High-Accuracy Clock Offsets Estimation Strategy of BDS-3 Using Multi-Source Observations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
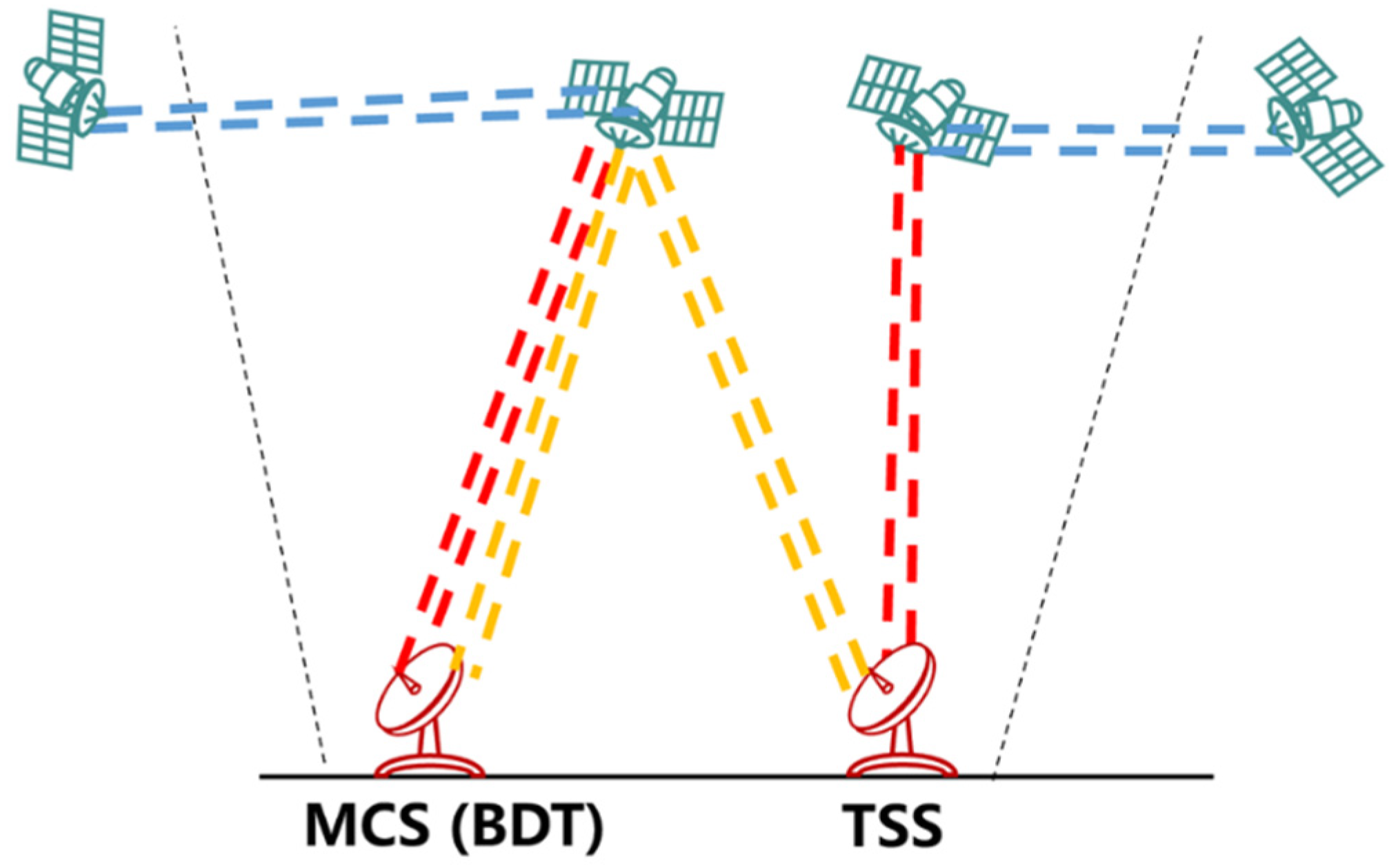
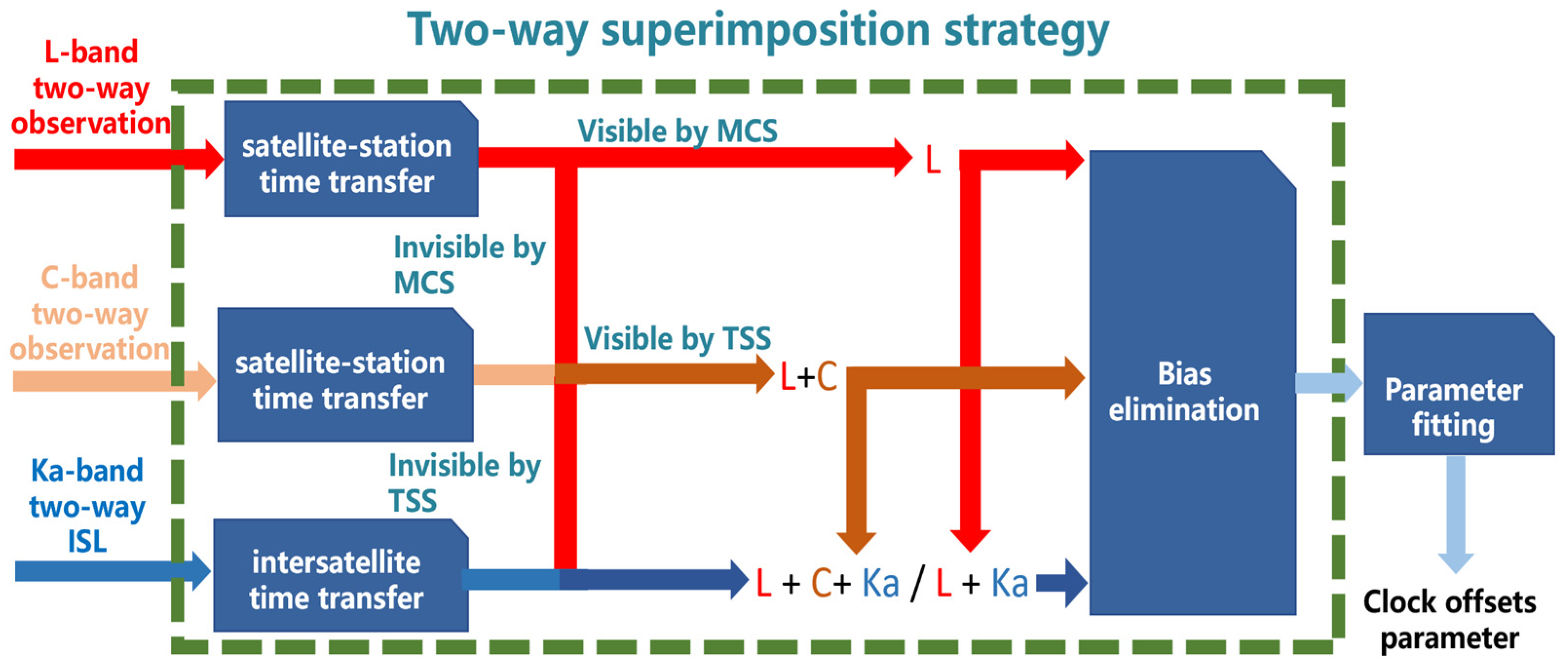
2.1. Two-Way Superimposition Strategy
2.1.1. Fundamental Principles Process
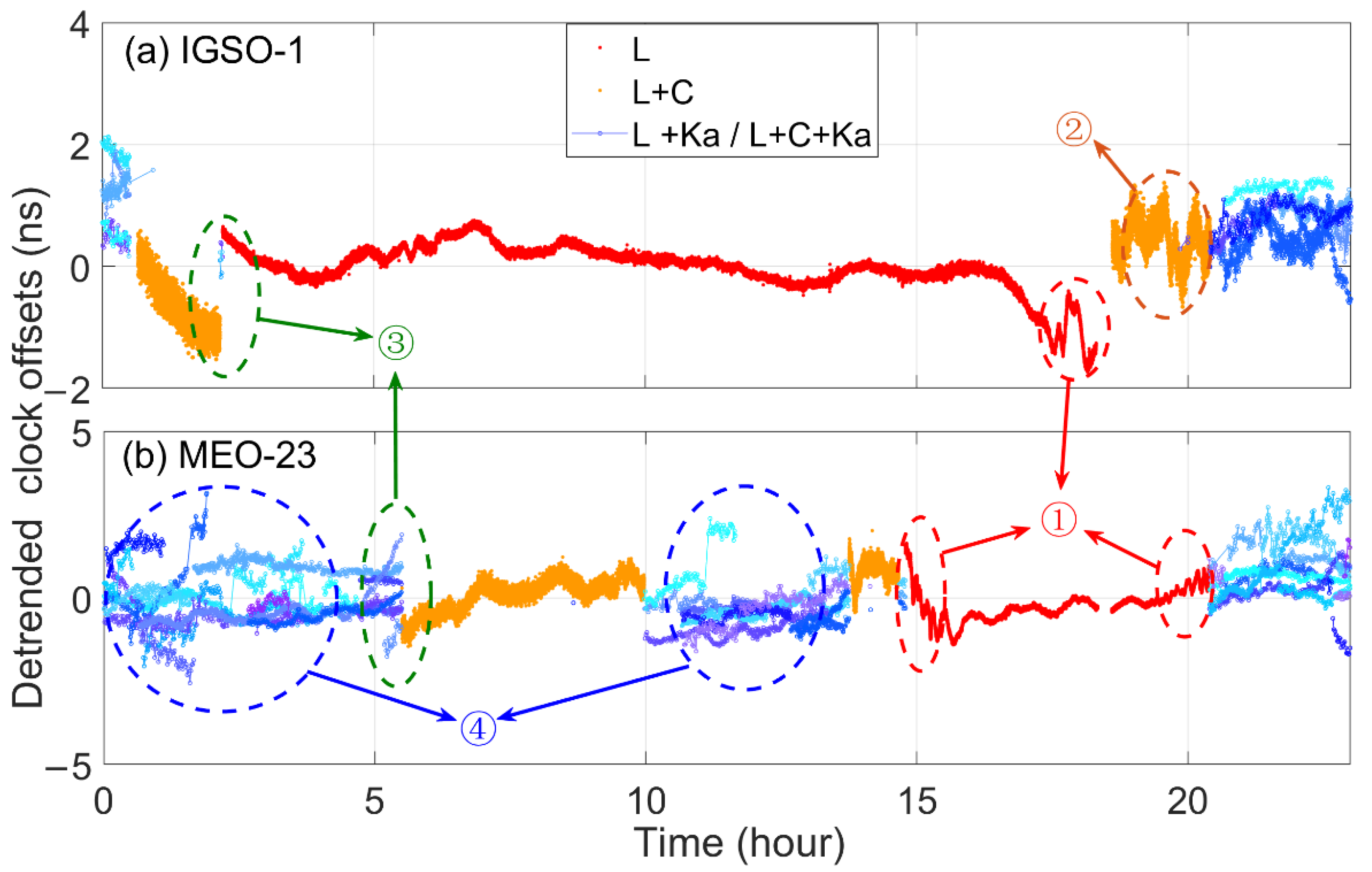
2.1.2. Problems
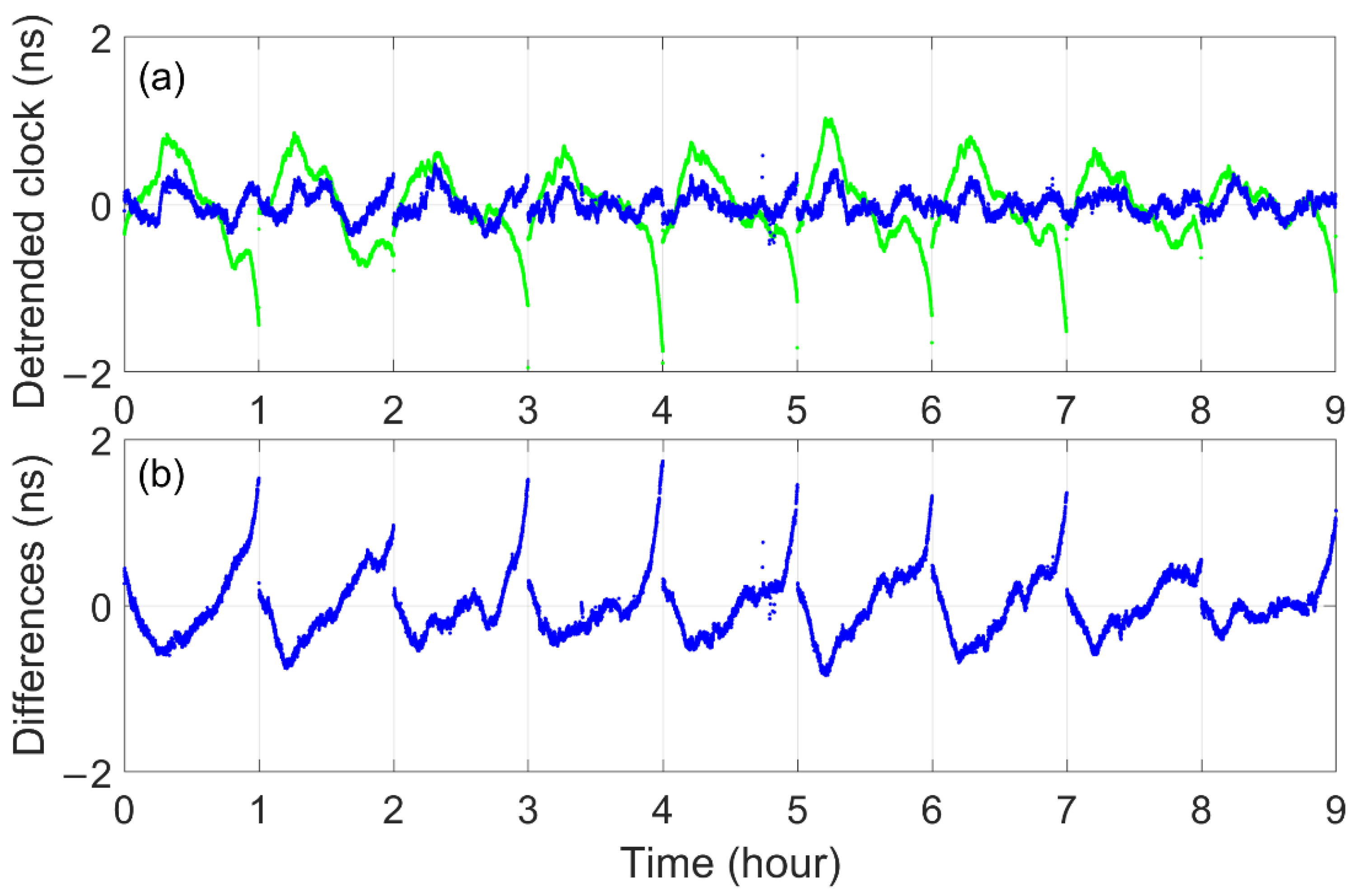
- Because there is little difference between the L-band uplinks and the L-band downlinks, Equation (1) cannot effectively eliminate the ionosphere delay and multipath effects. When the elevation of the L-band antenna is not low enough, the above residual errors will increase rapidly and decrease the accuracy of L-band two-way clock offsets (① in Figure 3).
