Flood Inflow Estimation in an Ungauged Simple Serial Cascade of Reservoir System Using Sentinel-2 Multi-Spectral Imageries: A Case Study of Imjin River, South Korea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methodology
2.1. Study Area and Data
2.1.1. The Injin River Basin
2.1.2. Hydrometeorological Data in the North Korean Area
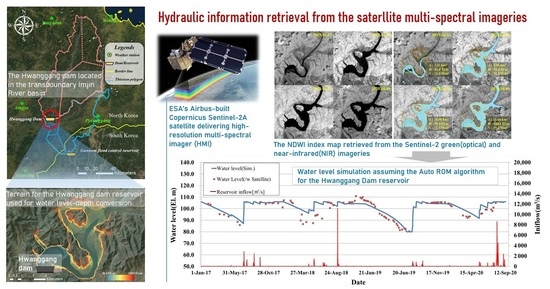
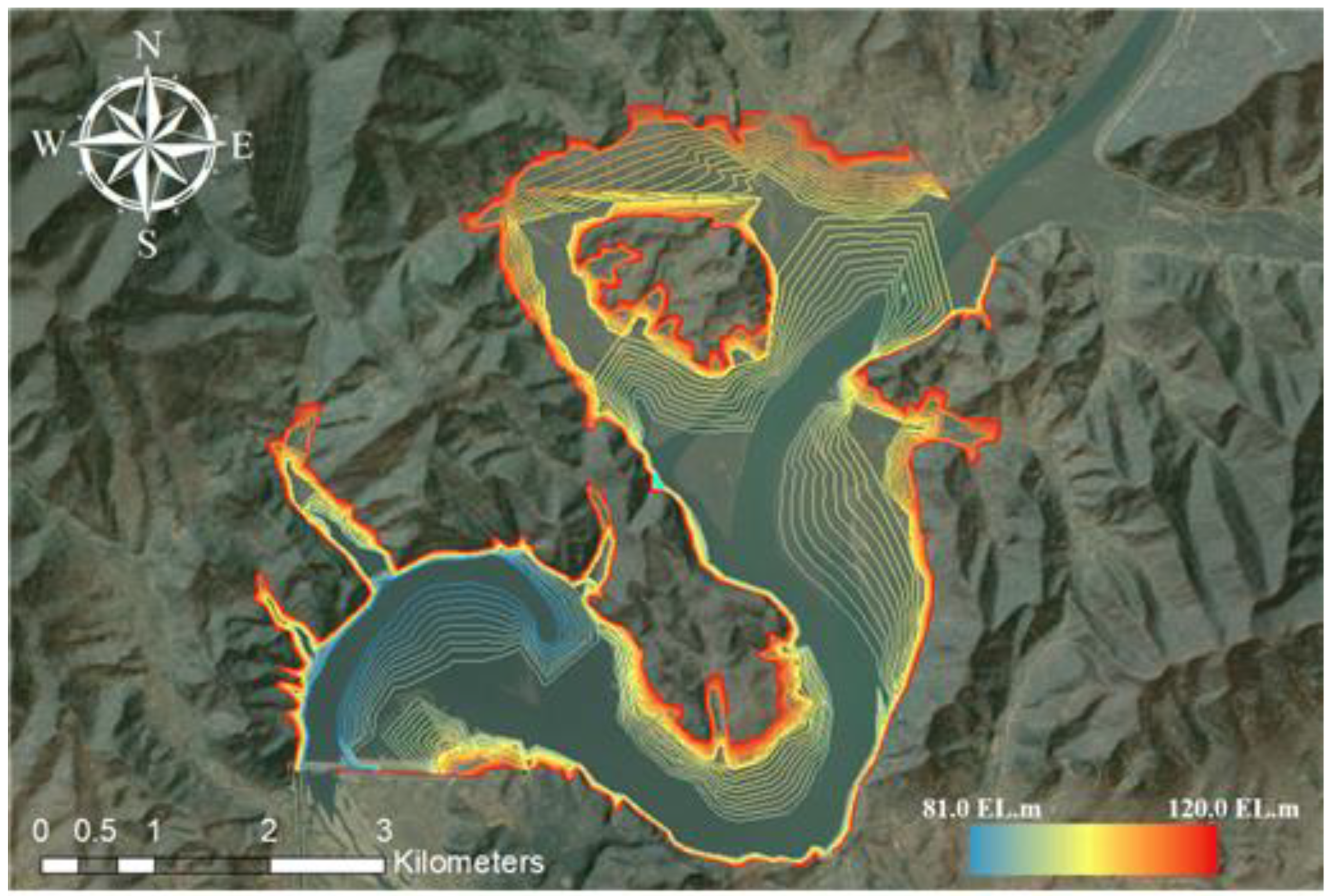
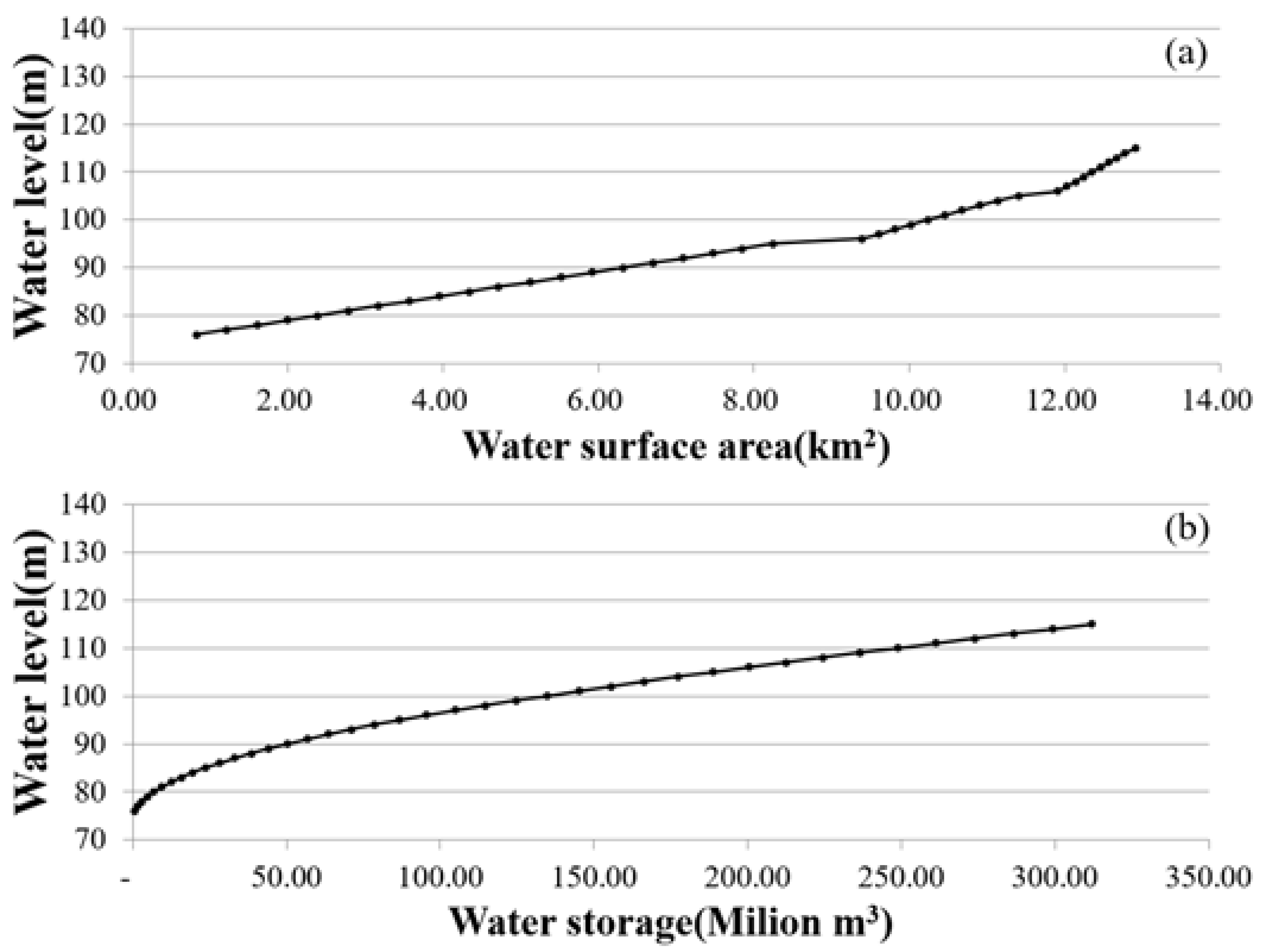
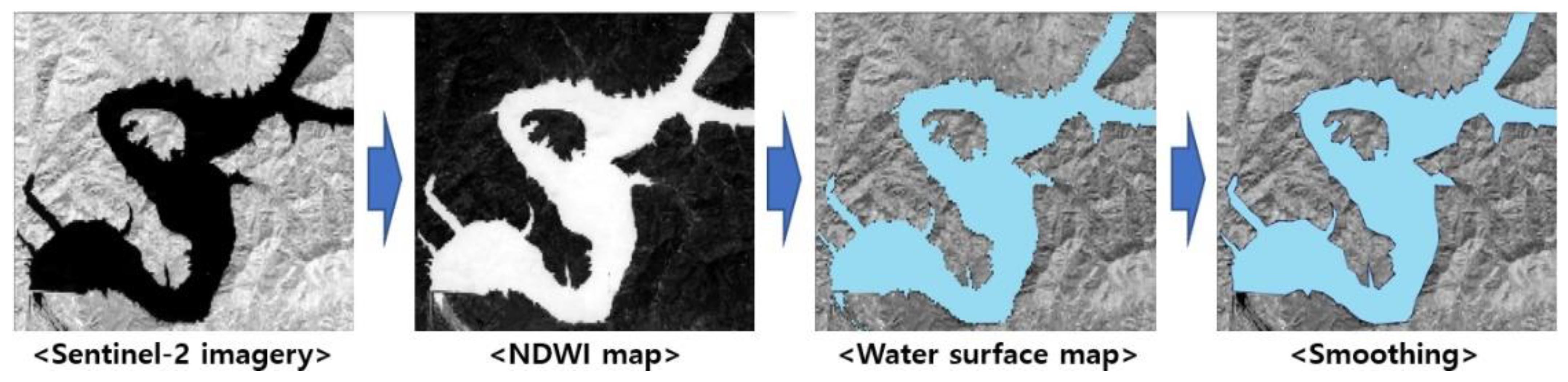
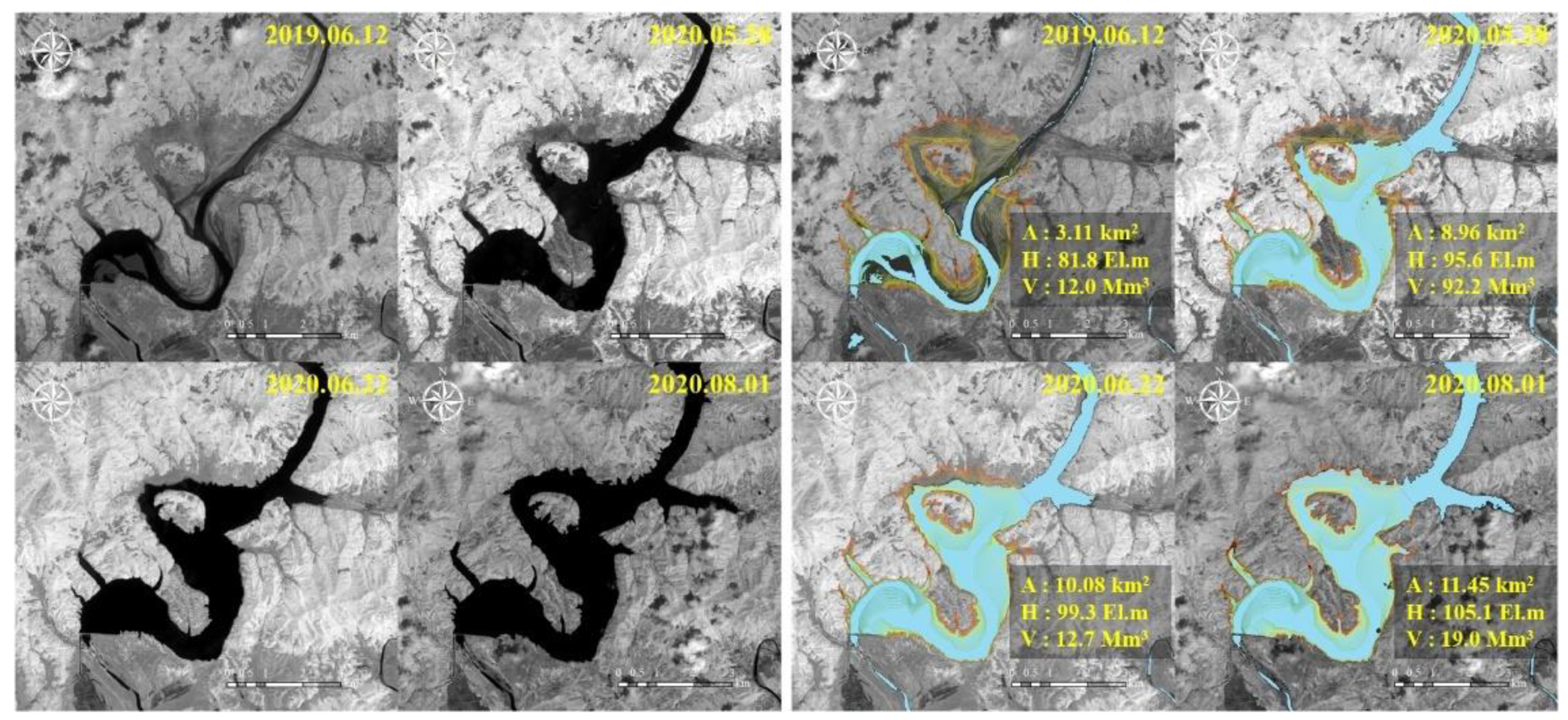
2.1.3. Sentinel-2 Multi-Spectral Data for the Hwanggang Dam Hydraulic Data Retrieval
2.2. Methodology
2.2.1. Conceptual Rainfall–Runoff Model
2.2.2. Reservoir Routing Model
- (1)
- If the water level of the reservoir is below the upper limit and above the lower limit, a specific amount of power generation is released regardless of the inflow.
- (2)
