Simulation Performance and Case Study of Extreme Events in Northwest China Using the BCC-CSM2 Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
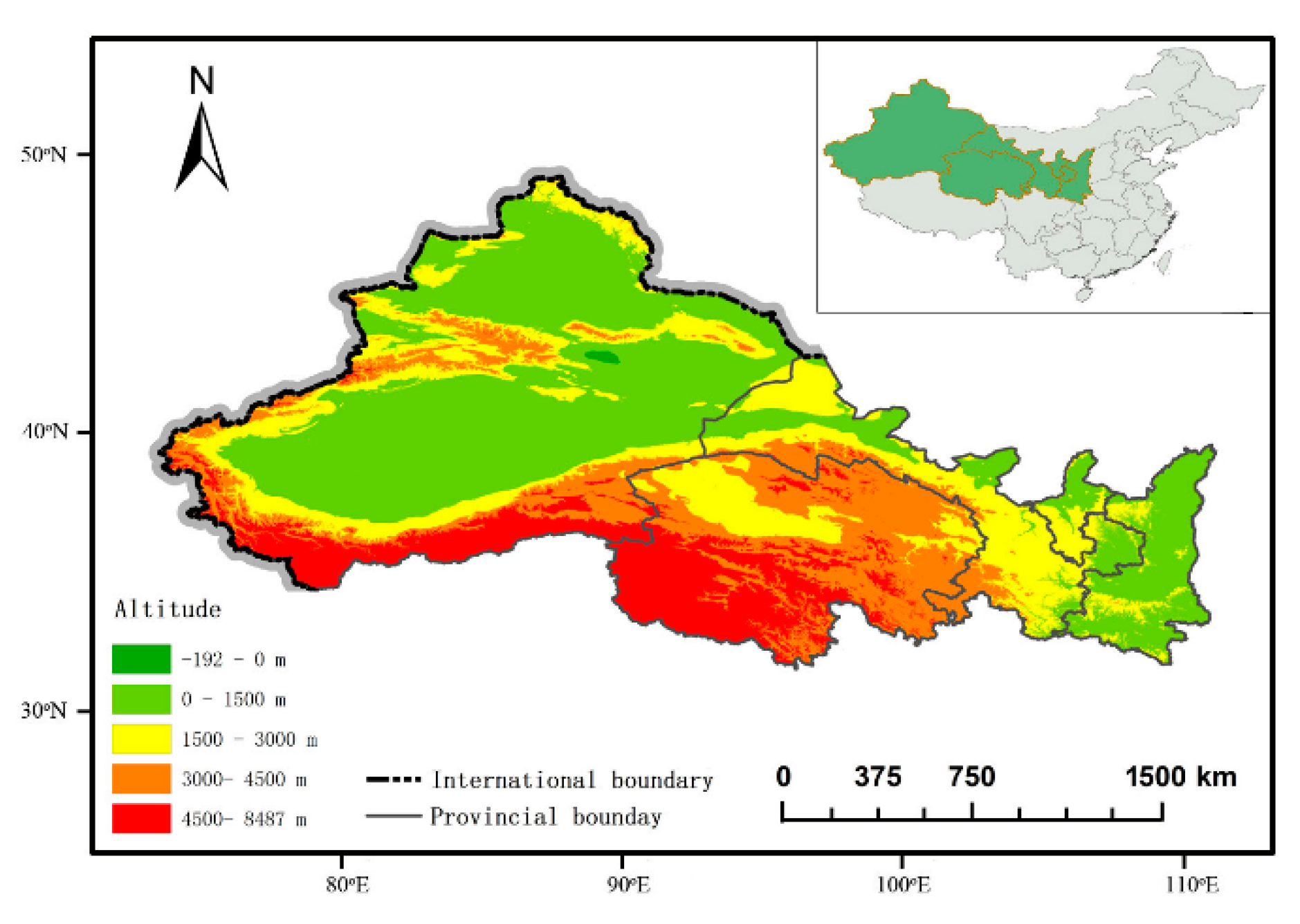
2.1. Data Source
2.2. Methodology
2.3. Selection of Individual Extreme Events
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Comparison of the Results of the Models with Different Resolutions
3.2. Analysis of Extreme Climate Indices
3.3. Analysis of Typical Extreme Weather Events
3.4. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, T.J.; Zou, L.W.; Chen, X.L. Commentary on the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 6 (CMIP6). Clim. Change Res. 2019, 15, 445–456. [Google Scholar]
- Eyring, V.; Bony, S.; Meehl, G.A.; Senior, C.A.; Stevens, B.; Stouffer, R.J.; Taylor, K.E. Overview of the Coupled Model Inercomparison Project Phase 6 (CMIP6) experimental design and organization. Geosci. Model Dev. 2016, 9, 1937–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, B.; Zhou, T.J.; Yu, Y.Q.; Wang, B. A perspective on Earth System Model development. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2008, 66, 857–869. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.J.; Xu, Y.F.; Zhou, T.J.; Chen, H.B.; Gao, S.T.; Wang, P.C.; Lu, R.Y.; Zhang, M.G. Atmospheric Science: A vigorous frontier science. Adv. Earth Sci. 2004, 19, 525–532. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.W.; Song, L.C.; Li, W.P.; Wang, Z.Z.; Zhang, H.; Xin, X.G.; Zhang, Y.W.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.L.; Wu, F.H.; et al. An overview of BCC climate system model development and application for climate change studies. J. Meteorol. Res. 2014, 28, 34–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.J.; Zou, L.W.; Wu, B.; Jin, C.X.; Song, F.F.; Chen, X.L.; Zhang, L.X. Development of earth/climate system models in China: A review from the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project perspective. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2014, 72, 892–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Din, J.U.; Bosso, L.; Hameed, S.; Kabir, M.; Younas, M.; Nawaz, M.A. Expanding or shrinking? Range shifts in wild ungulates under climate change in Pamir-Karakoram mountains, Pakistan. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0260031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.G.; Yuan, Y.D.; Li, X.M.; Zhang, J.C. Maximum entropy modeling to predict the impact of climate change on pine wilt disease in China. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 652500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.B.; Hu, D.; Tian, Z.P.; Lang, X.M. Differences between CMIP6 and CMIP5 models in simulating climate over China and the East Asian monsoon. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2020, 37, 1102–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, H.X.; Wang, H.J.; Sun, B.; Chen, H.P. Evaluation of CMIP6 model simulations of extreme precipitation in China and comparison with CMIP5. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2021, 79, 369–386. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Dong, M.; Wu, T.W.; Xin, X.G. Reproductions of northern hemisphere blocking in BCC models and possible reasons for the biases. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 45, 181–194. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, X.G.; Wu, T.W.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, F.; Li, W.P.; Zhang, Y.W.; Lu, Y.X.; Fang, Y.J.; Ji, W.H.; Zhang, L.; et al. Introduction of BCC models and its participation in CMIP6. Clim. Change Res. 2019, 15, 533–539. [Google Scholar]
