A Multi-Domain Collaborative Transfer Learning Method with Multi-Scale Repeated Attention Mechanism for Underwater Side-Scan Sonar Image Classification
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Data transformation rules, such as flipping, rotating, cropping, distorting, scaling, and adding noise, are used on the existing images to enhance data. Inoue [30] used two randomly selected images from the training set and processed them by basic data enhancement operations. Then, a new sample can be formed by averaging two processed images in pixel with one of the original sample labels set as the new label.
- Multiple samples are used to generate similar pseudo samples. The input optical image is preprocessed and combined with sonar image features to create semi synthetic training data to enhance the dataset [8,31]. The method of style transferring with a pre-trained CNN was adopted to generate pseudo SSS images, which can be added to the training set, finally achieving a similar improvement compared with the former method [32]. By changing the upsampling method of style transfer [33], the noise ratio can be changed by manually adjusting parameters, and the generated pseudo SSS images are more related to the real SSS images.
- The randomly generated samples with consistent distribution of the training dataset are created by the generative adversarial networks (GAN), which are trained to learn an image-translation from low-complexity ray-traced images to real sonar images [27,34]. Sung [35] et al. introduced a method of GAN to translate actual sonar images into simulator-like sonar images to generate a great deal of template images.
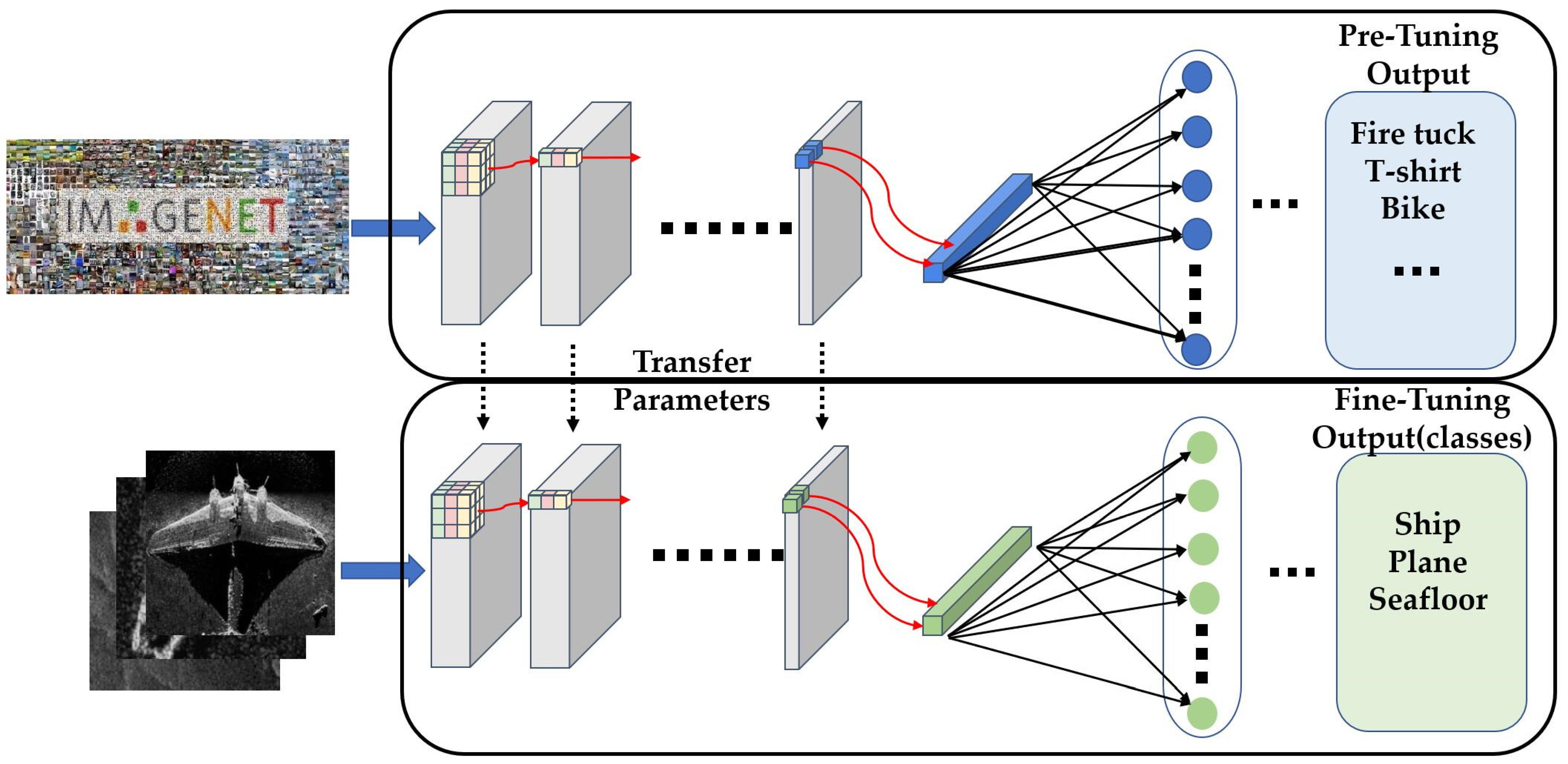
- An automatic side-scan sonar image classification method is proposed, which combines the multi-domain collaborative transfer learning (MDCTL) with the multi-scale repeated attention mechanism (MSRAM). The proposed MDCTL method transfers the parameters of low-level feature extraction layers learned from the SAR images and the high-level feature representation layers learned from the optical images, respectively, which gives a new way of transfer learning.
- By combining the channel attention mechanism (CAM) and the spatial attention mechanism (SAM) [43,44], the MSRAM makes the model do better in extracting and focusing on features of the target, and therefore more key features can be used for classification, which brings the model higher classification accuracy, as well as stability.
