Spatio-Temporal Dynamics and Driving Forces of Multi-Scale CO2 Emissions by Integrating DMSP-OLS and NPP-VIIRS Data: A Case Study in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Areas and Data Sources
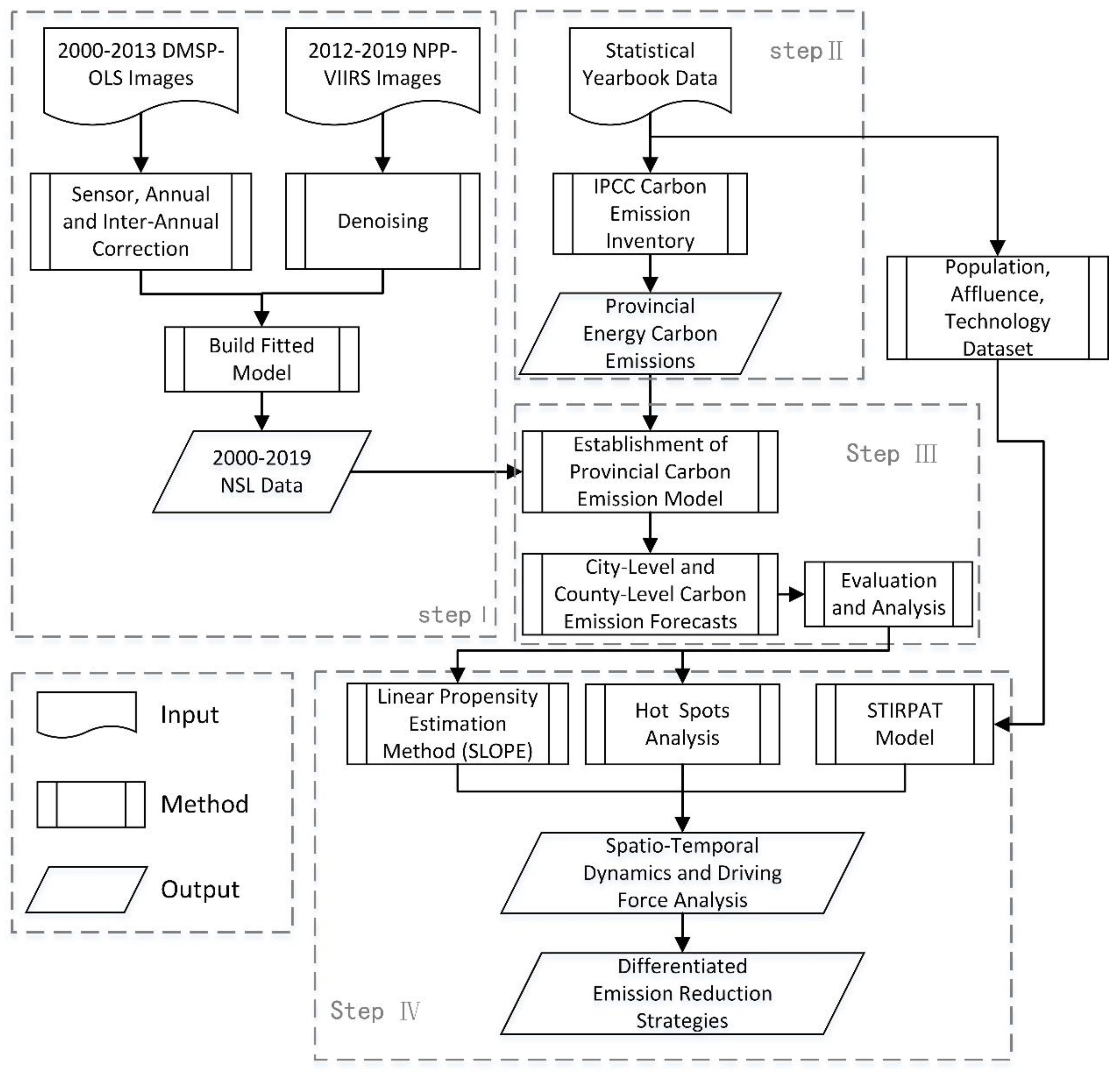
3. Methodology
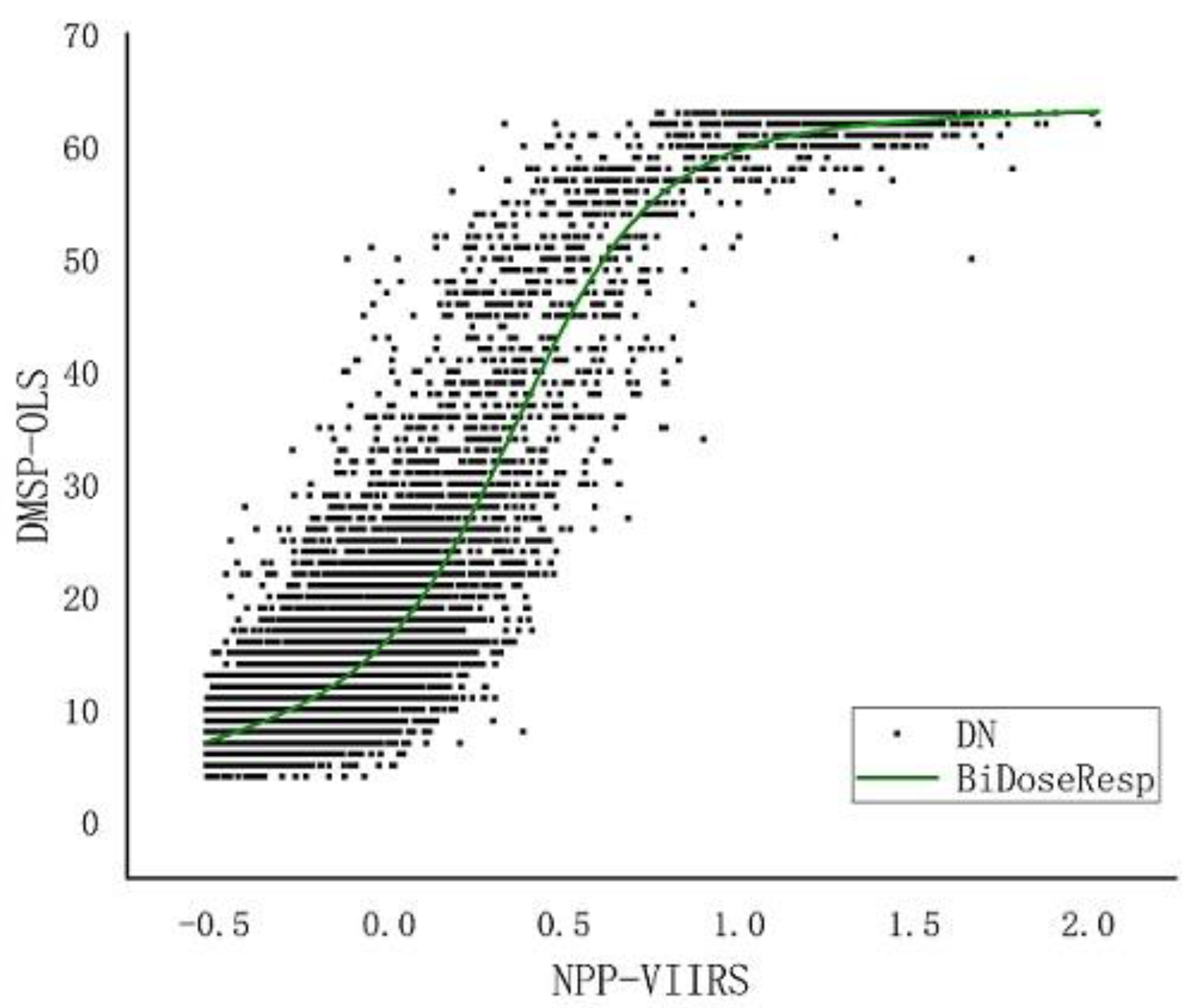
3.1. Integration of Two Kinds of Night Light Data
- DMSP-OLS data were corrected by sensor, within year and between years;
- Annual synthesis and denoising of NPP-VIIRS data;
- Using a model to integrate the former two datasets to obtain the stable nighttime lighting data from 2000–2019.
