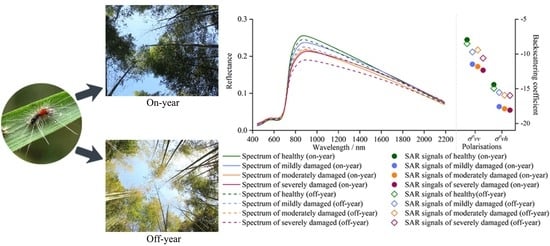
Monitoring Damage Caused by Pantana phyllostachysae Chao to Moso Bamboo Forests Using Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 Images
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Used
2.2.1. Field Observations
2.2.2. Remote Sensing Data Used
2.3. Mapping the Distribution of Bamboo Forests
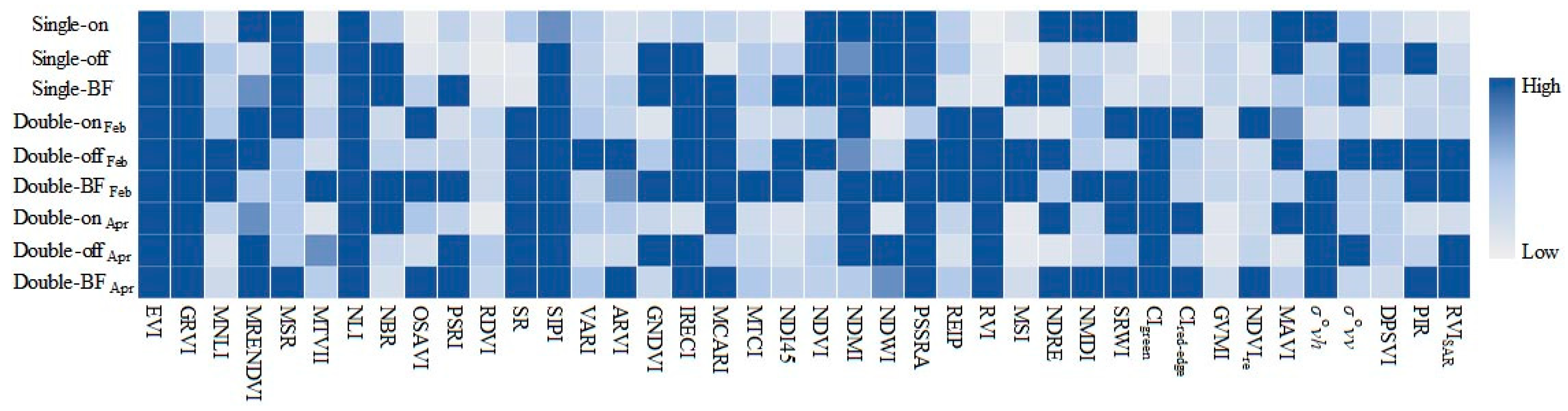
2.4. Feature Selection
2.5. Development of Severity Identification Model
2.5.1. Model Establishment and Optimization
2.5.2. Design of Model Scenario
2.5.3. Accuracy Evaluation
3. Results
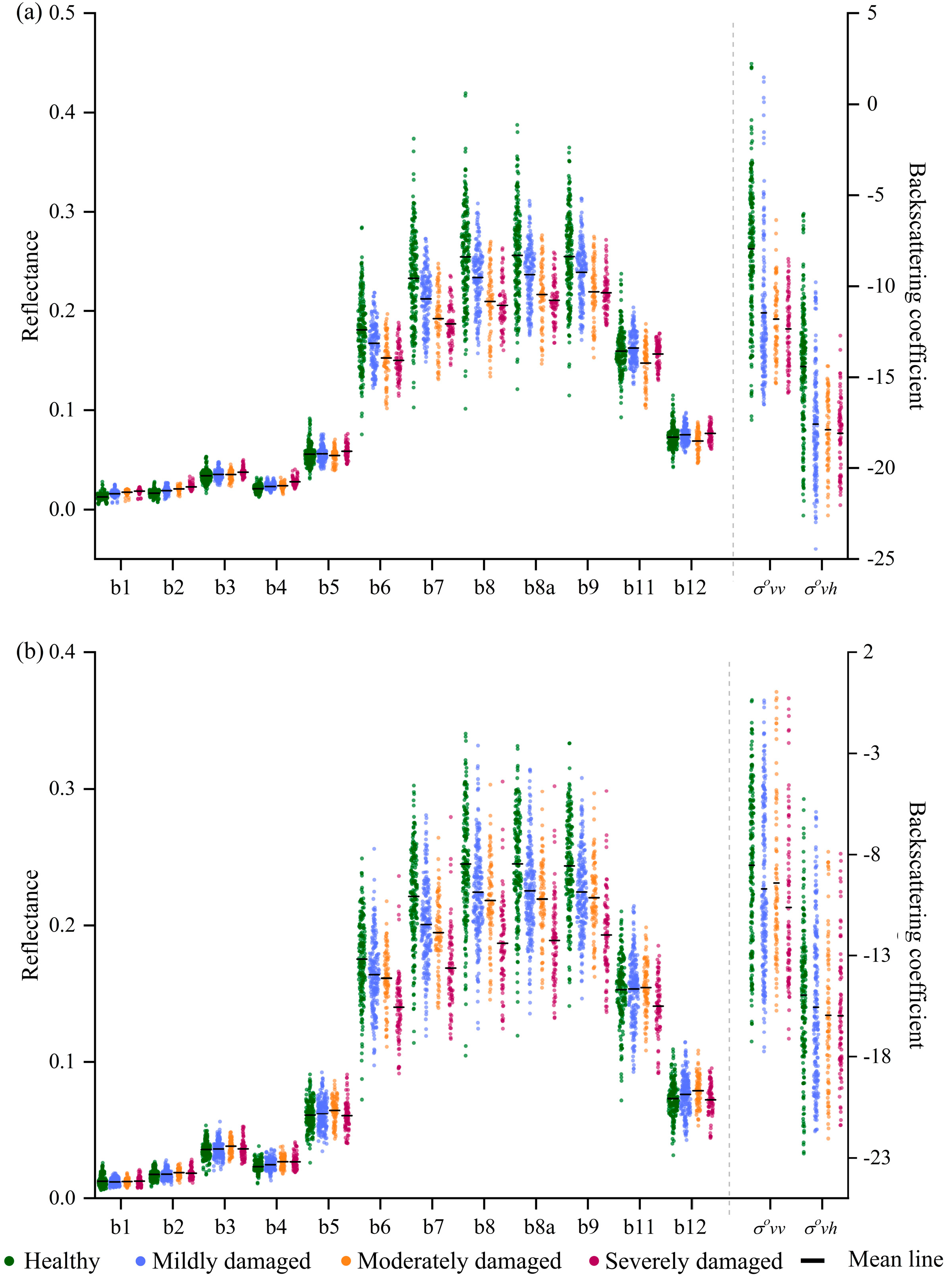
3.1. Optical and SAR Signals of Bamboo Forests with Different Damage Severities
3.2. Model Performance
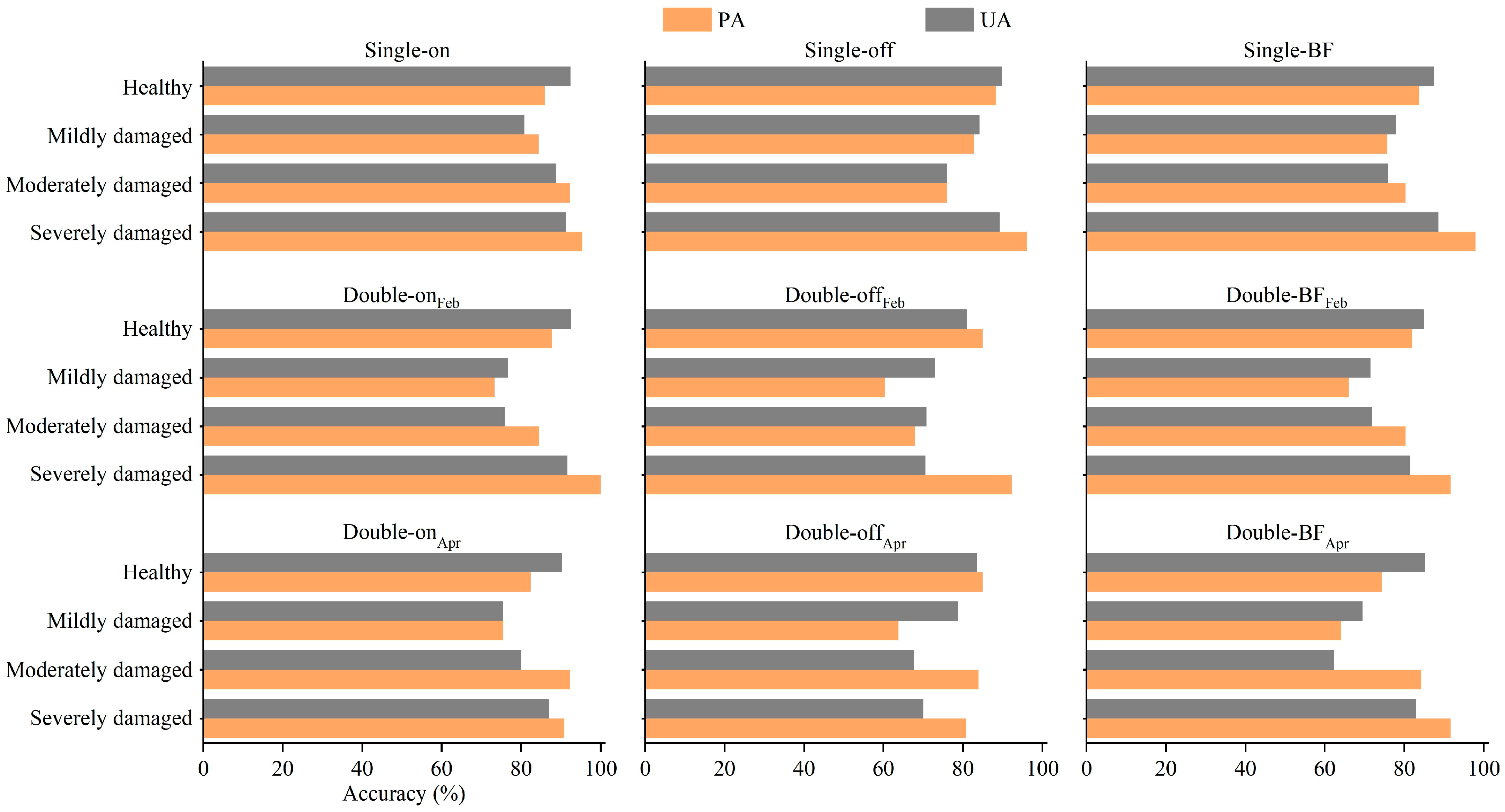
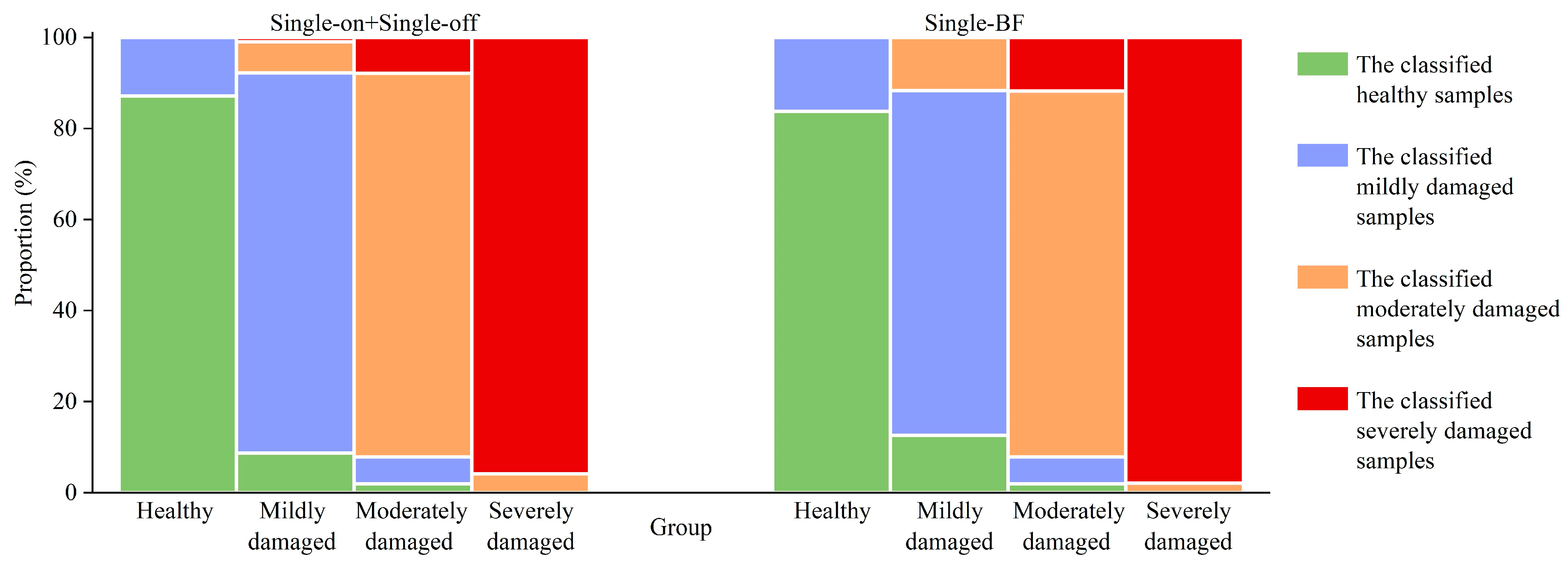
3.2.1. Classification Results
3.2.2. Contribution of SAR Features to Classification Model
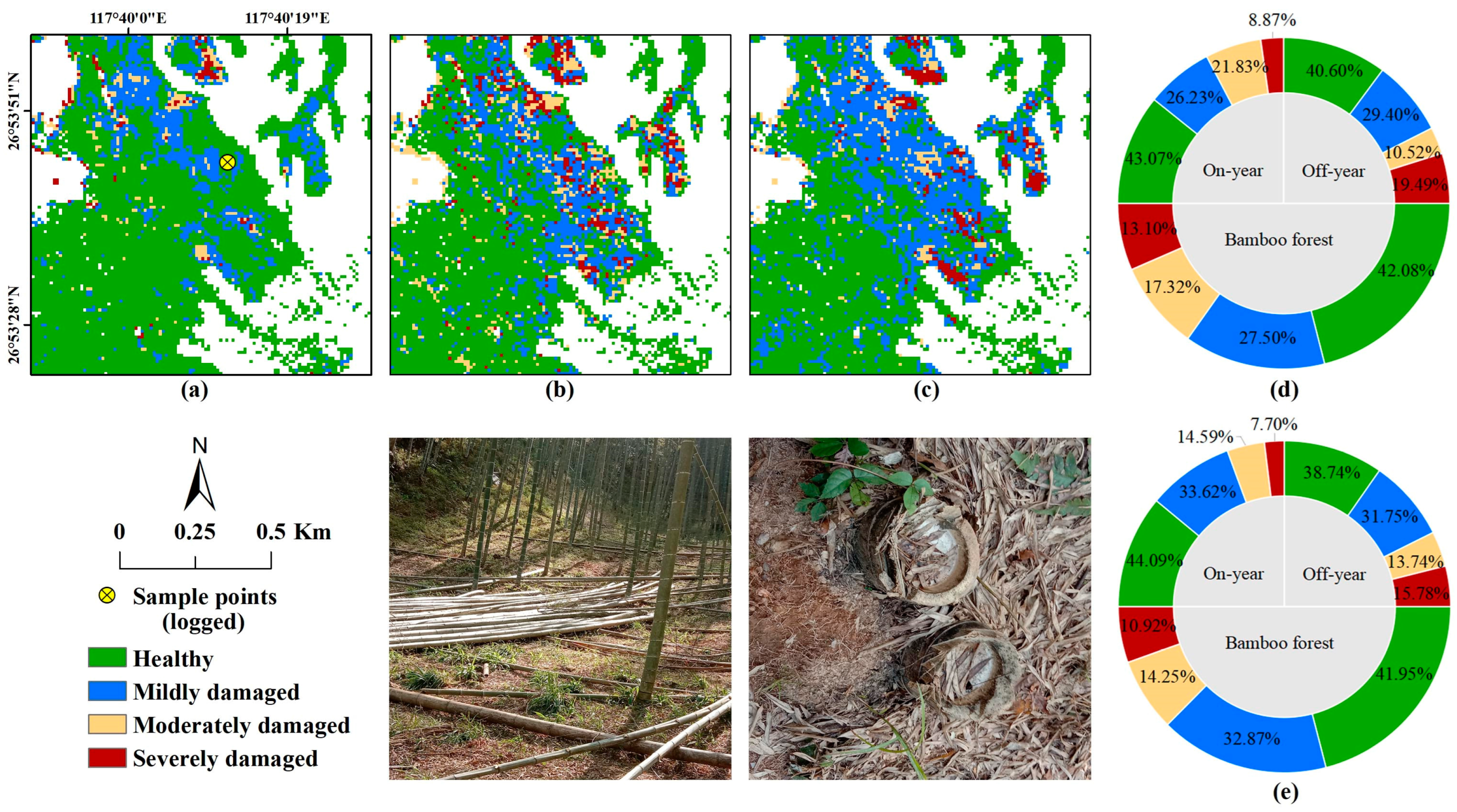
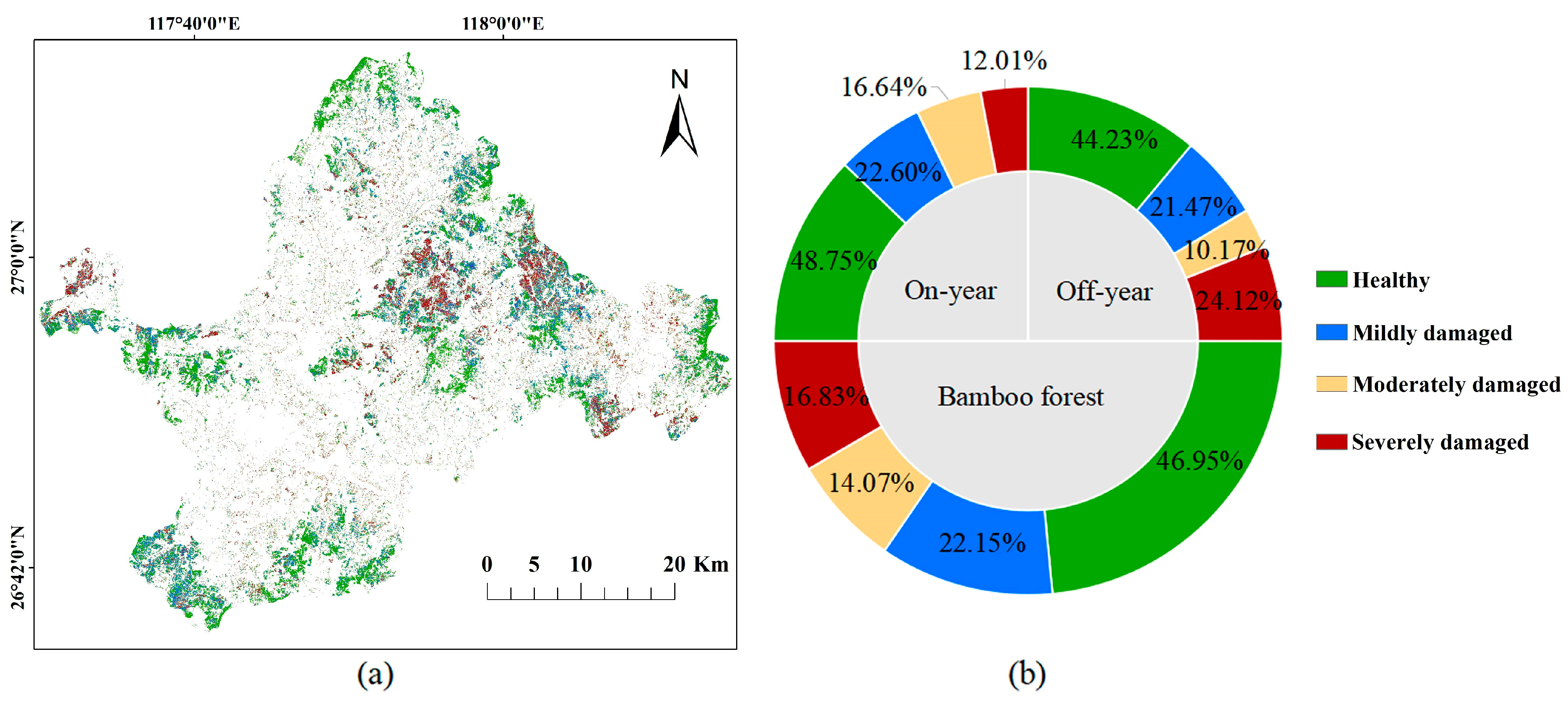
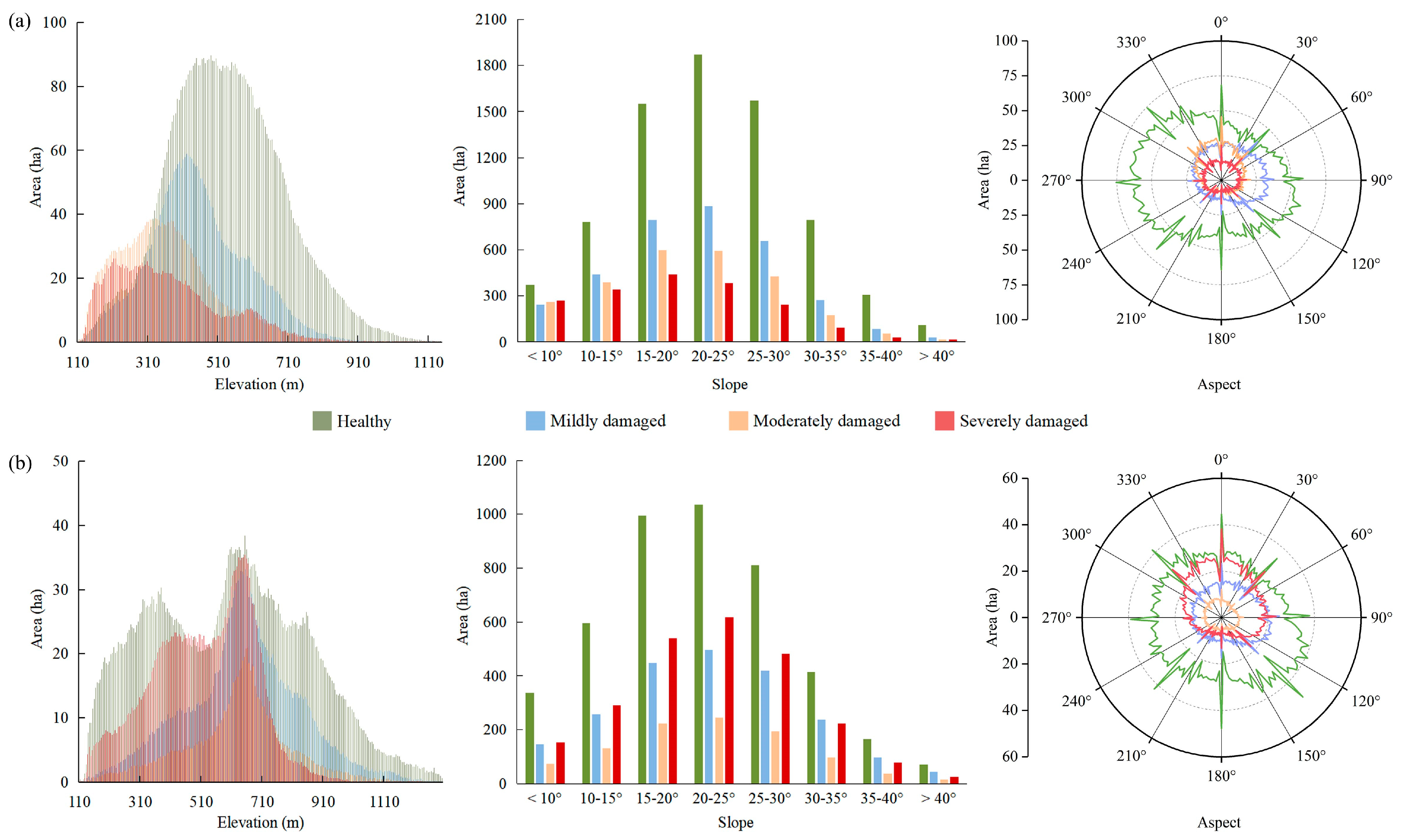
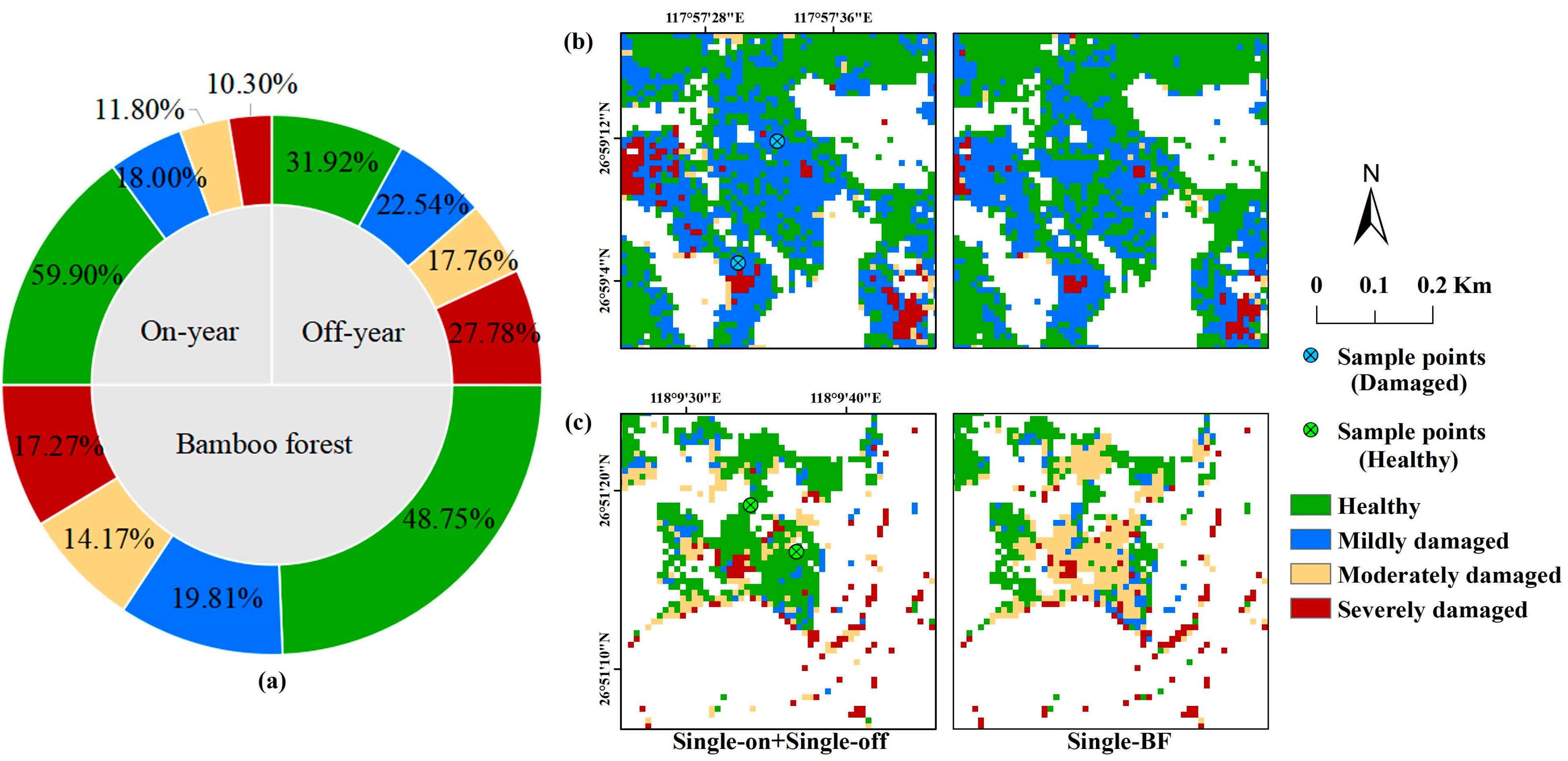
3.3. Distribution of PPC Damage
4. Discussion
4.1. Significance of SAR Features to PPC Monitoring
4.2. Interference Factors during the PPC Damage Identification
4.3. Limitations and Research Prospects
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Coniferous | Broadleaf | Off-Year Bamboo | On-Year Bamboo | PA (%) | UA (%) | OA (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coniferous | 191 | 28 | 2 | 2 | 85.65 | 90.09 | 90.88 |
| Broadleaf | 17 | 187 | 5 | 5 | 87.38 | 85.39 | |
| Off-year bamboo | 4 | 1 | 203 | 10 | 93.12 | 95.31 | |
| On-year bamboo | 0 | 3 | 3 | 216 | 97.30 | 92.70 |

| Index | Formula |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Vegetation Index | |
| Green Ratio Vegetation Index | |
| Modified Non-Linear Index | |
| Modified Red-Edge Normalized Difference Vegetation Index | |
| Modified Simple Ratio | |
| Modified Triangular Vegetation Index (Improved) | |
| Non-Linear Index | |
| Normalized Burn Ratio | |
| Optimized Soil-Adjusted Vegetation Index | |
| Plant Senescence Reflectance Index | |
| Renormalized Difference Vegetation Index | |