- The proposed MDCTL method has been tested on a new SSS dataset, which adds 115 more side-scan sonar images to the SeabedObjects-KLSG dataset. The new SSS dataset is now available at https://github.com/HHUCzCz/-SeabedObjects-KLSG--II (accessed on 16 November 2021). Feature response maps and class activation heatmaps are used to demonstrate the effect of the proposed MDCTL method with MSRAM.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Multi-Domain Collaborative Transfer Learning
2.1.1. Fine-Tuning
2.1.2. Transfer Learning from Multi-Domain
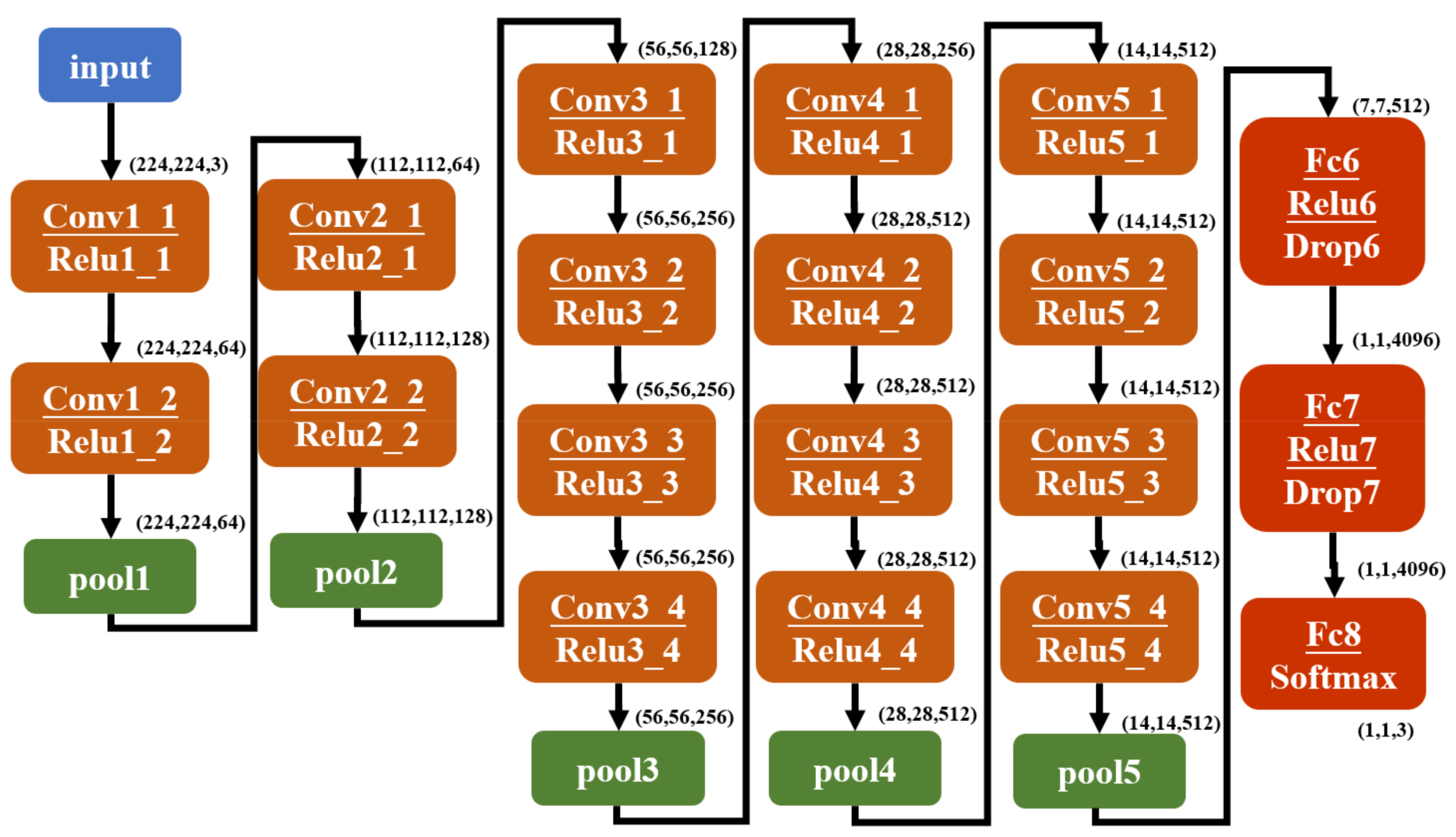
2.2. Backbone Network-VGG19
2.3. Attention Mechanism
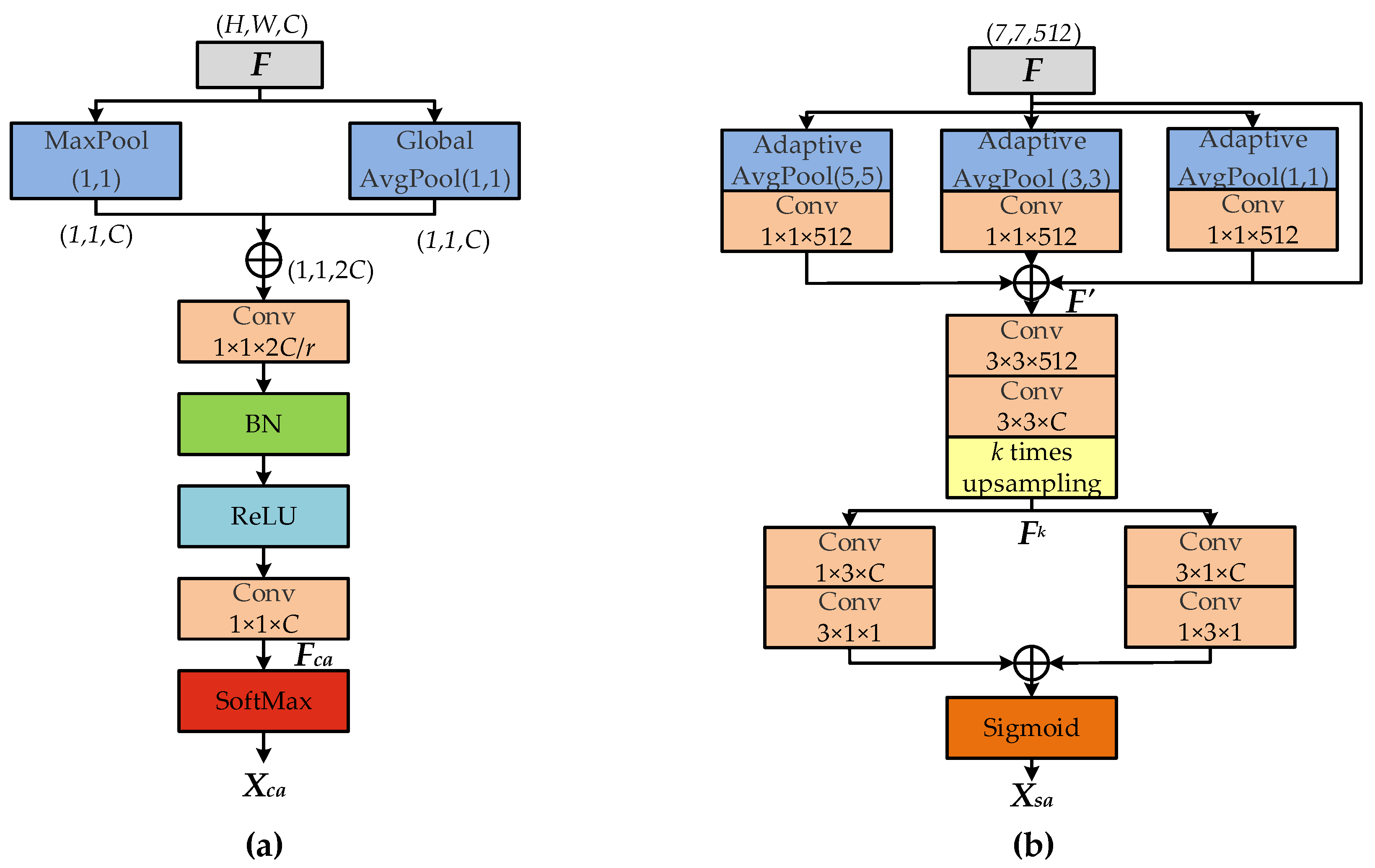
2.3.1. Channel Attention Module
2.3.2. Spatial Attention Module
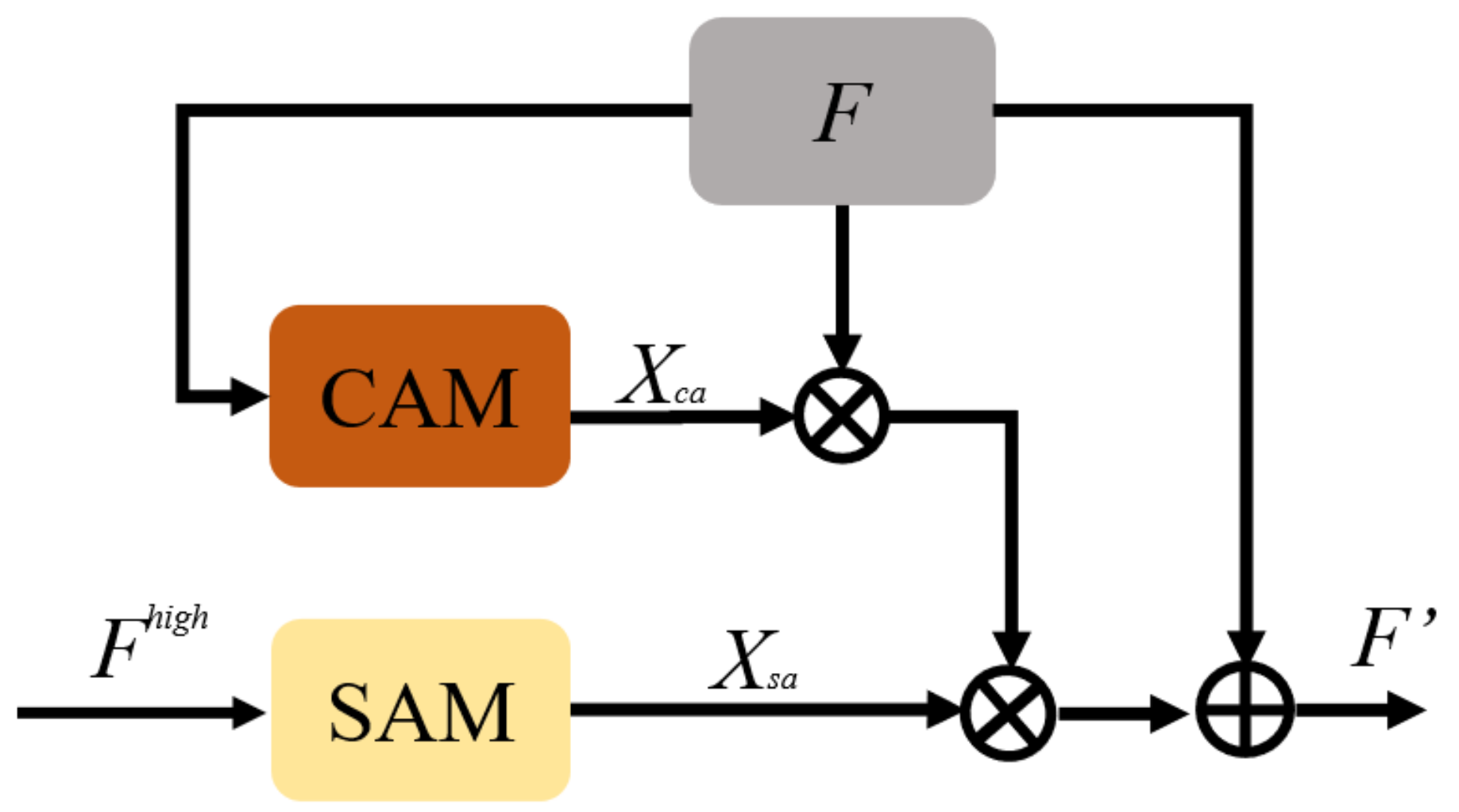
2.3.3. Multi-Scale Repeated Attention Module
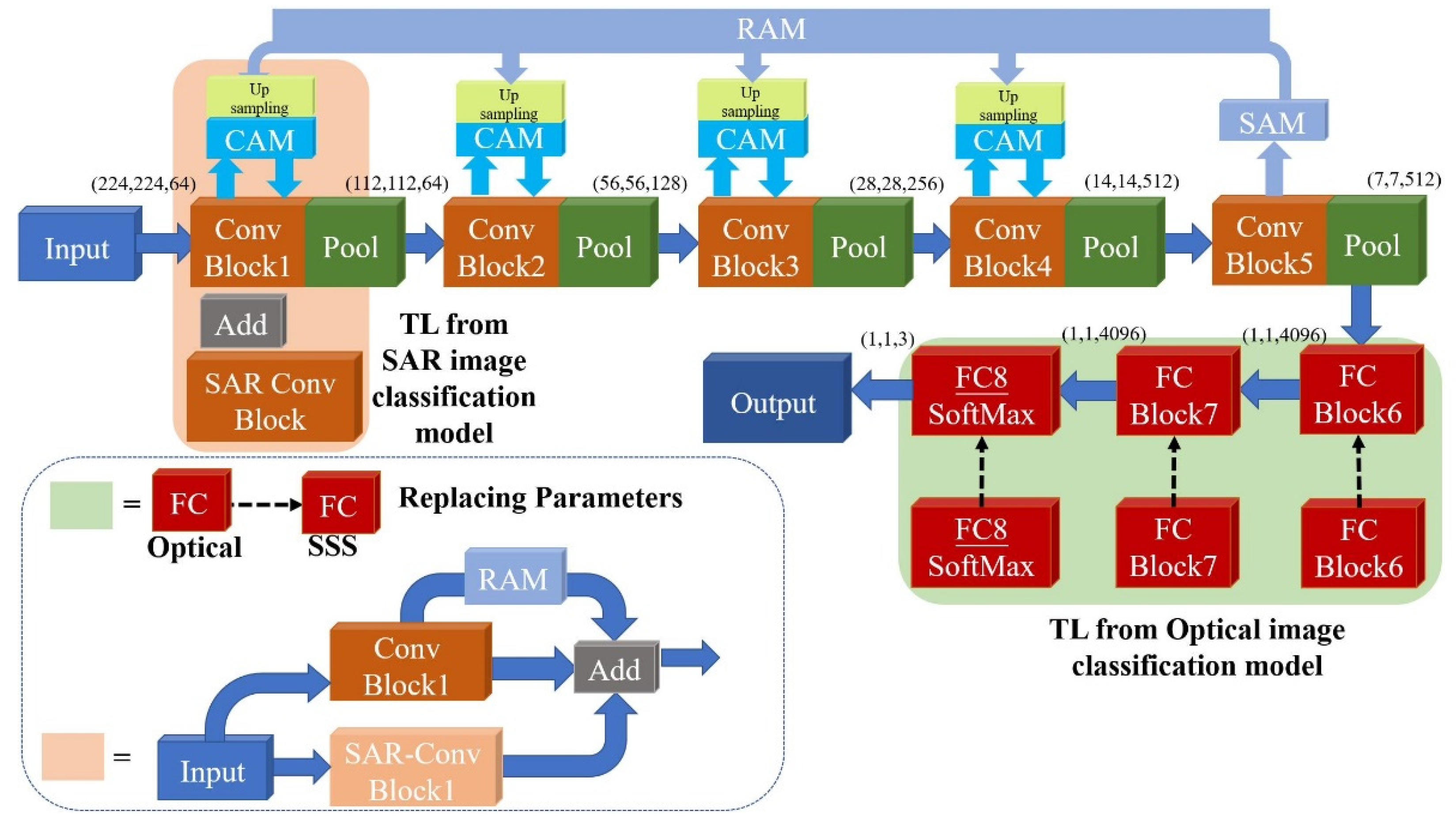
2.4. Proposed Network
- Multi-domain pre-training: Using the VGG19 pre-trained on ImageNet dataset, the corresponding classification models are trained on SAR images and optical images respectively;
- Parameter transfer: The VGG19 model, pre-trained on the ImageNet dataset, is set as the backbone. The first two convolutional blocks of the SAR image classification network are first transferred as a new feature extraction branch; the last three convolutional layers of the optical image classification network will then replace the corresponding layers of the SSS image classification network. The transferred parameters will be unfrozen and retrained to fit the SSS image classification task in the target domain;
- Adding multi-scale repeated attention mechanism: SAM is placed at the back end of the network to obtain the spatial attention map through the feature map output from the last convolution layer. Then, the spatial attention map will be upsampled into different scales to multiply with the channel weight matrix obtained from CAM.
