Near-Field 3D Sparse SAR Direct Imaging with Irregular Samples
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- A 3D sparse direct image reconstruction framework is established to solve the SAR imaging problem of irregular samples.
- We designed a NUFFT-RMA method to obtain the initial image position information. Subsequently, a threshold filtering method is put forward to reduce the dimensionality of the observation matrix. Finally, signal-processing techniques, such as storing the matrix in advance, are applied to achieve fine 3D sparse imaging.
- In contrast to previous compressed sensing methods, we propose replacing the interpolated data organized into vectors with raw data to avoid interpolation errors.
- This is the first attempt to develop a hybrid imaging algorithm of matched filtering combined with sparse reconstruction for 3D imaging in an irregular sampled scene. It can provide better performance in the suppression of sidelobes/grating lobes, the reduction of computation time and storage, and a significant improvement in the imaging quality of multiple targets.
2. Relevant Research Theories
2.1. MF Model
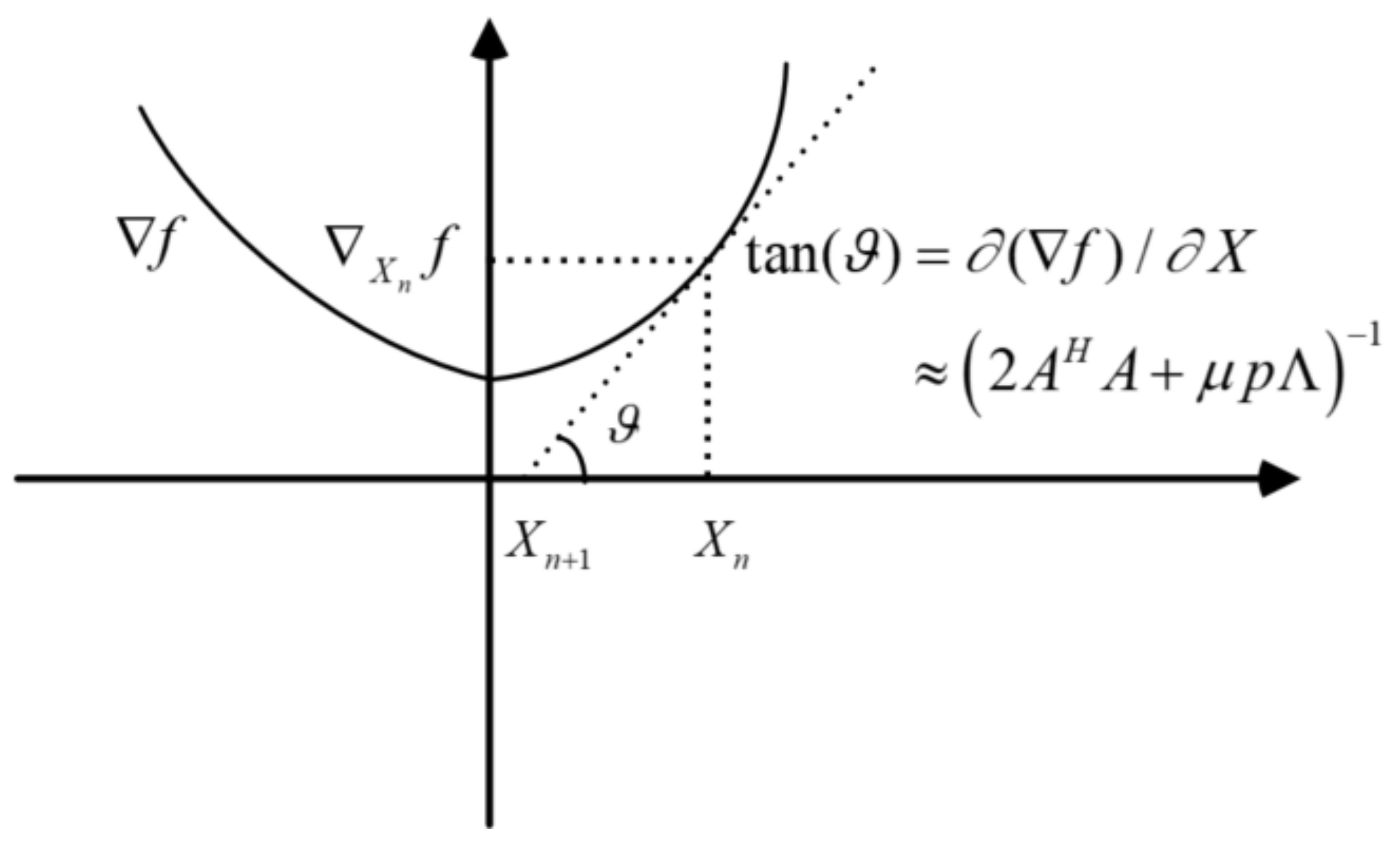
2.2. The Proposed Algorithm
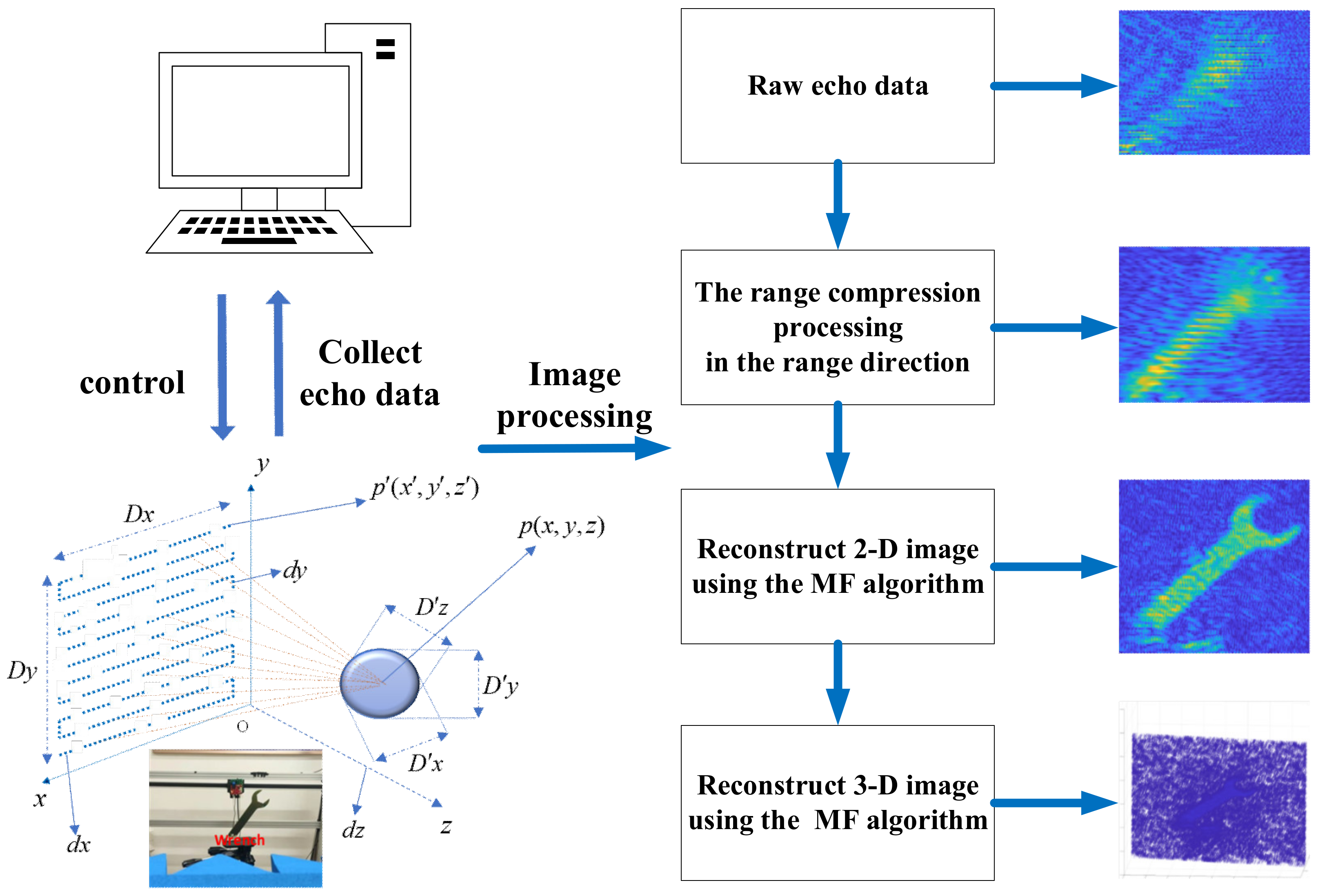
3. Imaging Results and Evaluation
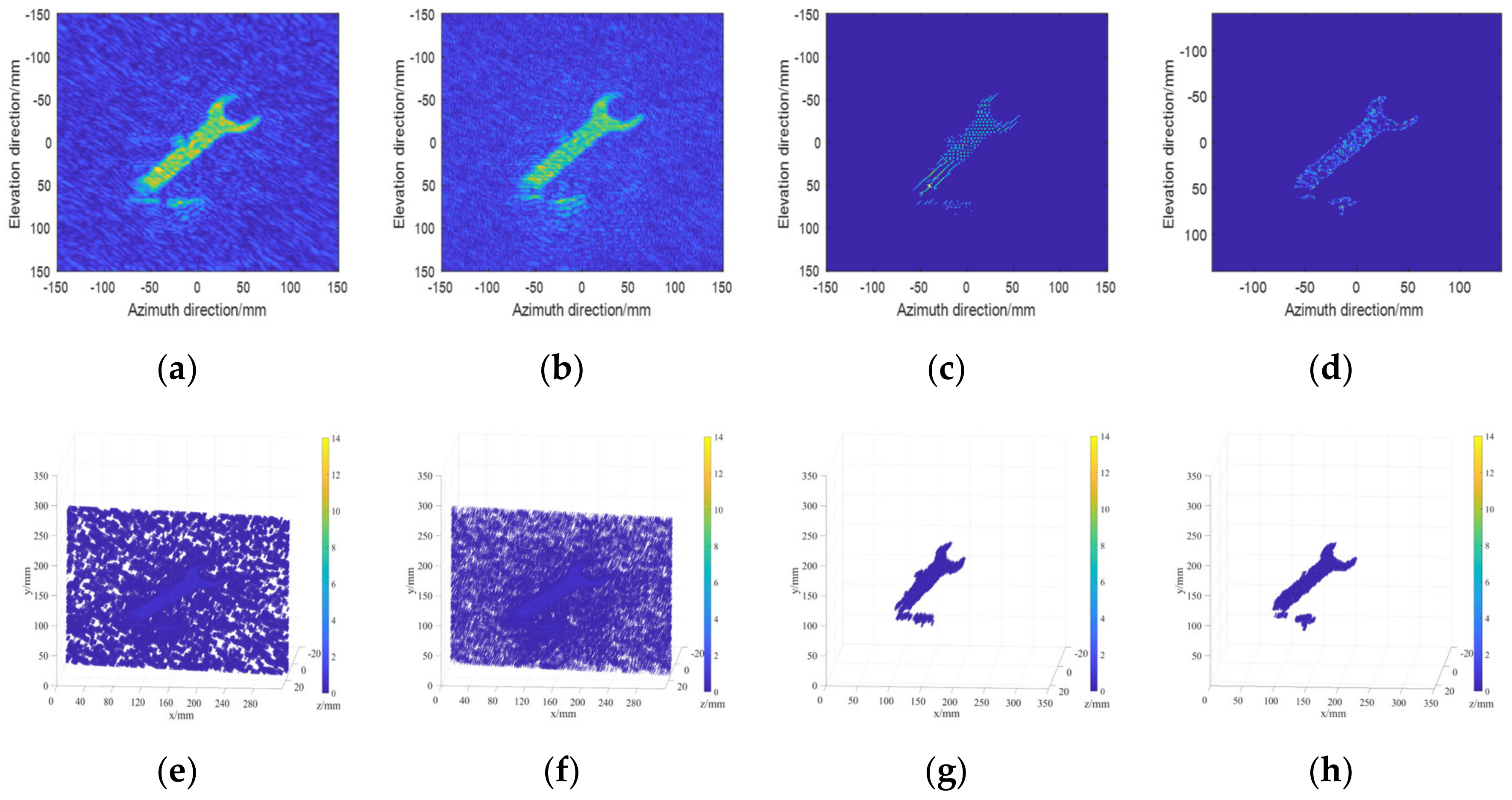
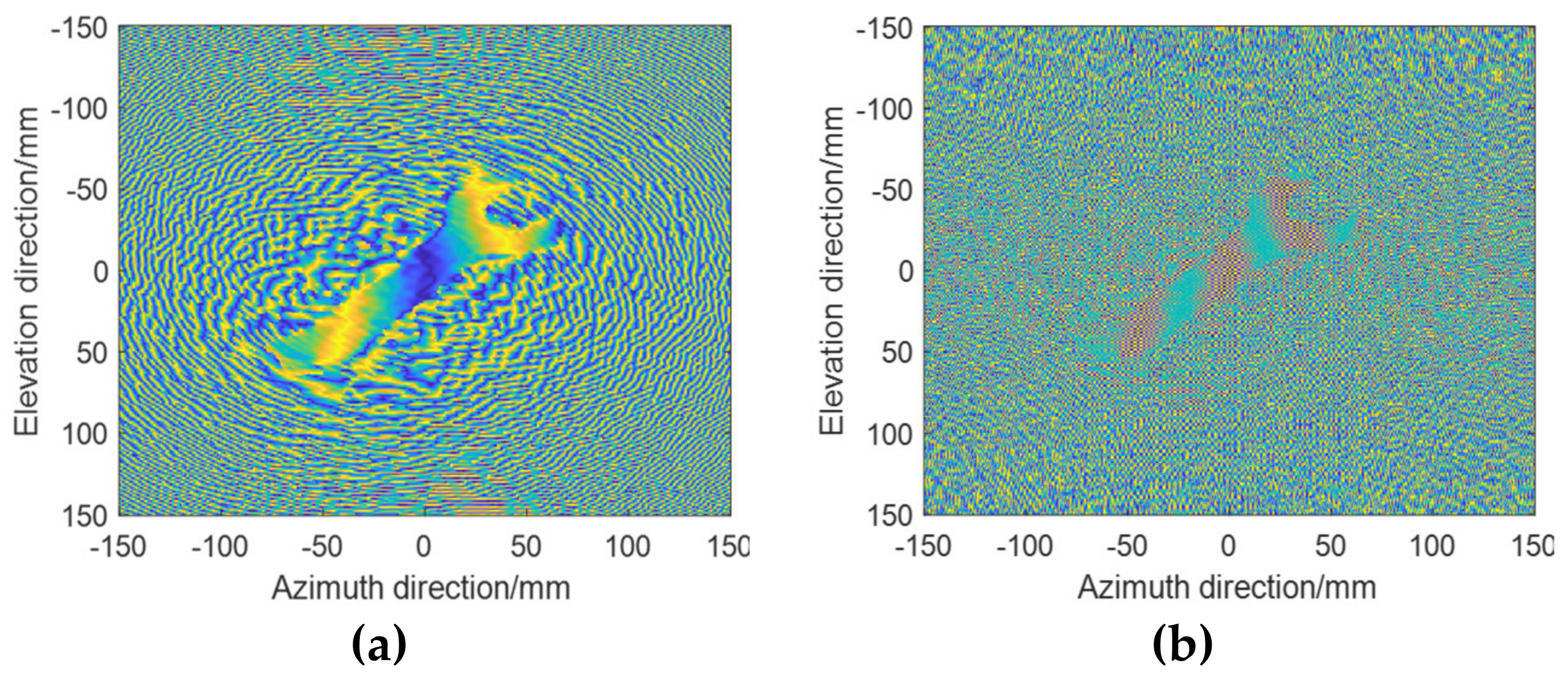
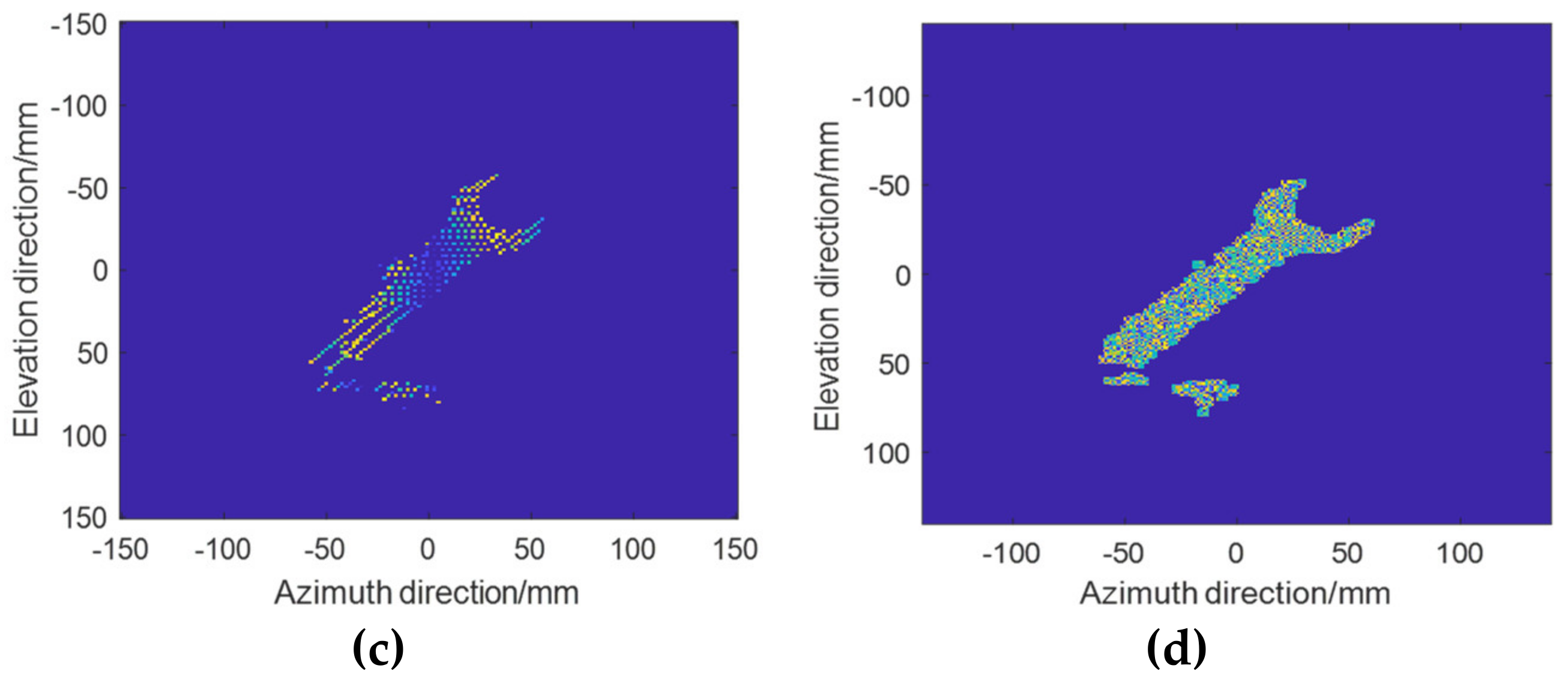
3.1. Imaging Results
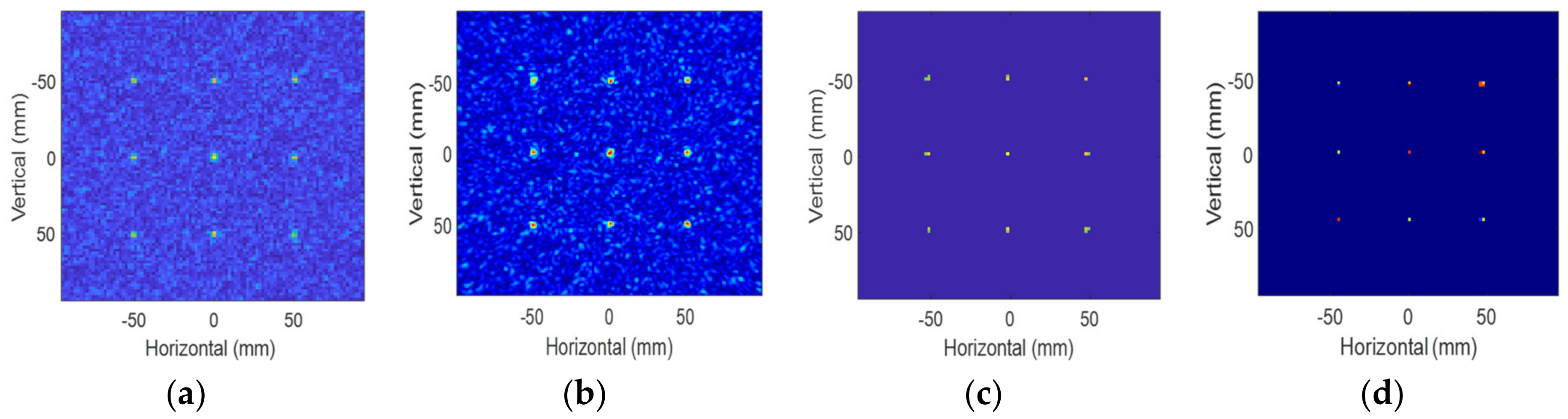
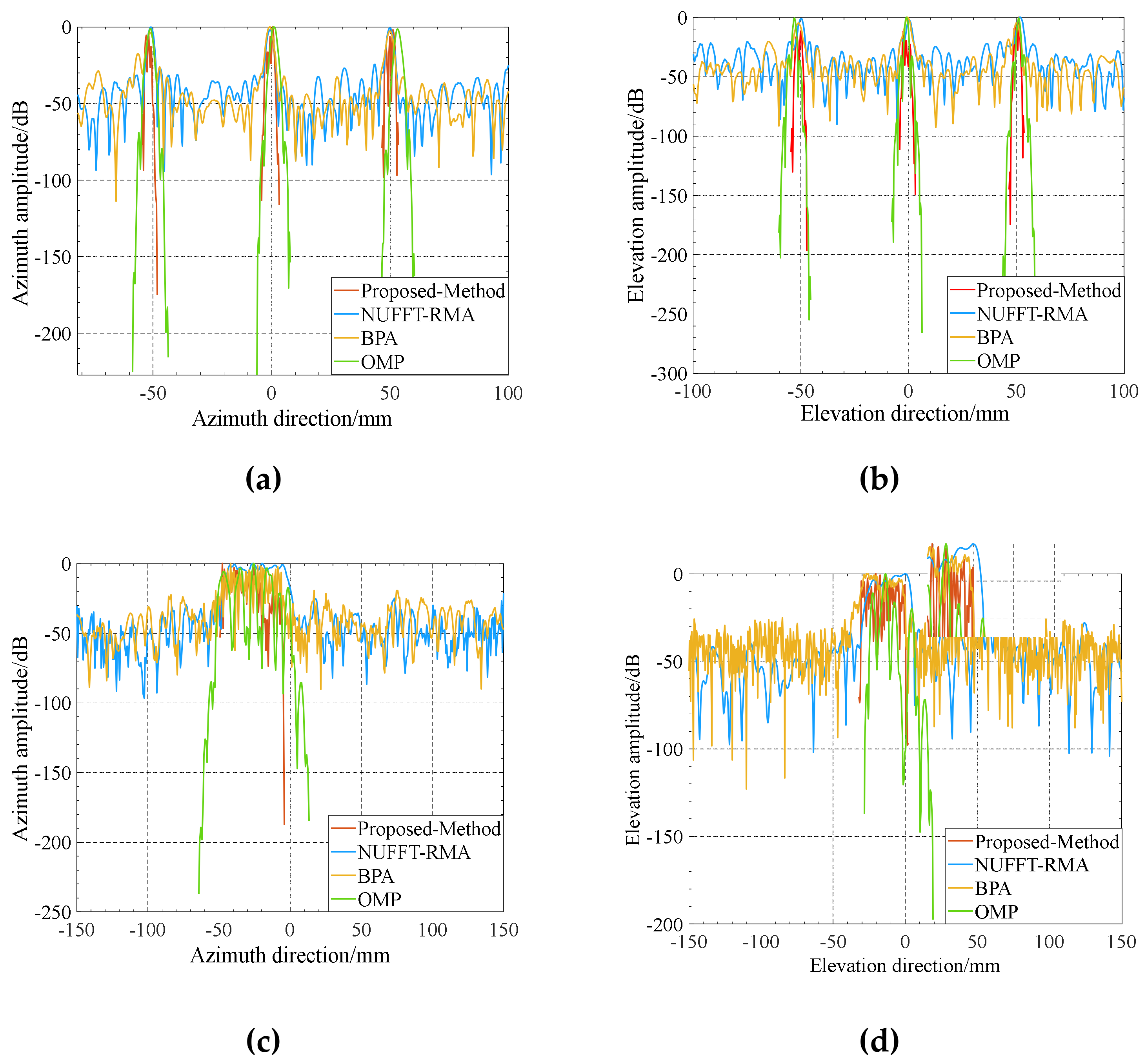
3.2. Evaluation of Imaging Results’ Characteristics
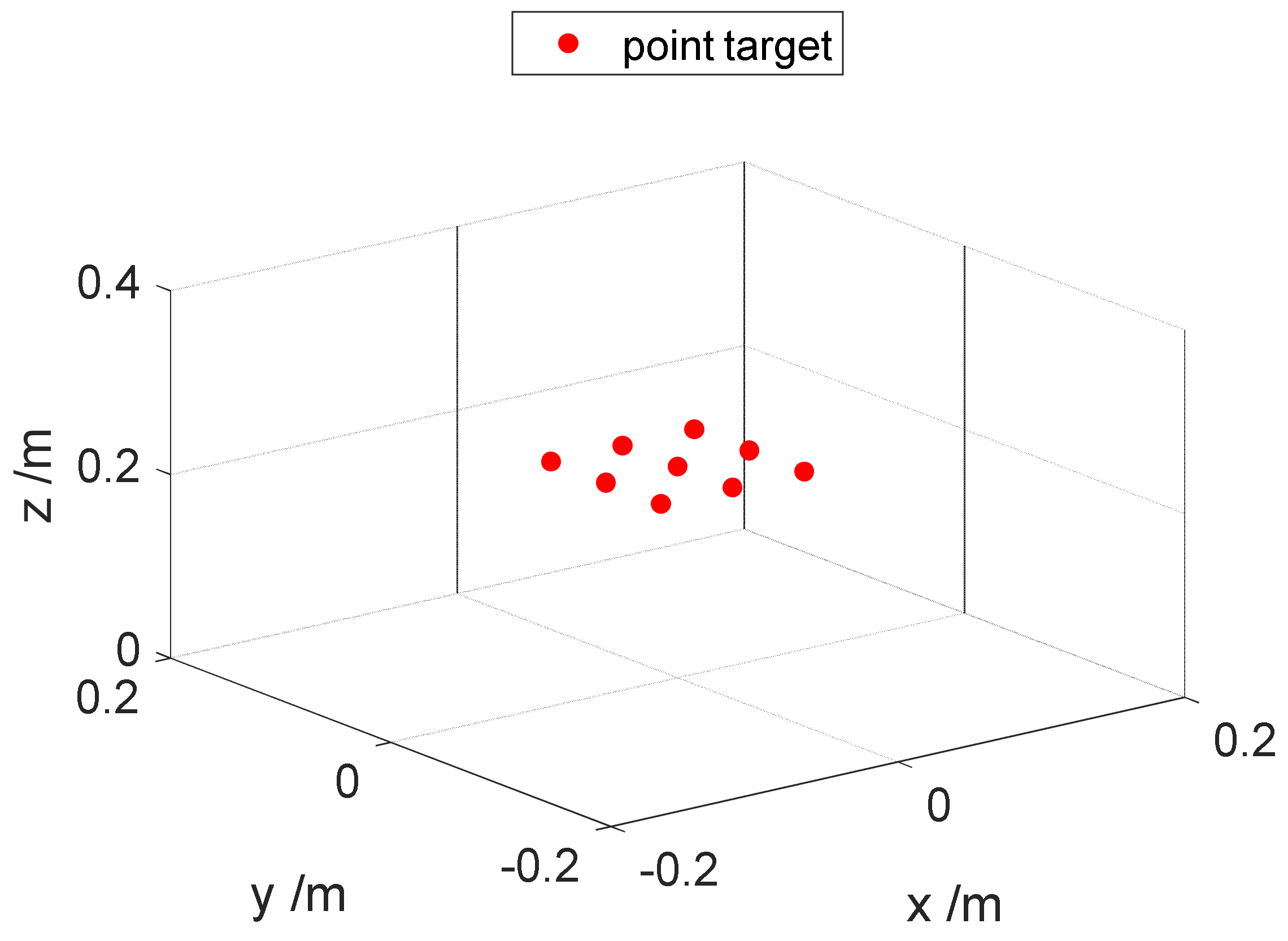
3.3. Imaging Evaluation with Multiple Targets