- If the water level of the reservoir is higher than the upper limit, all excess inflow is released.
- (3)
- If the water level in the reservoir is below the lower limit, stop the power generation and store the inflow.
- (4)
- It is assumed that the Hwanggang Dam can release a specific discharge through the gate operation regardless of the reservoir water level.
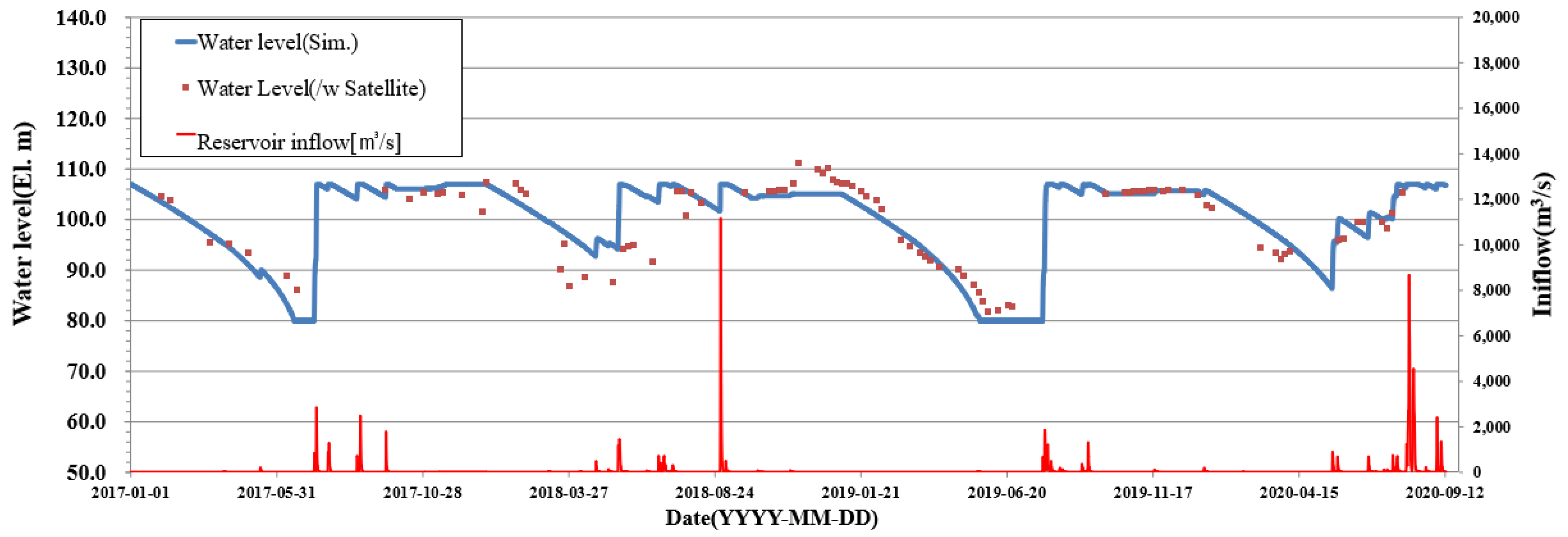
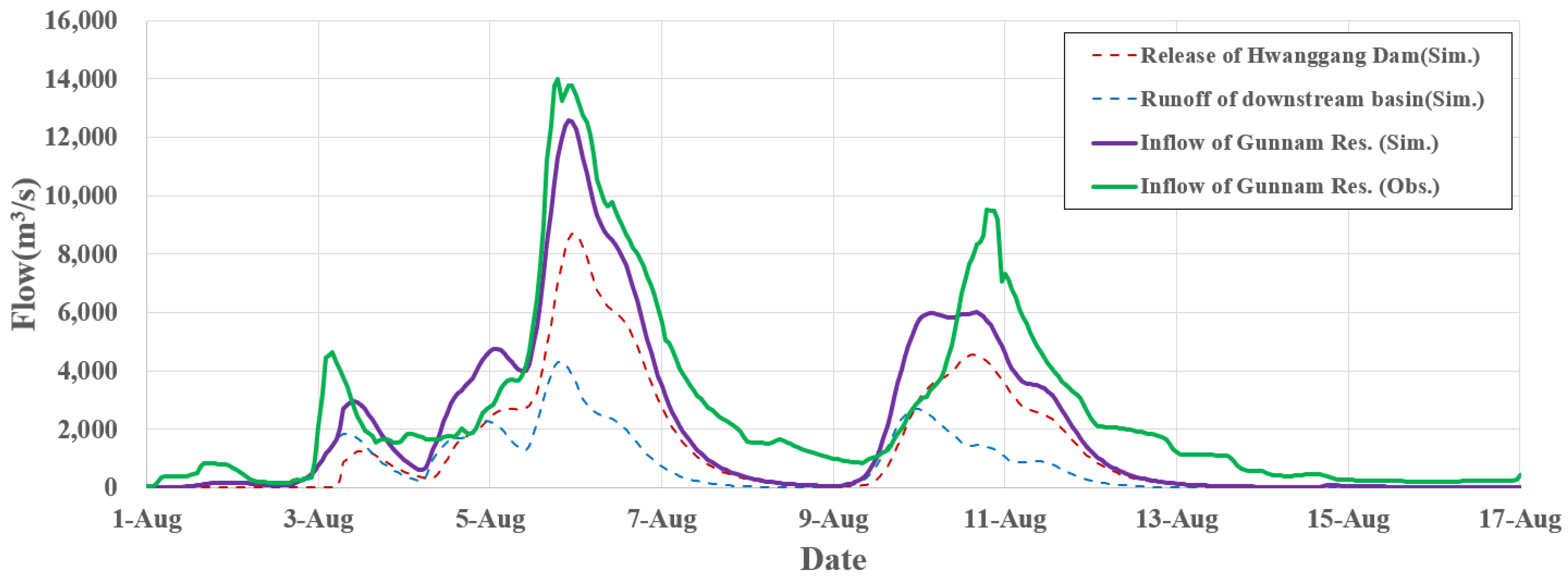
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, G.M.; Kang, B.; Hong, I.-P. Cooperative framework for conflict mitigation and shared use of South-North Korean transboundary rivers. KSCE J. Civil Environ. Eng. Res. 2008, 28, 505–514. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.H.; Hur, Y.T. Flood runoff simulation using physical based distributed model for Imjin-River basin. J. Korea Water Res. Ass. 2009, 42, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, D.P.