Abstract
The time-varying biases within carrier phase observations are integrated into satellite clock offset parameters for precise clock estimation. Consequently, when the precise satellite clock bias is applied to the third frequency observation for precise point positioning (PPP), a new type of inter-frequency clock bias (IFCB) with satellite dependence should be noticed. If the IFCB is estimated together with the receiver coordinates, tropospheric wet delay, ambiguity and other parameters, it will increase the computational burden and lead to more time consumption. In order to solve this problem, the IFCB of GPS Block IIF satellites were estimated using 162 global uniformly distributed Multi-GNSS Experiment (MGEX) stations. By analyzing the time-varying characteristic of each satellite IFCB and combining the lag characteristics of the final ephemeris products, a modeling method of short-term IFCB prediction based on the epoch-by-epoch sliding Pearson autocorrelation function is proposed. The feasibility of this method was verified through the Student’s t-distribution, comparison with the measured IFCB, the posteriori residual of the third frequency carrier phase and the kinematic/static PPP solutions. The results showed that since the IFCB period was not a complete 24 h, the difference in the IFCBs time series on different days was increasingly significant with the passage of lag time, and the correlation constantly decreased. The peak-to-peak amplitudes of the IFCB difference reached 1.13, 3.44, 6.86 and 11.25 cm when the lag time was 1, 9, 19 and 29 days, respectively. In addition, based on the lag characteristic of final precise ephemerides released by the International GNSS Service (IGS) analysis centers, the prediction accuracy of the IFCB was evaluated with a time lag of 7 days. The root mean square of the posteriori residuals at the third-frequency observation decreased by approximately 51.3% compared to that without considering for IFCB correction. The triple-frequency uncombined PPP in the horizontal and vertical directions improved by approximately 33.2% and 17.2% for the static PPP solutions and 50.2% and 39.7% for the kinematic PPP solutions, respectively. In general, the accuracy and convergence time of the triple-frequency uncombined PPP were equivalently improved when the predicted IFCB and the measured IFCB were used.
1. Introduction
With the continuous development of the global navigation satellite system (GNSS), the GPS Block IIF, BDS-2/BDS-3, Galileo, GLONASS-K and Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS) satellites have begun to provide signals on three or more frequencies [1,2,3,4]. This joint positioning of multi-frequency observations opens new prospects for precise point positioning (PPP) [5] in the analysis of ionospheric refraction effects [6], reflectometry of precipitable water vapor [7], integrity monitoring [8], cycle slip detection and repair [9] and, especially, for fast ambiguity resolution in relative positioning [10] and absolute positioning [11,12].
Although multi-frequency joint positioning can bring great advantages, there is still a thorny problem to be solved in the multi-frequency fusion PPP solution. This is due to the fact that the current GNSS satellite clock products are generated based on specific measurements, such as L1/L2 ionospheric-free (IF) combined observations for GPS, resulting in IF time-varying phase hardware delays in parts of the satellite terminal that are contained in satellite clock products. When this type of clock product is applied to the third-frequency observations or more for PPP, the posterior residues on the corresponding frequency show large fluctuations, namely, inconsistency between the first two frequencies (i.e., L1/L2) and the third-frequency or more observations. That is, an additional bias on the third-, quad-, or more frequency observations need to be processed, which is called the inter-frequency clock bias (IFCB) [13,14]. Montenbruck et al. found that the changing characteristics of the GPS IFCB time series were related to the relative position of the satellite–Earth–Sun by analyzing the law of period changes of the GPS IFCB, and the peak amplitudes reached over a dozen centimeters [13,15]. As for BeiDou-2, small bias variations were also recognized, but they were generally confined to peak amplitudes of approximately 2 cm. In contrast, the QZSS, BDS-3, and Galileo were shown to exhibit good consistency with different frequency carriers [16,17,18,19].
In the process of multi-frequency PPP resolution, in order to reduce the computational burden and avoid the problem of the overestimation of the parameter to be examined, three methods are traditionally used for GPS IFCB. The first is parametric estimation on the service side and correction directly in the observation model on the user side [20,21]. The second is to provide satellite clock products that include a third frequency (L5) [22]. The third is to reduce the weight of third-frequency observations without IFCB correction, and this method can be applied to satellites with small IFCB amplitudes such as the BeiDou system [23]. Considering that the difficulty in satellite clock product estimations and the advantages of multi-frequency observation data, more choices accompany the first processing strategy for IFCB. Montenbruck et al. proposed a method for combining the differences of two different IF combination observations and then estimating the difference epoch by epoch for the above differences [13]. The advantage of this method is that the ambiguity term can be eliminated under no cycle slip, and the common datum bias of each epoch IFCB will be absorbed into the ambiguity parameter. Li et al. proposed an efficient method derived from the epoch-differenced strategy for fast estimation of IFCBs for Block IIF satellites, and this method can eliminate the receiver terminal clock bias and significantly improves the computational efficiency [20,21]. Li et al. proposed a method of estimating the IFCB constant parts and the time-varying parts separately in view of the constant parts of the IFCB having a certain stability in the short term, and the constant part was estimated by three-frequency pseudo-range observations and the time-varying part by three-frequency phase observations. In reality, whichever method is used for IFCB estimation, a large number of global uniformly distributed GNSS continuous tracking stations are required, which is particularly detrimental to multi-frequency real-time PPP and PPP network solutions [24].
Therefore, the main way to handle IFCB is to build forecast models and make direct corrections on the user side. Forecast models of IFCB can be divided into two types. The first one is to study the IFCB time-varying characteristics using the harmonic analysis method and to establish the linear plus periodic model based on the fitting coefficient to implement the IFCB prediction. This approach requires the analysis of the IFCB using long time series. Gong et al. established long-term GPS and BDS IFCB empirical correction models using long-term GNSS observations, and a fourth-order Fourier coefficient fitting model that considered both linearity and periodicity was proposed for IFCB sequences [25]. Zhang and Pan established two function models composed of a linear term and a harmonic term with seven orders for MEO satellites and six orders for GEO and IGSO satellites to describe the IFCB variations based on 195 ground tracking stations for a whole year [26]. Another way to establish an IFCB forecast model is to calculate the IFCB correlation for two different time segments and then to extract the IFCB cycle’s characteristics and establish the IFCB forecast model based on the correlation coefficient. Pan et al. studied the time-varying characteristic of IFCB based on the correlation analysis using datasets from 129 globally distributed Multi-GNSS Experiment (MGEX) stations [14]. For the purpose of forecasting IFCB, the IFCB of the previous day was directly input into the next day in consideration of the periodic changes in the IFCB sequence. The validation results show that all of the prediction models could significantly improve the triple-frequency PPP accuracy. Unfortunately, except for the above IFCB forecasting methods, only a few more effective methods can be used, especially for the establishment of short-term prediction models.
Considering the time-varying characteristic of the IFCB and the lag characteristics of the final precision orbit and clock products released by the International GNSS Service (IGS) analysis centers, the epoch-by-epoch sliding Pearson autocorrelation function was used to extract the IFCB periodic features. Based on these, a high-precision IFCB short-term prediction model was established for the GPS Block IIF satellites to handle the problem of overestimation of the parameter to be estimated in multi-frequency PPP. We started with the triple-frequency uncombined PPP model that takes the IFCB into account. Subsequently, the estimation approach of the IFCB was introduced, and some important features were highlighted. Afterward, a short-term forecast model was constructed on the basis of analyzing the time-varying characteristics of the IFCB. Finally, a variety of evaluation methods were used to verify the feasibility of forecasting the IFCB, and the main points and the conclusions are summarized.
2. Methods
Taking GPS as an example, we first describe the triple-frequency uncombined PPP models in detail. Subsequently, an IFCB estimation method using three-frequency observations is successively developed.
2.1. Trible-Frequency Uncombined PPP
The basic model for the original multi-frequency GPS carrier phase and pseudo-range observations from receiver to satellite in units of length is [27]:
To facilitate the derivation of subsequent formulas, the following expressions are defined:
where superscript denotes a satellite system; and denote the measured code and carrier phase, respectively; is the geometric distance; is the speed of light; and are the clock offsets of the receiver and satellite, respectively; is the wet mapping function; is the zenith wet delay; is the frequency-dependent multiplier factor, which is independent of the satellite pseudorandom noise code; is the line-of-sight ionospheric delay on the frequency ; is the carrier wavelength on the frequency ; is the integer phase ambiguity on the frequency ; and are the time-invariance parts of the frequency-dependent receiver and satellite uncalibrated phase delay (UPD), respectively; and are the time-varying parts of the frequency-dependent receiver and satellite UPD, respectively; is the code hardware delay (CHD) from the receiver antenna to the signal correlator in the receiver; is the CHD from the satellite signal generator to the satellite antenna; and are the pseudo-range measurement noise and carrier measurement noise, respectively; is the signal frequency of the band of the system ; and are the frequency-dependent factors, respectively; and are the frequency-dependent satellite and receiver differential code bias, respectively; and are the IF combination of the CHD of the satellite and receiver, respectively; and are the differences in the time-varying part of the UPD on the differential frequency carrier phase in the satellite and receiver, respectively; and are the time-varying parts of IF combination of the UPD in the satellite and receiver, respectively. Other error items, such as phase center offsets and variations [28], phase windup [29], relativistic effect and tide loading, were assumed to be precisely corrected with their corresponding models.
Precise satellite clock products are generated by using the combination of IF observations. The carrier phase hardware delay is considered relatively stable for 24 h or for a period of time, estimated as a constant, ignoring the time-varying part . Therefore, the satellite clock offsets absorbs the IF combination satellite’s CHD and the time-varying part of IF combination satellite’s UPD [30].
Equation (3) is substituted into Equation (1) and then linearized using Taylor’s formula. Moving the known items to the left of the equation and merging the same parameter items above, the equations on each frequency can be written in detail in the following form.
For pseudo-range observables:
with
For carrier phase observables:
with
where is the unit vector of the component from the receiver to the satellite; is the vector of the receiver position increments relative to the priori position. For , since there is no difference code bias product between the first and third frequencies, we used two other DCB products for conversion. Similarly, the receiver clocks are expressed in a form similar to the satellite clock offsets:
We substituted (8) into (4) and (6) and merged the same parameter items. The pseudo-range and carrier phase observation equations can be expressed as follows:
with
In Equations (9) and (10), the recombination ionospheric delay, , absorbs the receiver differential code bias, the satellite’s and the receiver’s
;
() absorbs the time-varying part of the UPD in the first and second frequency, and this hardware delay bias does not require additional correction or estimation for its small magnitude (approximately 2 cm) and relatively low weight for the pseudo-range observation. () is an ambiguity at the corresponding frequency and absorbs the time-invariance part of the UPD, receiver differential code bias and the IF combination of the CHD in the receiver and satellite; is the satellite-independent inter-frequency bias parameter and, as for the triple-frequency PPP, the hardware biases on the L5 pseudo-range cannot be completely absorbed into the ionospheric delay, which was lumped in with the differential code biases between the L1 and L2 pseudo-ranges. is the IFCB related to the satellite (i.e., the difference between the current clock products computed with L1/L2 and the satellite clocks computed with L1/L5), and it is noticed for the new L5 signal provided by GPS Block IIF satellites. In order to avoid the increase in computational burden and consumption of time, the best strategy is to pre-estimate or forecast the IFCB when one executes triple- or multi-frequency PPP.