3. Results
3.1. Experimental Setup
3.1.1. Dataset Used
3.1.2. Experimental Details
3.2. Network Model Evaluating Indicator
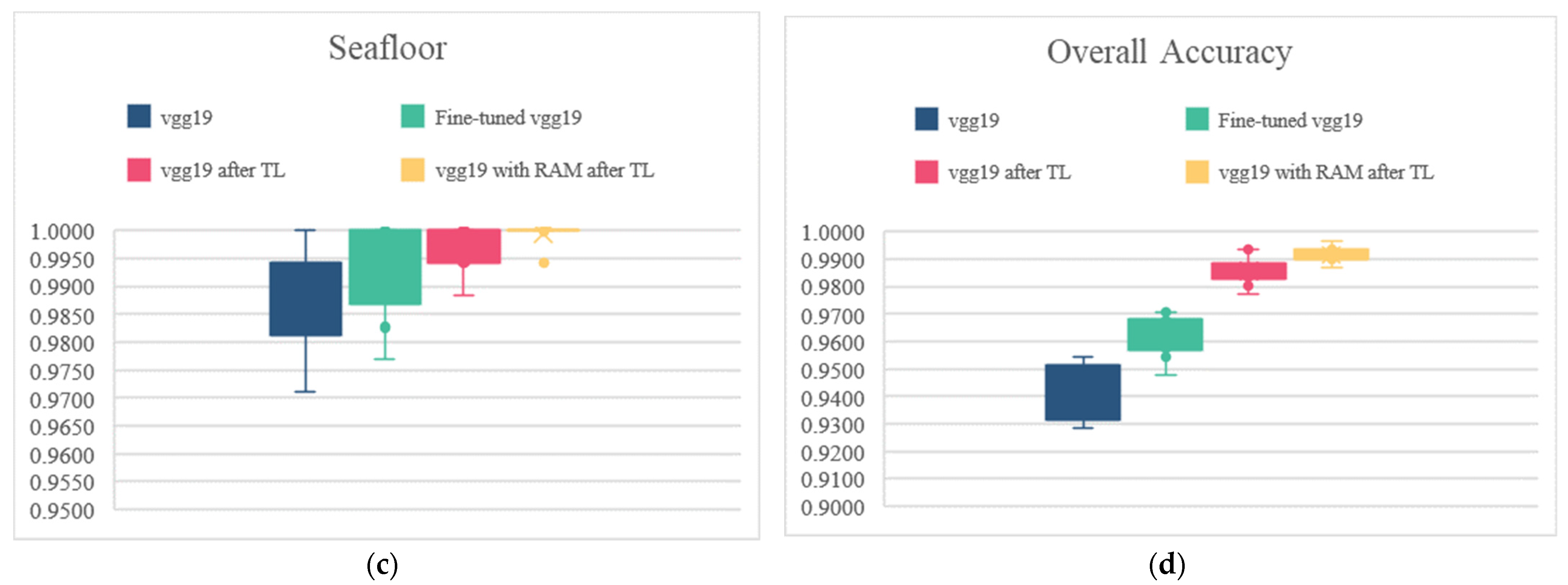
3.3. Performance Analysis
3.4. Visualization
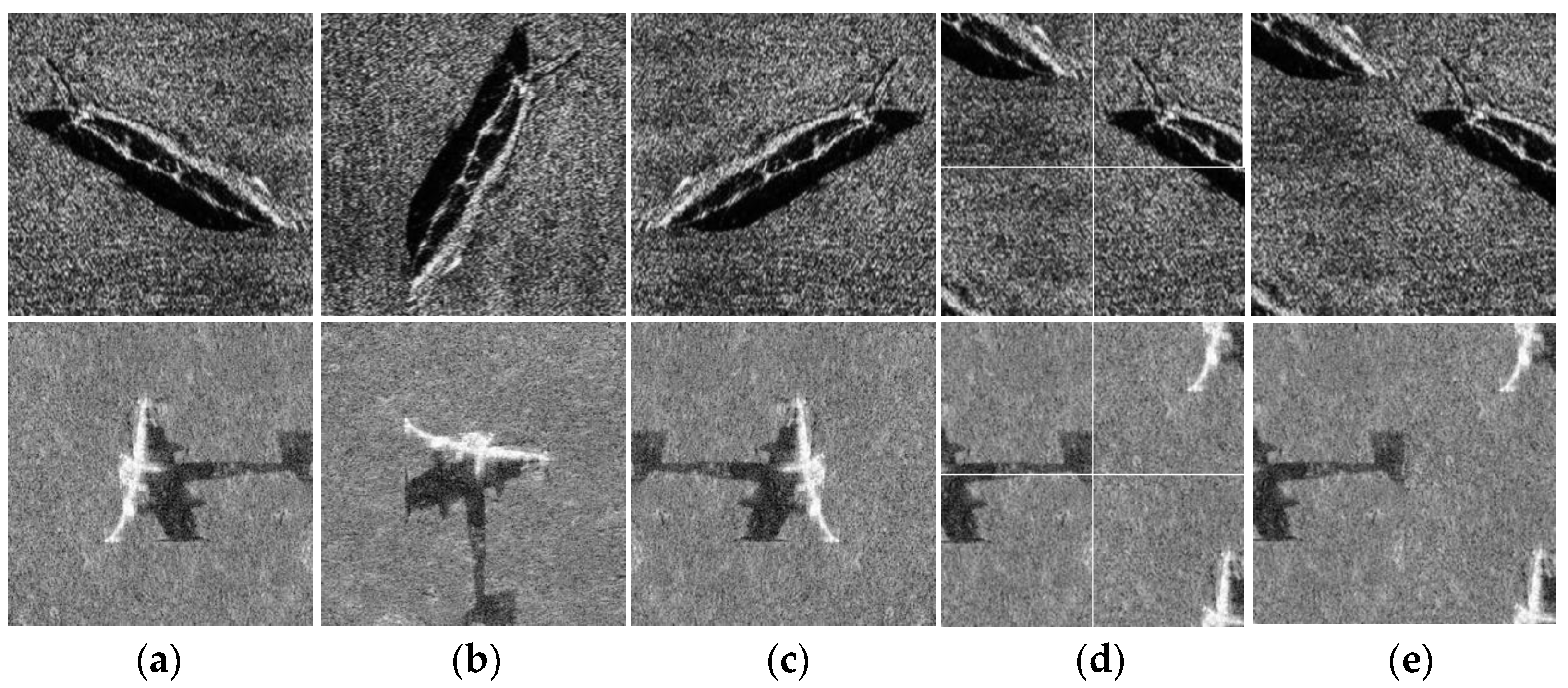
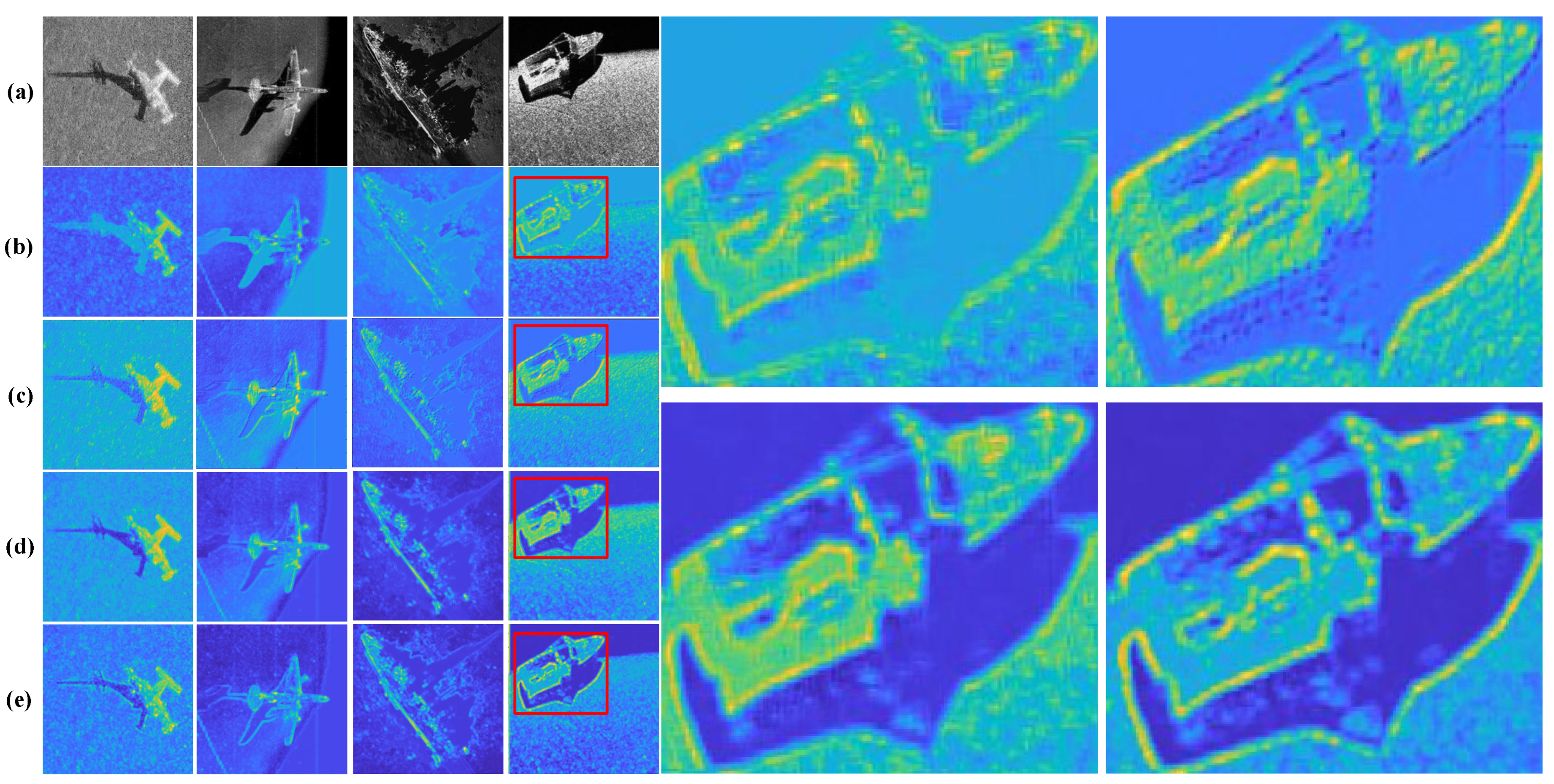
3.4.1. Feature Response Map Visualization
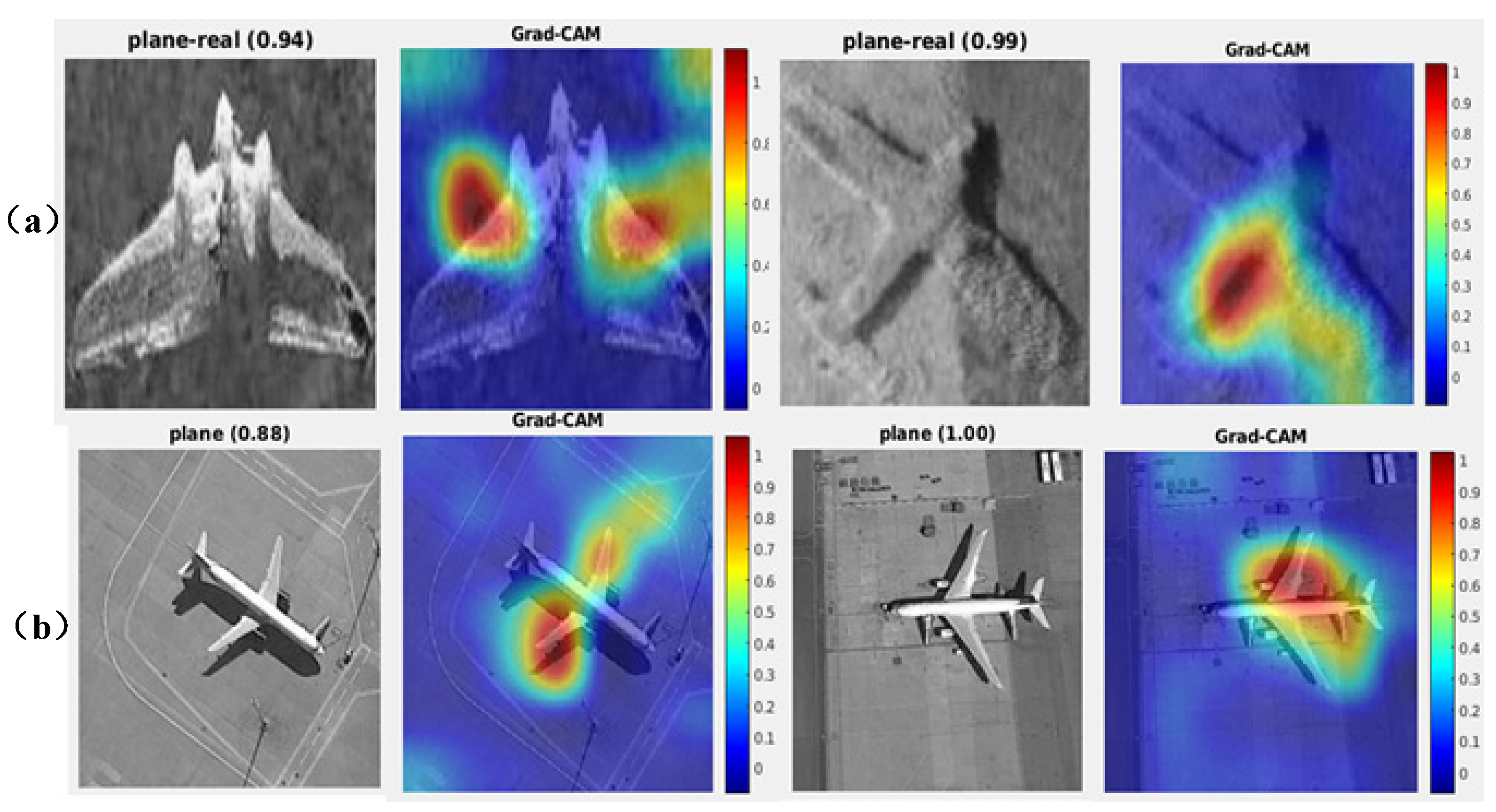
3.4.2. Heat Maps Based on Grad-CAM
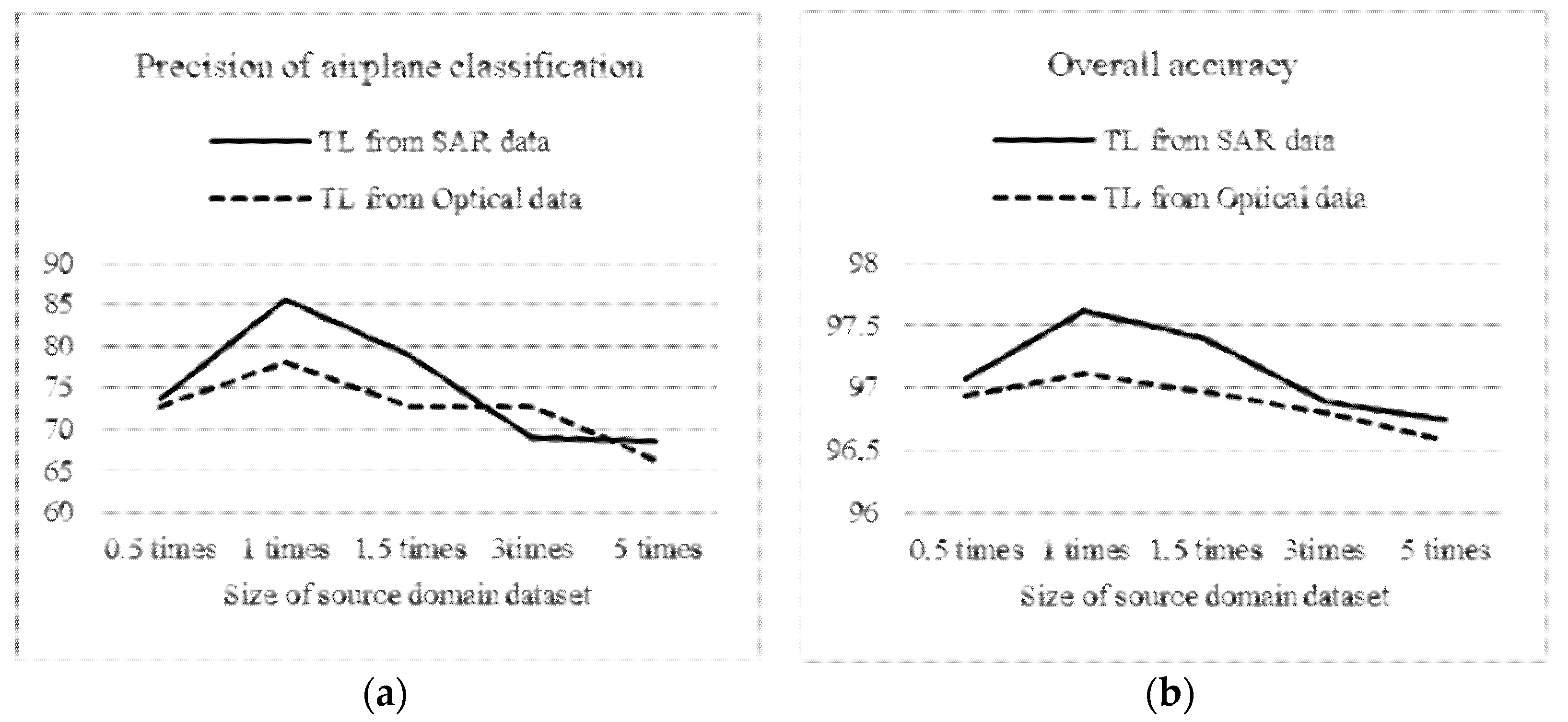
3.5. Details in MCDTL
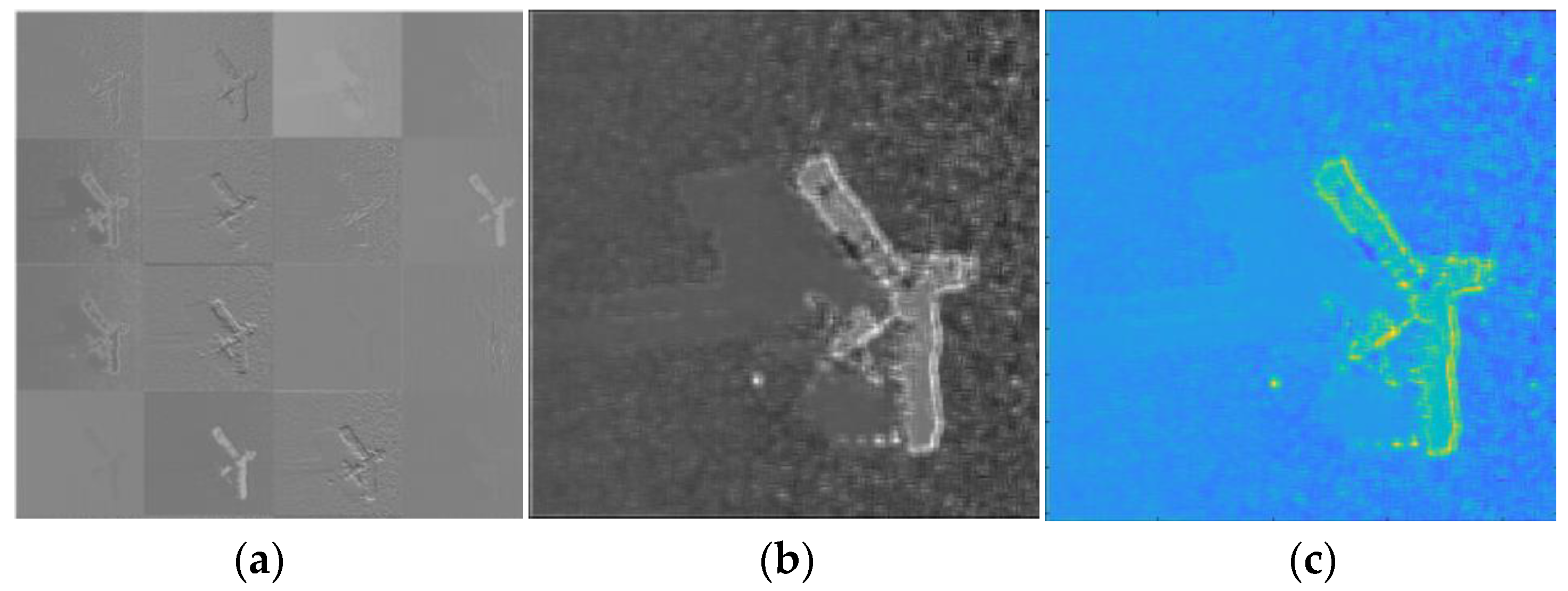
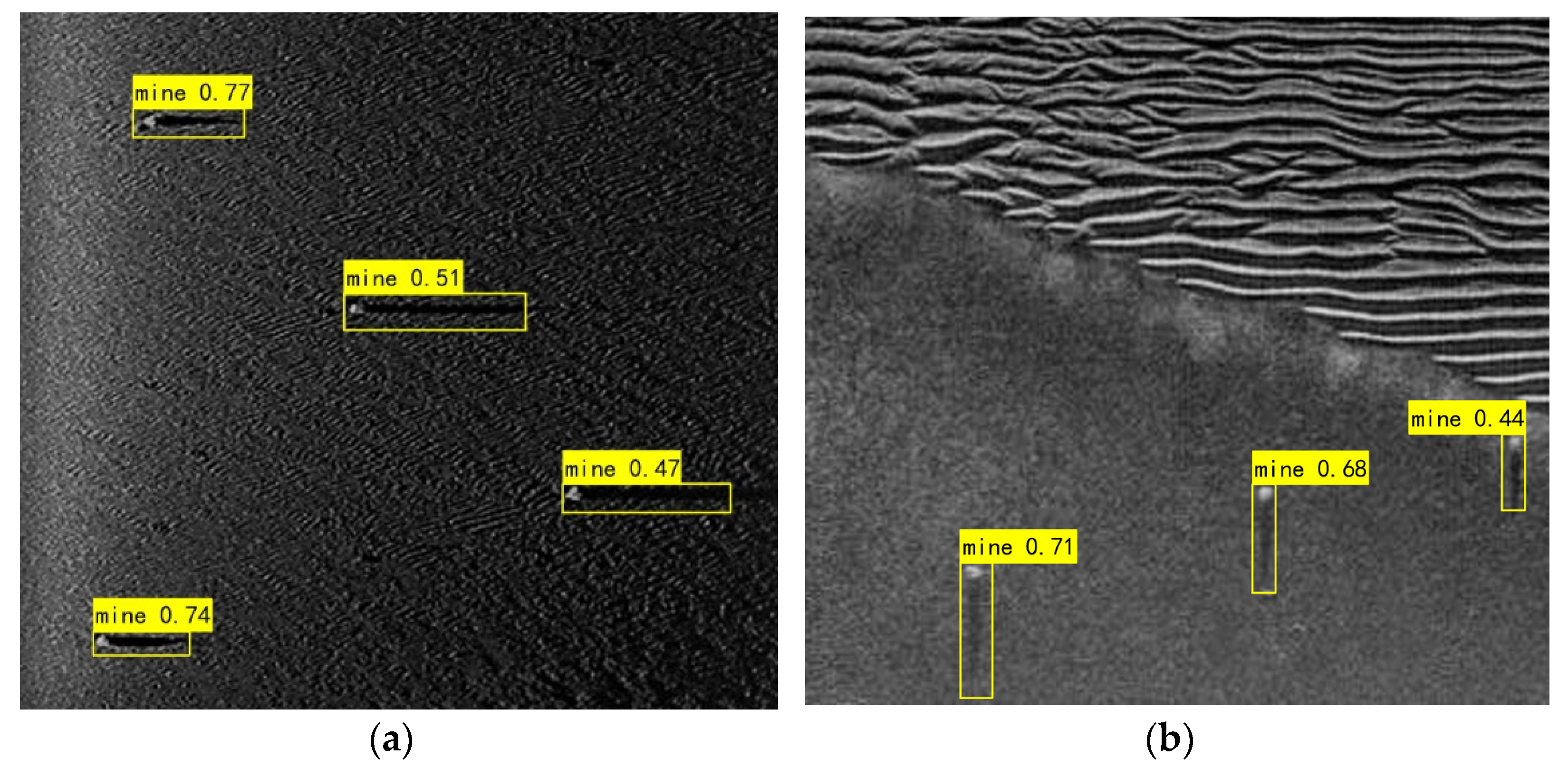
3.6. Applications for Detection
4. Discussion
4.1. Significance of the Proposed Method
4.2. Limitations of the Proposed Method
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kong, W.Z.; Hong, J.C.; Jia, M.Y.; Yao, J.L.; Gong, W.H.; Hu, H.; Zhang, H.G. YOLOv3-DPFIN: A Dual-Path Feature Fusion Neural Network for Robust Real-Time Sonar Target Detection. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 3745–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.C.; Zhao, J.H.; Gong, Q.H.; Huang, C.; Zheng, G.; Ma, J.Y. Real-Time Underwater Maritime Object Detection in Side-Scan Sonar Images Based on Transformer-YOLOv5. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Li, C.; Zhang, S.; Yang, P.; Li, X. Research on side-scan sonar image target classification method based on transfer learning. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2018 MTS/IEEE, Charleston, SC, USA, 22–25 October 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Vandrish, P.; Vardy, A.; Walker, D.; Dobre, O. Side-scan sonar image registration for AUV navigation. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Symposium on Underwater Technology and Workshop on Scientific Use of Submarine Cables and Related Technologies, Tokyo, Japan, 5–8 April 2011; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Zerr, B.; Stage, B.; Guerrero, A. Automatic Target Classification Using Multiple Sidescan Sonar Images of Different Orientations; NATO, SACLANT Undersea Research Centre: La Spezia, Italy, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Chew, A.L.; Tong, P.B.; Chia, C.S. Automatic detection and classification of man-made targets in side scan sonar images. In Proceedings of the 2007 Symposium on Underwater Technology and Workshop on Scientific Use of Submarine Cables and Related Technologies, Tokyo, Japan, 17–20 April 2007; pp. 126–132. [Google Scholar]
- Tellez, O.L. Underwater threat recognition: Are automatic target classification algorithms going to replace expert human operators in the near future? In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2019, Marseille, France, 17–20 June 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, G.Y.; Wu, Z.Y.; Li, J.B. Underwater Object Classification in Sidescan Sonar Images Using Deep Transfer Learning and Semisynthetic Training Data. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 47407–47418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.W.; Qin, X.M.; Wu, Z.Y.; Yang, F.L.; Wang, M.W.; Shang, J.H. Sediment Classification of Small-Size Seabed Acoustic Images Using Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 98331–98339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaillan, F.; Fraschini, C.; Courmontagne, P. Speckle noise reduction in SAS imagery. Signal Process. 2007, 87, 762–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazimierski, W.; Zaniewicz, G. Determination of Process Noise for Underwater Target Tracking with Forward Looking Sonar. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buslaev, A.; Iglovikov, V.I.; Khvedchenya, E.; Parinov, A.; Druzhinin, M.; Kalinin, A.A. Albumentations: Fast and flexible image augmentations. Information 2020, 11, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghannadi, M.A.; Saadaseresht, M. A modified local binary pattern descriptor for SAR image matching. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 16, 568–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, P.I.; Fernandez, J. Facial feature detection using Haar classifiers. J. Comput. Sci. Coll. 2006, 21, 127–133. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Xu, Q.Z.; Li, B. Ship Detection from Optical Satellite Images Based on Saliency Segmentation and Structure-LBP Feature. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 602–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Guo, W.; Zhang, Y. Detection of copy-move forgery in digital images using SIFT algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Pacific-Asia Workshop on Computational Intelligence and Industrial Application, Wuhan, China, 19–20 December 2008; pp. 272–276. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Zhao, L.; Huang, S.; Yan, L.; Dissanayake, G. L2-SIFT: SIFT feature extraction and matching for large images in large-scale aerial photogrammetry. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 91, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi, M.D.; Raj, M.V.; Murugan, S.S. Feature matching and assessment of similarity rate on geometrically distorted side scan sonar images. In Proceedings of the 2019 TEQIP III Sponsored International Conference on Microwave Integrated Circuits, Photonics and Wireless Networks (IMICPW), Tiruchirappalli, India, 22–24 May 2019; pp. 208–212. [Google Scholar]
- Myers, V.; Fawcett, J. A Template Matching Procedure for Automatic Target Recognition in Synthetic Aperture Sonar Imagery. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2010, 17, 683–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, S.; Petillot, Y.; Bell, J. An automatic approach to the detection and extraction of mine features in sidescan sonar. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2003, 28, 90–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymore, K.; McCallum, A.; Rosenfeld, R. Learning hidden Markov model structure for information extraction. In Proceedings of the AAAI-99 Workshop on Machine Learning for Information Extraction, Orlando, FL, USA, 18–19 July 1999; pp. 