Optical Turbulence Characteristics in the Upper Troposphere–Lower Stratosphere over the Lhasa within the Asian Summer Monsoon Anticyclone
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Sounding Data
2.2. Integrated Parameters
3. Results
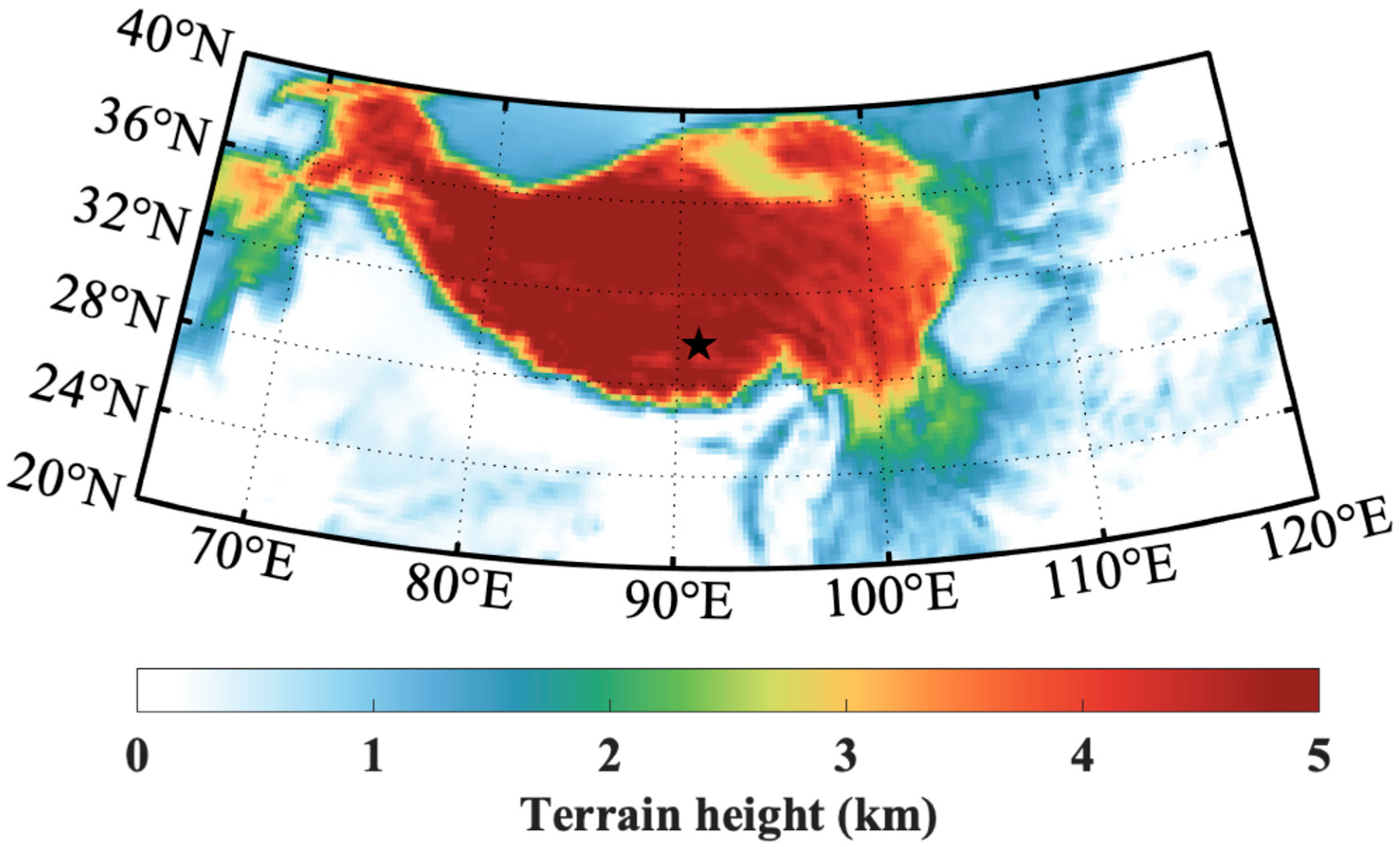
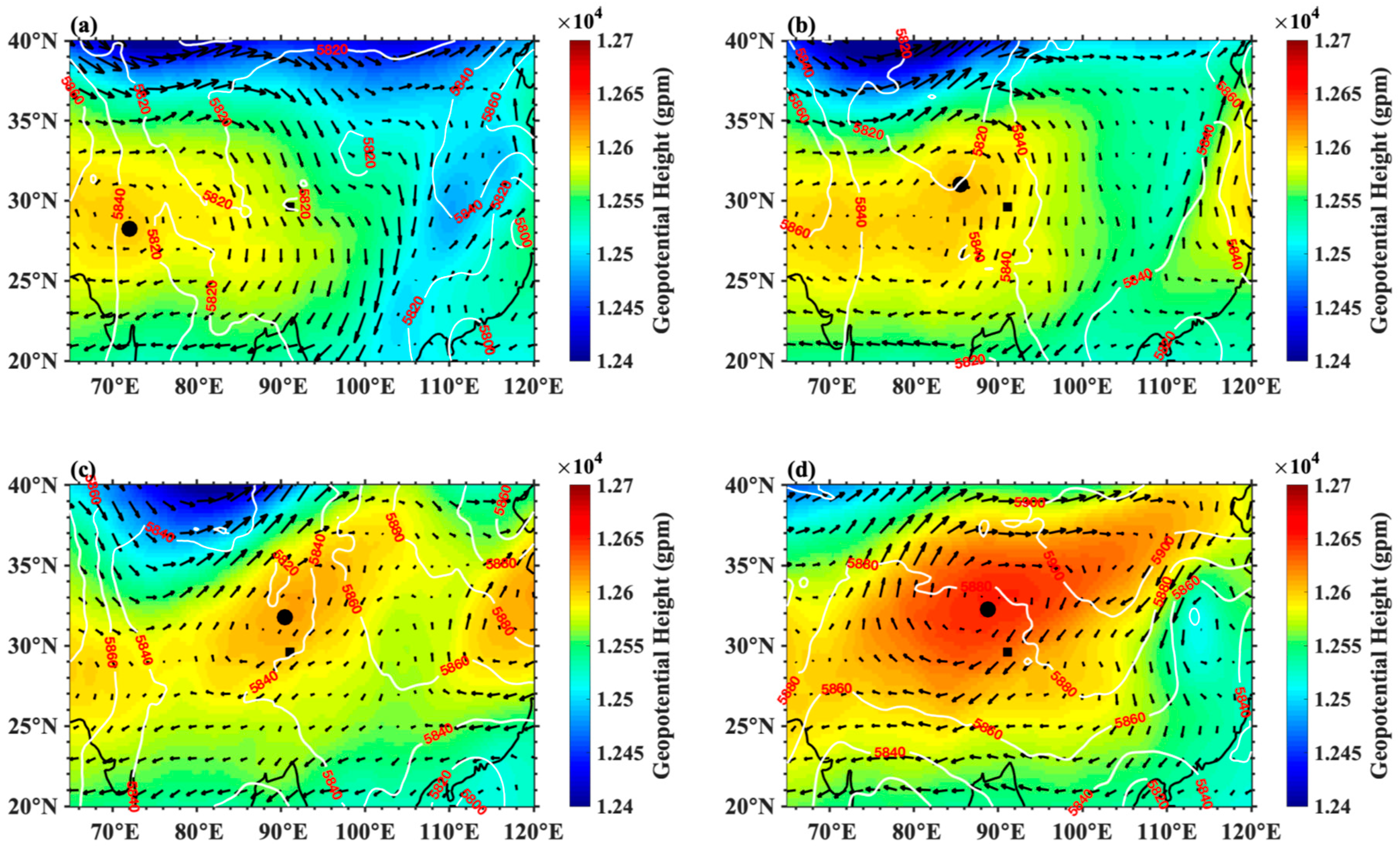
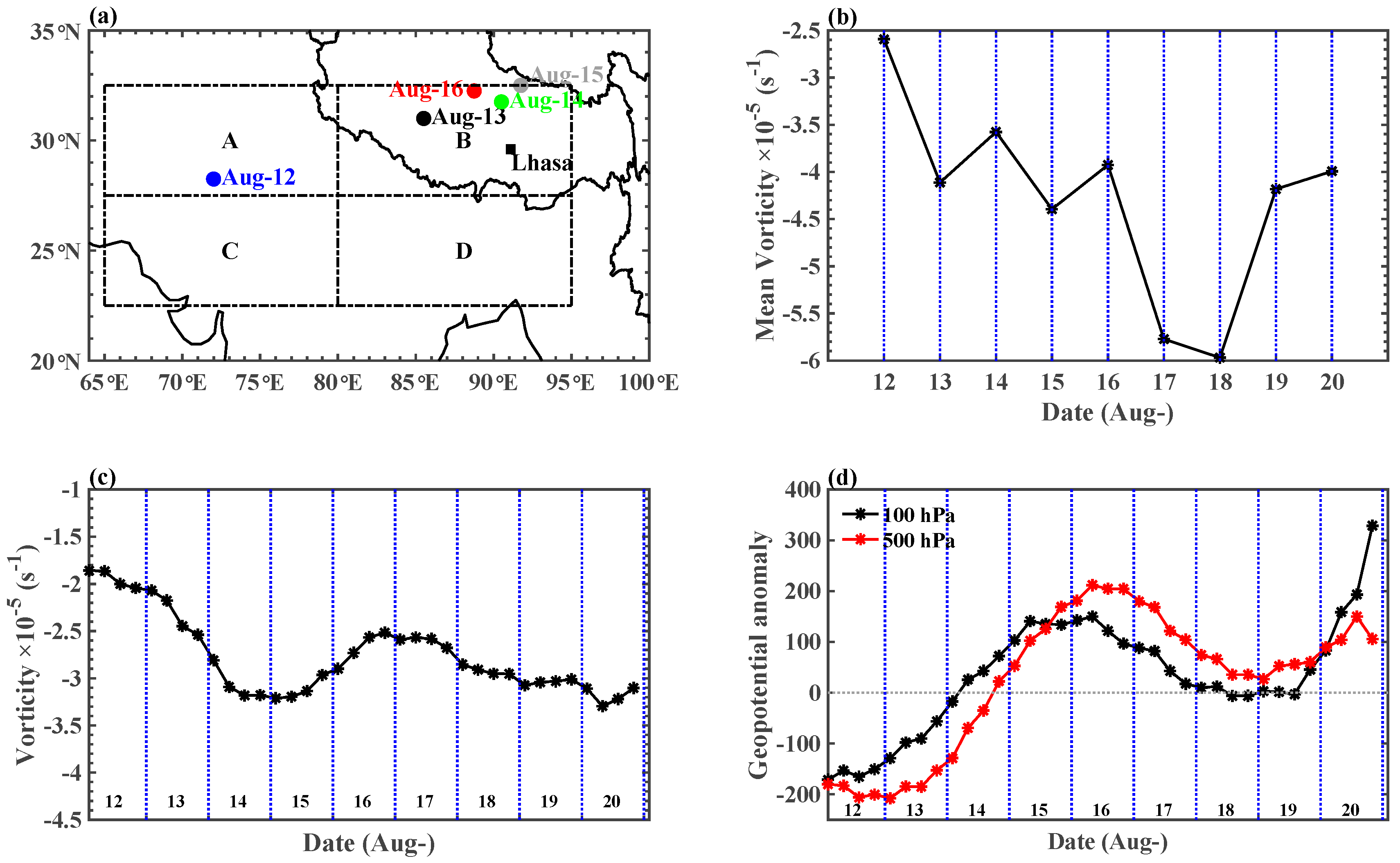
3.1. ASMA Activities during the Experimental Period
3.2. Characteristics of under Different ASMA Strength States
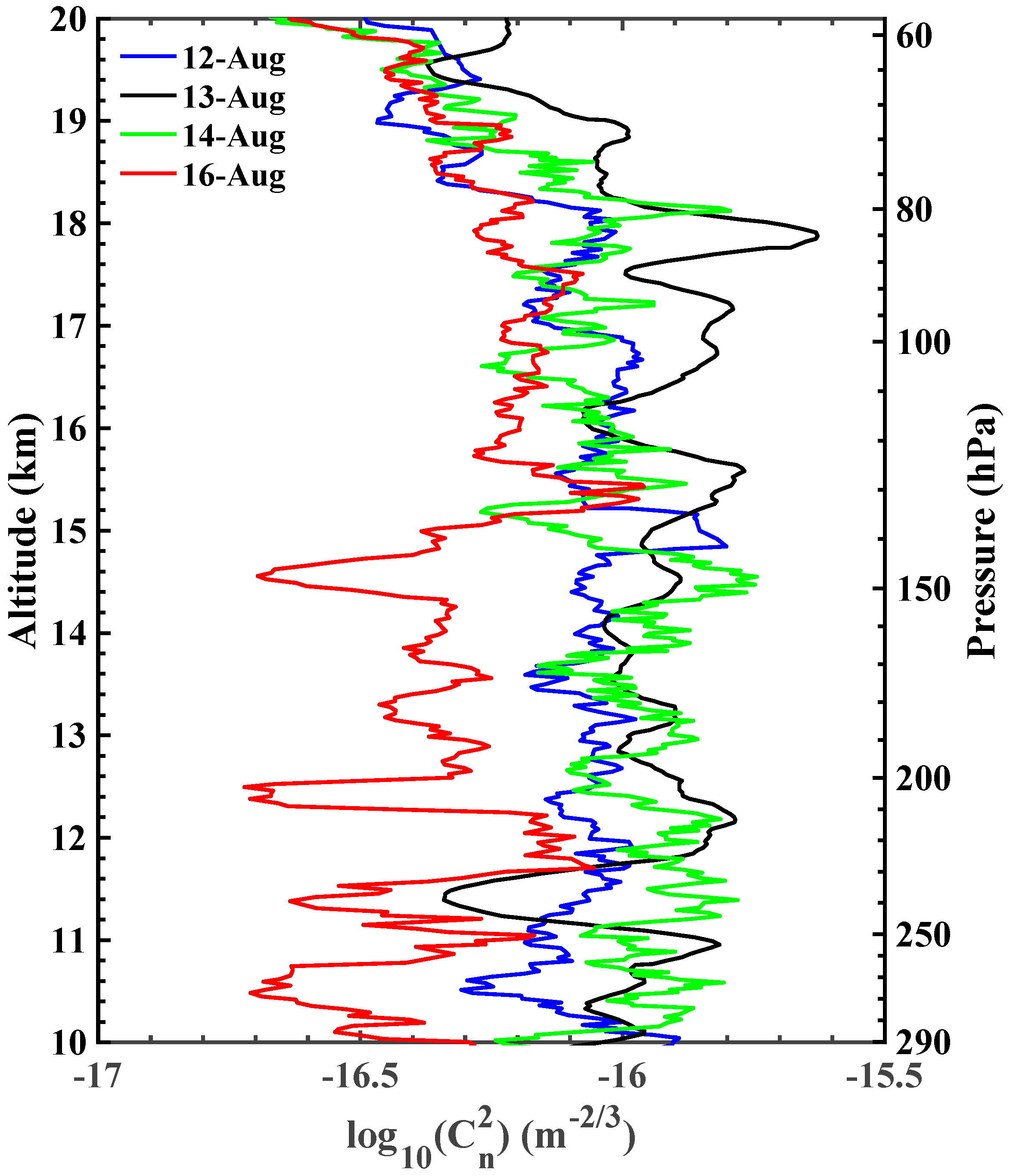
3.3. Contribution of Atmospheric Turbulence in UTLS to the Total Integrated Parameters
4. Discussion
4.1. Potential Temperature Gradient
4.2. Discussion on the Temperature Structure in UTLS
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lv, Y.; Guo, J.; Li, J.; Cao, L.; Chen, T.; Wang, D.; Chen, D.; Han, Y.; Guo, X.; Xu, H.; et al. Spatiotemporal characteristics of atmospheric turbulence over China estimated using operational high-resolution soundings. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 054050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Ma, Y.; Ma, W.; Hu, Z.; Ishikawa, H.; Zhongbo, S.; Sun, F. Analysis of turbulence characteristics over the northern Tibetan Plateau area. Adv. Atm. Sci. 2006, 23, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Highwood, E.J.; Hoskins, B.J. The tropical tropopause. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 124, 1579–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoskins, B.J.; Rodwell, M.J. A model of the Asian Summer Monsoon: 1. The global-scale. J. Atmos. Sci. 1995, 52, 1329–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randel, W.J.; Park, M. Deep convective influence on the Asian summer monsoon anticyclone and associated tracer variability observed with Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS). J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111, D12314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhou, L.; Wang, G. The Observed Impact of the South Asian Summer Monsoon on Land-Atmosphere Heat Transfers and Its Inhomogeneity over the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, C.; Yang, N.; Li, Y. Diurnal and