2.2. Method of IFCB Estimation
The IFCB is usually estimated by calculating the difference of two IF combination carrier phase observations. Take for instance the GPS and combining Equation (10), it is recognized that the difference of the IF combinations of the L1/L2 and L1/L5 carrier phases is equal to the IFCB plus an ambiguity term [19].
where is the difference in the double IF combination carrier phase observations; and are the IF combination carrier phase observations on the L1/L2 and L1/L5 frequencies, respectively; is the phase ambiguity of , which includes the constant ambiguity term and a constant phase hardware delay term. It should be noted that the frequency-related error terms in the Equation (12) were precisely corrected.
Without the cycle slip occurring, the ambiguity terms and phase hardware delay can be considered constant for two adjacent calendars or a period of time. Therefore, one can extract the IFCB through eliminating these constant terms by using the difference method of two adjacent calendars for the .
where the is the changing value of the for time and ; is the frequency-dependent IF combination coefficient (if GPS, ). Given that individual stations may be affected by observation noise and unmodeled errors, an iterative least squares estimation is usually required based on a ground observation network composed of multiple stations.
In iterative least squares estimation, firstly, the initial value of the at epoch is calculated using the equal weight method based on the group stations; secondly, the difference between the initial value and the obtained by each stations is calculate, and if the residual is greater than the set threshold, the weight of the station is reduced; thirdly, once more, an adjustment is implemented according to the new weight for each station; fourthly, the difference between the new adjustment value of the IFCB and obtained by each station is calculated again, and if the residual is greater than the threshold, the weight of the station is reduced again. The second to fourth steps are repeated until there are no stations left that need to reduce the weight, the iteration is stopped and the last iteration of the IFCB can be used to recover each epoch IFCB.
After obtaining an accurate value for each calendar, one calendar IFCB is selected as the reference benchmark. Through the method of accumulation calendar by calendar, each calendar IFCB containing the same reference benchmark can be recovered.
where is the IFCB of the reference calendar; is the final IFCB for correcting the third- or multi-frequency PPP for GNSS users. It is noted that the recovered IFCB of each calendar contains a common benchmark deviation but does not affect the PPP solution, as the bias will be absorbed into the ambiguity parameter. Moreover, in order to obtain high-precision IFCB estimates, when performing IF combinations for the carrier phase, it is necessary to select the observed noise scaling minimum combination.
3. Results
The IFCB amplitude of the BDS-3 and Galileo satellite systems varied in magnitudes of less than 2.0 cm, with negligible effects on multi-frequency PPP localization [14]. The BDS-2 satellite system’s change magnitude was approximately 4.0 cm, and PPP could be implemented by reducing the weight of the third-frequency observation value [16]. However, the IFCB change magnitude of GPS Block IIF satellites reached 20 cm, which must be corrected. Therefore, this study only focused on the modeling forecast of GPS satellites. We first estimated the IFCB of each GPS Block IIF satellite using global uniformly distributed GNSS continuous tracking stations. Subsequently, based on the analysis of IFCB time-varying characteristics, combined with the lag characteristics of the IGS final precise ephemeris product, a short-term prediction model was proposed for the GPS Block IIF satellites. The software used to implement IFCB estimation and forecasting was developed by our team based on the MATLAB tool.
3.1. Extraction of GPS IFCB
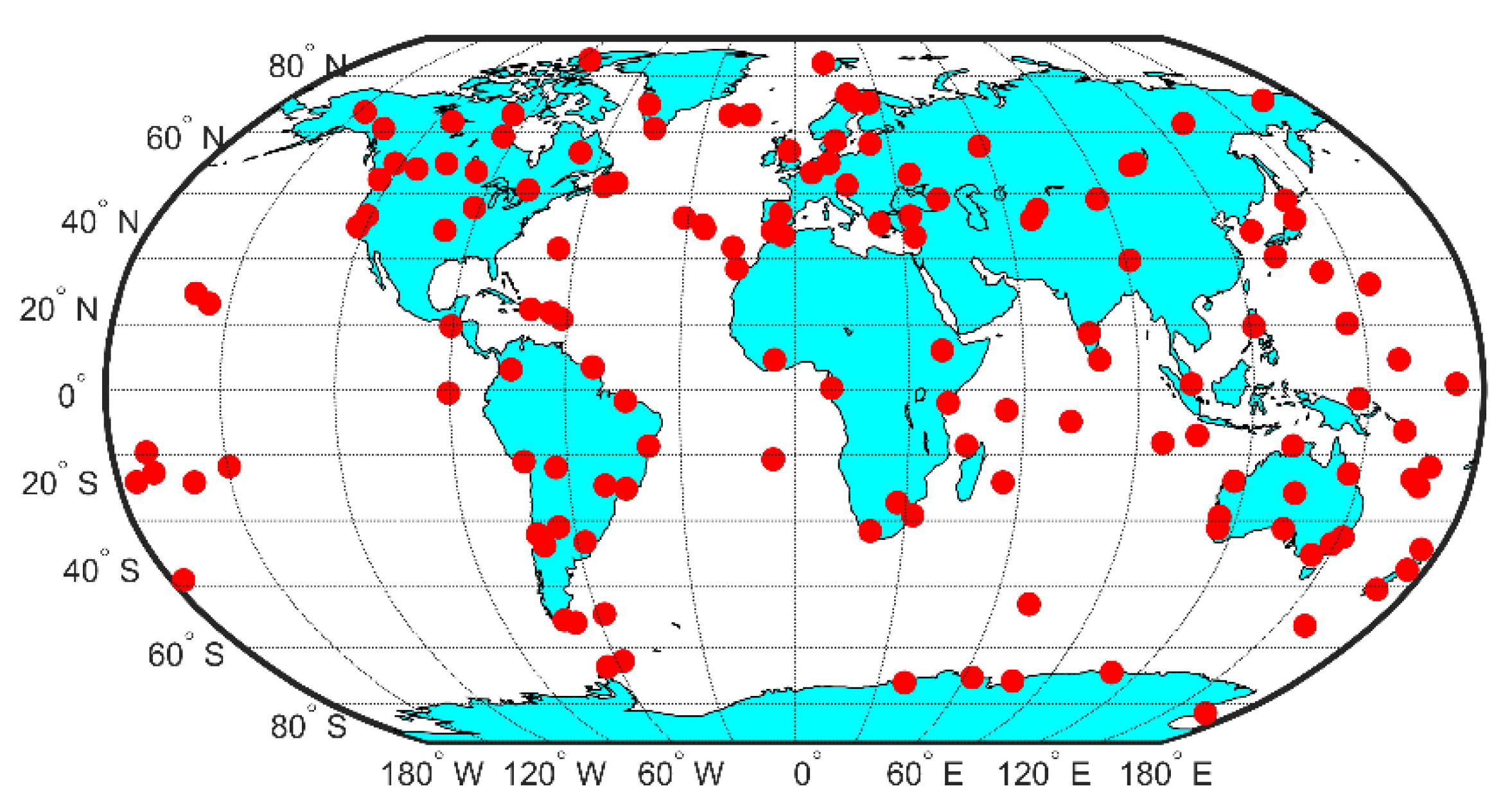
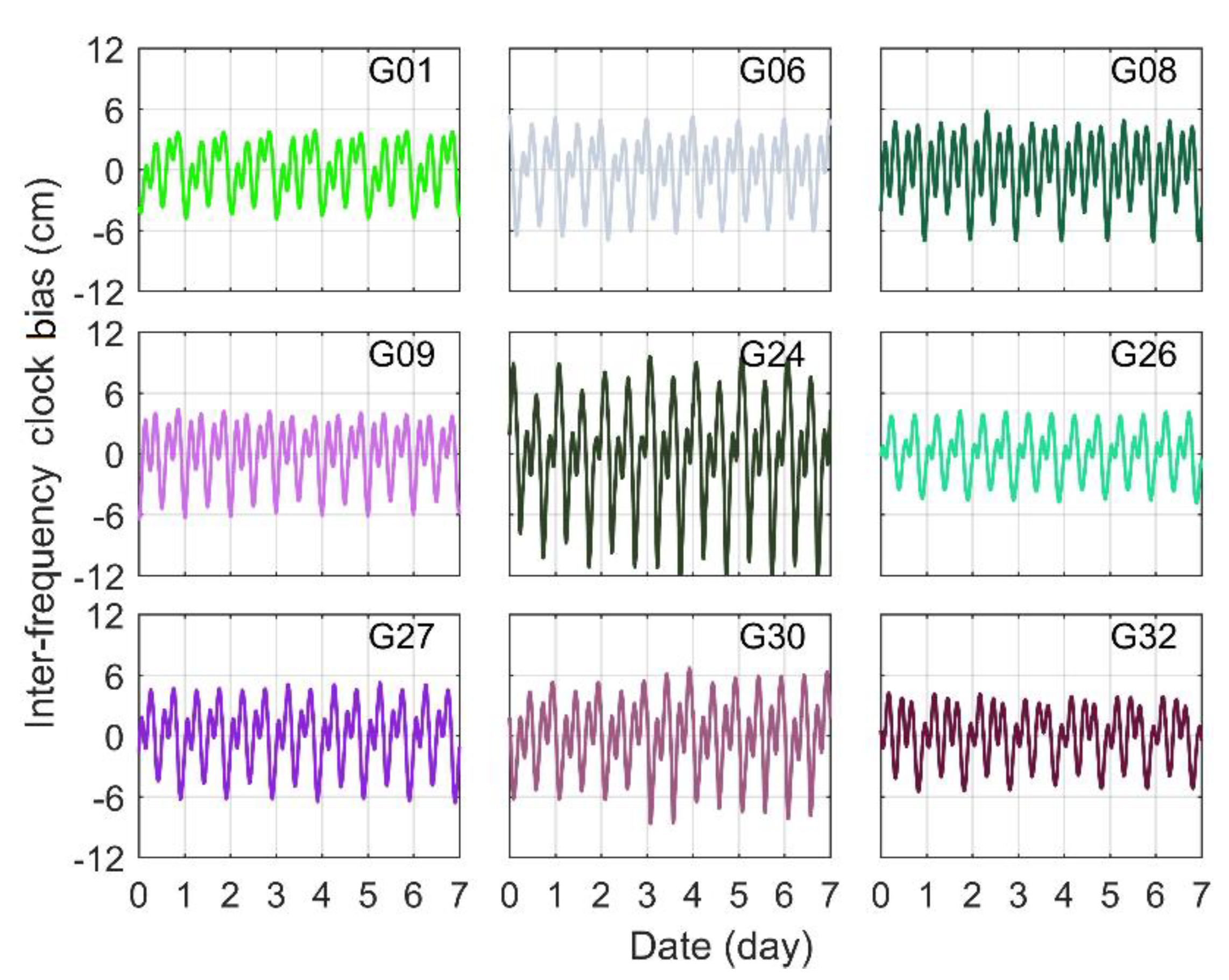
In order to ensure the continuity of the IFCB sequence, 162 globally distributed MGEX continuous tracking stations were selected, and the distribution of these stations is shown in Figure 1. The daily observations were selected from DOY 112 to 141 in 2020, and all stations could receive three-frequency signal data with a sampling interval of 30 s. The satellite and receiver PCO/PCV were corrected using igs14.atx files released by IGS, and the phase windup was corrected using the empirical model [29]. For the absence of L5 band correction parameters at the receiver terminal in the antenna file, similar frequency parameters were used for approximate correction. The detailed processing configurations are presented on Table 1, which also applies to the performance evaluation of triple-frequency PPP. However, the G03, G04, G10, G18 and G25 were not involved in the analysis, because the G04 and G18 are IIA and IIR-A satellites, respectively, and the G03, G10 and G25 satellites have few data available for the current time period. To facilitate the analysis of IFCB time-varying characteristics within a single day, only the first 7 days’ IFCB time series are given in Figure 2.
