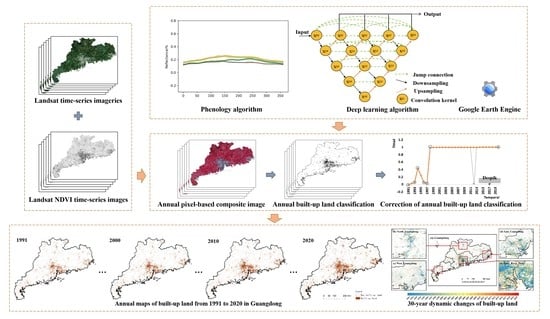
Annual Maps of Built-Up Land in Guangdong from 1991 to 2020 Based on Landsat Images, Phenology, Deep Learning Algorithms, and Google Earth Engine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
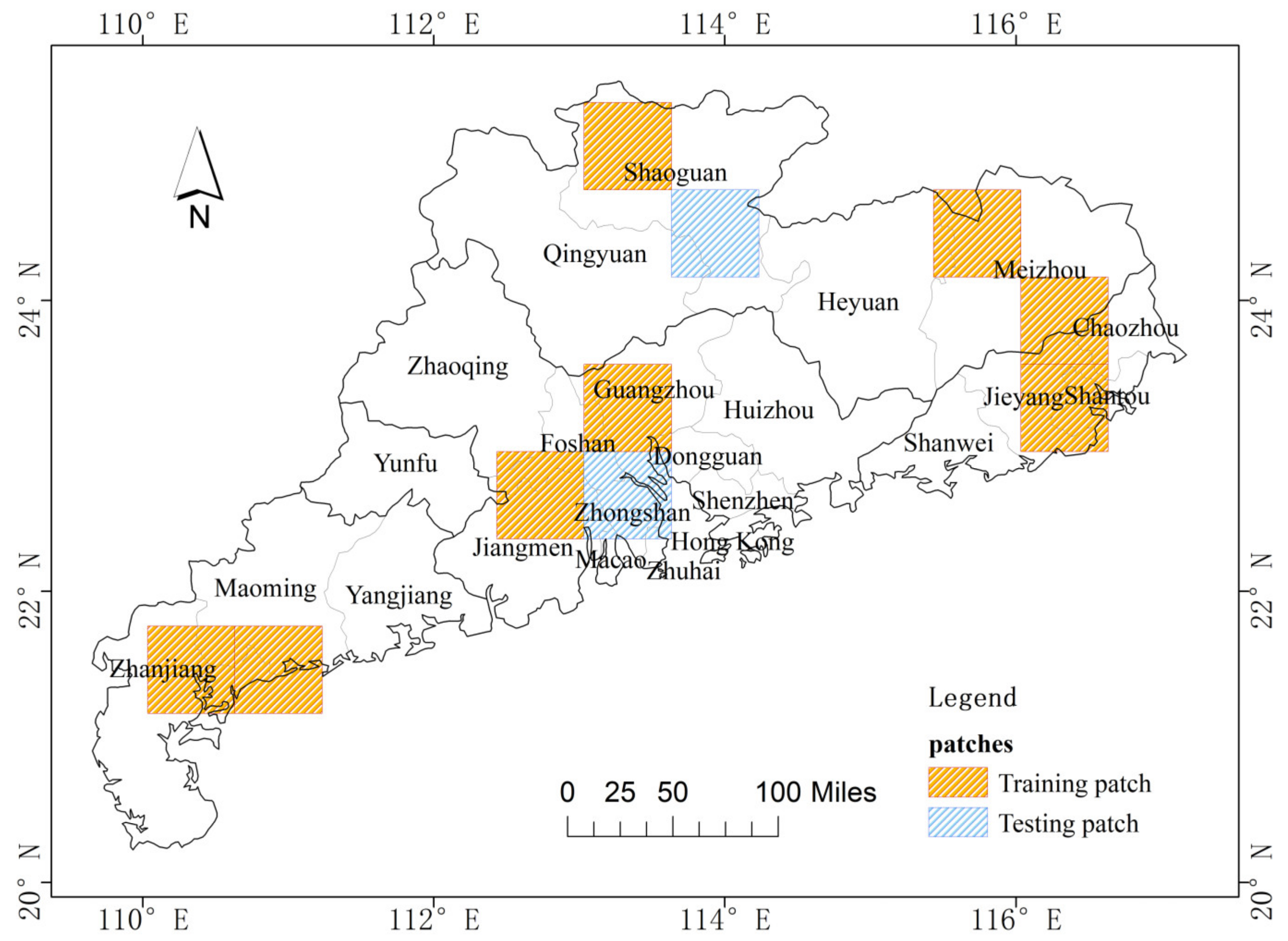
2.1. Study Area
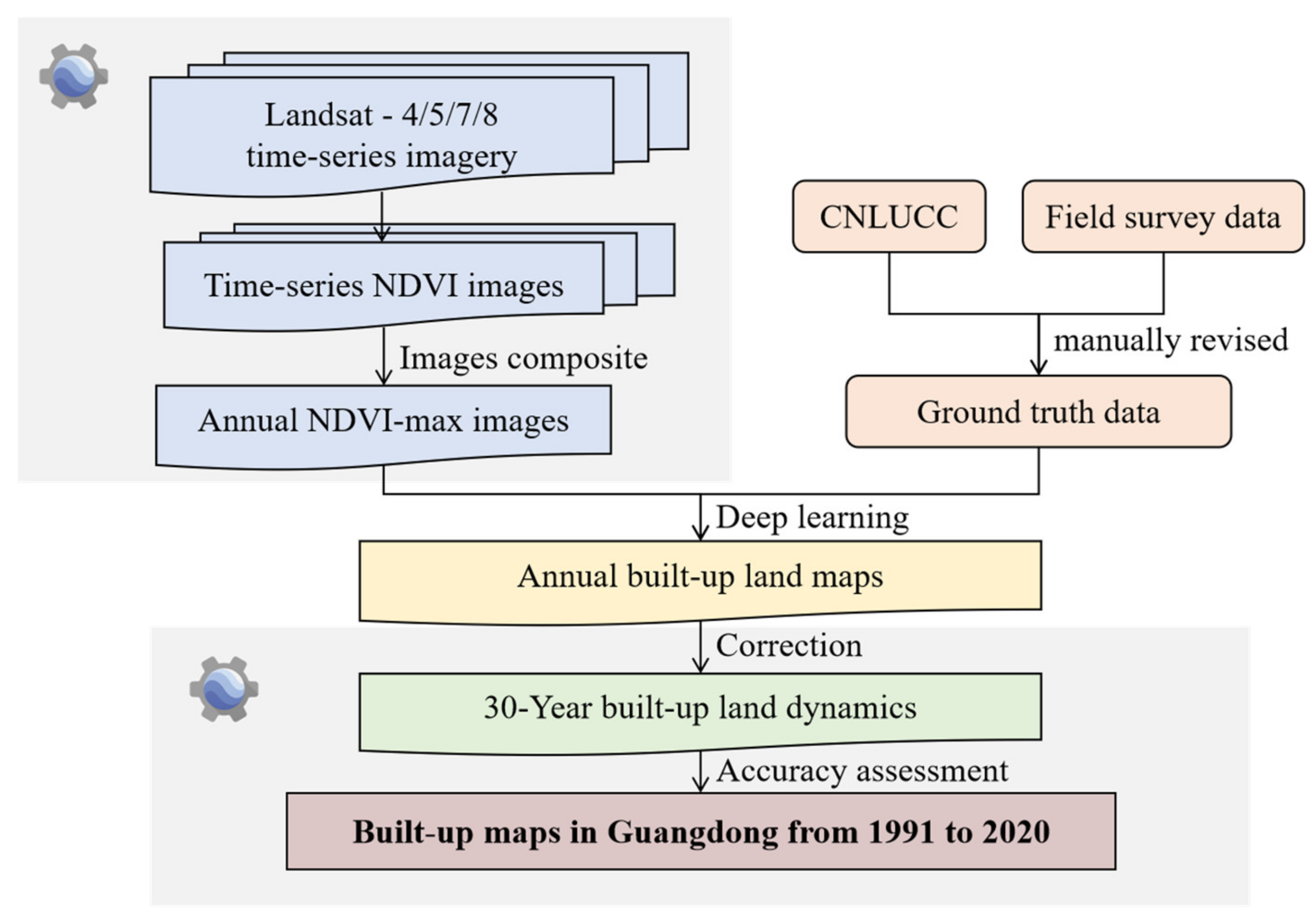
2.2. Data and Pre-Processing
2.2.1. Landsat Imagery
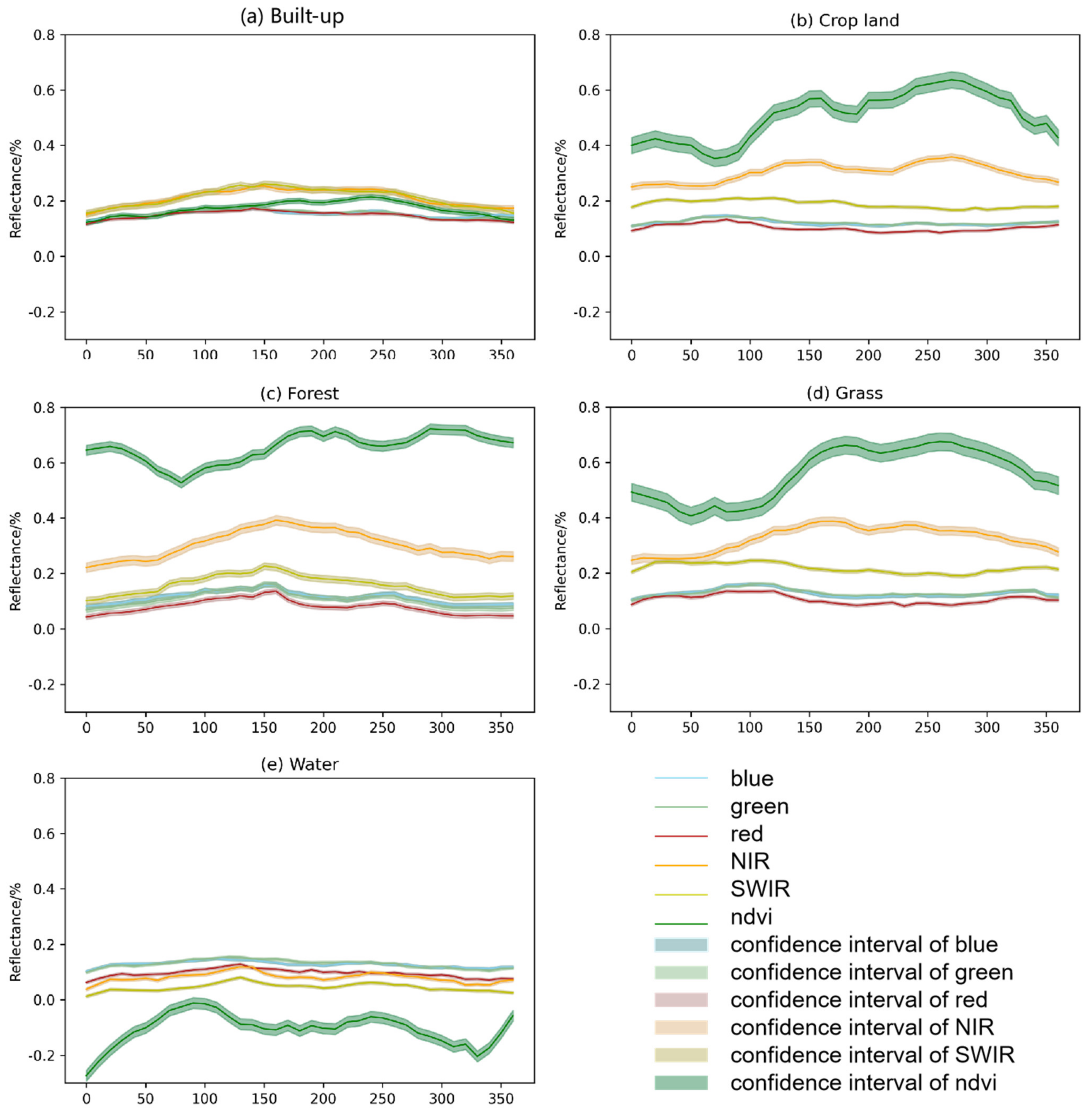
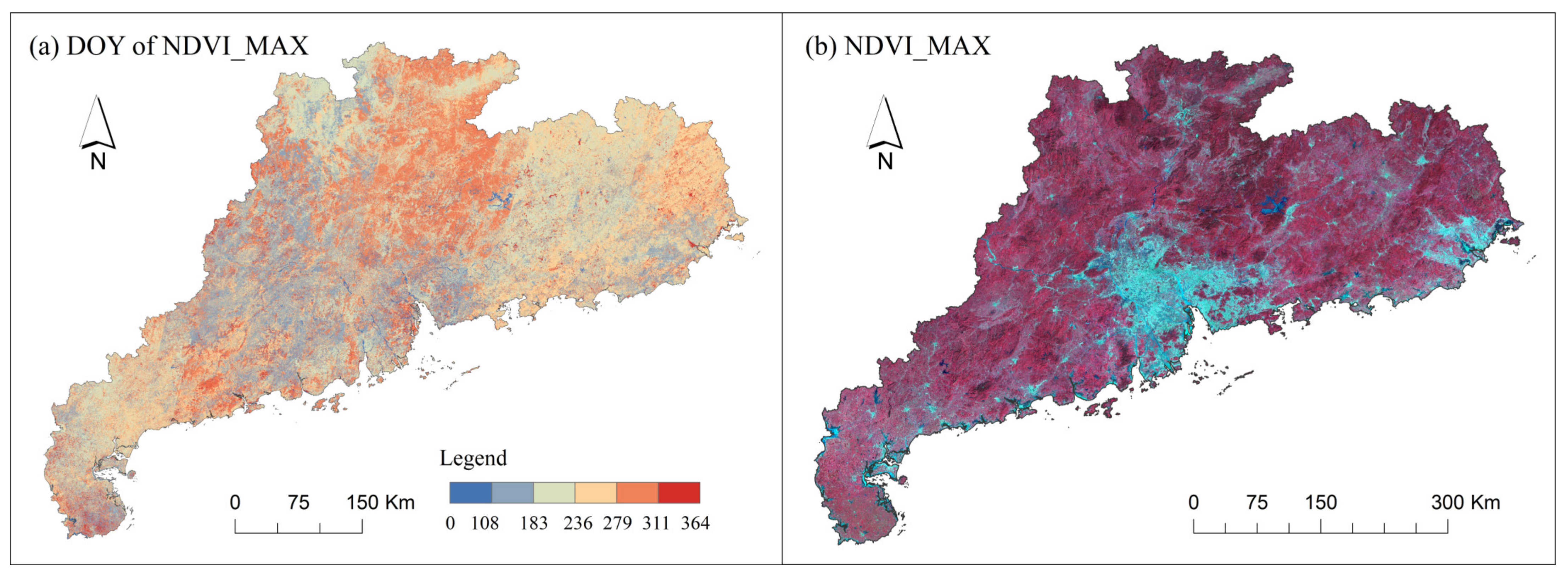
2.2.2. Vegetation Index
2.3. Algorithms for Identifying Time Series of Built-Up Land
2.3.1. Spectral Variability between Built-Up Land and Other Lands Based on Phenology
2.3.2. Annual Composite Feature Enhancement Images
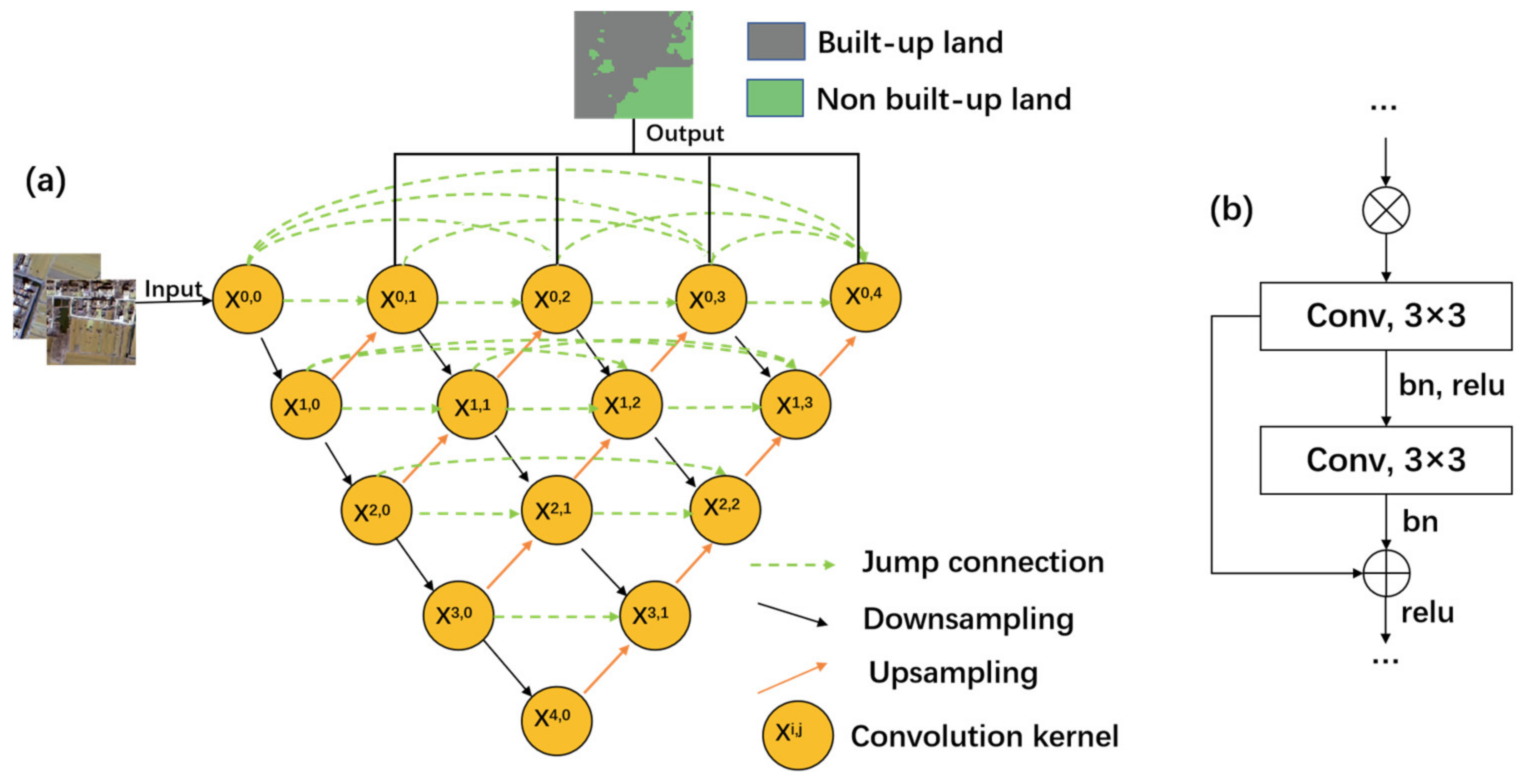
2.3.3. Deep Learning for Identifying Built-Up Land Per Year
Res-UNet++ Model for Identifying Built-Up Land
Deeplab-v3 and FCN Models for Comparison
Parameters and Design of Deep Learning Training
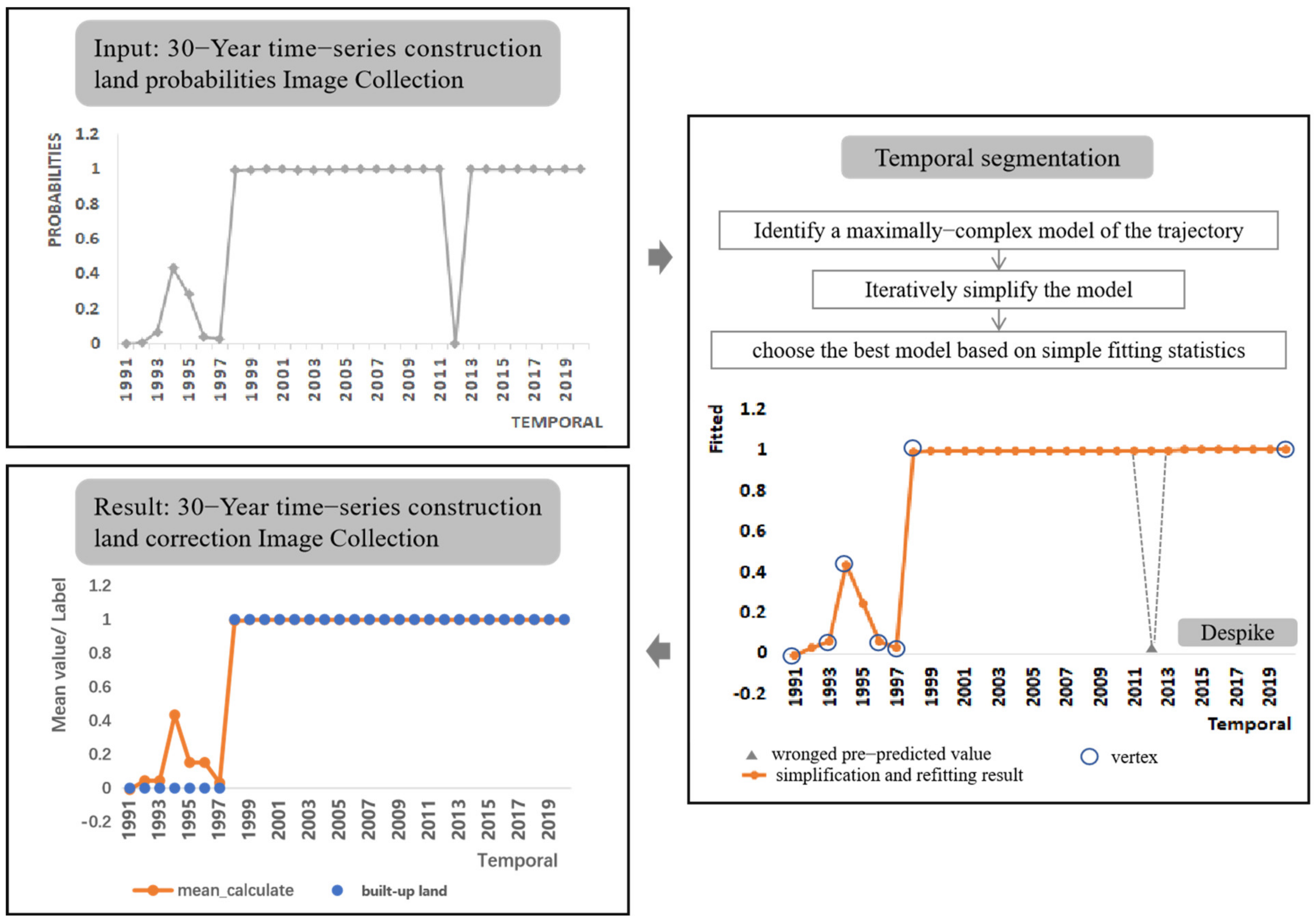
2.3.4. Correction of Time Series Built-Up Land by Temporal Segmentation Algorithm
2.4. Accuracy Assessment and Area Estimation
3. Results
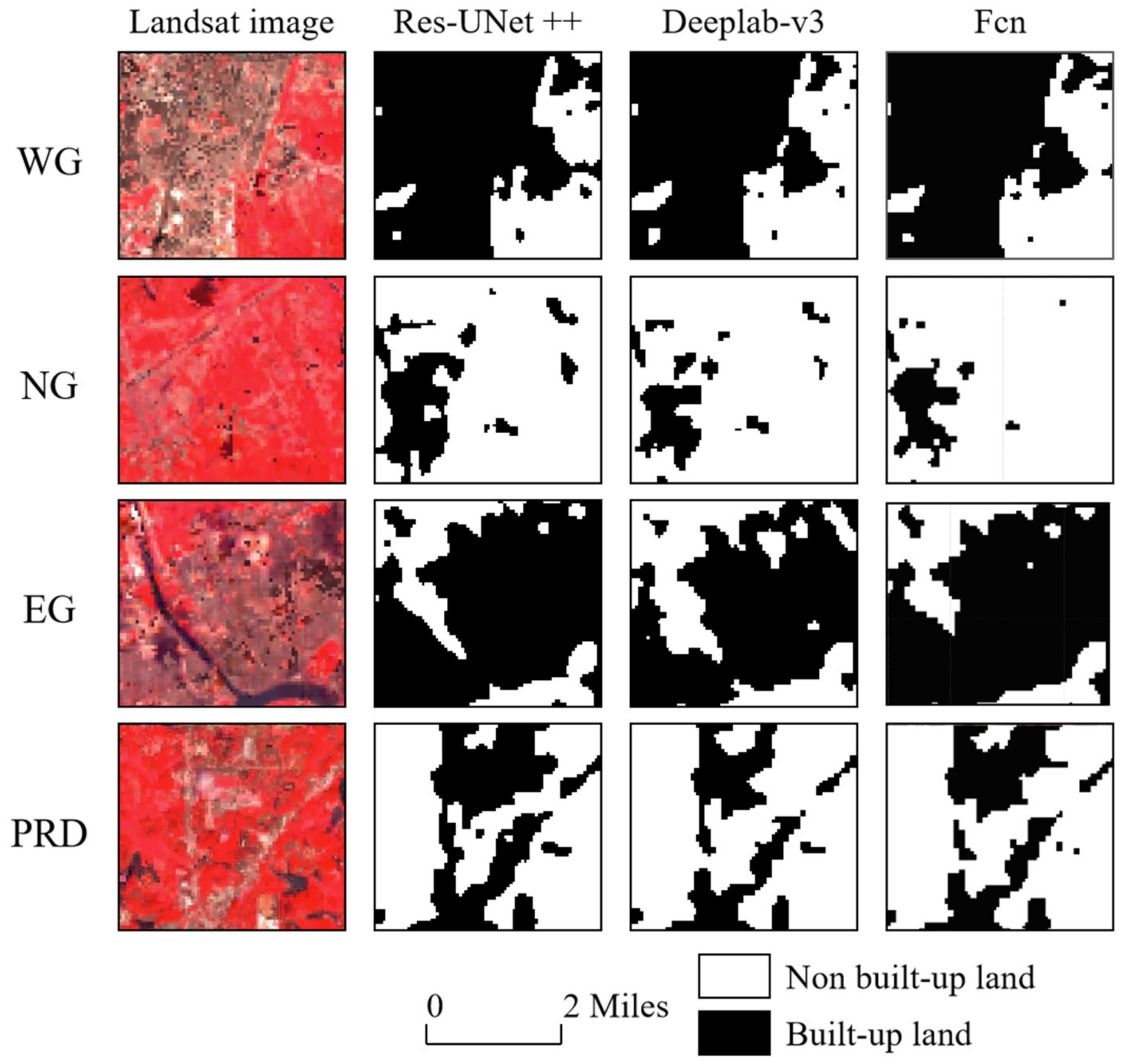
3.1. Model Comparison Experiment Result
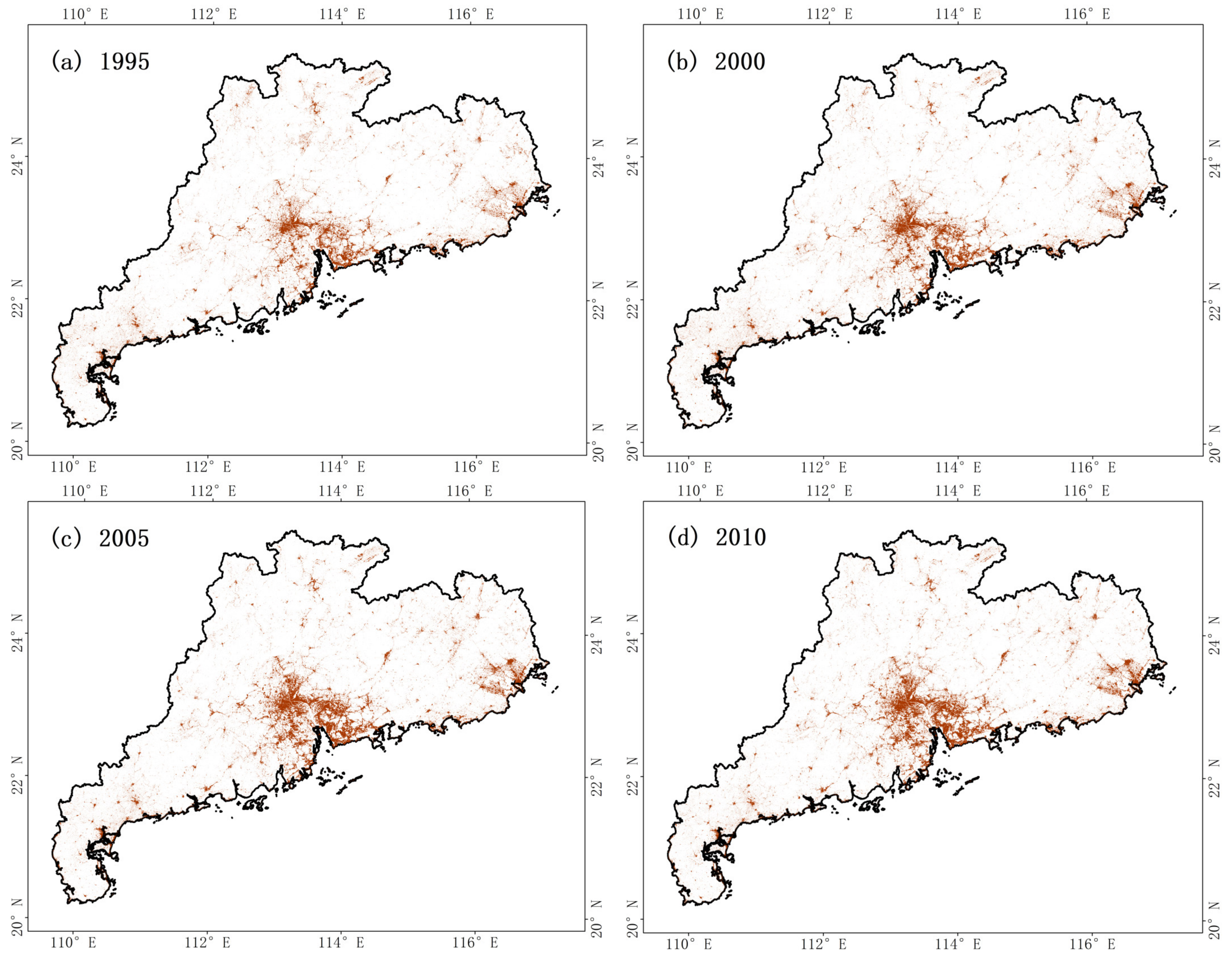
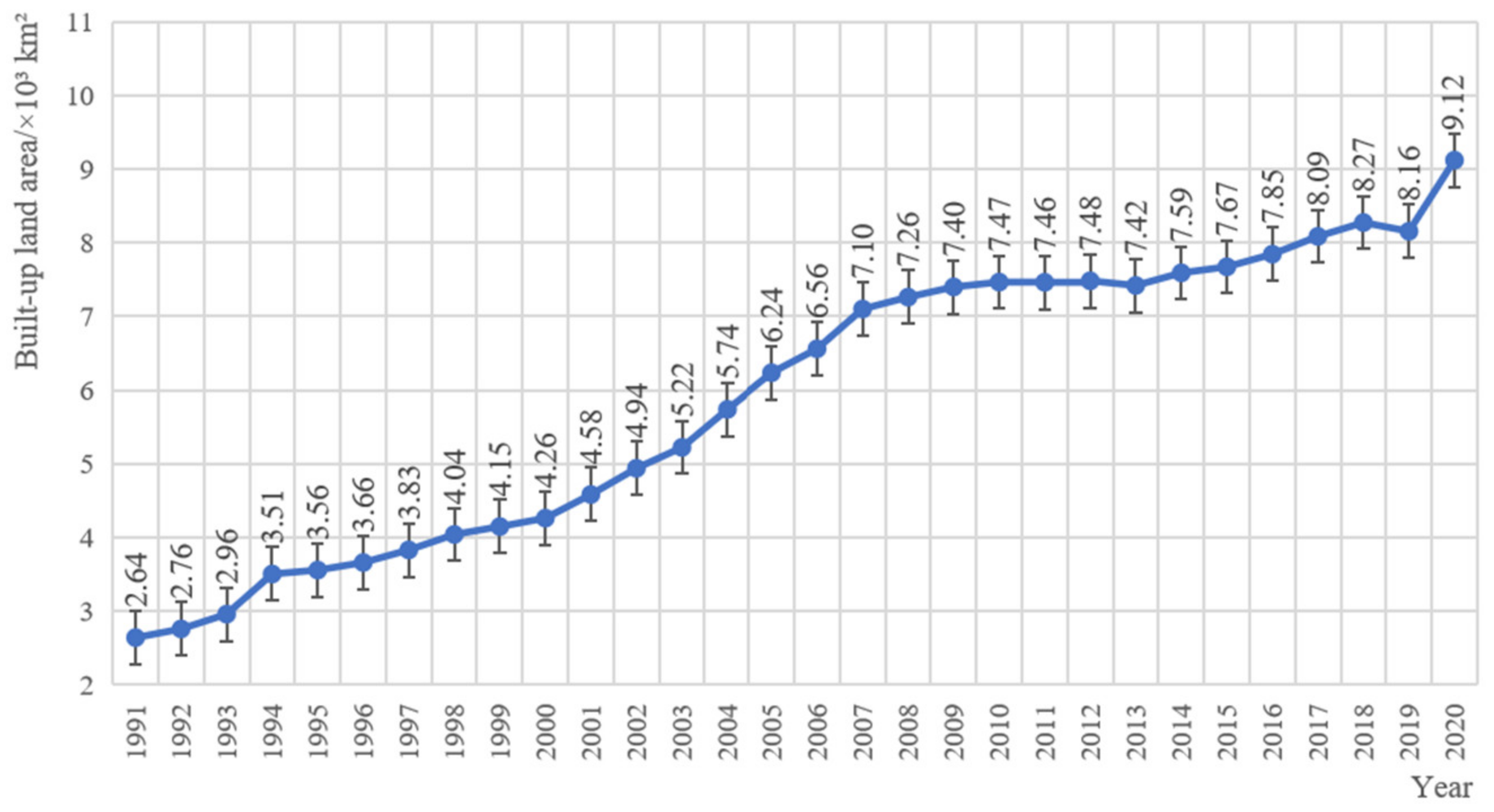
3.2. Assessment of Built-Up Land Maps from 1991 to 2020
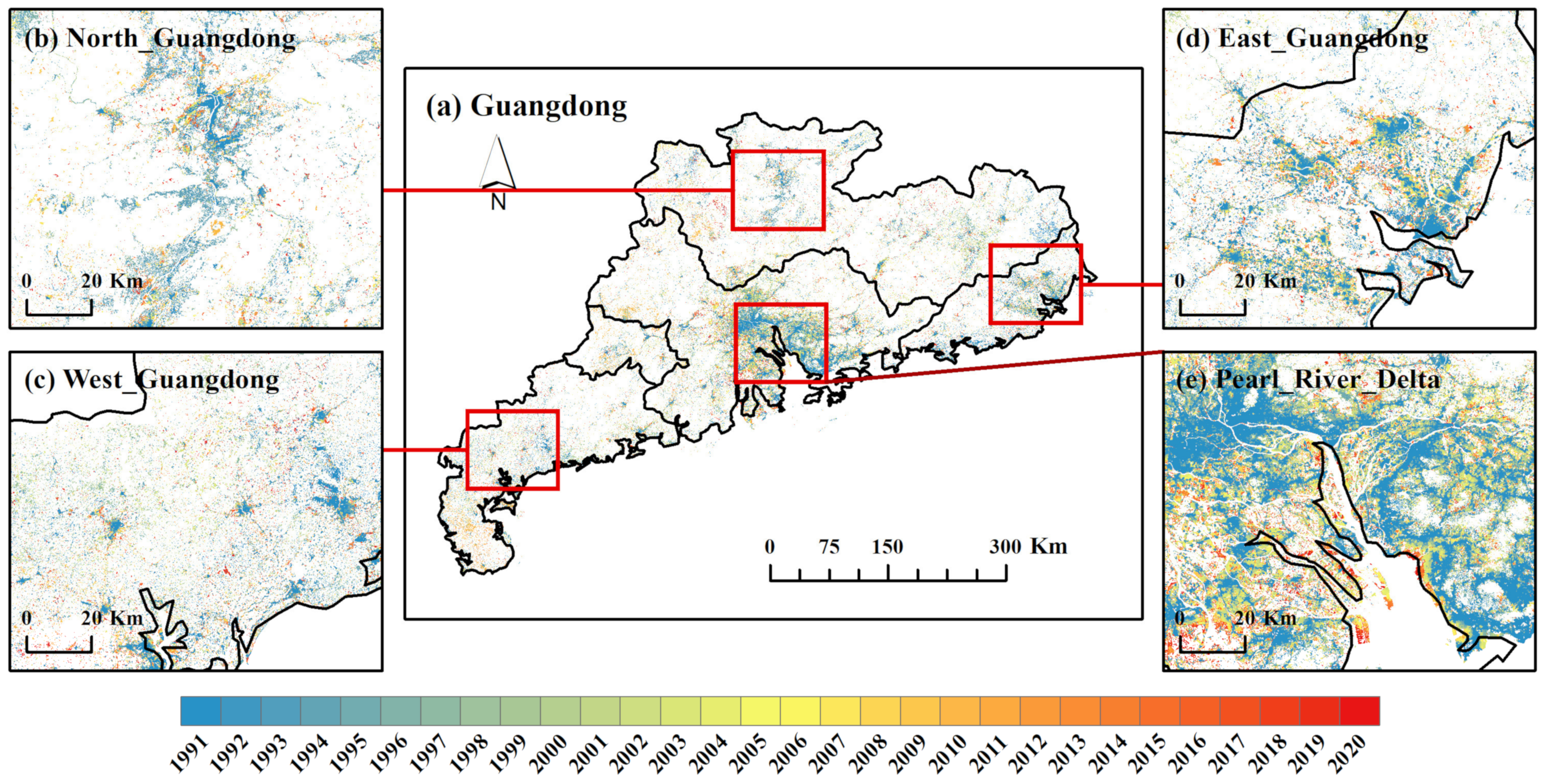
3.3. Spatial-Temporal Changes of Built-Up Land in Guangdong
4. Discussion
4.1. Algorithms for Mapping Annual Built-Up Land Maps
4.2. Comparison with Different Datasets
4.3. Advantages of Combining GEE and Deep Learning Methods
4.4. Implications and Future Work
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, W.; Yang, Y.C.; Duan, Z.L. On Intelligent Extraction of Built-up land Based on High-resolution Satellite Image. Geol. Anhui 2014, 24, 210–212. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, H.; Qi, S.; Tao, S.; Xu, H.; Yao, Y. An efficient approach to capture continuous impervious surface dynamics using spatial-temporal rules and dense Landsat time series stacks. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 229, 114–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q. Modeling Urban Growth Effects on Surface Runoff with the Integration of Remote Sensing and GIS. Environ. Manag. 