Phenological Changes and Driving Forces of Lake Ice in Central Asia from 2002 to 2020
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Lake Selection
2.2. Datasets
2.2.1. MODIS Daily Land Surface Temperature (LST) Products
2.2.2. Lake Information
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Quality Control and Lake Selection
2.3.2. MODIS Daily LST Combination
2.3.3. Lake Ice Penology Variable Extraction
3. Results
3.1. Validation of Ice Phenology Curve
3.2. Lake Ice Phenology Characteristics in Central Asia
3.3. Ice Phenology in Different Elevation Lakes
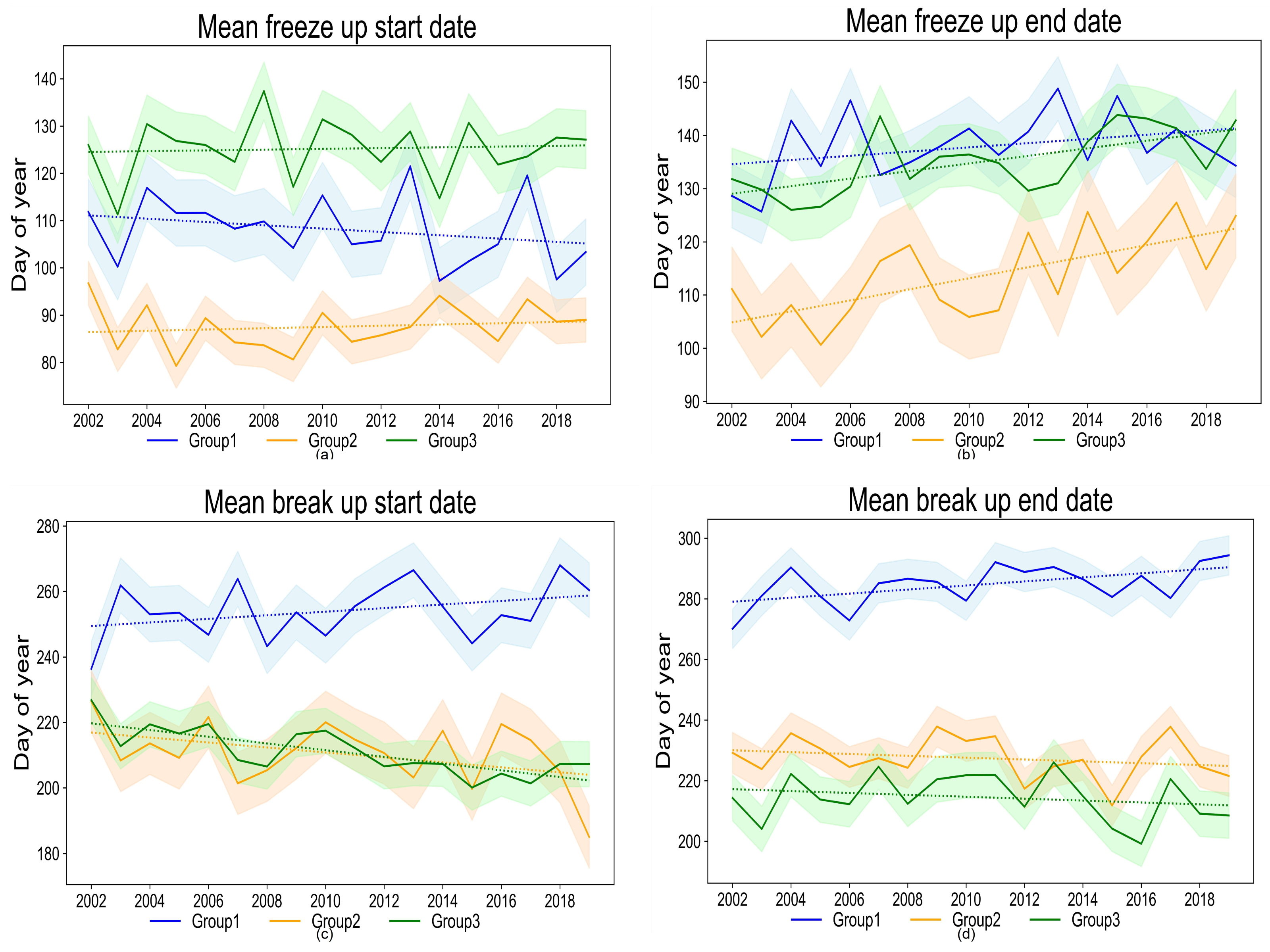
3.3.1. Group 1: Elevation Higher than 3000 m
3.3.2. Group 2: Elevation from 1000 m to 2000 m
3.3.3. Group 3: Elevation Lower than 1000 m
4. Discussion
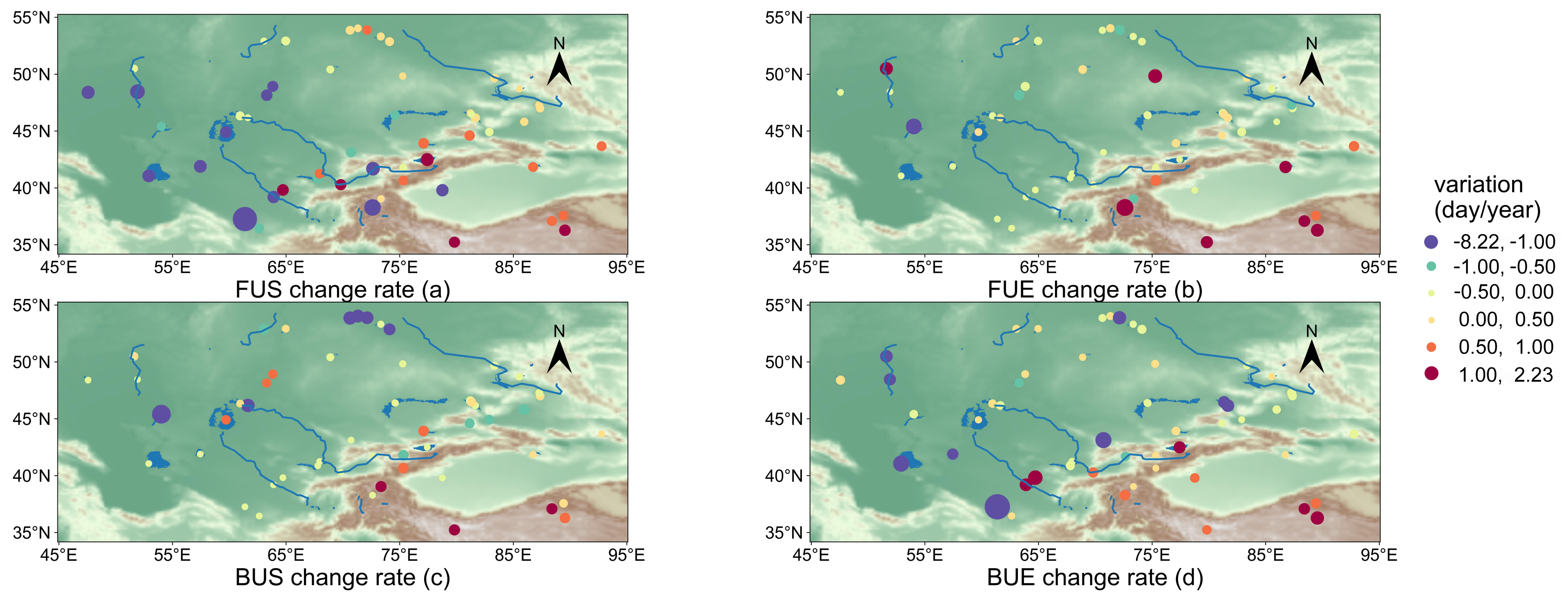
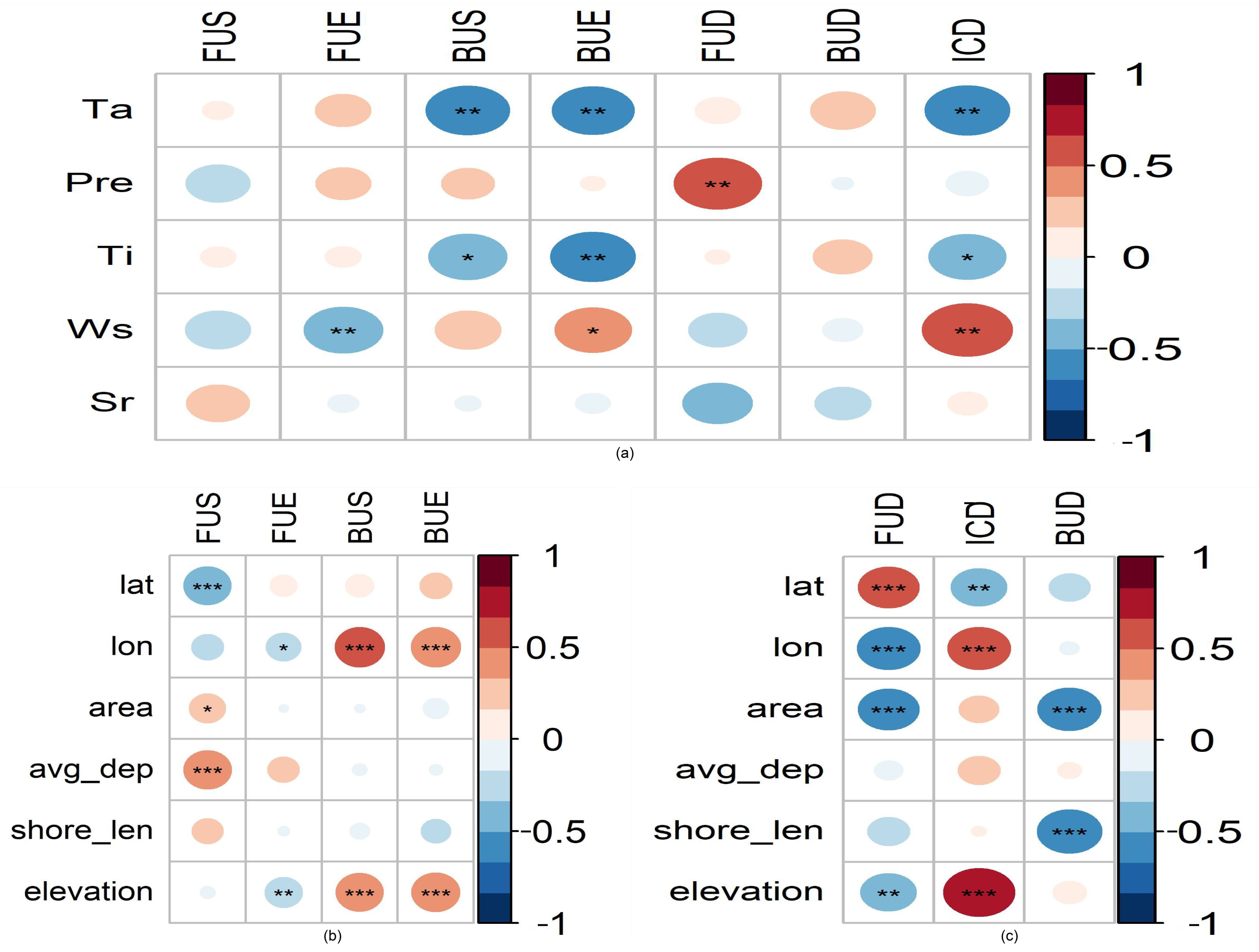
4.1. Correlation of Lake Ice Phenology Variables with Influencing Factors
4.2. Limitation and Prospection
- (1)
- Using multiple satellite data to retrieve lake ice phenology for all lakes, including small lakes.