3.2. Estimating CO2 Emissions According to IPCC
3.3. Estimating CO2 Emissions at Municipal and County Levels
3.4. Analysis of Spatio-Temporal Pattern
3.4.1. Linear Propensity Estimation (Slope)
3.4.2. Global Autocorrelation
3.4.3. Hot Spots Analysis
3.5. Spatial Econometrics Models
4. Results
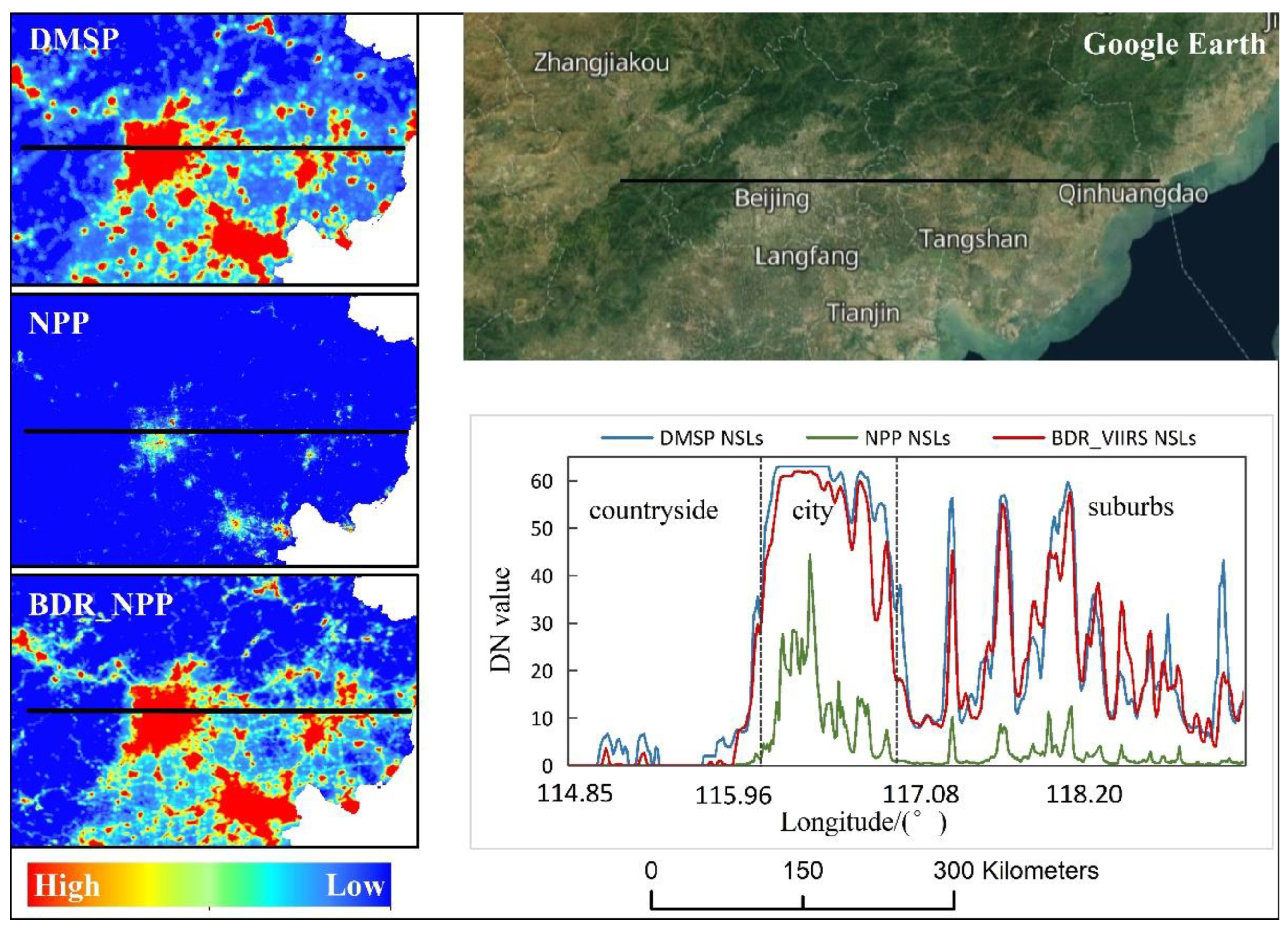
4.1. NSL Mutual Correction Results
4.2. Accuracy Evaluation of CO2 Emission Estimation
4.3. Spatio-Temporal Dynamics of CO2 Emissions
4.3.1. Temporal Variations
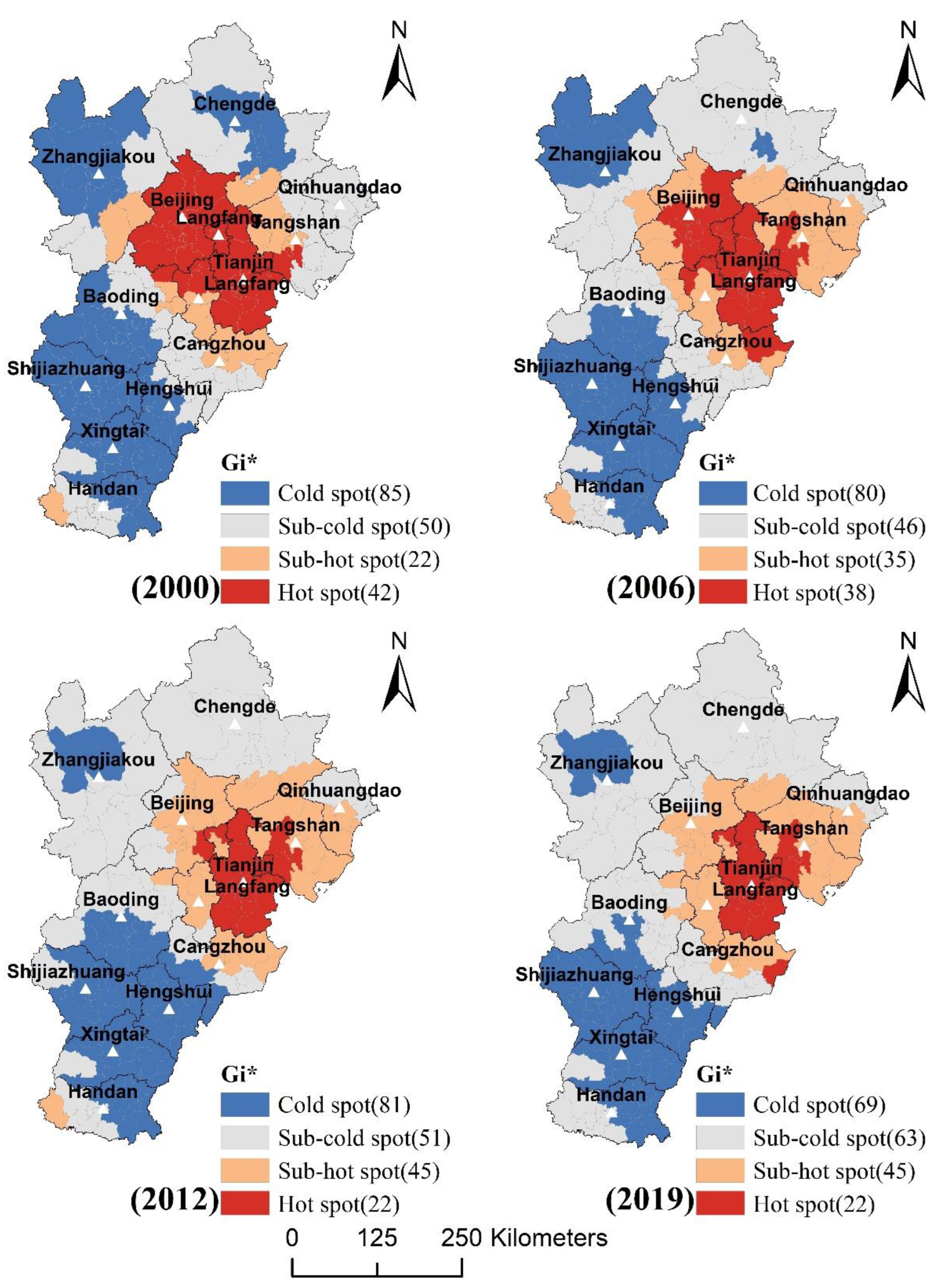
4.3.2. Spatial Variations
4.4. Analysis of Driving Force
5. Discussion
5.1. Accuracy Assessment of CO2 Emissions
5.2. The Role of Influencing Factors
5.3. Compared with Previous Studies
6. Conclusions and Policy Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Soytas, U.; Sari, R.; Ewing, B.T. Energy consumption, income, and carbon emissions in the United States. Ecol. Econ. 2007, 62, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciais, P.; Wang, Y.; Andrew, R.; Bréon, F.M.; Chevallier, F.; Broquet, G.; Nabuurs, G.J.; Peters, G.; McGrath, M.; Meng, W. Biofuel burning and human respiration bias on satellite estimates of fossil fuel CO2 emissions. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 074036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Wang, S.; Li, G. Changing urban forms and carbon dioxide emissions in China: A case study of 30 provincial capital cities. Appl. Energy 2015, 158, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Liao, J.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, H.; Huang, N.; Kuang, Y. China’s 19-year city-level carbon emissions of energy consumptions, driving forces and regionalized mitigation guidelines. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 35, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apergis, N.; Payne, J.E. The causal dynamics between coal consumption and growth: Evidence from emerging market economies. Appl. Energy 2010, 87, 1972–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
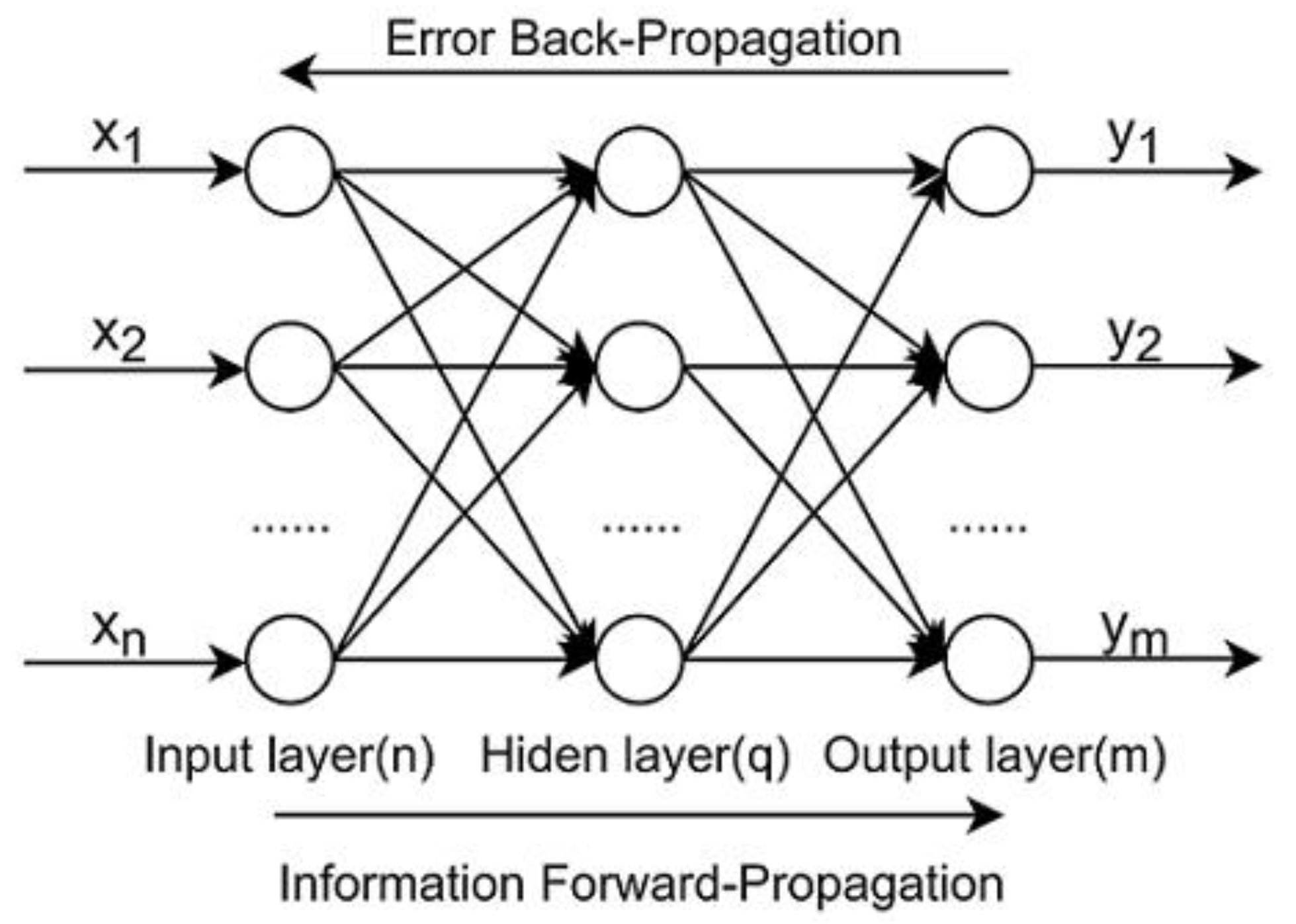
- Guo, D.; Chen, H.; Long, R. Can China fulfill its commitment to reducing carbon dioxide emissions in the Paris Agreement? Analysis based on a back-propagation neural network. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 27451–27462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Cai, B. A two-level comparison of CO2 emission data in China: Evidence from three gridded data sources. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 148, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallapaty, S. How China could be carbon neutral by mid-century. Nature 2020, 586, 482–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Liang, Z.; Fan, J.; Zhang, J.; Luo, Y.; Zhu, X. Spatial decomposition of city-level CO2 emission changes in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 296, 126613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Tian, M.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Peng, C. Quantification of provincial-level carbon emissions from energy consumption in China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 3658–3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, D.B.; Liu, G.; Løvik, A.N.; Modaresi, R.; Pauliuk, S.; Steinhoff, F.S.; Brattebø, H. Carbon emissions of infrastructure development. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 11739–11746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’neill, B.C.; Dalton, M.; Fuchs, R.; Jiang, L.; Pachauri, S.; Zigova, K. Global demographic trends and future carbon emissions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 17521–17526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral, S.; Câmara, G.; Monteiro, A.M.V.; Quintanilha, J.A.; Elvidge, C.D. Estimating population and energy consumption in Brazilian Amazonia using DMSP night-time satellite data. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2005, 29, 179–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, P.C.; Taylor, M.J.; Elvidge, C.D. Using DMSP OLS imagery to characterize urban populations in developed and developing countries. In Remote Sensing of Urban and Suburban Areas; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 329–348. [Google Scholar]
- Alahmadi, M.; Atkinson, P.M. Three-fold urban expansion in Saudi Arabia from 1992 to 2013 observed using calibrated DMSP-OLS night-time lights imagery. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, J.; Olivia, S.; Boe-Gibson, G.; Li, C. Which night lights data should we use in economics, and where? J. Dev. Econ. 2021, 149, 102602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chand, T.K.; Badarinath, K.; Elvidge, C.; Tuttle, B. Spatial characterization of electrical power consumption patterns over India using temporal DMSP-OLS night-time satellite data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 647–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Ziskin, D.; Baugh, K.E.; Tuttle, B.T.; Ghosh, T.; Pack, D.W.; Erwin, E.H.; Zhizhin, M. A