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Dobeck, G.J.; Hyland, J.C. Automated detection and classification of sea mines in sonar imagery. In Proceedings of the Detection and Remediation Technologies for Mines and Minelike Targets II, Orlando, FL, USA, 22 July 1997; pp. 90–110. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, S.A.; Yeh, M.L.; Ma, H.L. An Innovative Intelligent System with Integrated CNN and SVM: Considering Various Crops through Hyperspectral Image Data. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelebi, A.T.; Güllü, M.K.; Ertürk, S. Mine detection in side scan sonar images using Markov Random Fields with brightness compensation. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE 19th Signal Processing and Communications Applications Conference (SIU), Antalya, Turkey, 20–22 April 2011; pp. 916–919. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Malik, J. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 580–587. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. 2017, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.M.; Luo, X.W.; Wu, Z.Y.; Shang, J.H. Optimizing the Sediment Classification of Small Side-Scan Sonar Images Based on Deep Learning. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 29416–29428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerg, I.D.; Monga, V. Structural Prior Driven Regularized Deep Learning for Sonar Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Tang, J.S.; Zhong, H.P.; Ning, M.Q.; Liu, D.D.; Wu, K. Self-Trained Target Detection of Radar and Sonar Images Using Automatic Deep Learning; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, H. Data augmentation by pairing samples for images classification. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1801.02929. [Google Scholar]
- Barngrover, C.; Kastner, R.; Belongie, S. Semisynthetic versus real-world sonar training data for the classification of mine-like objects. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2014, 40, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ge, Q.; Ruan, F.X.; Qiao, B.J.; Zhang, Q.; Zuo, X.Y.; Dang, L.X. Side-Scan Sonar Image Classification Based on Style Transfer and Pre-Trained Convolutional Neural Networks. Electronics 2021, 10, 1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.L.; Ye, X.F.; Cao, D.X.; Hou, J.; Yang, H.B. Zero shot objects classification method of side scan sonar image based on synthesis of pseudo samples. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 173, 107691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiniger, Y.; Kraus, D.; Meisen, T. Generating Synthetic Sidescan Sonar Snippets Using Transfer-Learning in Generative Adversarial Networks. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, M.; Cho, H.; Kim, J.; Yu, S.-C. Sonar image translation using generative adversarial network for underwater object recognition. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Underwater Technology (UT), Kaohsiung, Taiwan, 16–19 April 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, S.J.; Yang, Q. A survey on transfer learning. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2009, 22, 1345–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.S. An application of pre-trained CNN for image classification. In Proceedings of the 2017 20th International Conference of Computer and Information Technology (ICCIT), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 22–24 December 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz, M.; Schulz, H.; Behnke, S. RGB-D object recognition and pose estimation based on pre-trained convolutional neural network features. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Seattle, WA, USA, 25–30 May 2015; pp. 1329–1335. [Google Scholar]
- Lasloum, T.; Alhichri, H.; Bazi, Y.; Alajlan, N. SSDAN: Multi-Source Semi-Supervised Domain Adaptation Network for Remote Sensing Scene Classification. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, M.; Kolouri, S.; Eaton, E.; Kim, K. Sar image classification using few-shot cross-domain transfer learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.Y.; Zhang, L.F.; You, J.N. Domain Transfer Learning for Hyperspectral Image Super-Resolution. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusu, A.A.; Rabinowitz, N.C.; Desjardins, G.; Soyer, H.; Kirkpatrick, J.; Kavukcuoglu, K.; Pascanu, R.; Hadsell, R. Progressive neural networks. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1606.04671. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.; Woo, S.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kweon, I.S. Bam: Bottleneck attention module. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.06514. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, X.X.; Suen, C.Y. A novel hybrid CNN-SVM classifier for recognizing handwritten digits. Pattern Recognit. 2012, 45, 1318–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itti, L.; Koch, C.; Niebur, E. A model of saliency-based visual attention for rapid scene analysis. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. 1998, 20, 1254–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]





| Categories | Airplane | Ship | Seafloor | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Numbers | ||||
| Total | 66 | 487 | 583 | |
| After dataset division | ||||
| Train | 46 | 271 | 408 | |
| Test | 20 | 146 | 175 | |
| Methods | OA (%) | Parameters (Million) | Complexity (GFLOPs) | Training Time (h) | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shallow CNN [9] | 83.19 | 0.062 | 0.0003 | 0.13 | 291.3 |
| GoogLeNet [27] | 91.86 | 6.99 | 1.6 | 0.12 | 114.9 |
| VGG11 fine-tuning + semisynthetic data [3] | 92.51 | 132.86 | 7.6 | 0.16 | 105.9 |
| VGG19 fine-tuning [8] | 94.67 | 143.67 | 19.7 | 0.23 | 87.9 |
| VGG19 fine-tuning + semisynthetic data [8] | 97.76 | 143.72 | 19.8 | 0.29 | 44.1 |
