Assimilation of Water Vapor Retrieved from Radar Reflectivity Data through the Bayesian Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
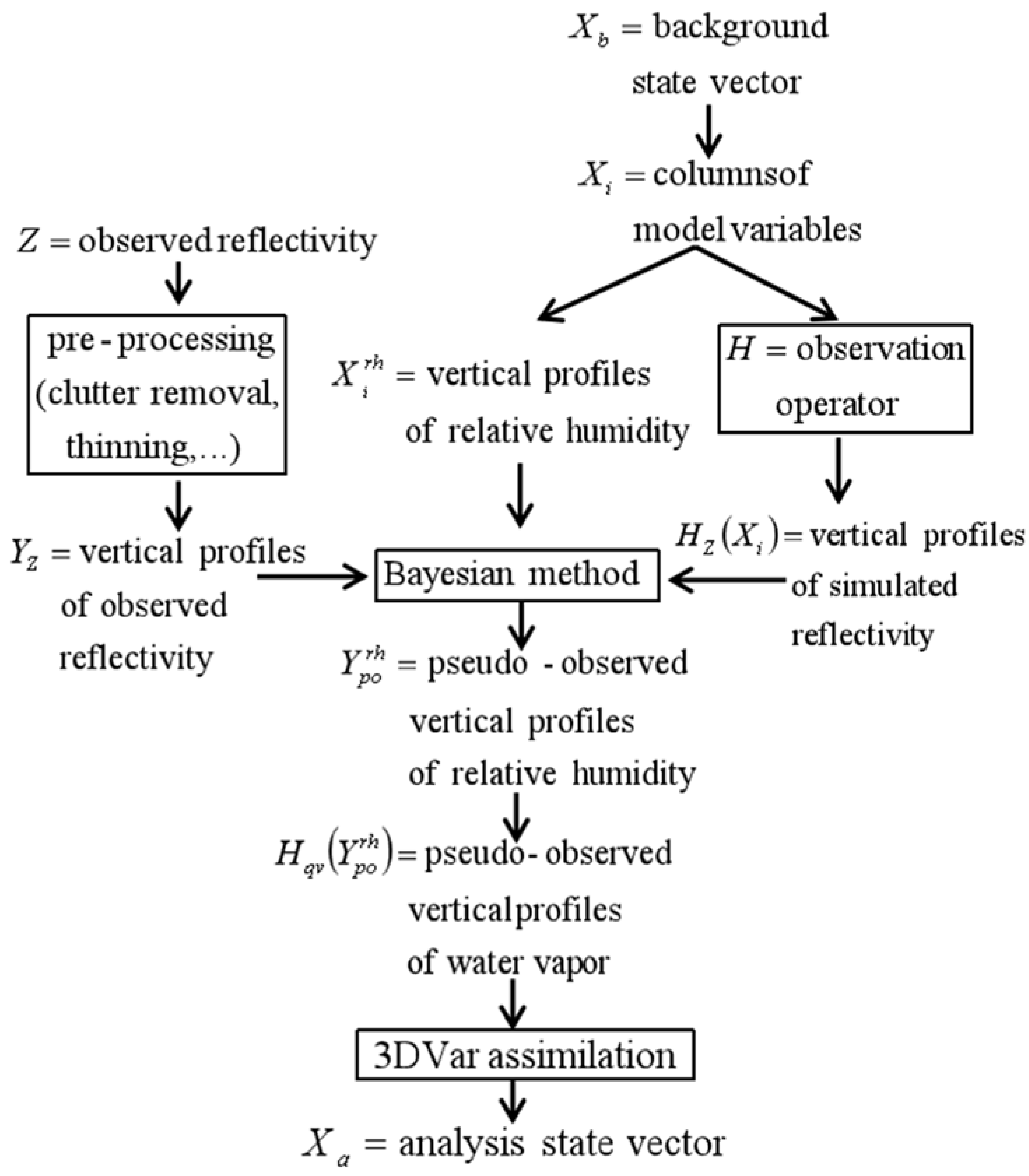
2. Methodology
2.1. Water Vapor Retrieval
2.2. Radar Reflectivity Assimilation
3. Model and Experimental Design
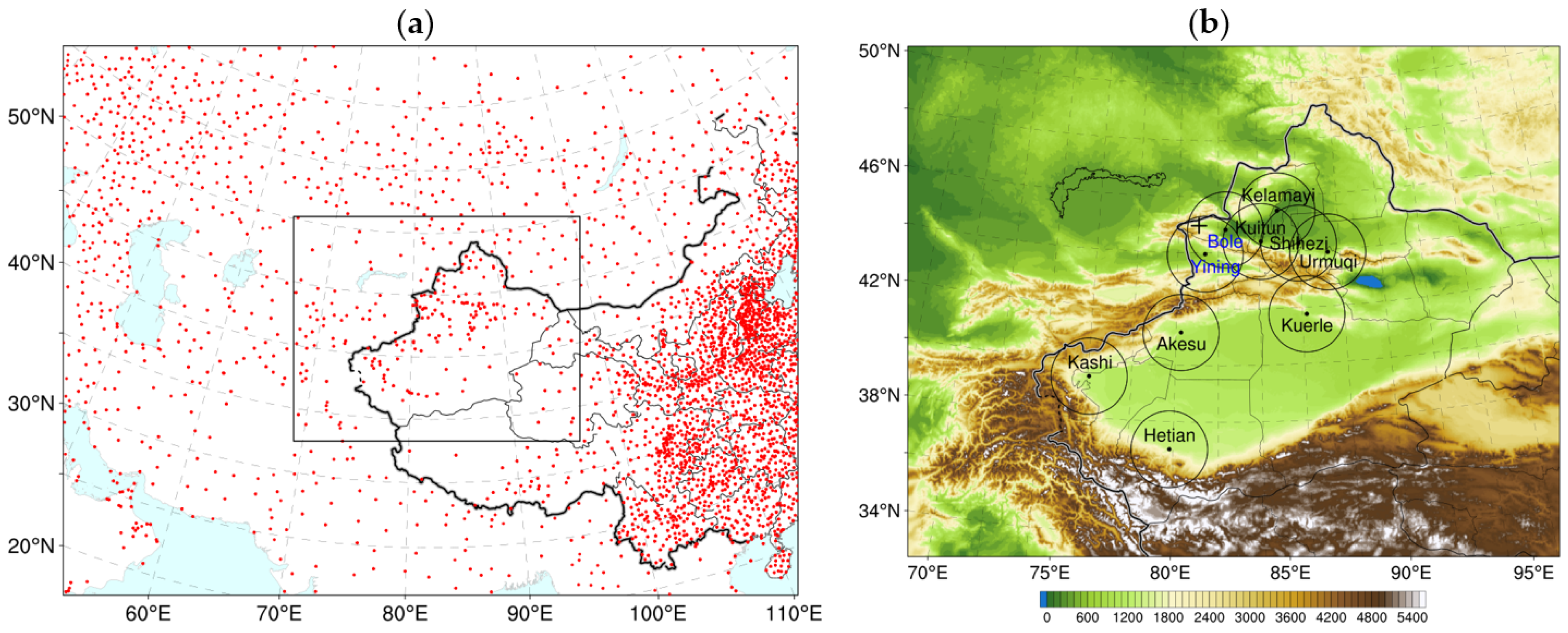
3.1. Model Configuration
3.2. Data Used for Assimilation and Validation
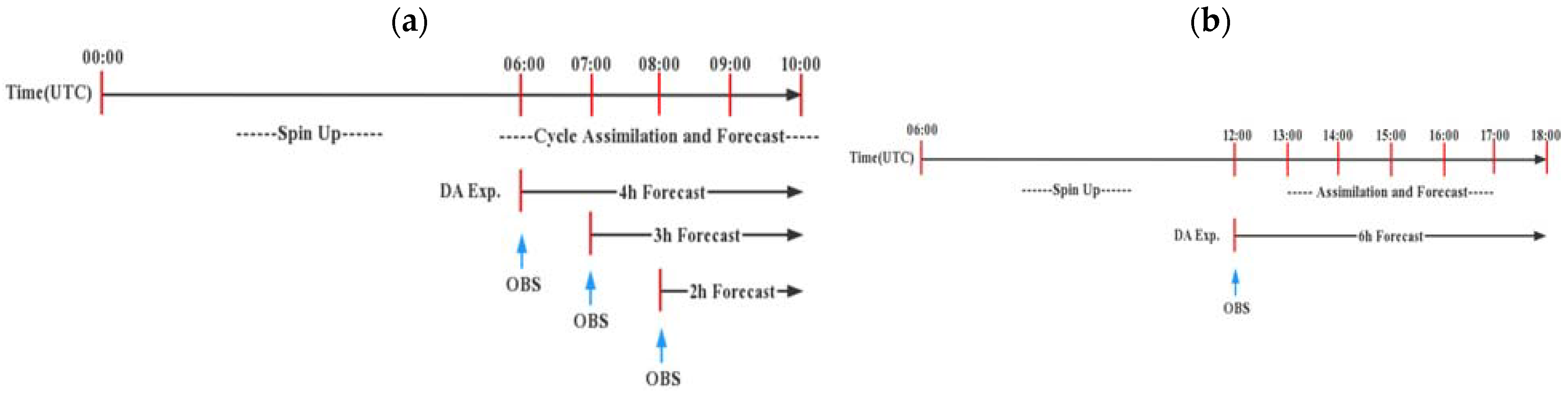
3.3. Experimental Design
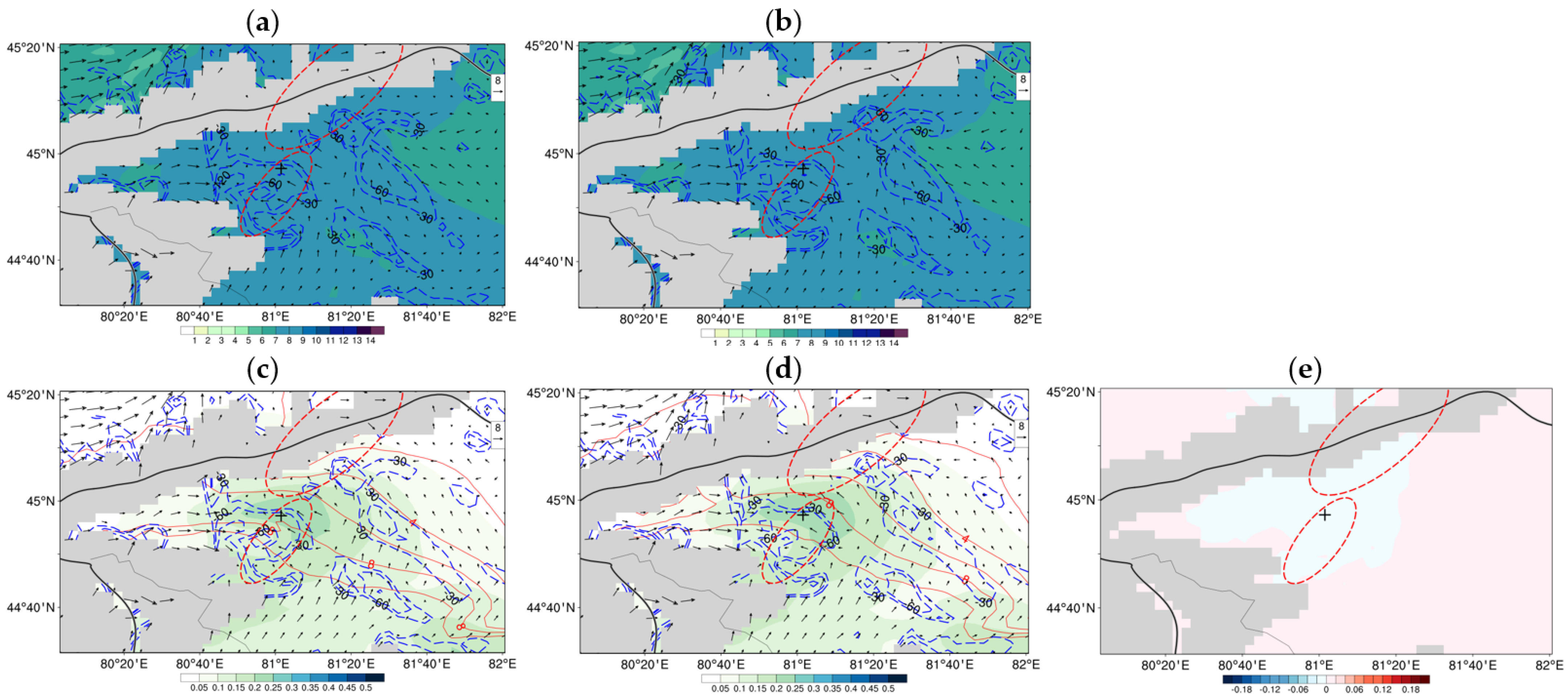
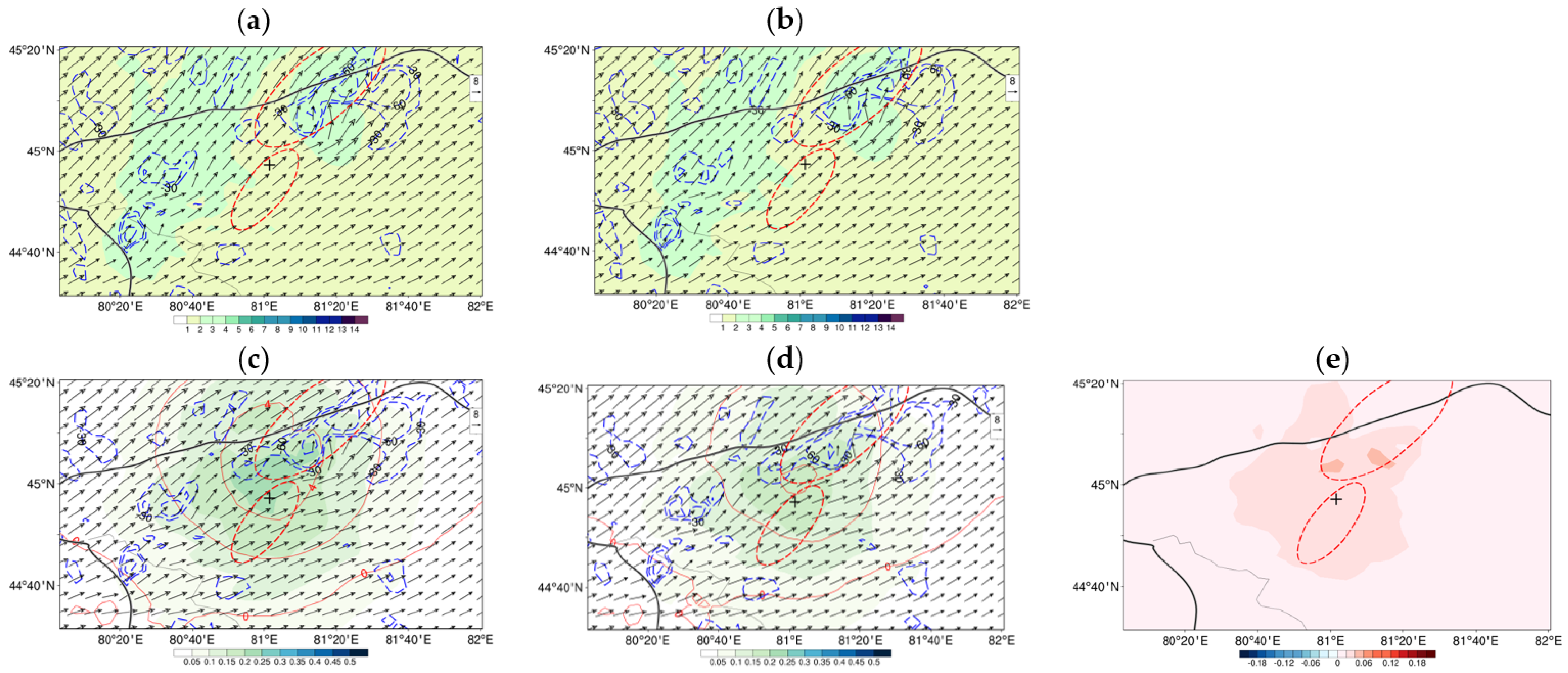
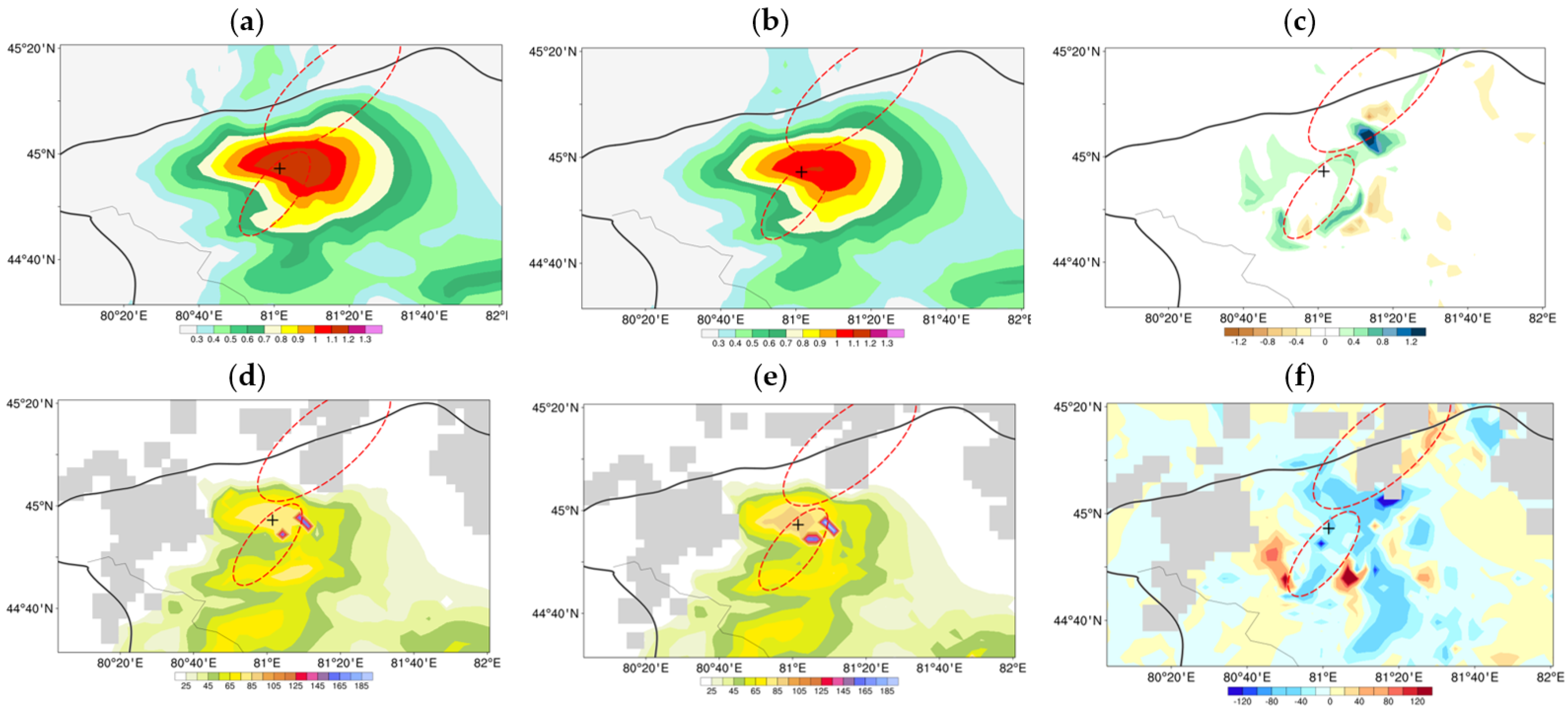
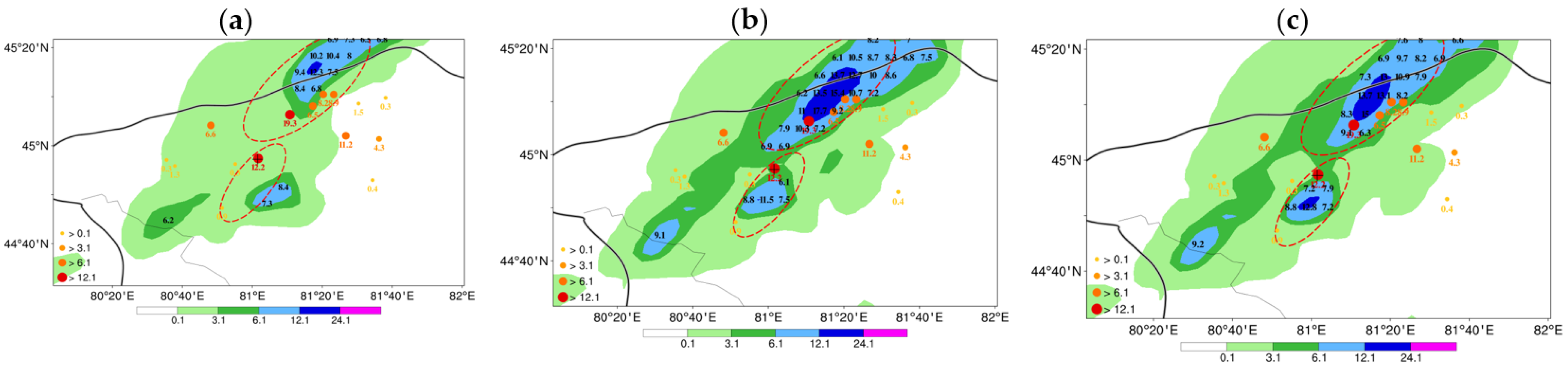
4. Result
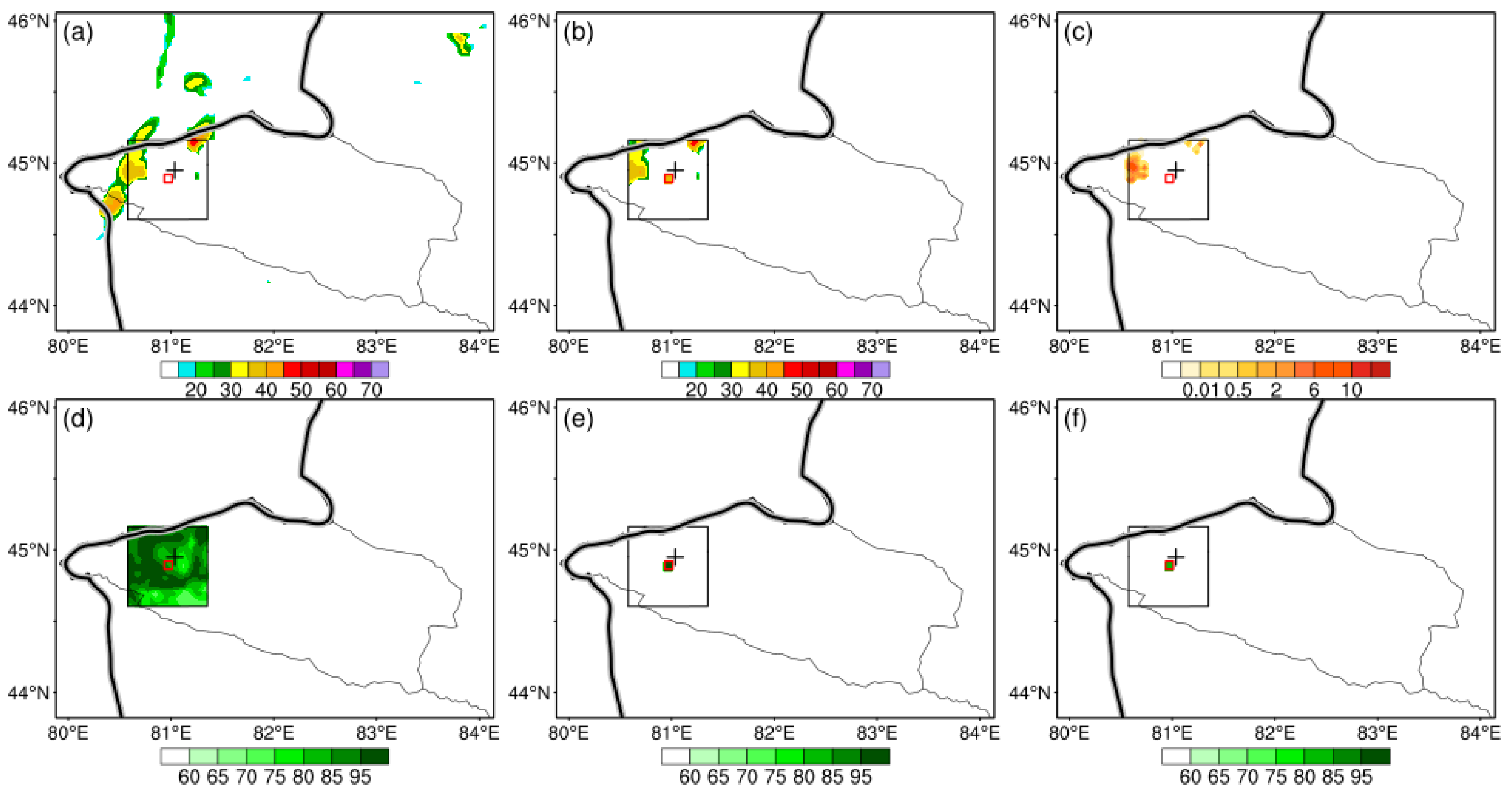
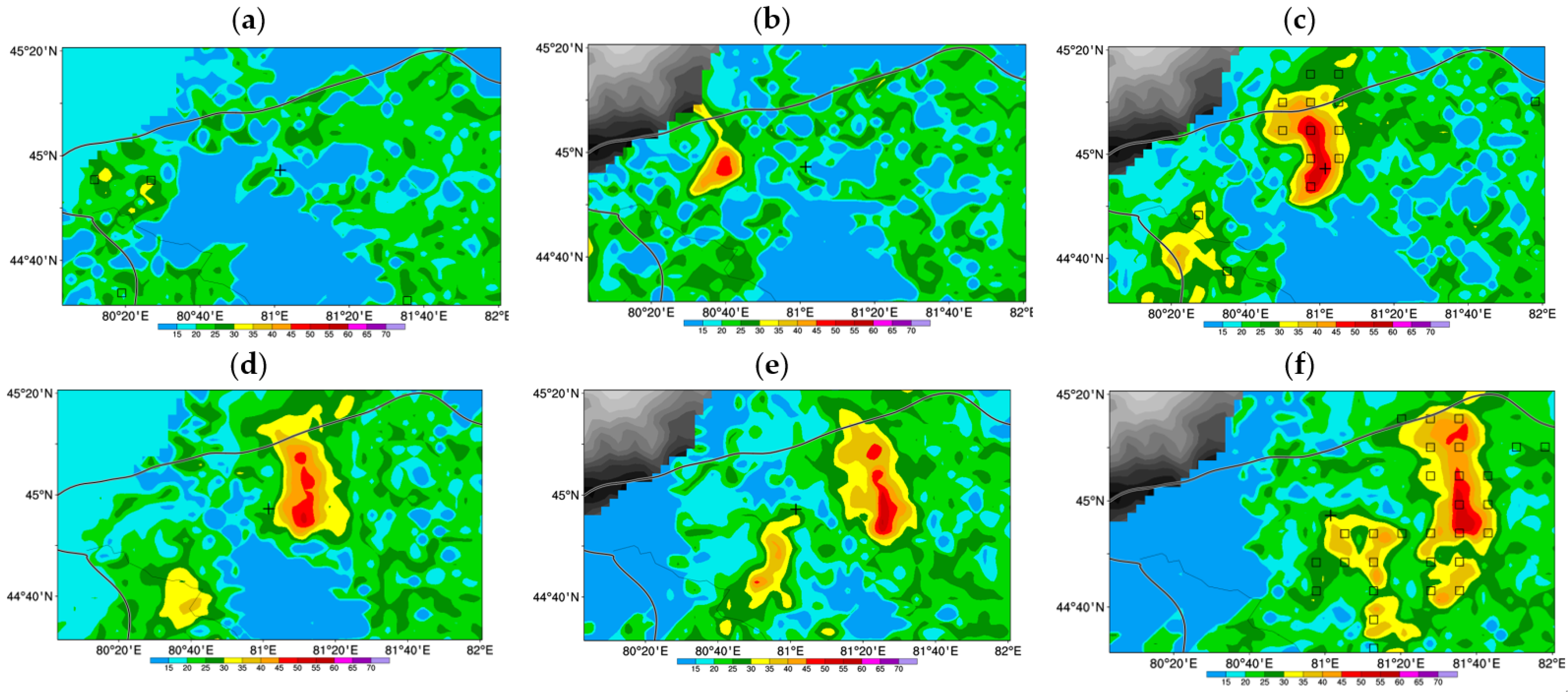
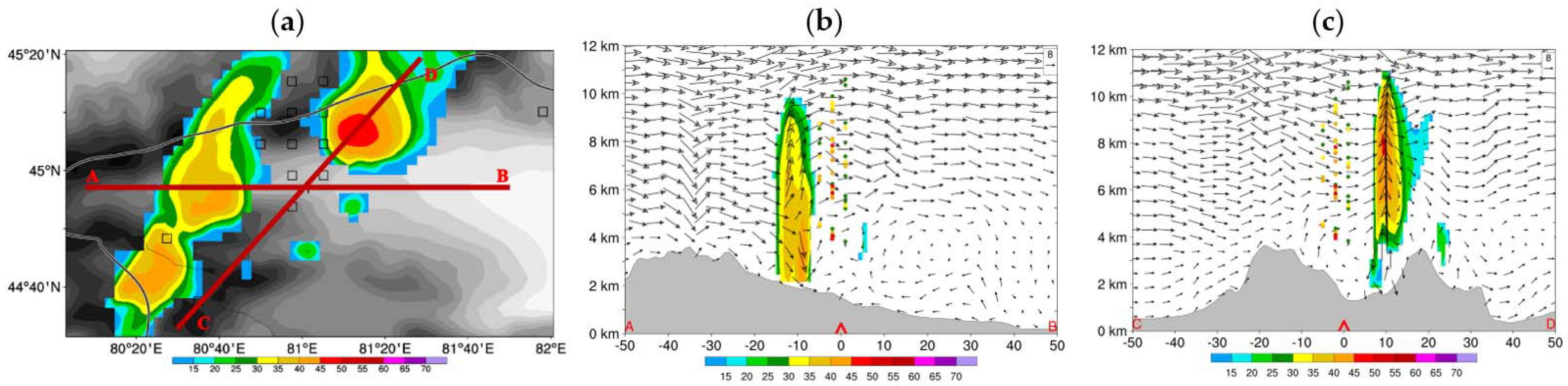
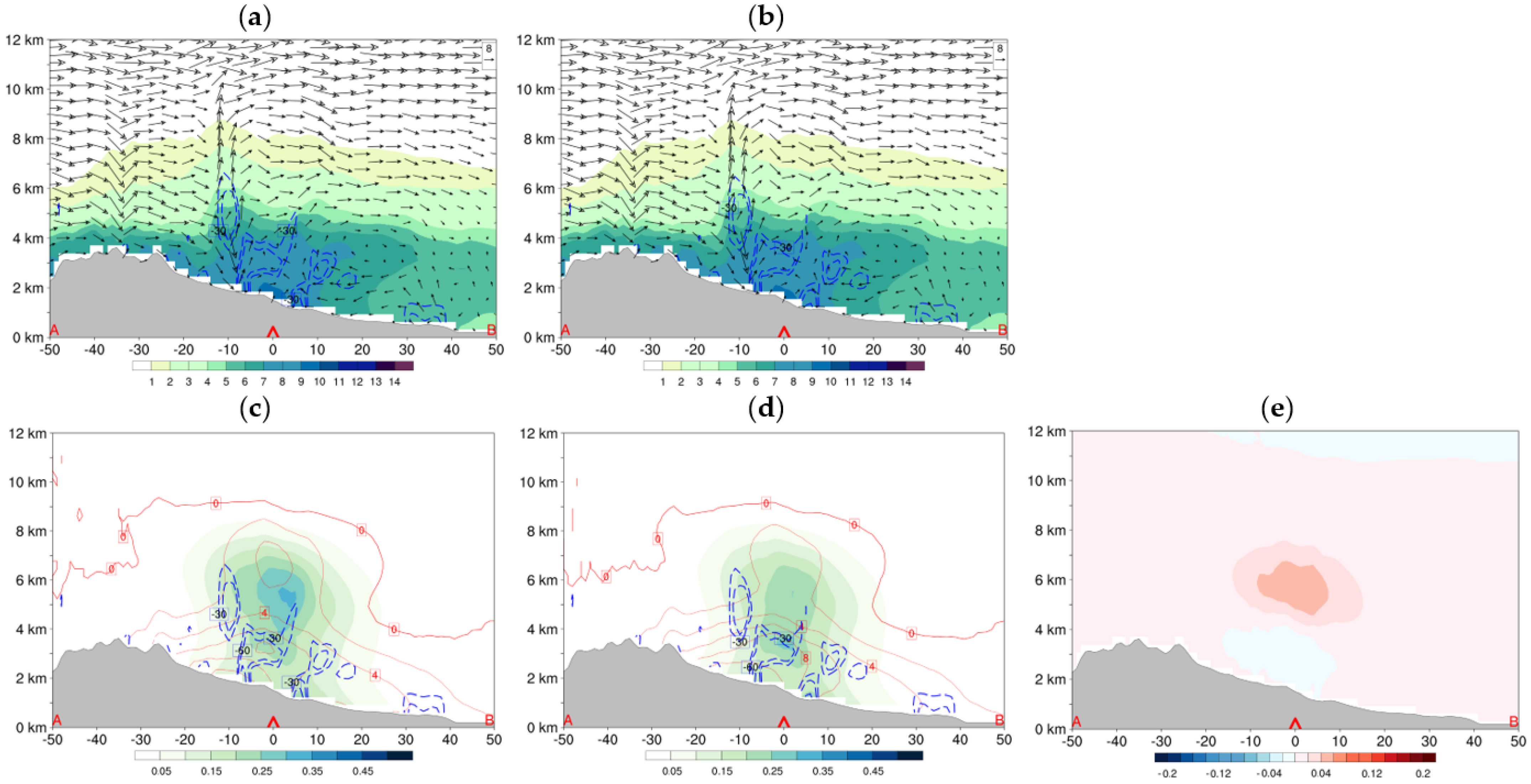
4.1. Test of Single Reflectivity Observation
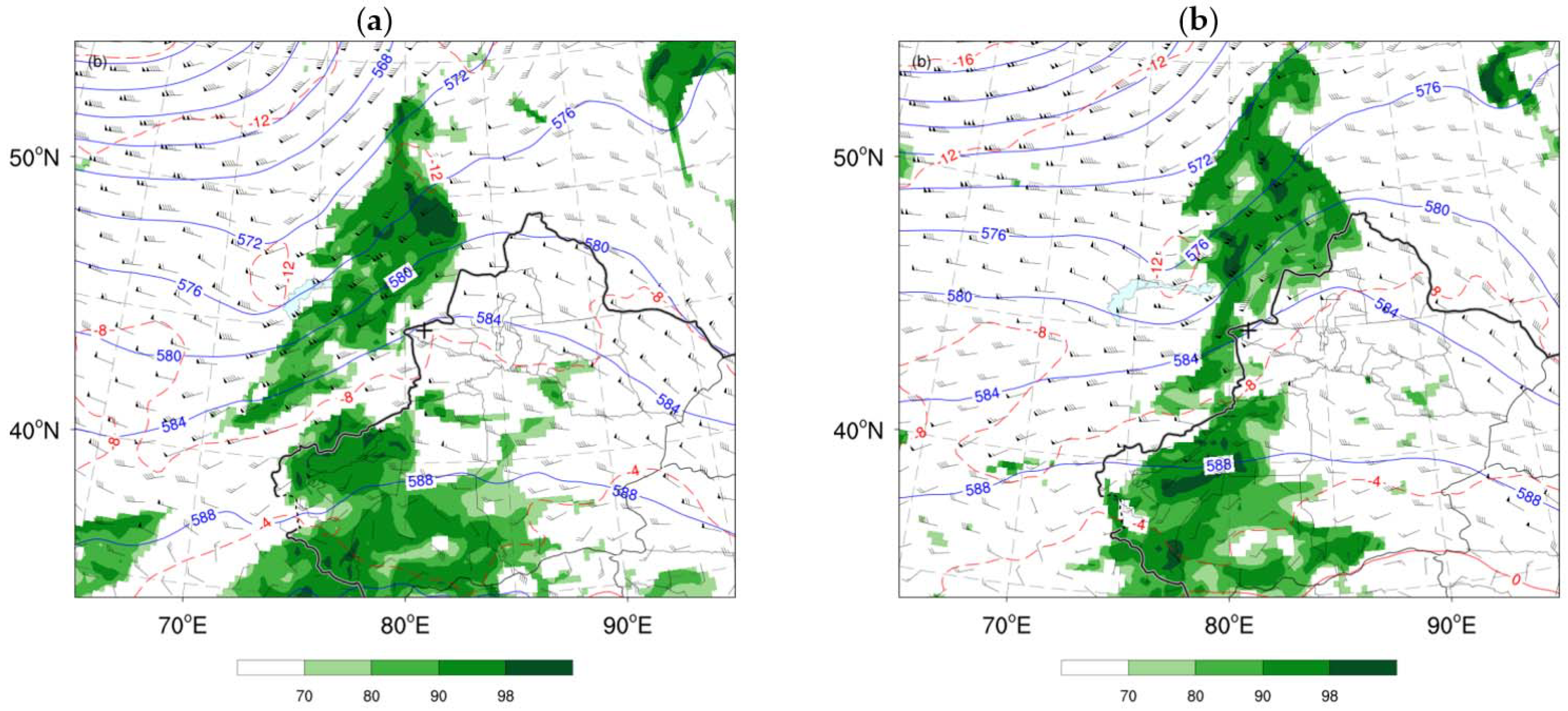
4.2. 30 July 2019 Case
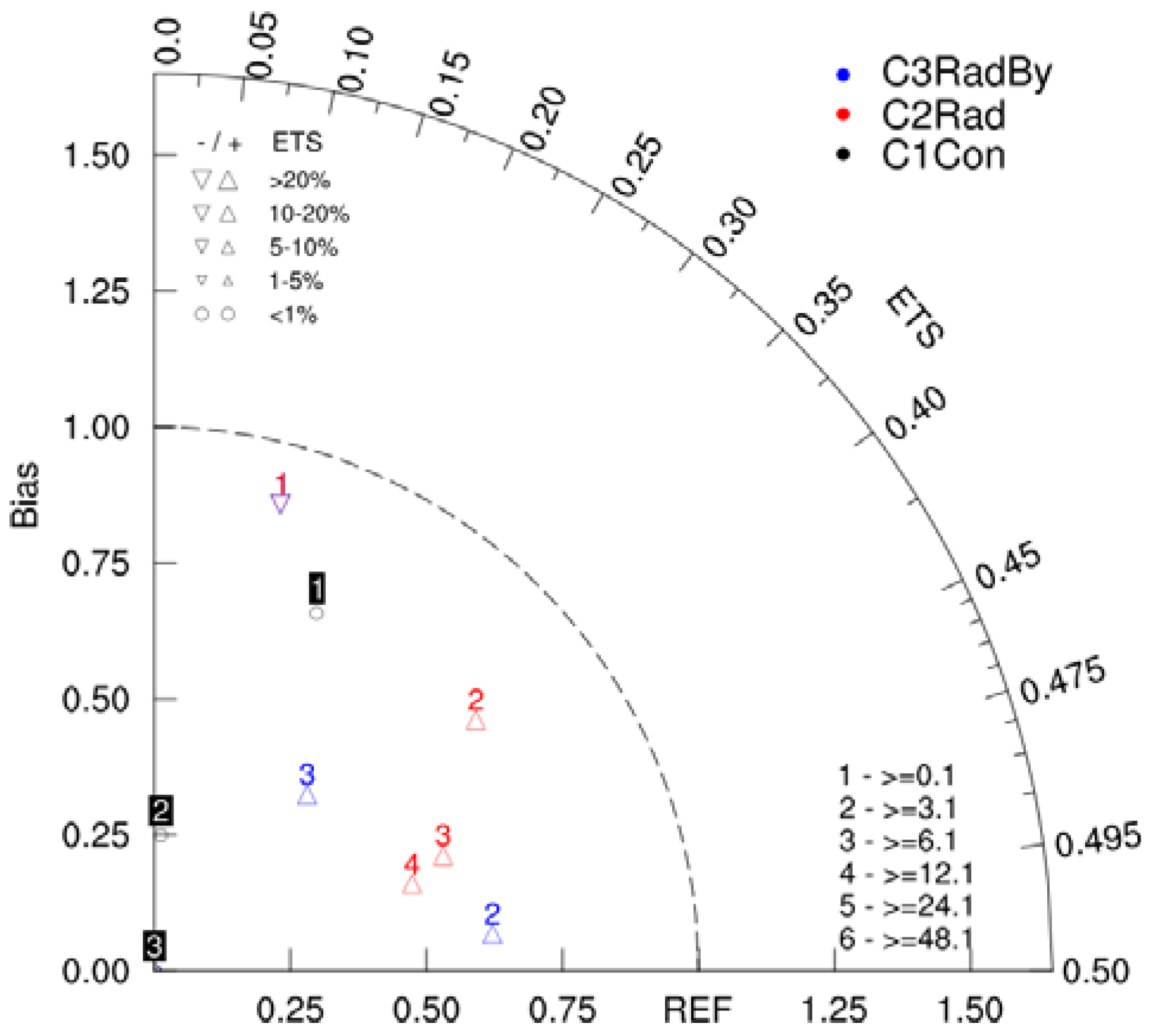
4.3. Continuous Monthly Experiments
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, J.; Crook, N.A. Dynamical and microphysical retrieval from Doppler radar observations using a cloud model and its adjoint. Part I: Model development and simulated data experiments. J. Atmos. Sci. 1997, 54, 1642–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Xue, M.; Shapiro, A.; Droegemeier, K.K. A variational analysis for the retrieval of three-dimensional mesoscale wind fields from two Doppler radars. Mon. Weather Rev. 1999, 127, 2128–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Xue, M.; Brewster, K.; Droegemeier, K.K. A three-dimensional data analysis method with recursive filter for Doppler radars. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2004, 21, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J. Convective-scale assimilation of radar data: Progress and challenges. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. J. Atmos.Sci. Appl. Meteorol. Phys. Oceanogr. 2005, 131, 3439–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Xue, M.; Brewster, K. 3DVAR and cloud analysis with WSR-88D Level-II data for the prediction of the Fort Worth tornadic thunderstorms. Part I: Cloud analysis and its impact. Mon. Weather Rev. 2006, 134, 675–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, C.C. Limitations and Potential of Complex Cloud Analysis and Its Improvement for Radar Reflectivity Data Assimilation Using OSSES. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, M.; Wang, D.; Gao, J.; Brewster, K.A.; Droegemeier, K.K. The Advanced Regional Prediction System (ARPS), storm-scale numerical weather prediction and data assimilation. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2003, 82, 139–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Stensrud, D.J. Assimilation of reflectivity data in a convective-scale, cycled 3DVAR framework with hydrometeor classification. J. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 69, 1054–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Smith, T.M.; Stensrud, D.J.; Fu, C.; Calhoun, K.; Manross, K.L.; Brogden, J.; Lakshmanan, V.; Wang, Y.; Thomas, K.W.; et al. A real-time weather-adaptive 3DVAR analysis system for severe weather detections and warnings. Weather Forecast. 2013, 28, 727–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Sun, J.; Fan, S.; Huang, X.Y. Indirect assimilation of radar reflectivity with WRF 3D-Var and its impact on prediction of four summertime convective eventsss. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2013, 52, 889–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Sun, J.; Zhang, X.; Huang, X.Y.; Auligne, T. Radar data assimilation with WRF 4D-Var. Part I: System development and preliminary testing. Mon. Weather Rev. 2013, 141, 2224–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Sun, J. Multiple-radar data assimilation and short-range quantitative precipitation forecasting of a squall line observed during IHOP_2002. Mon. Weather Rev. 2007, 135, 3381–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksoy, A.; Dowell, D.C.; Snyder, C. A multicase comparative assessment of the ensemble Kalman filter for assimilation of radar observations. Part I: Storm-scale analyses. Mon. Weather Rev. 2009, 137, 1805–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dowell, D.C.; Wicker, L.J.; Snyder, C. Ensemble Kalman filter assimilation of radar obervations of the 8 May 2003 Oklahoma City supercell: Influences of reflectivity observations on storm-scale analyses. Mon. Weather Rev. 2011, 139, 272–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, J.; Fu, C.; Stensrud, D.J.; Kain, J.S. OSSEs for an ensemble 3DVAR data assimilation system with radar observations of convective storms. J. Atmos. Sci. 2016, 73, 2403–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, A.; Gao, J.; Koch, S.E.; Wang, Y.; Pan, S.; Fierro, A.O.; Cui, C.; Min, J. Assimilation of Radar Radial Velocity, Reflectivity, and Pseudo–Water Vapor for Convective-Scale NWP in a Variational Framework. Mon. Weather Rev. 2019, 147, 2877–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albers, S.C.; McGinley, J.A.; Birkenheuer, D.L.; Smart, J.R. The Local Analysis and Prediction System (LAPS): Analyses of clouds, precipitation, and temperature. Weather Forecast. 