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, J.H. Runoff estimation of Imjin river basin through april 5th dam and Hwanggang dam construction of North Korea. J. Environ. Sci. Int. 2011, 20, 1635–1646. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Ahn, J.; Yi, J. A study on the measures to use Gunnam flood control reservoir through a reservoir simulation model. J. Korea Water Res. Ass. 2017, 50, 407–418. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.J.; Lee, C.W. Simulation of the flood damage area of the Imjin River basin in the case of North Korea’s Hwanggang Dam discharge. Korean J. Remote Sens. 2018, 34, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, S.H.; Lee, J.-K.; Jo, J.W. Evaluation of instream flow in the Imjingang River according to the operation of Hwanggang Dam in North Korea. Crisisonomy 2020, 16, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, D.T.T.; Kim, S.H.; Bae, D.H. Impacts of upstream structures on downstream discharge in the transboundary Imjin River basin, Korean Peninsula. App. Sci. 2020, 10, 3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, E.; Kang, B. Estimation of ungauged Hwanggang dam inflow using Sentinel-2 optical satellite imagery. J. Korea Water Res. Assoc. 2021, 54, 265–277. [Google Scholar]
- Baek, K.O.; Choi, Y.H.; Lim, D.H. A Plan for Preventing Disaster by Water at Imjin River; Gyeonggi Research Institute: Suwon-si, Korea, 2010; pp. 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Carroll, M.L.; Townshend, J.R.; DiMiceli, C.M.; Noojipady, P.; Sohlberg, R.A. A new global raster water mask at 250 m resolution. Int. J. Dig. Earth 2009, 2, 291–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Hu, C.; Chen, X.; Cai, X.; Tian, L.; Gan, W. Assessment of inundation changes of Poyang Lake using MODIS observations between 2000 and 2010. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 121, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Chen, Y.; Wu, J. Mapping spatio-temporal flood inundation dynamics at large river basin scale using time-series flow data and MODIS imagery. Int. J. App. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 26, 350–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, F.; Xu, B.; Huang, H.; Yu, Q.; Gong, P. Modelling spatial-temporal change of Poyang Lake using multitemporal Landsat imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 5767–5784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Li, W.; Zhou, D.; Tian, L.; Ling, F.; Wang, H.; Gui, Y.; Sun, B. Analysis of Landsat-8 OLI imagery for land surface water mapping. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 5, 672–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokni, K.; Ahmad, A.; Selamat, A.; Hazini, S. Water feature extraction and change detection using multitemporal Landsat imagery. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 4173–4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drusch, M.; Del Bello, U.; Carlier, S.; Colin, O.; Fernandez, V.; Gascon, F.; Hoersch, B.; Isola, C.; Laberinti, P.; Martimort, P. Sentinel-2: ESA’s optical high-resolution mission for GMES operational services. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFeeters, S.K. The use of the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. Modification of normalised difference water index (NDWI) to enhance open water features in remotely sensed imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, D.H.; Ahn, J.H.; Heo, J.H. Standard Guidelines for Flood Estimation; Ministry of Environment: Sejong-si, Korea, 2019.
