Assessment of Human-Induced Effects on Sea/Brackish Water Chlorophyll-a Concentration in Ha Long Bay of Vietnam with Google Earth Engine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
2.2.1. Remote Sensing Data
2.2.2. NOAA Chlorophyll-a Data
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. Workflow Chart
2.3.2. The Chlorophyll-a Model
2.3.3. Coding in GEE, Result Presentation and Analyses
2.3.4. Error Estimation
3. Results
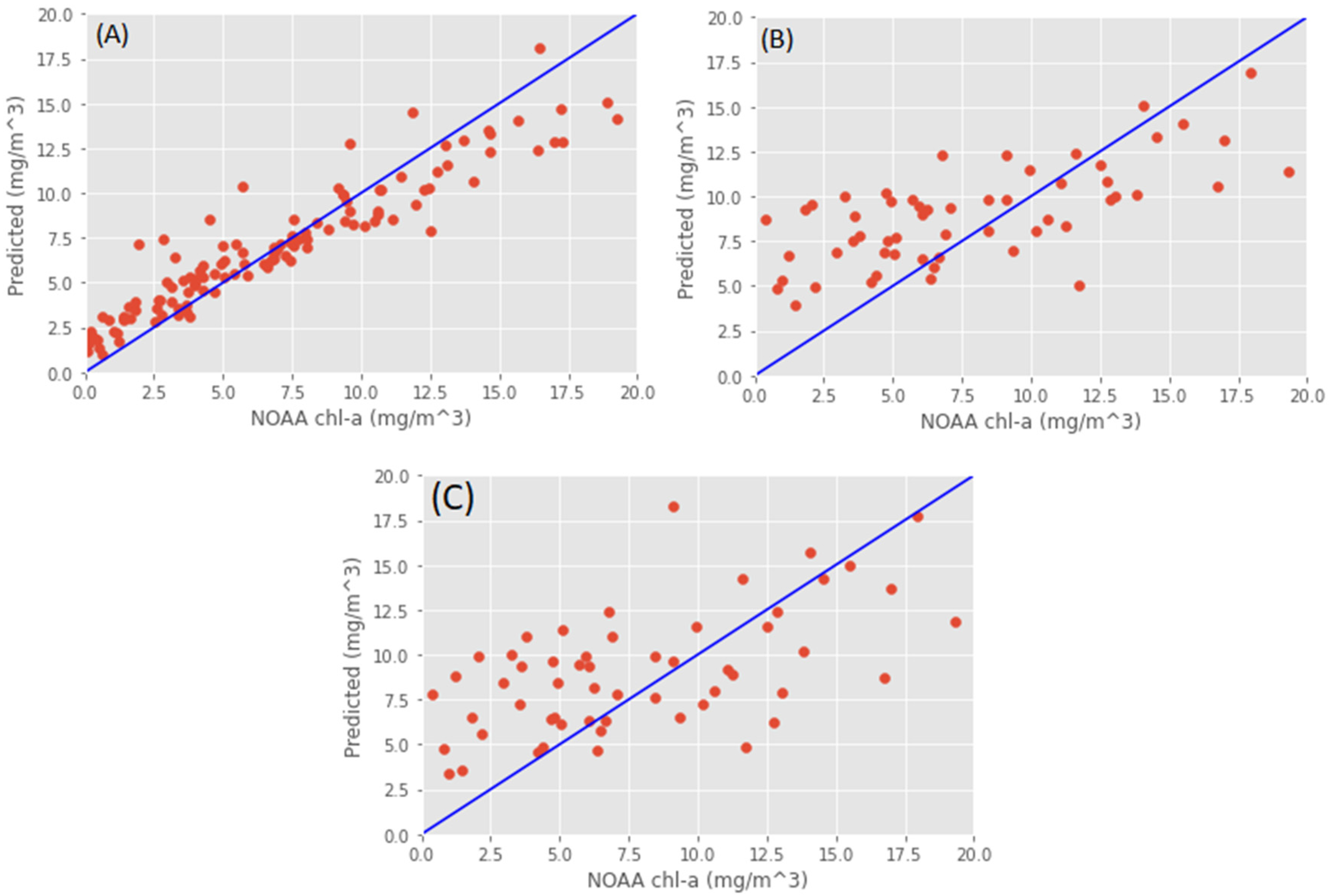
3.1. Model Calibration
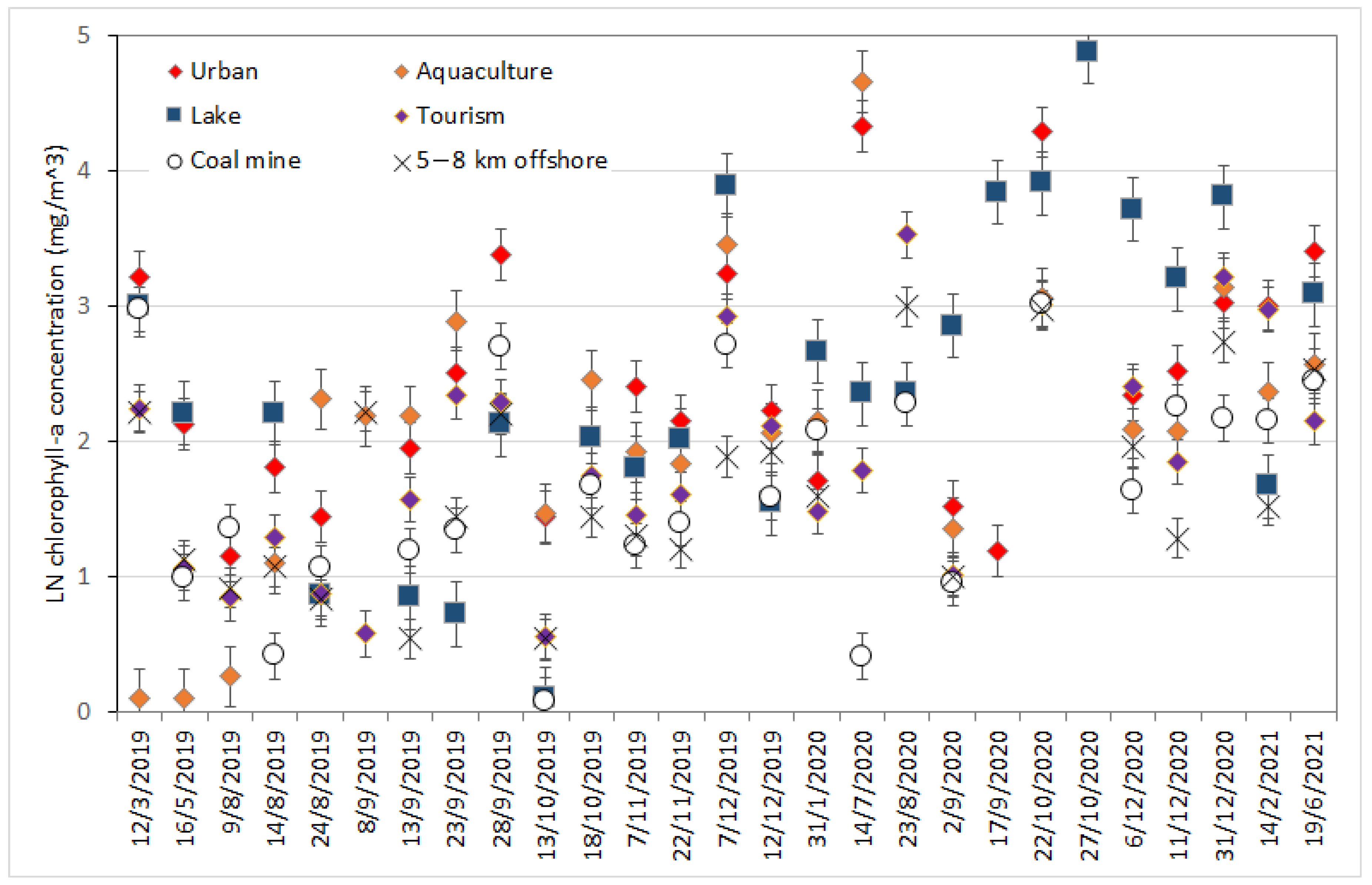
3.2. Change in Chlorophyll-a at Selected Locations
3.3. Seasonal Chlorophyll-a Distribution
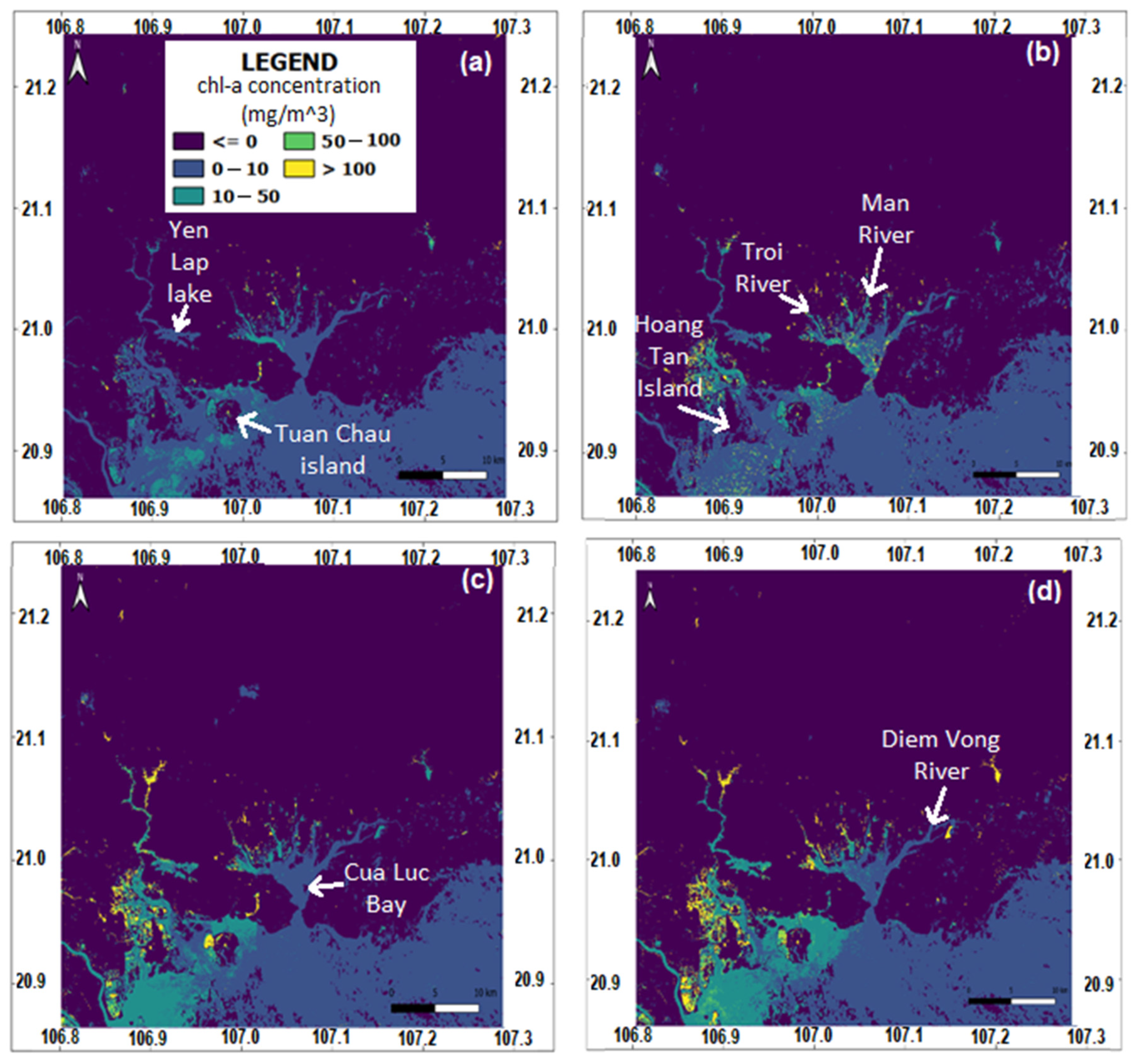
3.4. Mapping Chlorophyll-a Concentration
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heathwaite, A. Multiple stressors on water availability at global to catchment scales: Understanding human impact on nutrient cycles to protect water quality and water availability in the long term. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 241–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torbick, N.; Hession, S.; Hagen, S.; Wiangwang, N.; Becker, B.; Qi, J. Mapping inland lake water quality across the Lower Peninsula of Michigan using Landsat TM imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 7607–7624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondratyev, K.Y.; Pozdnyakov, D.V.; Pettersson, L. Water quality remote sensing in the visible spectrum. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1998, 19, 957–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartley, R.; Speirs, W.J.; Ellis, T.W.; Waters, D.K. A review of sediment and nutrient concentration data from Australia for use in catchment water quality models. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 65, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattab, M.F.O.; Merkel, B.J. Application of Landsat 5 and Landsat 7 images data for water quality mapping in Mosul Dam Lake, Northern Iraq. Arab. J. Geosci. 2014, 7, 3557–3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, J.C.; Zimba, P.V.; Everitt, J.H. Remote sensing techniques to assess water quality. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2003, 69, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholizadeh, M.H.; Melesse, A.M.; Reddi, L. A comprehensive review on water quality parameters estimation using remote sensing techniques. Sensors 2016, 16, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, I.; Oppelt, N.; Kuenzer, C. Application of remote sensing data for locust research and management—A review. Insects 2021, 12, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobley, C.D. The optical properties of water. Handb. Opt. 1995, 1, 43.3–43.56. [Google Scholar]
- Eid, M.M.M.; El-Bialee, N.M.; Elhegazy, H.; El-Khatib, S.I.; Hassan, H.E. Application of optical properties in water purification quality testing. Water Pract. Technol. 2021, 16, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CRCSI. Earth Observation: Data, Processing and Applications. Volume 3B: Applications—Surface Waters; Harrison, B.A., Anstee, J.M., Dekker, A.G., King, E.A., Griffin, D.A., Mueller, N., Phinn, S.R., Kovacs, E., Byrne, G., Eds.; CRCSI: Melbourne, Australia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Warren, M.A.; Simis, S.G.; Selmes, N. Complementary water quality observations from high and medium resolution Sentinel sensors by aligning chlorophyll-a and turbidity algorithms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 265, 112651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondeau-Patissier, D.; Gower, J.F.R.; Dekker, A.G.; Phinn, S.R.; Brando, V.E. A review of ocean color remote sensing methods and statistical techniques for the detection, mapping and analysis of phytoplankton blooms in coastal and open oceans. Prog. Oceanogr. 2014, 123, 123–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potes, M.; Costa, M.J.; Da Silva, J.C.B.; Silva, A.M.; Morais, M. Remote sensing of water quality parameters over Alqueva reservoir in the south of Portugal. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 3373–3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, B.W.; Lazorchak, J.M.; Howard, M.D.; Johnson, M.V.V.; Morton, S.L.; Perkins, D.A.; Reavie, E.D.; Scott, G.I.; Smith, S.A.; Steevens, J.A. Are harmful algal blooms becoming the greatest inland water quality threat to public health and aquatic ecosystems? Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA. Indicators: Chlorophyll a. 2013. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/national-aquatic-resource-surveys/indicators-chlorophyll (accessed on 4 September 2021).
- Chen, J.; Zhu, W.; Tian, Y.Q.; Yu, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, L. Remote estimation of colored dissolved organic matter and chlorophyll-a in Lake Huron using Sentinel-2 measurements. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2017, 11, 036007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drusch, M.; Del Bello, U.; Carlier, S.; Colin, O.; Fernandez, V.; Gascon, F.; Hoersch, B.; Isola, C.; Laberinti, P.; Martimort, P.; et al. Sentinel-2: ESA’s optical high-resolution mission for GMES operational services. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pompêo, M.; Moschini-Carlos, V.; Bitencourt, M.D.; Sòria-Perpinyà, X.; Vicente, E.; Delegido, J. Water quality assessment using Sentinel-2 imagery with estimates of chlorophyll a, Secchi disk depth, and Cyanobacteria cell number: The Cantareira System reservoirs (São Paulo, Brazil). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 34990–35011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciel, D.A.; Barbosa, C.C.F.; Novo, E.M.L.D.M.; Júnior, R.F.; Begliomini, F.N. Water clarity in Brazilian water assessed using Sentinel-2 and machine learning methods. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 182, 134–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molkov, A.A.; Fedorov, S.V.; Pelevin, V.V.; Korchemkina, E.N. Regional models for high-resolution retrieval of chlorophyll a and TSM concentrations in the Gorky Reservoir by Sentinel-2 imagery. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudheer, K.; Chaubey, I.; Garg, V. Lake water quality assessment from landsat thematic mapper data using neural network: An approach to optimal band combination selection1. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2006, 42, 1683–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, M.G.; Hicks, B.J.; Brabyn, L. Remote Sensing of Water Quality in the Rotorua Lakes; CBER Contract Report 51; The University of Waikato: Hamilton, New Zealand, 2007; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Menken, K.D.; Brezonik, P.L.; Bauer, M.E. Influence of chlorophyll and colored dissolved organic matter (CDOM) on lake reflectance spectra: Implications for measuring lake properties by remote sensing. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2006, 22, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sent, G.; Biguino, B.; Favareto, L.; Cruz, J.; Sá, C.; Dogliotti, A.; Palma, C.; Brotas, V.; Brito, A. Deriving Water Quality Parameters Using Sentinel-2 Imagery: A Case Study in the Sado Estuary, Portugal. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poddar, S.; Chacko, N.; Swain, D. Estimation of Chlorophyll-a in northern coastal Bay of Bengal using Landsat-8 OLI and Sentinel-2 MSI sensors. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, N.D.; Nierynck, E.; Van, T.; Hens, L. Land use changes and gis-database development for strategic environmental assessment in Ha Long Bay, Quang Ninh province, Vietnam. In Proceedings of the Application of Resource Information Technologies (GIS/GPS/RS) in Forest Land and Resources Management Conference, Hanoi, Vietnam, 19 June 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Rogowski, P.; Oceanography, S.I.O.; Zavala-Garay, J.; Shearman, K.; Terrill, E.; Wilkin, J.; Lam, T.H. Air-sea-land forcing in the Gulf of Tonkin: Assessing seasonal variability using modern tools. Oceanography 2019, 32, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Duy, T.; Ayoub, N.K.; Marsaleix, P.; Toublanc, F.; De Mey-Frémaux, P.; Piton, V.; Herrmann, M.; Duhaut, T.; Tran, M.C.; Ngo-Duc, T. Variability of the Red River plume in the Gulf of Tonkin as revealed by numerical modeling and clustering analysis. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 772139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuc, G.; Chormański, J. Sentinel-2 imagery for mapping and monitoring imperviousness in urban areas. The International Archives of Photogrammetry. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, 42, 43–47. [Google Scholar]