1996, 11, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, H.L. Radar data assimilation with WRF 4D-Var. Part II: Comparison with 3D-Var for a squall line over the U.S. Great Plains. Mon. Weather Rev. 2013, 141, 2245–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenkman, A.D.; Ming, X.; Shapiro, A.; Brewster, K.; Gao, J. The analysis and prediction of the 8–9 May 2007 Oklahoma tornadic mesoscale convective system by assimilation WSR-88D and CASA radar data using 3DVAR. Mon. Weather Rev. 2011, 139, 224–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tong, M.J.; Xue, M. Ensemble Kalman filter assimilation of Doppler radar data with a compressible nonhydrostatic model: OSS experiments. Mon. Weather Rev. 2005, 133, 1789–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Q. Generalized adjoint for physical processes with parameterized discontinuities. Part I: Basic issues and heuristic examples. J. Atmos. Sci. 1996, 53, 1123–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, G.; Gao, J.; Xue, M. Impacts of assimilating measurements of different state variables with a simulated supercell storm and three-dimensional variational method. Mon. Weather Rev. 2013, 141, 2759–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walbröl, A.; Crewell, S.; Engelmann, R.; Orlandi, E.; Griesche, H.; Radenz, M.; Hofer, J.; Althausen, D.; Maturilli, M.; Ebell, K. Atmospheric temperature, water vapor and liquid water path from two microwave radiometers during MOSAiC. Sci. Data 2022, 9, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shikhovtsev, A.Y.; Khaikin, V.B.; Mironov, A.P.; Kovadlo, P.G. Statistical Analysis of the Water Vapor Content in North Caucasus and