Frequency-Domain Electromagnetic Mapping of an Abandoned Waste Disposal Site: A Case in Sardinia (Italy)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
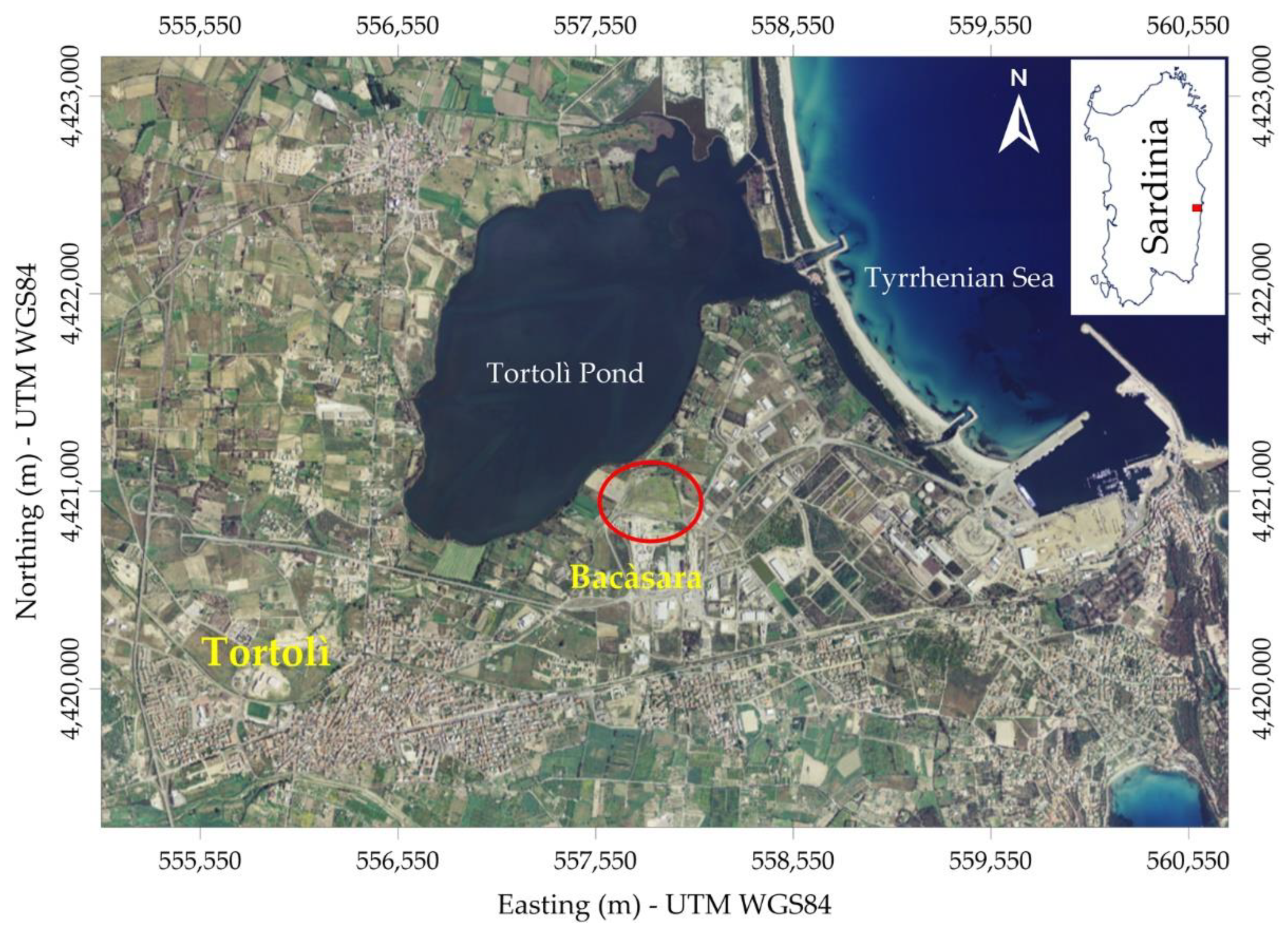
2.1. Site Location and Geological Background
2.2. Site History
2.3. Electromagnetic Induction Survey
2.3.1. Field Data Acquisition
2.3.2. Data Analysis and Processing
3. Results
3.1. Preliminary Descriptive Analysis
3.2. Data Processing and Analysis
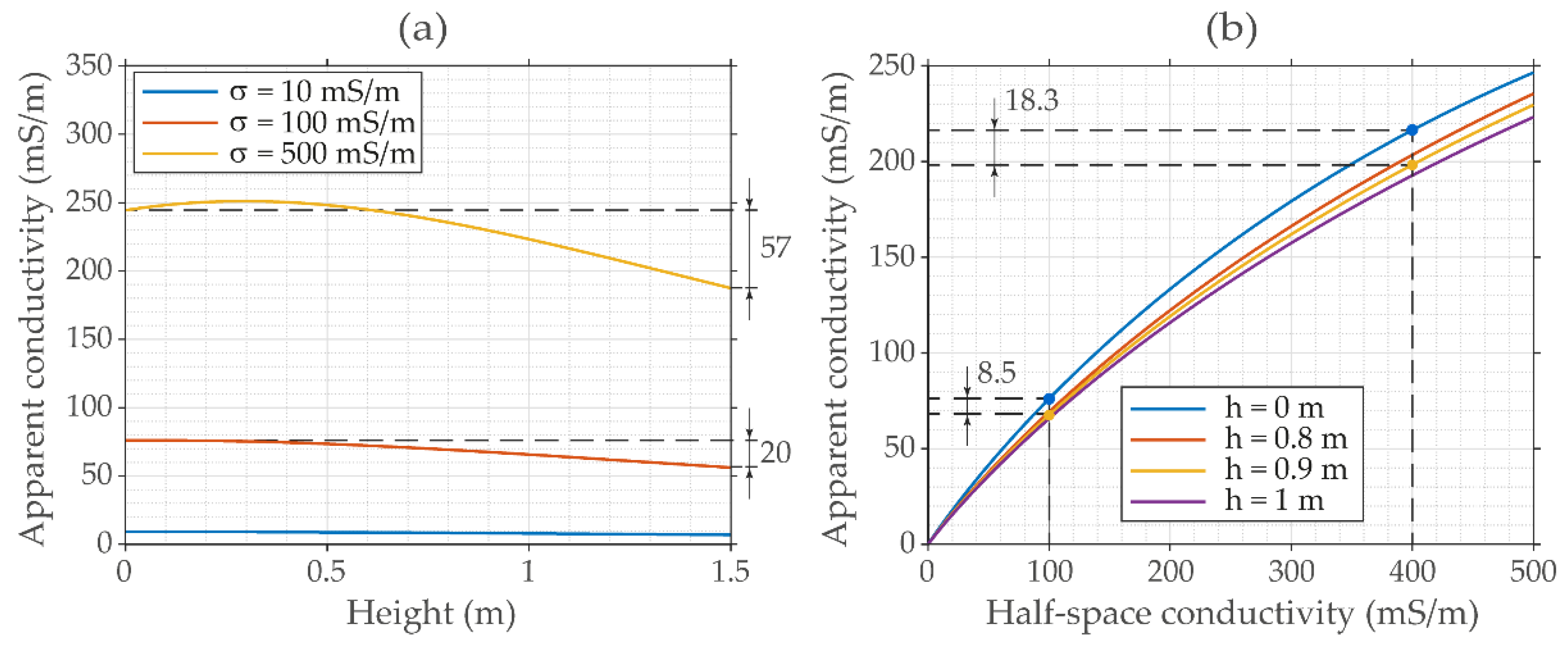
3.2.1. Correction for the Nonlinearity and for the Height of Measurements
3.2.2. Geostatistical Analysis
