Improved LiDAR Localization Method for Mobile Robots Based on Multi-Sensing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. AMCL-Based Multi-Sensing Fusion Localization Method
2.2. Multi-Source Data Fusion Method
2.3. Point Cloud Registration
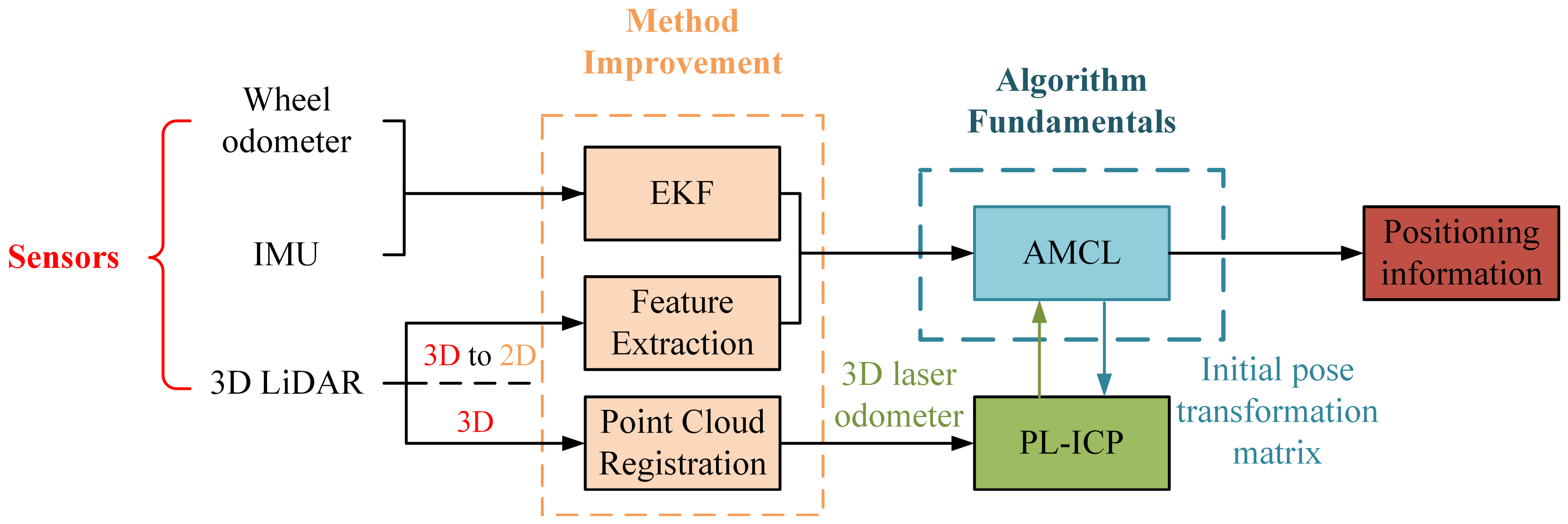
3. Principles and Models
3.1. AMCL and Laser Point Cloud Data Conversion
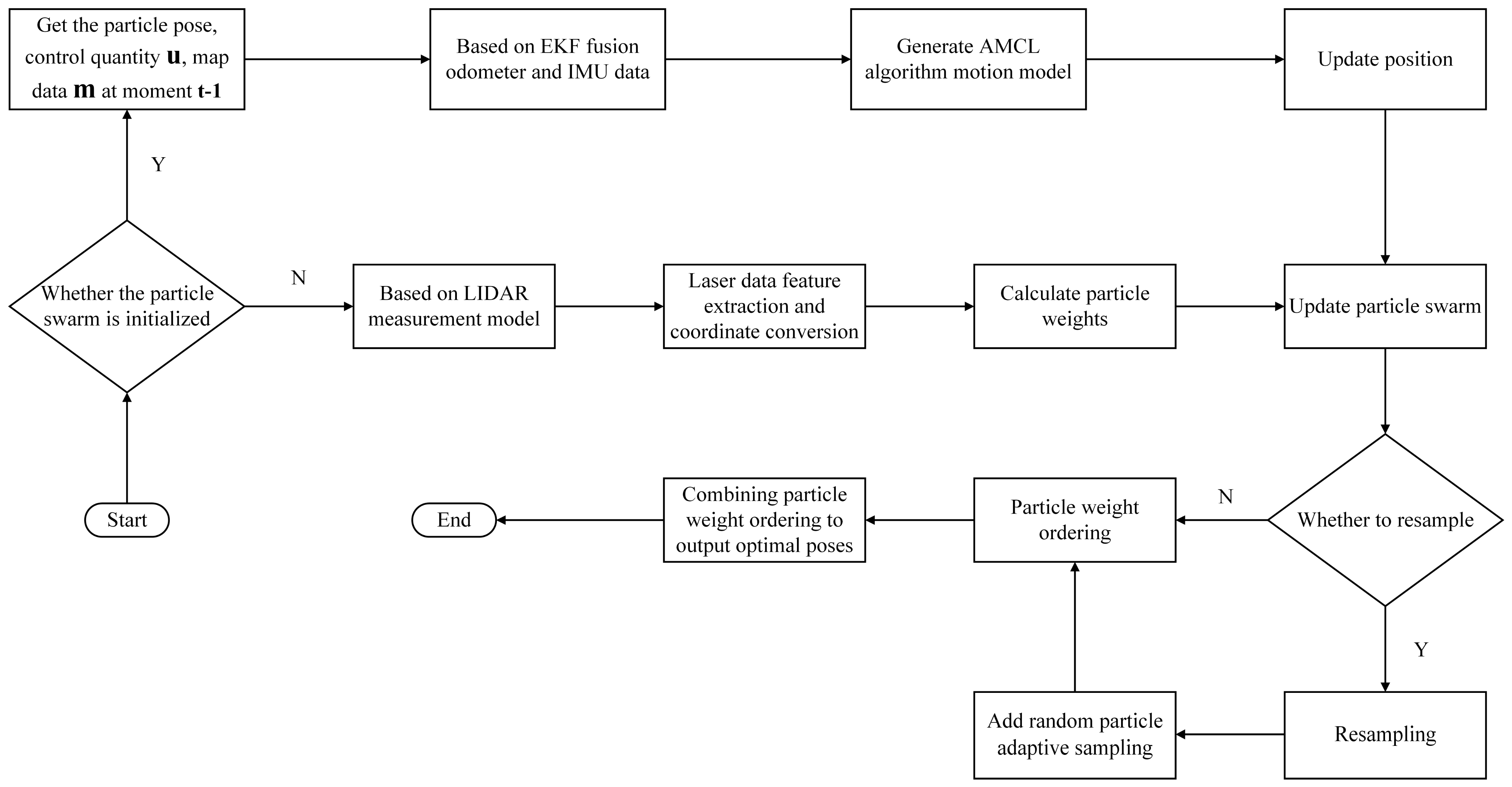
3.1.1. AMCL
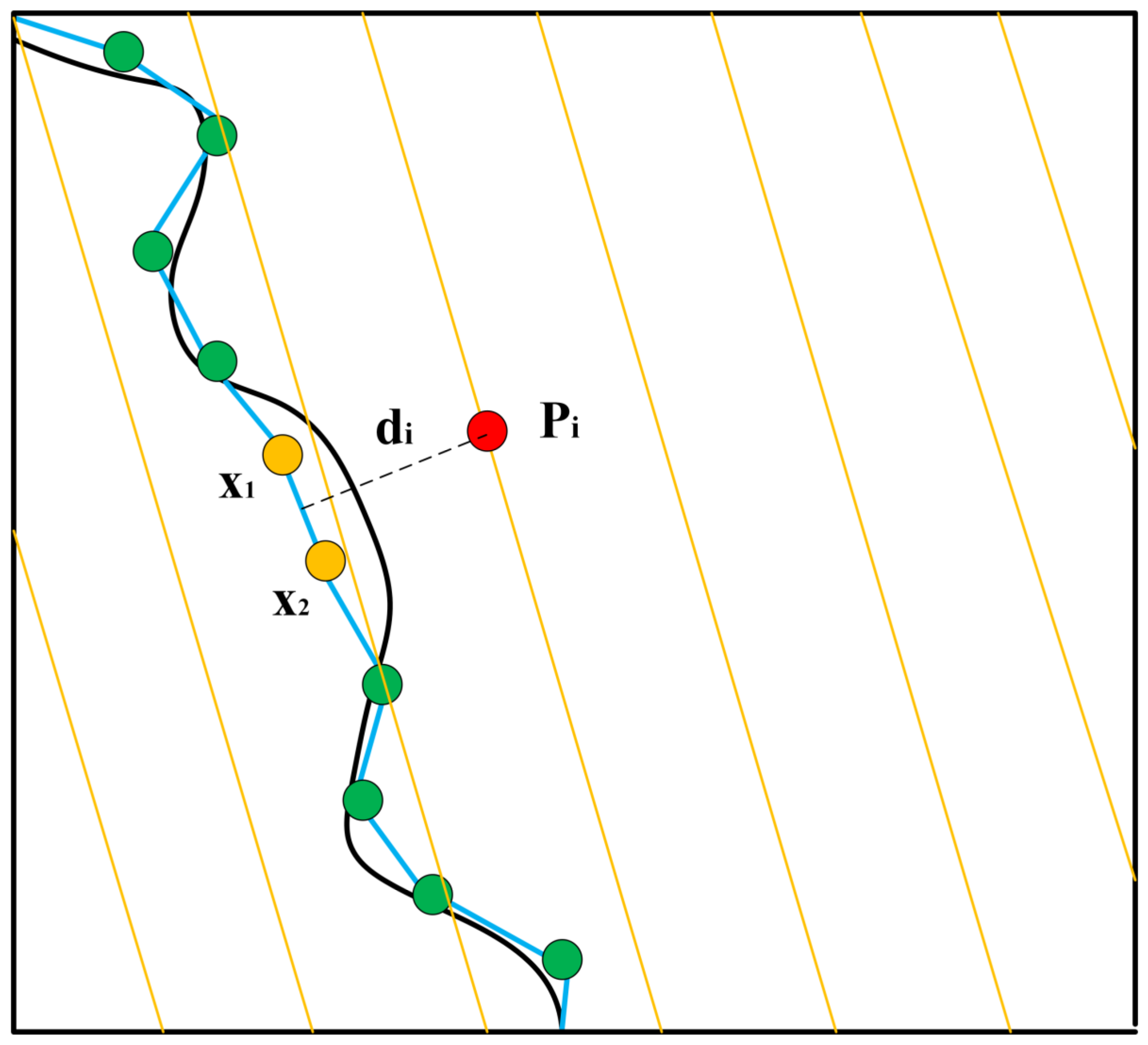
3.1.2. Laser Point Cloud Data Conversion
3.2. Improved AMCL Localization Algorithm Based on EKF Fusion
3.3. PL-ICP Point Cloud Matching Correction Based on the Improved AMCL
4. Results and Analyses
4.1. Simulation Experiments
4.1.1. Simulation Environment
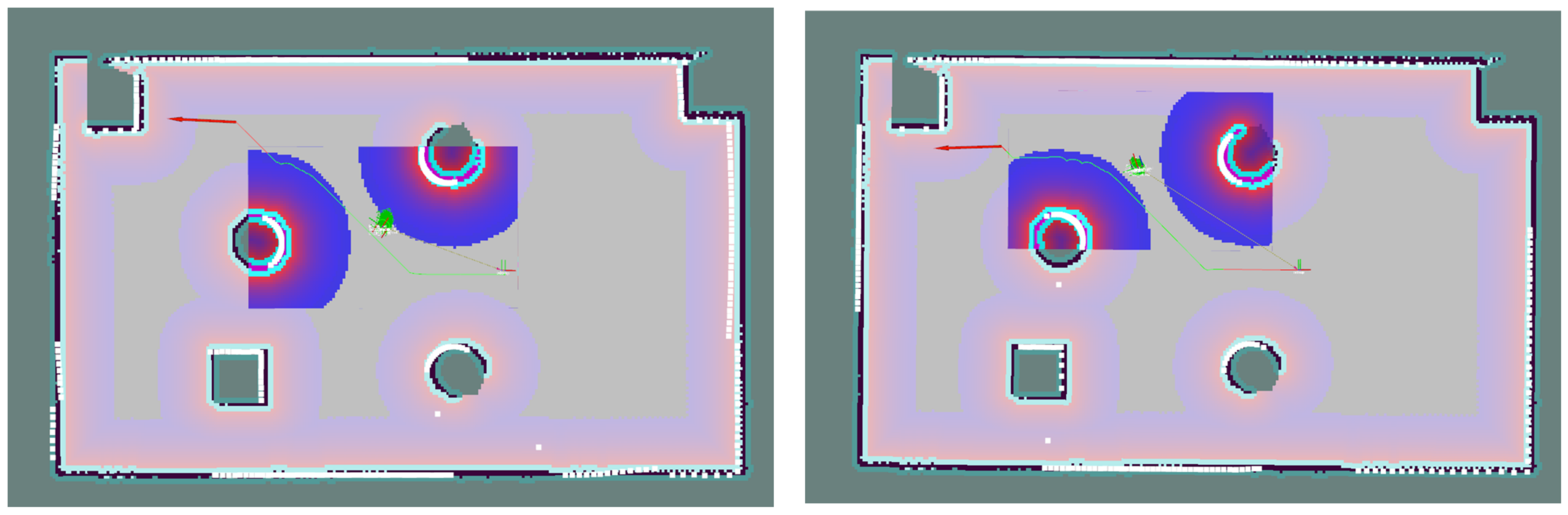
4.1.2. Point Cloud Matching Correction for AMCL Positioning
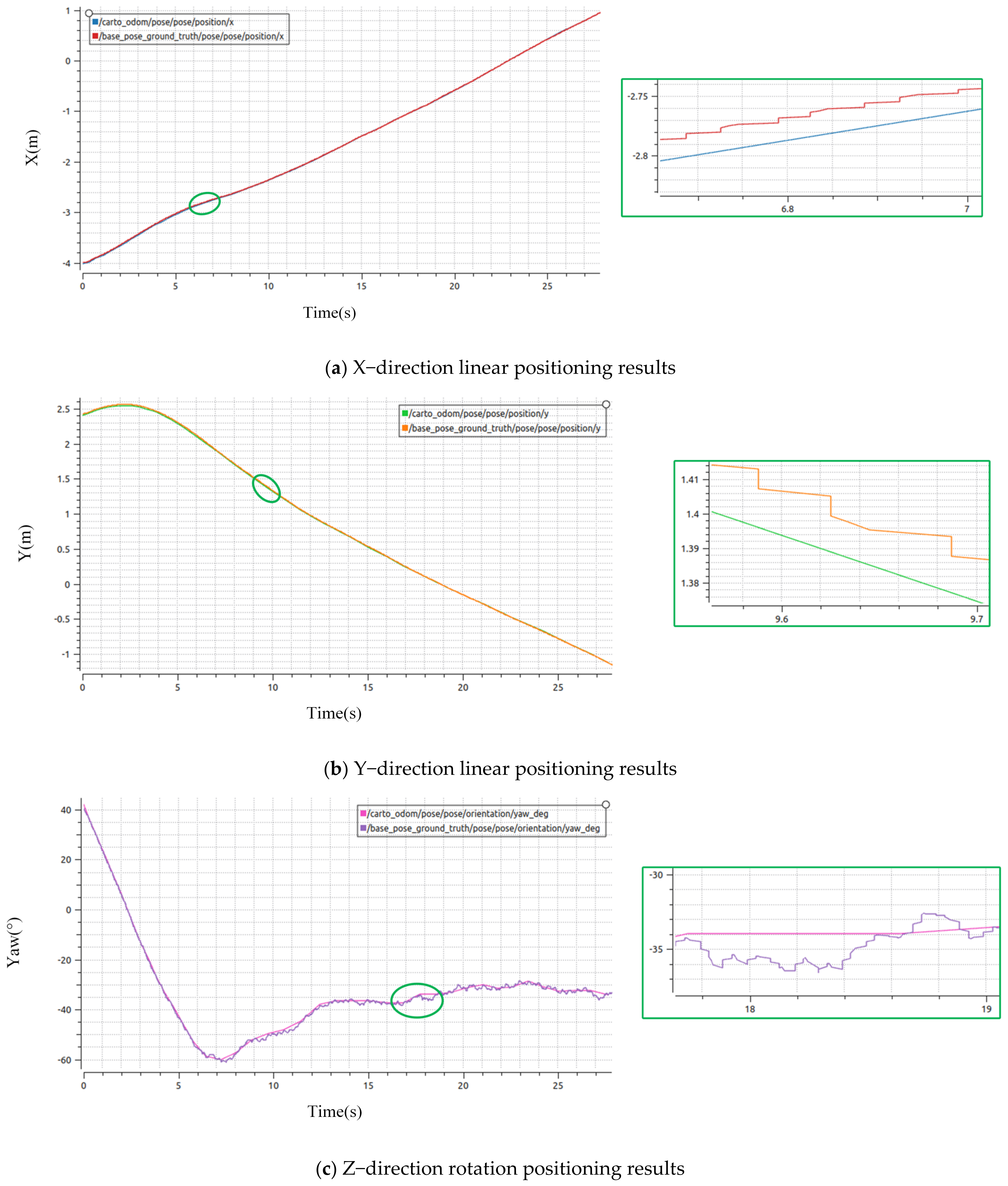
4.1.3. Analysis of Simulation Positioning Results
4.2. Practical Experiments
4.2.1. Practical Environment
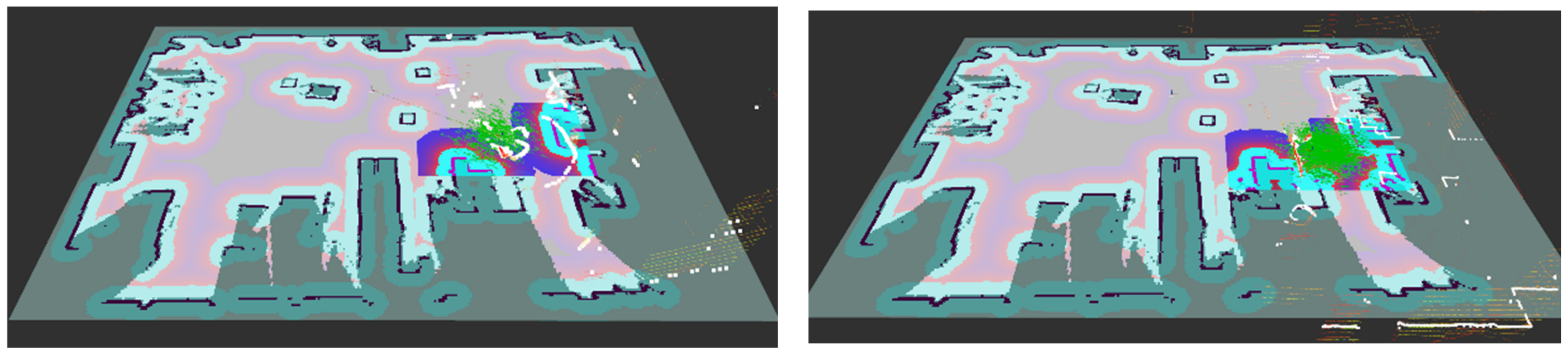
4.2.2. Point Cloud Matching Correction for AMCL Positioning
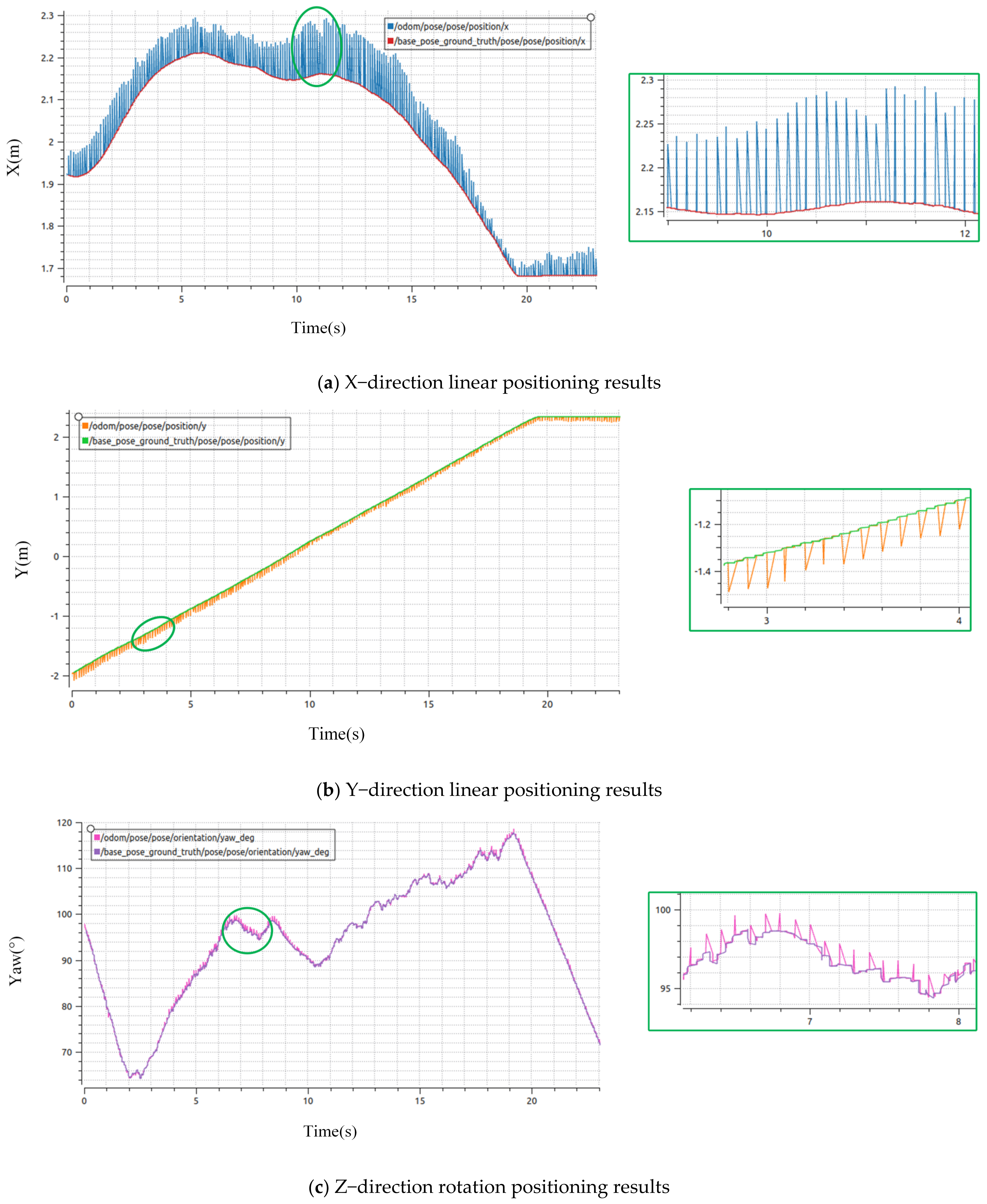
4.2.3. Analysis of Practical Positioning Results
5. Discussions
5.1. Discussion of Simulation Results
5.2. Discussion of Actual Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jie, L.; Jin, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Tan, X. A SLAM System with Direct Velocity Estimation for Mechanical and Solid-State LiDARs. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaff, P.; Burgard, W.; Fox, D. Robust monte-carlo localization using adaptive likelihood models. In European Robotics Symposium 2006; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 181–194. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, D.; Burgard, W.; Dellaert, F.; Thrun, S. Monte carlo localization: Efficient position estimation for mobile robots. AAAI IAAI 1999, 2, 343–349. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Wang, C.; Luo, W.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, B.; Wu, M. Research on Point Cloud Registering Method of Tunneling Roadway Based on 3D NDT-ICP Algorithm. Sensors 2021, 21, 4448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, K.W.; Tsai, G.J.; Li, Y.H.; Li, Y.; El-Sheimy, N. Navigation engine design for automated driving using INS/GNSS/3D LiDAR-SLAM and integrity assessment. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sefati, M.; Daum, M.; Sondermann, B.; Kreisköther, K.D.; Kampker, A. Improving vehicle localization using semantic and pole-like landmarks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Los Angeles, CA, USA, 11–14 June 2017; pp. 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Tee, Y.K.; Han, Y.C. Lidar-Based 2D SLAM for Mobile Robot in an Indoor Environment: A Review. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Green Energy, Computing and Sustainable Technology (GECOST), Miri, Malaysia, 7–9 July 2021; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, X. A mask attention interaction and scale enhancement network for SAR ship instance segmentation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, X. HTC+ for SAR Ship Instance Segmentation. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, X. A polarization fusion network with geometric feature embedding for SAR ship classification. Pattern Recognit. 2022, 123, 108365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Liu, B.; Zuo, L.; Zhang, J. High Precise Localization of Mobile Robot by Three Times Pose Correction. In Proceedings of the 2018 2nd International Conference on Robotics and Automation Sciences (ICRAS), Wuhan, China, 23–25 June 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, X.; Liu, C.; Shi, J.; Wei, S.; Ahmad, I.; Zhan, X.; Zhou, Y.; Pan, D.C.; Su, H. Balance learning for ship detection from synthetic aperture radar remote sensing imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 182, 190–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, X. High-speed ship detection in SAR images based on a grid convolutional neural network. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, X.; Shi, J.; Wei, S. Depthwise separable convolution neural network for high-speed SAR ship detection. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Miguel, M.