Effects of Ecological Programs and Other Factors on Soil Wind Erosion between 1981–2020
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
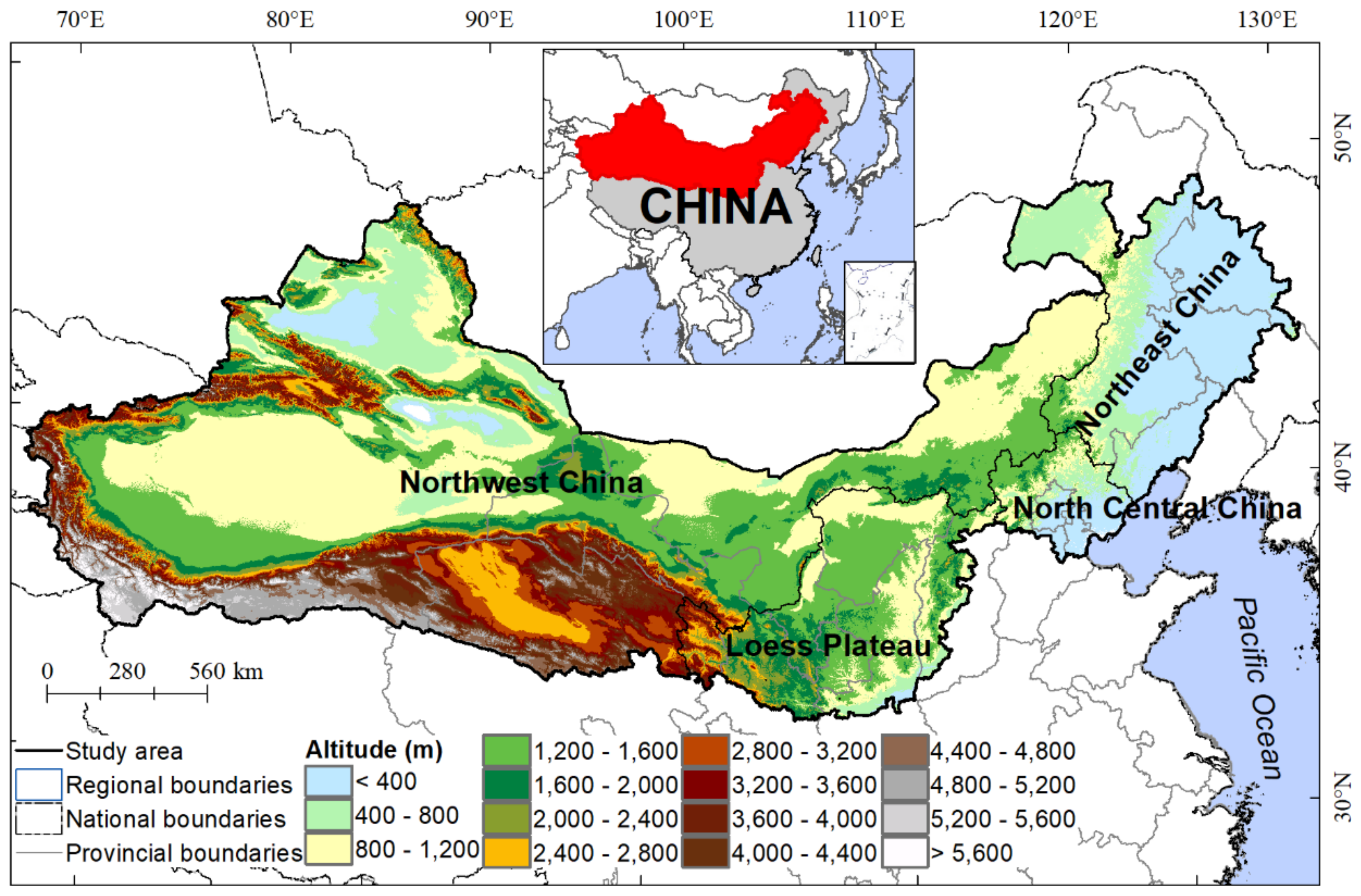
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection and Processing
2.3. Revised Soil Wind Erosion Model
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.4.1. Trend Analysis
2.4.2. Driving Force Analyses
3. Results
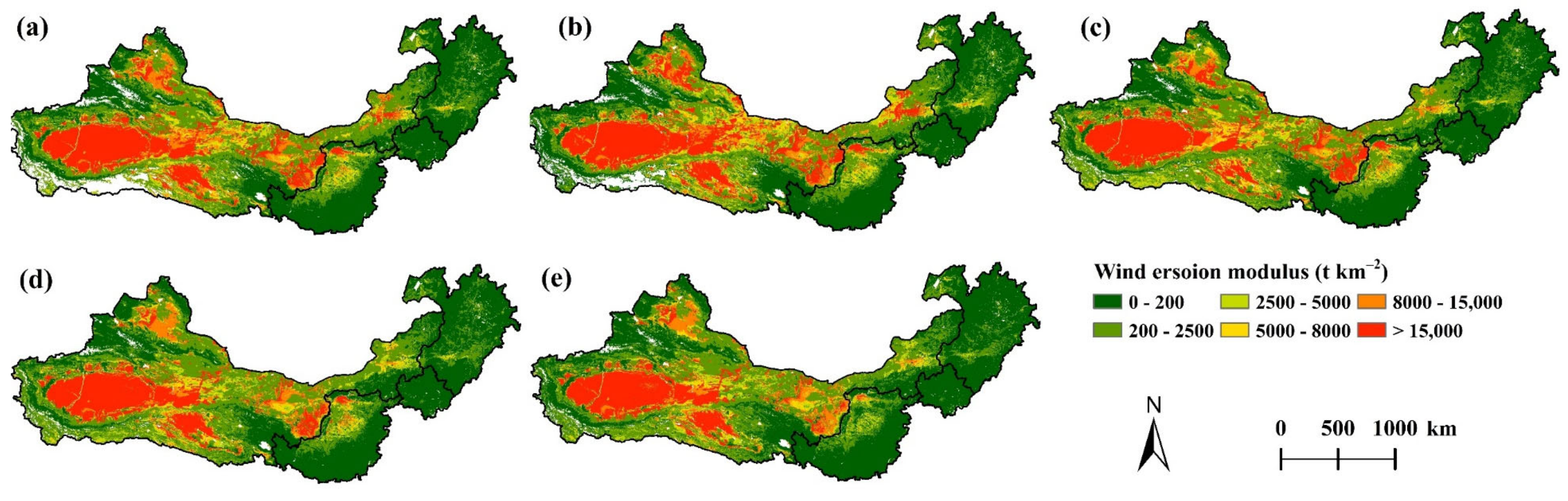
3.1. Spatial Pattern of Wind Erosion in the TNR
3.2. Spatiotemporal Variations in Wind Erosion
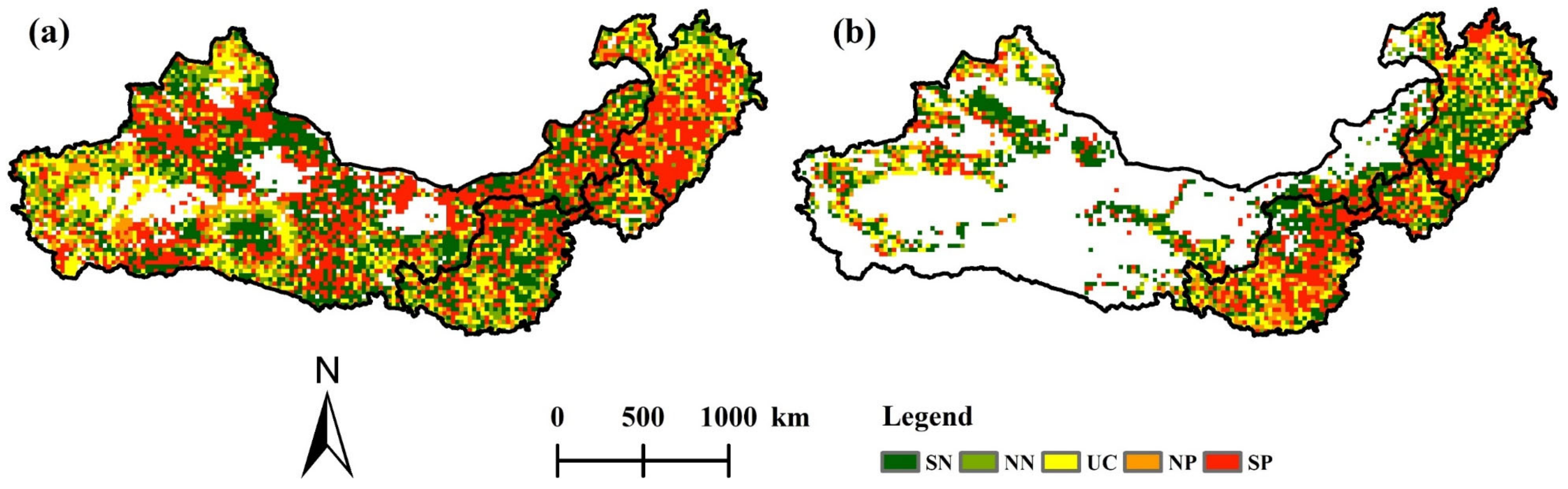
3.3. Spatiotemporal Variations in Driving Force Factors
3.3.1. Changes in Forest and Shrubland Areas Influenced by Ecological Programs
3.3.2. Climate Changes
3.3.3. Changes in Human Interference
4. Discussion
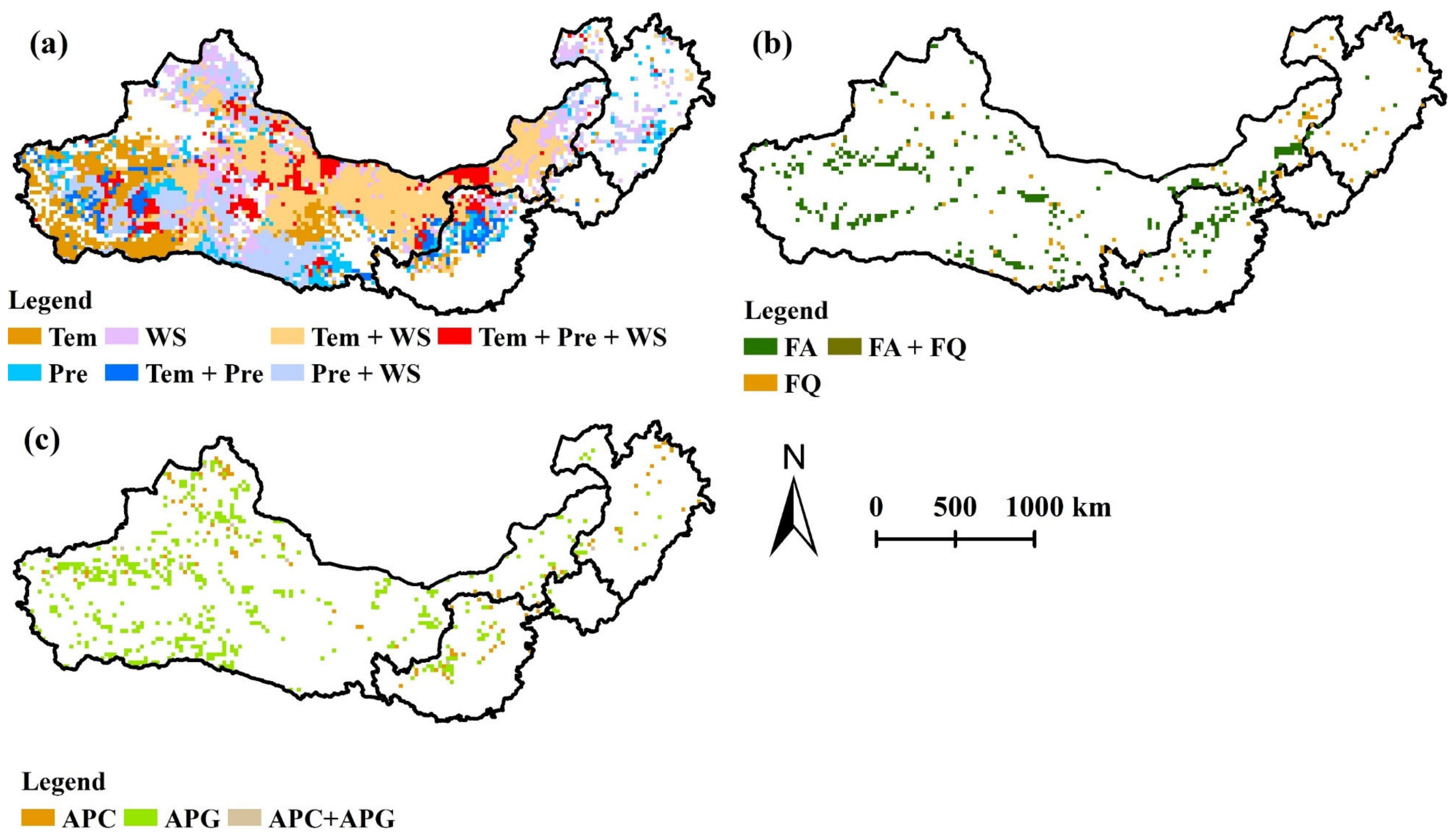
4.1. Correlations between Ecological Programs and Wind Erosion
4.2. Correlations between Climatic Factors and Wind Erosion
4.3. Correlations between Human Interference and Wind Erosion Change
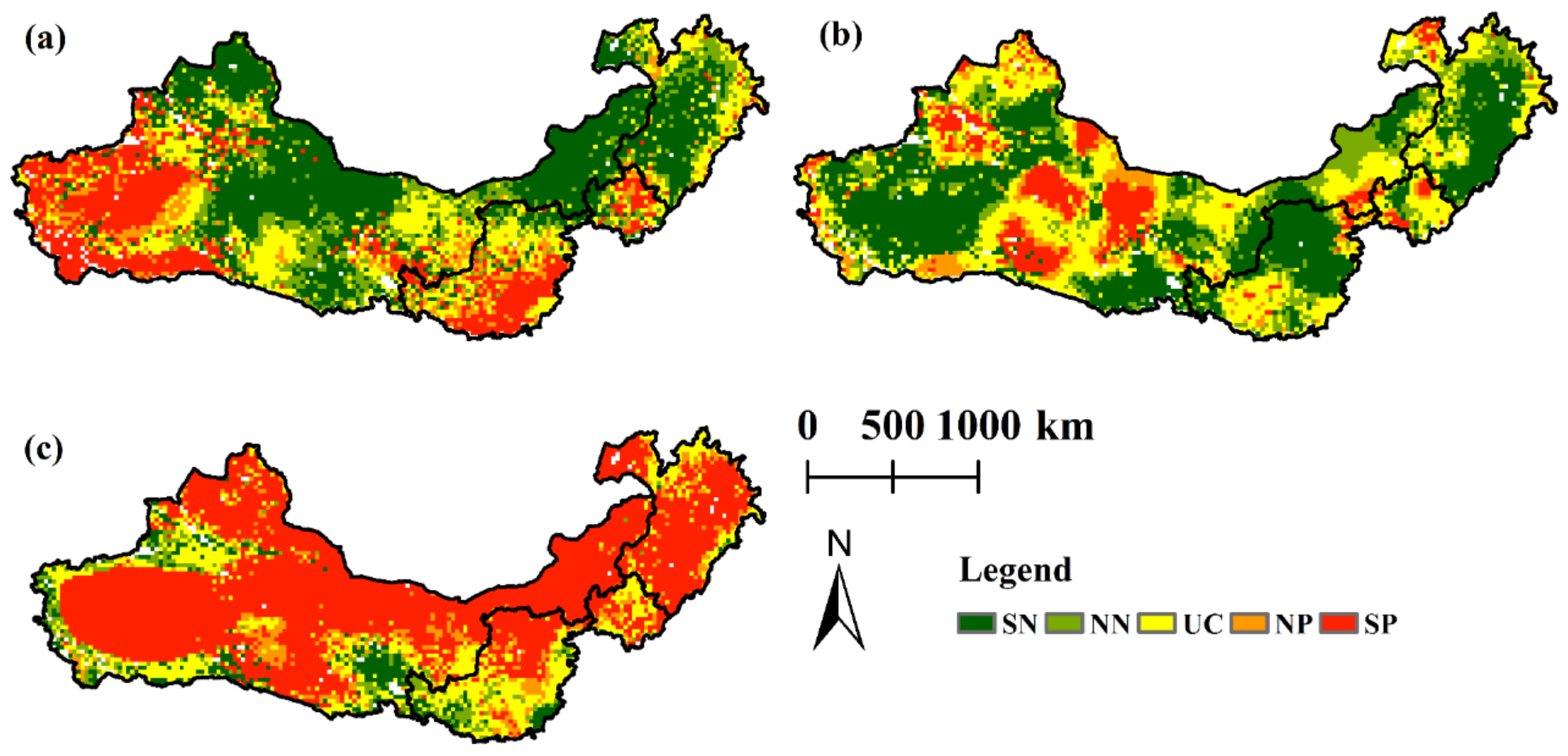
4.4. Comprehensive Effects Analysis of the Impact Factors on Wind Erosion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, L.; Xiao, Y.; Zheng, H.; Ouyang, Z.Y. Spatio-temporal variation of wind erosion in Inner Mongolia of China between 2001 and 2010. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Z.L.; Chang, C.P.; Wang, R.D.; Li, J.F. Comparison of different methods to determine wind-erodible fraction of soil with rock fragments under different tillage/management. Soil Till. Res. 2017, 168, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, M.J.; Buschiazzo, D.E. Soil coverage evolution and wind erosion risk on summer crops under contrasting tillage systems. Aeolian Res. 2015, 16, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.Q.; Xue, X.; Wang, T.; Deng, X.H. Assessment of wind-erosion risk in the watershed of the Ningxia-Inner Mongolia Reach of the Yellow River, northern China. Aeolian Res. 2015, 17, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuo, D.; Xu, M.; Gao, G. Relative contributions of wind and water erosion to total soil loss and its effect on soil properties in sloping croplands of the Chinese Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 1032–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Soil erosion and the global carbon