Figure 1.
Distribution of the MGEX stations.

Table 1.
GNSS processing configurations for IFCB estimation and evaluation of triple-frequency PPP.
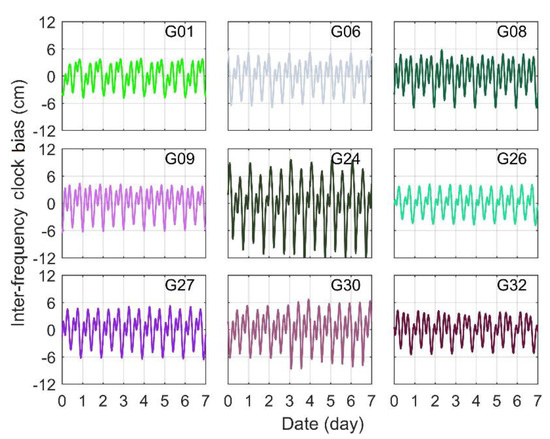
Figure 2.
IFCB time series of the Block IIF satellites.
The zero clock of the UTC was selected as the reference calendar to recover the daily IFCB, and the IFCB values of the zero clock were assumed to be 0. When a satellite at a station experienced cycle slip, the IFCB at the cycle slip calendar and the latter one calendar were no longer involved in the whole network adjustment calculation. If a satellite did not transmit a signal for a period of time for its own reasons, the moment that the satellite relaunched the signal was set to a reference calendar for the IFCB solution. It is noted that the current IFCB reference value is different from the reference value at the UTC zero clock, but it did not affect the PPP solution, because all benchmark deviations will be absorbed when the ambiguity is initialized. As shown in Figure 2, the change laws of the IFCB time series for all GPS Block IIF satellites were more consistent, and they all embodied the periodic characteristics of approximate one sidereal day and approximate half one sidereal day, respectively, and the IFCBs had good repeatability between adjacent days, showing strong consistency. Montenbruck et al. expounded that the change regulation of amplitude was related to the Sun’s elevation above the satellite’s orbital plane [13]. Except for the G24 satellite, the change magnitude of the IFCB amplitude was approximately 12 cm, while the G24 satellite had a change magnitude of over 20 cm. This bias was difficult to accept for PPP, where the posterior residual was only at the centimeter level and, therefore, the IFCB must be corrected.
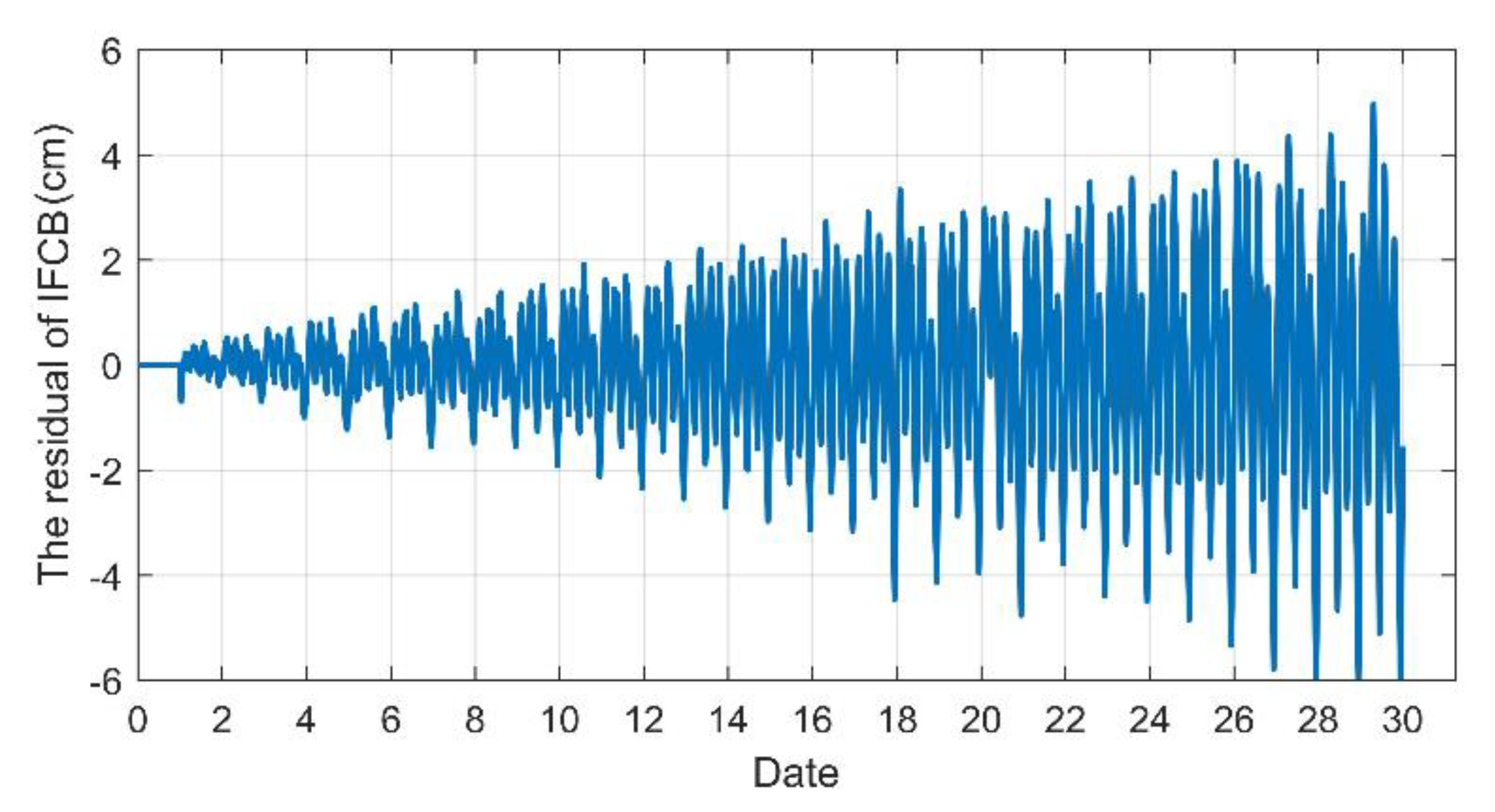
In order to investigate the difference in the IFCB time series in different days with the time lag, the IFCB of the first day (DOY 112) was differentiated from the other day, respectively, and the residual sequence is shown with the example of G01 in Figure 3. It is clear that the residuals relative to the IFCB time series of the first day gradually increased over the time lag. When the time lag was 1, 9, 19 and 29 days, the peak-to-peak amplitudes of the residuals reached 1.13, 3.44, 6.86 and 11.25 cm, respectively. This phenomenon was because the periods of the IFCB time series on different days were not strictly consistent, namely, the IFCB on different days shows an approximate period characteristic for all Block IIF satellites, and this approximation gradually becomes smaller with the increase in lag time. Following Pan et al. (2016), the IFCB periods of the Block IIF satellites roughly coincide with their orbital periods, which are close to the length of half a sidereal day [14]. Therefore, when the IFCB of one day is applied to other days, the periodic changes in the IFCB time series for different days must be considered.
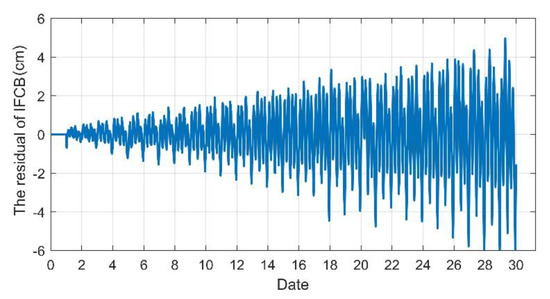
Figure 3.
Differences in the daily IFCBs relative the first day for the G01 satellite.
3.2. Time-Varying Characteristics of the IFCB
In real-time data processing or PPP network solutions, simultaneously receiving real-time data flow and performing IFCB estimation will significantly increase the program’s execution burden and calculation time, which is not conducive to real-time multi-frequency PPP and PPP network solutions. Considering that the final precision ephemerides products released by the IGS analysis centers usually lag no more than 7 days, therefore, in order to solve these problems, a short-term prediction model based on the epoch-by-epoch sliding Pearson autocorrelation function was proposed for the IFCB on the GPS Block IIF satellites according to the lag features of the final precision ephemerides product and the short-term variation characteristics of the IFCB described above. Firstly, the autocorrelation coefficient was calculated by the Pearson autocorrelation function [31].
In Equation (15), is the average value of IFCB of all days, which is different from the standard autocorrelation function; is the IFCB time series of the first day, which is the benchmark time series; is the IFCB time series that sliding calendars from the first epoch, with the same sequence length as ;
is the autocorrelation coefficient of and in the epoch; and are the standard deviations for the different time series, respectively.