- (2)
- Quantifying and evaluating how anthropogenic activities affect lake ice phenology variables.
- (3)
- Projecting future lake ice variations in different representative concentration pathways (RCPs).
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Lake Name | Mean FUS | Mean FUE | Mean BUS | Mean BUE | Mean FUD | Mean ICD | Mean BUD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Akkol | 88.67 | 129 | 213.44 | 242.16 | 40.33 | 84.44 | 28.72 |
| Aksayquin | 82.06 | 99.61 | 259.39 | 286.89 | 17.56 | 159.78 | 27.5 |
| Alakol | 125.39 | 144.89 | 219.06 | 236.28 | 19.5 | 74.17 | 17.22 |
| Aqqikkol | 88.39 | 101.72 | 242.33 | 280.33 | 13.33 | 140.61 | 38 |
| Arkatag | 77.56 | 92.67 | 271.5 | 310.17 | 15.11 | 178.83 | 38.67 |
| Ayakkum | 94.44 | 105.44 | 234.5 | 256.39 | 11 | 129.06 | 21.89 |
| Aydar | 146.78 | NA | NA | 164.28 | NA | NA | NA |
| Balkhash | 107.78 | 124.06 | 229.06 | 243.11 | 16.28 | 105 | 14.06 |
| Barkol | 67.5 | 90.89 | 218.72 | 248.61 | 23.39 | 127.83 | 29.89 |
| Biylikol | 132.17 | NA | NA | 178.06 | NA | NA | NA |
| Bosten | 122.72 | 143.27 | 220.89 | 234.5 | 20.56 | 77.62 | 13.61 |
| Chardarinskoye | 127.72 | NA | NA | 172.89 | NA | NA | NA |
| Chatyr-kel’ | 71.72 | 104.39 | 261.72 | 294.22 | 32.67 | 157.33 | 32.5 |
| Ebi | 102.89 | 124.06 | 209.78 | 231.33 | 21.17 | 85.72 | 21.56 |
| Inder | 102.39 | NA | NA | 224.78 | NA | NA | NA |
| Issyk Kul | 165.17 | NA | NA | 190.33 | NA | NA | NA |
| Jili | 110.83 | 136.56 | 221.94 | 250.56 | 25.72 | 85.38 | 28.61 |
| Kamyshlybas | 111.17 | 144.67 | 196.22 | 231.61 | 33.5 | 51.55 | 35.39 |
| Kara-Bogaz-Gol | 144.67 | NA | NA | 170.39 | NA | NA | NA |
| Karakul | 93 | 126.06 | 266.06 | 289.5 | 33.06 | 140 | 23.44 |
| Karasor | 84.06 | 120.06 | 228.67 | 254.28 | 36 | 108.61 | 25.61 |
| Karatomarskoye | 88.39 | 139.89 | 230.78 | 257.06 | 47.5 | 90.89 | 26.28 |
| Kaydak | 109.67 | 141.89 | 179.61 | 212.72 | 32.22 | 37.72 | 33.11 |
| Kayrakkumskoye | 134.39 | NA | NA | 159.83 | NA | NA | NA |
| Kayrakkumskoye1 | 139.11 | NA | NA | 173.25 | NA | NA | NA |
| Kilibek | 71.22 | 121.39 | 207.94 | 244.39 | 50.17 | 86.55 | 36.44 |
| Kishi’karoy | 76.67 | 118.22 | 219.67 | 245.39 | 41.56 | 101.45 | 25.72 |
| Kushmurun | 73.5 | 113.78 | 236.33 | 254.61 | 40.28 | 122.55 | 18.28 |
| Kuyumazarskoye | 149 | NA | NA | 166 | NA | NA | NA |
| Large Aral Sea | 108.56 | 129.83 | 211.56 | 227.22 | 21.28 | 81.73 | 15.67 |
| Manas | 93.78 | 119.28 | 209.33 | 230.83 | 25.5 | 90.05 | 21.5 |
| Markakol’ | 97.83 | 119.89 | 264.44 | 283.33 | 22.06 | 144.55 | 18.89 |
| Qapshaghay Bogeni Reservoir | 133.33 | 164.22 | 193.06 | 219.11 | 30.89 | 28.84 | 26.06 |
| Sailimu | 129.56 | 157.39 | 245.06 | 268.94 | 27.83 | 87.67 | 23.89 |
| Sarezskoye | 99.06 | 165.67 | 244.78 | 269.33 | 66.61 | 79.11 | 24.56 |