seasonal variations of surface energy and CO2 fluxes over a site in Western Tibetan Plateau. Atmos 2020, 11, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; He, B.; Liu, Y.; Bao, Q.; Ren, R. Location and variation of the summertime upper-troposphere temperature maximum over South Asia. Clim. Dyn. 2015, 45, 2757–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, J.; Li, D.; Bai, Z.; Li, Q.; Lyu, D.; Zhou, X. Transport of Asian surface pollutants to the global stratosphere from the Tibetan Plateau region during the Asian summer monsoon. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 7, 516–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Chen, Q. Variation of Atmospheric Composition in UTLS during a Strong Convection Process in Tibetan Plateau. Meteorol. Sci. Technol. 2017, 45, 1083–1089. [Google Scholar]
- Tomsche, L.; Pozzer, A.; Ojha, N.; Parchatka, U.; Lelieveld, J.; Fischer, H. Upper tropospheric CH4 and CO affected by the South Asian summer monsoon during the Oxidation Mechanism Observations mission. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 1915–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, J.W.; Jensen, E.J.; Pfister, L.; Yang, Q. Seasonal differences of vertical-transport efficiency in the tropical tropopause layer: On the interplay between tropical deep convection, large-scale vertical ascent, and horizontal circulationes. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, D05302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadnavis, S.; Semeniuk, K.; Pozzoli, L.; Schultz, M.G.; Ghude, S.D.; Das, S.; Kakatkar, R. Transport of aerosols into the UTLS and their impact on the Asian monsoon region as seen in a global model simulation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 8771–8786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Bian, J.; Lv, D. Advances and Prospects in the Study of Stratosphere-Troposphere Exchange. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2006, 30, 813–820. [Google Scholar]
