Arctic Multiyear Ice Areal Flux and Its Connection with Large-Scale Atmospheric Circulations in the Winters of 2002–2021
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data
2.1. Sea Ice Concentration Data
2.2. Sea Ice Motion Data
2.3. Atmospheric Data
3. Methods
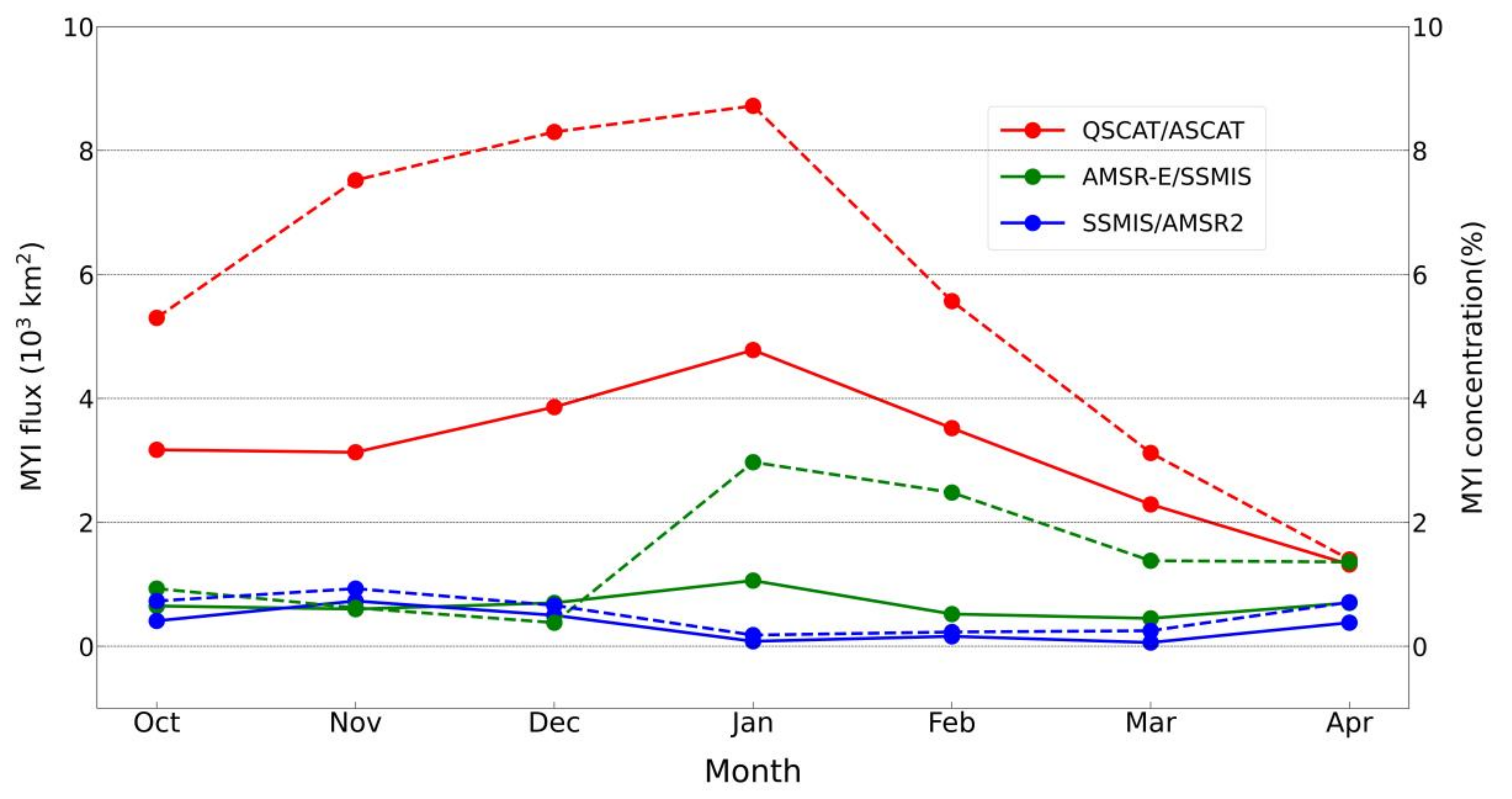
3.1. Improvement in the Retrieval of MYI Concentration
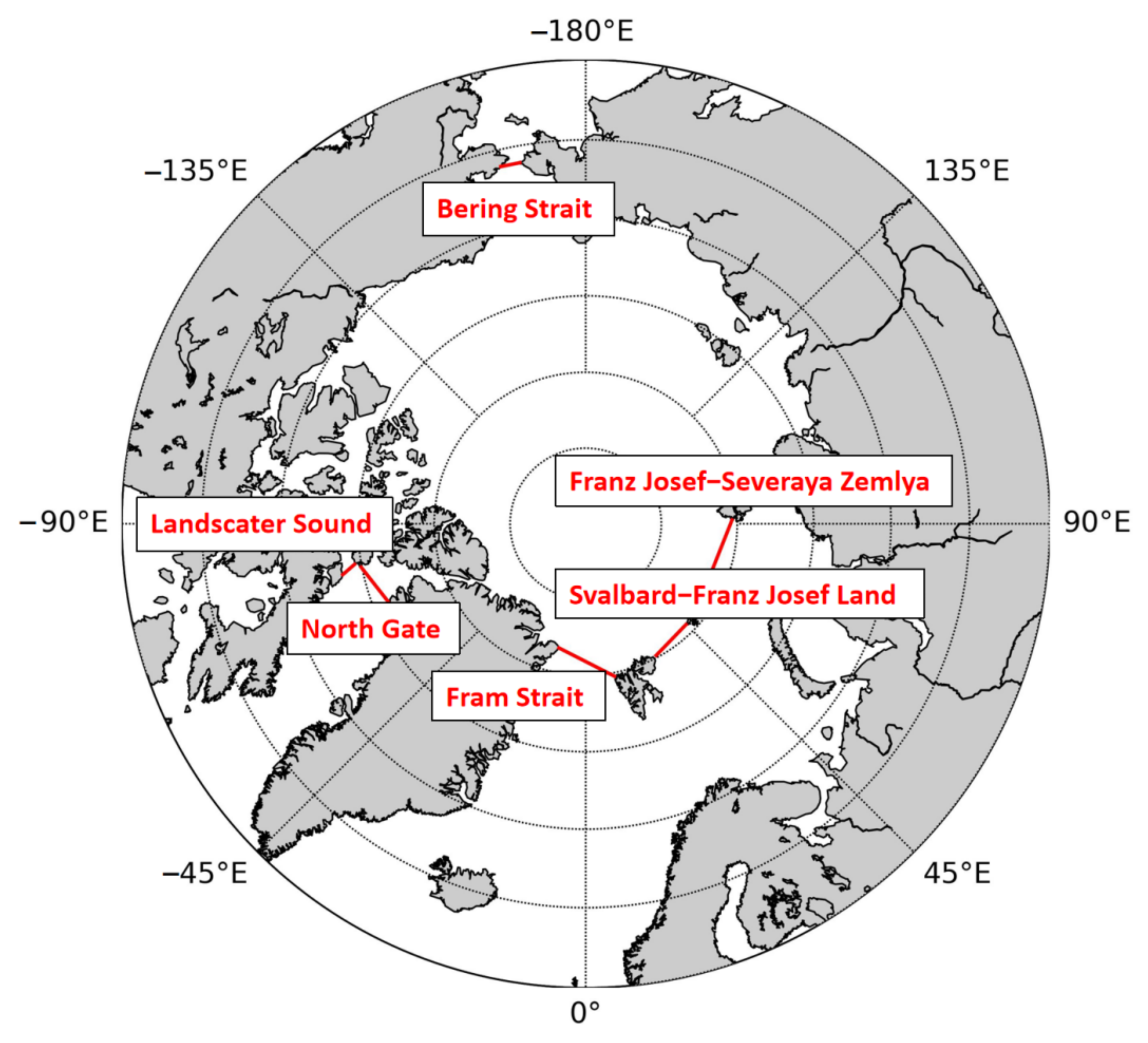
3.2. Areal Flux Calculation
3.3. Normalization of Preliminary Results
4. Results
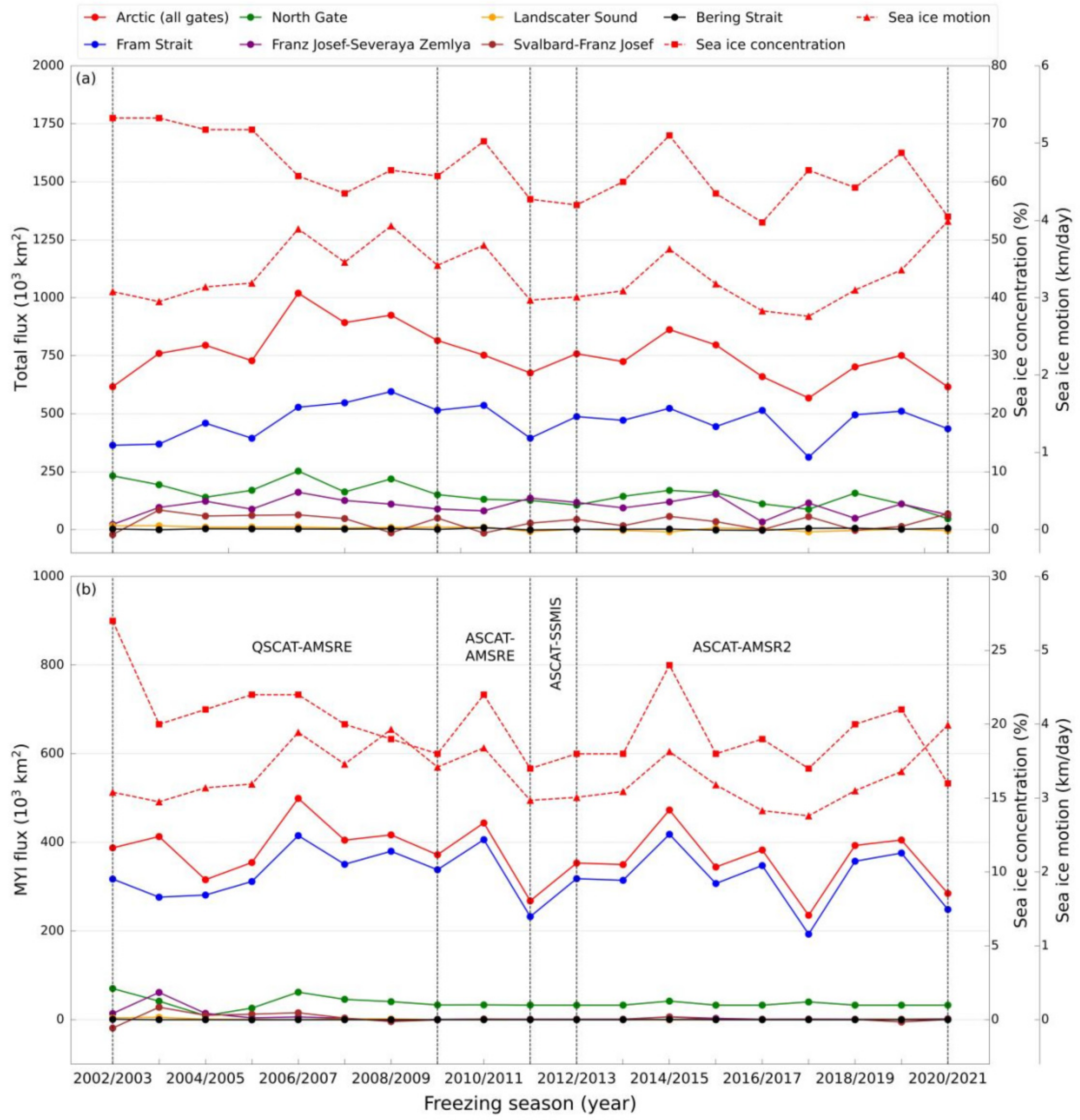
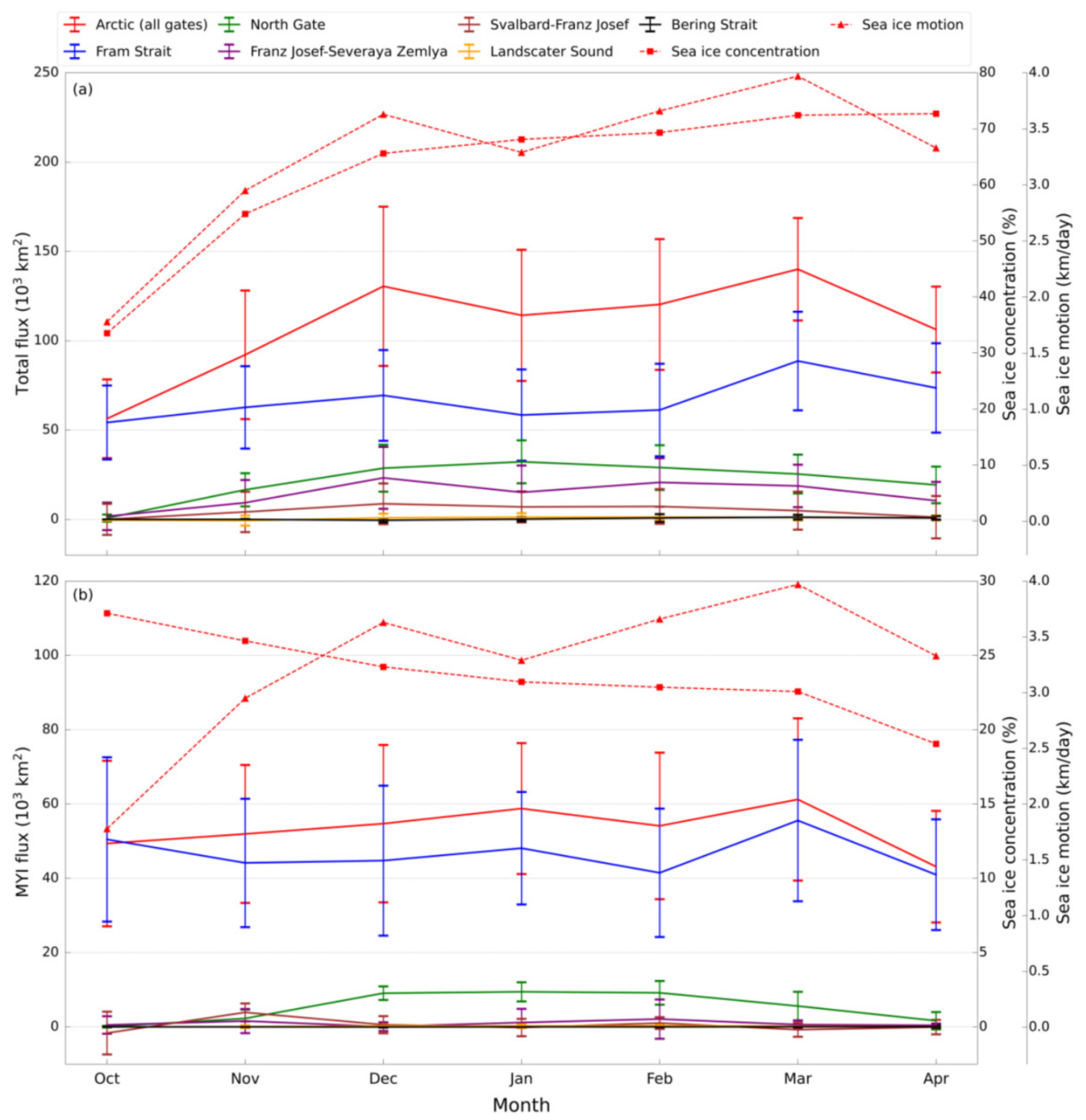
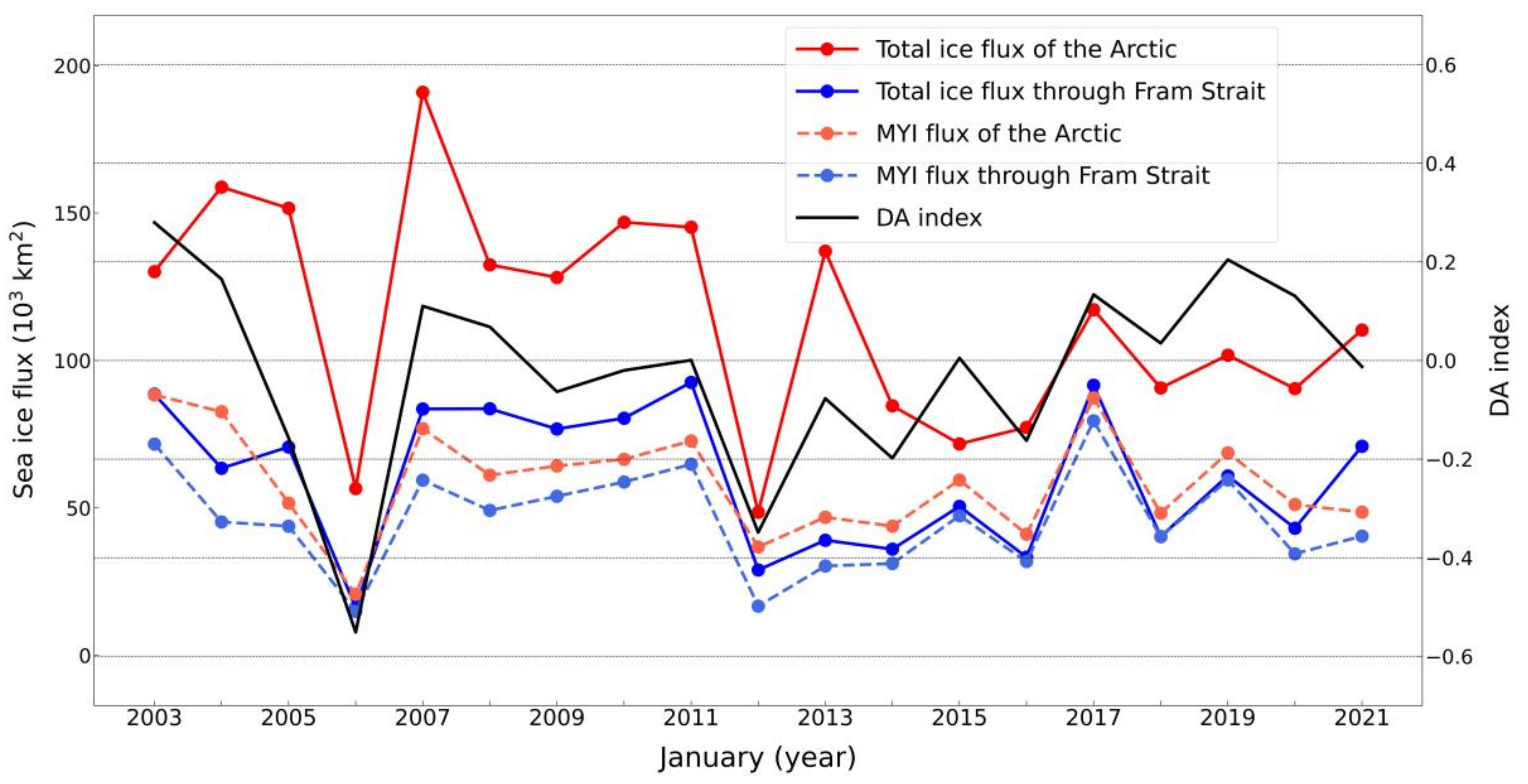
4.1. Time Series of Total Sea Ice and MYI Areal Flux
4.2. Contribution of Sea Ice Motion and Sea Ice Concentration to Areal Flux
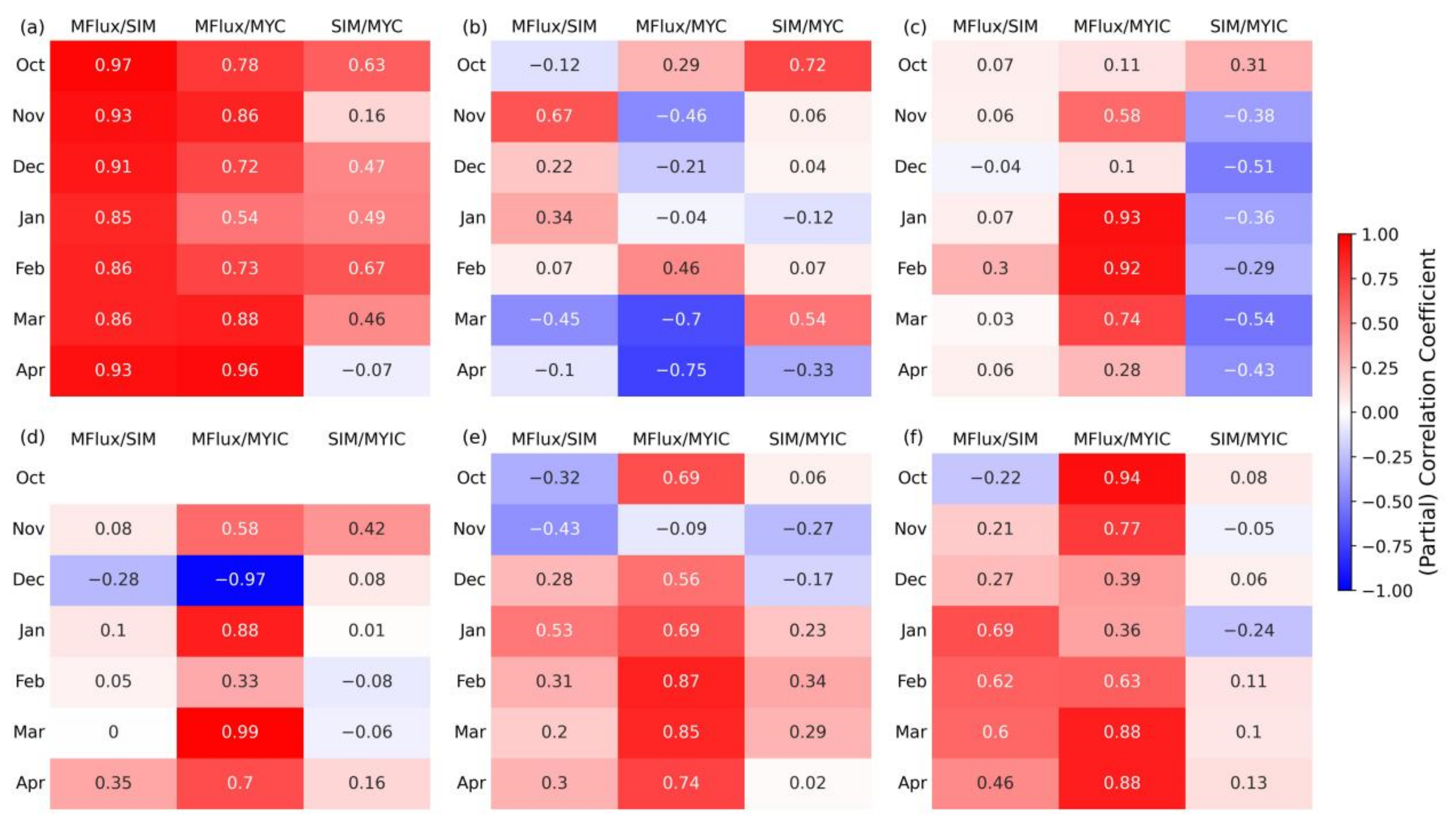
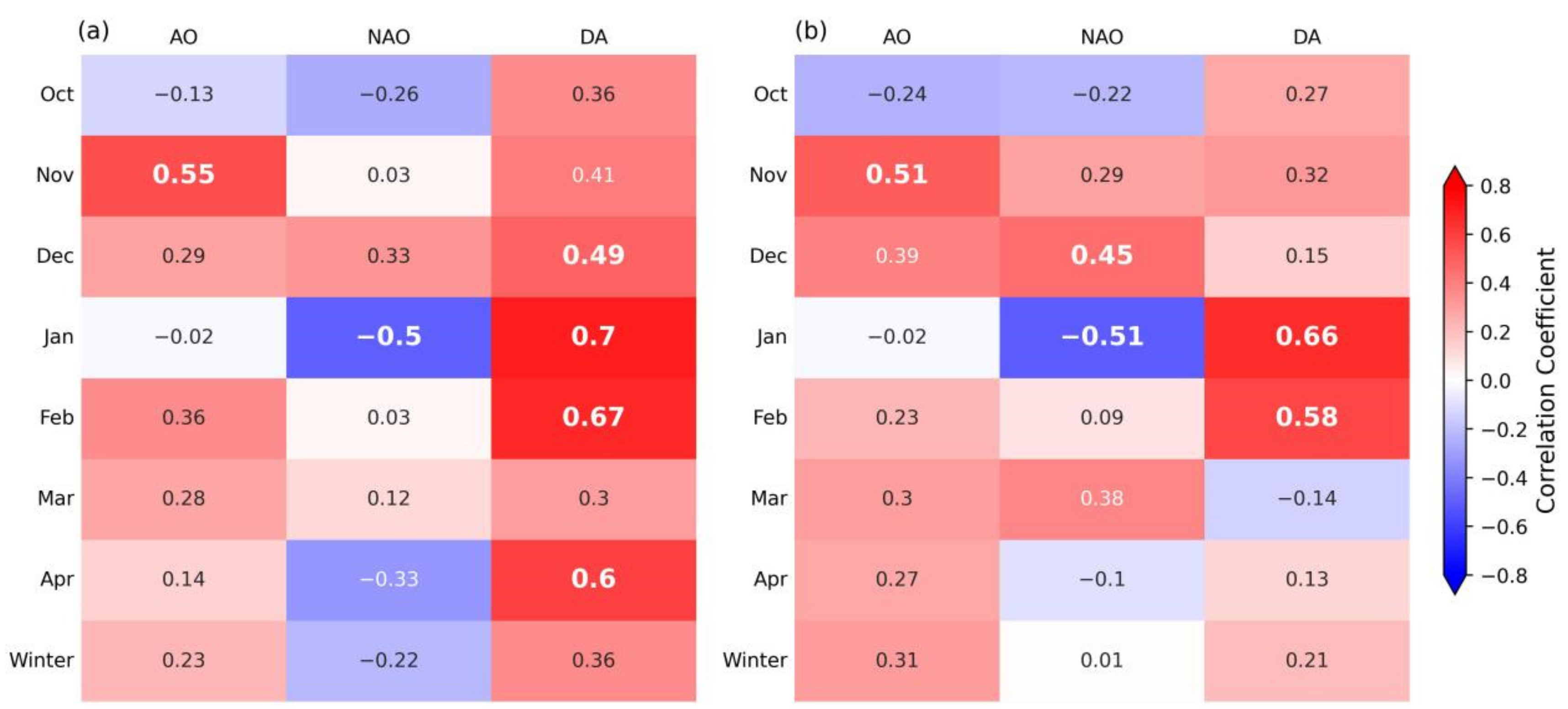
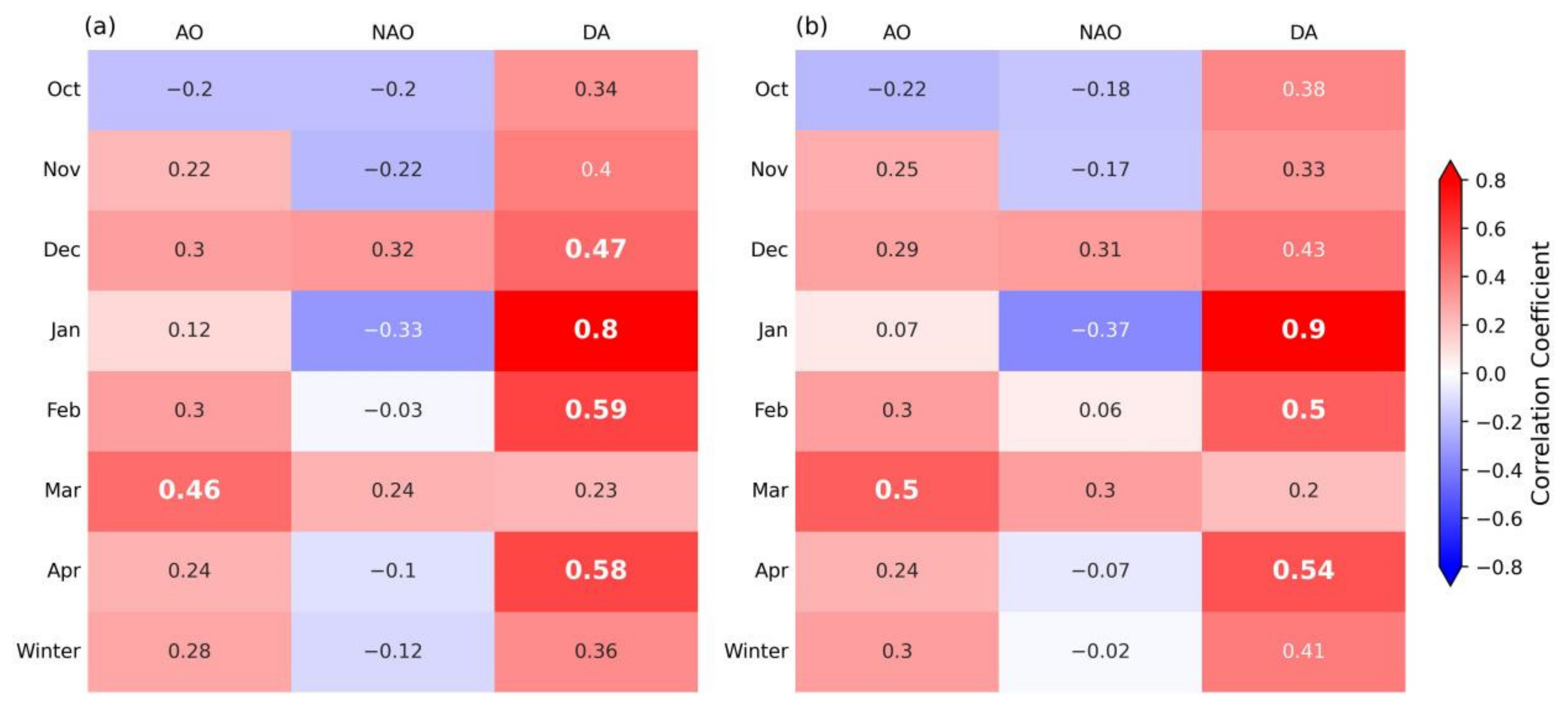
4.3. Connection between Sea Ice Outflow and Varying Atmospheric Indices
4.4. The Distinct Role of Arctic Dipole Anomaly
5. Discussion
5.1. Consistency of MYI Concentration Data and Its Influence on MYI Flux
5.2. Variability of MYI Areal Flux, Total Sea Ice Areal and Volume Flux
5.3. Correlation Analysis of Sea Ice Flux and Atmospheric Indices
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| ×103 km2 | October | November | December | January | February | March | April | Winter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fram Strait | 54.25 | 62.72 | 69.41 | 58.42 | 61.24 | 88.68 | 73.58 | 468.30 |
| S–FJ | 0.04 | 4.18 | 8.75 | 7.01 | 7.25 | 4.90 | 1.24 | 33.34 |
| FJ–SZ | 1.73 | 9.33 | 23.24 | 15.16 | 20.70 | 18.75 | 10.50 | 99.40 |
| Bering Strait | 0 | −0.02 | −0.46 | 0.16 | 0.81 | 1.24 | 0.80 | 2.54 |
| Lanscater Sound | −0.37 | −0.65 | 0.89 | 1.24 | 1.30 | 1.07 | 0.87 | 4.36 |
| North Gate | 0.72 | 16.58 | 28.67 | 32.25 | 29.03 | 25.40 | 19.31 | 151.01 |
| Arctic (all gates) | 56.36 | 92.15 | 130.49 | 114.24 | 120.33 | 140.01 | 106.30 | 759.02 |
| ×103 km2 | October | November | December | January | February | March | April | Winter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fram Strait | 50.47 | 44.14 | 44.76 | 48.10 | 41.48 | 55.56 | 40.97 | 325.92 |
| S–FJ | −1.66 | 3.90 | 0.58 | −0.18 | 1.04 | −0.76 | −0.06 | 2.87 |
| FJ–SZ | 0.51 | 1.58 | 0.07 | 1.17 | 2.10 | 0.61 | 0.42 | 6.47 |