budget. Environ. Int. 2003, 29, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, P.; Lugato, E.; Montanarella, L.; Panagos, P. A new assessment of soil loss due to wind erosion in european agricultural soils using a quantitative spatially distributed modelling approach. Land Degrad. Dev. 2016, 28, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.B.; Gao, Y.; Sun, D.F.; Liu, L.L.; Cui, Y.Z.; Zhu, W.J. Wind erosion changes in a semi-arid sandy area, Inner Mongolia, China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, D.; Li, D. Variation of wind erosion and its response to ecological programs in northern China in the period 1981-2015. Land Use Policy 2020, 99, 104871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Zhu, J. A methodological approach for spatial downscaling of TRMM precipitation data in North China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 36, 144–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Zhu, J. Temperature-based approaches for estimating monthly reference evapotranspiration based on MODIS data over North China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2014, 121, 695–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Zhu, J. A new climatic classification of afforestation in Three-North regions of China with multi-source remote sensing data. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2015, 127, 465–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zheng, X.; Gao, T.; Song, L.; Zhang, T. Quantitative analysis of the socioeconomic development impacts of the Three-North Afforestation Program on Horqin Sandy Land. Chin. J. Ecol. 2020, 39, 3567–3575. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Kuang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, X.; Qin, Y.; Ning, J.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, R.; Yan, C.; et al. Spatiotemporal characteristics, patterns, and causes of land-use changes in China since the late 1980s. J. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.B.; Peng, J.; Zhao, C.N.; Xu, Z.H.; Dong, J.Q.; Gao, Y. Wind speed in spring dominated the decrease in wind erosion across the Horqin Sandy Land in Northern China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 127, 107599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, J.a.; Zou, X.; Mao, R.; Gong, D.; Feng, X. Wind Erosion Climate change