Unsupervised SAR Image Change Type Recognition Using Regionally Restricted PCA-Kmean and Lightweight MobileNet
Abstract
:1. Introduction
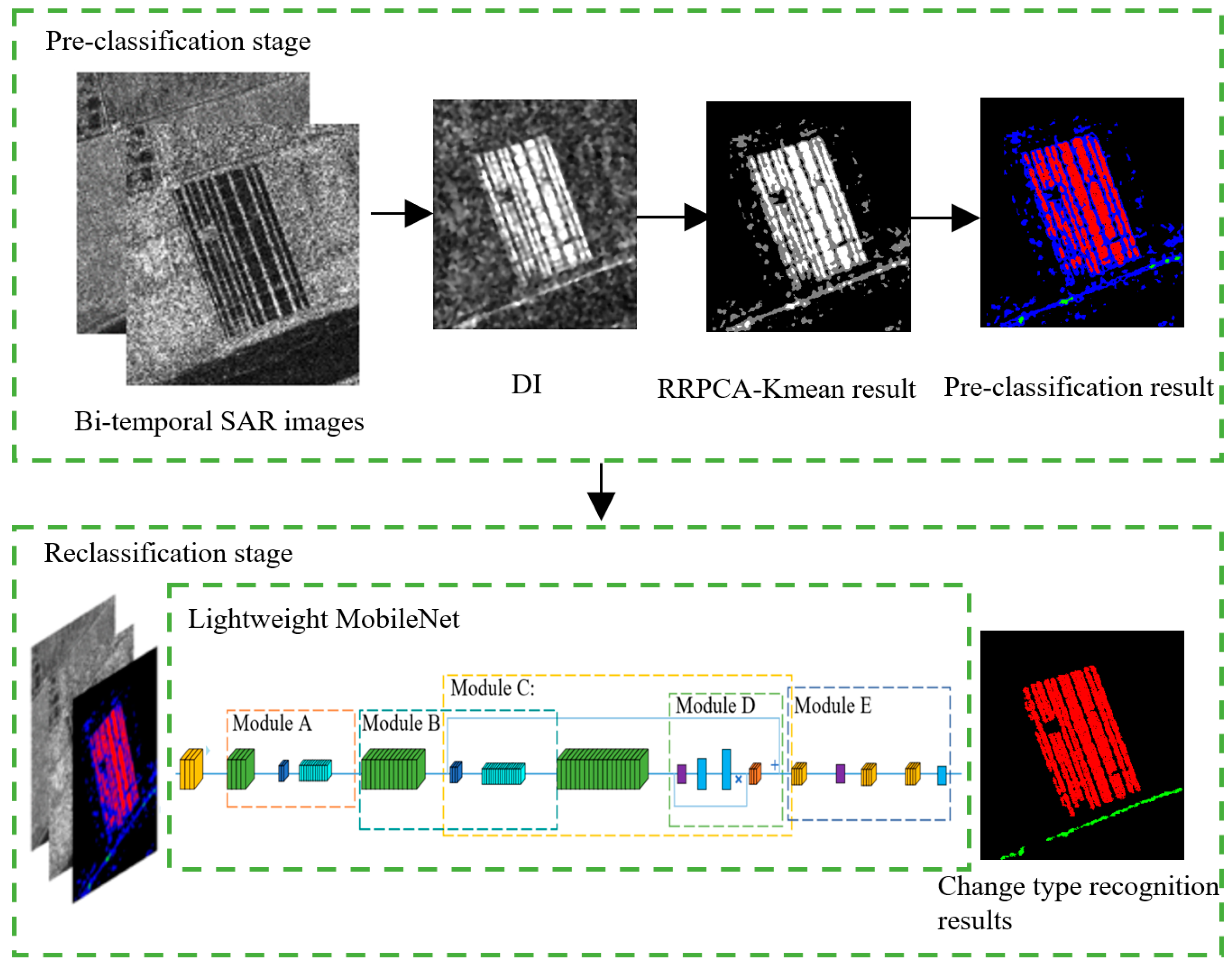
2. Methodology
2.1. RRPCA-Kmean Clustering Algorithm
| Algorithm 1 RRPCA-Kmean Algorithm |
| Input: DI Step 1: Extract the PCA feature vector. Step 2: Run the k-mean clustering algorithm to generate three classes , and . where is a pseudo-changed class, is a pseudo-intermediate class, and is a pseudo-unchanged class. Step 3: Calculate the ratio of the mean value to the number of pixels for each class and arrange them from smallest to largest to obtain three classes , the initial pre-classification results. Step 4: Perform mathematical morphological erosion of the pre-classified result map using a 50 × 50 all-1 matrix. Step 5: Take out the pre-classified result map within the corrupted range, the RRPCA-Kmean result map. Output: RRPCA-Kmean result map containing . |
2.2. Generation of Training Samples
2.3. Lightweight MobileNet Classification Model
3. Results
3.1. Datasets
3.2. Evaluation Metric
3.3. Analysis of Results
3.4. Analysis of the Patch Size
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chunga, K.; Livio, F.A.; Martillo, C.; Lara-Saavedra, H.; Ferrario, M.F.; Zevallos, I.; Michetti, A.M. Landslides triggered by the 2016 Mw 7.8 Pedernales, Ecuador earthquake: Correlations with ESI-07 intensity, lithology, slope and PGA-h. Geosciences 2019, 9, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferrario, M. Landslides triggered by multiple earthquakes: Insights from the 2018 Lombok (Indonesia) events. Nat. Hazards 2019, 98, 575–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lê, T.T.; Froger, J.-L.; Minh, D.H.T. Multiscale framework for rapid change analysis from SAR image time series: Case study of flood monitoring in the central coast regions of Vietnam. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 269, 112837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoumi, Z. Flood susceptibility assessment for ungauged sites in urban areas using spatial modeling. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2022, 15, e12767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Sun, R.; Zhong, L.; Meng, R.; Huang, C.; Zeng, X.; Wang, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z. Monthly mapping of forest harvesting using dense time series Sentinel-1 SAR imagery and deep learning. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 269, 112822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, A.; Upadhyaya, D.B.; Thiyaku, S.; Tomer, S.K. Use of Multi-sensor Satellite Remote Sensing Data for Flood and Drought Monitoring and Mapping in India. In Civil Engineering for Disaster Risk Reduction; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 27–41. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Su, X.; Yuan, Q.; Wang, Q. Spatial–Temporal Gray-Level Co-Occurrence Aware CNN for SAR Image Change Detection. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 19, 4018605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Qi, Z.; Shi, Z. Remote sensing image change detection with transformers. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Su, W.; Gu, H. SAR Image Change Detection Based on Semisupervised Learning and Two-Step Training. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 19, 4008905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Quan, S.; Yang, Z.; Guo, W.; Zhang, Z.; Gan, H. A Two-Stage Method for Ship Detection Using PolSAR Image. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Su, H.; Zhang, C.; Gu, X.; Tan, X.; Atkinson, P.M. Robust unsupervised small area change detection from SAR imagery using deep learning. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 173, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Wang, X.; Gao, Y.; Dong, J.; Wang, S. Sea ice change detection in SAR images based on convolutional-wavelet neural networks. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 16, 1240–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Ma, X.; Zhou, X.; Wang, H. Saliency-guided deep neural networks for SAR image change detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 7365–7377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Su, H.; Zhang, C.; Atkinson, P.M.; Tan, X.; Zeng, X.; Jian, X. A Robust Imbalanced SAR Image Change Detection Approach Based on Deep Difference Image and PCANet. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.01768. [Google Scholar]
- Celik, T. Unsupervised change detection in satellite images using principal component analysis and k-means clustering. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2009, 6, 772–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yuan, Z.; Du, Q.; Li, X. GETNET: A general end-to-end 2-D CNN framework for hyperspectral image change detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 57, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gong, M.; Zhao, J.; Liu, J.; Miao, Q.; Jiao, L. Change detection in synthetic aperture radar images based on deep neural networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2015, 27, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Dong, J.; Li, B.; Xu, Q. Automatic change detection in synthetic aperture radar images based on PCANet. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 1792–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iandola, F.N.; Han, S.; Moskewicz, M.W.; Ashraf, K.; Dally, W.J.; Keutzer, K. SqueezeNet: AlexNet-level accuracy with 50x fewer parameters and< 0.5 MB model size. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1602.07360. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Lin, M.; Sun, J. Shufflenet: An extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 6848–6856. [Google Scholar]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L.-C. Mobilenetv2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4510–4520. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, X.; Gao, F.; Dong, J.; Du, Q.; Li, H.-C. Change detection in synthetic aperture radar images using a dual-domain network. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Type | Filter Shape | Input Size |
|---|---|---|
| Conv | 3 × 3 × 32 | 10 × 10 × 1 |