- Sang, Y.H.; Ren, H.L.; Shi, X.L.; Xu, X.F.; Chen, H.S. Improvement of soil moisture simulation in Eurasia by the Beijing Climate Center Climate System Model from CMIP5 to CMIP6. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 38, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.H.; Chen, H.P. Assessment and projection of changes in temperature extremes over the mid-high latitudes of Asia based on CMIP6 models. Trans. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 44, 592–603. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.P.; Ji, M.X.; Liu, Y.Z.; Zhang, L.; Gong, D.Y. An overview of arid and semi-arid climate change. Clim. Change Res. 2013, 9, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.Z.; Liu, X.D.; Ma, Z.G. Analysis on the drought characteristics in the main arid regions in the world since recent hundred-odd years. Arid. Zone Res. 2004, 21, 97–103. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.G.; Fu, Z.B. The fact of global aridity in the second half of the 20th century and its relationship with large-scale background. Sci. China 2007, 37, 222–233. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Z.A.; Wu, T.W.; Song, M.H.; Ma, X.B.; Cai, Y.; Liang, X.Y. Arid disaster and advances in arid climate researches over Northwest China. Adv. Earth Sci. 2001, 16, 28–38. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Hu, Y.Q.; Cao, X.Y.; Liu, W.M. On some problems of arid climate system of Northwest China. J. Desert Res. 2000, 20, 357–362. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.X. The history of the arid climate research in LIPAP. Plateau Meteorol. 1989, 8, 103–106. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.X.; Wang, J.S.; Li, Q.Y. Spatial and temporal distribution of water vapor and its variation trend in atmosphere over Northwest China. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2003, 25, 149–156. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.F.; Shen, Y.P.; Li, D.L.; Zhang, G.W.; Ding, Y.J.; Hu, R.J.; Kang, E.S. Discussion on the present climate change from warm-dry to warm-wet in Northwest China. Quat. Sci. 2003, 23, 152–164. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, S.S.; Lian, L.S.; Ma, T.; Zhang, K.; Han, T. Spatiotemporal variation of temperature and precipitation in Northwest China in recent 54 years. Arid. Zone Res. 2018, 35, 68–76. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Deng, Z.Y.; Zhao, Y.D.; Qiao, J. The impacts of global climatic change on the agriculture in Northwest China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2008, 28, 329–337. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhu, B.; Yang, J.H.; Ma, P.L.; Liu, X.Y.; Lu, G.Y.; Wang, Y.H.; Yu, H.P.; Liu, W.P.; Wang, D.W. New characteristics about the climate humidification trend in Northwest China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2021, 66, 3757–3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.N. Spatial and temporal variations of summer precipitation in Northwest China over the past 55 years. J. Mar. Meteorol. 2018, 38, 50–59. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Y.; Chen, H.Y.; Fang, S.B.; Yu, W.G. Variation characteristics of extreme climate events in Northwest China during 1961–2010. J. Arid. Meteorol. 2017, 33, 963–969. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.L. Changes in Weather and Climate Extremes. Clim. Change Res. 2012, 8, 90–98. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.M.; Huang, A.N.; Wu, H.M. Evaluation of the performance of Beijing Climate Center Climate System Model with different horizontal resolution in simulating the annual surface temperature over Central Asia. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 39, 535–547. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.W.; Lu, Y.X.; Fang, Y.J.; Xin, X.G.; Li, L.; Li, W.P.; Jie, W.H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.M.; Zhang, L.; et al. The Beijing Climate Center Climate System Model (BCC-CSM): The main progress from CMIP5 to CMIP6. Geosci. Model Dev. Discuss. 2019, 12, 1573–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, M.S.; Xiong, S.W.; Liang, Y.F. Comparative study of calculated threshold values in regional extreme precipitation. J. Meteorol. Sci. 2013, 33, 549–554. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, W.H.; Lin, X.; Zhu, Y.F.; Xu, Y.; Fu, J.L. Climatic regime shift and decadal anomalous events in China. Clim. Change 2007, 84, 167–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.Y.; Collins, W.D.; Wehner, M.F.; Williamson, D.L.; Olson, J.G.; Algieri, C. Impact of horizontal resolution on simulation of precipitation extremes in an aqua-planet version of Community Atmospheric Model (CAM3). Tellus A 2011, 63, 884–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zolina, O.; Kapala, A.; Simmer, C.; Gulev, S.K. Analysis of extreme precipitation over Europe from different reanalyses: A comparative assessment. Glob. Planet. Change 2004, 44, 129–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.Y. Meteorological Statistical Analysis and Forecast Method, 4th ed.; China Meteorological Press: Beijing, China, 2016; pp. 23–37. [Google Scholar]
- Anand, V.; Oinam, B.; Singh, I.H. Predicting the current and future potential spatial distribution of endangered Rucervus eldii eldii (Sangai) using MaxEnt model. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, H.; Sun, Y. Characteristics of extreme temperature and precipitation in China in 2017 based on ETCCDI indices. Adv. Clim. Change Res. 2018, 9, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Zhou, B.T.; Qin, D.H.; Wu, J.; Gao, R.; Song, L.C. Changes in mean and extreme temperature and precipitation over the arid region of Northwestern China: Observation and Projection. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2017, 34, 289–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillmann, J.; Kharin, V.V.; Zhang, X.; Zwiers, F.W.; Bronaugh, D. Climate extremes indices in the CMIP5 multimodel ensemble: Part 1. Model evaluation in the present climate. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 1716–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ye, D.X.; Sun, J.M. Climatic characteristics in China in 2006. Meteorol. Mon. 2007, 33, 112–117. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, X.Q. High temperature in central and western China, rainstorm caused by typhoon-July 2006. Meteorol. Mon. 2006, 32, 117–123. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.M.; Qian, C.; Zhang, W.J.; He, D.; Qi, Y.J. Extreme temperature indices in Eurasia in a CMIP6 multi-model ensemble: Evaluation and projection. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 41, 5368–5385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.X.; Xin, X.G.; Xiao, C.; Li, Y.H.; Wu, Y.; Tang, H.Y. Performance of BCC-CSM models with different horizontal resolutions in simulating extreme climate events in China. J. Meteorol. Res. 2019, 33, 720–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.N.; Zhang, Y.C.; Zhu, J. Effects of the physical process ensemble technique on simulation of summer precipitation over China. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2009, 23, 713–724. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Gao, X.J.; Shi, Y. Changes of 20-year return temperature and precipitation extremes over China simulated by RegCM3. Clim. Change Res. 2012, 8, 243–249. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, J.; Huang, A.N.; Shi, X.L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.W.; Cao, L.; Wu, Y. Evaluating the performance of BCC-CSM2-MR model in simulating the land surface processes in China. Plateau Meteorol. 2022, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.M.; Huang, A.N.; Jiang, Y.M.; Zhao, Y. Evaluation of the performance of BCC-CSM climate model with different horizontal resolution in simulating the summer precipitation over Central China. Arid. Land Geogr. 2016, 39, 1305–1318. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, D.Q.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Y.C.; Huang, A.N. Uncertainties on the simulated summer precipitation over Eastern China from the CMIP5 models. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 9035–9047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Label | Index Name | Definition | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| TXx | Max TX | Annual maximum of the daily maximum temperature | °C |
| TNx | Max TN | Annual maximum of the daily minimum temperature | °C |
| TXn | Min TX | Annual minimum of the daily maximum temperature | °C |
| TNn | Min TN | Annual minimum of the daily minimum temperature | °C |
| TN10p | Cold nights | Percentage of days with daily minimum temperatures < 10th percentile | % |
| TX10p | Cold days | Percentage of days with daily maximum temperatures < 10th percentile | % |
| TN90p | Warm nights | Percentage of days with daily minimum temperatures > 90th percentile | % |
| TX90p | Warm days | Percentage of days with daily maximum temperatures > 90th percentile | % |
| Extreme Events | Event 1 | Event 2 | Event 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Extreme high-temperature events | 31 July–4 August 2006 | 25 July 2011 | 2–3 August 2013 |
| Extreme low-temperature events | 28 January–3 February 2008 | 22 January 2012 | 11 January 2011 |
| Extreme precipitation events | 8–9 July 2014 | 2–3 July 2011 | 19–21 June 2013 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, M.; Pei, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wu, T. Simulation Performance and Case Study of Extreme Events in Northwest China Using the BCC-CSM2 Model. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4922. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194922
Song M, Pei Y, Zhang S, Wu T. Simulation Performance and Case Study of Extreme Events in Northwest China Using the BCC-CSM2 Model. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(19):4922. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194922
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Minhong, Yufei Pei, Shaobo Zhang, and Tongwen Wu. 2022. "Simulation Performance and Case Study of Extreme Events in Northwest China Using the BCC-CSM2 Model" Remote Sensing 14, no. 19: 4922. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194922
APA StyleSong, M., Pei, Y., Zhang, S., & Wu, T. (2022). Simulation Performance and Case Study of Extreme Events in Northwest China Using the BCC-CSM2 Model. Remote Sensing, 14(19), 4922. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194922