fifteen year record of global natural gas flaring derived from satellite data. Energies 2009, 2, 595–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Chen, Y.; Yu, B.; Xu, T.; Chen, Z.; Liu, R.; Li, L.; Wu, J. Modeling spatiotemporal CO2 (carbon dioxide) emission dynamics in China from DMSP-OLS nighttime stable light data using panel data analysis. Appl. Energy 2016, 168, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, J.; Peng, J.; Cao, Q. The uncertainty of nighttime light data in estimating carbon dioxide emissions in China: A comparison between DMSP-OLS and NPP-VIIRS. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Chen, Y.; Ji, G.; Wang, Z. Residential carbon dioxide emissions at the urban scale for county-level cities in China: A comparative study of nighttime light data. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 180, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Q.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Shang, Y. Multiscale analysis on spatiotemporal dynamics of energy consumption CO2 emissions in China: Utilizing the integrated of DMSP-OLS and NPP-VIIRS nighttime light datasets. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 134394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, L.; Graus, W.; Worrell, E.; Huang, B. Estimating CO2 (carbon dioxide) emissions at urban scales by DMSP/OLS (Defense Meteorological Satellite Program’s Operational Linescan System) nighttime light imagery: Methodological challenges and a case study for China. Energy 2014, 71, 468–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Gao, M.; Cheng, S.; Hou, W.; Song, M.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Shan, Y. County-level CO2 emissions and sequestration in China during 1997–2017. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, B.W. The LMDI approach to decomposition analysis: A practical guide. Energy Policy 2005, 33, 867–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Liu, L.-C.; Wu, G.; Wei, Y.-M. Analyzing impact factors of CO2 emissions using the STIRPAT model. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2006, 26, 377–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaika, D.; Zervas, E. The Environmental Kuznets Curve (EKC) theory—Part A: Concept, causes and the CO2 emissions case. Energy Policy 2013, 62, 1392–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaninsky, A. Factorial decomposition of CO2 emissions: A generalized Divisia index approach. Energy Econ. 2014, 45, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brizga, J.; Feng, K.; Hubacek, K. Drivers of CO2 emissions in the former Soviet Union: A country level IPAT analysis from 1990 to 2010. Energy 2013, 59, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcan, B.; Ulucak, R. An empirical investigation of nuclear energy consumption and carbon dioxide (CO2) emission in India: Bridging IPAT and EKC hypotheses. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2021, 53, 2056–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- York, R.; Rosa, E.A.; Dietz, T. STIRPAT, IPAT and ImPACT: Analytic tools for unpacking the driving forces of environmental impacts. Ecol. Econ. 2003, 46, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Zhou, C.; Pei, T.; Haynie, S.; Fan, J. Responses of Suomi-NPP VIIRS-derived nighttime lights to socioeconomic activity in China’s cities. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 5, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, C.; Cheng, W.; Li, M.; Huang, K. Building a series of consistent night-time light data (1992–2018) in Southeast Asia by integrating DMSP-OLS and NPP-VIIRS. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 58, 1843–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeswani, R.; Kulshrestha, A.; Gupta, P.K.; Srivastav, S. Evaluation of the consistency of DMSP-OLS and SNPP-VIIRS Night-time Light Datasets. J. Geomat 2019, 13, 98–105. [Google Scholar]
- Liddle, B.; Lung, S. Age-structure, urbanization, and climate change in developed countries: Revisiting STIRPAT for disaggregated population and consumption-related environmental impacts. Popul. Environ. 2010, 31, 317–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbaz, M.; Chaudhary, A.; Ozturk, I. Does urbanization cause increasing energy demand in Pakistan? Empirical evidence from STIRPAT model. Energy 2017, 122, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, M.; Zhou, J. Has air pollution emission level in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region peaked? A panel data analysis. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 119, 106875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, X.; Shao, S. Decoupling CO2 emissions and industrial growth in China over 1993–2013: The role of investment. Energy Econ. 2016, 60, 275–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yin, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X. An empirical research on the influencing factors of regional CO2 emissions: Evidence from Beijing city, China. Appl. Energy 2012, 100, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Guan, D.; Moore, S.; Lee, H.; Su, J.; Zhang, Q. Climate policy: Steps to China’s carbon peak. Nature 2015, 522, 279–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W. The contribution of foreign direct investment to clean energy use, carbon emissions and economic growth. Energy Policy 2013, 55, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Tan, X.; Li, Y.; Hu, L. Economic growth, foreign direct investment and CO2 emissions in China: A panel granger causality analysis. Sustainability 2016, 8, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, X.; Wu, R.; Cai, T. Revisiting the environmental Kuznets curve for city-level CO2 emissions: Based on corrected NPP-VIIRS nighttime light data in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 268, 121575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Liu, Y. The Peak Value of Carbon Emissions in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region Based on the STIRPAT Model and Scenario Design. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2016, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

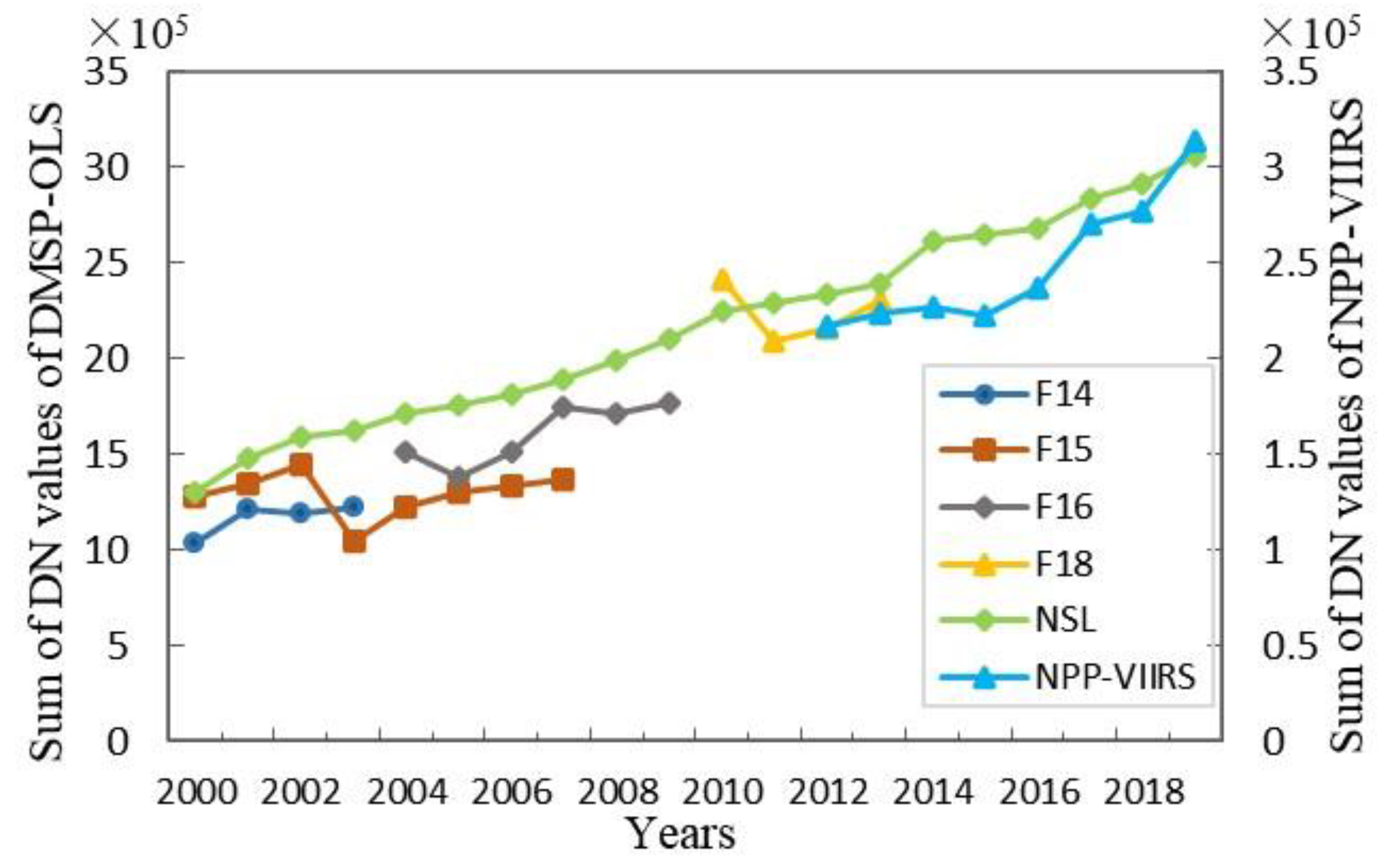
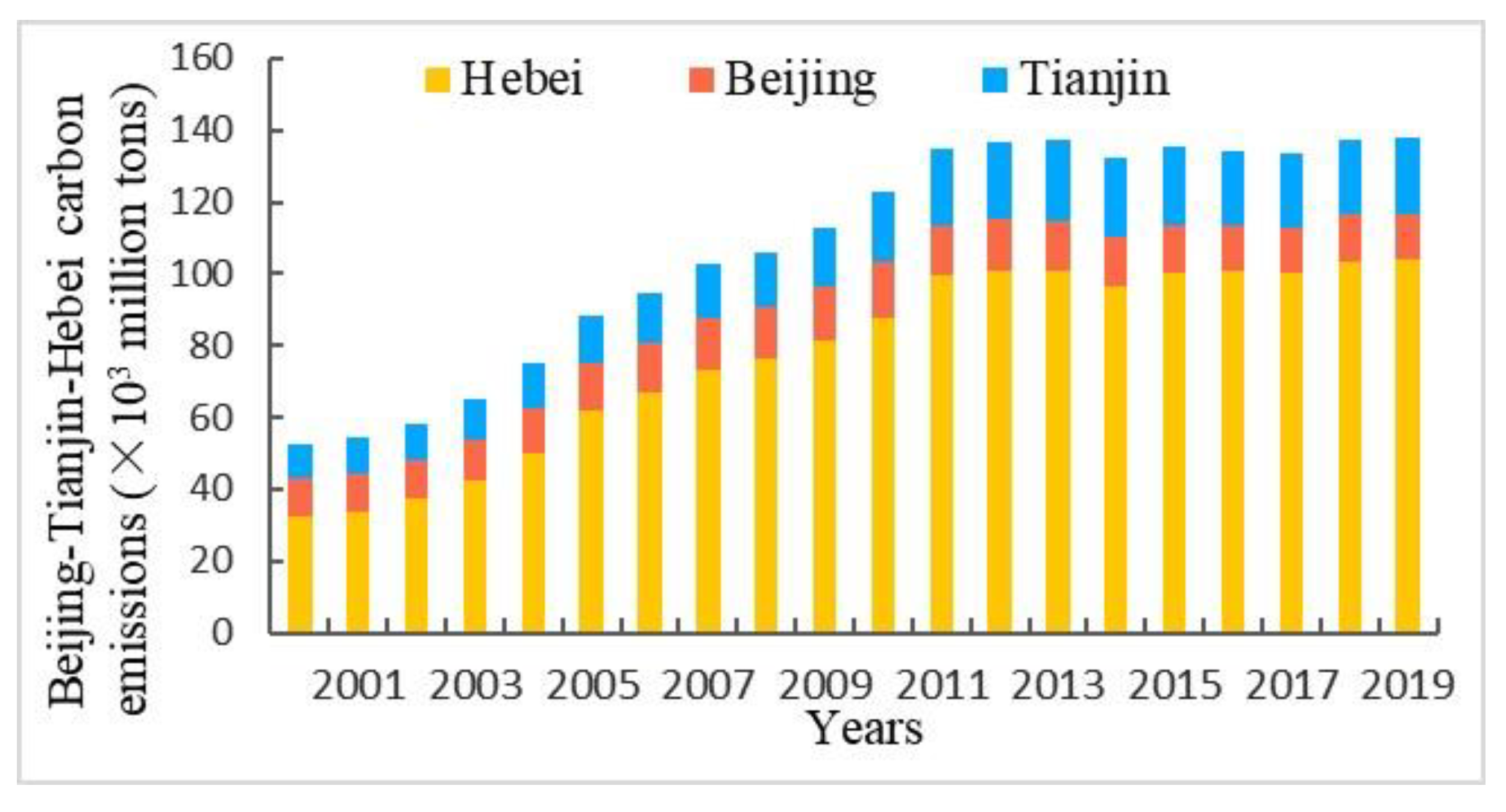
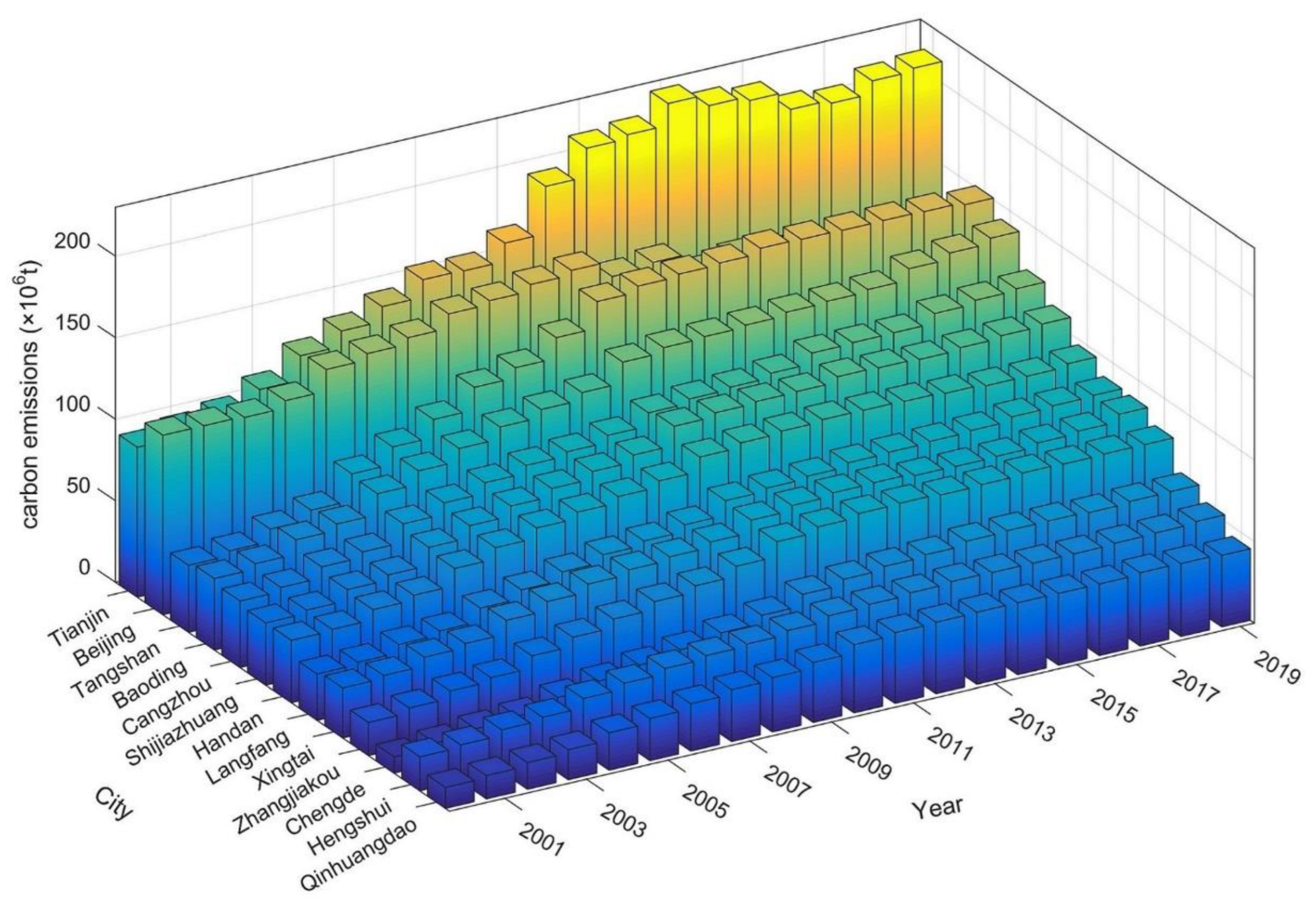

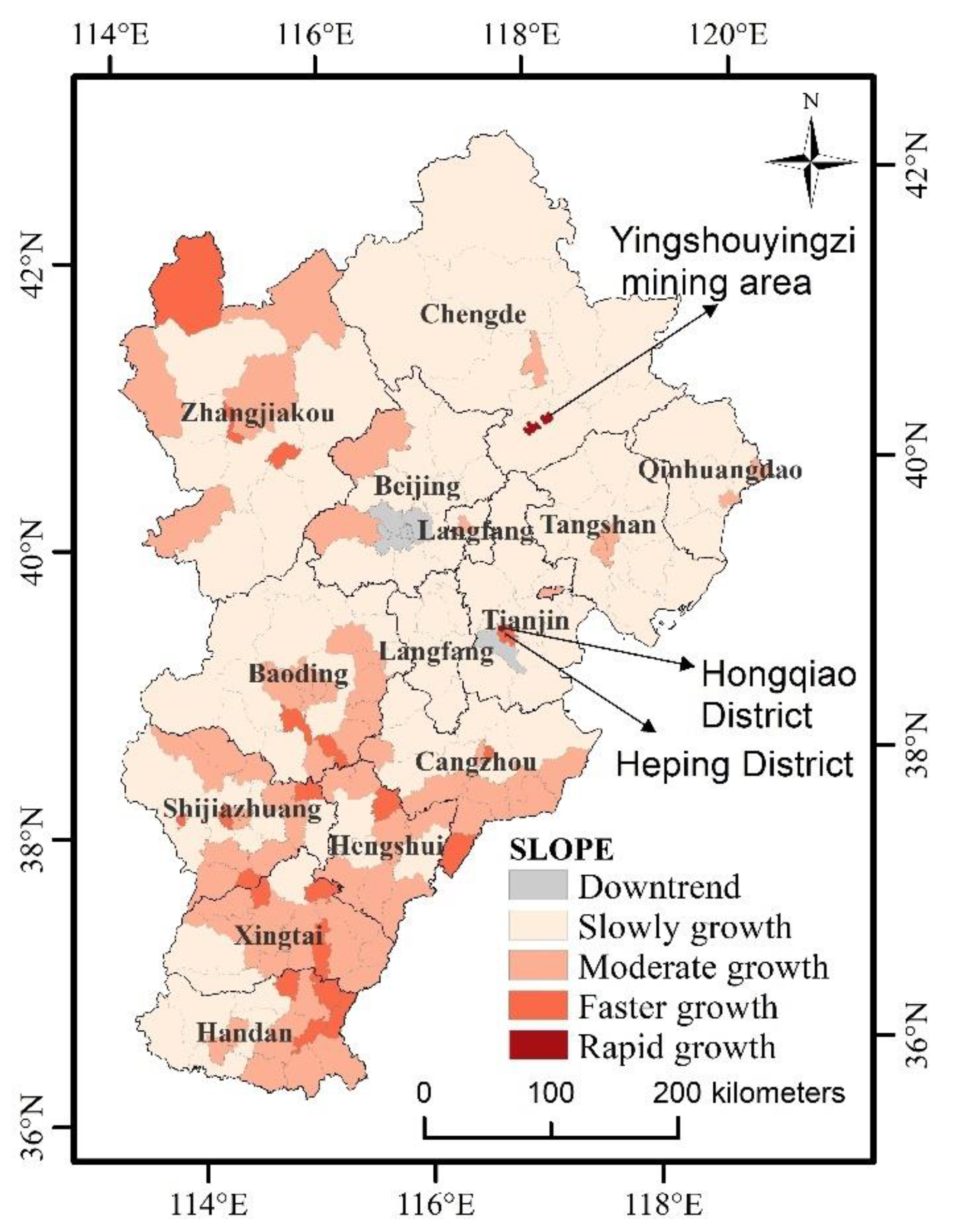
| A1 | A2 | LOGx01 | LOGx02 | h1 | h2 | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −35.4269 | 64.19793 | 0.36666 | −1.98149 | 2.24954 | 0.41862 | 0.47464 |
| Energy Type | SCE Conversion Factor (tSCE/t) | CO2 Emission Factor (t/SCE) |
|---|---|---|
| Raw coal | 0.7143 | 0.7559 |
| Coke | 0.9714 | 0.855 |
| Crude oil | 1.4286 | 0.5857 |
| Gasoline | 1.4714 | 0.5538 |
| Kerosene | 1.4714 | 0.5714 |
| Diesel fuel | 1.4571 | 0.5921 |
| Fuel oil | 1.4286 | 0.6185 |
| Natural gas | 13.3 | 0.4483 |
| Electricity | 1.229 | 0.272 |
| Variable | Factor | Symbol | Indicator | Unit | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| dependent variable | Environmental | CO2 emissions | CE | Urban carbon emissions | 104 tons |
| independent variable | population factor | total population | p | Year-end total population | 104 people |
| Urbanization rate | UR | The proportion of urban population to total population | % | ||
| Wealth factor | GDP per capita | PP | GDP per capita | Yuan | |