in Northern China during 1981–2016. Int. J. Disast. Risk Sci. 2020, 11, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.Q.; Wang, T.; Xue, X.; Li, S. Estimation of soil organic carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus losses induced by wind erosion in Northern China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 1006–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, H.; Sharratt, B.; Feng, G.; Lei, J. Evaluation of two empirical wind erosion models in arid and semi-arid regions of China and the USA. Environ. Modell. Softw. 2017, 91, 28–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, X.F.; Zhu, J.T.; Yan, W.; Zhao, C.Y. Assessment of soil conservation services of four river basins in Central Asia under global warming scenarios. Geoderma 2020, 375, 114533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodruff, N.P.; Armbrust, D.V. A monthly climatic factor for wind erosion equation. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1968, 23, 103–104. [Google Scholar]
- Fryrear, D.W.; Saleh, A.; Bilbro, J.D.; Schromberg, H.M.; Stout, J.E.; Zobeck, T. Revised Wind Erosion Equation; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Buschiazzo, D.E.; Zobeck, T.M. Validation of WEQ, RWEQ and WEPS wind erosion for different arable land management systems in the Argentinean Pampas. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2008, 33, 1839–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, S.M.; Sterk, G.; Karssenberg, D. Wind erosion modelling in a Sahelian environment. Environ. Modell. Softw. 2005, 20, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.Q.; Wang, T.; Xue, X. Potential wind erosion rate response to climate and land-use changes in the watershed of the Ningxia-Inner Mongolia reach of the Yellow River, China, 1986–2013. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2017, 42, 1923–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, X.L.; Zhang, Z.X.; Yi, L.; Zuo, L.J.; Wen, Q.K.; Liu, F.; Xu, J.Y.; Hu, S.G.; Liu, B. Assessment of soil erosion change and its relationships with land use/cover change in China from the end of the 1980s to 2010. Catena 2016, 137, 256–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, H.; Wang, M.; Jiang, H.; Peng, J.; Wang, Y. Impacts of climate change on wind erosion in Southern Africa between 1991 and 2015. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 2169–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenta, A.A.; Tsunekawa, A.; Haregeweyn, N.; Poesen, J.; Tsubo, M.; Borrelli, P.; Panagos, P.; Vanmaercke, M.; Broeckx, J.; Yasuda, H.; et al. Land susceptibility to water and wind erosion risks in the East Africa region. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 135016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, P.; Panagos, P.; Ballabio, C.; Lugato, E.; Weynants, M.; Montanarella, L. Towards a Pan-European assessment of land susceptibility to wind erosion. Land Degrad. Dev. 2016, 27, 1093–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheper, S.; Weninger, T.; Kitzler, B.; Lackóová, L.; Cornelis, W.; Strauss, P.; Michel, K. Comparison of the spatial wind erosion patterns of erosion risk mapping and quantitative modeling in Eastern Austria. Land 2021, 10, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, H.; Zhang, C. Impacts of climate change on key soil ecosystem services and interactions in Central Asia. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 116, 106490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Zhang, H.Y.; Zhang, Z.D.; Wang, D.W. Model-based assessment soil loss by wind and water erosion in China’s Loess Plateau: Dynamic change, conservation effectiveness, and strategies for sustainable restoration. Glob. Planet Chang. 2019, 172, 396–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, W.W.; Zhang, Z.X. Impacts of land-use changes on soil erosion in water-wind crisscross erosion region of China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, H.; Liu, X.; Jia, X.; Li, S.; Fan, Y. Assessment of the effects of ecological restoration projects on soil wind erosion in Northern China in the past two decades. Catena 2022, 215, 106360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fryrear, D.W.; Bilbro, J.D.; Saleh, A.; Schomberg, H.; Stout, J.E.; Zobeck, T.M. RWEQ: Improved wind erosion technology. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2000, 55, 183–189. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, N.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, X.; Cheng, H. Spatial and temporal evolutions of vegetation coverage in the Tarim River Basin and their responses to phenology. Catena 2022, 217, 106489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Fan, J.; Cao, W.; Harris, W.; Li, Y.; Chi, W.; Wang, S. Response of wind erosion dynamics to climate change and human activity in Inner Mongolia, China during 1990 to 2015. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 1038–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Ma, X.; Zhang, C. Predicting the spatiotemporal variation in soil wind erosion across Central Asia in response to climate change in the 21st century. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 136060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, S.; Sanchez-Azofeifa, G.A.; Duran, S.M.; Calvo-Rodriguez, S. Estimation of aboveground net primary productivity in secondary tropical dry forests using the Carnegie-Ames-Stanford approach (CASA) model. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 075004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Fan, J.W.; Cao, W.; Zhong, H.P.; Harris, W.; Gong, G.L.; Zhang, Y.X. Changes in multiple ecosystem services between 2000 and 2013 and their driving factors in the Grazing Withdrawal Program, China. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 116, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Liu, J.G.; Zhang, H.Y.; Zhang, Z.D.; Wang, D.W. China’s progress towards sustainable land degradation control: Insights from the northwest arid regions. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 127, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.J.; Xu, D.Y. Sand fixation function response to climate change and land use in northern China from 1981 to 2015. Aeolian Res. 2019, 40, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y. Integrated Wind-Erosion Modelling. In Physics And Modelling Of Wind Erosion; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 303–360. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, C.; Li, D.Q.; Wang, D.W.; Zhang, L.B. Quantification and assessment of changes in ecosystem service in the Three-River Headwaters Region, China as a result of climate variability and land cover change. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 66, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.Z.; Zhang, Q.F.; Liu, G.H. Lake eutrophication associated with geographic location, lake morphology and climate in China. Hydrobiologia 2010, 644, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belušić, D.; Fuentes-Franco, R.; Strandberg, G.; Jukimenko, A. Afforestation reduces cyclone intensity and precipitation extremes over Europe. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 074009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Zhu, J.J.; Xing, Z.F. Assessment of the effects of shelterbelts on crop yields at the regional scale in Northeast China. Agr. Syst. 2016, 143, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, W.; Zhao, Y.; Kuang, W.; He, H. Impacts of anthropogenic land use/cover changes on soil wind erosion in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 668, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.F.; Azorin-Molina, C.; Shi, P.J.; Lin, D.G.; Guijarro, J.A.; Kong, F.; Chen, D.L. Impact of near-surface wind speed variability on wind erosion in the eastern agro-pastoral transitional zone of Northern China, 1982–2016. Agr. Forest Meteorol. 2019, 271, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, G.; Liu, J.; Shao, Q.; Zhai, J. Sand-Fixing Function under the Change of Vegetation Coverage in a Wind Erosion Area in Northern China. J. Resour. Ecol. 2014, 5, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, K. Characteristics of magnetic susceptibility on cropland and pastureland slopes in an area influenced by both wind and water erosion and implications for soil redistribution patterns. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 199, 104568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Song, A.; Li, D.; Ding, X.; Wang, Z. Assessing the relative role of climate change and human activities in desertification of North China from 1981 to 2010. Front. Earth Sci. 2018, 13, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Y.; Zhan, J.; Liu, W.; Sun, Y.; Agyemang, F.B.; Liang, L.; Li, Z. Spatiotemporal dynamics and drivers of wind erosion on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 123, 107340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.J.; Xu, D.Y.; Wang, Z.Y.; You, X.G.; Zhang, X.Y.; Song, A.L. The dynamics of sand-Stabilization services in Inner Mongolia, China from 1981 to 2010 and its relationship with climate change and human activities. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 88, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, X.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Gong, J.; Li, S.; Dou, H.; Dang, D. Soil wind erosion evaluation and sustainable management of typical steppe in Inner Mongolia, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 277, 111488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