| Sarygamysh | 150.33 | NA | NA | 194.28 | NA | NA | NA |
| Saryyazin Skoye | 136.06 | NA | NA | 153.33 | NA | NA | NA |
| Sasykkol | 105.78 | 126.44 | 221.06 | 240.94 | 20.67 | 94.62 | 19.89 |
| Seletyteniz | 64.5 | 89.89 | 235.17 | 251.89 | 25.39 | 145.28 | 16.72 |
| Shalkar | 101.06 | 157.11 | 208.78 | 236.89 | 56.05 | 51.67 | 28.11 |
| Shalkarteniz | 72.61 | 123.44 | 212.11 | 237.28 | 50.83 | 79.94 | 25.17 |
| Small Aral Sea | 110.78 | 132.17 | 215.72 | 240.39 | 21.39 | 83.55 | 24.67 |
| Song-kel | 94.22 | 113.78 | 252.44 | 291.11 | 19.56 | 138.66 | 38.67 |
| Sor Khaki | 97.5 | NA | NA | 225.28 | NA | NA | NA |
| Tengiz | 74.61 | 96.67 | 234 | 252.28 | 22.06 | 137.33 | 18.28 |
| Toktogul’skoye | 154.28 | NA | NA | 197.11 | NA | NA | NA |
| Tudakol | 144.56 | NA | NA | 167.89 | NA | NA | NA |
| Ul’ken-karoy | 72.28 | 131.06 | 224.94 | 244.89 | 58.78 | 93.88 | 19.95 |
| Ulungur | 108.28 | 131.33 | 230.94 | 252.56 | 23.06 | 99.61 | 21.62 |
| Uyaly | 113.39 | 148.44 | 208.72 | 232.17 | 355.06 | 60.28 | 23.45 |
| Xiaoxihaiz Shuiku | 139.5 | NA | NA | 195.56 | NA | NA | NA |
| Zaysan | 97.89 | 116.56 | 241.17 | 255.22 | 18.67 | 124.61 | 14.05 |
| Zhalauly | 82.83 | 118.17 | 218.56 | 245.06 | 35.33 | 100.39 | 26.5 |
References
- Vaughan, D.; Stocker, T.; Qin, D.; Plattner, G.; Tignor, M.; Allen, S.; Boschung, J.; Nauels, A.; Xia, Y.; Bex, V.; et al. Climate Change: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.M.; Miao, Q.L.; Xiong, L.I. Variation Characteristics of Temperature over Northern China in Recent 50 Years. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2005, 25, 448. [Google Scholar]
- Masson-Delmotte, V.; Zhai, P.; Pirani, A.; Connors, S.L.; Péan, C.; Berger, S.; Caud, N.; Chen, Y.; Goldfarb, L.; Gomis, M.; et al. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021; p. 2. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, R.; Duan, H.; Hu, C.; Feng, X.; Li, A.; Ju, W.; Jiang, J.; Yang, G. A half-century of changes in China’s lakes: Global warming or human influence? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Song, C.; Reager, J.T.; Yao, F.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Sheng, Y.; MacDonald, G.M.; Brun, F.; Schmied, H.M.; Marston, R.A.; et al. Recent global decline in endorheic basin water storages. Nat. Geosci. 2018, 11, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bai, J.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; Yang, L.; Fang, H. Changes in the area of inland lakes in arid regions of central Asia during the past 30 years. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 178, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, X.; Feng, M.; Sun, Q.; Sexton, J.O.; Channan, S.; Liu, J. The Decrease in Lake Numbers and Areas in Central Asia Investigated Using a Landsat-Derived Water Dataset. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, Y.; Ye, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q. Recent lake area changes in Central Asia. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Kropáček, J.; Maussion, F.; Chen, F.; Hoerz, S.; Hochschild, V. Analysis of ice phenology of lakes on the Tibetan Plateau from MODIS data. Cryosphere 2013, 7, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, Q.; Yao, X.; Zhang, H.; Duan, H.; Jin, H.; Chen, J.; Cao, J. Analysis of the Variability and Influencing Factors of Ice Thickness during the Ablation Period in Qinghai Lake Using the GPR Ice Monitoring System. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, T. Seasonal cycles of lakes on the Tibetan Plateau detected by Sentinel-1 SAR data. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 703, 135563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surdu, C.M.; Duguay, C.R.; Fernández Prieto, D. Evidence of recent changes in the ice regime of lakes in the Canadian High Arctic from spaceborne satellite observations. Cryosphere 2016, 10, 941–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murfitt, J.; Duguay, C.R. 50 years of lake ice research from active microwave remote sensing: Progress and prospects. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 264, 112616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Ke, C.Q.; Duan, Z. Monitoring ice variations in Qinghai Lake from 1979 to 2016 using passive microwave remote sensing data. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 607, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Blagrave, K.; Magnuson, J.J.; O’Reilly, C.M.; Oliver, S.; Batt, R.D.; Magee, M.R.; Straile, D.; Weyhenmeyer, G.A.; Winslow, L.; et al. Widespread loss of lake ice around the Northern Hemisphere in a warming world. Nat. Clim. Change 2019, 9, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampton, S.E.; Galloway, A.W.; Powers, S.M.; Ozersky, T.; Woo, K.H.; Batt, R.D.; Labou, S.G.; O’Reilly, C.M.; Sharma, S.; Lottig, N.R.; et al. Ecology under lake ice. Ecol. Lett. 2017, 20, 98–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolway, R.; Merchant, C. Worldwide alteration of lake mixing regimes in response to climate change. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weyhenmeyer, G.A.; Livingstone, D.M.; Meili, M.; Jensen, O.; Benson, B.; Magnuson, J.J. Large geographical differences in the sensitivity of ice-covered lakes and rivers in the Northern Hemisphere to temperature changes. Glob. Change Biol. 2011, 17, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Ke, C.Q.; Yao, G.; Shen, X. MODIS-observed variations of lake ice phenology in Xinjiang, China. Clim. Change 2020, 158, 575–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.; Duguay, C. Modelling lake ice phenology with an examination of satellite-detected subgrid cell variability. Adv. Meteorol. 