| Simple Ratio | |
| Structure Insensitive Pigment Index | |
| Visible Atmospherically Resistant Index | |
| Atmospherically Resistant Vegetation Index | |
| Green Normalized Difference Vegetation | |
| Inverted Red-Edge Chlorophyll Index | |
| Modified Chlorophyll Absorption Ratio Index | |
| Meris Terrestrial Chlorophyll Index | |
| Normalized Difference Index | |
| Normalized Difference Vegetation Index | |
| Normalized Difference Moisture Index | |
| Normalized Difference Water Index | |
| Pigment Specific Simple Ratio algorithm | |
| Red-Edge Inflection Point Index | |
| Ratio Vegetation Index | |
| Moisture Stress Index | |
| Normalized Difference Red-Edge | |
| Normalized Multi-band Drought Index | |
| Simple Ratio Water Index | |
| Green Chlorophyll Index | |
| Red-Edge Chlorophyll Index | |
| Global Vegetation Moisture Index | |
| Normalized Difference Vegetation Index Red-Edge | |
| Moisture Adjusted Vegetation Index | |
| Dual Polarization SAR Vegetation Index | |
| Polarization Intensity Ratio | |
| Radar Vegetation Index | |
| Backscattering at Cross-polarization (VH) and Co-polarization (VV) |
| Model | Hyper-Parameters | Features | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LR | NE | MD | MCW | GAM | ||
| Single-onSpec | 0.24 | 83 | 6 | 1 | 0 | EVI, MRENDVI, MSR, NLI, NDVI, NDMI, NDWI, PSSRA, NDRE, NMDI, SRWI, MAVI |
| Single-offSpec | 0.35 | 70 | 6 | 1 | 0 | GRVI, NLI, NBR, SIPI, GNDVI, IRECI, NDVI, NDMI, NDWI, PSSRA, NDRE, GVMI, MAVI |
References
- FAO. Global Forest Resources Asessment 2020: Main Report; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- National Forestry and Grassland Administration. China Forest Resources Report (2014–2018); China Forestry Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2019.
- Cao, L.; Coops, N.C.; Sun, Y.; Ruan, H.H.; Wang, G.B.; Dai, J.S.; She, G.H. Estimating canopy structure and biomass in bamboo forests using airborne LiDAR data. ISPRS-J. Photogramm. 2019, 148, 114–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, F.J.; Li, P.H.; Zhou, G.M.; Du, H.Q.; Xu, X.J.; Shi, Y.J.; Mo, L.F.; Zhou, Y.F.; Tu, G.Q. Development of the BIOME-BGC model for the simulation of managed Moso bamboo forest ecosystems. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 172, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.P.; Hou, Y.M.; You, M.S. Effects of different management measures on the composition and structure of arthropod community in Phyllostachys heterocycla cv. pubescens forest. Acta Entomol. Sin. 2005, 48, 928–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.L.; Wang, B.Y. Life history of Pantana phyllostachysae and relationships between the insect and meteorological conditions. J. Zhejiang For. Coll. 1993, 10, 342–345. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, S.W.; Ye, X.Y.; Li, T.S.; Lu, S.Q.; Yang, Z.W.; Lu, M.Z. Type of distribution and method of density estimation for Pantana phyllostachysae. For. Res. 1993, 6, 579–582. [Google Scholar]
- Senf, C.; Seidl, R.; Hostert, P. Remote sensing of forest insect disturbances: Current state and future directions. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2017, 60, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Rogan, J.; Zhu, Z.; Hawbaker, T.J.; Hart, S.J.; Andrus, R.A.; Meddens, A.J.H.; Hicke, J.A.; Eastman, J.R.; Kulakowski, D. Detecting subtle change from dense Landsat time series: Case studies of mountain pine beetle and spruce beetle disturbance. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 263, 112560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldea, M.; Hamilton, J.G.; Resti, J.P.; Zangerl, A.R.; Berenbaum, M.R.; DeLucia, E.H. Indirect effects of insect herbivory on leaf gas exchange in soybean. Plant Cell Environ. 2005, 28, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, H.; Wang, J.M.; Chen, X.M.; Yang, Z.X.; Liang, J.S. Photosynthetic traits and antioxidative defense responses of Pinus yunnanensis after joint attack by bark beetles Tomicus yunnanensis and T. minor. J. For. Res. 2018, 30, 2031–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilipović, A.; Drekić, M.; Stojnić, S.; Nikolić, N.; Trudić, B.; Milović, M.; Poljaković-Pajnic, L.; Borišev, M.; Orlović, S. Physiological responses of two pedunculate oak (Quercus robur L.) families to combined stress conditions—Drought and herbivore attack. Sumar. List. 2020, 144, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bárta, V.; Lukeš, P.; Homolová, L. Early detection of bark beetle infestation in Norway spruce forests of Central Europe using Sentinel-2. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2021, 100, 102335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, R.; Rahimzadeh-Bajgiran, P.; Weiskittel, A.; Meneghini, A.; MacLean, D.A. Spruce budworm tree host species distribution and abundance mapping using multi-temporal Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 satellite imagery. ISPRS-J. Photogramm. 2021, 172, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periasamy, S. Significance of dual polarimetric synthetic aperture radar in biomass retrieval: An attempt on Sentinel-1. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 217, 537–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soudani, K.; Delpierre, N.; Berveiller, D.; Hmimina, G.; Vincent, G.; Morfin, A.; Dufrêne, É. Potential of C-band Synthetic Aperture Radar Sentinel-1 time-series for the monitoring of phenological cycles in a deciduous forest. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2021, 104, 102505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, S.; Breidenbach, J.; Kändler, G. Early detection of bark beetle green attack using TerraSAR-X and RapidEye data. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 1912–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.W.; Li, N.; Zang, Z.; Lu, D.S.; Wang, G.X.; Wang, N. Examining phenological variation of on-year and off-year bamboo forests based on the vegetation and environment monitoring on a New Micro-Satellite (VENµS) time-series data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 42, 2203–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.L.; Jiang, H.; Cai, Z.J.; Zhou, X.L.; Peng, C.H. The response of the net primary production of Moso bamboo forest to the On and Off-year management: A case study in Anji County, Zhejiang, China. Forest Ecol. Manag. 