Urban Tree Classification Based on Object-Oriented Approach and Random Forest Algorithm Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) Multispectral Imagery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. UAV Image Acquisition and Preprocessing
2.3. Research Methods
2.3.1. Image Segmentation
2.3.2. Object Features
- Spectrum features (SPEC) include the average or standard deviation of the five bands (blue, green, red, red edge and near-infrared), the maximum difference, and overall brightness value, amounting to 12 in total.
- Index features (INDE) include RGR, VARI, SIPI, SR, TVI, NDGI, NDVI, NDWI, CIWI, MSWI, DVI, RVI, amounting to 12 in total (Table 1).
- Texture features (GLCM) include mean (GLCM_Mean_All), standard deviation (GLCM_SD_All), entropy GLCM_Ent_All), homogeneity (GLCM_Homo_All), contrast (GLCM_Con_All), dissimilarity (GLCM_Diss_All), angular second moment (GLCM_Ang_All) and correlation of Gray-level co-occurrence matrix (GLCM_Corre_All), amounting to 8 in total (Table 2).
- Geometric features (GEOM) include area, length/width, length, width, border length (Border_length), shape index (Shape_index), density, main direction (Main_direction), asymmetry, roundness, boundary index (Border_index), number of pixels (No_pix), compactness, volume, ellipse fitting, rectangle fitting (Rect_Fit), maximum ellipse radius (Rad_largest_ellipse), minimum ellipse radius (Rad_smallest_ellipse), amounting to 18 in total.
2.3.3. Sub-Feature Sets Construction for Different Schemes
2.3.4. Training and Verification Samples
2.3.5. Classifier
2.3.6. Accuracy Evaluation
3. Results
3.1. Image Segmentation in eCognition
3.2. RF Parameter Tuning
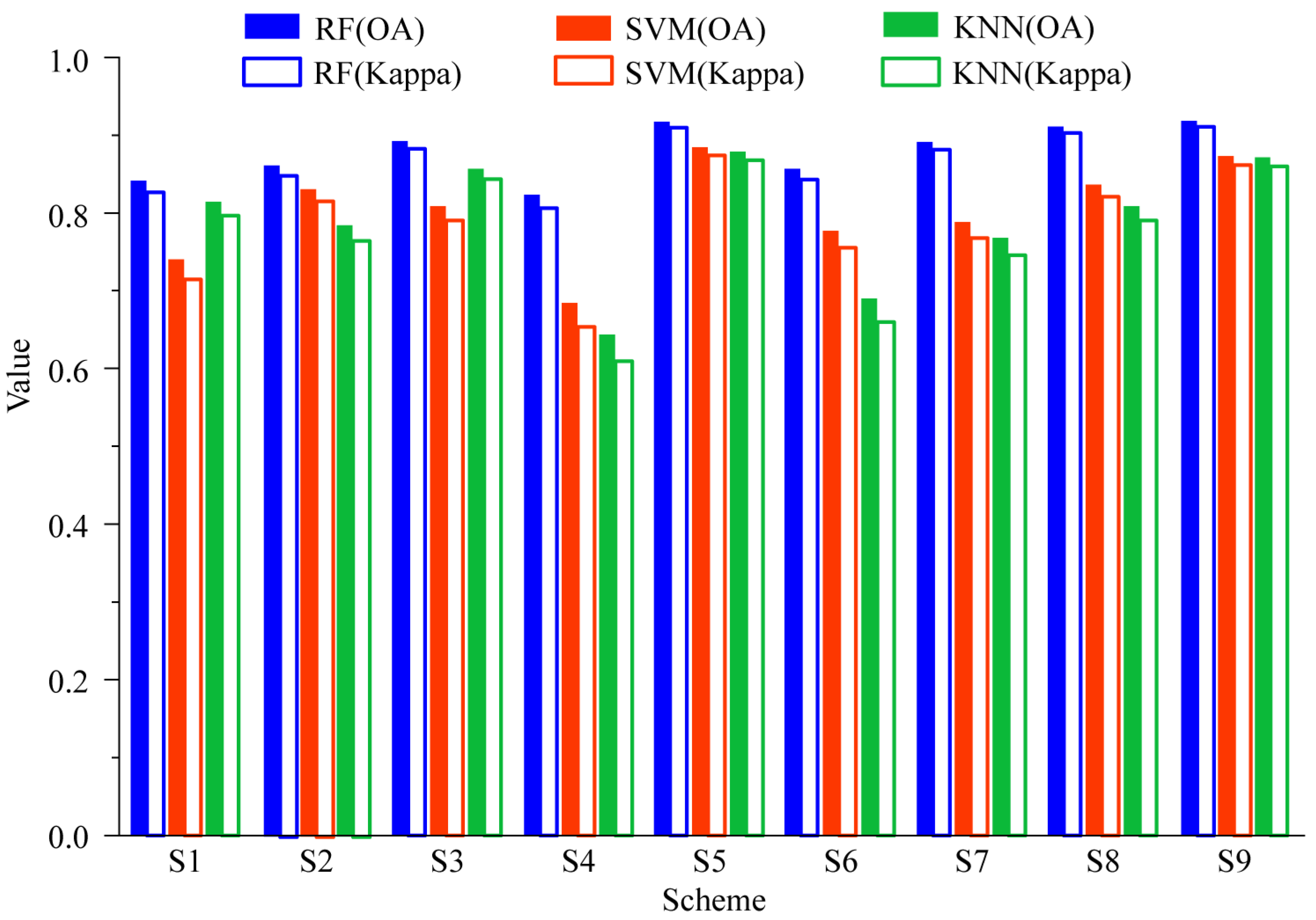
3.3. Accuracy Assessment
3.4. Feature Importance
3.5. Classification Map of the Study Area
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| UAV | unmanned aerial vehicle |
| ESP2 | estimation of scale parameter 2 |
| RFE | recursive feature elimination |
| RF | random forest |
| SVM | support vector machine |
| KNN | k-nearest neighbor |
| OA | overall accuracy |
| Kappa | kappa coefficient |
| SPEC | spectrum features |
| INDE | index features |
| GLCM | texture features |
| GEOM | geometric features |
| OOB | out-of-bag |
| ANN | artificial neural network |
References
- Cheng, X.; Nizamani, M.M.; Jim, C.; Qureshi, S.; Liu, S.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, S.; Balfour, K.; Wang, H. Response of urban tree DBH to fast urbanization: Case of coastal Zhanjiang in south China. Urban Ecosyst. 2022, 25, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, H.J.; Hutchins, M.G.; Miller, J.D. How robust is the evidence for beneficial hydrological effects of urban tree planting? Hydrol. Sci. J. 2021, 66, 1306–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pataki, D.E.; Alberti, M.; Cadenasso, M.L.; Felson, A.J.; McDonnell, M.J.; Pincetl, S.; Pouyat, R.V.; Setälä, H.; Whitlow, T.H. The Benefits and Limits of Urban Tree Planting for Environmental and Human Health. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 9, 603757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumnitz, S.; Devisscher, T.; Mayaud, J.R.; Radic, V.; Coops, N.C.; Griess, V.C. Mapping trees along urban street networks with deep learning and street-level imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2021, 175, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillero, N.; Arenas-Castro, S.; Enriquez Urzelai, U.; Vale, C.G.; Sousa-Guedes, D.; Martínez-Freiría, F.; Real, R.; Barbosa, A.M. Want to model a species niche? A step-by-step guideline on correlative ecological niche modelling. Ecol. Model. 