- Ploeger, F.; Gottschling, C.; Griessbach, S.; Grooss, J.U.; Guenther, G.; Konopka, P.; Mueller, R.; Riese, M.; Stroh, F.; Tao, M.; et al. A potential vorticity-based determination of the transport barrier in the Asian summer monsoon anticyclone. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 13145–13159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterley, T.; Wilson, R.W.; Sarazin, M. Determination of the profile of atmospheric optical turbulence strength from SLODAR data. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2006, 369, 835–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hach, Y.; Jabiri, A.; Ziad, A.; Bounhir, A.; Sabil, M.; Abahamid, A.; Benkhaldoun, Z. Meteorological profiles and optical turbulence in the free atmosphere with NCEP/NCAR data at Oukaimeden—I. Meteorological parameters analysis and tropospheric wind regimes. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 420, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masciadri, E.; Jabouille, P. Improvements in the optical turbulence parameterization for 3D simulations in a region around a telescope. Astron. Astrophys. 2001, 376, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhao, T.; Sun, J.; Yao, W.; Zhou, M. Structures of convection and turbulent kinetic energy in boundary layer over the southeastern edge of the Tibetan Plateau. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2015, 58, 1198–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Koike, T.; Fujii, H.; Tamura, T.; Xu, X.D.; Bian, L.G.; Zhou, M.Y. The daytime evolution of the atmospheric boundary layer and convection over the Tibetan Plateau: Observations and simulations. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn 2004, 82, 1777–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.L.; Ma, Y.M.; Kelder, H.; Su, Z.; Yang, K. On the behaviour of the tropopause folding events over the Tibetan Plateau. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 5113–5122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadnavis, S.; Kalita, G.; Kumar, K.R.; Gasparini, B.; Li, J.-L.F. Potential impact of carbonaceous aerosol on the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere (UTLS) and precipitation during Asian summer monsoon in a global model simulation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 11637–11654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Liao, H.; Xu, J.; Zhou, G. The chemical effects on the summertime ozone in the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere over the Tibetan Plateau and the South Asian monsoon region. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2019, 131, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randel, W.J.; Park, M.; Emmons, L.; Kinnison, D.; Bernath, P.; Walker, K.A.; Boone, C.; Pumphrey, H. Asian monsoon transport of pollution to the stratosphere. Science 2010, 328, 611–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovadlo, P.G.; Shikhovtsev, A.Y.; Kopylov, E.A.; Kiselev, A.V.; Russkikh, I.V. Study of the Optical Atmospheric Distortions using Wavefront Sensor Data. RuPhJ 2021, 63, 1952–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, H.W.; Osborn, J.; Wilson, R.W.; Butterley, T.; Avila, R.; Dhillon, V.S.; Morris, T.J. Stereo-SCIDAR: Optical turbulence profiling with high sensitivity using a modified SCIDAR instrument. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 437, 3568–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummel, J.R.; Hazen, D.A.; Beland, R.R. Modeling optical turbulence parameters with high resolution radiosonde data. In Proceedings of the Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics, Baltimore, Maryland, 24 April 1989; p. THK46. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Huang, H.; Qian, X.; Wang, P.; Cui, C. Thermosonde meaurement of temperature structure parameter and temperature spectral power-law exponent profile in the lower stratosphere. Acta Opt. Sin. 2014, 34, 0501001. [Google Scholar]
- Xiaoqing, W.; Xianmei, Q.; Honghua, H.; Ping, W.; Chaolong, C.; Chun, Q. Measurment of seeing, isoplanatic angle, and coherence time by using balloon-borne microthermal probes at Gaomeigu. Acta Astron. Sin. 2014, 55, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, C.; Wu, X.; Li, X.; Luo, T.; Su, C.; Zhu, W. Mesoscale optical turbulence simulations above Tibetan Plateau: First attempt. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 4571–4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatarski, V.I. Wave Propagation in a Turbulent Medium; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Jing, X.; Jia, W.