2012, 2012, 529064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Pavelsky, T.M. Remote sensing of lake ice phenology across a range of lakes sizes, ME, USA. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.; Duguay, C.R.; Xu, L. Assessment of machine learning classifiers for global lake ice cover mapping from MODIS TOA reflectance data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 253, 112206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q. geemap: A Python package for interactive mapping with Google Earth Engine. J. Open Source Softw. 2020, 5, 2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boqiang, Q. A Preliminary Investigation of Lake Evolution in 20-century in Inland Mainland Asia with Relation to the Global Warming. J. Lake Sci. 1999, 11, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Dozier, J. A generalized split-window algorithm for retrieving land-surface temperature from space. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1996, 34, 892–905. [Google Scholar]
- Messager, M.L.; Lehner, B.; Grill, G.; Nedeva, I.; Schmitt, O. Estimating the volume and age of water stored in global lakes using a geo-statistical approach. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnuson, J.J.; Robertson, D.M.; Benson, B.J.; Wynne, R.H.; Livingstone, D.M.; Arai, T.; Assel, R.A.; Barry, R.G.; Card, V.; Kuusisto, E.; et al. Historical trends in lake and river ice cover in the Northern Hemisphere. Science 2000, 289, 1743–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Latifovic, R.; Pouliot, D. Analysis of climate change impacts on lake ice phenology in Canada using the historical satellite data record. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 106, 492–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, K.; Kirillin, G. An Automatic Method to Detect Lake Ice Phenology Using MODIS Daily Temperature Imagery. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Wu, Y.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, B.; Li, J.; Zhang, F.; Shen, Q. Uncertainty and variation of remotely sensed lake ice phenology across the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, X.; Li, L.; Zhao, J.; Sun, M.; Li, J.; Gong, P.; An, L. Spatial-temporal variations of lake ice phenology in the Hoh Xil region from 2000 to 2011. J. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, B.J.; Magnuson, J.J.; Jensen, O.P.; Card, V.M.; Hodgkins, G.; Korhonen, J.; Livingstone, D.M.; Stewart, K.M.; Weyhenmeyer, G.A.; Granin, N.G. Extreme events, trends, and variability in Northern Hemisphere lake-ice phenology (1855–2005). Clim. Change 2012, 112, 299–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, C.; Lei, Y.; Qiu, Y. Contrasting Lake Ice Phenology Changes in the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau Revealed by Remote Sensing. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 18, 2132–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirillin, G.; Leppäranta, M.; Terzhevik, A.; Granin, N.; Bernhardt, J.; Engelhardt, C.; Efremova, T.; Golosov, S.; Palshin, N.; Sherstyankin, P.; et al. Physics of seasonally ice-covered lakes: A review. Aquat. Sci. 2012, 74, 659–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartosiewicz, M.; Ptak, M.; Woolway, R.I.; Sojka, M. On thinning ice: Effects of atmospheric warming, changes in wind speed and rainfall on ice conditions in temperate lakes (Northern Poland). J. Hydrol. 2021, 597, 125724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooney, G.G.; Van Lipzig, N.; Thiery, W. Estimating the effect of rainfall on the surface temperature of a tropical lake. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 6357–6369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qu, B.; Kang, S.; Chen, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, G. Lake ice and its effect factors in the Nam Co Basin, Tibetan Plateau. Adv. Clim. Change Res. 2012, 8, 327–333. [Google Scholar]
- Palecki, M.; Barry, R. Freeze-up and breakup of lakes as an index of temperature changes during the transition seasons: A case study for Finland. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 1986, 25, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouraev, A.V.; Semovski, S.V.; Shimaraev, M.N.; Mognard, N.M.; Legrésy, B.; Rémy, F. The ice regime of Lake Baikal from historical and satellite data: Relationship to air temperature, dynamical, and other factors. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2007, 52, 1268–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vavrus, S.J.; Wynne, R.H.; Foley, J.A. Measuring the sensitivity of southern Wisconsin lake ice to climate variations and lake depth using a numerical model. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1996, 41, 822–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, L.; Vanderkelen, I.; Gudmundsson, L.; Tan, Z.; Perroud, M.; Stepanenko, V.M.; Debolskiy, A.V.; Droppers, B.; Janssen, A.B.; Woolway, R.I.; et al. Attribution of global lake systems change to anthropogenic forcing. Nat. Geosci. 2021, 14, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Wu, S.; Zhuang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Hou, G.; Luo, G.; Hu, Z. Where Anthropogenic Activity Occurs, Anthropogenic Activity Dominates Vegetation Net Primary Productivity Change. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