2021, 456, 109671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Y.; Zhong, R.; Cao, S. Orbita hyperspectral satellite image for land cover classification using random forest classifier. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2021, 15, 014519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Wei, J.; Lin, Y.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Deng, H.; Yang, K. Extraction of Olive Crown Based on UAV Visible Images and the U2-Net Deep Learning Model. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pádua, L.; Vanko, J.; Hruška, J.; Adão, T.; Sousa, J.J.; Peres, E.; Morais, R. UAS, sensors, and data processing in agroforestry: A review towards practical applications. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 2349–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, P.; Mansor, S.; Farjad, B.; Ghaderpour, E. Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV)-based remote sensing for early-stage detection of Ganoderma. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langhammer, J. UAV monitoring of stream restorations. Hydrology 2019, 6, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martins, B.H.; Suzuki, M.; Yastika, P.E.; Shimizu, N. Ground surface deformation detection in complex landslide area—bobonaro, Timor-Leste—using SBAS DinSAR, UAV photogrammetry, and field observations. Geosciences 2020, 10, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Chang, S.; Sun, L.; An, L.; Chen, Y.; Xu, J. Classification of Street Tree Species Using UAV Tilt Photogrammetry. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, L.; Zhang, H.; Ge, Y.; Čepl, J.; Stejskal, J.; EL-Kassaby, Y.A. Closing the gap between phenotyping and genotyping: Review of advanced, image-based phenotyping technologies in forestry. Ann. Forest Sci. 2022, 79, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, C.M.; Adam, E. Machine Learning Classification of Endangered Tree Species in a Tropical Submontane Forest Using WorldView-2 Multispectral Satellite Imagery and Imbalanced Dataset. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyport, R.N.; Oommen, T.; Martha, T.R.; Sajinkumar, K.S.; Gierke, J.S. A comparative analysis of pixel- and object-based detection of landslides from very high-resolution images. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2018, 64, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myint, S.W.; Gober, P.; Brazel, A.; Grossman-Clarke, S.; Weng, Q. Per-pixel vs. object-based classification of urban land cover extraction using high spatial resolution imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1145–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collin, F.D.; Durif, G.; Raynal, L.; Lombaert, E.; Gautier, M.; Vitalis, R.; Marin, J.M.; Estoup, A. Extending approximate Bayesian computation with supervised machine learning to infer demographic history from genetic polymorphisms using DIYABC Random Forest. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2021, 21, 2598–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.; Wu, C.; Kao, J. Artificial intelligence in precision medicine in hepatology. J. Gastroen. Hepatol. 