- ESA. 2021. Available online: https://scihub.copernicus.eu/dhus/#/home (accessed on 30 December 2021).
- Toolbox, Sentinel-2 Toolbox. Available online: http://step.esa.int/main/toolboxes/sentinel-2-toolbox (accessed on 15 December 2021).
- NOAA. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Archive. Available online: https://data.noaa.gov/dataset/dataset/chlorophyll-noaa-viirs-snpp-near-real-time-global-level-3-2018-present-experimental-weekly (accessed on 15 October 2021).
- O’Reilly, J.E.; Maritorena, S.; Mitchell, B.G.; Siegel, D.A.; Carder, K.L.; Garver, S.A.; Kahru, M.; McClain, C. Ocean color chlorophyll algorithms for SeaWiFS. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean 1998, 103, 24937–24953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, W.J.; Bowles, J.H.; Corson, M.R. Expected improvements in the quantitative remote sensing of optically complex waters with the use of an optically fast hyperspectral spectrometer—A modeling study. Sensors 2015, 15, 6152–6173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessin, G.; Ossipova, V.; Lips, I.; Raudsepp, U. Identification of the Coastal Zone of the Central and Eastern Gulf of Finland by Numerical Modeling, Measurements, and Remote Sensing of Chlorophyll a. In Eutrophication in Coastal Ecosystems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 187–198. [Google Scholar]
- Hang, V.T.T. Assessing the Status and Changes of Water Environment in Cua Luc Bay and Propose Solutions to Reduce Pollution (Translated). Đánh giá thực trạng, diễn biến môi trừờng nước vịnh cửa lục và đề xuất giải pháp giảm thiểu ô nhiễm (original Vietnamese version). Master’s Thesis, Resource and Environment Research Center, Hanoi National University, Hanoi, Vietnam, 2013; pp. 1–94. [Google Scholar]
- NOAA. Upwelling Is a Process in Which Deep, Cold Water Rises toward the Surface. 2021. Available online: https://oceanservice.noaa.gov/facts/upwelling.html (accessed on 15 February 2021).