- Because the noise of C-band measurements is far from other bands’ measurements. The noise of clock offsets will become large when the satellite clock offsets are calculated through C-band two-way inter-stations clock offsets (② in Figure 3).
- Affected by temperature, antenna attitude, illumination, etc., the time delay of antennas has fluctuations, which are difficult to predict. Therefore, once the tracking antenna changes, the “step errors” will appear in the clock offsets (③ in Figure 3).
- The BDS-3 follows a time-division multiple access (TDMA) structure. One satellite connects with different visible satellites at different time in one connectivity cycle. Because an overseas satellite establishes links with different satellites frequently, the different “step errors” will be reflected in the clock offsets of overseas satellites, which are like the noise (④ in Figure 3).
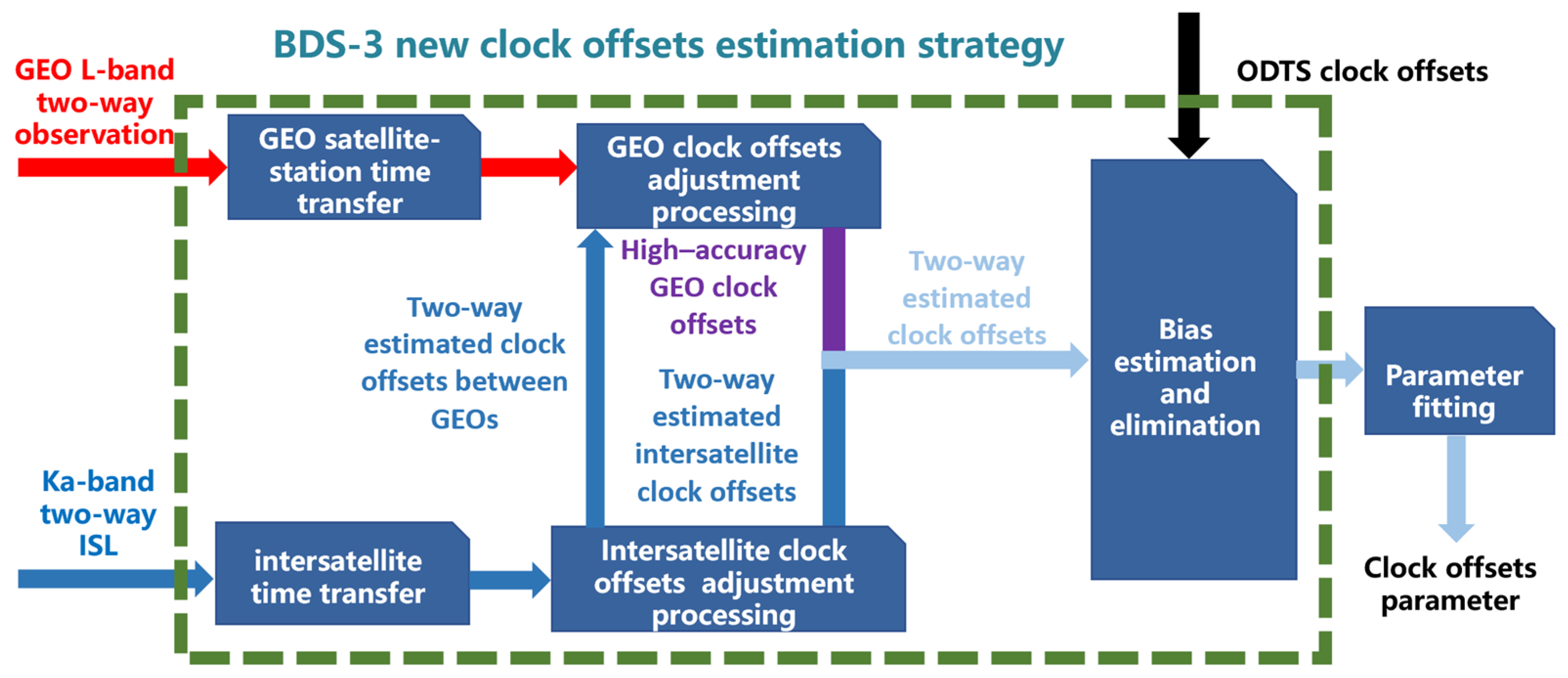
2.2. The New Strategy
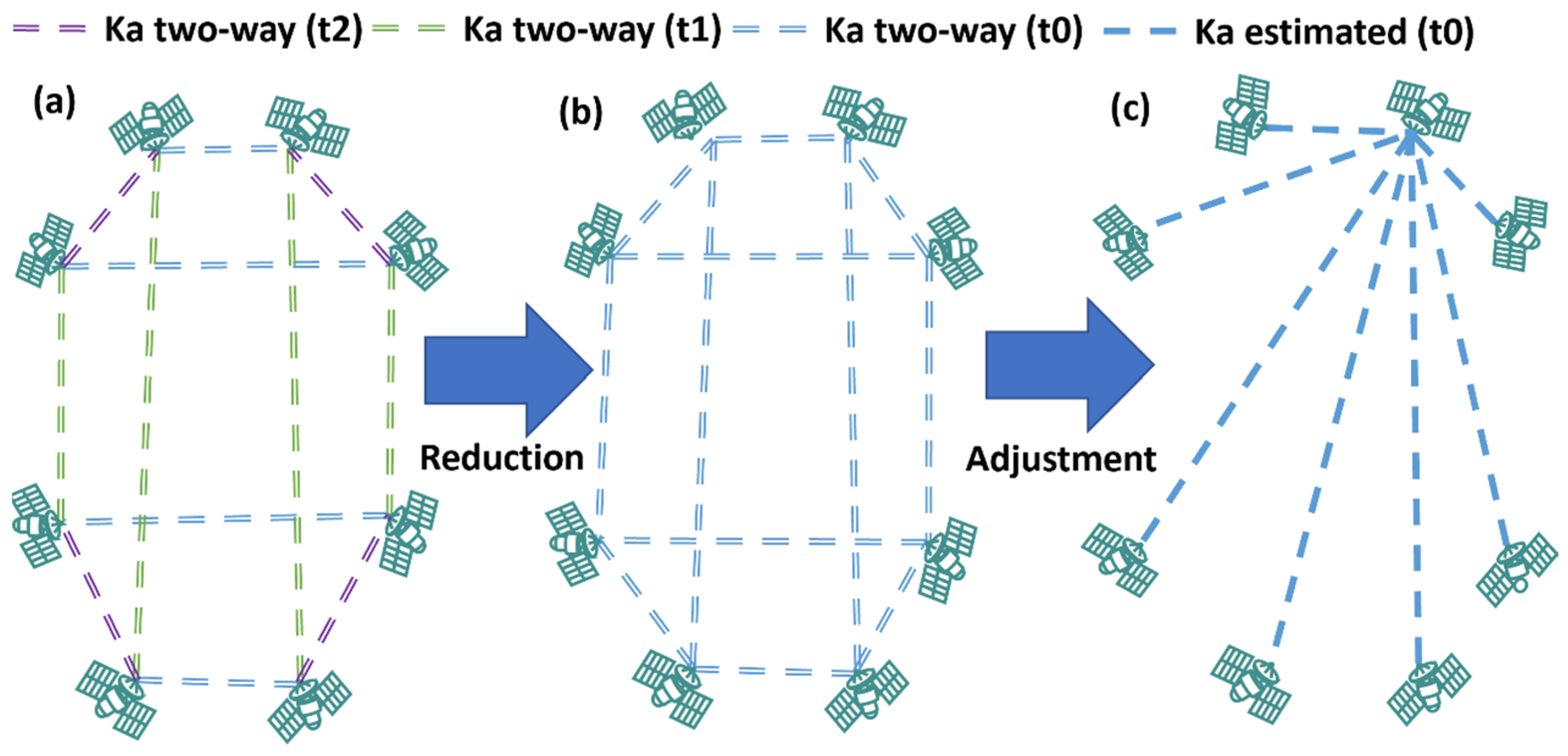
2.2.1. Estimation of Inter-Satellite Clock Offsets
2.2.2. Estimation of Clock Offsets with Respect to BDT
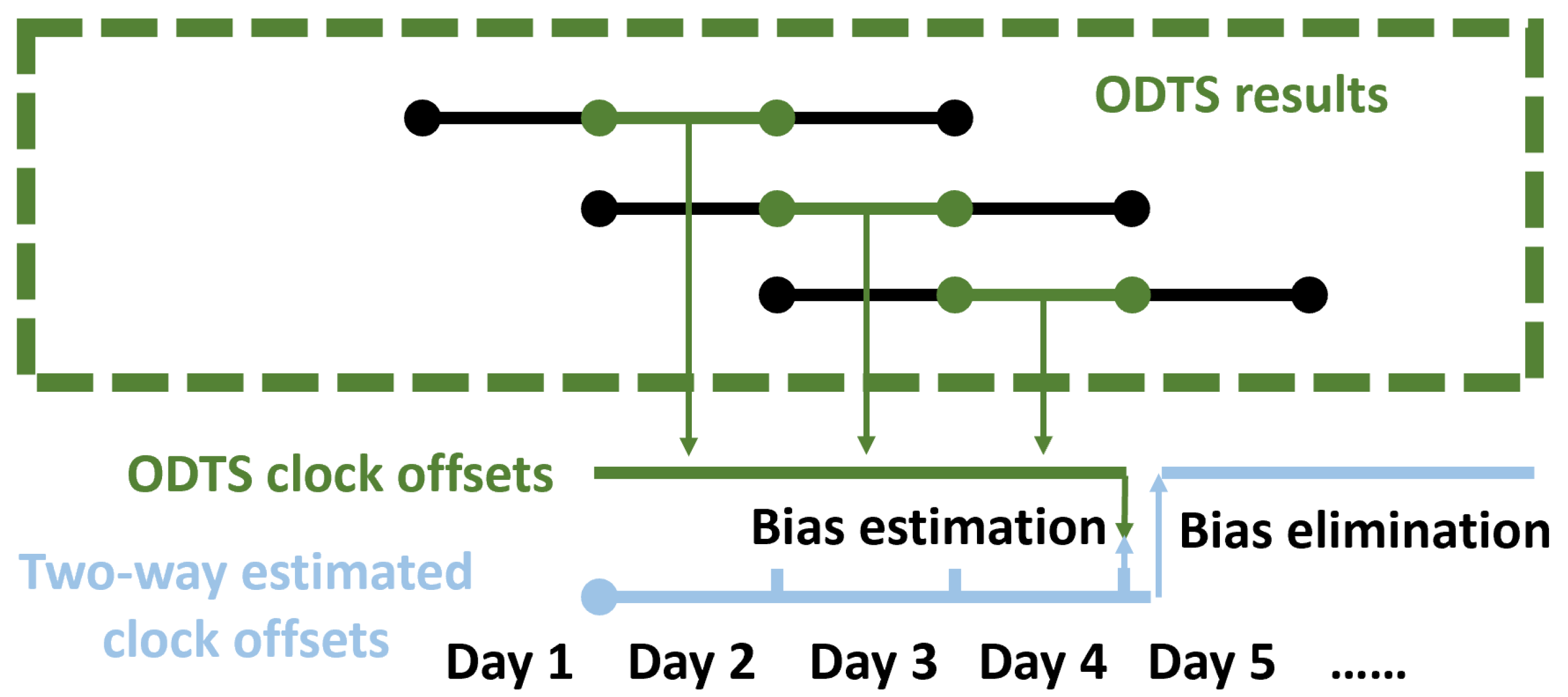
2.2.3. Estimation and Elimination of the Bias of Two-Way Clock Offsets
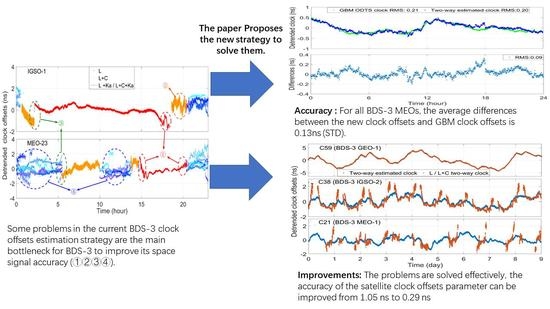