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sheen, D.; McMakin, D.; Hall, T. Three-Dimensional Millimeter-Wave Imaging for Concealed Weapon Detection. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2001, 49, 1581–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheen, D.M.; McMakin, D.L.; Hall, T.E. Combined Illumination Cylindrical Millimeter-Wave Imaging Technique for Concealed Weapon Detection. In Proceedings of the Conference on Passive Millimeter-Wave Imaging Technology IV, Orlando, FL, USA, 20 July 2000; pp. 52–60. [Google Scholar]
- Di Meo, S.; Matrone, G.; Pasian, M.; Bozzi, M.; Perregrini, L.; Magenes, G.; Mazzanti, A.; Svelto, F.; Summers, P.E.; Renne, G.; et al. High-Resolution Mm-wave Imaging Techniques and Systems for Breast Cancer Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Workshop Series on Advanced Materials and Processes for RF and THz Applications, Pavia, Italy, 20–22 September 2017; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Mirbeik-Sabzevari, A.; Li, S.; Garay, E.; Nguyen, H.-T.; Wang, H.; Tavassolian, N. Synthetic Ultra-High-Resolution Millimeter-Wave Imaging for Skin Cancer Detection. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 66, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.W.; Thiagarajan, S.; Willis, R.; Makris, Y.; Torlak, M. Improved static hand gesture classification on deep convolutional neural networks using novel sterile training technique. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 10893–10902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.W.; Furxhi, O.; Torlak, M. An FCNN-based super-resolution mmWave radar framework for contactless musical instrument interface. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2021, 24, 2315–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharkovsky, S.; Zoughi, R. Microwave and Millimeter Wave Nondestructive Testing and Evaluation-Overview and Recent Advances. IEEE Instrum. Meas. Mag. 2007, 10, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasr, M.T.; Kharkovsky, S.; Bohnert, R.; Hirst, B.; Zoughi, R. 30 GHz linear High-resolution and Rapid Millimeter Wave Imaging System for NDE. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2013, 61, 4733–4740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, S. Concealed object detection for activate millimeter wave image. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 9909–9917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanik, M.E.; Torlak, M. Near-field 2-D SAR imaging by millimeter-wave radar for concealed item detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE radio and Wireless Symposium (RWS), Orlando, FL, USA, 20–23 January 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, M.; Jiang, X.; Wu, R.; Zhou, F.; Bao, Z. Motion Compensation for UAV SAR based on Raw Radar Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 2870–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rankin, G.; Tirkel, A.; Leukhin, A. Millimeter Wave Array for UAV Imaging MIMO Radar. In Proceedings of the 2015 16th International Radar Symposium, Dresden, Germany, 24–26 June 2015; pp. 499–504. [Google Scholar]
- Elgy, J.; Andre, D.; Finnis, M. Volumetric SAR near-field upsampling and basebanding. Electron. Lett. 2020, 56, 622–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Guo, W.; Luo, Y. Transferable SAR Image Classification Crossing Different Satellites under Open Set Condition. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, T. Implementation of Real-time Automotive SAR Imaging. In Proceedings of the 11th Sensor Array and Multichannel Signal Processing Workshop, Hangzhou, China, 8–11 June 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Song, S.; Xing, S.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Pang, B. Validation of near-field millimeter wave radar-based RD and RMA time-frequency domain imaging algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 6th Information Technology and Mechatronics Engineering Conference (ITOEC), Chongqing, China, 4–6 March 2022; pp. 1885–1889. [Google Scholar]