| Foreign investment | FAI | foreign investment | Ten thousand dollars | ||
| technical factors | Secondary industry | TI2 | Proportion of added value of secondary industry in GDP | % | |
| Industrial added value | LAV | Annual industrial added value | billion | ||
| Model | R2 | RMSE | RE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | Linear | 0.5600 | 1186.443 | 0.0753 |
| quadratic fit | 0.6129 | 1387.492 | 0.0902 | |
| Exponential function | 0.5231 | 2094.901 | 0.1294 | |
| Power function | 0.5934 | 1169.759 | 0.0754 | |
| bp-neural network | 0.9799 | 260.061 | 0.0158 | |
| Tianjin | Linear | 0.8674 | 1741.121 | 0.0793 |
| quadratic fit | 0.9327 | 2799.401 | 0.1281 | |
| Exponential function | 0.7828 | 2503.933 | 0.1081 | |
| Power function | 0.8483 | 1846.445 | 0.0768 | |
| bp-neural network | 0.9978 | 314.669 | 0.0146 | |
| Hebei | Linear | 0.8497 | 9870.159 | 0.1334 |
| quadratic fit | 0.9574 | 10281.500 | 0.1341 | |
| Exponential function | 0.7357 | 14073.120 | 0.1645 | |
| Power function | 0.8179 | 11682.530 | 0.1306 | |
| bp-neural network | 0.9963 | 2455.139 | 0.0269 |
| Variables | Ln(UR) | Ln(FAI) | Ln(GC) | Ln(CI) | Ln(PC) | Constant | Sig F | R-Squared | K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| coefficient | 1.090 *** (0.258) | −0.029 * (0.016) | 0.037 ** (0.013) | 0.246 *** (0.044) | 0.025 *** (0.007) | 2.938 * (1.069) | 0.0000 | 0.858 | 0.15 |
| Tianjin | Shijiazhuang | Tangshan | Qinhuangdao | Handan | Xingtai | |
| Ln(P) | 0.249 *** (0.038) | 1.711 *** (0.529) | 1.941 *** (0.218) | 0.323 *** (0.106) | 0.436 ** (0.181) | |
| Ln(UR) | 1.418 *** (0.088) | 0.572 *** (0.154) | 0.406 *** (0.097) | 0.258 ** (0.115) | 0.282 *** (0.046) | 0.339 *** (0.044) |
| Ln(PP) | 0.132 *** (0.012) | 0.092 ** (0.042) | 0.149 *** (0.013) | 0.151 *** (0.019) | 0.129 *** (0.010) | 0.134 *** (0.009) |
| Ln(FAI) | 0.037 ** (0.017) | 0.106 *** (0.017) | 0.081 *** (0.019) | 0.027 ** (0.012) | ||
| Ln(TI2) | 0.265 *** (0.086) | |||||
| Ln(LAV) | 0.142 *** (0.012) | 0.297 *** (0.055) | 0.177 *** (0.020) | 0.235 *** (0.029) | 0.142 *** (0.015) | 0.216 *** (0.021) |
| Constant | −2.32 *** (0.682) | 3.731 *** (0.401) | −7.706 ** (3.447) | −7.598 *** (1.485) | 3.136 *** (0.757) | 1.999 * (1.125) |
| Sig F | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| R-squared | 0.980 | 0.9541 | 0.963 | 0.939 | 0.943 | 0.961 |
| K | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.26 | 0.24 | 0.4 | 0.25 |
| Baoding | Zhangjiakou | Chengde | Cangzhou | Langfang | Hengshui | |