| SPDRDL [28] | 97.38 | 40.16 | 5.8 | 0.43 | 41.7 |
| FL-DARTS [29] | 99.07 | 12.12 | 125.1 | 1.42 | 24.9 |
| MDCTL+MSRAM | 99.21 | 143.70 | 19.9 | 0.41 | 60.7 |
| Backbone Networks | Precision (%) | OA (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Airplane | Seafloor | Ship | ||
| AlexNet | 47.3 | 97.6 | 97.2 | 94.14 |
| GoogleNet | 47.0 | 97.1 | 97.3 | 94.46 |
| VGG16 | 57.9 | 96 | 96.3 | 94.50 |
| VGG19 | 42.1 | 98.2 | 97.4 | 94.67 |
| ResNet18 | 31.6 | 98.1 | 91.3 | 91.86 |
| ResNet50 | 47.5 | 97.9 | 93.9 | 93.50 |
| DenseNet | 47.7 | 98.0 | 95.7 | 94.14 |
| SAR TL | Optical TL | MSRAM | OA (%) | Variance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 94.87 | 0.2741 | |||
| ✓ | 97.72 | 0.9526 | ||
| ✓ | 97.12 | 1.0844 | ||
| ✓ | ✓ | 98.34 | 0.7748 | |
| ✓ | 95.89 | 0.2033 | ||
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 99.21 | 0.1511 |
| Methods | Transferred Layers | Precision (%) | OA (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Airplane | Seafloor | Ship | |||
| Freeze Parameters | 1 conv block | 57.8 | 98.3 | 96.5 | 95.12 |
| 2 conv blocks | 57.9 | 98.8 | 96.4 | 95.76 | |
| 3 conv blocks | 47.4 | 99.4 | 96.5 | 95.34 | |
| Retrain Parameters | 1 conv block | 68.4 | 99.7 | 96.5 | 96.74 |
| 2 conv blocks | 89.5 | 99.4 | 96.5 | 97.72 | |
| 3 conv blocks | 68.4 | 99.5 | 93.9 | 95.45 | |
| Methods | Backbone | AP@0.5 (Mine) | Average IOU | FPS | GFLOPs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSD | ResNet50 | 0.67 | 0.791 | 23.5 | 5.8 |
| YOLOv3 | Darknet53 | 0.79 | 0.804 | 39.2 | 158.2 |
| YOLOv5 | CSPDarknet53 | 0.89 | 0.831 | 37.3 | 17.1 |
| TR-YOLOv5s | CSPDarknet53+TR | 0.91 | 0.828 | 38.7 | 17.2 |
| RPN + our method | SARTL+MSRAM | 0.94 | 0.865 | 34 | 19.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, Z.; Huo, G.; Li, H. A Multi-Domain Collaborative Transfer Learning Method with Multi-Scale Repeated Attention Mechanism for Underwater Side-Scan Sonar Image Classification. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14020355
Cheng Z, Huo G, Li H. A Multi-Domain Collaborative Transfer Learning Method with Multi-Scale Repeated Attention Mechanism for Underwater Side-Scan Sonar Image Classification. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(2):355. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14020355
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Zhen, Guanying Huo, and Haisen Li. 2022. "A Multi-Domain Collaborative Transfer Learning Method with Multi-Scale Repeated Attention Mechanism for Underwater Side-Scan Sonar Image Classification" Remote Sensing 14, no. 2: 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14020355
APA StyleCheng, Z., Huo, G., & Li, H. (2022). A Multi-Domain Collaborative Transfer Learning Method with Multi-Scale Repeated Attention Mechanism for Underwater Side-Scan Sonar Image Classification. Remote Sensing, 14(2), 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14020355