Crimea. Atmos. Ocean Opt. 2022, 35, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philipona, R.; Kräuchi, A.; Kivi, R.; Peter, T.; Wild, M.; Dirksen, R.; Fujiwara, M.; Sekiguchi, M.; Hurst, D.F.; Becker, R. Balloon-borne radiation measurements demonstrate radiative forcing by water vapor and clouds. Meteorol. Z. 2020, 29, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Hu, Z.; Liu, P.; Zhang, F. Impact of Water Vapor on the Development of a Supercell Over Eastern China. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 881579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caumont, O.; Ducrocq, V.; Wattrelot, E.; Jaubert, G.; Pradier-Vabre, S. 1D+3DVar assimilation of radar reflectivity data: A proof of concept. Tellus 2010, 62A, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattrelot, E.; Caumont, O.; Mahfouf, J.F. Operational implementation of the 1D+3D-Var assimilation method of radar reflectivity data in the AROME model. Mon. Weather Rev. 2014, 142, 1852–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kummerow, C.; Hong, Y.; Olson, W.S.; Yang, S.; Adler, R.F.; McCollum, J.; Ferraro, R.; Petty, G.; Shin, D.B.; Wilheit, T.T. The evolution of the Goddard profiling algorithm (GPROF) for rainfall estimation from passive microwave sensors. J. Appl. Meteor. 2001, 40, 1801–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, W.S.; Kummerow, C.D.; Heymsfield, G.M.; Giglio, L. A method for combined passive-active microwave retrievals of cloud and precipitation profiles. J. Appl. Meteor. 1996, 35, 1763–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenc, A.C. Analysis methods for numerical weather prediction. Q. J. R. Meteor. Soc. 1986, 112, 1177–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, D.M.; Huang, W.; Guo, Y.R.; Bourgeois, A. A three-dimensional variational (3DVAR) data assimilation system for use with MM5. NCAR Tech. Note 2003, 68. [Google Scholar]
