The Effect of Space Objects on Ionospheric Observations: Perspective of SYISR
Abstract
1. Introduction
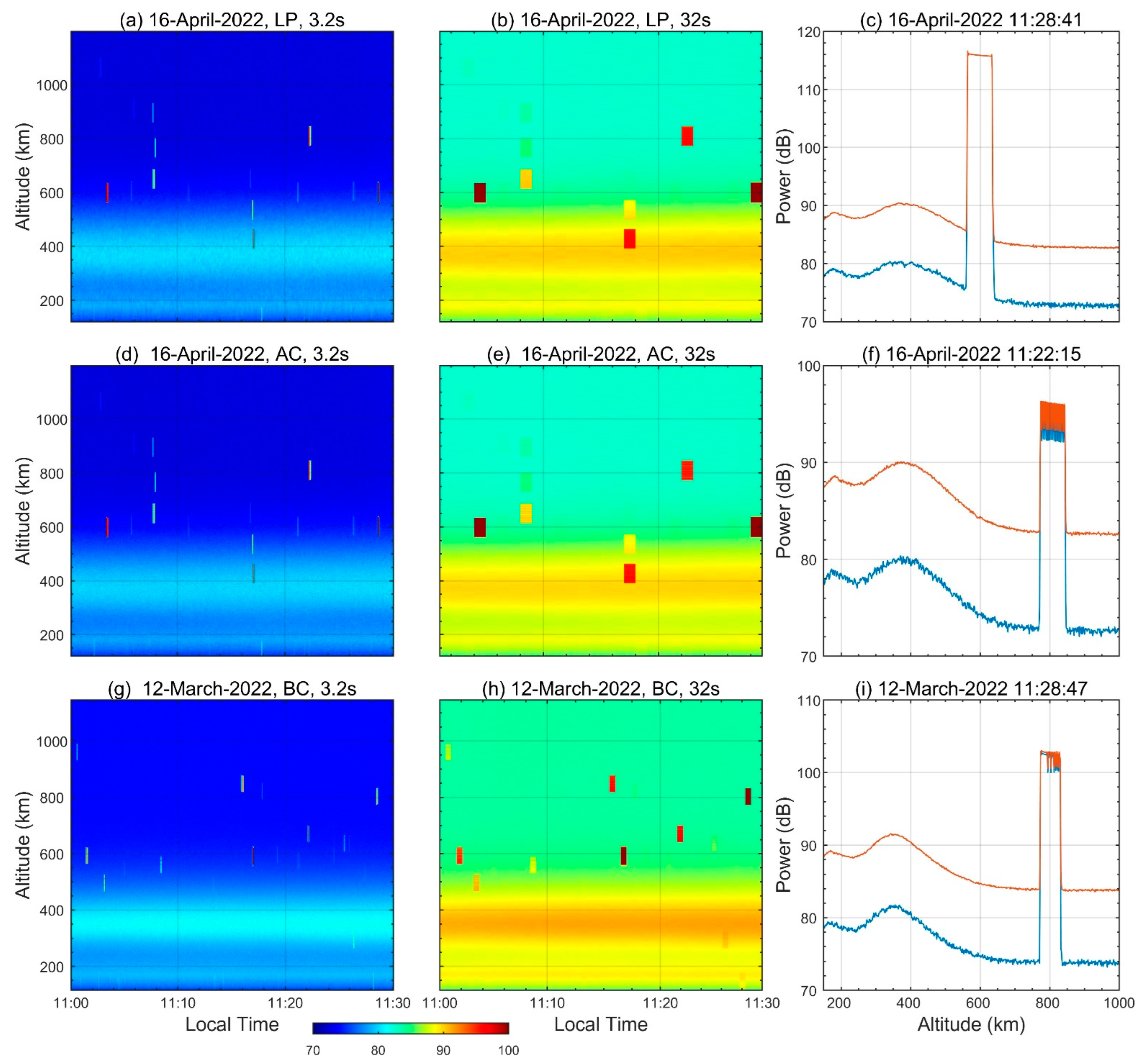
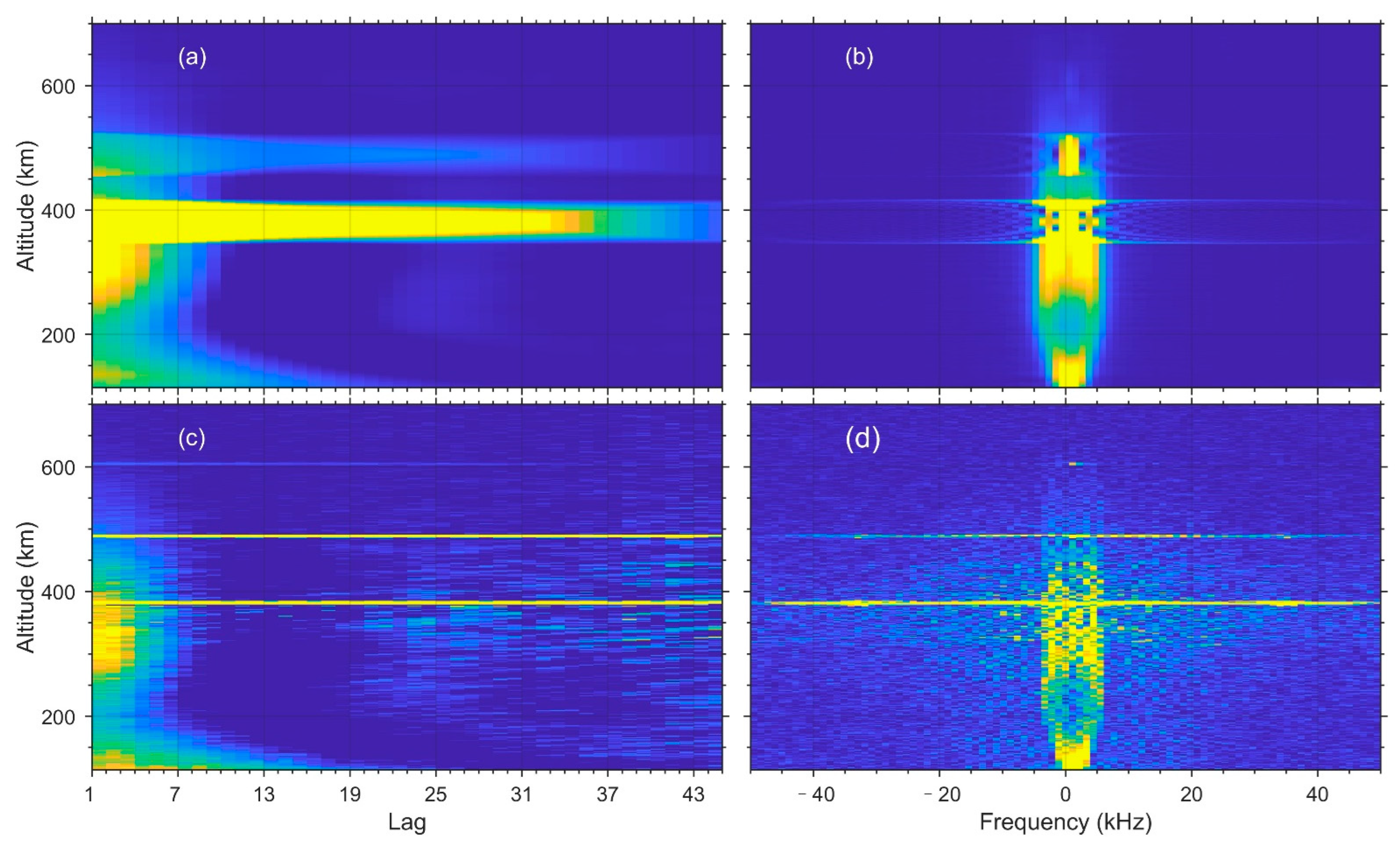
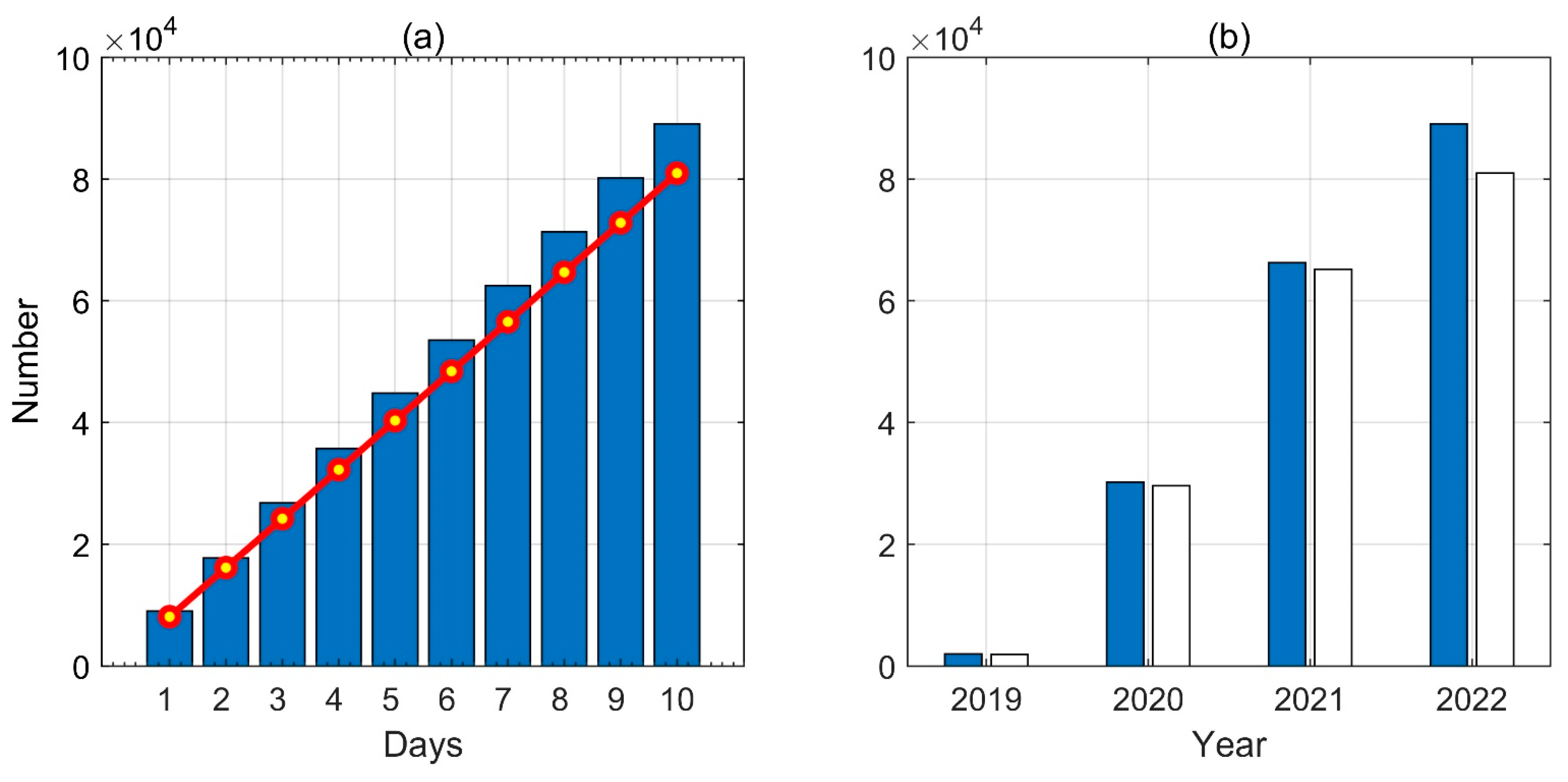
2. Space Objects in the SYISR Ionospheric Observations
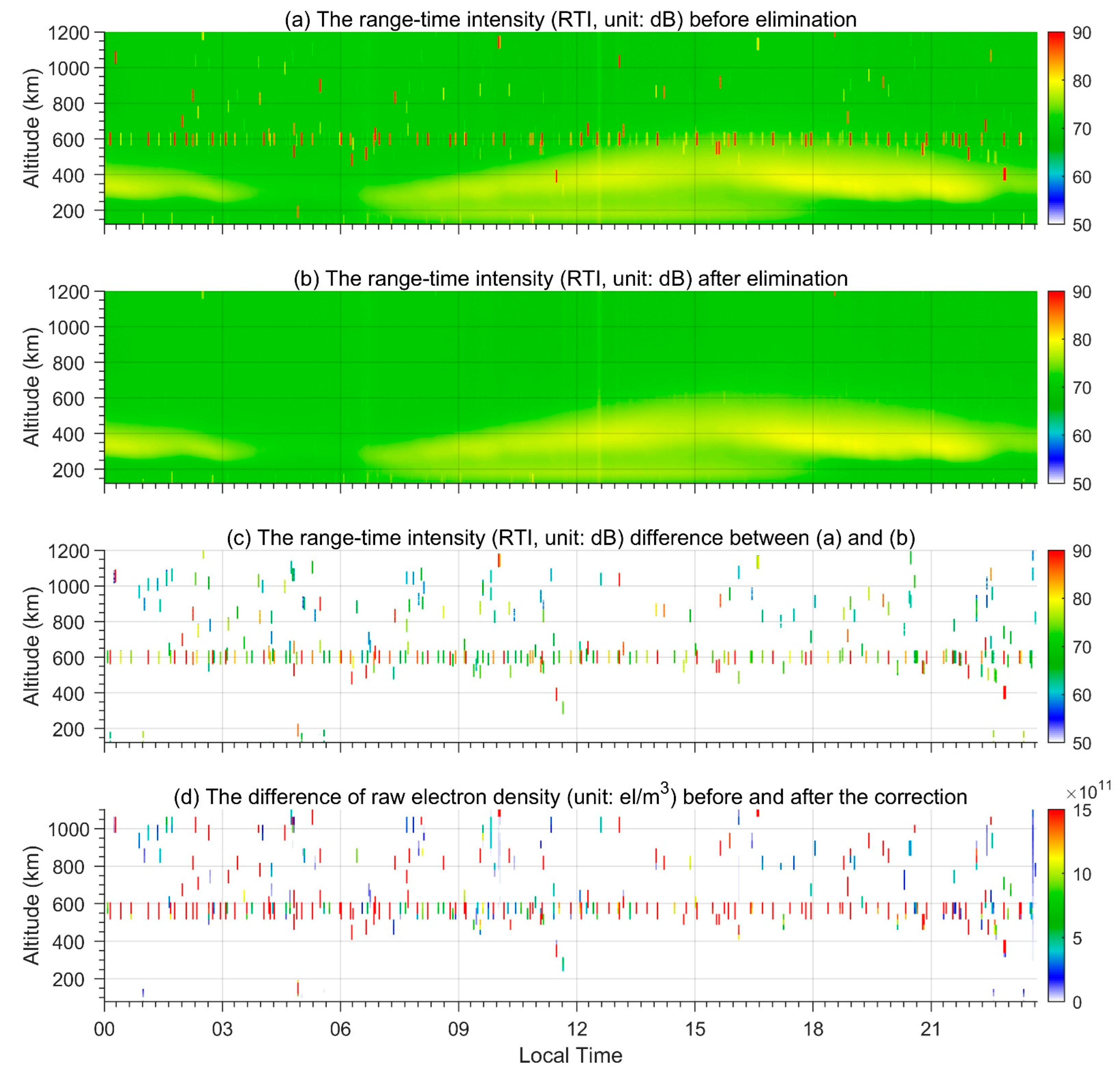
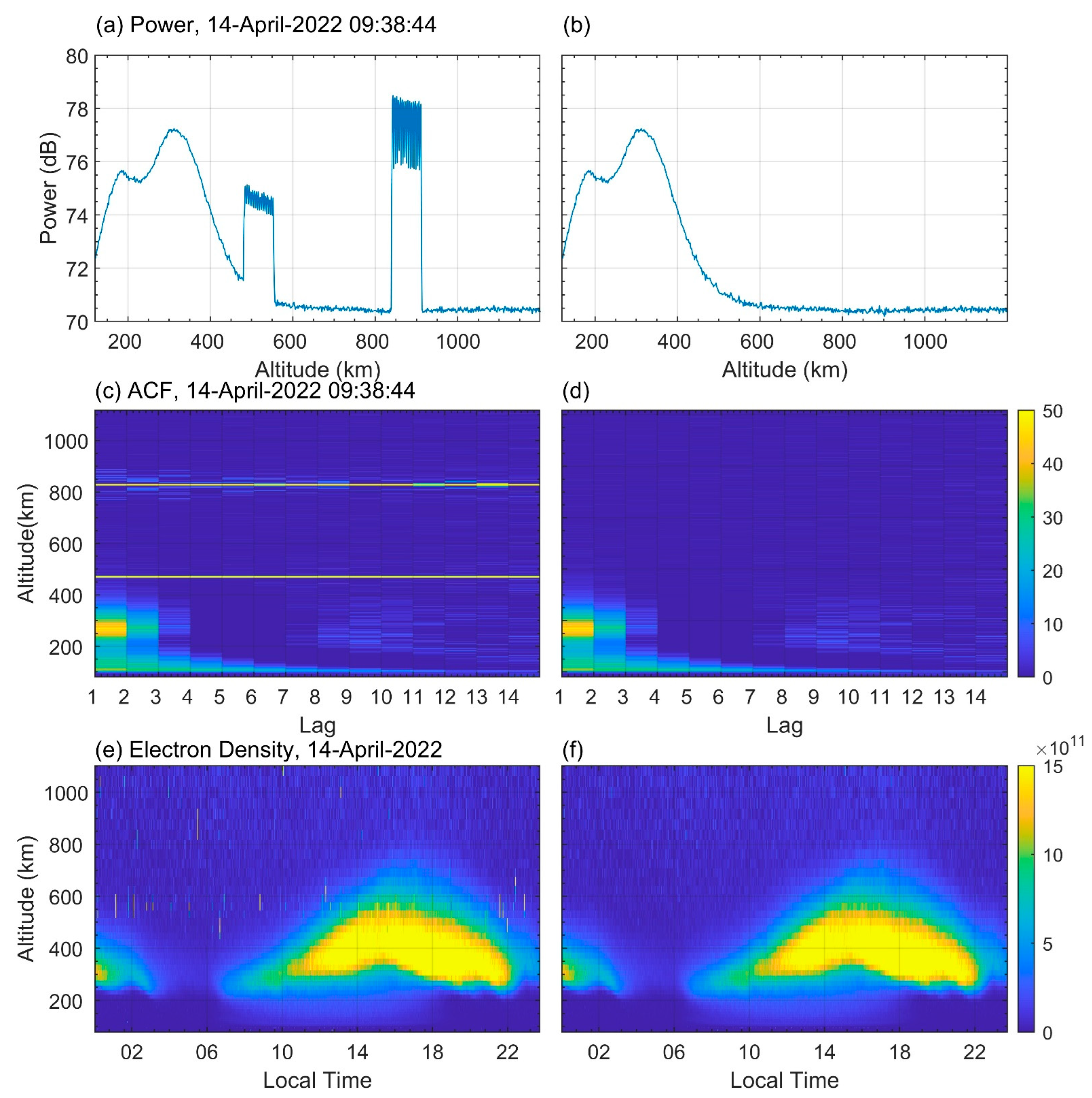
3. Preliminary Attempts to Eliminate Space Object Pollution
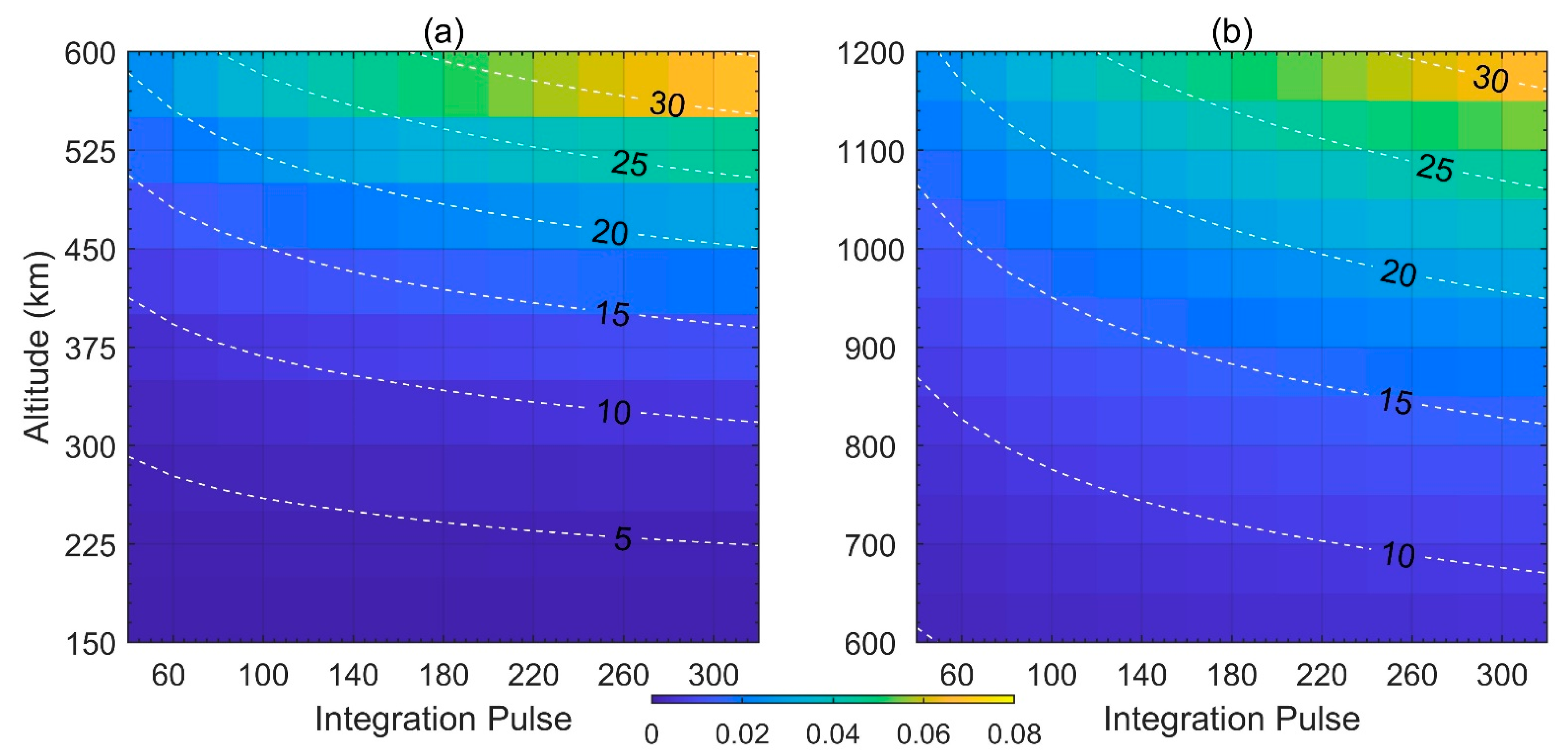
4. Assessment of the Effect of Constellation Satellites on SYISR Observations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bassa, C.G.; Hainaut, O.R.; Galadi, E.D. Analytical simulations of the effect of satellite constellations on optical and near-infrared observations. EDP Sci. A&A 2021, 657, A75. [Google Scholar]
- Curzi, G.; Modenini, D.; Tortora, P. Large constellations of small satellites: A survey of near future challenges and missions. Aerospace 2020, 7, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shutler, J.D.; Yan, X.; Cnossen, I.; Schulz, L.; Watson, A.J.; Glaßmeier, K.H.; Hawkins, N.; Nasu, H. Atmospheric impacts of the space industry require oversight. Nat. Geosci. 