | 13 June 2017–20 September 2021 | Sequential estimation and DS-InSAR |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, G.; Zhao, C.; Wang, B.; Liu, X.; Chen, H. Land Subsidence Monitoring and Dynamic Prediction of Reclaimed Islands with Multi-Temporal InSAR Techniques in Xiamen and Zhangzhou Cities, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2930. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14122930
Li G, Zhao C, Wang B, Liu X, Chen H. Land Subsidence Monitoring and Dynamic Prediction of Reclaimed Islands with Multi-Temporal InSAR Techniques in Xiamen and Zhangzhou Cities, China. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(12):2930. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14122930
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Guangrong, Chaoying Zhao, Baohang Wang, Xiaojie Liu, and Hengyi Chen. 2022. "Land Subsidence Monitoring and Dynamic Prediction of Reclaimed Islands with Multi-Temporal InSAR Techniques in Xiamen and Zhangzhou Cities, China" Remote Sensing 14, no. 12: 2930. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14122930
APA StyleLi, G., Zhao, C., Wang, B., Liu, X., & Chen, H. (2022). Land Subsidence Monitoring and Dynamic Prediction of Reclaimed Islands with Multi-Temporal InSAR Techniques in Xiamen and Zhangzhou Cities, China. Remote Sensing, 14(12), 2930. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14122930