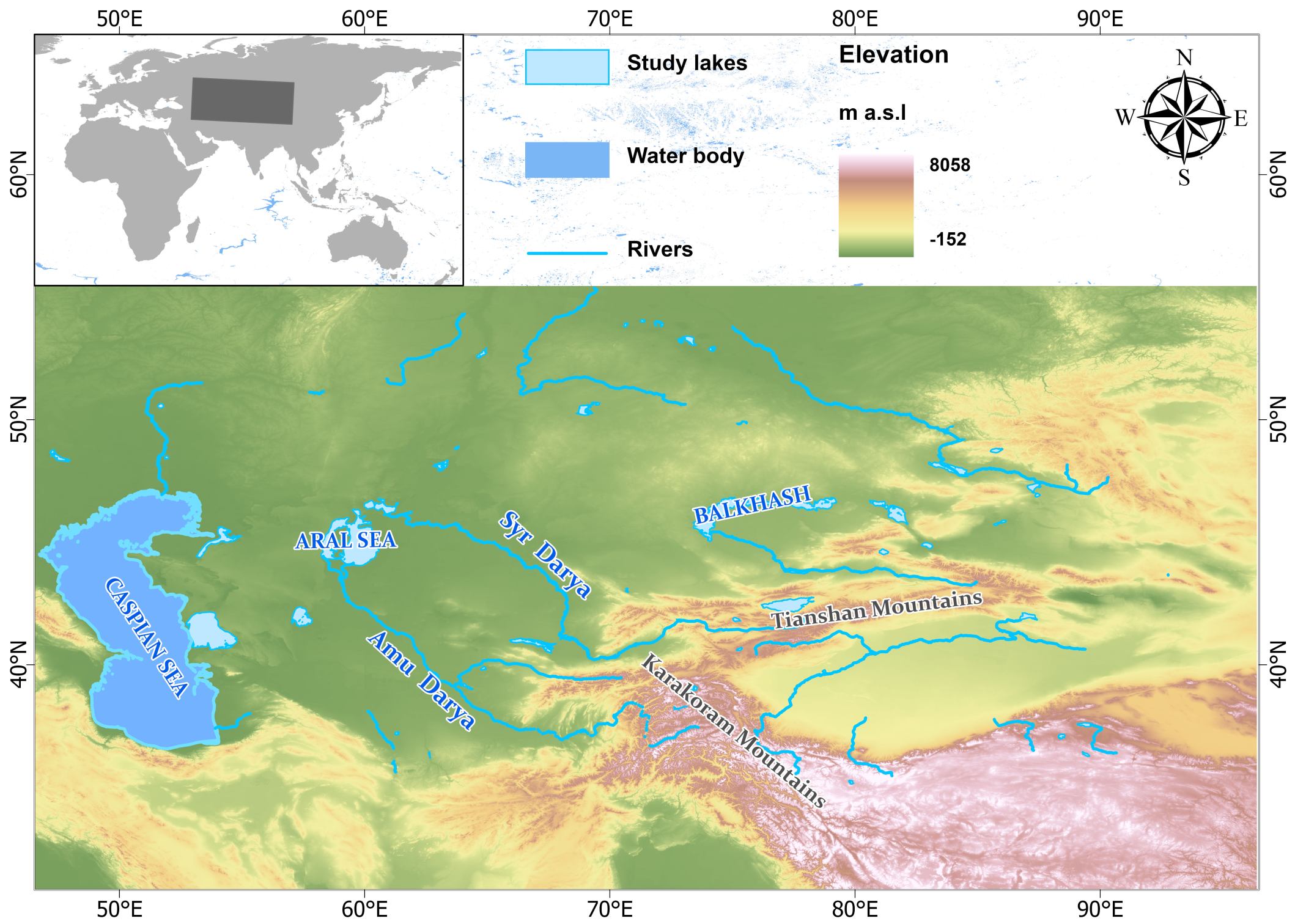
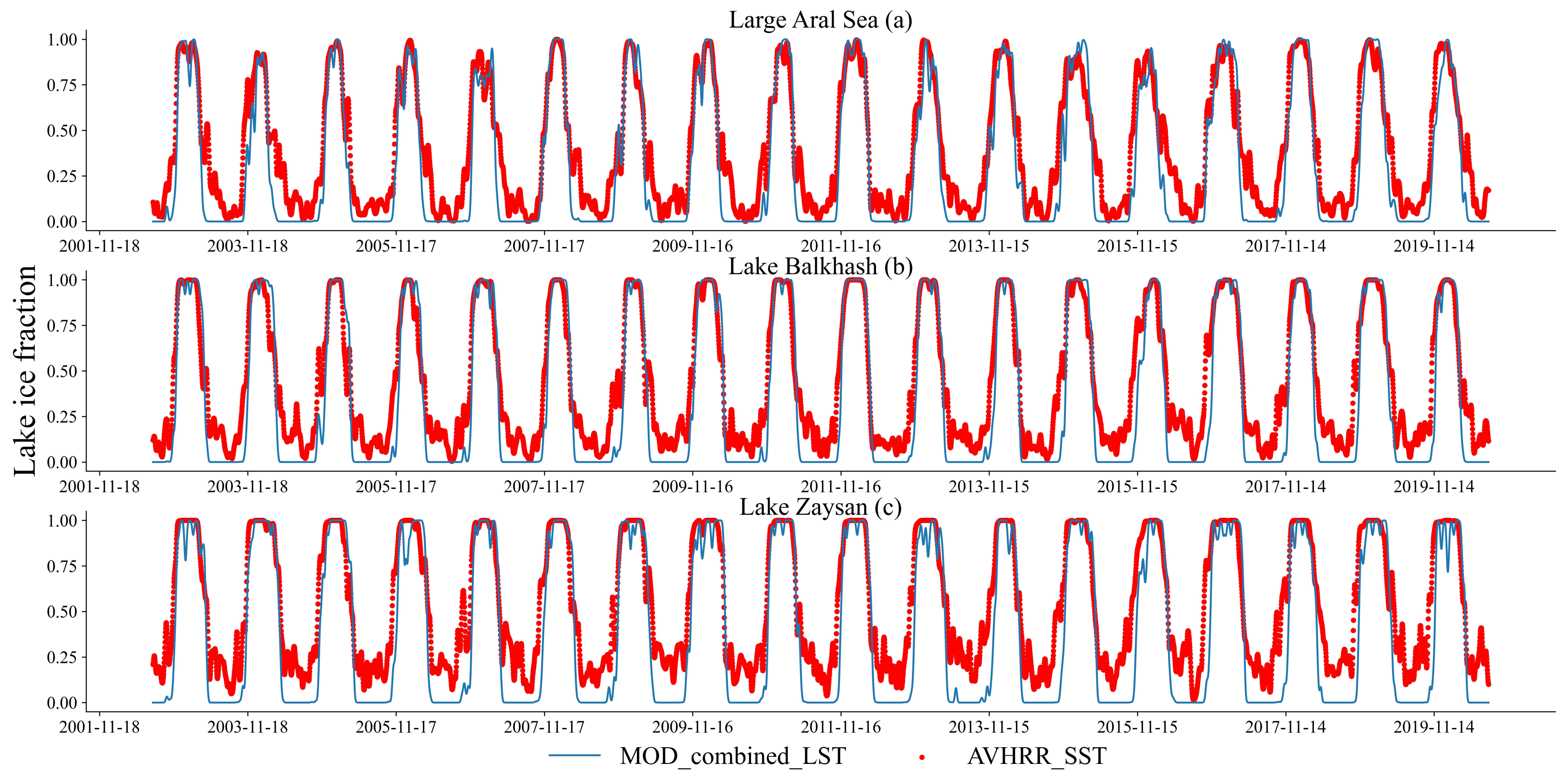
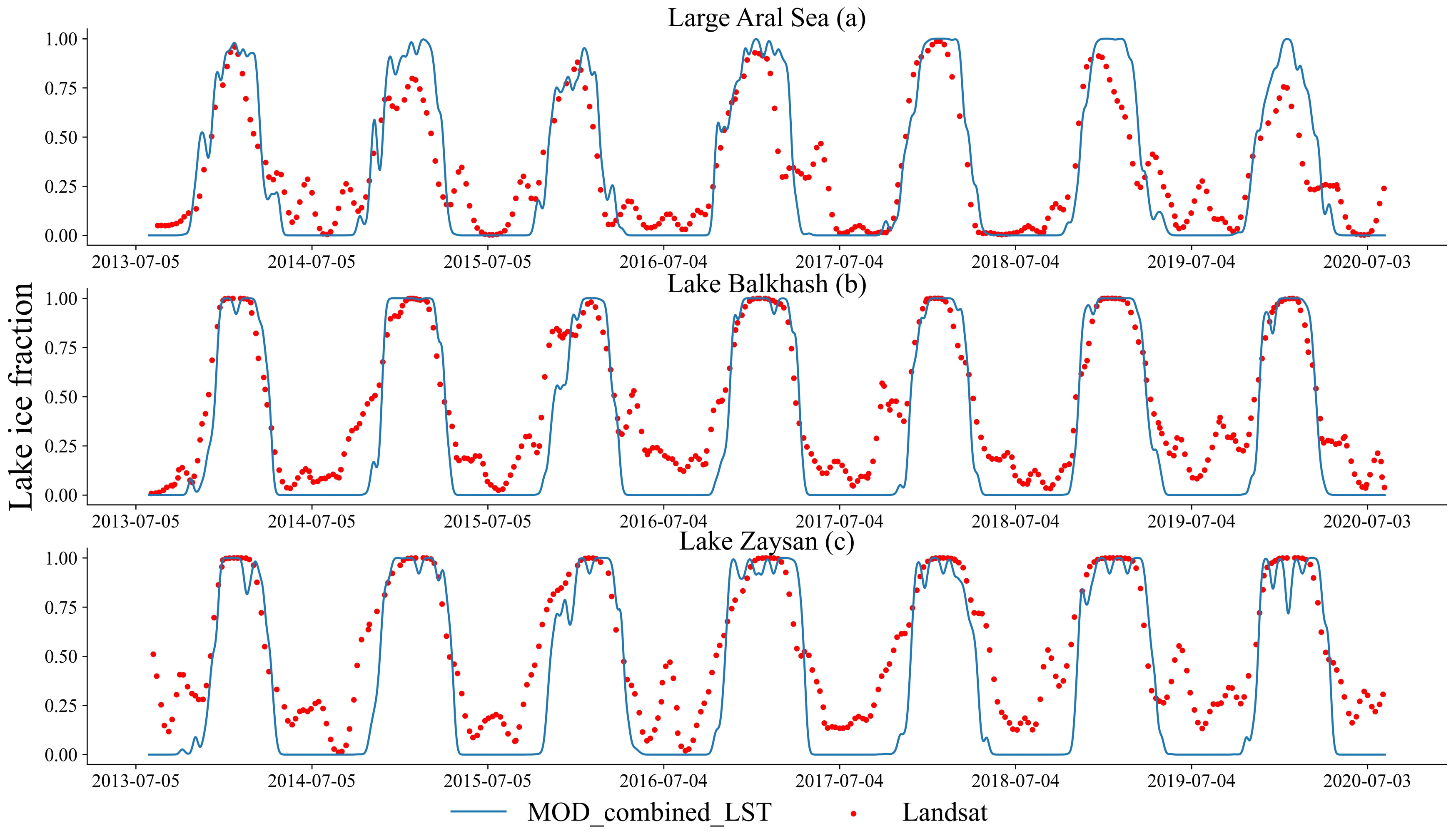
| MODIS vs. AVHRR | MODIS vs. Landsat8 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Large Aral Sea | Lake Balkhash | Lake Zaysan | Large Aral Sea | Lake Balkhash | Lake Zaysan | |
| R | 0.80 | 0.81 | 0.71 | 0.77 | 0.79 | 0.68 |
| RMSE | 0.17 | 0.19 | 0.23 | 0.18 | 0.19 | 0.25 |
| Lake Type | FUS (doy) | FUE (doy) | BUS (doy) | BUE (doy) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Not completely frozen in winter | 137.02 | NA | NA | 180.32 |
| Completely frozen in winter | 94.95 | 125.26 | 227.35 | 252.20 |
| Group | FUS | FUE | BUS | BUE | Elevation (m) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Doy | Trend (Day/Year) | Mean Doy | Trend (Day/Year) | Mean Doy | Trend (Day/Year) | Mean Doy | Trend (Day/Year) | ||
| 1 | 87.56 | 0.13 | 113.67 | 1.04 ** | 254.09 | 0.55 | 284.74 | 0.67 ** | 3925 |
| 2 | 125.22 | 0.08 | 135.08 | 0.71 ** | 220.32 | −0.65 ** | 231.20 | 0.15 | 1535 |
| 3 | 108.14 | −0.35 | 137.95 | 0.40 | 210.86 | −0.82 ** | 217.60 | −0.31 | 207 |
| Group | FUD | ICD | BUD | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Duration | Trend (Day/Year) | Mean Duration | Trend (Day/Year) | Mean Duration | Trend (Day/Year) | |
| 1 | 26.74 | 0.84 ** | 140.42 | −0.49 | 31.34 | 0.05 |
| 2 | 23.46 | −0.02 | 109.42 | −0.71 * | 21.57 | 0.08 |
| 3 | 32.90 | 0.02 | 89.18 | −0.41 | 24.71 | 0.31 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hou, G.; Yuan, X.; Wu, S.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, X.; Xie, C.; Ling, Q.; Long, W.; Luo, G. Phenological Changes and Driving Forces of Lake Ice in Central Asia from 2002 to 2020. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4992. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194992
Hou G, Yuan X, Wu S, Ma X, Zhang Z, Cao X, Xie C, Ling Q, Long W, Luo G. Phenological Changes and Driving Forces of Lake Ice in Central Asia from 2002 to 2020. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(19):4992. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194992
Chicago/Turabian StyleHou, Guanyu, Xiuliang Yuan, Shixin Wu, Xiaofei Ma, Zihui Zhang, Xingwen Cao, Conghui Xie, Qing Ling, Weiyi Long, and Geping Luo. 2022. "Phenological Changes and Driving Forces of Lake Ice in Central Asia from 2002 to 2020" Remote Sensing 14, no. 19: 4992. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194992
APA StyleHou, G., Yuan, X., Wu, S., Ma, X., Zhang, Z., Cao, X., Xie, C., Ling, Q., Long, W., & Luo, G. (2022). Phenological Changes and Driving Forces of Lake Ice in Central Asia from 2002 to 2020. Remote Sensing, 14(19), 4992. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194992