| Module A | 3 × 3 × 32 | 5 × 5 × 32 |
| Module B | 3 × 3 × 96 | 5 × 5 × 96 |
| Module C | 1 × 1 × 24 × 144 | 3 × 3 × 24 |
| Module D | 3 × 3 | 3 × 3 × 144 |
| Module E | 1 × 1 × 24 × 32 | 3 × 3 × 24 |
| Dataset | A | B | C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sensor | Radarsat-2 | Radarsat-2 | GaoFen-3 |
| Location | Yellow River, China | Yellow River, China | Yellow River, China |
| Band | C | C | C |
| Polarization | VV | VV | VV |
| Date | 2008.06 | 2008.06 | 2021.07.20 |
| 2009.06 | 2009.06 | 2021.07.24 | |
| Size | 257 × 289 | 233 × 356 | 300 × 300 |
| Resolution | 8 m | 8 m | 5 m |
| Changes | Farming | Flood | Farming |
| Method | Results on the A dataset | ||||
| k (%) | LW Area (%) | WL Area (%) | OA (%) | AA (%) | |
| CNN | 82.80 | 78.90 | 37.58 | 74.97 | 58.24 |
| SqueezeNet | 72.95 | 65.10 | 41.75 | 62.68 | 53.42 |
| ShuffleNet | 78.83 | 73.98 | 40.00 | 70.08 | 56.99 |
| MobileNet v2 | 84.02 | 79.79 | 48.73 | 76.72 | 64.26 |
| LMNet | 87.64 | 84.00 | 49.61 | 81.59 | 66.80 |
| Method | Results on the B dataset | ||||
| k (%) | LW Area (%) | WL Area (%) | OA (%) | AA (%) | |
| CNN | 61.31 | 61.59 | 28.22 | 45.93 | 44.90 |
| SqueezeNet | 66.69 | 58.18 | 38.89 | 51.67 | 48.54 |
| ShuffleNet | 72.89 | 64.13 | 47.29 | 58.77 | 55.71 |
| MobileNet v2 | 76.52 | 66.41 | 55.45 | 63.22 | 60.93 |
| LMNet | 81.10 | 71.32 | 63.93 | 69.23 | 67.62 |
| Method | Results on the C dataset | ||||
| k (%) | LW Area (%) | WL Area (%) | OA (%) | AA (%) | |
| CNN | 69.39 | 61.36 | 45.59 | 56.01 | 53.47 |
| SqueezeNet | 66.18 | 70.66 | 31.60 | 52.95 | 51.13 |
| ShuffleNet | 74.00 | 73.44 | 44.32 | 62.15 | 58.88 |
| MobileNet v2 | 74.94 | 68.24 | 49.93 | 62.53 | 59.09 |
| LMNet | 78.96 | 71.32 | 59.86 | 67.79 | 65.59 |
| Methods | CNN | SqueezeNet | ShuffleNet | MobileNet v2 | LMNet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Times | 1.3 min | 7.3 min | 21.4 min | 32.2 min | 5.4 min |
| Parameters | 39.7 k | 9.8 M | 863 k | 3 M | 158 k |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, W.; Lin, Z.; Gao, G.; Niu, C.; Lu, W. Unsupervised SAR Image Change Type Recognition Using Regionally Restricted PCA-Kmean and Lightweight MobileNet. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6362. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14246362
Liu W, Lin Z, Gao G, Niu C, Lu W. Unsupervised SAR Image Change Type Recognition Using Regionally Restricted PCA-Kmean and Lightweight MobileNet. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(24):6362. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14246362
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Wei, Zhikang Lin, Gui Gao, Chaoyang Niu, and Wanjie Lu. 2022. "Unsupervised SAR Image Change Type Recognition Using Regionally Restricted PCA-Kmean and Lightweight MobileNet" Remote Sensing 14, no. 24: 6362. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14246362
APA StyleLiu, W., Lin, Z., Gao, G., Niu, C., & Lu, W. (2022). Unsupervised SAR Image Change Type Recognition Using Regionally Restricted PCA-Kmean and Lightweight MobileNet. Remote Sensing, 14(24), 6362. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14246362