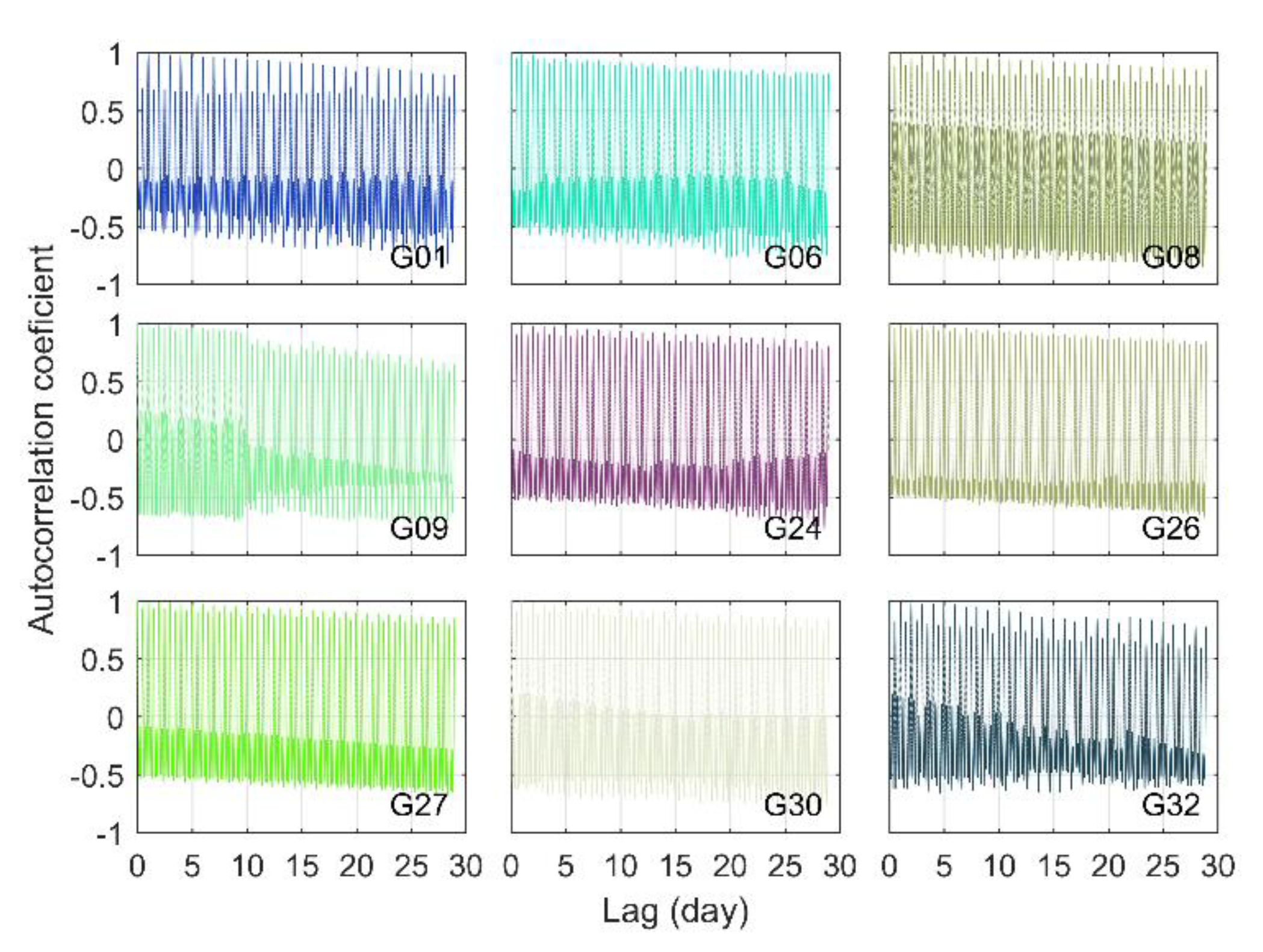
The autocorrelation coefficients of the IFCB time series for the GPS Block IIF satellites are given in Figure 4. As the lag time increased, the autocorrelation coefficient of the satellite IFCB time series gradually decreased, i.e., the correlation gradually decreased. The autocorrelation coefficient sequences shows two wave peaks within 24 h (the primary and secondary peaks, respectively), indicating that there was a major- and subperiod in the IFCB time series, with approximately one sidereal day and a half-sidereal day, respectively. This result corresponded to the changing features of the IFCB time series in the GPS satellite system. To accurately analyze the changing characteristics of the IFCB period, the epoch moments corresponding to the primary and secondary peaks of the autocorrelation coefficient time series for each GPS Block IIF satellite were extracted as shown in Figure 6.
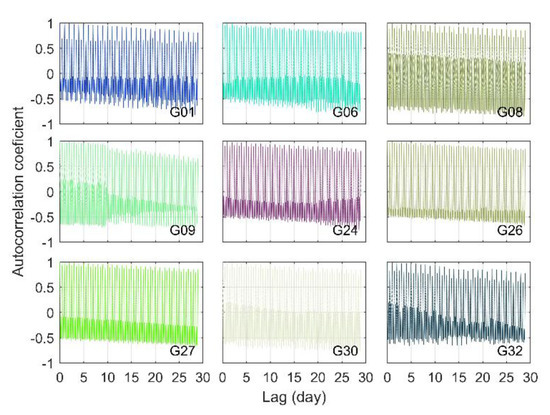
Figure 4.
Autocorrelation coefficients of the GPS Block IIF satellites.
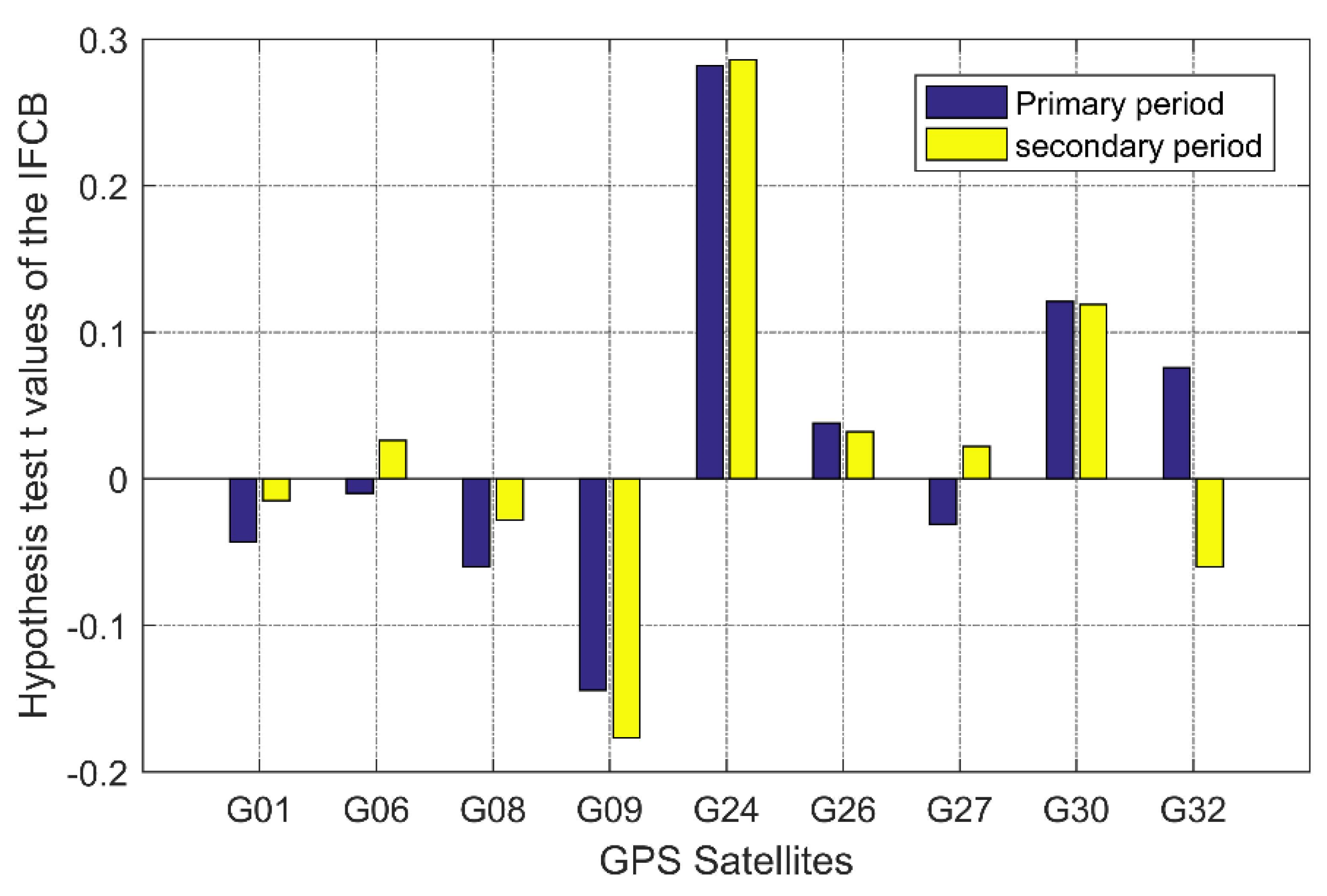
In order to verify the validity of the IFCB period extracted by the Pearson autocorrelation function in this paper, a hypothesis test scheme obeying the t-distribution was set: (1) an IFCB time series of 30 days was divided into two time periods: days 1–15 and days 16–30; (2) the IFCB time series on days 1 and 16 were used as the benchmark values, and the autocorrelation coefficient in the two periods of time could be obtained based on the epoch-by-epoch sliding Pearson autocorrelation function; (3) the epoch moments corresponding to the peaks of the autocorrelation coefficient could be extracted separately, thus obtaining two independent samples; (4) suppose that the average period was equal over the two time periods, namely, , and the statistics formula and degrees of freedom were and , respectively, where and are the sample means; is the calculated value, and the resulting values are shown in Figure 5; (5) according to the Figure 5, the values of all satellites were within the acceptance domain and far less than the threshold, namely, it accepts the original hypothesis, where the threshold was 1.701, as determined according to the degrees of freedom and confidence intervals. This indicates that the period of the IFCB time series had good consistency in the short term for modeling prediction.
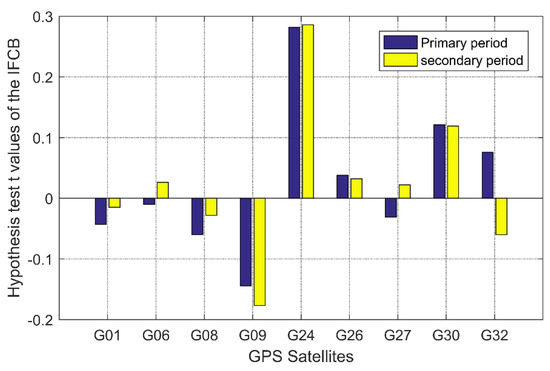
Figure 5.
Hypothesis test t values of the IFCB.