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, S. Ergodicity of turbulence measurements upon complex terrain in Loess Plateau. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2021, 64, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Sun, Z.; Chen, H.; Zhu, W.; Zeng, G.; Ni, D. Analysis on the Multi-center Structure of Summer South Asia High and Its Thermal Influence Factors. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2016, 40, 1089–1106. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Wu, G.X.; Qian, Y.F. The bimodality of the 100 hPa South Asia High and its relationship to the climate anomaly over East Asia in summer. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2002, 80, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.-S.; Kim, B.-J.; Zhang, R.; Nam, J.-C.; Park, K.-J.; Kim, J.-Y.; Kim, D.-W. Possible influence of South Asian high on summer rainfall variability in Korea. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 46, 833–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Zhang, R.; Wen, M.; Kim, B.-J.; Nam, J.-C. Interannual Variation of the South Asian High and Its Relation with Indian and East Asian Summer Monsoon Rainfall. J. Clim. 2015, 28, 2623–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, T. The characteristics of the atmospheric heating and the atmospheric circulation in southeast Asia during the active periods of 500hPa high pressure over the Qinghai-Xizang plateau in summer. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 1994, 52, 194–200. [Google Scholar]
- Garny, H.; Randel, W.J. Dynamic variability of the Asian monsoon anticyclone observed in potential vorticity and correlations with tracer distributions. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 13421–13433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougeault, P.; Lacarrere, P. Parameterization of orography-induced turbulence in a mesobeta-scale model. Mon. Weather Rev. 1989, 117, 1872–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yao, Y.; Liu, L. A review of atmoshperic optical turbulence modeling research. Prog. Astron. 