2021, 36, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georganos, S.; Grippa, T.; Niang Gadiaga, A.; Linard, C.; Lennert, M.; Vanhuysse, S.; Mboga, N.; Wolff, E.; Kalogirou, S. Geographical random forests: A spatial extension of the random forest algorithm to address spatial heterogeneity in remote sensing and population modelling. Geocarto Int. 2021, 36, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Granger, J.E.; Mahdianpari, M.; Puestow, T.; Warren, S.; Mohammadimanesh, F.; Salehi, B.; Brisco, B. Object-based random forest wetland mapping in Conne River, Newfoundland, Canada. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2021, 15, 38506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, C.; Yin, L.; Feng, X. Urban forest monitoring based on multiple features at the single tree scale by UAV. Urban For. Urban Green. 2021, 58, 126958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G. Application of NCIWI in water body information extraction of city. Sci. Surv. Mapp. 2016, 41, 44–49. [Google Scholar]
- Merzlyak, M.N.; Gitelson, A.A.; Chivkunova, O.B.; Rakitin, V.Y. Non-destructive optical detection of pigment changes during leaf senescence and fruit ripening. Physiol. Plant. 1999, 106, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baret, F.; Guyot, G. Potentials and limits of vegetation indices for LAI and APAR assessment. Remote Sens. Environ. 1991, 35, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstraete, M.M.; Pinty, B.; Myneni, R.B. Potential and limitations of information extraction on the terrestrial biosphere from satellite remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 1996, 58, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LI, X.; Li, H.; Chen, D.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Liu, C.; Hu, G. Multiple Classifiers Combination Method for Tree Species Identification Based on GF-5 and GF-6. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2020, 56, 93–104. [Google Scholar]
- Gamon, J.A.; Surfus, J.S. Assessing leaf pigment content and activity with a reflectometer. New Phytol. 1999, 143, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Person, R.S.; Kudina, L.P. Discharge frequency and discharge pattern of human motor units during voluntary contraction of muscle. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1972, 32, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, A.; Didan, K.; Miura, T.; Rodriguez, E.P.; Gao, X.; Ferreira, L.G. Overview of the radiometric and biophysical performance of the MODIS vegetation indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W. Winter Wheat Nitrogen Nutrition Diagnosis Based on the UAV Remote Sensing. Master’s Thesis, Henan Polytechnic University, Jiaozuo, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.; Huang, M.; Huang, W.; Liu, L.; Wang, J. Analysis of Winter Wheat Stripe Rust Characteristic Spectrum and Establishing of Inversion Models. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Anchorage, AK, USA, 20–24 September 2004; Volume 6, pp. 4318–4320. [Google Scholar]