2022, 15, 598–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, A.; Lowenthal, J.; Prem, P.; Vidaurri, M. The impact of satellite constellations on space as an ancestral global commons. Nat. Astron. 2020, 4, 1043–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boley, A.C.; Wright, E.; Lawler, S.; Hickson, P.; Balam, D. Plaskett 1.8 m Observations of Starlink Satellites. Astron. J. 2022, 163, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mroz, P.; Otarola, A.; Prince, T.A.; Dekany, R.; Duev, D.A.; Graham, M.J.; Steven, L.G.; Frank, J.M.; Michael, S.M. Impact of the SpaceX Starlink satellites on the Zwicky transient facility survey observations. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2022, 924, L30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocifaj, M.; Kundracik, F.; Barentine, J.C.; Bará, S. The proliferation of space objects is a rapidly increasing source of artificial night sky brightness. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. Lett. 2021, 504, L40–L44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawler, S.M.; Boley, A.C.; Rein, H. Visibility predictions for near-future satellite mega constellations: Latitudes near 50° will experience the worst light pollution. Astron. J. 2022, 163, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcdowell, J.C. The low earth orbit satellite population and impacts of the SpaceX Starlink constellation. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2020, 892, L36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porteous, J.; Samson, A.M.; Berrington, K.A.; Mccrea, I.W. Automated detection of satellite contamination in incoherent scatter radar spectra. Ann. Geophys. 2003, 21, 1177–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietveld, M.T.; Collis, P.N.; Vaneyken, A.P.; Lovhaug, U.P. Coherent echoes during EISCAT uhf common programmes. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 1996, 58, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markkanen, J.; Lehtinen, M.; Landgraf, M. Real-time space debris monitoring with EISCAT. Adv. Space Res. 2005, 35, 1197–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolls, M. Space