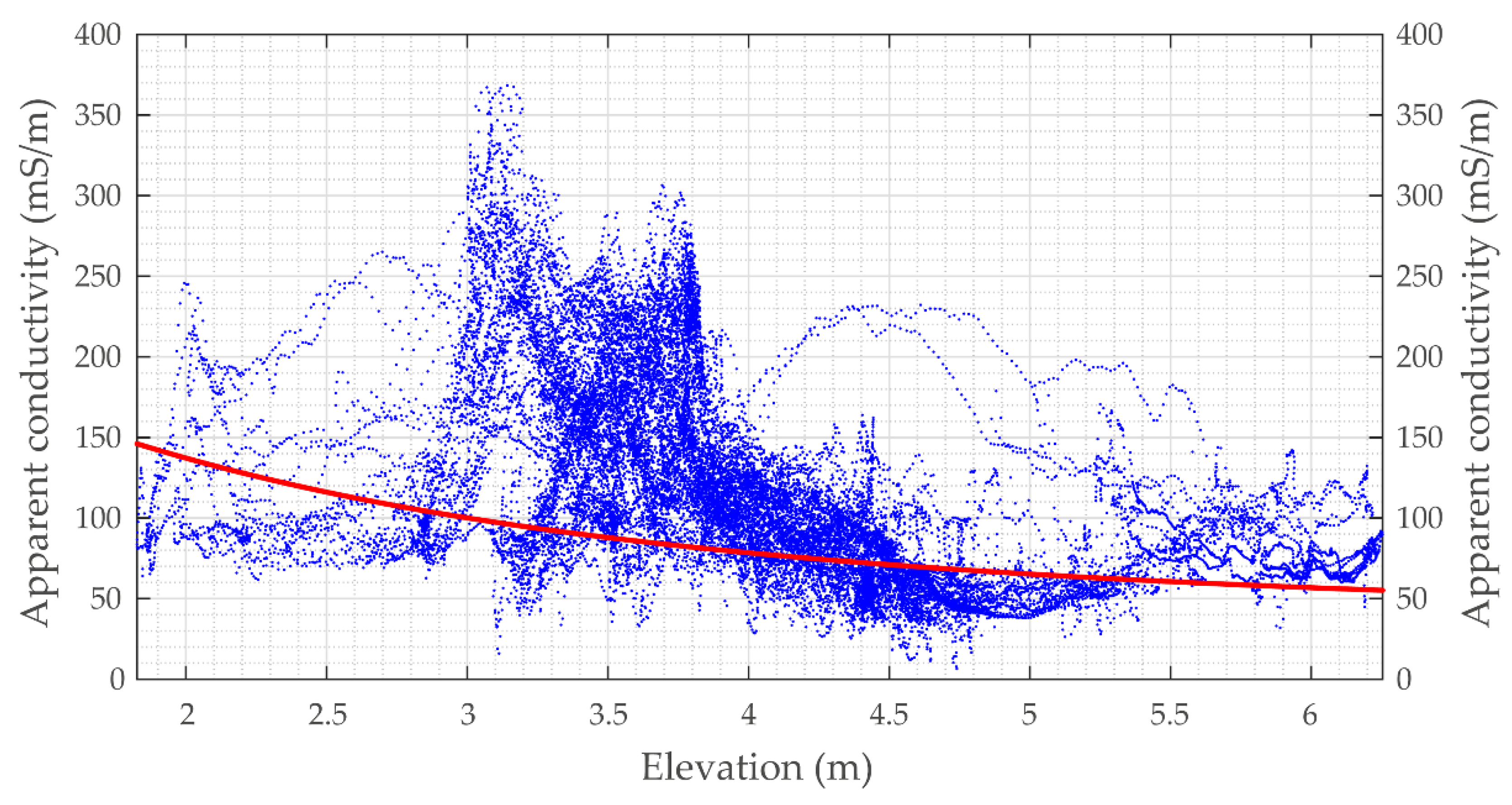
3.2.3. Correlation between Conductivity and Topography
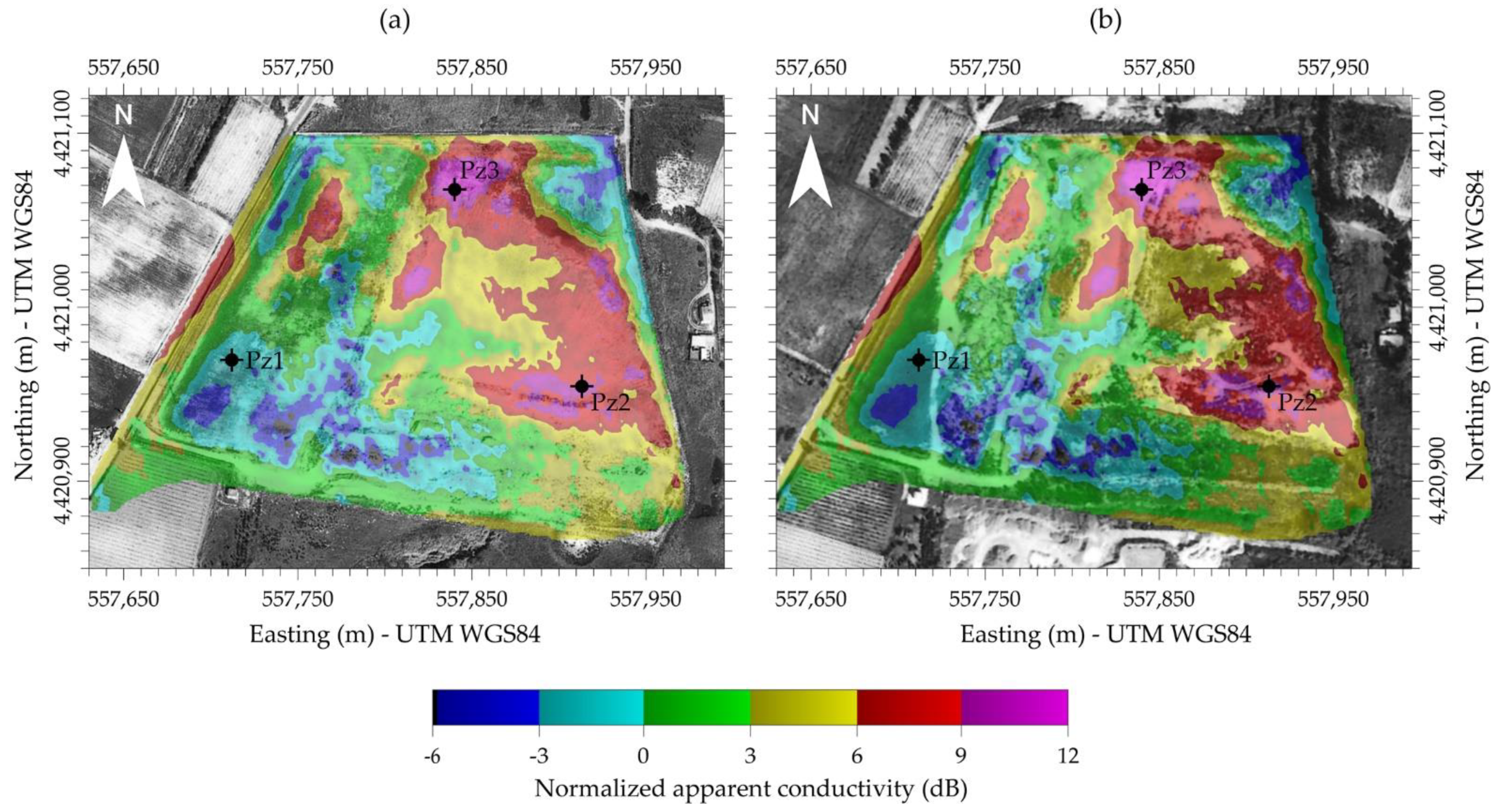
3.3. Apparent Conductivity Map Interpretation
4. Ground Truthing
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AIC | Akaike’s information criterion |
| B | Induction number |
| BC | Binomial coefficient |
| CV | Coefficient of variation |
| dB | Decibel |
| ECa | Apparent electrical conductivity |
| EMI | Electromagnetic induction |
| ERT | Electrical resistivity tomography |
| FDEM | Frequency-domain electromagnetic |
| GPS | Global positioning system |
| HCP | Horizontal coplanar |