2018, 409, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Du, H.; Zhou, G.; Mao, F.; Li, X.; Zhu, D.; Li, Y.; Cui, L. Remote estimation of canopy leaf area index and chlorophyll content in Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis (Carriere) J. Houz.) forest using MODIS reflectance data. Ann. For. Sci. 2018, 75, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.Y.; Xu, Z.H.; Yang, X.; Shi, J.M.; Hu, X.Y.; Ju, W.M. Monitoring the severity of Pantana phyllostachysae Chao on bamboo using leaf hyperspectral data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipponi, F. Sentinel-1 GRD preprocessing workflow. Proceedings 2019, 18, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodu, N. Super-resolving multiresolution images with band-independent geometry of multispectral pixels. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote 2017, 55, 4610–4617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, J.; Tajo, L.; Sarma, K.K. Bamboo resources mapping using satellite technology. Curr. Sci. 2010, 99, 650–653. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, S.; Song, B.; Liu, C.; Gong, P.; Luo, J.; Zhang, M.; Xiong, T. Bamboo forest mapping in China using the dense Landsat 8 image archive and Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, N. Application of aerial remote sensing technology for detection of fire blight infected pear trees. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 168, 105147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.K.; Zhang, X.J.; Xu, M.; Liu, Y.L.; Qian, J.; Zhang, Q. Estimation model of equivalent water thickness in the road area. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2020, 22, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.G.; Sun, H.; Li, C.J.; Ma, K.S.; Chen, S.; Long, J.P.; Ren, L.X. Retrieving the forest aboveground biomass by combining the red edge bands of Sentinel-2 and GF-6. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 8222–8236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaes, X.; Defourny, P.; Wegmuller, U.; Della Vecchia, A.; Guerriero, L.; Ferrazzoli, P. C-band polarimetric indexes for maize monitoring based on a validated radiative transfer model. IEEE T. Geosci. Remote 2006, 44, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasirzadehdizaji, R.; Balik Sanli, F.; Abdikan, S.; Cakir, Z.; Sekertekin, A.; Ustuner, M. Sensitivity analysis of multi-temporal sentinel-1 SAR parameters to crop height and canopy coverage. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Zhang, D. Feature selection and analysis on correlated gas sensor data with recursive feature elimination. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2015, 212, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.Q.; Guestrin, C. XGBoost: A scalable tree boosting system. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (KDD), San Francisco, CA, USA, 13 August 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.G.; Ma, R.H.; Melack, J.M.; Duan, H.T.; Liu, M.; Kutser, T.; Xue, K.; Shen, M.; Qi, T.C.; Yuan, H.L. Landsat observations of chlorophyll-a variations in Lake Taihu from 1984 to 2019. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2022, 106, 102642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.Q.; Ding, J.L.; Ge, X.Y.; Li, X.H.; Han, L.J.; Wang, Z. Estimation of soil organic carbon content in the Ebinur Lake wetland, Xinjiang, China, based on multisource remote sensing data and ensemble learning algorithms. Sensors 2022, 22, 2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, N.V.; Bowyer, K.W.; Hall, L.O.; Kegelmeyer, W.P. SMOTE: Synthetic minority over-sampling technique. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2002, 16, 321–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandberg, G.; Soja, M.J.; Ulander, L.M.H. Impact and modeling of topographic effects on P-band SAR backscatter from boreal forests. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 July 2011; pp. 3522–3525. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.W.; Li, N.; Lu, D.S.; Chen, Y.Y. Mapping Moso bamboo forest and its on-year and off-year distribution in a subtropical region using time-series Sentinel-2 and Landsat 8 data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.J.; Du, H.Q.; Zhou, G.M.; Mao, F.J.; Zhang, M.; Han, N.; Fan, W.L.; Liu, H.; Huang, Z.H.; He, S.B.; et al. Phenology estimation of subtropical bamboo forests based on assimilated MODIS LAI time series data. ISPRS-J. Photogramm. 