Á.; García, F.; Armingol, J.M. Improved LiDAR probabilistic localization for autonomous vehicles using GNSS. Sensors 2020, 20, 3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Wei, Y. A Robust Localization System Fusion Vision-CNN Relocalization and Progressive Scan Matching for Indoor Mobile Robots. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Jiang, Q.; Hu, L.; Wang, Y. Text-MCL: Autonomous mobile robot localization in similar environment using text-level semantic information. Machines 2022, 10, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obregón, D.; Arnau, R.; Campo-Cossío, M.; Nicolás, A.; Pattinson, M.; Tiwari, S.; Ansuategui, A.; Tubío, C.; Reyes, J. Adaptive Localization Configuration for Autonomous Scouting Robot in a Harsh Environment. In Proceedings of the 2020 European Navigation Conference (ENC), Dresden, Germany, 23–24 November 2020; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Fikri, A.A.; Anifah, L. Mapping and Positioning System on Omnidirectional Robot Using Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (Slam) Method Based on Lidar. J. Teknol. 2021, 83, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portugal, D.; Araújo, A.; Couceiro, M.S. A reliable localization architecture for mobile surveillance robots. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Symposium on Safety, Security, and Rescue Robotics (SSRR), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 4–6 November 2020; pp. 374–379. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, K.; Wang, M.; Fu, M.; Yang, Y.; Yin, Z. Observability analysis and adaptive information fusion for integrated navigation of unmanned ground vehicles. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 67, 7659–7668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, L.; Yang, J.; Cao, C.; Wang, W.; Ran, Y.; Tan, Z.; Luo, M. A Review of Multi-Sensor Fusion SLAM Systems Based on 3D LIDAR. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempster A, P. New methods for reasoning towards posterior distributions based on sample data. Ann. Math. Stat. 1966, 37, 355–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germain, M.; Voorons, M.; Boucher, J.M.; Benie, G.B. Fuzzy statistical classification method for multiband image fusion. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Information Fusion. FUSION 2002. (IEEE Cat. No. 02EX5997), Annapolis, MD, USA, 8–11 July 2002; pp. 178–184. [Google Scholar]