| IGM | Italian Military Geographic Institute |
| IP | Induced polarization |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
| K | Kurtosis |
| LIN | Low induction number |
| LIN ECa | Apparent electrical conductivity at LIN condition |
| P | In-phase component |
| Q | Quadrature component |
| Q1 | First quartile |
| Q3 | Third quartile |
| RMSE | Root-mean-square error |
| S | Skewness |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| UTM | Universal Transverse Mercator |
| VCP | Vertical coplanar |
| WGS84 | World Geodetic System 84 |
Appendix A
| Apparent Conductivity | In-Phase Component | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modality | Critical Bandwidth | Significance Level | H | Critical Bandwidth | Significance Level | H |
| 1 | 11.088 | 0.000s | 1 | 0.2437 | 0.340 | 0 |
| 2 | 7.5971 | 0.180 | 0 | 0.2388 | 0.020 | 1 |
| 3 | 6.8776 | 0.056 | 0 | 0.1881 | 0.072 | 0 |
| 4 | 6.1645 | 0.028 | 1 | 0.1637 | 0.150 | 0 |
| 5 | 5.0021 | 0.170 | 0 | 0.1190 | 0.918 | 0 |
Appendix B
References
- Council Directive 1999/31/EC of 26 April 1999 on the landfill of waste. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/1999/31/oj (accessed on 30 August 2021).