- Parrish, D.F.; Derber, J.C. The National Meteorological Center’s spectral statistical-interpolation analysis system. Mon. Weather Rev. 1992, 120, 1747–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannister, R.N. A review of forecast error covariance statistics in atmospheric variational data assimilation. II: Modelling the forecast error covariance statistics. Q. J. R.Meteor. Soc. 2008, 134, 1971–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skamarock, W.C.; Klemp, J.B.; Dudhia, J.; Gill, D.O.; Barker, D.; Duda, M.G.; Powers, J.G. A Description of the Advanced Research WRF Version 3 (No. NCAR/TN-475+STR). University Corporation for Atmospheric Research. 2008. Available online: https://opensky.ucar.edu/islandora/object/technotes:500 (accessed on 15 August 2021).
- National Center for Atmospheric Research. The Research Data Archive. Available online: https://rda.ucar.edu/datasets/ (accessed on 10 August 2021).
- Hong, S.-Y.; Lim, J.-O.J. The WRF single-moment 6-class microphysics scheme (WSM6). J. Korean Meteor. Soc. 2006, 42, 129–151. [Google Scholar]
- Iacono, M.J.; Delamere, J.S.; Mlawer, E.J.; Shephard, M.W.; Clough, S.A.; Collins, W.D. Radiative forcing by long–lived greenhouse gases: Calculations with the AER radiative transfer models. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D13103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewari, M.; Chen, F.; Wang, W.; Dudhia, J.; LeMone, M.A.; Mitchell, K.; Ek, M.; Gayno, G.; Wegiel, J.; Cuenca, R.H. Implementation and verification of the unified NOAH land surface model in the WRF model. In Proceedings of the 20th Conference on Weather Analysis and Forecasting/16th Conference on Numerical Weather Prediction, Seattle, WA, USA, 12–16 January 2004; pp. 