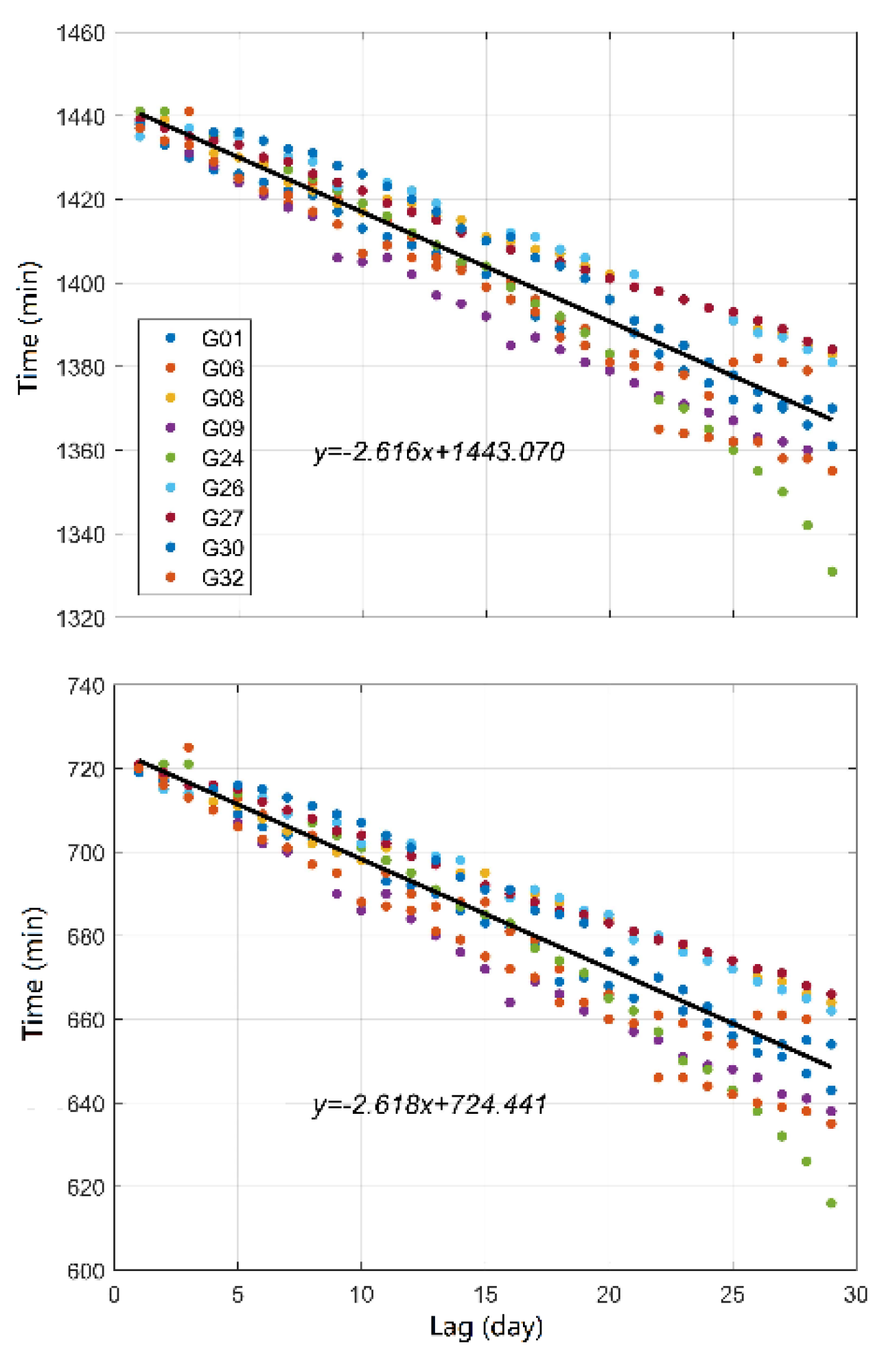
The top and bottom panels in Figure 6 exhibit the epoch moments corresponding to the peaks of the time series of the autocorrelation coefficient for the GPS Block IIF satellite IFCBs, respectively. As the lag time increased, the epoch moments were not constant but presented an approximately linear decrease in regularity. The reason for this phenomenon is that the GPS IFCB sequence period is not a complete 24 h, and the changing characteristics of the IFCB time series are related to the relative position of the satellite–Earth–Sun. To analyze the reduction characteristics in detail, the epoch moments corresponding to the primary and secondary peaks were fitted by linear functions according to the change characteristics of peak moments for all GPS satellites. As shown in the black, solid lines in Figure 6, there was excellent agreement between the epoch moments and the linear function. According to the slope of the fitting function, the mean difference of the peaks over the adjacent days was approximately 2.62 min for all satellites.
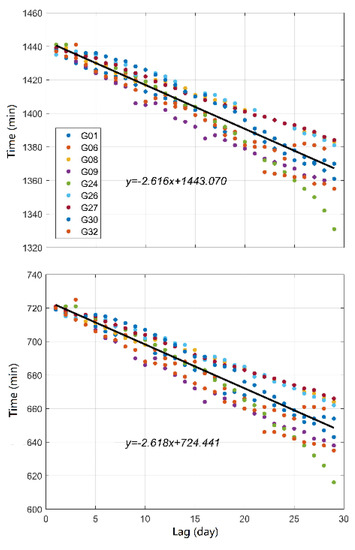
Figure 6.
Epoch moments corresponding to the primary peak (top) and secondary peak (bottom) of the autocorrelation coefficients.
In order to realize accurate IFCB short-term prediction, a least squares linear fitting function was performed for each satellite based on the epoch moments corresponding to the primary and secondary peaks. The primary and secondary peaks were the largest and second largest places in the time series of the correlation coefficients in one day, respectively. The fitting results of the primary period and secondary period are shown in Table 2, where a and b represent the first-order term coefficient and the constant term of the linear function, and the root mean square (RMS) was calculated by the fitting values and the real values corresponding to the epoch moments. It is worth mentioning that the primary period and secondary periods were the epoch intervals corresponding to two adjacent primary peaks and secondary peaks. The primary and secondary periods are equal in the theory. However, due to the error, there were small differences between them; thus, we first calculated the fitting coefficient of each peak moment and then calculated the average to establish the prediction model. Taking the G01 satellite as an example, when the lag days were n, the difference of the peak moment was approximately 3.04n min compared to the first day. Therefore, the differences in the initial moment caused by lagging days need to be fully taken into account for IFCB prediction. In fact, the periodic features presented by the GPS Block IIF satellite IFCB basically coincide with the satellite’s own orbital motion period, which is related to the bias between the solar day and sidereal day and the influence of other satellite dynamics factors.

Table 2.
The fitting results of the primary period and secondary period.
Pan et al. used the IFCB of the previous day to forecast the current day, and the prediction accuracy of IFCB was 0.6 cm, which indicated that the IFCBs on different days were highly related in terms of fluctuation size and periodicity [14]. From the above analysis, the initial moments of the IFCB time series on different days did not strictly correspond with the increase in lag time, and there was a regularity bias. When the observation data used to estimate IFCB were not available in time, it was necessary to implement short-term modeling forecasts for the IFCB in the current time period. Considering that the release time of IGS final precision ephemeris products generally lags by 7 days, we used IFCB on day n to predict IFCB on day n + 7 in view of the periodic regularity changes of the IFCB time series. To verify and compare the accuracy of the forecast model proposed, the IFCB of the day n + 7 was directly predicted with the day n without accounting for the IFCB period change as shown in Figure 7.
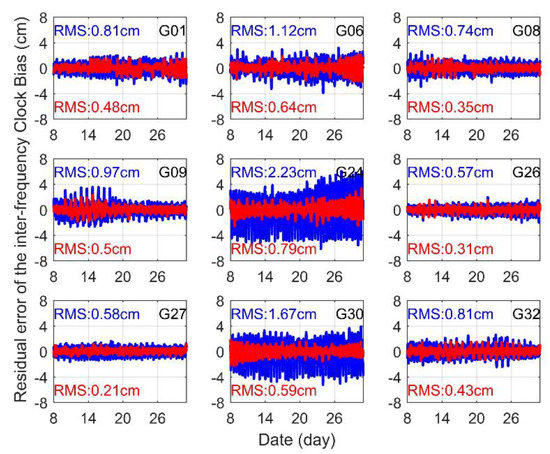
Figure 7.
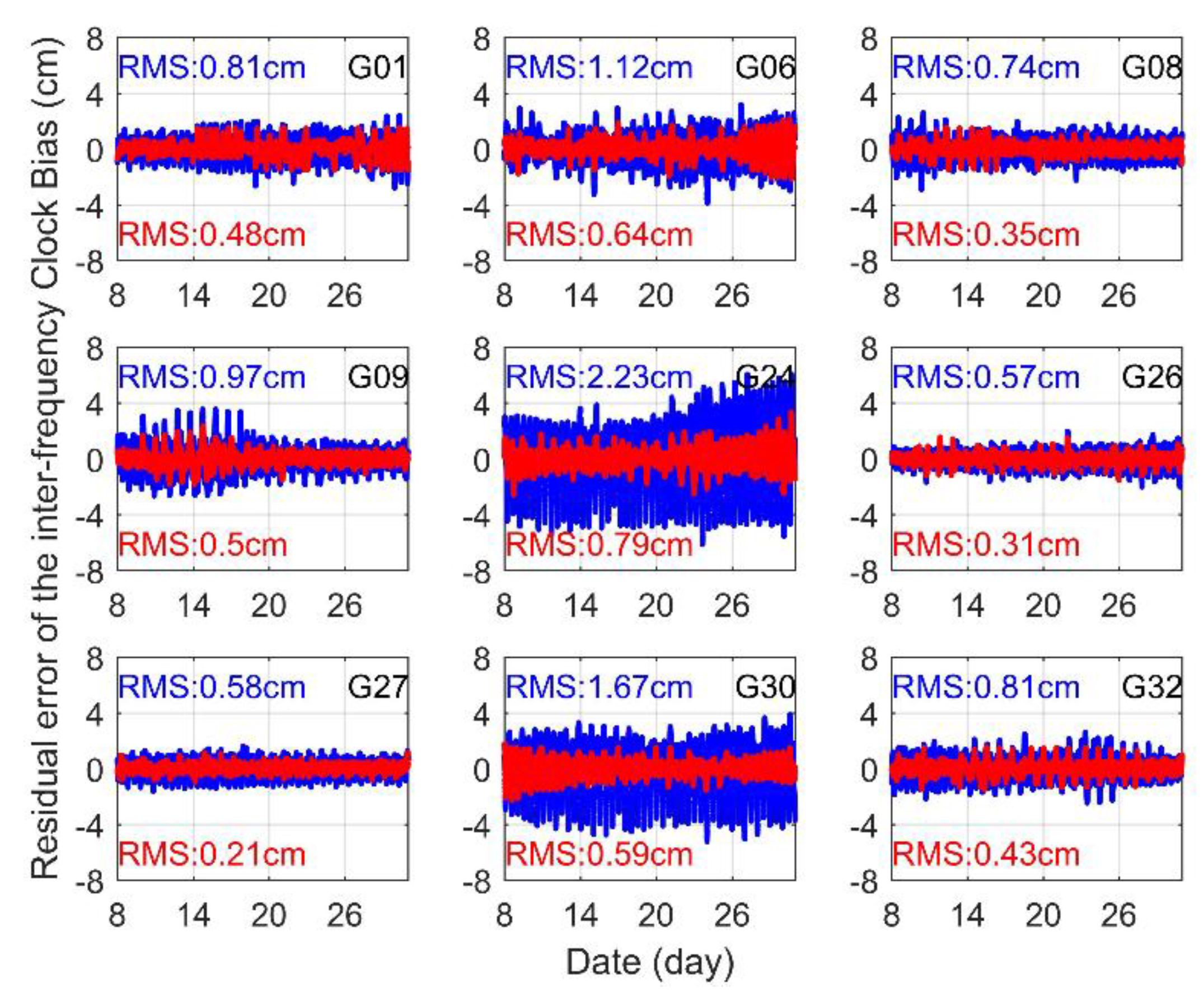
Prediction residual of the IFCB for GPS Block IIF satellites. The blue and red lines indicate unconsidered periodic variation and considered periodic variation, respectively.