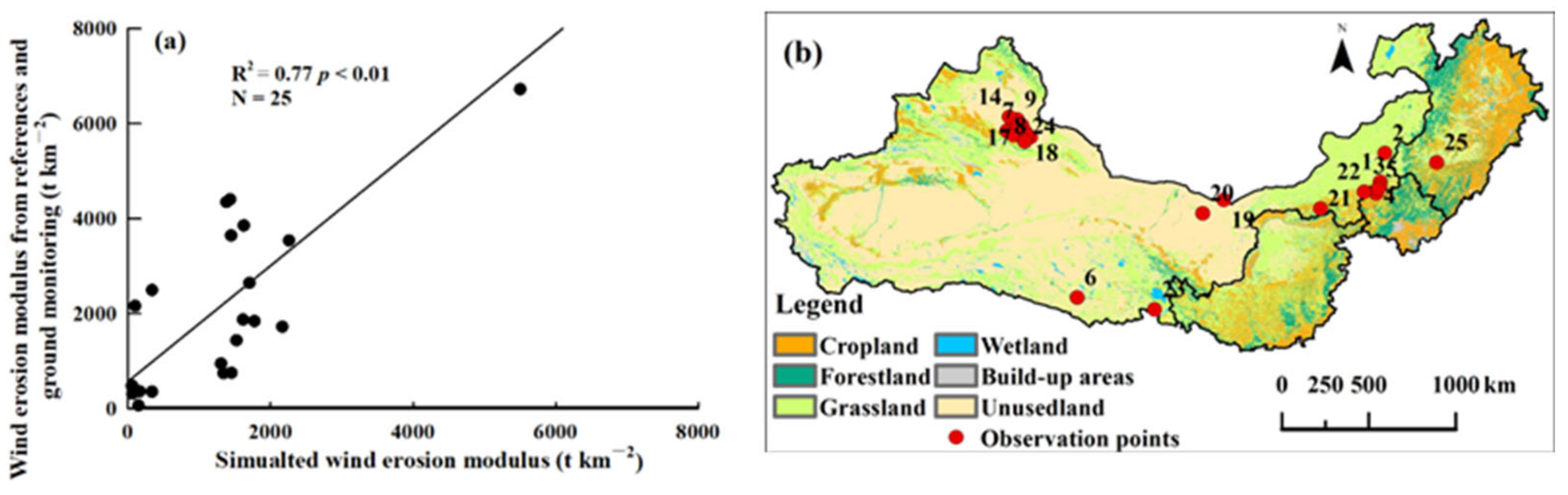






| ID | Name | Location | Year | Wind Erosion Modulus from References and Ground Monitoring (t km−2) | Simulated Wind Erosion Modulus (t km−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Zhengxiangbai Qi | 115.55E, 42.33N | 2007 | 351.00 | 339.54 |
| 2 | Xilinghot | 116.10E, 43.76N | 2007 | 360.00 | 167.40 |
| 3 | Taipusi Qi 1 | 115.49E, 42.11N | 2008 | 418.00 | 70.06 |
| 4 | Taipusi Qi 2 | 115.17E, 41.76N | 2008 | 480.00 | 56.90 |
| 5 | Taipusi Qi 3 | 115.34E, 41.96N | 2008 | 310.00 | 66.23 |
| 6 | Geermi s1 | 94.92E, 36.42N | 1997 | 8414.00 | 4965.99 |
| 7 | zhd 1 | 88.60E, 44.39N | 2015 | 739.66 | 1341.49 |
| 8 | zhd 2 | 88.60E, 44.37N | 2015 | 945.06 | 1308.22 |
| 9 | zhd 3 | 89.20E, 45.05N | 2015 | 4404.01 | 1433.64 |
| 10 | zhd 4 | 89.17E, 44.66N | 2015 | 3538.01 | 2260.93 |
| 11 | zhd 5 | 89.61E, 44.79N | 2015 | 1720.08 | 2167.11 |
| 12 | zhd 6 | 89.61E, 44.27N | 2015 | 3644.22 | 1447.71 |
| 13 | zhd 8 | 90.35E, 44.27N | 2015 | 2644.08 | 1706.66 |
| 14 | zhd 9 | 88.59E, 45.11N | 2015 | 3855.57 | 1627.36 |
| 15 | zhd10 | 89.11E, 44.24N | 2015 | 749.35 | 1453.61 |
| 16 | zhd 11 | 89.91E, 44.50N | 2015 | 1871.13 | 1616.11 |
| 17 | zhd 12 | 89.35E, 44.79N | 2015 | 1840.09 | 1776.69 |
| 18 | zhd 13 | 90.09E, 44.32N | 2015 | 1437.38 | 1525.16 |
| 19 | Bayannaoer 1 | 104.47E, 41.80N | 2006 | 64.58 | 150.85 |
| 20 | Halahelin | 103E, 41.10N | 2006 | 6723.06 | 5500.07 |
| 21 | Wuchuan County | 111.21E, 41.21N | 2018 | 2160.17 | 102.78 |
| 22 | Bashang Region | 114.35E, 41.90N | 2005 | 8362.34 | 6780.01 |
| 23 | Gonghe Basin | 100E, 36.10N | 1999 | 2491.00 | 341.15 |
| 24 | Zhd | 90E, 44N | 2016 | 4345.99 | 1383.63 |
| Levels | Vegetation Coverage (%) | Wind Erosion Modulus (t/(km2/a)) |
|---|---|---|
| Tolerable erosion | >70 | <200 |
| Mild erosion | 50–70 | 200–2500 |
| Moderate erosion | 30–50 | 2500–5000 |
| Severe erosion | 10–30 | 5000–8000 |
| More severe erosion | <10 | 8000–15,000 |
| Very severe erosion | <10 | >15,000 |