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Kain, J.S. The Kain–Fritsch convective parameterization: An update. J. Appl. Meteor. 2004, 43, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleim, J.E. A Combined Local and Nonlocal Closure Model for the Atmospheric Boundary Layer. Part I: Model Description and Testing. J. Appl. Meteor. Climatol. 2007, 46, 1383–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Meteorological Information Center. China Meteorological Data Sharing Service System. Available online: http://data.cma.cn/ (accessed on 23 August 2021).
- Peng, L.; Yang, Y.; Xin, Y.; Wang, C. Impact of Lightning Data Assimilation on Forecasts of a Leeward Slope Precipitation Event in the Western Margin of the Junggar Basin. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, A.J.; Xue, M.; Weisman, M.L. Neighborhood based verification of precipitation forecasts from convection allowing NCAR WRF Model simulations and the operational NAM. Weather Forecast. 2010, 25, 1495–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Model and Configurations | |
|---|---|
| Version | v3.9.1, nonhydrostatic = true |
| Domain 1 | 712 × 532, nominal 9 km |
| Domain 2 | 832 × 652, nominal 3 km |
| Vertical computation layers | 50 |
| Pressure top | 10 hPa |
| Lateral boundary conditions | NCEP-FNL |
| Microphysics | WSM6 |
| Longwave radiation | RRTMG |
| Shortwave radiation | RRTMG |
| Land surface | Unified Noah land-surface model |
| Deep convection | Kain–Fritsch |
| Planetary-boundary and surface layer | ACM2 |