- Gwon, O.I.; Sim, M.P. Reservoir operation at flood time by transformed reservoir flood(TRF) reservoir operation method(ROM). J. Korea Water Res. Ass. 1998, 31, 105–113. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, D.Z.; Li, Y.P.; Huang, G.H. A factorial-based dynamic analysis method for reservoir operation under fuzzy-stochastic uncertainties. Water Res. Manag. 2013, 27, 4591–4610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unver, O.I.; Mays, L.W. Model for real-time optimal flood control operation of a reservoir system. Water Res. Manag. 1990, 4, 21–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

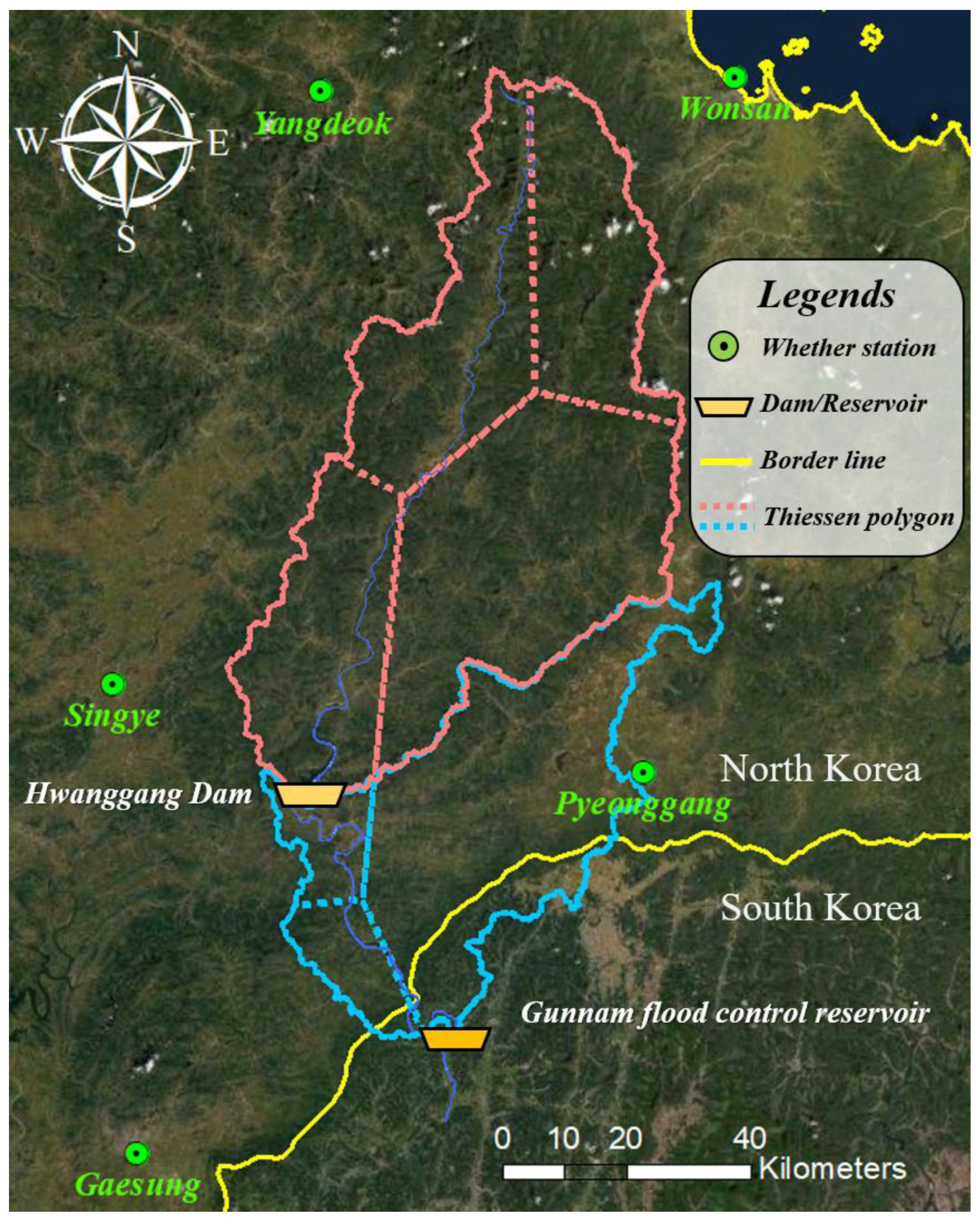




| Location | Yangdeok | Wonsan | Singye | Pyeonggang | Gaesung |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upstream of Hwanggang Dam | 0.225 | 0.184 | 0.210 | 0.381 | - |
| Downstream of Hwanggang Dam | - | - | 0.099 | 0.787 | 0.114 |
| Sentinel-2 Band | Sentinel-2A | Sentinel-2B | Spatial Resolution (m) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Central Wavelength (nm) | Bandwidth (nm) | Central Wavelength (nm) | Bandwidth (nm) | ||
| Band 3 (Green) | 559.8 | 36 | 559.0 | 36 | 10 |
| Band 8 (NIR) | 832.8 | 106 | 832.9 | 105 | 10 |
| Band 12 (SWIR) | 2202.1 | 175 | 2185.7 | 185 | 20 |
| No. | Basin Name | Area (km2) | River Length (km) | Elevation of the Farthest Point (EL.m) | Elevation of Outlet Point (EL.m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01 | Upstream of Imjin River | 1101.5 | 85.0 | 1285 | 140 |
| 02 | Upstream of Gomitan Stream | 1093.7 | 108.6 | 1086 | 140 |
| 03 | Icheon water level sta. | 666.1 | 57.4 | 714 | 67 |
| 04 | Upstream of Pyeongan Stream | 404.7 | 80.0 | 1086 | 52 |
| 05 | Confluence of Yeockok Stream | 244.8 | 45.3 | 612 | 42 |
| 06 | Lake Bongrae | 498.8 | 73.0 | 491 | 42 |
| 07 | Gumnam Flood Control Reservoir | 183.0 | 21.1 | 326 | 35 |
| No. | Basin Name | Clark Unit Hydrograph | Muskingum Flow Routing | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tc (hr) | K (hr) | C0 | C1 | C2 | ||
| 01 | Upstream of Imjin River | 6.60 | 9.21 | 0.0266 | 0.4160 | 0.5575 |