2021, 173, 262–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, R.; Dennison, P.E.; Zhao, F.; Shendryk, I.; Rickert, A.; Hanavan, R.P.; Cook, B.D.; Serbin, S.P. Mapping canopy defoliation by herbivorous insects at the individual tree level using bi-temporal airborne imaging spectroscopy and LiDAR measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 215, 170–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Xiang, S.; Li, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Li, Z.; Yao, X.; Li, Q.; et al. Monitoring the severity of Pantana phyllostachysae Chao infestation in Moso bamboo forests based on UAV multi-spectral remote sensing feature selection. Forests 2022, 13, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

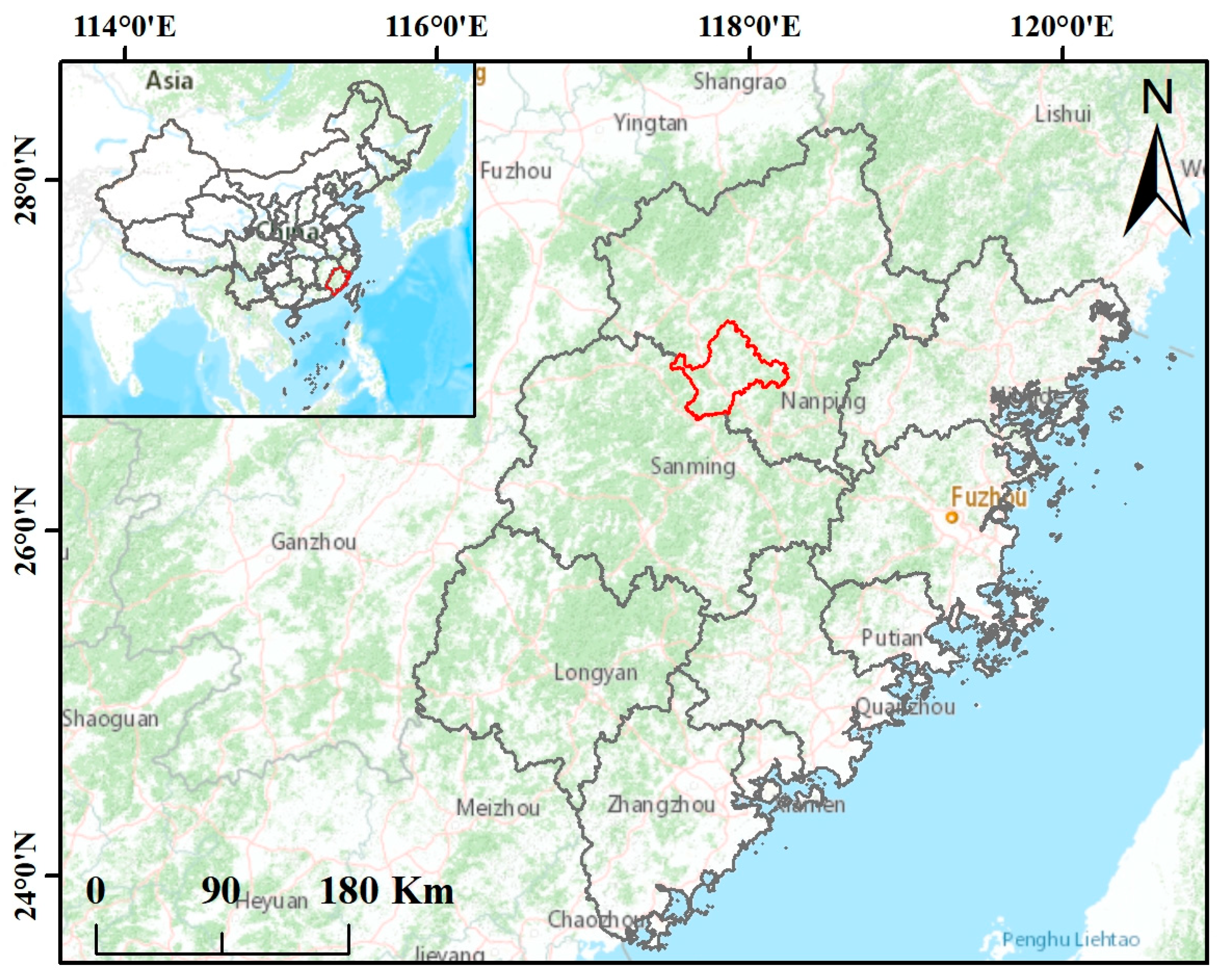




| Sensors | Observation Time | Tile/Absolute Orbit Numbers |
|---|---|---|
| Sentinel-2 | 21 February 2020 | T50RNQ, T50RNR, T50RPQ |
| 16 April 2020 | ||
| 23 October 2020 | ||
| Sentinel-1 | 22 February 2020 | 031, 364 |
| 22 April 2020 | 032, 239 | |
| 19 October 2020 | 034, 864 |
| Scenario | Model Input | Model Abbreviation |
|---|---|---|
| Single-time observation (October) | On-year samples | Single-on |
| Off-year samples | Single-off | |
| Total | Single-BF | |
| Double-time observation (October–February) | On-year samples | Double-onFeb |
| Off-year samples | Double-offFeb | |
| Total | Double-BFFeb | |
| Double-time observation (October–April) | On-year samples | Double-onApr |
| Off-year samples | Double-offApr | |
| Total | Double-BFApr |
| Model | Hyper-Parameters | OA (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LR | NE | MD | MCW | GAM | Training Set | Test Set | |
| Single-on | 0.32 | 73 | 6 | 1 | 0 | 89.29 ± 1.05 | 88.00 |
| Single-off | 0.28 | 62 | 6 | 1 | 0.3 | 88.65 ± 1.15 | 85.80 |
| Single-BF | 0.3 | 183 | 6 | 1 | 0 | 85.24 ± 1.30 | 82.76 |
| Double-onFeb | 0.3 | 109 | 6 | 2 | 0 | 87.22 ± 1.24 | 84.67 |
| Double-offFeb | 0.3 | 61 | 6 | 1 | 0 | 80.72 ± 1.97 | 75.15 |