- Chin, L. Application of neural networks in target tracking data fusion. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1994, 30, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrun, S.; Burgard, W.; Fox, D. Probabilistic Robotics; China Machine Press: Beijing, China, 1999; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, X.; Li, K.; Huang, B.; Cao, Y. A Multi-Sensor Data-Fusion Method Based on Cloud Model and Improved Evidence Theory. Sensors 2022, 22, 5902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartigan, J.A.; Wong, M.A. Algorithm AS 136: A k-means clustering algorithm. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. C Appl. Stat. 1979, 28, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.C.; Jahanshahi, M.R. NB-CNN: Deep learning-based crack detection using convolutional neural network and Naïve Bayes data fusion. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 65, 4392–4400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zhang, F. Fast-lio: A fast, robust lidar-inertial odometry package by tightly-coupled iterated kalman filter. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 3317–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Gu, J.; Ou, Y.; Zhang, W.; Pu, J.; Peng, H. IRobot self-localization using EKF. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Information and Automation (ICIA), Ningbo, China, 31 July–4 August 2016; pp. 801–806. [Google Scholar]
- Aybakan, T.; Kerestecioğlu, F. Indoor positioning using federated Kalman filter. In Proceedings of the 2018 3rd International Conference on Computer Science and Engineering (UBMK), Sarajevo, Bosnia and Hercegovina, 20–23 September 2018; pp. 483–488. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, J.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, M. Distributed weighted robust Kalman filter fusion for uncertain systems with autocorrelated and cross-correlated noises. Inf. Fusion 2013, 14, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julier, S.J.; LaViola, J.J. On Kalman filtering with nonlinear equality constraints. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2007, 55, 2774–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Pang, F.; Ran, Y.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, L.; Tan, Z.; Wei, C.; Luo, M. An indoor mobile robot positioning algorithm based on adaptive federated Kalman Filter. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 23098–23107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moravec, H.; Elfes, A. High resolution maps from wide angle sonar. In Proceedings of the 1985 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, St. Louis, MI, USA, 25–28 March 1985; pp. 116–121. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Ni, D.; Li, K. RFID-based vehicle positioning and its applications in connected vehicles. Sensors 2014, 14, 4225–4238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, T.; Stouch, D. A generalized extended kalman filter implementation for the robot operating system. In Intelligent Autonomous Systems 13; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 335–348. [Google Scholar]
- Besl, P.J.; McKay, N.D. Method for registration of 3-D shapes. In Sensor Fusion IV: Control Paradigms and Data Structures; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1992; pp. 586–606. [Google Scholar]
- Biber, P.; Straßer, W. The normal distributions transform: A new approach to laser scan matching. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS 2003), (Cat. No. 03CH37453), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–31 October 2003; pp. 2743–2748. [Google Scholar]
- Censi, A. An ICP variant using a point-to-line metric. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Pasadena, CA, USA, 19–23 May 2008; pp. 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Segal, A.; Haehnel, D.; Thrun, S. Generalized-icp. In Robotics: Science and Systems; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009; p. 435. Available online: https://www.robots.ox.ac.uk/~avsegal/resources/papers/Generalized_ICP.pdf (accessed on 12 August 2022).