- Kan, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Yang, L.; Tang, L.; Fu, Q. Perturbation-based method for near-field cross-section imaging. Electron. Lett. 2016, 53, 110–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Narciandi, G.; Laviada, J.; Las-Heras, F. Towards turning smartphones into mmWave scanners. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 45147–45154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.W.; Torlak, M. Efficient 3-D Near-Field MIMO-SAR Imaging for Irregular Scanning Geometries. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 10283–10294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Narciandi, G.; Laviada, J.; Alvarez-Lopez, Y.; Ducournau, G.; Luxey, C.; Belem-Goncalves, C.; Gianesello, F.; Nachabe, N.; Del Rio, C.; Las-Heras, F. Freehand system for antenna diagnosis based on amplitude-only data. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2021, 69, 4988–4998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Lu, J.; Xing, S.; Quan, S.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Lian, J. Near Field 3-D Millimeter-Wave SAR Image Enhancement and Detection with Application of Antenna Pattern Compensation. Sensors 2022, 22, 4509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, M.; Wei, J.; Liu, S.; Shi, J.; Zhang, X.; Fan, F. 3DRIED: A high-resolution 3-D millimeter-wave radar dataset dedicated to imaging and evaluation. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, K.; Wang, Q.; Burkholder, R.J. A fast back-projection approach to diffraction tomography for near-field microwave imaging. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2019, 18, 2170–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Aubry, P.; Yarovoy, A. 3-D Short-Range Imaging With Irregular MIMO Arrays Using NUFFT-Based Range Migration Algorith. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 4730–4742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanik, M.E.; Torlak, M. Near-Field MIMO-SAR Millimeter-Wave Imaging with Sparsely Sampled Aperture Data. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 31801–31819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, H.; Yang, Q.; Zeng, Y.; Deng, B. An Efficient MMW 3D Imaging Algorithm for Near-Field MIMO-SAR with Nonuniform Transmitting Array. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2022, 21, 2035–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, W.; Song, H.; Shang, X.; Zheng, J. Improved RMA based on Nonuniform Fast Fourier Transforms(NUFFT’s). In Proceedings of the 2008 9th International Conference on Signal Processing, Beijing, China, 26–29 October 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Wang, H.; Deng, G.; Yang, Q.; Zeng, Y.; Deng, B. Efficient Millimeter-Wave Imaging Algorithm for Layered Dielectrics Based on MIMO-SAR with Nonuniform Transmitting Array. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2022, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkholder, R.J.; Browne, K.E. Coherence factor enhancement of through-wall radar images. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2010, 9, 842–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Wang, H.; Deng, B.; Liu, K.; Cheng, B. A side-lobe suppression method based on coherence factor for terahertz array imaging. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 5584–5588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungang, Y.; Xiaotao, H.; Tian, J. Compressed Sensing Radar Lmaging; Publishing House of Sciense: Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhan, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, L.; Shi, J.; Wei, S. An RCS Measurement Method Using Sparse Imaging Based 3-D SAR Complex Image. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2021, 21, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Pu, L.; Pu, L.; Shi, J.; Wei, S. Fast Bayesian Compressed Sensing Algorithm via Relevance Vector Machine for LASAR 3D Imaging. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Sun, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, Z. Phase coherence factor for mitigation of sidelobe artifacts in through-the-wall radar imaging. J. Electromagn. Waves Appl. 2013, 27, 716–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, T.T.; Wang, L. Orthogonal matching pursuit for sparse signal recovery with noise. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2011, 57, 4680–4688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Zhu, D. High-resolution SAR imaging from azimuth periodically gapped raw data via generalised orthogonal matching pursuit. Electron. Lett. 2018, 54, 1235–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.X.; Bamler, R. Super-resolution of sparse reconstruction for tomographic SAR imaging-demonstration with real data. In Proceedings of the EUSAR 2012, 9th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Nuernberg, Germany, 23–26 April 2012; pp. 215–218. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, S.-J.; Zhang, X.-L.; Shi, J.; Xiang, G. Sparse reconstruction for SAR imaging based on compressed sensing. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2010, 109, 63–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yanik, M.E. Millimeter-Wave Imaging Using MIMO-SAR Techniques; The University of Texas at Dallas: Richardson, TX, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Brekhovskikh, L.M.; Godin, O.A. Acoustics of Layered Media II: Point Sources and Bounded Beams; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2013; Volume 10. [Google Scholar]