In Figure 7, the computational method of both types of residuals was all relative to the real IFCB. As shown, when the IFCB prediction was implemented using the first method, the prediction residue was relatively large, and the statistics displayed that the maximum IFCB prediction residue was approximately 7.5 cm for all satellites. Especially for the G24 and G30 satellites, the RMS values reached 2.23 and 1.67 cm, respectively. The reason for this is that the peak and peak moment on different days differed greatly in the IFCB time series, causing the moment corresponding to the wave peak lagging 7 days to deviate significantly from the moment corresponding to the first day. However, when the second approach was adopted, the periodic change characteristics in the lag case was considered, and the resulting predicted residuals were significantly reduced, especially for the G24 and G30 satellites, effectively remedying the defects of the first prediction method. The average RMS of the predicted residual for all satellites was less than 0.50 cm, the minimum RMS was approximately 0.21 cm and the maximum RMS was approximately 0.79 cm. Compared to the first prediction method, the average RMS of all satellites decreased by approximately 52.5% when the second method was adopted, which better meets the requirement of high-precision for real-time multi-frequency PPP and PPP network solutions.
4. Discussion
In order to compare the positioning impact of the actual measurement of IFCB, forecasted IFCB and no IFCB correction on three-frequency uncombined PPP, datasets from 38 globally distributed MGEX stations were used to implement the post-processing multi-frequency PPP performance evaluation. Because the DOY 119 was the first day that could be used for verifying the prediction performance after a lag of 7 days, GPS observations on this day were used for triple-frequency PPP performance evaluation. Figure 8 shows the distribution of these test stations. All these stations could receive GPS three-frequency data, and the sampling interval of the observed data was 30 s. The precision orbital and clock were provided by the final products released by Wuhan University (ftp://igs.gnsswhu.cn, Wuhan, China, 18 April 2020). The precise coordinates of the stations are available in the file “igs20Pwwwwd.snx” released by IGS. During data processing, three strategies were used to implement the three-frequency uncombined kinematic PPP and static PPP models: (1) without IFCB correction (without IFCB); (2) the predicted IFCB with a time lag of 7 days (with pred-IFCB); (3) the actual measurement of the IFCB (with real-IFCB).
Figure 8.
Distribution of the test stations.
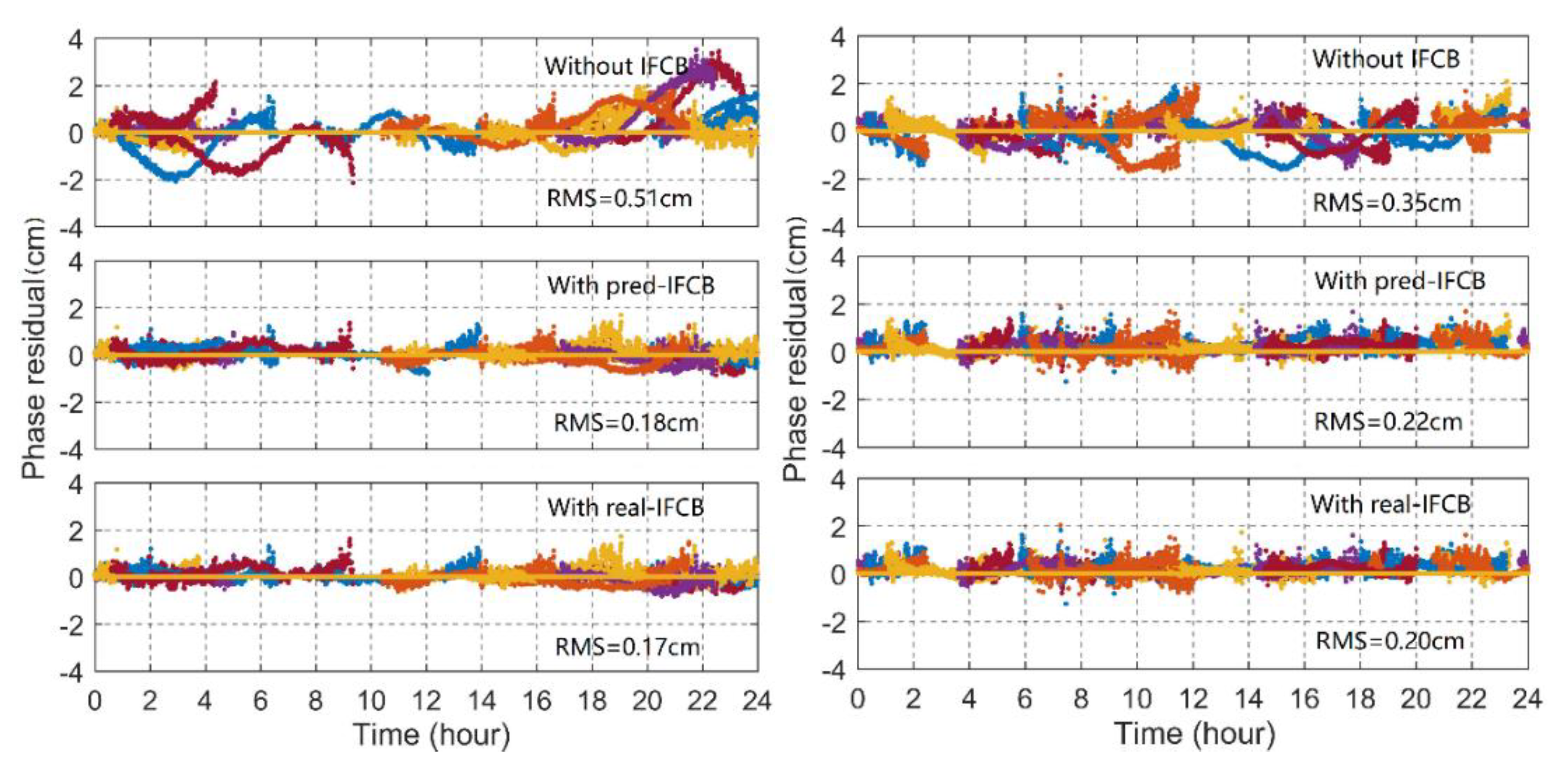
The DJIG and YEL2 stations were taken as examples to show the uncombined PPP posterior residual at the third frequency as shown in Figure 9. Different colors represent different satellites. If the functional model was accurately established and the various modeling errors were precisely corrected, the posterior residuals of the three-frequency PPP should conform to the traditional stochastic noise distribution [32]. Figure 9 shows that in addition to the observed noise, the unmodeled systematic bias caused by IFCB was fused to the posterior residuals. When the IFCB correction was applied to three-frequency PPP, the posterior residuals improved significantly, and the average RMS of all Block IIF satellites for all stations was reduced from 0.43 to 0.21 cm, approximately 53.8%, which indicates that the systematic bias caused by IFCB was greatly diminished. In the same way, when the predicted IFCB with the time lag of 7 days was applied to the three-frequency PPP solution, the posterior residual was also significantly improved, and the percentage decrease was approximately 51.3%. The RMS statics show that the forecasted IFCB was basically the same as the actual measurement of the IFCB, and it could also meet the high-precision three-frequency uncombined PPP requirements.
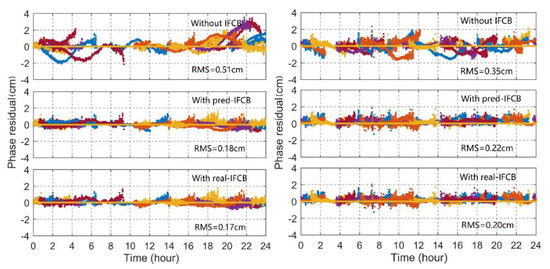
Figure 9.
Phase observation residuals for triple-frequency uncombined PPP at the DJIG (left panel) and YEL2 (right panel) stations.
Based on above three schemes, triple-frequency uncombined static PPP and kinematic PPP post-processing were performed. Table 3 and Figure 10 show the mean coordinate errors and convergence time series of the GPS static PPP model, respectively, where the mean coordinate errors were obtained by averaging the coordinate errors time series of the last two hours of all stations in the 24 h solution, while the convergence time series were obtained by calculating the quadratic mean epoch by epoch. The analysis shows that the positioning accuracy of 24 h PPP solutions under the three schemes was better than 2 cm in the horizontal direction and better than 3 cm in the vertical direction. Compared with no IFCB correction, PPP solutions using forecasted IFCB and measured IFCB increased by 33.2%, 14.3% and 17.2% and 35.1%, 14.9% and 18.7% in the east, north and vertical directions, respectively. In Table 3, although the positioning accuracy improved at the millimeter to centimeter scale, it is of great significance to the crustal movement monitoring required by high-precision positioning [33,34,35].

Table 3.
Mean coordinate residuals of triple-frequency un-combined PPP of three cases (cm).