- Serafin, J.; Grisetti, G. NICP: Dense normal based point cloud registration. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Hamburg, Germany, 28 September–3 October 2015; pp. 742–749. [Google Scholar]
- Nüchter, A. Parallelization of Scan Matching for Robotic 3D Mapping; EMCR: Dourdan, French, 2007; Available online: https://robotik.informatik.uni-wuerzburg.de/telematics/download/ecmr2007.pdf (accessed on 12 August 2022).
- Qiu, D.; May, S.; Nüchter, A. GPU-accelerated nearest neighbor search for 3D registration. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision Systems, Liège, Belgium, 13–15 October 2009; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 194–203. [Google Scholar]


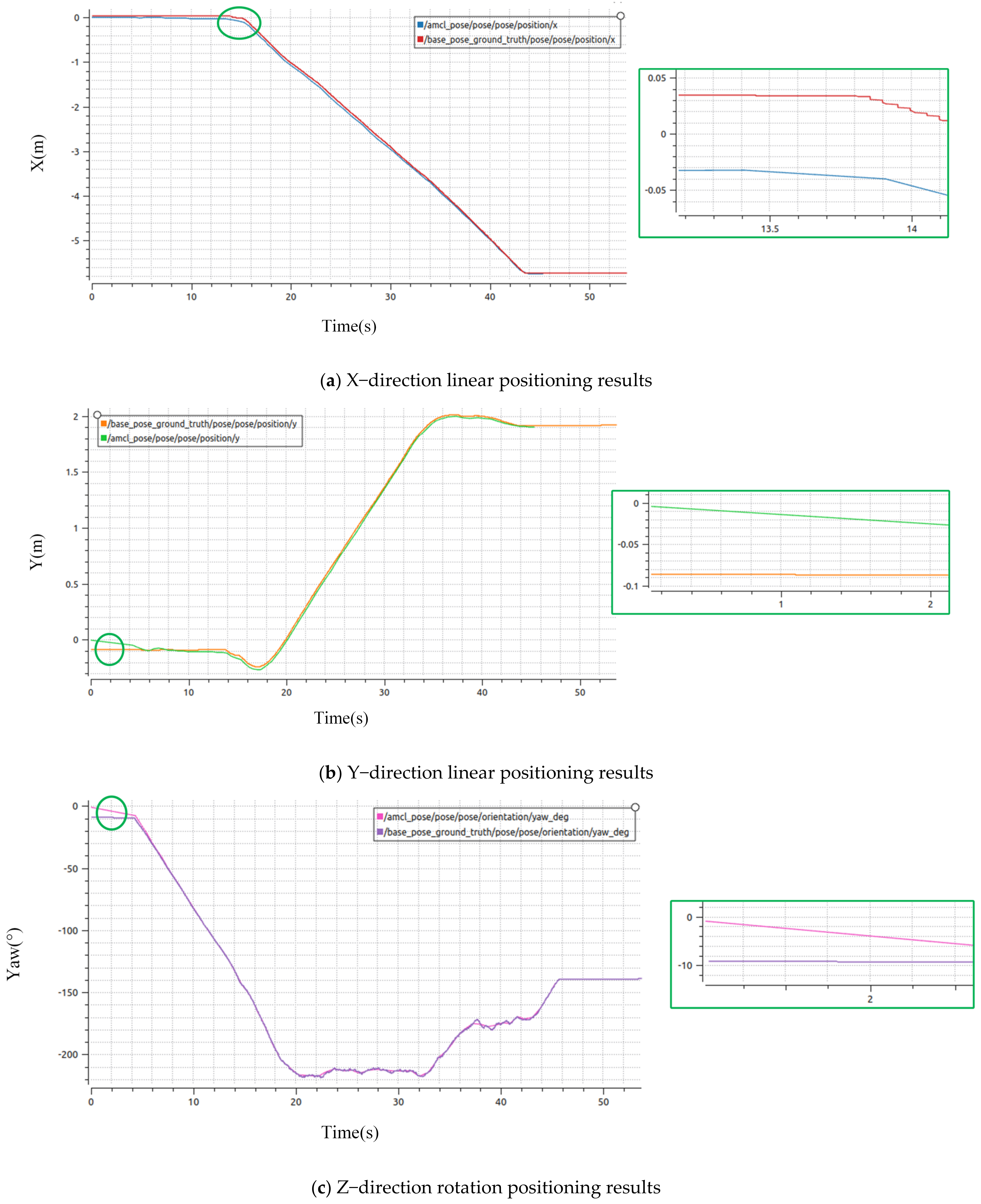


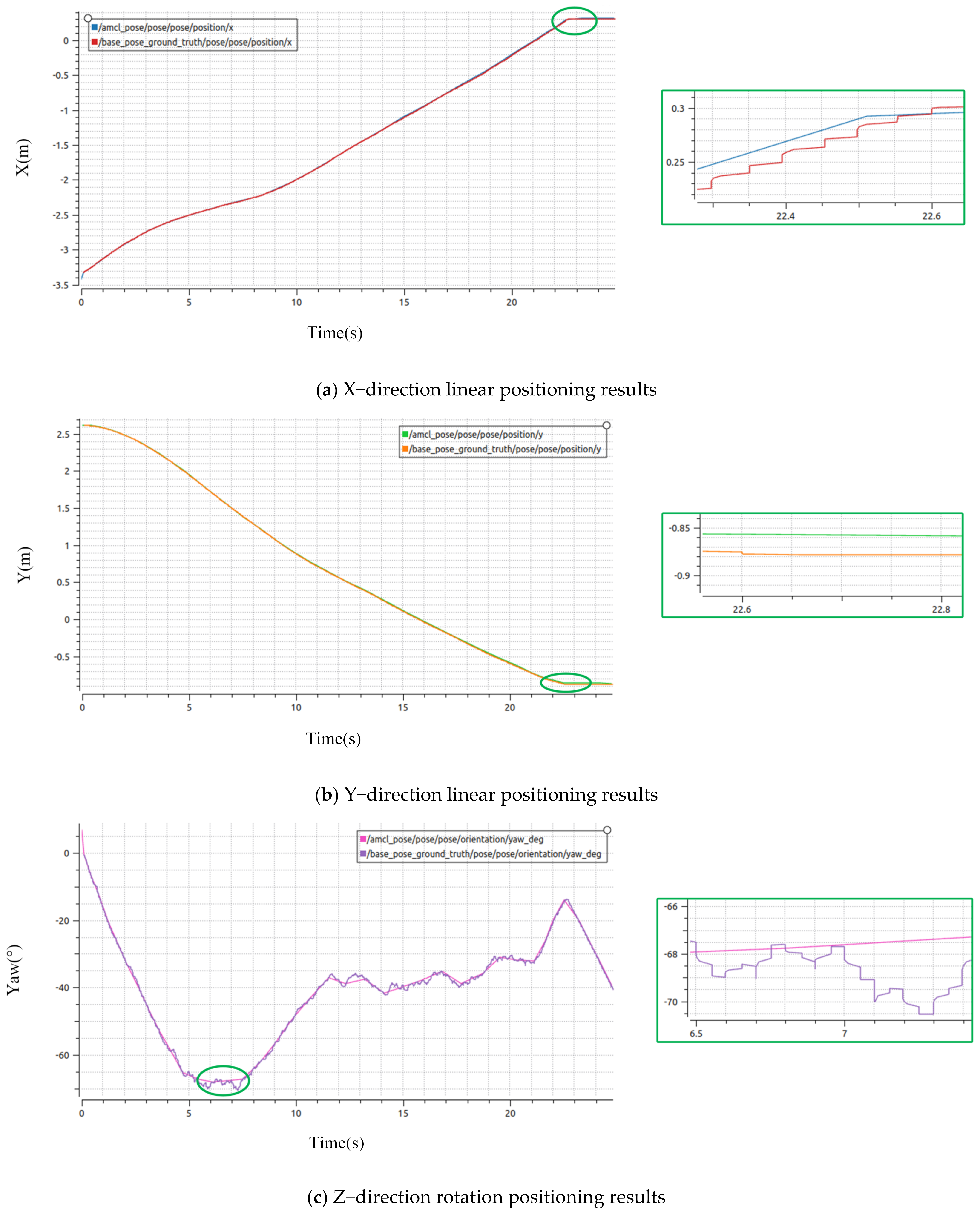

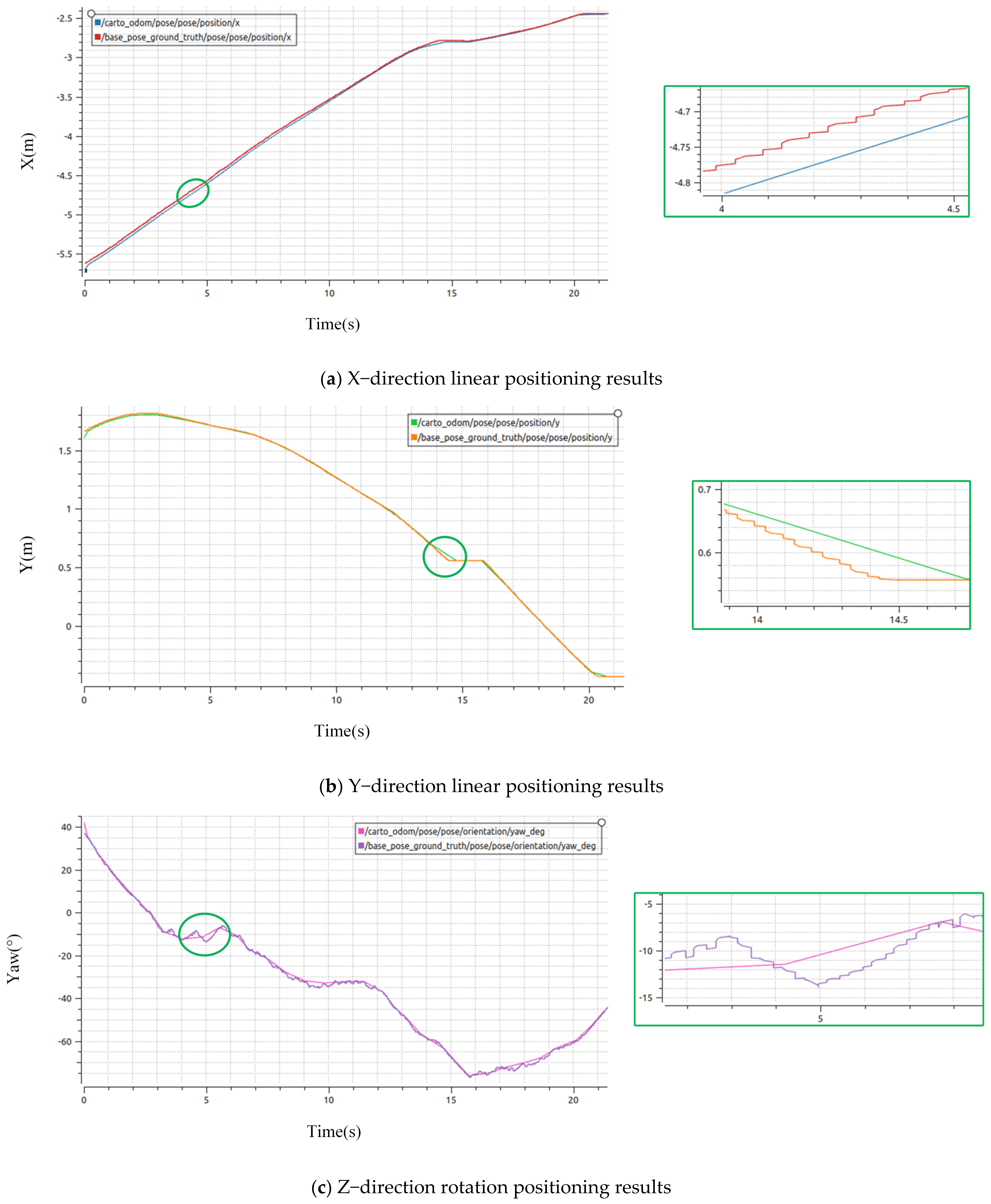
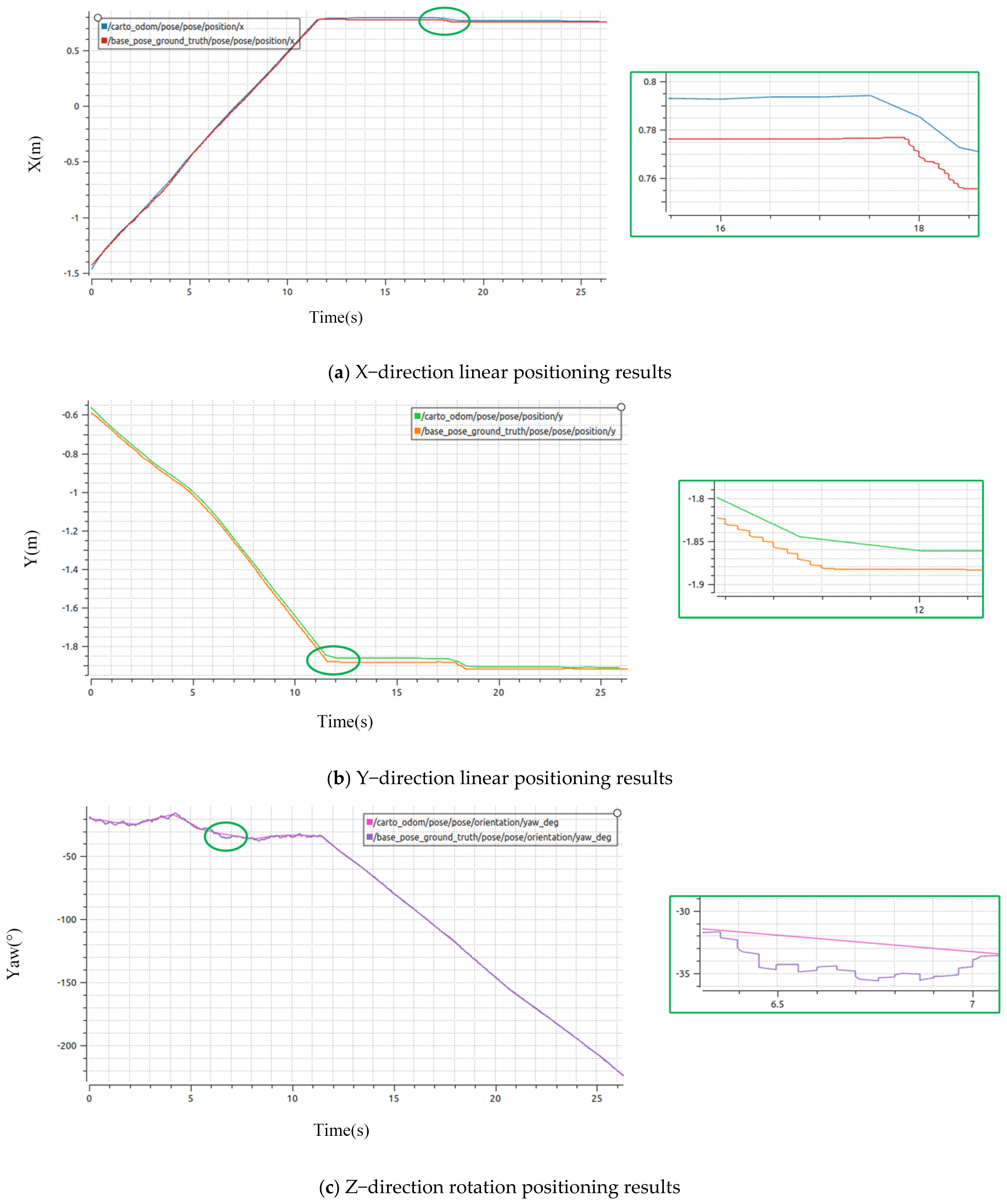