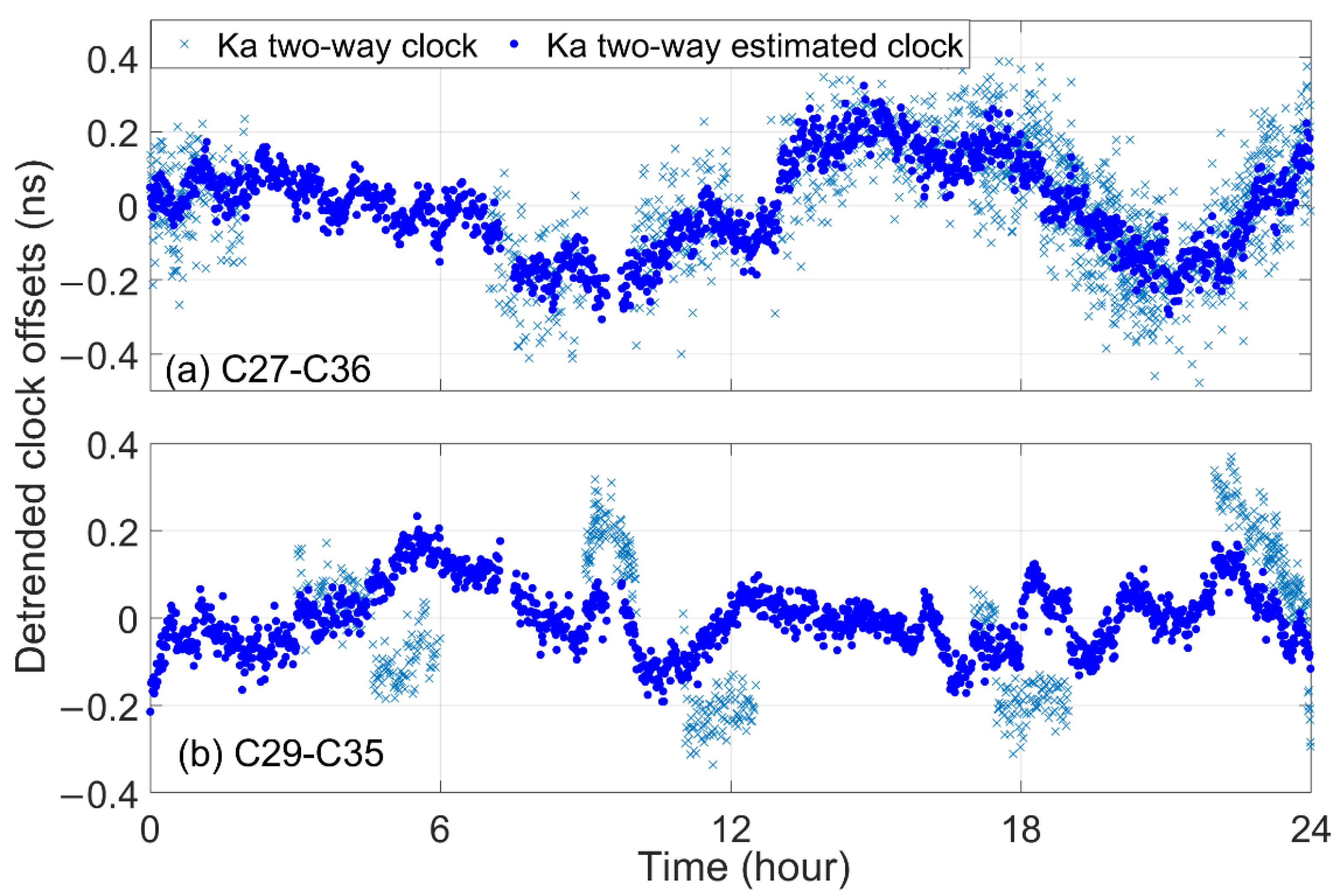
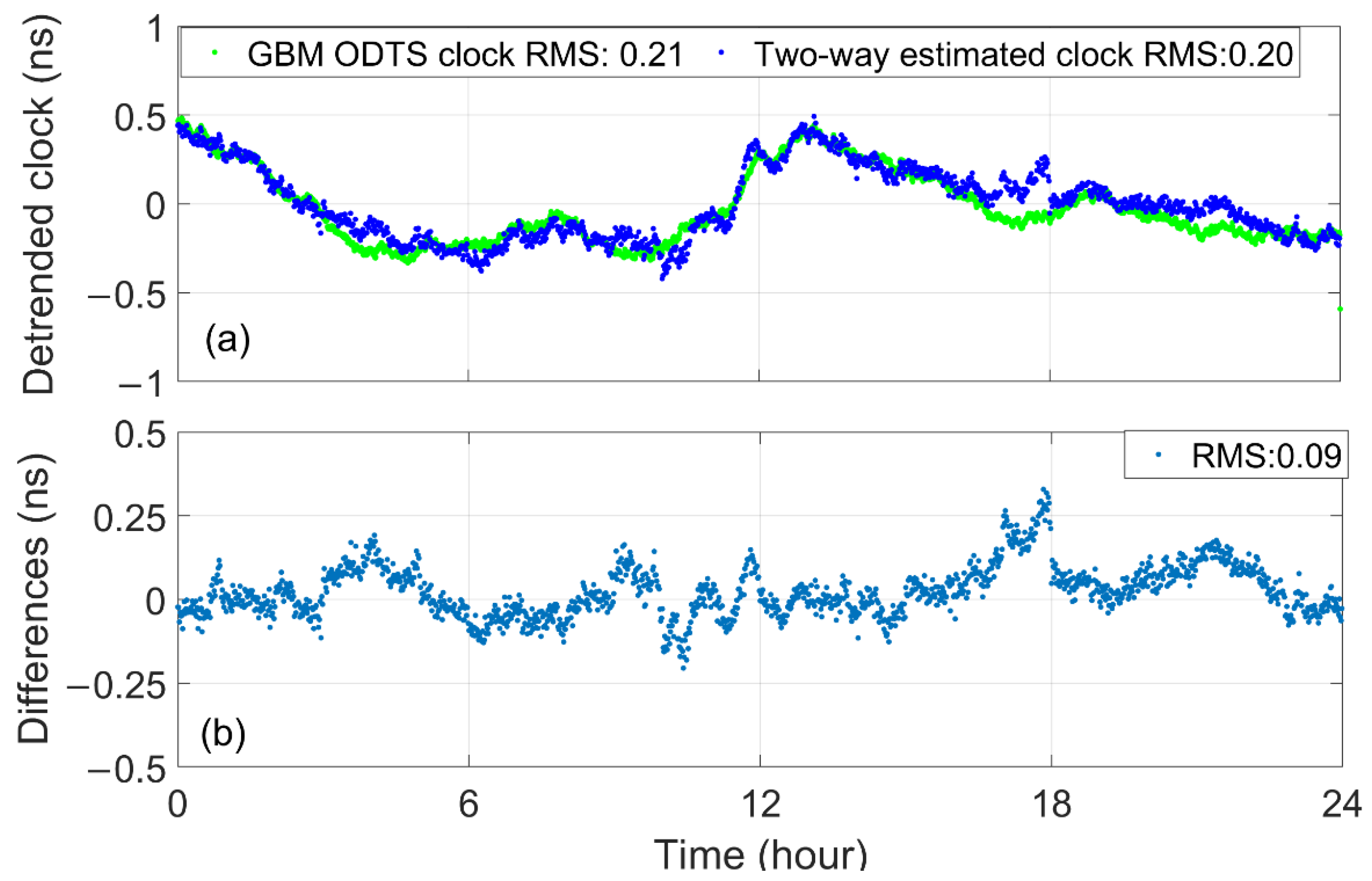
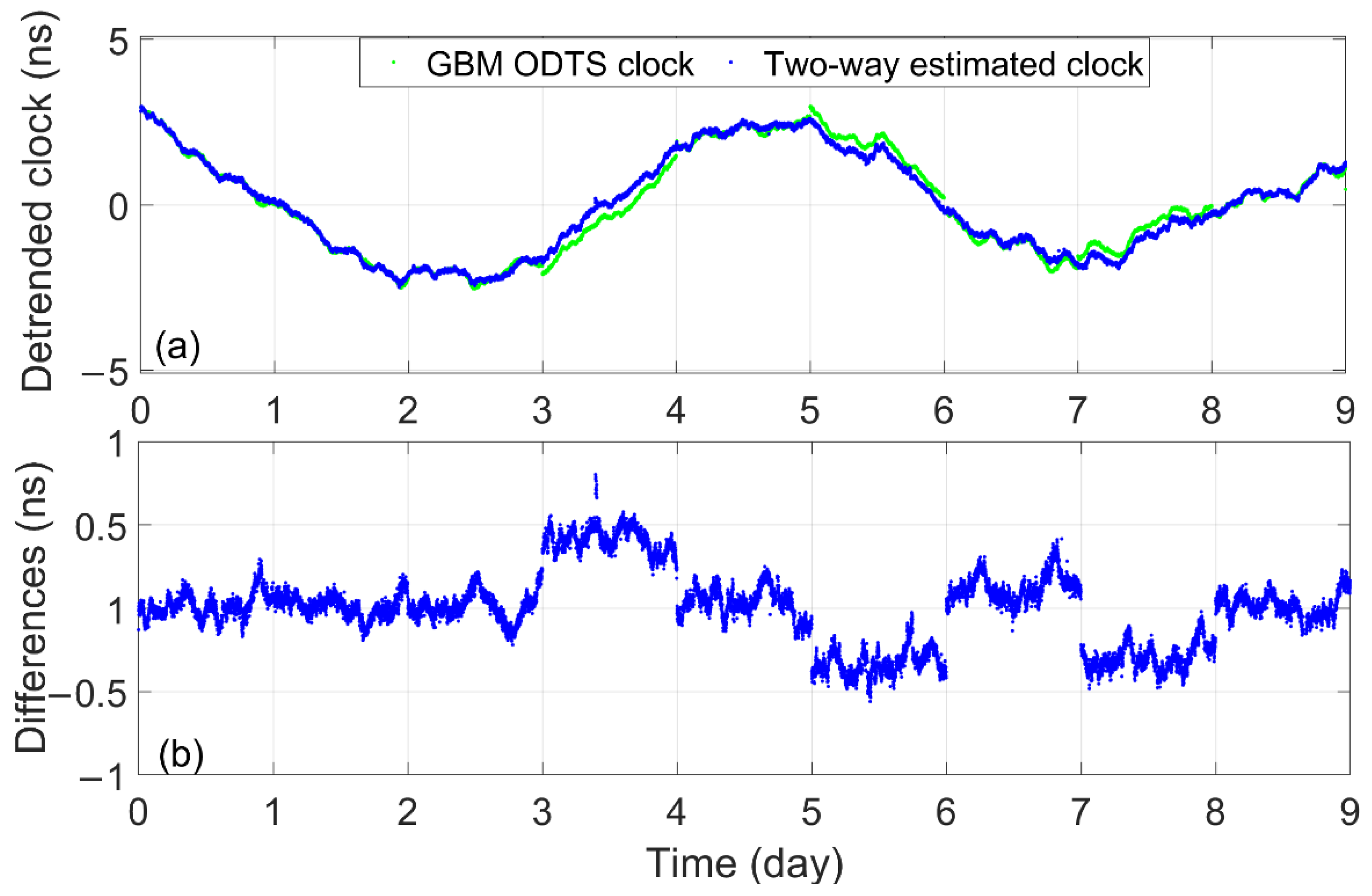
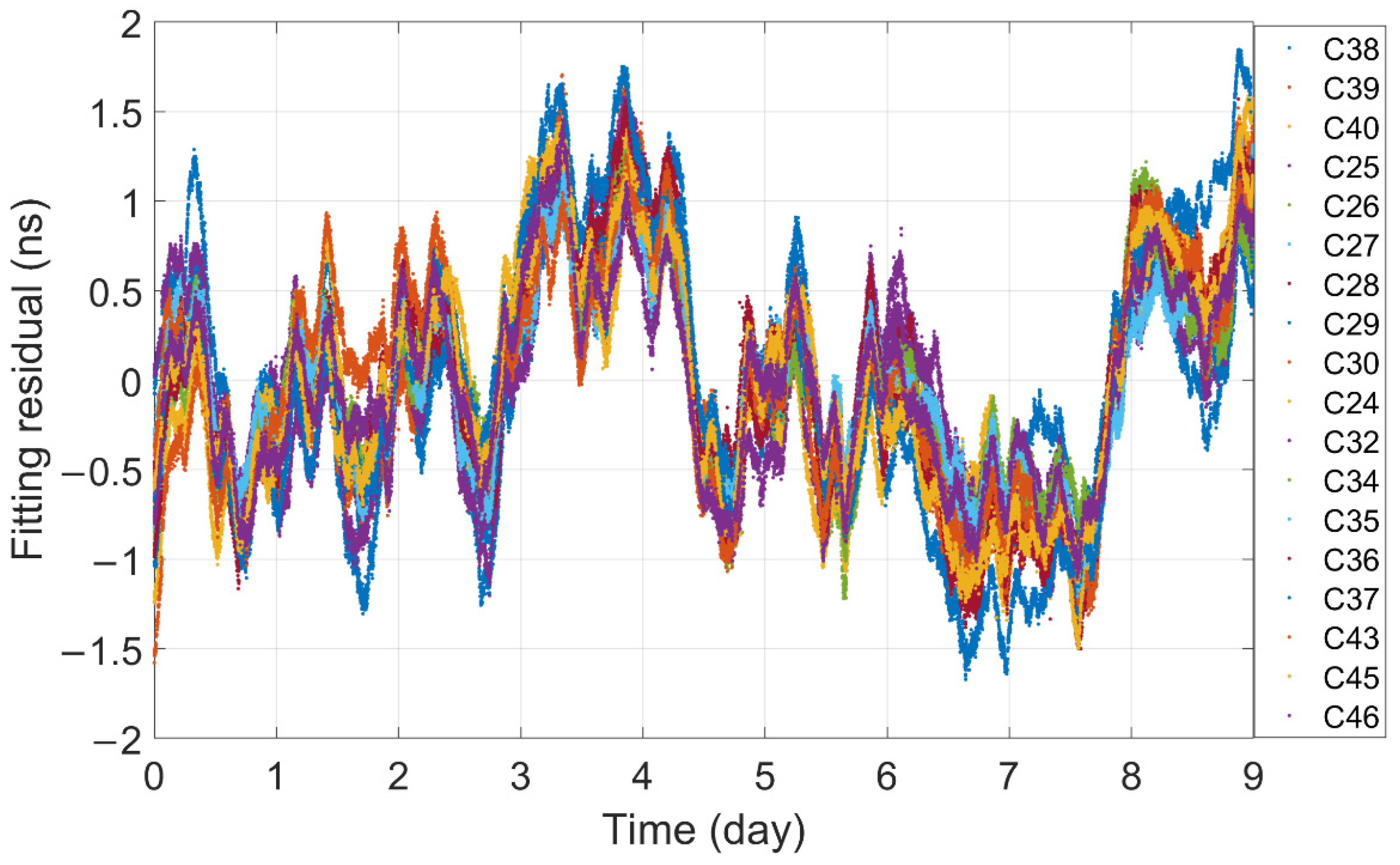
3. Results
- Because the new strategy uses the least square estimation method to estimate clock offsets and will not consider C-band two-way inter-station clock offsets with large noise, the clock offsets can always keep higher precision.