| Double-BFFeb | 0.25 | 207 | 6 | 1 | 0 | 81.59 ± 1.46 | 78.06 |
| Double-onApr | 0.3 | 172 | 6 | 1 | 0 | 86.90 ± 1.09 | 83.33 |
| Double-offApr | 0.32 | 89 | 6 | 1 | 0 | 78.36 ± 1.28 | 76.92 |
| Double-BFApr | 0.15 | 101 | 6 | 1 | 0 | 79.08 ± 0.72 | 75.24 |
| Compared Groups | σovh/Single-On | Σovv/Single-Off | PIR/Single-Off |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthy–Mildly damaged | 0.000 ** | 0.000 ** | 0.001 ** |
| Healthy–Moderately damaged | 0.000 ** | 0.003 ** | 0.302 |
| Healthy–Severely damaged | 0.000 ** | 0.000 ** | 0.007 ** |
| Mildly damaged–Moderately damaged | 0.121 | 0.429 | 0.242 |
| Mildly damaged–Severely damaged | 0.054 | 0.492 | 0.998 |
| Moderately damaged–Severely damaged | 0.999 | 0.120 | 0.648 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, L.; Zhu, T.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Ju, W. Monitoring Damage Caused by Pantana phyllostachysae Chao to Moso Bamboo Forests Using Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 Images. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5012. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14195012
Huang X, Zhang Q, Hu L, Zhu T, Zhou X, Zhang Y, Xu Z, Ju W. Monitoring Damage Caused by Pantana phyllostachysae Chao to Moso Bamboo Forests Using Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 Images. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(19):5012. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14195012
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Xuying, Qi Zhang, Lu Hu, Tingting Zhu, Xin Zhou, Yiwei Zhang, Zhanghua Xu, and Weimin Ju. 2022. "Monitoring Damage Caused by Pantana phyllostachysae Chao to Moso Bamboo Forests Using Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 Images" Remote Sensing 14, no. 19: 5012. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14195012
APA StyleHuang, X., Zhang, Q., Hu, L., Zhu, T., Zhou, X., Zhang, Y., Xu, Z., & Ju, W. (2022). Monitoring Damage Caused by Pantana phyllostachysae Chao to Moso Bamboo Forests Using Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 Images. Remote Sensing, 14(19), 5012. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14195012