| First-Level Indicators | Second-Level Indicators | Data Source and Processing | Data Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ecological programs | Area porportion of forest and shrubland in a 1 km × 1 km grid | Visual interpretation using multiphase remote sensing images (Zheng and Zhu 2017) | 0.95 |
| LAI of forest and shrubland | MODIS LAI (2001–2020) and LAI (1981–1999) were calculated based on the relationship between NOAA-NDVI and MODIS-LAI | 0.71 | |
| NPP of forest and shrubland | CASA model | 0.82 | |
| Human interference | Area proportion of cropland in a 1 km × 1 km grid | Same as the area of forest and shrubland | 0.95 |
| Area proportion of grassland in a 1 km × 1 km grid | Same as the area of forest and shrubland | 0.95 | |
| Climate changes | Spring mean wind speed | Spatialization of meteorological data using the ANUSPLIN and cokriging interpolation method | 0.8 |
| Spring mean temperature | 0.83 | ||
| Spring precipitation | 0.85 |
| Year | Coniferous Forest | Broad-Leaved Forest | Coniferous and Broad-Leaved Forest | Shrubland | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1981 | 38,098 | 87,861 | 17,454 | 70,587 | 214,001 |
| 1990 | 57,988 | 105,992 | 23,505 | 103,491 | 290,976 |
| 2000 | 59,493 | 114,577 | 21,591 | 114,577 | 310,238 |
| 2010 | 49,345 | 110,095 | 20,132 | 165,192 | 344,763 |
| 2020 | 45,536 | 118,817 | 15,135 | 199,118 | 378,606 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, J.; Zheng, X.; Zhao, L.; Fan, J.; Liu, J. Effects of Ecological Programs and Other Factors on Soil Wind Erosion between 1981–2020. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5322. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14215322
Wu J, Zheng X, Zhao L, Fan J, Liu J. Effects of Ecological Programs and Other Factors on Soil Wind Erosion between 1981–2020. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(21):5322. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14215322
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Jinzhou, Xiao Zheng, Lanlin Zhao, Junmei Fan, and Jinghong Liu. 2022. "Effects of Ecological Programs and Other Factors on Soil Wind Erosion between 1981–2020" Remote Sensing 14, no. 21: 5322. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14215322
APA StyleWu, J., Zheng, X., Zhao, L., Fan, J., & Liu, J. (2022). Effects of Ecological Programs and Other Factors on Soil Wind Erosion between 1981–2020. Remote Sensing, 14(21), 5322. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14215322