| 02 | Upstream of Gomitan Stream | 8.66 | 11.98 | 0.0162 | 0.4097 | 0.5741 |
| 03 | Icheon water level sta. | 4.84 | 6.79 | 0.0316 | 0.4190 | 0.5494 |
| 04 | Upstream of Pyeongan Stream | 6.30 | 8.64 | 0.0368 | 0.4221 | 0.5412 |
| 05 | Confluence of Yeockok Stream | 3.88 | 5.39 | - | - | - |
| 06 | Lake Bongrae | 6.49 | 8.97 | 0.0303 | 0.4182 | 0.5515 |
| 07 | Gumnam Flood Control Reservoir | 1.99 | 2.84 | - | - | - |
| Parameter | High Water Level | Low Water Level | Constant Release | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nov~Dec | Jan~Oct | |||
| State value | 107.0 EL.m | 80.0 EL.m | 20.0 m3/s | 35.0 m3/s |
| Index | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 (~Aug) | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | 0.94 | 0.47 | 0.97 | 0.75 | 0.76 |
| RMSE | 3.07 | 5.81 | 2.25 | 3.18 | 3.97 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.G.; Kang, B.; Kim, S. Flood Inflow Estimation in an Ungauged Simple Serial Cascade of Reservoir System Using Sentinel-2 Multi-Spectral Imageries: A Case Study of Imjin River, South Korea. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3699. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153699
Kim JG, Kang B, Kim S. Flood Inflow Estimation in an Ungauged Simple Serial Cascade of Reservoir System Using Sentinel-2 Multi-Spectral Imageries: A Case Study of Imjin River, South Korea. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(15):3699. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153699
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Jin Gyeom, Boosik Kang, and Sungmo Kim. 2022. "Flood Inflow Estimation in an Ungauged Simple Serial Cascade of Reservoir System Using Sentinel-2 Multi-Spectral Imageries: A Case Study of Imjin River, South Korea" Remote Sensing 14, no. 15: 3699. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153699
APA StyleKim, J. G., Kang, B., & Kim, S. (2022). Flood Inflow Estimation in an Ungauged Simple Serial Cascade of Reservoir System Using Sentinel-2 Multi-Spectral Imageries: A Case Study of Imjin River, South Korea. Remote Sensing, 14(15), 3699. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153699