- Weyl, H. Ausbreitung elektromagnetischer Wellen über einem ebenen Leiter. Ann. Phys. 1919, 365, 481–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarov, A.; Minchev, D. 2-D Sparse Decomposition and L 0 Norm Minimization in SAR Imaging. In Proceedings of the 2020 21st International Radar Symposium (IRS), Warsaw, Poland, 5–8 October 2020; pp. 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Qiao, Z.-J. Resolution enhancement for ISAR imaging via improved statistical compressive sensing. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2016, 2016, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cetin, M.; Karl, W. Feature-Enhanced Synthetic Aperture Radar Image Formation Based on Nonquadratic Regularization. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2001, 10, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, X. Fast Entropy Minimization Based Autofocusing Technique for ISAR Imaging. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2015, 63, 3425–3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

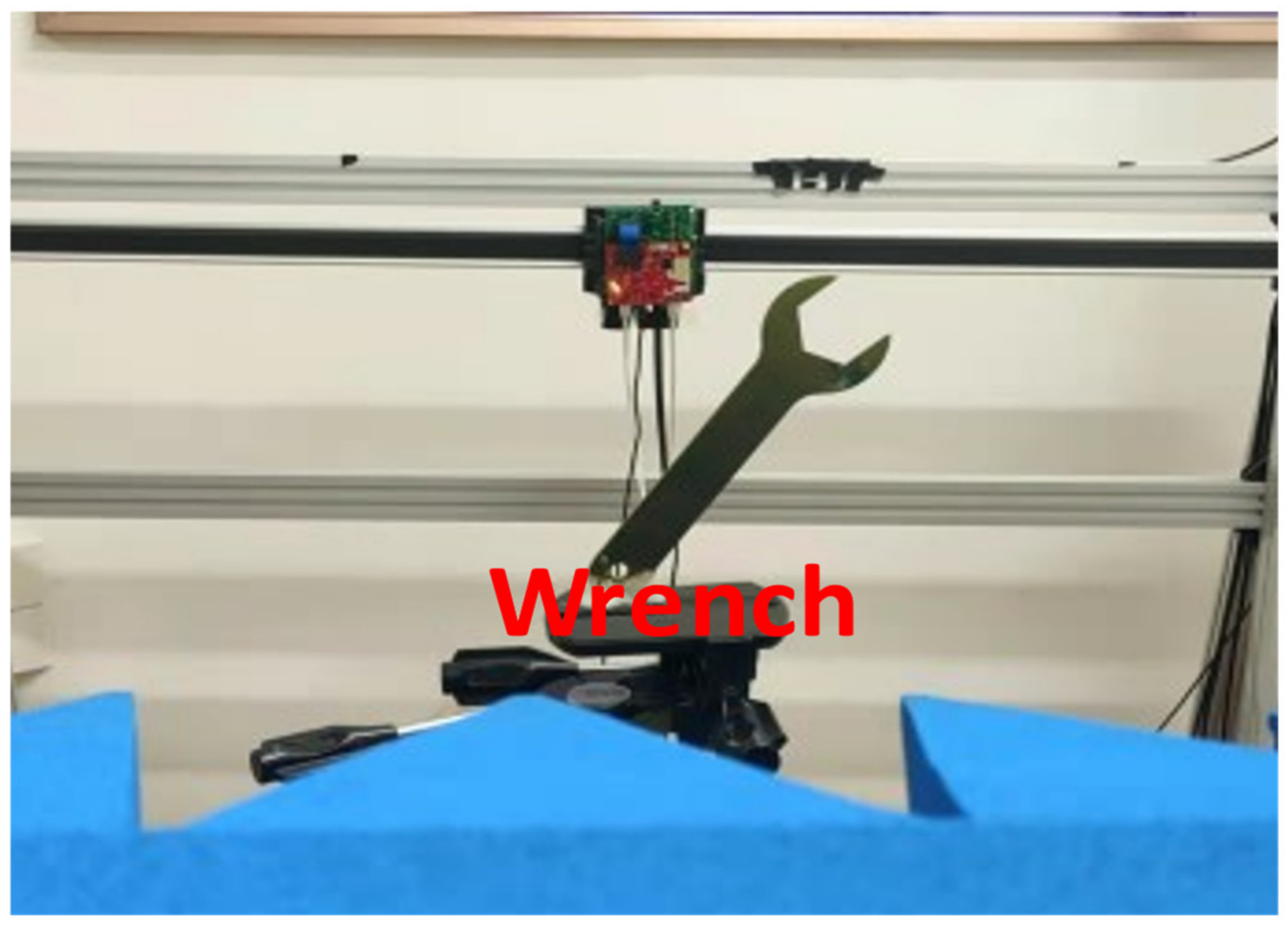



| 3D Sparse SAR Direct Imaging with Irregular Samples |
|---|
| 1. Initial imaging by NUFFT-RMA to get the imaging result . |
| 2. According to Equation (18), determine the target area . |
| 3. For the sparse SAR imaging |
| a. According to the target area and imaging result ,take the idea of Cetin’s process, and obtain the cost function . |
| b. Using the Gaussian iterative method to Simplify the derivative equation. |
| c. Obtain and store and in advance and Calculate iteratively according to Equation (21), and get the final calculation results |
| Parameter Type | Numerical Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Centre carrier frequency | 79 | GHz |