- Gitelson, A.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Stark, R.; Rundquist, D. Novel algorithms for remote estimation of vegetation fraction. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 80, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rondeaux, G.; Steven, M.; Baret, F. Optimization of soil-adjusted vegetation indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 1996, 55, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Yang, C.; Li, E.; Cai, X.; Yang, J.; Xia, Y. Object-Based Wetland Vegetation Classification Using Multi-Feature Selection of Unoccupied Aerial Vehicle RGB Imagery. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, N.; Rashid, M.M.; Wibowo, S.; Xu, C.; Morshed, A.; Wasimi, S.A.; Moore, S.; Rahman, S.M. Early Weed Detection Using Image Processing and Machine Learning Techniques in an Australian Chilli Farm. Agriculture 2021, 11, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Qi, B.; Liu, H.; Guo, D.; Lu, L.; Fu, Q.; Shao, Y. Using Time Series Sentinel-1 Images for Object-Oriented Crop Classification in Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäyrä, J.; Keski-Saari, S.; Kivinen, S.; Tanhuanpää, T.; Hurskainen, P.; Kullberg, P.; Poikolainen, L.; Viinikka, A.; Tuominen, S.; Kumpula, T.; et al. Tree species classification from airborne hyperspectral and LiDAR data using 3D convolutional neural networks. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 256, 112322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Deng, H. Extraction of urban impervious surface based on the visible images of UAV and OBIA-RF algorithm. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2022, 38, 225–234. [Google Scholar]
- Garg, R.; Kumar, A.; Prateek, M.; Pandey, K.; Kumar, S. Land cover classification of spaceborne multifrequency SAR and optical multispectral data using machine learning. Adv. Space Res. 2022, 69, 1726–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukdar, S.; Singha, P.; Mahato, S.; Pal, S.; Liou, Y.A.; Rahman, A. Land-use land-cover classification by machine learning classifiers for satellite observations—A review. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, B.; Liu, M.; He, H.; Lan, F.; He, X.; Liu, L.; Huang, L.; Fan, D.; Zhao, M.; Jia, Z. Comparison of optimized object-based RF-DT algorithm and SegNet algorithm for classifying Karst wetland vegetation communities using ultra-high spatial resolution UAV data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2021, 104, 102553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Wu, X.; Wang, S. Object-oriented Vegetation Classification Method based on UAV and Satellite Image Fusion. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2020, 174, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sothe, C.; Dalponte, M.; Almeida, C.M.D.; Schimalski, M.B.; Lima, C.L.; Liesenberg, V.; Miyoshi, G.T.; Tommaselli, A.M.G. Tree species classification in a highly diverse subtropical forest integrating UAV-based photogrammetric point cloud and hyperspectral data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dobrinić, D.; Gašparović, M.; Medak, D. Sentinel-1 and 2 Time-Series for Vegetation Mapping Using Random Forest Classification: A Case Study of Northern Croatia. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahnejad, A.; Panagiotidis, D. Tree species classification and health status assessment for a mixed broadleaf-conifer forest with UAS multispectral imaging. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Index Features | Formula | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| CIWI | NDVI + RE | [22] |
| DVI | NIR − RE | [23] |
| NDVI | (NIR − R)/(NIR + R) | [24] |