| Bering Strait | 0 | 0 | −0.03 | 0.01 | 0 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.07 |
| Lanscater Sound | −0.01 | 0.05 | 0.26 | 0.23 | 0.31 | 0.19 | 0.09 | 1.13 |
| North Gate | 0.06 | 2.27 | 9.07 | 9.44 | 9.17 | 5.60 | 1.65 | 37.26 |
| Arctic (all gates) | 49.37 | 51.94 | 54.71 | 58.78 | 54.11 | 61.23 | 43.13 | 373.72 |
References
- Meier, W.N.; Hovelsrud, G.K.; Van Oort, B.E.; Key, J.R.; Kovacs, K.M.; Michel, C.; Haas, C.; Granskog, M.A.; Gerland, S.; Perovich, D.K. Arctic sea ice in transformation: A review of recent observed changes and impacts on biology and human activity. Rev. Geophys. 2014, 52, 185–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannessen, O.M.; Bengtsson, L.; Miles, M.W.; Kuzmina, S.I.; Semenov, V.A.; Alekseev, G.V.; Nagurnyi, A.P.; Zakharov, V.F.; Bobylev, L.P.; Pettersson, L.H. Arctic climate change: Observed and modelled temperature and sea-ice variability. Tellus A Dyn. Meteorol. Oceanogr. 2004, 56, 328–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroeve, J.; Notz, D. Changing state of Arctic sea ice across all seasons. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 103001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thackeray, C.W.; Hall, A. An emergent constraint on future Arctic sea-ice albedo feedback. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2019, 9, 972–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donohoe, A.; Blanchard-Wrigglesworth, E.; Schweiger, A.; Rasch, P.J. The effect of atmospheric transmissivity on model and observational estimates of the sea ice albedo feedback. J. Clim. 2020, 33, 5743–5765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cavalieri, D.J.; Parkinson, C.L. Arctic sea ice variability and trends, 1979–2010. Cryosphere 2012, 6, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Comiso, J.C.; Parkinson, C.L.; Gersten, R.; Stock, L. Accelerated decline in the Arctic sea ice cover. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L01703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Comiso, J.C. Large decadal decline of the Arctic multiyear ice cover. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 1176–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroeve, J.; Holland, M.M.; Meier, W.; Scambos, T.; Serreze, M. Arctic sea ice decline: Faster than forecast. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, R. Near zero replenishment of the Arctic multiyear sea ice cover at the end of 2005 summer. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L05501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, R.; Untersteiner, N. The thinning of Arctic sea ice. Phys. Today 2011, 64, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ricker, R.; Girard-Ardhuin, F.; Krumpen, T.; Lique, C. Satellite-derived sea ice export and its impact on Arctic ice mass balance. Cryosphere 2018, 12, 3017–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bi, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, W.; Fu, M.; Huang, H. Recent satellite-derived sea ice volume flux through the Fram Strait: 2011–2015. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2018, 37, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semmling, A.M.; Rösel, A.; Divine, D.V.; Gerland, S.; Stienne, G.; Reboul, S.; Ludwig, M.; Wickert, J.; Schuh, H. Sea-ice concentration derived from GNSS reflection measurements in Fram Strait. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 10350–10361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serreze, M.C.; Barrett, A.P.; Slater, A.G.; Woodgate, R.A.; Aagaard, K.; Lammers, R.B.; Steele, M.; Moritz, R.; Meredith, M.; Lee, C.M. The large-scale freshwater cycle of the Arctic. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spreen, G.; Kern, S.; Stammer, D.; Hansen, E. Fram Strait sea ice volume export estimated between 2003 and 2008 from satellite data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L19502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spreen, G.; de Steur, L.; Divine, D.; Gerland, S.; Hansen, E.; Kwok, R. Arctic sea ice volume export through Fram Strait from 1992 to 2014. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2020, 125, e2019JC016039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, R.; Cunningham, G.; Pang, S. Fram Strait sea ice outflow. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, R. Outflow of Arctic Ocean sea ice into the Greenland and Barents Seas: 1979–2007. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 2438–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwok, R.; Toudal Pedersen, L.; Gudmandsen, P.; Pang, S. Large sea ice outflow into the Nares Strait in 2007. J. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krumpen, T.; Janout, M.; Hodges, K.; Gerdes, R.; Girard-Ardhuin, F.; Hölemann, J.A.; Willmes, S. Variability and trends in Laptev Sea ice outflow between 1992–2011. Cryosphere 2013, 7, 349–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agnew, T.; Lambe, A.; Long, D. Estimating sea ice area flux across the Canadian Arctic Archipelago using enhanced AMSR-E. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bi, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Liang, Y.; Huang, J.; Liu, Y.; Fu, M. Baffin Bay sea ice inflow and outflow: 1978–1979 to 2016–2017. Cryosphere 2019, 13, 1025–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belmonte Rivas, M.; Otosaka, I.; Stoffelen, A.; Verhoef, A. A scatterometer record of sea ice extents and backscatter: 1992–2016. Cryosphere 2018, 12, 2941–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Bi, H.; Liang, Y. A Satellite-Observed Substantial Decrease in Multiyear Ice Area Export through the Fram Strait over the Last Decade. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahn, A.; Tremblay, B.; Mysak, L.A.; Newton, R. Effect of the large-scale atmospheric circulation on the variability of the Arctic Ocean freshwater export. Clim. Dyn. 2010, 34, 201–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikolajewicz, U.; Sein, D.V.; Jacob, D.; Königk, T.; Podzun, R.; Semmler, T. Simulating Arctic sea ice variability with a coupled regional atmosphere-ocean-sea ice model. Meteorol. Z. 2005, 14, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, M.; Ke, C.; Cheng, B.; Shen, X.; He, Y.; Sha, D. The Roles of Sea Ice Export, Atmospheric and Oceanic Factors in the Seasonal and Regional Variability of Arctic Sea Ice during 1979–2020. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wettstein, J.J.; Deser, C. Internal variability in projections of twenty-first-century Arctic sea ice loss: Role of the large-scale atmospheric circulation. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 527–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thompson, D.W.; Wallace, J.M. The Arctic Oscillation signature in the wintertime geopotential height and temperature fields. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1998, 25, 1297–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hurrell, J.W. Decadal trends in the North Atlantic Oscillation: Regional temperatures and precipitation. Science 1995, 269, 676–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, B.; Wang, J.; Walsh, J.E. Dipole anomaly in the winter Arctic atmosphere and its association with sea ice motion. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 210–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, R.; Rothrock, D.A. Variability of Fram Strait ice flux and North Atlantic oscillation. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1999, 104, 5177–5189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwok, R.; Spreen, G.; Pang, S. Arctic sea ice circulation and drift speed: Decadal trends and ocean currents. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2013, 118, 2408–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, T.; Hilmer, M. The link between the North Atlantic Oscillation and Arctic sea ice export through Fram Strait. J. Clim. 2001, 14, 3932–3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rigor, I.G.; Wallace, J.M.; Colony, R.L. Response of sea ice to the Arctic Oscillation. J. Clim. 2002, 15, 2648–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z. Reexamination of Fram Strait sea ice export and its role in recently accelerated Arctic sea ice retreat. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 53, 1823–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lei, R.; Gui, D.; Hutchings, J.K.; Wang, J.; Pang, X. Backward and forward drift trajectories of sea ice in the northwestern Arctic Ocean in response to changing atmospheric circulation. Int. J. Climatol. 2019, 39, 4372–4391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, F.; Pang, X.; Lei, R.; Zhai, M.; Zhao, X.; Cai, Q. Arctic sea ice motion change and response to atmospheric forcing between 1979 and 2019. Int. J. Climatol. 2022, 42, 1854–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokr, M.; Lambe, A.; Agnew, T. A new algorithm (ECICE) to estimate ice concentration from remote sensing observations: An application to 85-GHz passive microwave data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 4104–4121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffen, K.; Abdalati, W.; Stroeve, J. Climate sensitivity studies of the Greenland ice sheet using satellite AVHRR, SMMR, SSM/I and in situ data. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 1993, 51, 239–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tschudi, M.A.; Meier, W.N.; Stewart, J.S. An enhancement to sea ice motion and age products at the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC). Cryosphere 2020, 14, 1519–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H. The ERA5 Atmospheric Reanalysis. In Proceedings of the AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts, San Francisco, CA, USA, 12–16 December 2016; p. NG33D-01. [Google Scholar]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, H.; Sun, K.; Zhou, X.; Huang, H.; Xu, X. Arctic Sea ice area export through the Fram Strait estimated from satellite-based data: 1988–2012. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 3144–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Watanabe, E.; Ikeda, M.; Mizobata, K.; Walsh, J.E.; Bai, X.; Wu, B. Is the Dipole Anomaly a major driver to record lows in Arctic summer sea ice extent? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shokr, M.; Agnew, T.A. Validation and potential applications of Environment Canada Ice Concentration Extractor (ECICE) algorithm to Arctic ice by combining AMSR-E and QuikSCAT observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 128, 315–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Shokr, M.; Heygster, G.; Spreen, G. Improving multiyear sea ice concentration estimates with sea ice drift. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, Y.; Shokr, M.; Aaboe, S.; Aldenhoff, W.; Eriksson, L.E.; Heygster, G.; Melsheimer, C.; Girard-Ardhuin, F. Inter-comparison and evaluation of sea ice type concentration algorithms. Cryosphere Discuss. 2019, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hao, G.; Su, J. A study of multiyear ice concentration retrieval algorithms using AMSR-E data. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2015, 34, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, N.K.; Shokr, M. Sea Ice: Physics and Remote Sensing; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Y.; Heygster, G.; Shokr, M. Improving multiyear ice concentration estimates with reanalysis air temperatures. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 54, 2602–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukernik, M.; Deser, C.; Alexander, M.; Tomas, R. Atmospheric forcing of Fram Strait sea ice export: A closer look. Clim. Dyn. 2010, 35, 1349–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smedsrud, L.H.; Sirevaag, A.; Kloster, K.; Sorteberg, A.; Sandven, S. Recent wind driven high sea ice area export in the Fram Strait contributes to Arctic sea ice decline. Cryosphere 2011, 5, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thorndike, A.; Colony, R. Sea ice motion in response to geostrophic winds. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1982, 87, 5845–5852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, R. Arctic sea ice thickness, volume, and multiyear ice coverage: Losses and coupled variability (1958–2018). Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 105005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Bi, H.; Sun, K.; Huang, H.; Liu, Y.; Yan, L. Arctic sea ice volume export through the Fram Strait from combined satellite and model data: 1979–2012. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2017, 36, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, B.; Krumpen, T.; Smedsrud, L.H.; Gerdes, R. Fram Strait sea ice export affected by thinning: Comparing high-resolution simulations and observations. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 53, 3257–3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, R.; Osborn, T.; Hurrell, J.; Meincke, J.; Blindheim, J.; Adlandsvik, B.; Vinje, T.; Alekseev, G.; Maslowski, W. The Arctic ocean response to the North Atlantic oscillation. J. Clim. 2000, 13, 2671–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilmer, M.; Jung, T. Evidence for a recent change in the link between the North Atlantic Oscillation and Arctic sea ice export. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000, 27, 989–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smedsrud, L.H.; Halvorsen, M.H.; Stroeve, J.C.; Zhang, R.; Kloster, K. Fram Strait sea ice export variability and September Arctic sea ice extent over the last 80 years. Cryosphere 2017, 11, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwok, R. Baffin Bay ice drift and export: 2002–2007. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moore, G.W.K.; Howell, S.E.L.; Brady, M.; Xu, X.; McNeil, K. Anomalous collapses of Nares Strait ice arches leads to enhanced export of Arctic sea ice. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Winter (October–April) of Years | ECICE Input Data | Input Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| 2002–2009 | QSCAT, AMSR-E | σ0hh, σ0vv, Tb37h, Tb37v |
| 2009–2011 | ASCAT, AMSR-E | σ0, Tb19h, Tb37h, GR37v19v |
| 2011–2012 | ASCAT, SSMIS | σ0, Tb19h, Tb37h, GR37v19v |
| 2012–2021 | ASCAT, AMSR2 | σ0, Tb19h, Tb37h, GR37v19v |
| Fluxgates | Length (km) | Number of Grids |
|---|---|---|
| Fram Strait | 455 | 36 |
| Svalbard–Franz Josef (S–FJ) | 314 | 25 |
| Franz Josef–Severnaya Zemlya (FJ–SZ) | 473 | 38 |
| Bering Strait | 132 | 11 |
| Lanscater Sound | 112 | 9 |
| North Gate | 314 | 25 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuang, H.; Luo, Y.; Ye, Y.; Shokr, M.; Chen, Z.; Wang, S.; Hui, F.; Bi, H.; Cheng, X. Arctic Multiyear Ice Areal Flux and Its Connection with Large-Scale Atmospheric Circulations in the Winters of 2002–2021. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3742. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153742
Kuang H, Luo Y, Ye Y, Shokr M, Chen Z, Wang S, Hui F, Bi H, Cheng X. Arctic Multiyear Ice Areal Flux and Its Connection with Large-Scale Atmospheric Circulations in the Winters of 2002–2021. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(15):3742. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153742
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuang, Huiyan, Yanbing Luo, Yufang Ye, Mohammed Shokr, Zhuoqi Chen, Shaoyin Wang, Fengming Hui, Haibo Bi, and Xiao Cheng. 2022. "Arctic Multiyear Ice Areal Flux and Its Connection with Large-Scale Atmospheric Circulations in the Winters of 2002–2021" Remote Sensing 14, no. 15: 3742. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153742
APA StyleKuang, H., Luo, Y., Ye, Y., Shokr, M., Chen, Z., Wang, S., Hui, F., Bi, H., & Cheng, X. (2022). Arctic Multiyear Ice Areal Flux and Its Connection with Large-Scale Atmospheric Circulations in the Winters of 2002–2021. Remote Sensing, 14(15), 3742. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153742