| Ln(P) | 1.501 *** (0.223) | 4.195 *** (0806) | 2.425 *** (0.820) | 1.409 *** (0.317) | ||
| Ln(UR) | 0.258 *** (0.050) | 0.432 *** (0.063) | 0.639 *** (0.085) | 0.634 *** (0.085) | 0.741 *** (0.083) | 0.330 *** (0.055) |
| Ln(PP) | 0.115 *** (0.015) | 0.142 *** (0.010) | 0.166 *** (0.016) | 0.199 *** (0.022) | 0.114 *** (0.019) | 0.100 *** (0.018) |
| Ln(FAI) | 0.053 ** (0.025) | 0.028 ** (0.013) | 0.100 *** (0.026) | |||
| Ln(TI2) | 0.412 *** (0.076) | |||||
| Ln(LAV) | 0.163 *** (0.030) | 0.190 *** (0.019) | 0.251 *** (0.029) | 0.069 ** (0.029) | 0.153 *** (0.022) | 0.176 *** (0.034) |
| Constant | −5.056 *** (1.622) | −21.436 *** (4.898) | −11.487 ** (4.676) | 4.236 *** (0.185) | 1.089 ** (0.433) | −3.430 * (1.945) |
| Sig F | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| R-squared | 0.933 | 0.943 | 0.988 | 0.985 | 0.990 | 0.900 |
| K | 0.33 | 0.48 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.37 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, S.; Shao, H.; Wang, H.; Xian, W.; Shao, Q.; Yin, Z.; Qi, J. Spatio-Temporal Dynamics and Driving Forces of Multi-Scale CO2 Emissions by Integrating DMSP-OLS and NPP-VIIRS Data: A Case Study in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4799. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194799
Xia S, Shao H, Wang H, Xian W, Shao Q, Yin Z, Qi J. Spatio-Temporal Dynamics and Driving Forces of Multi-Scale CO2 Emissions by Integrating DMSP-OLS and NPP-VIIRS Data: A Case Study in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei, China. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(19):4799. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194799
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, Shiyu, Huaiyong Shao, Hao Wang, Wei Xian, Qiufang Shao, Ziqiang Yin, and Jiaguo Qi. 2022. "Spatio-Temporal Dynamics and Driving Forces of Multi-Scale CO2 Emissions by Integrating DMSP-OLS and NPP-VIIRS Data: A Case Study in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei, China" Remote Sensing 14, no. 19: 4799. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194799
APA StyleXia, S., Shao, H., Wang, H., Xian, W., Shao, Q., Yin, Z., & Qi, J. (2022). Spatio-Temporal Dynamics and Driving Forces of Multi-Scale CO2 Emissions by Integrating DMSP-OLS and NPP-VIIRS Data: A Case Study in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei, China. Remote Sensing, 14(19), 4799. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194799







