Performance of DGPS Smartphone Positioning with the Use of P(L1) vs. P(L5) Pseudorange Measurements
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. DGPS Positioning Based on the Least Squares Method
3. Field Experiments
4. Numerical DGPS Analysis of Single Epoch Solutions
5. Static DGPS Sequential Positioning
6. Discussion
7. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ashkenazi, V.; Hill, C.J.; Ochieng, W.Y.; Nagle, J. Wide-Area Differential GPS: A Performance Study. Navigation 1993, 40, 297–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, D.; Dalbelo, L.; Monico, J.; Shimabukuro, M. First Brazilian Real Time Network DGPS through the Internet: Development, Application and Availability Analyses. J. Geod. Sci. 2012, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa SM, A.; Lima, A.; de Moura, N.J.; Abreu, M.A.; da Silva, A.L.; Fortes, L.P.; Ramos, A.M. RBMC in Real Time via NTRIP and Its Benefits in RTK and DGPS Surveys. In Geodesy for Planet Earth; International Association of Geodesy Symposia book series (IAG SYMPOSIA); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 136, pp. 917–922. [Google Scholar]
- Odijk, D.; Wanninger, L. Differential Positioning. In Springer Handbook of Global Navigation Satellite Systems; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, D.; Ji, S.; Lu, Y.; Chen, W.; Li, Z. Improving DGNSS Performance through the Use of Network RTK Corrections. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Song, J.; No, H.; Han, D.; Kim, D.; Park, B.; Kee, C. Accuracy Improvement of DGPS for Low-Cost Single-Frequency Receiver Using Modified Flächen Korrektur Parameter Correction. ISPRS Int. J. GeoInf. 2017, 6, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Shu, B.; Xu, L.; Qian, C.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, M. Accounting for inter-system bias in DGNSS positioning with GPS/GLONASS/BDS/Galileo. J. Navig. 2017, 70, 686–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenbruck, O.; Hauschild, A. Differential code bias estimation using multi-GNSS observations and global ionosphere maps. In Proceedings of the 2014 international technical meeting of the Institute of Navigation, San Diego, CA, USA, 27–29 January 2014; pp. 802–812. [Google Scholar]
- Hakansson, M.; Jensen, A.B.O.; Horemuz, M.; Hedling, G. Review of code and phase biases in multi-GNSS positioning. GPS Solut. 2017, 21, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, L.; Jin, S.; Hoque, M. Estimation of GPS Diferential Code Biases Based on Independent Reference Station and Recursive Filter. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sohn, D.-H.; Park, K.-D.; Tae, H. Modeling DGNSS Pseudo-Range Correction Messages by Utilizing Satellite Repeat Time. Sensors 2017, 17, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, J.; Yan, R.; Deng, C.; Tang, W.; Zou, X.; Shen, M.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y. GPS + BDS Network Real-Time Differential Positioning Using a Position Domain Estimation Method. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Villiger, A.; Schaer, S.; Dach, R.; Prange, L.; Sušnik, A.; Jäggi, A. Determination of GNSS pseudo-absolute code biases and their long-term combination. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 1487–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachapelle, G.; Gratton, P.; Horrelt, J.; Lemieux, E.; Broumandan, A. Evaluation of a Low Cost Hand Held Unit with GNSS Raw Data Capability and Comparison with an Android Smartphone. Sensors 2018, 18, 4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Banville, S.; Van Diggelen, F. Precision GNSS for everyone precise positioning using raw GPS measurements from android smart phones. GPS World 2016, 27, 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Pirazzi, G.; Mazzoni, A.; Biagi, L.; Crespi, M. Preliminary performance analysis with a GPS+Galileo enabled chipset embedded in a smartphone. In Proceedings of the 30th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS+ 2017), Portland, OR, USA, 25–29 September 2017; pp. 101–115. [Google Scholar]
- Paziewski, J.; Sieradzki, R.; Baryla, R. Signal characterization and assessment of code GNSS positioning with low-power consumption smartphones. GPS Solut. 2019, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Realini, E.; Caldera, S.; Pertusini, L.; Sampietro, D. Precise GNSS positioning using smart devices. Sensors 2017, 17, 2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Tao, X.; Zhu, F.; Shi, X.; Wang, F. Quality assessment of GNSS observations from an Android N smartphone and positioning performance analysis using time differenced filtering approach. GPS Solut. 2018, 22, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakansson, M. Characterization of GNSS observations from a Nexus 9 Android tablet. GPS Solut. 2018, 23, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.; Shi, X.; Zhu, F.; Tao, X.; Wang, F. Quality analysis of multi-GNSS raw observations and a velocity-aided positioning approach based on smartphones. Adv. Space Res. 2019, 63, 2358–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robustelli, U.; Baiocchi, V.; Pugliano, G. Assessment of dual frequency GNSS observations from a Xiaomi Mi8 Android smartphone and positioning performance analysis. Electronics 2019, 8, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romero-Andrade, R.; Zamora-Maciel, A.; Uriarte-Adrian, J.; Pivot, F.; Trejo-Soto, M.E. Comparative analysis of precise point positioning processing technique with GPS low-cost in different technologies with academic software. Measurement 2019, 136, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semler, Q.; Mangin, L.; Moussaoui, A.; Semin, E. Development of a low-cost centimetric GNSS positioning solution for Android applications. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, XLII-2/W17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Q.; Sun, M.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, P. Precise Point Positioning Using Dual-Frequency GNSS Observations on Smartphone. Sensors 2019, 19, 2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shinghal, G.; Bisnath, S. Conditioning and PPP processing of smartphone GNSS measurements in realistic environments. Satell. Navig. 