2001, 28, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klöcking, B.; Haberlandt, U. Impact of land use changes on water dynamics––A case study in temperate meso and macroscale river basins. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2002, 27, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.S.; Xu, H.Q.; Zhou, R. A Study on Urban Impervious Surface Area and Its Relation with Urban Heat Island: Quanzhou City, China. Remote Sens. Technol. Appl. 2007, 22, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Arbuthnott, K.G.; Hajat, S. The Health Effects of Hotter Summers and Heat Waves in the Population of the United Kingdom: A Review of the Evidence. Environ. Health 2017, 16, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santamouris, M. Recent Progress on Urban Overheating and Heat Island Research. Integrated Assessment of the Energy, Environmental, Vulnerability and Health Impact. Synergies with the Global Climate Change. Energy Build. 2019, 207, 109482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnfield, A.J. Two Decades of Urban Climate Research: A Review of Turbulence, Exchanges of Energy and Water, and the Urban Heat Island. Int. J. Clim. 2003, 23, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarrat, C.; Lemonsu, A.; Masson, V.; Guédalia, D. Impact of Urban Heat Island on Regional Atmospheric Pollution. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 40, 1743–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q.; Lu, D. A sub-pixel analysis of urbanization effect on land surface temperature and its in-terplay with impervious surface and vegetation coverage in Indianapolis, United States. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2008, 10, 68–83. [Google Scholar]
- Feizizadeh, B.; Blaschke, T. Examining Urban Heat Island Relations to Land Use and Air Pollution: Multiple Endmember Spectral Mixture Analysis for Thermal Remote Sensing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 1749–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čeplová, N.; Kalusová, V.; Lososová, Z. Effects of Settlement Size, Urban Heat Island and Habitat Type on Urban Plant Biodiversity. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 159, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Qu, R.; Liu, X.L.; Ma, H.R.; Shi, Z.T. Study on Impervious Surface Identification Method and Its Application Based on Sentinel-2 Data. Geogr. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2021, 37, 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.P.; Hu, G.H.; Chen, Y.M.; Li, X.; Xu, X.C.; Li, S.Y.; Pei, F.S.; Wang, S.J. High-resolution multi-temporal mapping of global urban land using Landsat images based on the Google Earth Engine Platform. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 209, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firozjaei, M.K.; Sedighi, A.; Kiavarz, M.; Qureshi, S.; Haase, D.; Alavipanah, S.K. Automated Built-Up Extraction Index: A New Technique for Mapping Surface Built-Up Areas Using LANDSAT 8 OLI Imagery. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Chen, S.; Yang, C.; He, L.; Hou, M.; Shi, T. A comparative study of impervious surface extraction using Sentinel-2 imagery. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 53, 274–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Wu, C.; Zhang, B.; Gao, L.; Plaza, A. Impervious Surface Extraction from Multispectral Images via Morphological Attribute Profiles Based on Spectral Analysis. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 4775–4790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, M.; Yao, Y. Mapping seasonal impervious surface dynamics in Wuhan urban agglomeration, China from 2000 to 2016. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. ITC J. 2018, 70, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Wei, Y.; Dai, Q. A Novel Remote Sensing Index for Extracting Impervious Surface Distribution from Landsat 8 OLI Imagery. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, T.; Tang, H. A Comprehensive Evaluation of Approaches for Built-Up Area Extraction from Landsat OLI Images Using Massive Samples. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdelhady, H.U.; Troy, C.D.; Habib, A.; Manish, R. A Simple, Fully Automated Shoreline Detection Algorithm for High-Resolution Multi-Spectral Imagery. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Weng, Q. Annual dynamics of impervious surface in the Pearl River Delta, China, from 1988 to 2013, using time series Landsat imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 113, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xun, L.; Chai, X. Crop classification based on multi-source remote sensing data fusion and LSTM algorithm. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2019, 35, 129–137. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, A.-X.; Hao, Y.; Xu, C. Multi-Level Classification Based on Trajectory Features of Time Series for Monitoring Impervious Surface Expansions. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dominici, D.; Zollini, S.; Alicandro, M.; Della Torre, F.; Buscema, P.M.; Baiocchi, V. High Resolution Satellite Images for Instantaneous Shoreline Extraction Using New Enhancement Algorithms. Geosciences 2019, 9, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xi, Y.; Thinh, N.X.; Li, C. Preliminary comparative assessment of various spectral indices for built-up land derived from Landsat-8 OLI and Sentinel-2A MSI imageries. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 52, 240–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, C.; Zhu, Z. Continuous subpixel monitoring of urban impervious surface using Landsat time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 238, 110929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhong, Y.; Guan, Q.; Lu, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, D. A Global Context-aware and Batch-independent Network for road extraction from VHR satellite imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 175, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, L.; Chen, X.; Gao, Y.; Jiang, M. Automatically Monitoring Impervious Surfaces Using Spectral Generalization and Time Series Landsat Imagery from 1985 to 2020 in the Yangtze River Delta. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 2021, 9873816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Fei, Y.; Wu, T.; Jin, R.; Xiao, T. A Novel Impervious Surface Extraction Method Integrating POI, Vehicle Trajectories, and Satellite Imagery. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 8804–8814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Xiong, S.; Li, Y. Automatic Extraction of Built-Up Areas from Panchromatic and Multispectral Remote Sensing Images Using Double-Stream Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 3988–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Zhao, X.; Wu, M.; Wang, C. Extracting Urban Impervious Surface from WorldView-2 and Airborne LiDAR Data Using 3D Convolutional Neural Networks. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2019, 47, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, F.; Wang, X.; Zha, M. Extracting built-up land area of airports in China using Sentinel-2 imagery through deep learning. Geocarto Int. 2021, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Y.; Ning, J.; Kuang, W.H.; Xu, X.L.; Zhang, S.W.; Yan, C.Z.; Li, R.D.; Wu, S.X.; Hu, Y.F.; Du, G.M.; et al. Spatio-temporal patterns and characteristics of land-use change in China during 2010–2015. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2018, 73, 789–802. [Google Scholar]
- Foga, S.; Scaramuzza, P.L.; Guo, S.; Zhu, Z.; Dilley, R.D., Jr.; Beckmann, T.; Schmidt, G.L.; Dwyer, J.L.; Hughes, M.J.; Laue, B. Cloud Detection Algorithm Comparison and Validation for Operational Landsat Data Products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 194, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, S.; Fan, F. A Hierarchical Extraction Method of Impervious Surface Based on NDVI Thresholding Integrated with Multispectral and High-Resolution Remote Sensing Imageries. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 1461–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Li, X.; Zhang, W. 40-Year (1978–2017) human settlement changes in China refected by impervious surfaces from satellite remote sensing. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tucker, C.J. Red and Photographic Infrared Linear Combinations for Monitoring Vegetation. Remote Sens. Environ. 1979, 8, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ablin, R.; Sulochana, C.; Prabin, G. An investigation in satellite images based on image enhancement techniques. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 53, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Md Mahfuzur Rahman, S.; Tajbakhsh, N.; Liang, J. UNet++: A Nested U-Net Architecture for Medical Image Segmentation. In Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support, Proceedings of the 4th International Workshop, DLMIA 2018, and 8th International Workshop, ML-CDS 2018, Granada, Spain, 20 September 2018; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 11045, pp. 