| Platform speed | 20 | mm/s |
| Bandwidth | 4 | GHz |
| Simulation synthetic aperture size | 200 × 200 | mm2 |
| Measured wrench synthetic aperture size | 300 × 300 | mm2 |
| Vertical distance between scissor and radar | 230 | mm |
| Vertical distance between wrench and radar | 300 | mm |
| Method | Mean Difference of Principal Lobes in Simulation | Mean Difference of Principal Lobes in Real Data |
|---|---|---|
| BPA | −6.24 dB | −3.18 dB |
| NUFFT-RMA | −2.23 dB | −7.62 dB |
| OMP | −18.96 dB | −9.26 dB |
| Proposed method | −3.68 dB | −2.49 dB |
| Method | Contrast | Entropy | Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BPA | 210.0024 | 4.7544 | 213.6 |
| NUFFT-RMA | 216.1602 | 5.0380 | 3.1 |
| OMP | 232.1175 | 3.9752 | 998.4 |
| Proposed method | 240.2525 | 3.8008 | 3.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xing, S.; Song, S.; Quan, S.; Sun, D.; Wang, J.; Li, Y. Near-Field 3D Sparse SAR Direct Imaging with Irregular Samples. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6321. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14246321
Xing S, Song S, Quan S, Sun D, Wang J, Li Y. Near-Field 3D Sparse SAR Direct Imaging with Irregular Samples. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(24):6321. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14246321
Chicago/Turabian StyleXing, Shiqi, Shaoqiu Song, Sinong Quan, Dou Sun, Junpeng Wang, and Yongzhen Li. 2022. "Near-Field 3D Sparse SAR Direct Imaging with Irregular Samples" Remote Sensing 14, no. 24: 6321. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14246321
APA StyleXing, S., Song, S., Quan, S., Sun, D., Wang, J., & Li, Y. (2022). Near-Field 3D Sparse SAR Direct Imaging with Irregular Samples. Remote Sensing, 14(24), 6321. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14246321