Debris Measurements using the Advanced Modular Incoherent Scatter Radar. In Proceedings of the Advanced Maui Optical and Space Surveillance Technologies Conference (AMOS), Wailea, HI, USA, 27–30 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Yue, X.; Ding, F.; Ning, B.; Jin, L.; Ke, C.; Zhang, N.; Wang, Y.; Yin, H.; Li, M.; et al. Simulation and Observational Evaluation of Space Debris Detection by Sanya Incoherent Scatter Radar. Radio Sci. 2022, 57, e2022RS007472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Wan, W.; Ning, B.; Jin, L. An active phased array radar in China. Nat. Astron. 2022, 6, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Wan, W.; Ning, B.; Jin, L.; Ke, C.; Ding, F.; Zhao, B.; Zeng, L.; Deng, X.; Wang, J.; et al. Development of the Sanya Incoherent Scatter Radar and Preliminary Results. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2022, 127, e2022JA030451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougherty, J.P.; Farley, D.T. A theory of incoherent scattering of radio waves by a Plasma. Proc. R. Soc. A-Math. Phys. Sci. 1960, 259, 79–99. [Google Scholar]
- Fejer, J.A. Scattering of radio waves by an ionized gas in thermal equilibrium. Can. J. Phys. 1960, 38, 1114–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowles, K.L. Observation of vertical-incidence scatter from the ionosphere at 41 mc/sec. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1958, 1, 454–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, W.E. Incoherent scattering of radio waves by free electrons with applications to space exploration by radar. Proc. IRE 1958, 46, 1824–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huuskonen, A.; Lehtinen, M.S.; Pirttil, J. Fractional lags in alternating codes: Improving incoherent scatter measurements by using lag estimates at noninteger multiples of baud length. Radio Sci. 1996, 31, 245–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtinen, M.S. Statistical Theory of Incoherent Scatter Radar Measurements. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Lehtinen, M.S.; Huuskonen, A. General incoherent scatter analysis and guisdap. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 1996, 58, 435–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, S. OS-CFAR theory for multiple targets and nonuniform clutter. Aerospace and Electronic Systems. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1988, 24, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunch, J.R.; Fierro, R.D. A constant-false-alarm-rate algorithm. Linear Algebra Appl. 1992, 172, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, P.P.; Kassam, S.A. Analysis of CFAR processors in nonhomogeneous background. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2002, 24, 427–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohling, H. Radar CFAR thresholding in clutter and multiple target situations. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1983, 19, 608–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CeleStrack Website. Available online: https://celestrak.org/#satellitedata/catalog (accessed on 8 July 2022).

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Yue, X.; Ding, F.; Ning, B.; Jin, L.; Ke, C.; Zhang, N.; Luo, J.; Wang, Y.; Yin, H.; et al. The Effect of Space Objects on Ionospheric Observations: Perspective of SYISR. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5092. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14205092
Wang J, Yue X, Ding F, Ning B, Jin L, Ke C, Zhang N, Luo J, Wang Y, Yin H, et al. The Effect of Space Objects on Ionospheric Observations: Perspective of SYISR. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(20):5092. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14205092
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Junyi, Xinan Yue, Feng Ding, Baiqi Ning, Lin Jin, Changhai Ke, Ning Zhang, Junhao Luo, Yonghui Wang, Hanlin Yin, and et al. 2022. "The Effect of Space Objects on Ionospheric Observations: Perspective of SYISR" Remote Sensing 14, no. 20: 5092. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14205092
APA StyleWang, J., Yue, X., Ding, F., Ning, B., Jin, L., Ke, C., Zhang, N., Luo, J., Wang, Y., Yin, H., Li, M., & Cai, Y. (2022). The Effect of Space Objects on Ionospheric Observations: Perspective of SYISR. Remote Sensing, 14(20), 5092. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14205092