| Experiments | Observations | Pseudo Water Vapor | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 30 July 2019 case | C1Con | Domain 1: SYNOP Domain 2: SYNOP + radar radial velocity | _ |
| C2Rad | Domain 1: SYNOP Domain 2: SYNOP + radar radial velocity + reflectivity | The original scheme: , With , . | |
| C3RadBy | Same as C2Rad | The updated scheme: , With . | |
| July 2019 Continuous experiments | E1Con | Same as C1Con | _ |
| E2Rad | Same as C2Rad | Same as C2Rad | |
| E3RadBy | Same as C2Rad | Same as C3RadBy |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Fan, S.; Ali, M.; Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Aihaiti, A. Assimilation of Water Vapor Retrieved from Radar Reflectivity Data through the Bayesian Method. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5897. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14225897
Liu J, Fan S, Ali M, Li H, Zhang H, Wang Y, Aihaiti A. Assimilation of Water Vapor Retrieved from Radar Reflectivity Data through the Bayesian Method. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(22):5897. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14225897
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Junjian, Shuiyong Fan, Mamtimin Ali, Huoqing Li, Hailiang Zhang, Yu Wang, and Ailiyaer Aihaiti. 2022. "Assimilation of Water Vapor Retrieved from Radar Reflectivity Data through the Bayesian Method" Remote Sensing 14, no. 22: 5897. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14225897
APA StyleLiu, J., Fan, S., Ali, M., Li, H., Zhang, H., Wang, Y., & Aihaiti, A. (2022). Assimilation of Water Vapor Retrieved from Radar Reflectivity Data through the Bayesian Method. Remote Sensing, 14(22), 5897. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14225897