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, D.; Zhang, Y.; Guan, H. End-to-End Change Detection for High Resolution Satellite Images Using Improved UNet++23. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeong, M.; Choi, H.; Choi, J. Analysis of Change Detection Results by UNet++ Models According to the Characteristics of Loss Function. Korean J. Remote Sens. 2020, 36, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diakogiannis, F.I.; Waldner, F.; Caccetta, P.; Wu, C. ResUNet-a: A Deep Learning Framework for Semantic Segmentation of Remotely Sensed Data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 162, 94–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully Convolutional Networks for Semantic Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 640–651. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.-H.K.; Qiu, C.; Schmitt, M.; Zhu, X.X.; Sabel, C.E.; Prishchepov, A.V. Mapping horizontal and vertical urban densification in Denmark with Landsat time-series from 1985 to 2018: A semantic segmentation solution. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 251, 112096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. DeepLab: Semantic Image Segmentation with Deep Convolutional Nets, Atrous Convolution, and Fully Connected CRFs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kennedy, R.E.; Yang, Z.; Cohen, W.B. Detecting trends in forest disturbance and recovery using yearly Landsat time series: 1. LandTrendr—Temporal segmentation algorithms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2897–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olofsson, P.; Foody, G.M.; Herold, M.; Stehman, S.V.; Woodcock, C.E.; Wulder, M.A. Good practices for estimating area and assessing accuracy of land change. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 148, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, R.; Lees, B. Assessing the Classification Accuracy of Multisource Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1994, 47, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhennache, R.; Bouden, T.; Taleb-Ahmed, A.; Cheddad, A. A new spectral index for the extraction of built-up land features from Landsat 8 satellite imagery. Geocarto Int. 2019, 34, 1531–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, X.; Wu, Z.; Dai, Z.; Yin, J.; Zhang, C. An Improved Method for Urban Built-Up Area Extraction Supported by Multi-Source Data. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.C.; Li, B.J.; Liu, X.P.; Li, X.; Shi, Q. Mapping annual global land cover changes at a 30m res-olution from 2000 to 2015. Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 2021, 25, 1896–1921. [Google Scholar]

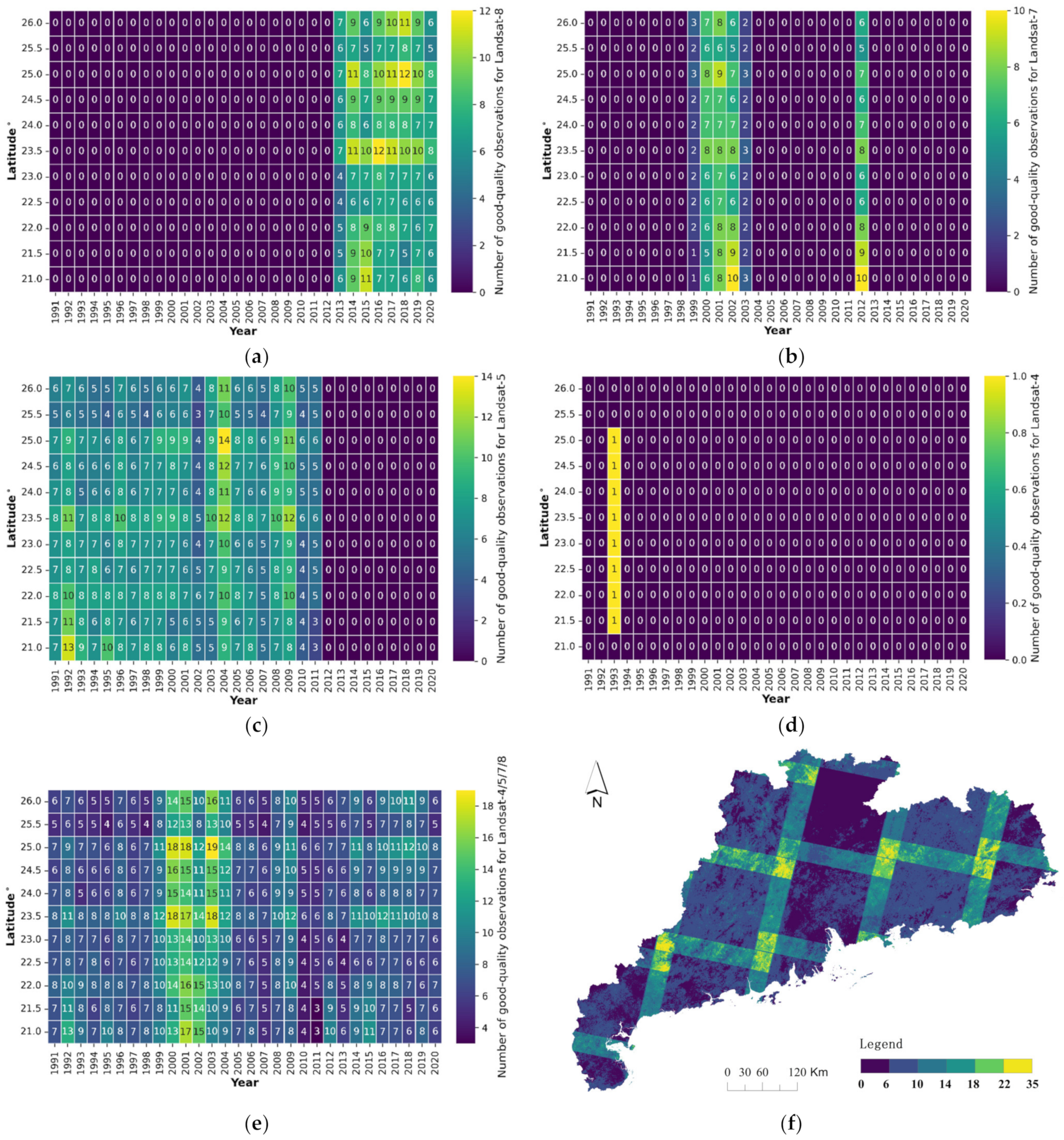





| Year | Number | Year | Number | Year | Number | Year | Number | Year | Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1991 | 267 | 1997 | 271 | 2003 | 427 | 2009 | 335 | 2015 | 359 |
| 1992 | 289 | 1998 | 281 | 2004 | 377 | 2010 | 210 | 2016 | 371 |
| 1993 | 225 | 1999 | 368 | 2005 | 271 | 2011 | 195 | 2017 | 387 |
| 1994 | 236 | 2000 | 603 | 2006 | 285 | 2012 | 202 | 2018 | 394 |
| 1995 | 250 | 2001 | 585 | 2007 | 232 | 2013 | 273 | 2019 | 341 |
| 1996 | 290 | 2002 | 530 | 2008 | 297 | 2014 | 372 | 2020 | 352 |
| Model | OA | Kappa | UA | PA | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N-BL | BL | N-BL | BL | |||
| Res-UNet++ | 0.99 | 0.96 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 1.00 | 0.83 |
| Deeplab-v3 | 0.94 | 0.78 | 0.93 | 0.97 | 1.00 | 0.53 |
| FCN | 0.95 | 0.82 | 0.95 | 0.93 | 1.00 | 0.55 |
| Sub-Regions | Reference | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N-BL | BL | Total | UA | |||
| WG | Map | N-BL | 0.94 | 0.01 | 0.95 | 0.99 |
| BL | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.97 | ||
| Total | 0.94 | 0.06 | 1.00 | |||
| PA | 1.00 | 0.86 | OA = 0.99 | |||
| NG | Map | N-BL | 0.94 | 0.01 | 0.95 | 0.99 |
| BL | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.97 | ||
| Total | 0.94 | 0.06 | 1.00 | |||
| PA | 1.00 | 0.86 | OA = 0.99 | |||
| EG | Map | N-BL | 0.93 | 0.02 | 0.95 | 0.98 |
| BL | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 1.00 | ||
| Total | 0.93 | 0.067 | 1.00 | |||
| PA | 1.00 | 0.76 | OA = 0.98 | |||
| PRD | Map | N-BL | 0.94 | 0.01 | 0.95 | 0.99 |
| BL | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.97 | ||
| Total | 0.94 | 0.06 | 1.00 | |||
| PA | 1.00 | 0.86 | OA = 0.99 | |||
| Year | OA | Kappa | UA | PA | Area (95% CI) (×103 km2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BL | N-BL | BL | N-BL | ||||