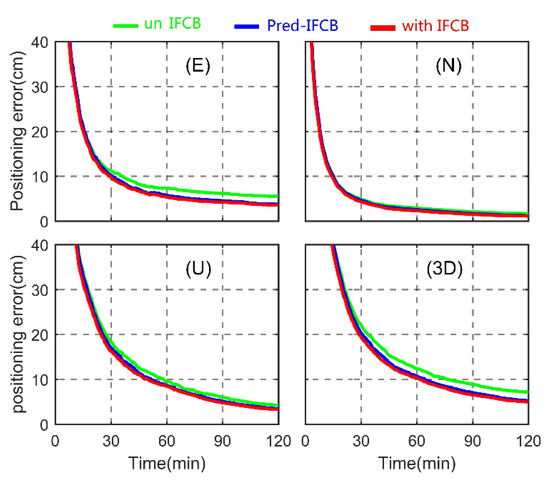
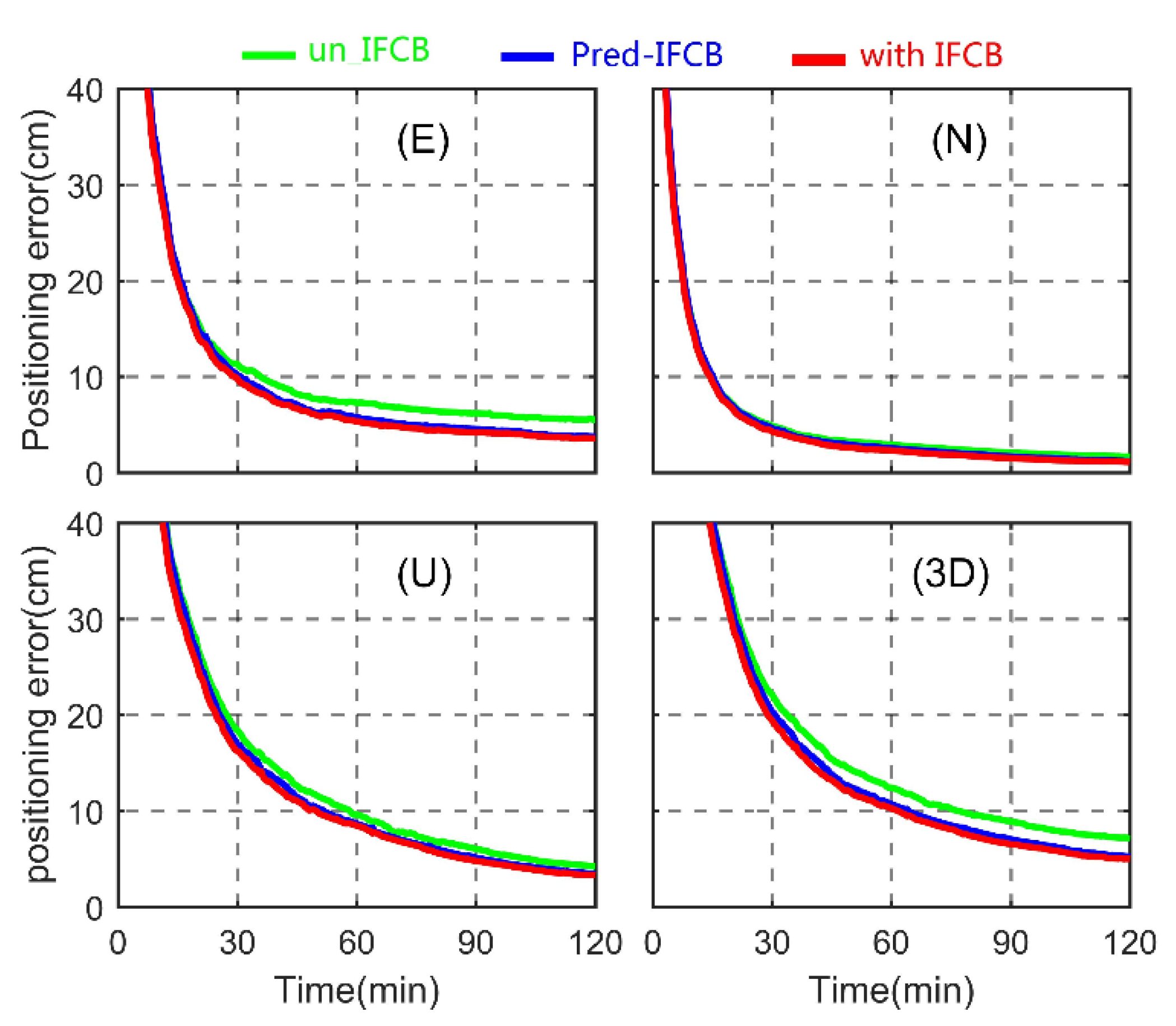
Figure 10.
Average convergence time series of static PPP for east (E), north (N), up (U) and three dimensional (3D) directions.
As shown in the Figure 10, due to the smaller magnitude of IFCB and the larger positioning errors in the convening stage, the positioning accuracy of the three triple-frequency PPP cases is at the same level in the first 25 min. By analyzing the convergence time, it can be seen that without IFCB correction, the solution time required for the coordinate errors of PPP to reach 10 cm in the east, north and vertical directions was approximately 36, 15 and 48 min, respectively. If the forecasted IFCB was used, the corresponding three settlement time were approximately 26, 13 and 42 min, respectively. If measured IFCB was used, the corresponding three settlement times were approximately 24, 12 and 40 min respectively. The results show that the IFCB bias has a great influence on the convergence time of GPS three-frequency uncombined PPP, and when the IFCB correction is applied, the convergence speed can be significantly improved. It is worth noting that the convergence time was defined as the time required for the coordinate residuals to converge within 10 cm and remain stable in the subsequent epochs. In addition, compared with no IFCB correction, the IFCB prediction method proposed in this paper can still significantly improve the positioning performance of three-frequency uncombined PPP, especially in the eastern direction. The main reason may be that the satellite moves from north to south, and the dilution of precision values in the eastern direction are worse than those in the northern direction.
For the kinematic PPP solution, the coordinate parameters of the station were estimated by epoch as white noise, which can better reflect the performance of the established PPP model [36]. As shown in Figure 11, compared with no IFCB correction, the positioning accuracy of GPS satellites in the three directions significantly improved when the forecasted IFCB and the measured IFCB were used. Statistics show that when the measured IFCB correction was used, the average RMS of kinematic PPP residual of all stations were approximately 1.75, 1.73 and 5.14 cm in east, north and vertical direction, respectively, and the positioning accuracy in horizontal direction and vertical direction improved by approximately 51.0% and 41.5% compared with no IFCB correction. When the forecast IFCB correction was used, the average RMS of the kinematic PPP residual was approximately 1.88, 1.81 and 5.50 cm, respectively, the positioning accuracy in horizontal direction and vertical direction improved by approximately 50.2% and 39.7% compared with no IFCB correction. It can be seen that IFCB has a significant impact on GPS kinematic PPP, especially in the east direction. Moreover, the improvement of kinematic positioning performance by using measured IFCB and forecast IFCB is basically the same. It should be noted that in the calculation of coordinate residual RMS in this paper, the coordinate residual in the PPP convergence period was excluded, and the residual data were collected from 2 h.
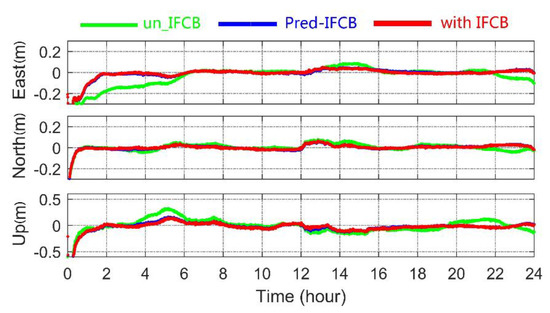
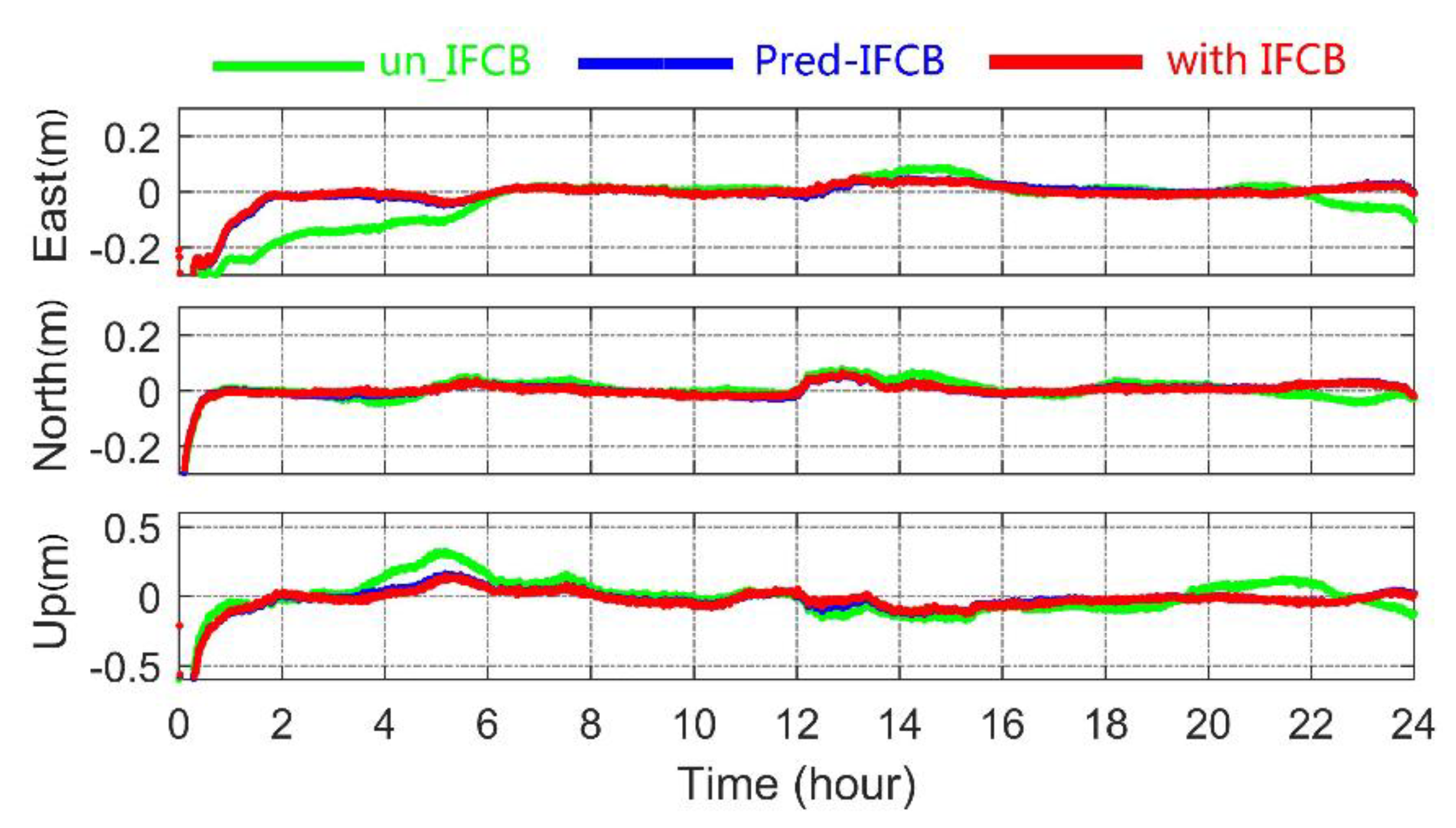
Figure 11.