- Council Directive 92/43/EEC of 21 May 1992 on the Conservation of Natural Habitats and of Wild Fauna and Flora. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/1992/43/oj (accessed on 30 August 2021).
- Shannon, C.E. Communication in the Presence of Noise. Proc. IRE 1949, 37, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassiani, G.; Binley, A.; Kemna, A.; Wehrer, M.; Orozco, A.F.; Deiana, R.; Boaga, J.; Rossi, M.; Dietrich, P.; Werban, U.; et al. Noninvasive characterization of the Trecate (Italy) crude-oil contaminated site: Links between contamination and geophysical signals. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 8914–8931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boaga, J.; Ghinassi, M.; D’Alpaos, A.; Deidda, G.P.; Rodriguez, G.; Cassiani, G. Geophysical investigations unravel the vestiges of ancient meandering channels and their dynamics in tidal landscapes. Sci. Reports 2018, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lesch, S.M.; Strauss, D.J.; Rhoades, J.D. Spatial Prediction of Soil Salinity Using Electromagnetic Induction Techniques: 1. Statistical Prediction Models: A Comparison of Multiple Linear Regression and Cokriging. Water Resour. Res. 1995, 31, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, P.; Duplaá, M.C. Laterally filtered 1D inversions of small-loop, frequency-domain EMI data from a chemical waste site. Geophysics 2008, 73, F143–F149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paine, J.G. Determining salinization extent, identifying salinity sources, and estimating chloride mass using surface, borehole, and airborne electromagnetic induction methods. Water Resour. Res. 2003, 39, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pellerin, L. Applications of Electrical And Electromagnetic Methods for Environmental And Geotechnical Investigations. Surv. Geophys. 2002, 23, 101–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, R.; Yang, J. Quantitative evaluation of soil salinity and its spatial distribution using electromagnetic induction method. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 1961–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadoon, K.Z.; Moghadas, D.; Jadoon, A.; Missimer, T.M.; Al-Mashharawi, S.K.; McCabe, M.F. Estimation of soil salinity in a drip irrigation system by using joint inversion of multicoil electromagnetic induction measurements. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 3490–3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moghadas, D.; Jadoon, K.Z.; McCabe, M.F. Spatiotemporal monitoring of soil water content profiles in an irrigated field using probabilistic inversion of time-lapse EMI data. Adv. Water Resour. 2017, 110, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monteiro Santos, F.A.; Triantafilis, J.; Bruzgulis, K. A spatially constrained 1D inversion algorithm for quasi-3D conductivity imaging: Application to DUALEM-421 data collected in a riverine plain. Geophysics 2011, 76, B43–B53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanahan, P.W.; Binley, A.; Whalley, W.R.; Watts, C.W. The Use of Electromagnetic Induction to Monitor Changes in Soil Moisture Profiles beneath Different Wheat Genotypes. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2015, 79, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Von Hebel, C.; Rudolph, S.; Mester, A.; Huisman, J.A.; Kumbhar, P.; Vereecken, H.; Van Der Kruk, J. Three-dimensional imaging of subsurface structural patterns using quantitative large-scale multiconfiguration electromagnetic induction data. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 2732–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boaga, J.; Viezzoli, A.; Cassiani, G.; Deidda, G.P.; Tosi, L.; Silvestri, S. Resolving the thickness of peat deposits with contact-less electromagnetic methods: A case study in the Venice coastland. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 139361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deidda, G.P.; Díaz de Alba, P.; Rodriguez, G.; Vignoli, G. Inversion of Multiconfiguration Complex EMI Data with Minimum Gradient Support Regularization: A Case Study. Math. Geosci. 2020, 52, 945–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schultz, G.; Ruppel, C. Inversion of inductive electromagnetic data in highly conductive terrains. Geophysics 2005, 70, G16–G28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deidda, G.P.; Bonomi, E.; Manzi, C. Inversion of electrical conductivity data with Tikhonov regularization approach: Some considerations. Ann. Geophys. 2003, 46, 549–558. [Google Scholar]