- The final two-way clock offsets between the satellite atomic clock onboard and BDT are only realized through the two-way observation between the MCS larger diameter antennas and GEOs, and the elevation of antennas tracking to GEOs is unchanged all the time. The problem of antennas with low elevation no longer exists.
- The new strategy only introduces three larger-diameter L-band antennas, each of which tracks to the specific GEO anytime. On this basis, the new strategy introduces the bias parameters to absorb the inconsistencies of observations of larger-diameter L-band antennas. All of the above considerations are able to suppress the “step errors.”
- In the new strategy, the concept of intraregional satellite and overseas satellite no longer exist. All satellites play the same role in the inter-satellite clock offsets estimation. Furthermore, their clock offsets with respect to BDT are not dependent on ISL plans and antenna status but can be calculated through the same clock offsets (reference GEO). Therefore, even if IGSOs and MEOs are not able to be observed by ground antenna, the accuracy of their clock offsets will not be lost.
4. Conclusions
- The two-way estimated clock offsets retain the advantages of two-way clock offsets, which are less affected by propagation and position errors than one-way downlink clock offsets.
- All ISLs maintain the inter-satellite relative variation of two-way estimated clock offsets. The inter-satellite relative variation of two-way estimated clock offsets is independent of satellite-ground links.
- All satellite clock offsets are traced to BDT by the same clock offsets, which are only affected by the observations of three large-diameter L-band antennas.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, F.; Wei, Z.; Ming, F.; Zeng, A. The first realization of BeiDou coordinate system and Its assessment. J. Surv. Eng. 2021, 147, 04021004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beidou Timescale Description, 2017, 01. Available online: http://en.beidou.gov.cn/SYSTEMS/Officialdocument/201912/P020191202322231024298.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2017).
- Han, C.; Liu, L.; Cai, Z.; Lin, Y. The space–time references of BeiDou navigation satellite system. Satel. Navig. 2021, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Cai, H.; Meng, Y. BDS-3 RNSS technical characteristics and service performance. Acta Geod. Et Cartogr. Sin. 2019, 48, 810. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, S.; Wu, B.; Hu, X.; Cao, Y.; Yu, Y. Signal-Space Accuracy BeiDou navigation satellite system: Challenges and solutions. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 2017, 2017, 019531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenbruck, O.; Steigenberger, P.; Hauschild, A. Broadcast versus precise ephemerides: A multi-GNSS perspective. GPS Solut. 2015, 19, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, D.L.M.; Raquet, J.F. Broadcast vs. Precise GPS ephemerides: A historical perspective. GPS Solut. 2003, 7, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenbruck, O.; Steigenberger, P.; Hauschild, A. Comparing the ‘Big 4′-A User’s View on GNSS Performance. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/ION Position, Location and Navigation Symposium (PLANS), Portland, OR, USA, 20–23 April 2020; pp. 407–418. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Tang, C.; Song, Y.; Hu, X.; Zhou, S.; Chang, Z. Analysis of signal-in-space ranging error of GNSS navigation message. Sci. Sin. Phys. Mech. Astron. 2021, 51, 019508. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Geng, T.; Zhao, Q.; Xie, X.; Zhou, R. Initial assessment of BDS-3 preliminary system signal-in-space range error. GPS Solut. 2019, 24, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Mao, Y.; Sun, B. Basic performance and future developments of BeiDou global navigation satellite system. Satell. Navig. 2020, 1, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Hu, X.; Tang, C.; Zhou, S.; Yang, Y.; Pan, J.; Ren, H.; Ma, Y.; Tian, Q.; Wu, B.; et al. SIS accuracy and service performance of the BDS-3 basic system. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 2020, 63, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Hu, X.; Zhou, S.; Tang, C.; Guo, R.; Zhu, L.; Tang, G.; Hu, G. Time synchronization of new-generation BDS satellites using inter-satellite link measurements. Adv. Space Res. Off. J. Comm. Space Res. 2018, 61, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steigenberger, P.; Montenbruck, O. Galileo status: Orbits, clocks, and positioning. GPS Solut. 2016, 21, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ge, M.; Dai, X.; Ren, X.; Fritsche, M.; Wickert, J.; Schuh, H. Accuracy and reliability of multi-GNSS real-time precise positioning: GPS, GLONASS, BeiDou, and Galileo. J. Geod. 2015, 89, 607–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formichella, V.; Galleani, L.; Signorile, G.; Sesia, I. Time–frequency analysis of the Galileo satellite clocks: Looking for the J2 relativistic efect and other periodic variations. GPS Solut. 2021, 25, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Tang, G.; Han, C.; Shi, X.; Guo, R.; Zhu, L. The method and experiment analysis of two-way common-view satellite time transfer for compass system. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 2015, 58, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Hu, X.; Liu, L.; Guo, R.; Zhu, L.; Chang, Z.; Tang, C.; Gong, X.; Li, R.; Yu, Y. Applications of two-way satellite time and frequency transfer in the BeiDou navigation satellite system. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 2016, 59, 109511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Hu, X.; Zhou, S.; Tang, C.; Wang, D.; Yang, Y.; Dong, W. Full-ISL clock offset estimation and prediction algorithm for BDS3. GPS Solut. 2021, 25, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dow, J.M.; Neilan, R.E.; Rizos, C. The International GNSS Service in a changing landscape of Global Navigation Satellite Systems. J. Geod. 2009, 83, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Wang, Q.; Dardanelli, G. A Review on Multi-GNSS for Earth Observation and Emerging Applications. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenbruck, O.; Steigenberger, P.; Prange, L.; Deng, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Perosanz, F.; Romero, I.; Noll, C.; Stürze, A.; Weber, G.; et al. The Multi-GNSS Experiment (MGEX) of the International GNSS Service (IGS)-Achievements, prospects and challenges. Adv. Space Res. Off. J. Comm. Space Res. 2017, 59, 1671–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhao, Q.; Guo, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, G. The contribution of intersatellite links to BDS-3 orbit determination: Model refinement and comparisons. Navigation 2019, 66, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, C.; Hu, X.; Zhou, S.; Liu, L.; Pan, J.; Chen, L.; Guo, R.; Zhu, L.; Hu, G.; Li, X.; et al. Initial results of centralized autonomous orbit determination of the new-generation BDS satellites with inter-satellite link measurements. J. Geod. 2018, 92, 1155–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.Y.; Xiaogong, H.U.; Tang, C.P.; Zhou, S.; Li, R.; Zhu, L.; Tang, G.; Hu, G.; Chang, Z.; Wu, S.; et al. System error calibration for time division multiple access inter-satellite payload of new-generation Beidou satellites. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2017, 62, 2671–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Hu, X.; Chen, J.; Guo, R.; Tang, C.; Zhou, S.; Zhao, L.; Xu, J. Inter-Satellite link enhanced orbit determination for BeiDou-3. J. Navig. 2020, 73, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Tang, C.; Hu, X.; Zhu, X.; Sun, L.; Yang, Y.; Chang, Z.; Yang, J. Long-Term Frequency Stability Analysis for RRFM and Power-Law Noise Determination of the BeiDou-3 Satellite On-Board Atomic Clocks. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 1002515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Cai, Z. Relativistic effects to the onboard BeiDou satellite clocks. Navigation 2019, 66, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhou, S.; Hu, X.; Liu, L.; Shuai, T.; Xie, Y.; Tang, C.; Pan, J.; Zhu, L.; Chang, Z. Performance of the BDS3 experimental satellite passive hydrogen maser. GPS Solut. 2018, 22, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Tang, C.; Chen, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, S.; Hu, X.; Tian, Q.; Yang, Y. Pseudorange Bias Analysis and Preliminary Service Performance Evaluation of BDSBAS. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.; Cao, Y.; Hu, X.; Tang, C.; Zhou, S.; Guo, R.; Li, X.; Tian, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yang, J. A Study on Pseudorange Biases in BDS B1I/B3I Signals and the Impacts on Beidou Wide Area Differential Services. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ding, Q.; Gao, W.; Li, J.; Xu, Y.; Sun, B. Principle and performance of BDSBAS and PPP-B2b of BDS-3. Satell. Navig. 2022, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhiguo, D.E.N.G.; Jungang, W.A.N.G.; Maorong, G.E. The GBM rapid product and the improvement from the undifferenced ambiguity. Resolution. Acta Geodeatica Et Cartogr. Sin. 2022, 51, 544–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Guo, J.; Hu, Y.; Sun, B.; Wu, J.; Zhao, D.; He, Z. Influence of Precise Products on the Day-Boundary Discontinuities in GNSS Carrier Phase Time Transfer. Sensors 2021, 21, 1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, F.; Ye, S.; Chen, D.; Tang, L.; Wang, C.; Ge, M.; Neitzel, F. Advancing the Solar Radiation Pressure Model for BeiDou-3 IGSO Satellites. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Satellite PRN | The STD of the Differences between Two Kinds of Clock Offsets (ns) | 24 h Fitting Residual (ns) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ODTS Clock (GBM) | Two-Way Estimated Clock | ||
| C38 | 0.25 | 0.26 | 0.12 |
| C39 | 0.36 | 0.37 | 0.09 |
| C40 | 0.39 | 0.39 | 0.08 |
| C25 | 0.16 | 0.18 | 0.11 |
| C26 | 0.16 | 0.14 | 0.09 |
| C27 | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.11 |
| C28 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.12 |
| C29 | 0.19 | 0.13 | 0.22 |
| C30 | 0.15 | 0.17 | 0.10 |
| C20 | 0.07 | 0.18 | 0.16 |
| C21 | 0.09 | 0.21 | 0.21 |
| C22 | 0.07 | 0.18 | 0.17 |
| C23 | 0.14 | 0.18 | 0.14 |
| C24 | 0.12 | 0.16 | 0.17 |
| C32 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.12 |
| C33 | 0.12 | 0.18 | 0.14 |
| C34 | 0.15 | 0.13 | 0.08 |
| C35 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.10 |
| C36 | 0.14 | 0.13 | 0.07 |
| C37 | 0.11 | 0.15 | 0.10 |
| C41 | 0.08 | 0.10 | 0.10 |
| C42 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.11 |
| C43 | 0.15 | 0.24 | 0.15 |
| C44 | 0.12 | 0.20 | 0.16 |
| C45 | 0.23 | 0.26 | 0.08 |
| C46 | 0.23 | 0.25 | 0.11 |
| C59 | 0.50 | 0.65 | 0.32 |
| C60 | 0.61 | 1.00 | 0.17 |
| MEO | 0.14 | 0.19 | 0.13 |
| IGSO | 0.40 | 0.71 | 0.11 |
| GEO | 0.36 | 1.10 | 0.36 |
| Average of all satellites | 0.19 | 0.23 | 0.13 |
| PRN | RMS (ns) | 95% Error (ns) |
|---|---|---|
| C19 | 0.27 | 0.55 |
| C20 | 0.27 | 0.58 |
| C21 | 0.31 | 0.66 |
| C22 | 0.31 | 0.67 |
| C23 | 0.30 | 0.61 |
| C24 | 0.29 | 0.62 |
| C25 | 0.28 | 0.59 |
| C26 | 0.29 | 0.65 |
| C27 | 0.26 | 0.56 |
| C28 | 0.28 | 0.62 |
| C29 | 0.30 | 0.64 |
| C30 | 0.27 | 0.59 |
| C32 | 0.27 | 0.57 |
| C33 | 0.28 | 0.59 |
| C34 | 0.28 | 0.59 |
| C35 | 0.28 | 0.59 |
| C36 | 0.27 | 0.56 |
| C37 | 0.25 | 0.53 |
| C38 | 0.28 | 0.62 |
| C39 | 0.26 | 0.53 |
| C40 | 0.26 | 0.56 |
| C41 | 0.29 | 0.65 |
| C42 | 0.26 | 0.54 |
| C43 | 0.28 | 0.57 |
| C44 | 0.37 | 0.77 |
| C45 | 0.27 | 0.58 |
| C46 | 0.3 | 0.62 |
| C59 | 0.33 | 0.71 |
| C60 | 0.36 | 0.86 |
| C61 | 0.38 | 0.66 |
| Average of all satellites | 0.29 | 0.61 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, J.; Tang, C.; Zhou, S.; Song, Y.; Liu, J.; Xiang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tian, Q.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Z.; et al. High-Accuracy Clock Offsets Estimation Strategy of BDS-3 Using Multi-Source Observations. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4674. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14184674
Yang J, Tang C, Zhou S, Song Y, Liu J, Xiang Y, Liu Y, Tian Q, Yang Y, Yang Z, et al. High-Accuracy Clock Offsets Estimation Strategy of BDS-3 Using Multi-Source Observations. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(18):4674. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14184674
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Jianhua, Chengpan Tang, Sanshi Zhou, Yezhi Song, Jinhuo Liu, Yu Xiang, Yuchen Liu, Qiuning Tian, Yufei Yang, Zuo Yang, and et al. 2022. "High-Accuracy Clock Offsets Estimation Strategy of BDS-3 Using Multi-Source Observations" Remote Sensing 14, no. 18: 4674. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14184674
APA StyleYang, J., Tang, C., Zhou, S., Song, Y., Liu, J., Xiang, Y., Liu, Y., Tian, Q., Yang, Y., Yang, Z., & Hu, X. (2022). High-Accuracy Clock Offsets Estimation Strategy of BDS-3 Using Multi-Source Observations. Remote Sensing, 14(18), 4674. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14184674