Kinematic PPP positioning errors for three different directions at HARB.
5. Conclusions
Given that modernized GPS as well as the newly emerging navigation satellite systems provides triple-, quad-, and multi-frequency signals, but the IGS analysis centers traditionally use dual-frequency, such as GPS L1/L2, ionosphere-free combination model for precise satellite clock estimation, results in the obtained clock products containing time-varying parts of ionospheric-free combination uncalibrated phase delay of the satellites. Thus, the clock product cannot be directly applied to the third-frequency observation value (L5) for multi-frequency PPP. If the IFCB and receiver coordinates, tropospheric wet delay, ambiguity and other parameters are estimated together, it will increase the computational burden and lead to more time consumption, which is especially not conducive to real-time PPP and PPP network solutions.
To resolve this problem, a month’s observation data from 162 global uniformly distributed MGEX stations were selected to estimate the IFCB of nine GPS Block IIF satellites. Based on the analysis of the IFCB time-varying characteristics and the lag characteristics of the final ephemeris products, a modeling method of short-term IFCB prediction based on the epoch-by-epoch sliding Pearson autocorrelation function was proposed. The feasibility of the new method was verified by the Student’s t-distribution, the comparison with the measured IFCB, posteriori residuals of the third-frequency carrier phase and the kinematic/static PPP solutions, respectively. A large number of experiments showed that the forecasted IFCB with a lag of 7 days had good consistency with the measured IFCB, which basically improved the positioning accuracy and convergence time of the three-frequency uncombined PPP with the same effect. Compared to no IFCB correction, the posterior residual at third frequency was significantly improved when the predicted IFCB correction was used, and the RMS value decreased by approximately 51.3%. The static and kinematic solutions for triple-frequency uncombined PPP in 24 h can be improved by 33.2% and 17.2% and 50.2% and 39.7% in the horizontal and vertical directions, respectively, and the performance of convergence time also improved.
Author Contributions
All authors made significant contributions to this study. Conceptualization, C.Y. and Y.D.; methodology, S.X.; software, C.Y. and C.X.; validation, C.Y., H.W. and S.G.; formal analysis, C.Y.; resources, S.G.; writing—original draft preparation, C.Y.; writing—review and editing, C.X.; funding acquisition, C.Y. and Y.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (grant number: 41974010) and the Beijing Key Laboratory of Urban Spatial Information Engineering (grant number: 20220120).
Data Availability Statement
The GPS precise ephemerides product provided by Wuhan University is available at ftp://igs.gnsswhu.cn. The MGEX observation for estimating the IFCB and evaluating the forecasting method is available at ftp://igs.ign.fr//pub/igs/data/. The corrections of satellite and receiver PCO/PCV and the precise coordinates of the MGEX stations are available in file “igs14.atx” and “igs20Pwwwwd.snx” released by IGS, respectively. All the data and products are publicly available through the respective organizations’ website.
Acknowledgments
The contribution of data from IGS is appreciated. We also would like to express our great appreciation to Pan Li for kindly providing the IFCB software and related technical support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Li, W.; Kacmarik, M. Assessment of multi-GNSS precise orbit and clock products from different analysis centers based on precise point positioning. Acta Geodyn. Geomater. 2021, 18, 387–397. [Google Scholar]
- Lyu, D.; Zeng, F.; Ouyang, X.; Zhang, H. Real-time clock comparison and monitoring with multi-GNSS precise point positioning: GPS, GLONASS and Galileo. Adv. Space Res. 2020, 65, 560–571. [Google Scholar]
- Ai, Q.; Maciuk, K.; Lewinska, P.; Borowski, L. Characteristics of Onefold Clocks of GPS, Galileo, BeiDou and GLONASS Systems. Sensors 2021, 21, 2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Cai, H.; Chen, G.; Jiao, W.; He, Q. Multi-GNSS Combined Orbit and Clock Solutions at iGMAS. Sensors 2022, 22, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsobeiey, M. Precise point positioning using triple-frequency GPS measurements. J. Navig. 2015, 68, 480–492. [Google Scholar]
- Chernogor, L.; Garmash, K.; Guo, Q.; Lou, Y.; Zheng, Y. Ionospheric Storm Effects over the People’s Republic of China on 14 May 2019, Results from Multipath Multi-Frequency Oblique Radio Sounding. Adv. Space Res. 2020, 66, 226–242. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.; Gao, Y. A comparison of three PPP integer ambiguity resolution methods. GPS Solut. 2014, 18, 519–528. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Hu, X.; Chen, J.; Bian, L.; Wang, W.; Li, R.; Wang, X.; Rao, Y.; Meng, X.; Wu, B. Initial analysis of the BDS satellite autonomous integrity monitoring capability. GPS Solut. 2019, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Melachroinos, S. An enhanced cycle slip repair algorithm for real-time multi-GNSS, multi-frequency data processing. GPS Solut. 2019, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odijk, D.; Arora, B.; Teunissen, P. Predicting the Success Rate of Long-baseline GPS+Galileo (Partial) Ambiguity Resolution. J. Navig. 2014, 67, 385–401. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Ge, M.; Zhang, H.; Wickert, J. A method for improving uncalibrated phase delay estimation and ambiguity-fixing in real-time precise point positioning. J. Geod. 2013, 87, 405–416. [Google Scholar]
- Schaer, S.; Villiger, A.; Arnold, D.; Dach, R.; Prange, L.; Jäggi, A. The CODE ambiguity-fixed clock and phase bias analysis products: Generation, properties, and performance. J. Geod. 2021, 95, 81. [Google Scholar]
- Montenbruck, O.; Hugentobler, U.; Dach, R.; Steigenberger, P.; Hauschild, A. Apparent clock variations of the Block IIF-1 (SVN62) GPS satellite. GPS Solut. 2012, 16, 303–313. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Xin, L. Characteristics of inter-frequency clock bias for Block IIF satellites and its effect on triple-frequency GPS precise point positioning. GPS Solut. 2016, 21, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Montenbruck, O.; Hauschild, A.; Steigenberger, P.; Langley, R. Three’s the challenge: A close look at GPS SVN62 triplefrequency signal combinations finds carrier-phase variations on the new L5. GPS World 2010, 21, 8–19. [Google Scholar]
- Montenbruck, O.; Hauschild, A.; Steigenberger, P.; Hugentobler, U.; Teunissen, P.; Nakamura, S. Initial assessment of the COMPASS/BeiDou-2 regional navigation satellite system. GPS Solut. 2013, 17, 211–222. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Zhu, W. Inter-frequency clock bias for BeiDou. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2014, 43, 1127–1131. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.; Wang, G.; Liu, Z.; Hu, Z.; Dai, Z.; Liu, J. Analysis of BeiDou satellite measurements with code multipath and geometry-free ionospheric-free combinations. Sensors 2016, 16, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Xin, L.; Lu, C.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, J. Considering Inter-Frequency Clock Bias for BDS Triple-Frequency Precise Point Positioning. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Zhou, X.; Wu, B. Fast estimation and analysis of the interfrequency clock bias for Block IIF satellites. GPS Solut. 2013, 17, 347–355. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Li, B.; Xiao, G.; Wang, J.; Xu, T. Improved method for estimating the inter-frequency satellite clock bias of triple-frequency GPS. GPS Solut. 2016, 20, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Geng, J. GPS satellite clock determination in case of inter-frequency clock biases for triple-frequency precise point positioning. J. Geod. 2018, 92, 1133–1142. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Zhang, X.; Ge, M.; Schuh, H. Three-frequency BDS precise point positioning ambiguity resolution based on raw observables. J. Geod. 2018, 92, 1357–1369. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Li, B.; Wang, J.; Xu, T. A method for estimating BeiDou Inter-frequency satellite clock bias. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2016, 45, 140–146. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, X.; Gu, S.; Lou, Y.; Zheng, F.; Yang, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J. Research on empirical correction models of GPS Block IIF and BDS satellite inter-frequency clock bias. J. Geod. 2020, 94, 36. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Pan, L. Modeling and predicting inter-frequency clock bias of BDS-2 GEO, IGSO and MEO satellites for triple-frequency precise point positioning. GPS Solut. 2022, 26, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Dong, D.; Li, W.; Jiang, X.; Wickert, J. GAMP: An open-source software of multi-GNSS precise point positioning using undifferenced and uncombined observations. GPS Solut. 2018, 22, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, G.; Luzum, B. IERS Technical Note No. 36, IERS Conventions; International Earth Rotation and Reference Systems Service: Frankfurt, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Wu, S.; Hajj, G.; Bertiger, W.; Lichten, S. Effects of antenna orientation on GPS carrier phase. Manuscr. Geod. 1993, 18, 91–98. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, L.; Zhang, X.; Guo, F.; Liu, J. GPS inter-frequency clock bias estimation for both uncombined and ionospheric-free combined triple-frequency precise point positioning. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 473–487. [Google Scholar]
- Coppola, A.; Comegna, A.; Dragonetti, G.; Lamaddalena, N.; Kader, A.; Comegna, V. Average moisture saturation effects on temporal stability of soil water spatial distribution at field scale. Soil Till Res. 2011, 114, 155–164. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Li, J.; Zeng, Q.; Guo, F.; Wu, R.; Zhang, X. An Improved Robust Kalman Filtering Strategy for GNSS Kinematic Positioning Considering Small Cycle Slips. Adv. Space Res. 2019, 63, 2724–2734. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Braitenberg, C.; Serpelloni, E. Interference of tectonic signals in subsurface hydrologic monitoring through gravity and GPS due to mountain building. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2018, 167, 148–159. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, C.; Dang, Y.; Dai, H.; Yang, Q.; Wang, X. Crustal deformation characteristics of Sichuan-Yunnan region in China on the constraint of multi-periods of GPS velocity fields. Adv. Space Res. 2018, 61, 180–2189. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y.; Chen, R.; Yi, S.; Wang, W.; Ding, H.; Shen, W.; Chen, L. Contemporary Mountain-Building of the Tianshan and its Relevance to Geodynamics Constrained by Integrating GPS and GRACE Measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2019, 124, 12171–12188. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, F.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Ren, X. Modeling and assessment of triple-frequency BDS precise point positioning. J. Geod. 2016, 90, 1223–1235. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).