- Deidda, G.P.; Fenu, C.; Rodriguez, G. Regularized solution of a nonlinear problem in electromagnetic sounding. Inverse Probl. 2014, 30, 125014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nobes, D.C.; Armstrong, M.J.; Close, M.E. Delineation of a landfill leachate plume and flow channels in coastal sands near Christchurch, New Zealand, using a shallow electromagnetic survey method. Hydrogeol. J. 2000, 8, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguera, J.F.; Rivero, L.; Font, X.; Navarro, A.; Martínez, F. Simultaneous use of geochemical and geophysical methods to characterise abandoned landfills. Environ. Geol. 2002, 41, 898–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woldt, W.E.; Hagemeister, M.E.; Jones, D.D. Characterization of an Unregulated Landfill Using Surface-Based Geophysics and Geostatistics. Groundwater 1998, 36, 966–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudreault, J.P.; Dubé, J.S.; Chouteau, M.; Winiarski, T.; Hardy, É. Geophysical characterization of contaminated urban fills. Eng. Geol. 2010, 116, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caterina, D.; Isunza Manrique, I.; Inauen, C.; Watlet, A.; Dashwood, B.; De Rijdt, R.; Dumont, G.; Chambers, J.; Nguyen, F. Contribution of geophysical methods to the study of old landfills: A case study in Onoz (Belgium). In Proceedings of the 17th International Waste Management an Landfill Symposium, Santa Margerita di Pula (CA), Italy, 30 September–4 October 2019; p. 15. [Google Scholar]
- Yannah, M.; Martens, K.; Van Camp, M.; Walraevens, K. Geophysical exploration of an old dumpsite in the perspective of enhanced landfill mining in Kermt area, Belgium. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2019, 78, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Maio, R.; Fais, S.; Ligas, P.; Piegari, E.; Raga, R.; Cossu, R. 3D geophysical imaging for site-specific characterization plan of an old landfill. Waste Manag. 2018, 76, 629–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumont, G.; Robert, T.; Marck, N.; Nguyen, F. Assessment of multiple geophysical techniques for the characterization of municipal waste deposit sites. J. Appl. Geophys. 2017, 145, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, A.; Lanz, E.; Maurer, H.; Boerner, D. A template for geophysical investigations of small landfills. Lead. Edge 1999, 18, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes, R.; Martínez-Graña, A.; Martínez Catalán, J.; Arribas, P.; Sánchez San Román, F.; Zazo, C. Integration of GIS, Electromagnetic and Electrical Methods in the Delimitation of Groundwater Polluted by Effluent Discharge (Salamanca, Spain): A Case Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Senos Matias, M.; Marques da Silva, M.; Ferreira, P.; Ramalho, E. A geophysical and hydrogeological study of aquifers contamination by a landfill. J. Appl. Geophys. 1994, 32, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soupios, P.; Papadopoulos, N.; Papadopoulos, I.; Kouli, M.; Vallianatos, F.; Sarris, A.; Manios, T. Application of integrated methods in mapping waste disposal areas. Environ. Geol. 2007, 53, 661–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaudelet, P.; Schmutz, M.; Pessel, M.; Franceschi, M.; Guérin, R.; Atteia, O.; Blondel, A.; Ngomseu, C.; Galaup, S.; Rejiba, F.; et al. Mapping of contaminant plumes with geoelectrical methods. A case study in urban context. J. Appl. Geophys. 2011, 75, 738–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.P.; Chen, C.C.; Tong, L.T.; Chang, P.Y.; Chen, Y.C.; Dong, T.H.; Liu, H.C.; Lin, C.P.; Yang, K.H.; Ho, C.J.; et al. Applying FDEM, ERT and GPR at a site with soil contamination: A case study. J. Appl. Geophys. 2015, 121, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wait, J.R. Mutual coupling of loops lying on the ground. Geophysics 1954, 19, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wait, J.R. Mutual Electromagnetic Coupling of Loops over a Homogeneous Ground. Geophysics 1955, 20, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeill, J.D. Electromagnetic Terrain Conductivity Measurements at Low Induction Numbers; Geonics Ltd.: Mississauga, ON, Canada, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Beamish, D. Low induction number, ground conductivity meters: A correction procedure in the absence of magnetic effects. J. Appl. Geophys. 2011, 75, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goovaerts, P. Geostatistics for Natural Resources Evaluation; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1997; ISBN 0195115384. [Google Scholar]
- Webster, R.; Oliver, M.A. Geostatistics for Environmental Scientists, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2007; ISBN 978-0-470-02858-2. [Google Scholar]
- Montero, J.M.; Fernández-Avilés, G.; Mateu, J. Spatial and Spatio-Temporal Geostatistical Modeling and Kriging; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2015; ISBN 9781118413180. [Google Scholar]