| 1995 | 0.98 | 0.90 | 0.93 | 0.99 | 0.55 | 1.00 | 4.98 (±0.94) |
| 2000 | 0.99 | 0.92 | 0.94 | 0.99 | 0.63 | 1.00 | 5.37 (±1.76) |
| 2005 | 0.98 | 0.91 | 0.94 | 0.98 | 0.66 | 1.00 | 6.93 (±1.02) |
| 2010 | 0.99 | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.99 | 0.85 | 1.00 | 7.87 (±0.71) |
| 2015 | 0.98 | 0.93 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.73 | 1.00 | 9.17 (±1.90) |
| 2020 | 0.99 | 0.96 | 0.97 | 0.99 | 0.83 | 1.00 | 10.65 (±1.56) |
| Regions | Reference | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BL | N-BL | |||||
| Bare Land | Sand | Mixed Pixel | Crop Land | |||
| Mapped as BL | WG | 30 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| NG | 29 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| EG | 29 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |
| PRD | 29 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |
| Total | 117 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, H.; Xiao, X.; Qin, Y.; Qiao, Z.; Long, S.; Tang, X.; Liu, L. Annual Maps of Built-Up Land in Guangdong from 1991 to 2020 Based on Landsat Images, Phenology, Deep Learning Algorithms, and Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3562. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153562
Xu H, Xiao X, Qin Y, Qiao Z, Long S, Tang X, Liu L. Annual Maps of Built-Up Land in Guangdong from 1991 to 2020 Based on Landsat Images, Phenology, Deep Learning Algorithms, and Google Earth Engine. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(15):3562. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153562
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Han, Xiangming Xiao, Yuanwei Qin, Zhi Qiao, Shaoqiu Long, Xianzhe Tang, and Luo Liu. 2022. "Annual Maps of Built-Up Land in Guangdong from 1991 to 2020 Based on Landsat Images, Phenology, Deep Learning Algorithms, and Google Earth Engine" Remote Sensing 14, no. 15: 3562. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153562
APA StyleXu, H., Xiao, X., Qin, Y., Qiao, Z., Long, S., Tang, X., & Liu, L. (2022). Annual Maps of Built-Up Land in Guangdong from 1991 to 2020 Based on Landsat Images, Phenology, Deep Learning Algorithms, and Google Earth Engine. Remote Sensing, 14(15), 3562. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153562