- Niveditha, S.K.; Haridevi, C.; Hardikar, R.; Ram, A. Phytoplankton assemblage and chlorophyll a along the salinity gradient in a hypoxic eutrophic tropical estuary-Ulhas Estuary, West Coast of India. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 180, 113719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, E.T.; Kratzer, S.; Philipson, P. Satellite-based water quality monitoring for improved spatial and temporal retrieval of chlorophyll-a in coastal waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 158, 417–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.G.; Hong, S.; Chon, T.-S.; Joo, G.-J. Spatial patterning of chlorophyll a and water-quality measurements for determining environmental thresholds for local eutrophication in the Nakdong River basin. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amani, M.; Ghorbanian, A.; Ahmadi, S.A.; Kakooei, M.; Moghimi, A.; Mirmazloumi, S.M.; Moghaddam, S.H.A.; Mahdavi, S.; Ghahremanloo, M.; Parsian, S.; et al. Google earth engine cloud computing platform for remote sensing big data applications: A comprehensive review. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 5326–5350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, P.; Mohan, M.; Nayak, S.R.; Navalgund, R.R. Comparison of ocean color chlorophyll algorithms for IRS-P4 OCM sensor usingin-situ data. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2002, 30, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlevan, N.; Smith, B.; Schalles, J.; Binding, C.; Cao, Z.; Ma, R.; Alikas, K.; Kangro, K.; Gurlin, D.; Nguyen, H.; et al. Seamless retrievals of chlorophyll-a from Sentinel-2 (MSI) and Sentinel-3 (OLCI) in inland and coastal waters: A machine-learning approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 240, 111604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, C.; De Matos Valerio, A.; Ward, N.; Loken, L.; Sawakuchi, H.O.; Kampel, M.; Richey, J.; Stadler, P.; Crawford, J.; Striegl, R.; et al. Performance of Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 surface reflectance products for river remote sensing retrievals of chlorophyll-a and turbidity. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 224, 104–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toming, K.; Kutser, T.; Laas, A.; Sepp, M.; Paavel, B.; Nõges, T. First experiences in mapping lake water quality parameters with Sentinel-2 MSI imagery. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhellemont, Q.; Ruddick, K. Advantages of high quality SWIR bands for ocean colour processing: Examples from Landsat-8. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 161, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterckx, S.; Knaeps, E.; Adriaensen, S.; Reusen, I.; De Keukelaere, L.; Hunter, P.; Giardino, C.; Odermatt, D. OPERA: An atmospheric correction for land and water. In Proceedings of the Sentinel-3 for Science Workshop, Venice, Italy, 2–5 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Main-Knorn, M.; Pflug, B.; Louis, J.; Debaecker, V.; Müller-Wilm, U.; Gascon, F. Sen2Cor for sentinel-2. In Proceedings of the SPIE 10427, Image and Signal Processing for Remote Sensing XXIII, Warsaw, Poland, 11–14 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Yang, D.; Xu, L.; Gao, G.; He, Z.; Cui, X.; Jiang, W.; Feng, X.; Yin, B. Three types of typhoon-induced upwellings enhance coastal algal blooms: A case study. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean 2022, 127, e2022JC018448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; Cui, H.; Jia, X.; Huang, X. Occurrence and ecotoxicity of sulfonamides in the aquatic environment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 820, 153178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farmaki, E.G.; Thomaidis, N.S.; Pasias, I.N.; Rousis, N.I.; Baulard, C.; Papaharisis, L.; Efstathiou, C.E. Advanced multivariate techniques for the classification and pollution of marine sediments due to aquaculture. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 763, 144617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asim, M.; Brekke, C.; Mahmood, A.; Eltoft, T.; Reigstad, M. Improving chlorophyll-a estimation from Sentinel-2 (MSI) in the Barents Sea using machine learning. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 5529–5549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, M.H.; Lins, R.C.; Harmel, T.; Fragoso, C.R., Jr.; Martínez, J.M.; Motta-Marques, D. Atmospheric and sunglint correction for retrieving chlorophyll-a in a productive tropical estuarine-lagoon system using Sentinel-2 MSI imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 174, 215–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaik, I.; Mohammad, S.; Nagamani, P.V.; Begum, S.K.; Kayet, N.; Varaprasad, D. Assessment of chlorophyll-a retrieval algorithms over Kakinada and Yanam turbid coastal waters along east coast of India using Sentinel-3A OLCI and Sentinel-2A MSI sensors. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2021, 24, 100644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, T.D.; Luong-Van, J.; Austin, C.M. Impact of shrimp farm effluent on water quality in coastal areas of the world heritage-listed Ha Long Bay. Am. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 8, 104–116. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyễn, T.T.N.; Đồng, K.L.; Nguyễn, C.H. Development of Water Quality Index for Coastal Zone and Application in the Hạ Long Bay. VNU J. Sci. Earth Environ. Sci. 2013, 29, 43–52. [Google Scholar]
- Bui, D.T. Environmental Impacts of Coastal Shrimp Farming in North Vietnam; Charles Darwin University: Darwin, Australia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hestir, E.L.; Brando, V.E.; Bresciani, M.; Giardino, C.; Matta, E.; Villa, P.; Dekker, A.G. Measuring freshwater aquatic ecosystems: The need for a hyperspectral global mapping satellite mission. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 167, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Sentinel-2 Bands | Spatial Resolution (m) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Band 1—Coastal aerosol | 0.443 | 0.020 | 60 |
| Band 2—Blue | 0.490 | 0.066 | 10 |
| Band 3—Green | 0.560 | 0.035 | 10 |
| Band 4—Red | 0.665 | 0.030 | 10 |
| Band 5—Vegetation red edge | 0.705 | 0.015 | 20 |
| Band 6—Vegetation red edge | 0.740 | 0.015 | 20 |
| Band 7—Vegetation red edge | 0.783 | 0.020 | 20 |
| Band 8—NIR | 0.842 | 0.012 | 10 |
| Band 8A—Vegetation red edge | 0.865 | 0.020 | 20 |
| Band 9—Water vapor | 0.945 | 0.020 | 60 |
| Band 10—SWIR—Cirrus | 1.375 | 0.030 | 60 |
| Band 11—SWIR | 1.610 | 0.090 | 20 |
| Band 12—SWIR | 2.190 | 0.018 | 20 |
| Parameters | Original OC-2 [26] | Calibrated Model Training Phase | Calibrated Model Testing Phase |
|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | 0.30 | 0.85 | 0.81 |
| RMSE (mg/m3) | 4.15 | 2.30 | 2.80 |
| Coefficients of Equation (2) | a0 = 0.341 a1 = −3.0010 a2 = 2.811 a3 = −2.041 a4 = 0.0400 | a0 = 0.354 a1 = −2.8009 a2 = 2.902 a3 = −1.977 a4 = 0.0750 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Quang, N.H.; Nguyen, M.N.; Paget, M.; Anstee, J.; Viet, N.D.; Nones, M.; Tuan, V.A. Assessment of Human-Induced Effects on Sea/Brackish Water Chlorophyll-a Concentration in Ha Long Bay of Vietnam with Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4822. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194822
Quang NH, Nguyen MN, Paget M, Anstee J, Viet ND, Nones M, Tuan VA. Assessment of Human-Induced Effects on Sea/Brackish Water Chlorophyll-a Concentration in Ha Long Bay of Vietnam with Google Earth Engine. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(19):4822. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194822
Chicago/Turabian StyleQuang, Nguyen Hong, Minh Nguyen Nguyen, Matt Paget, Janet Anstee, Nguyen Duc Viet, Michael Nones, and Vu Anh Tuan. 2022. "Assessment of Human-Induced Effects on Sea/Brackish Water Chlorophyll-a Concentration in Ha Long Bay of Vietnam with Google Earth Engine" Remote Sensing 14, no. 19: 4822. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194822
APA StyleQuang, N. H., Nguyen, M. N., Paget, M., Anstee, J., Viet, N. D., Nones, M., & Tuan, V. A. (2022). Assessment of Human-Induced Effects on Sea/Brackish Water Chlorophyll-a Concentration in Ha Long Bay of Vietnam with Google Earth Engine. Remote Sensing, 14(19), 4822. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194822