- Benson, R.C.; Glaccum, R.A.; Noel, M.R. Geophysical techniques for sensing buried wastes and waste migration: An application review. In Proceedings of the Surface and Borehole Geophysical Methods in Ground Water Investigations: NWWA/EPA Conference; Nielsen, D.R., Curl, M., Eds.; Natl Water Well Assn: San Antonio, TX, USA, 1984; pp. 533–566. [Google Scholar]
- Caminha-Maciel, G.; Figueiredo, I. Error Analysis in Measured Conductivity under Low Induction Number Approximation for Electromagnetic Methods. ISRN Geophys. 2013, 2013, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deidda, G.P.; Díaz de Alba, P.; Fenu, C.; Lovicu, G.; Rodriguez, G. FDEMtools: A MATLAB package for FDEM data inversion. Numer. Algorithms 2020, 84, 1313–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Callegary, J.B.; Ferre, T.P.A.; Groom, R.W. Vertical Spatial Sensitivity and Exploration Depth of Low-Induction-Number Electromagnetic-Induction Instruments. Vadose Zo. J. 2007, 6, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wait, J.R. A note on the electromagnetic response of a stratified earth. Geophysics 1962, XXVII, 382–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frischknecht, F.C. Electromagnetic Physical Scale Modeling. In Electromagnetic Methods in Applied Geophysics: Volume 1, Theory; Nabighian, M.N., Ed.; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Houston, TX, USA, 1987; pp. 364–441. ISBN 9781560802631. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, E.R. Height-above-ground effects on penetration depth and response of electromagnetic induction soil conductivity meters. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2009, 68, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borchers, B.; Uram, T.; Hendrickx, J.M.H. Tikhonov Regularization of Electrical Conductivity Depth Profiles in Field Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1997, 61, 1004–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrickx, J.M.H.; Borchers, B.; Corwin, D.L.; Lesch, S.M.; Hilgendorf, A.C.; Schlue, J. Inversion of Soil Conductivity Profiles from Electromagnetic Induction Measurements. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2002, 66, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monier-Williams, M.E.; Greenhouse, J.P.; Mendes, J.M.; Ellert, N. Terrain Conductivity Mapping with Topographic Corrections at Three Waste Disposal Sites in Brazil. In Geotechnical and Environmental Geophysics: Volume II, Environmental and Groundwater; Ward, S.H., Ed.; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Houston, TX, USA, 1990; p. 352. ISBN 978-1-56080-001-9. [Google Scholar]
- Fröhlich Gugler, A.I.M.; Gex, P. Electromagnetic survey of a Celtic tumulus. J. Appl. Geophys. 1996, 35, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, V.R.N.; Porsani, J.L.; Mendonça, C.A.; Rodrigues, S.I.; Deblasis, P.D. Reduction of topography effect in inductive electromagnetic profiles: Application on coastal sambaqui (shell mound) archaeological site in Santa Catarina state, Brazil. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2009, 36, 2089–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenhouse, J.P.; Slaine, D.D. The use of the reconnaissance electromagnetic method to map contaminant migration. Groundw. Monit. Remediat. 1983, 3, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAS Institute Inc. SAS/STAT User’s Guide; SAS Institute Inc: Cary, NC, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Akaike, H. A New Look at the Statistical Model Identification. IEEE Trans. Automat. Contr. 1974, 19, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, B.W. Using Kernel Density Estimates to Investigate Multimodality on JSTOR. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1981, 43, 97–99. [Google Scholar]
- Deidda, G.P.; Díaz de Alba, P.; Rodriguez, G. Identifying the magnetic permeability in multi-frequency EM data inversion. Electron. Trans. Numer. Anal. 2017, 47, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Warrick, A.W.; Nielsen, D.R. Spatial Variability of Soil Physical Properties in the Field. In Applications of Soil Physics; Hillel, D., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1980; pp. 319–344. ISBN 978-0-12-348580-9. [Google Scholar]
- Tukey, J.W. Exploratory Data Analysis, 1st ed.; Addison-Wesley Publishing Company: Reading, MA, USA, 1977; ISBN 9780201076165. [Google Scholar]
- Freeman, J.B.; Dale, R. Assessing bimodality to detect the presence of a dual cognitive process. Behav. Res. Methods 2013, 45, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Penn, A. Bootmode 2022. Matlab Central File Exchange. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/66671-bootmode (accessed on 2 December 2021).