2012, 30, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wu, X.; Su, C.; Yang, Q.; Xu, J.; Luo, T.; Huang, C.; Qing, C. Reliable model to estimate the profile of the refractive index structure parameter (Cn2) and integrated astroclimatic parameters in the atmosphere. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 12454–12470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alappattu, D.P.; Kunhikrishnan, P.K. First observations of turbulence parameters in the troposphere over the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea using radiosonde. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Fu, Y.; Xiao, Q. Is the tropopause higher over the Tibetan Plateau? Observational evidence from Constellation Observing System for Meteorology, Ionosphere, and Climate (COSMIC) data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, D21121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhou, S. Review of researches on tropopause in recent 30 years. Meteorol. Sci. Technol. 2010, 38, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandil, H.A.; Abdelkader, M.M.; Moaty, A.A.; Elhadidi, B.; Sherif, A.O. Simulation of atmospheric temperature inversion over greater CAIRO using the MMS MESO-SCALE atmospheric model. Egypt J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2006, 9, 15–30. [Google Scholar]
- Liou, Y.A.; Yan, S.K. Two-year Microwave Radiometric Observations of Low-level Boundary-layer Temperature Inversion Signatures. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Geoscience & Remote Sensing Symposium, Denver, CO, USA, 31 July 2006–4 August 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Gettelman, A.; Forster, P.M.D. A climatology of the tropical tropopause layer. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2002, 80, 911–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, T.; Wickert, J.; Beyerle, G.; Reigber, C. Tropical tropopause parameters derived from GPS radio occultation measurements with CHAMP. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109, D13105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, H.; Wienhold, F.G.; Hoor, P.; Bujok, O.; Schiller, C.; Siegmund, P.; Ambaum, M.; Scheeren, H.A.; Lelieveld, J. Tracer correlations in the northern high latitude lowermost stratosphere: Influence of cross-tropopause mass exchange. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000, 27, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoor, P.; Fischer, H.; Lange, L.; Lelieveld, J.; Brunner, D. Seasonal variations of a mixing layer in the lowermost stratosphere as identified by the CO-O3 correlation from in situ measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, ACL1-1–ACL1-11. [Google Scholar]
- Zahn, A.; Brenninkmeijer, C.A.M.; Maiss, M.; Scharffe, D.H.; Crutzen, P.J.; Hermann, M.; Heintzenberg, J.; Wiedensohler, A.; Gusten, H.; Heinrich, G.; et al. Identification of extratropical two-way troposphere-stratosphere mixing based on CARIBIC measurements of O-3, CO, and ultrafine particles. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2000, 105, 1527–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessler, A.E.; Palm, S.P.; Spinhirne, J.D. Tropical cloud-top height distributions revealed by the Ice, Cloud, and Land Elevation Satellite (ICESat)/Geoscience Laser Altimeter System (GLAS). J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111, D12215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Jin, S. Effect of gravity waves on the tropopause temperature, height and water vapor in Tibet from COSMIC GPS Radio Occultation observations. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 2016, 138, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
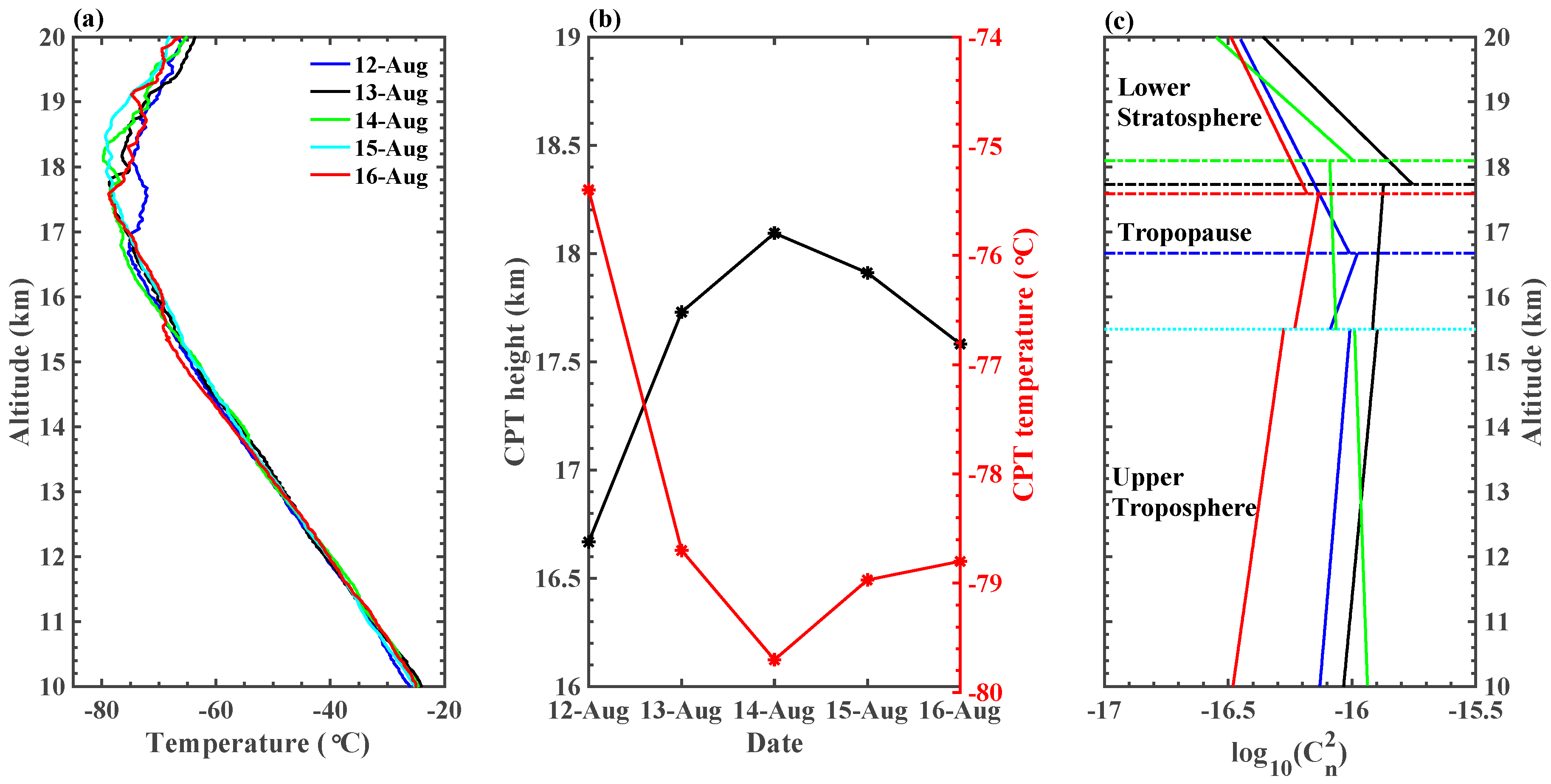
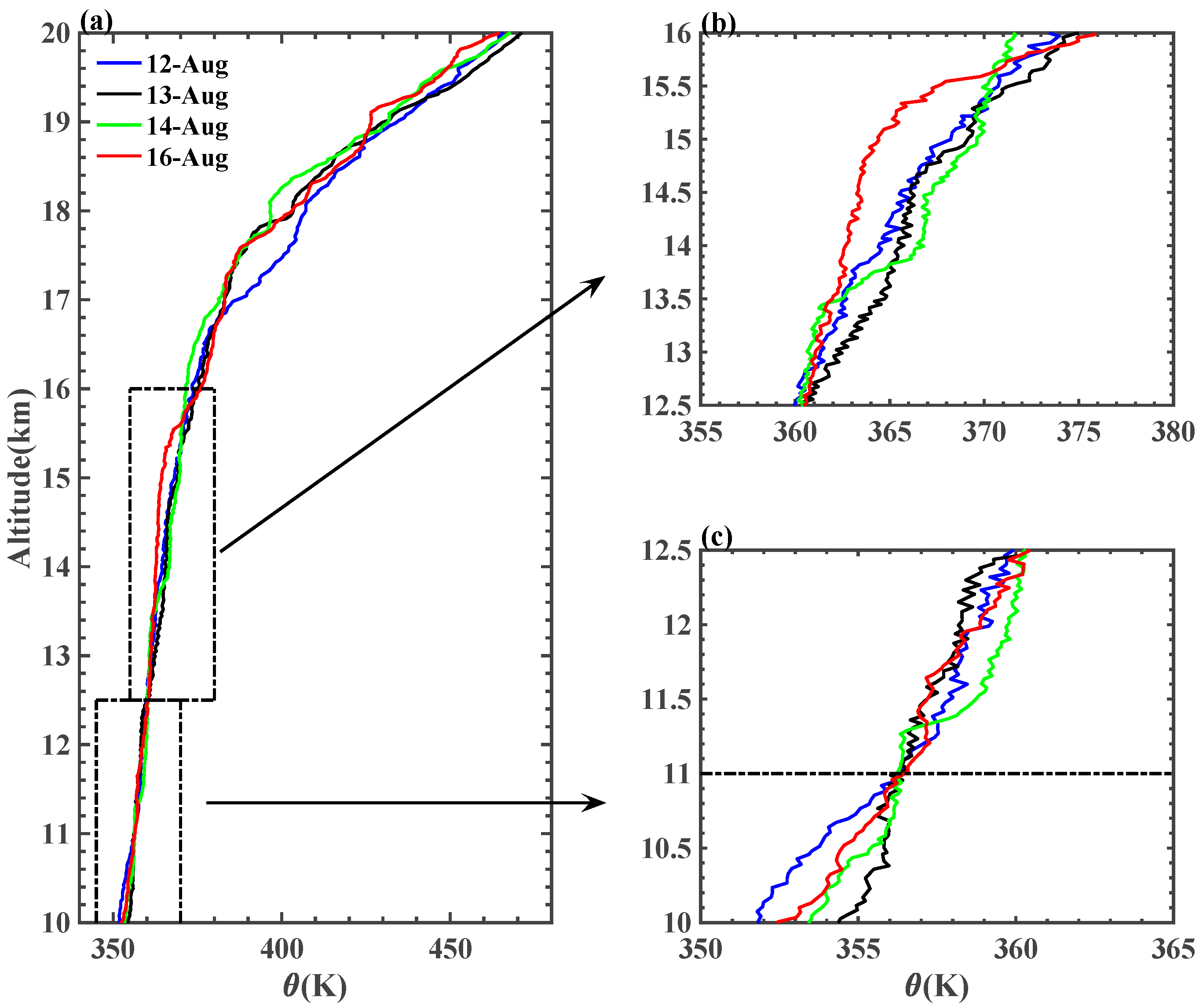
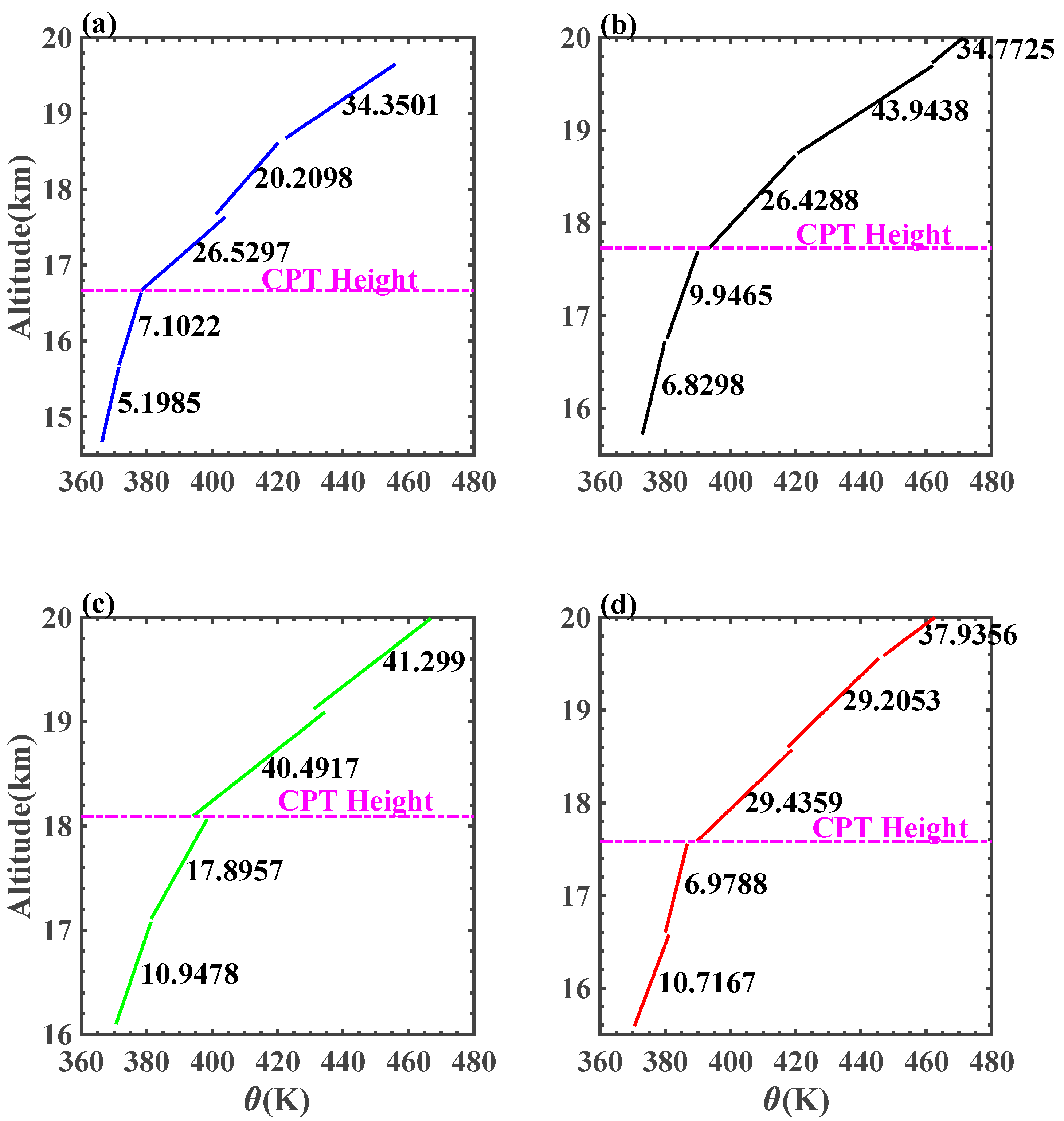
| Radiosonde Number | Release Time (LT) | Release Altitude (m ASL) | Termination Altitude (m ASL) | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 12 August 2018 19:24:36 | 3653.6 | 21,810.0 | Cloudy |
| 2 | 13 August 2018 19:28:03 | 3654.1 | 23,221.1 | Cloudy |
| 3 | 14 August 2018 19:40:46 | 3652.8 | 30,658.8 | Cloudy |
| 4 | 15 August 2018 19:04:16 | 3658.2 | 29,956.9 | Storm; micro-thermal sensors was destroyed |
| 5 | 16 August 2018 19:20:15 | 3652.2 | 31,206.0 | Cloudy |