| Methods | Experiments | Maximum Error in X Direction | Maximum Error in Y Direction | Maximum Error in Yaw Angle |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6 cm | 6 cm | 4 degs | |
| AMCL | 2 | 7 cm | 8 cm | 8 degs |
| 3 | 4 cm | 2 cm | 6 degs | |
| 1 | 2 cm | 0.5 cm | 2.5 degs | |
| Ours | 2 | 2 cm | 2.5 cm | 3.5 degs |
| 3 | 1.5 cm | 2 cm | 3.5 degs | |
| 1 | 5 cm | 4 cm | 3 degs | |
| Cartographer | 2 | 2 cm | 3 cm | 3 degs |
| 3 | 2 cm | 1.6 cm | 2.5 degs |
| Method | Position Mean (m) | Position Std (m) | Yaw Mean (°) | Yaw Std (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMCL | 0.094 | 0.0329 | 9.183 | 2.383 |
| Ours | 0.061 | 0.0236 | 6.097 | 1.171 |
| Cartographer | 0.079 | 0.0260 | 5.540 | 1.135 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Wu, H.; Wei, Y.; Ren, M.; Zhao, C. Improved LiDAR Localization Method for Mobile Robots Based on Multi-Sensing. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6133. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14236133
Liu Y, Wang C, Wu H, Wei Y, Ren M, Zhao C. Improved LiDAR Localization Method for Mobile Robots Based on Multi-Sensing. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(23):6133. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14236133
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yanjie, Chao Wang, Heng Wu, Yanlong Wei, Meixuan Ren, and Changsen Zhao. 2022. "Improved LiDAR Localization Method for Mobile Robots Based on Multi-Sensing" Remote Sensing 14, no. 23: 6133. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14236133
APA StyleLiu, Y., Wang, C., Wu, H., Wei, Y., Ren, M., & Zhao, C. (2022). Improved LiDAR Localization Method for Mobile Robots Based on Multi-Sensing. Remote Sensing, 14(23), 6133. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14236133