- Efron, B.; Tibshirani, R. An Introduction to the Bootstrap, 1st ed.; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1994; ISBN 9780412042317. [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa, I.C.; Neto, E.A.; Seidel, E.J.; De Oliveira, M.S. Proposal of the spatial dependence evaluation from the power semivariogram model. Bol. Ciências Geodésicas 2017, 23, 461–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
















| Apparent Conductivity (mS/m) | In-Phase (ppt) | |
|---|---|---|
| Mean | 82.95 | 5.13 |
| Median | 73.47 | 4.79 |
| Standard Deviation | 38.34 | 3.88 |
| Variance | 1470.13 | 15.04 |
| IQR | 53.83 | 3.17 |
| Q1 1 | 54.00 | 3.32 |
| Q3 1 | 107.83 | 6.49 |
| Minimum | 5.5 | −20.47 |
| Maximum | 207.9 | 20.47 |
| CV (%) | 46.22 | 75.52 |
| Skewness | 0.94 | 0.56 |
| Kurtosis | 3.65 | 12.01 |
| c0 | c1 | c2 | c3 | c4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | −0.2768 | 1.217 | 4.243 × 10−3 | −6.002 × 10−6 | 2.512 × 10−8 |
| 95% confidence bounds | ±0.0092 | 0 | ±0.008 × 10−3 | ±0.054 × 10−6 | ±0.011 × 10−8 |
| KERRYPNX | LIN ECa (mS/m) | Filtered In-Phase 1 (ppt) |
|---|---|---|
| Mean | 127.28 | 4.88 |
| Median | 108.84 | 4.74 |
| Standard Deviation | 66.06 | 2.19 |
| Variance | 4364.54 | 4.81 |
| IQR | 94.57 | 2.91 |
| Q1 1 | 76.43 | 3.37 |
| Q3 1 | 171.00 | 6.28 |
| Minimum | 6.54 | -1.43 |
| Maximum | 371.06 | 11.22 |
| CV (%) | 51.91 | 44.95 |
| Skewness | 0.88 | 0.16 |
| Kurtosis | 3.16 | 3.08 |
| Variable | Model | Slope | Exponent | Nugget C0 | Partial Sill C | Range a (m) | Sill C0 + C | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ECa 1 | Spherical | 0 | 1800 | 37 | 2380 | 0.9978 | ||
| Power | 1.2 | 580 (*) | 30 (*) | |||||
| In-phase 1 | Spherical | 1.5 | 2 | 15.5 | 3.5 | 0.9829 | ||
| Linear | 0.0085 | |||||||
| ECa 2 | Spherical | 30 | 2300 | 37 | 2330 | 0.9504 | ||
| ECa 3 | Spherical | 30 | 2000 | 37 | 2730 | 0.9995 | ||
| Power | 1.63 | 700 | 38 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deidda, G.P.; Himi, M.; Barone, I.; Cassiani, G.; Casas Ponsati, A. Frequency-Domain Electromagnetic Mapping of an Abandoned Waste Disposal Site: A Case in Sardinia (Italy). Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14040878
Deidda GP, Himi M, Barone I, Cassiani G, Casas Ponsati A. Frequency-Domain Electromagnetic Mapping of an Abandoned Waste Disposal Site: A Case in Sardinia (Italy). Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(4):878. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14040878
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeidda, Gian Piero, Mahjoub Himi, Ilaria Barone, Giorgio Cassiani, and Albert Casas Ponsati. 2022. "Frequency-Domain Electromagnetic Mapping of an Abandoned Waste Disposal Site: A Case in Sardinia (Italy)" Remote Sensing 14, no. 4: 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14040878
APA StyleDeidda, G. P., Himi, M., Barone, I., Cassiani, G., & Casas Ponsati, A. (2022). Frequency-Domain Electromagnetic Mapping of an Abandoned Waste Disposal Site: A Case in Sardinia (Italy). Remote Sensing, 14(4), 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14040878