| 12 August 2018 | 13 August 2018 | 14 August 2018 | 16 August 2018 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (″) | 1.08 | 1.32 | 1.19 | 0.82 | |
| 1.30 | 1.63 | 1.60 | 1.11 | ||
| 73.73% | 70.21% | 61.09% | 59.76% | ||
| (″) | 0.44 | 0.35 | 0.41 | 0.56 | |
| 0.40 | 0.30 | 0.35 | 0.45 | ||
| 85.58% | 78.82% | 77.84% | 69.65% | ||
| 12 August 2018 | 13 August 2018 | 14 August 2018 | 16 August 2018 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upper troposphere (10–15.5 km) | 0.02 | 0.02 | −0.01 | 0.04 |
| Tropopause (15.5 km—CPT) | 0.09 | 0.02 | −0.01 | 0.05 |
| Lower stratosphere (CPT—20 km) | −0.13 | −0.27 | −0.29 | −0.13 |
| 12 August 2018 | 13 August 2018 | 14 August 2018 | 16 August 2018 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10–11 km | 4.84 | 1.48 | 3.29 | 3.48 |
| 11–12.5 km | 2.19 | 2.03 | 2.96 | 2.6 |
| 12.5–16 km | 3.79 | 3.65 | 3.73 | 3.24 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, K.; Wang, F.; Weng, N.; Wu, X.; Li, X.; Luo, T. Optical Turbulence Characteristics in the Upper Troposphere–Lower Stratosphere over the Lhasa within the Asian Summer Monsoon Anticyclone. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4104. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14164104
Zhang K, Wang F, Weng N, Wu X, Li X, Luo T. Optical Turbulence Characteristics in the Upper Troposphere–Lower Stratosphere over the Lhasa within the Asian Summer Monsoon Anticyclone. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(16):4104. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14164104
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Kun, Feifei Wang, Ningquan Weng, Xiaoqing Wu, Xuebin Li, and Tao Luo. 2022. "Optical Turbulence Characteristics in the Upper Troposphere–Lower Stratosphere over the Lhasa within the Asian Summer Monsoon Anticyclone" Remote Sensing 14, no. 16: 4104. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14164104
APA StyleZhang, K., Wang, F., Weng, N., Wu, X., Li, X., & Luo, T. (2022). Optical Turbulence Characteristics in the Upper Troposphere–Lower Stratosphere over the Lhasa within the Asian Summer Monsoon Anticyclone. Remote Sensing, 14(16), 4104. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14164104