| NDGI | (NIR − G)/(NIR + G) | [25] |
| NDWI | (G − NIR)/(G + NIR) | [26] |
| RGR | R/G | [27] |
| SR | NIR/RE | [28] |
| SIPI | (NIR − B)/(NIR + B) | [29] |
| VIopt | 1.45 × (NIR × NIR + 1)/(RE + 0.45) | [30] |
| TVI | 60 × (NIR − G)/100 × (NIR + G) | [31] |
| VARI | (G − R)/(G + R) | [32] |
| GOSAVI | (1 + 0.16) × (NIR − G)/(NIR + G + 0.16) | [33] |
| Feature Type | Formula | Parametric Descriptions |
|---|---|---|
| Mean | Degree of texture regularity | |
| Standard deviation | Deviation between pixel gray value and mean | |
| Entropy | Measures the degree of the disorder among pixels in the image | |
| Homogeneity | Texture uniformity | |
| Contrast | Measures the contrast based on the local gray level variation | |
| Dissimilarity | Texture contrast | |
| Angular second moment | Measures the uniformity or energy of the gray level distribution of the image | |
| Correlation | Measures the linear dependency of gray levels of neighboring pixels |
| ID of Schemes | Feature Subsets | SPEC | GLCM | INDE | GEOM | Total Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | SPEC | 12 | 12 | |||
| S2 | SPEC + GLCM | 12 | 8 | 20 | ||
| S3 | SPEC + INDE | 12 | 12 | 24 | ||
| S4 | SPEC + GEOM | 12 | 18 | 30 | ||
| S5 | SPEC + GLCM + INDE | 12 | 8 | 12 | 32 | |
| S6 | SPEC + GLCM + GEOM | 12 | 8 | 18 | 38 | |
| S7 | SPEC + INDE + GEOM | 12 | 12 | 18 | 42 | |
| S8 | All | 12 | 8 | 12 | 18 | 50 |
| S9 | All_RFE | 12 | 6 | 12 | 30 |
| Category | Total Samples | Training Samples | Validation Samples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alstonia scholaris | 90 | 54 | 36 |
| Banyan | 150 | 90 | 60 |
| Camphor | 80 | 48 | 32 |
| Eucalyptus | 110 | 60 | 40 |
| Willow | 90 | 54 | 36 |
| Cinnamomum japonicum | 90 | 54 | 36 |
| Palmae plants | 80 | 48 | 32 |
| Shrub | 140 | 84 | 56 |
| Lawn | 160 | 96 | 64 |
| Building | 150 | 90 | 60 |
| Road | 150 | 90 | 50 |
| Water | 60 | 36 | 24 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Q.; Zhang, J.; Guo, S.; Ye, Z.; Deng, H.; Hou, X.; Zhang, H. Urban Tree Classification Based on Object-Oriented Approach and Random Forest Algorithm Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) Multispectral Imagery. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3885. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14163885
Guo Q, Zhang J, Guo S, Ye Z, Deng H, Hou X, Zhang H. Urban Tree Classification Based on Object-Oriented Approach and Random Forest Algorithm Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) Multispectral Imagery. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(16):3885. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14163885
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Qian, Jian Zhang, Shijie Guo, Zhangxi Ye, Hui Deng, Xiaolong Hou, and Houxi Zhang. 2022. "Urban Tree Classification Based on Object-Oriented Approach and Random Forest Algorithm Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) Multispectral Imagery" Remote Sensing 14, no. 16: 3885. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14163885
APA StyleGuo, Q., Zhang, J., Guo, S., Ye, Z., Deng, H., Hou, X., & Zhang, H. (2022). Urban Tree Classification Based on Object-Oriented Approach and Random Forest Algorithm Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) Multispectral Imagery. Remote Sensing, 14(16), 3885. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14163885