2021, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabove, P.; Di Pietra, V. Single-Baseline RTK Positioning Using Dual-Frequency GNSS Receivers Inside Smartphones. Sensors 2019, 19, 4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, W.; Li, Y.; Duan, S. Xiaomi Mi 8 smartphone GNSS data quality analysis and single-frequency RTK positioning performance evaluation. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2020, 14, 1410–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darugna, F.; Wübbena, J.; Ito, A.; Wübbena, T.; Wübbena, G.; Schmitz, M. RTK and PPP-RTK Using Smartphones: From Short-Baseline to Long-Baseline Applications. ION Inst. Navig. 2019, 3932–3945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachapelle, G.; Gratton, P. GNSS precise point positioning with Android smartphones and comparison with high performance receivers. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Signal, Information and Data Processing (ICSIDP), Chongqing, China, 11–13 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tomaštík, J.; Varga, M. Practical applicability of processing static, short-observation-time raw GNSS measurements provided by a smartphone under tree vegetation. Measurement 2021, 178, 109397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabove, P.; Di Pietra, V. Towards high accuracy GNSS real-time positioning with smartphones. Adv. Space Res. 2019, 63, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Q.; Geng, J.; Li, G.; Guo, J. Precise point positioning with ambiguity resolution using an external survey-grade antenna enhanced dual-frequency android GNSS data. Measurement 2020, 157, 107634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Li, G. On the feasibility of resolving Android GNSS carrier-phase ambiguities. J. Geod. 2019, 93, 2621–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Xu, L.; Zhang, B.; Liu, T. Raw GNSS observations from Android smartphones: Characteristics and short-baseline RTK positioning performance. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2021, 32, 084012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaštík, J.; Chudá, J.; Tunák, D.; Chudý, F.; Kardoš, M. Advances in smartphone positioning in forests: Dual-frequency receivers and raw GNSS data. For. Int. J. For. Res. 2020, 94, 292–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uradziński, M.; Bakuła, M. Assessment of static positioning accuracy using low-cost smartphone GPS devices for geodetic survey points’ determination and monitoring. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanninger, L.; Heelbarth, A. GNSS code and carrier phase observations of a Huawei P30 smartphone: Quality assessment and centimeter-accurate positioning. GPS Solut. 2020, 24, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, L.; Wang, F.; Sang, J.; Lin, X.; Gong, X.; Zhang, W. Characteristics Analysis of Raw Multi-GNSS Measurement from Xiaomi Mi 8 and Positioning Performance Improvement with L5/E5 Frequency in an Urban Environment. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paziewski, J.; Fortunato, M.; Mazzoni, A.; Odolinski, R. An analysis of multi-GNSS observations tracked by recent Android smartphones and smartphone-only relative positioning results. Measurement 2021, 175, 109162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robustelli, U.; Paziewski, J.; Pugliano, G. Observation Quality Assessment and Performance of GNSS Standalone Positioning with Code Pseudoranges of Dual-Frequency Android Smartphones. Sensors 2021, 21, 2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paziewski, J. Recent advances and perspectives for positioning and applications with smartphone GNSS observations. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2020, 31, 091001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specht, C.; Szot, T.; Dąbrowski, P.; Specht, M. Testing GNSS receiver accuracy in Samsung Galaxy series mobile phones at a sports stadium. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2020, 31, 064006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specht, C.; Dabrowski, P.S.; Pawelski, J.; Specht, M.; Szot, T. Comparative analysis of positioning accuracy of GNSS receivers of Samsung Galaxy smartphones in marine dynamic measurements. Adv. Space Res. 2019, 63, 3018–3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, D.; Kee, C.; Seo, J.; Park, B. Position Accuracy Improvement by Implementing the DGNSS-CP Algorithm in Smartphones. Sensors 2016, 16, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weng, D.; Gan, X.; Chen, W.; Ji, S.; Lu, Y. A New DGNSS Positioning Infrastructure for Android Smartphones. Sensors 2020, 20, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pepe, M.; Costantino, D.; Vozza, G.; Alfio, V.S. Comparison of Two Approaches to GNSS Positioning Using Code Pseudoranges Generated by Smartphone Device. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uradzinski, M.; Kim, D.; Langley, R.B. The usefulness of internet-based (NTrip) RTK for navigation and intelligent transportation systems. In Proceedings of the 1st International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation, Savannah, GA, USA, 24–28 September 2008; Volume 4, pp. 1967–1975. [Google Scholar]
- Uradzinski, M.; Liu, J.; Jiang, W. Towards precise car navigation: Detection of relative vehicle position on highway for collision avoidance. In Proceedings of the 2010 Ubiquitous Positioning Indoor Navigation and Location Based Service, Kirkkonummi, Finland, 14–15 October 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasuski, K. Aircraft positioning using SPP method in GPS system. Aircr. Eng. Aerosp. Technol. 2018, 90, 1213–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasuski, K.; Cwiklak, J.; Grzegorzewski, M. Aircraft positioning using GPS/GLONASS code observations. Aircr. Eng. Aerosp. Technol. 2019, 92, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grewal, M.S.; Andrews, A.P.; Bartone, C.G. Global Navigation Satellite Systems, Inertial Navigation, and Integration, 3rd ed.; John Wiley Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann-Wellenhof, B.; Lichtenegger, H.; Collins, J. GNSS—Global Navigation Satellite Systems: GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, and More; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Sobczyk, M. Statystyka; Wydawnictwo naukowe PWN: Warsaw, Poland, 2021. [Google Scholar]


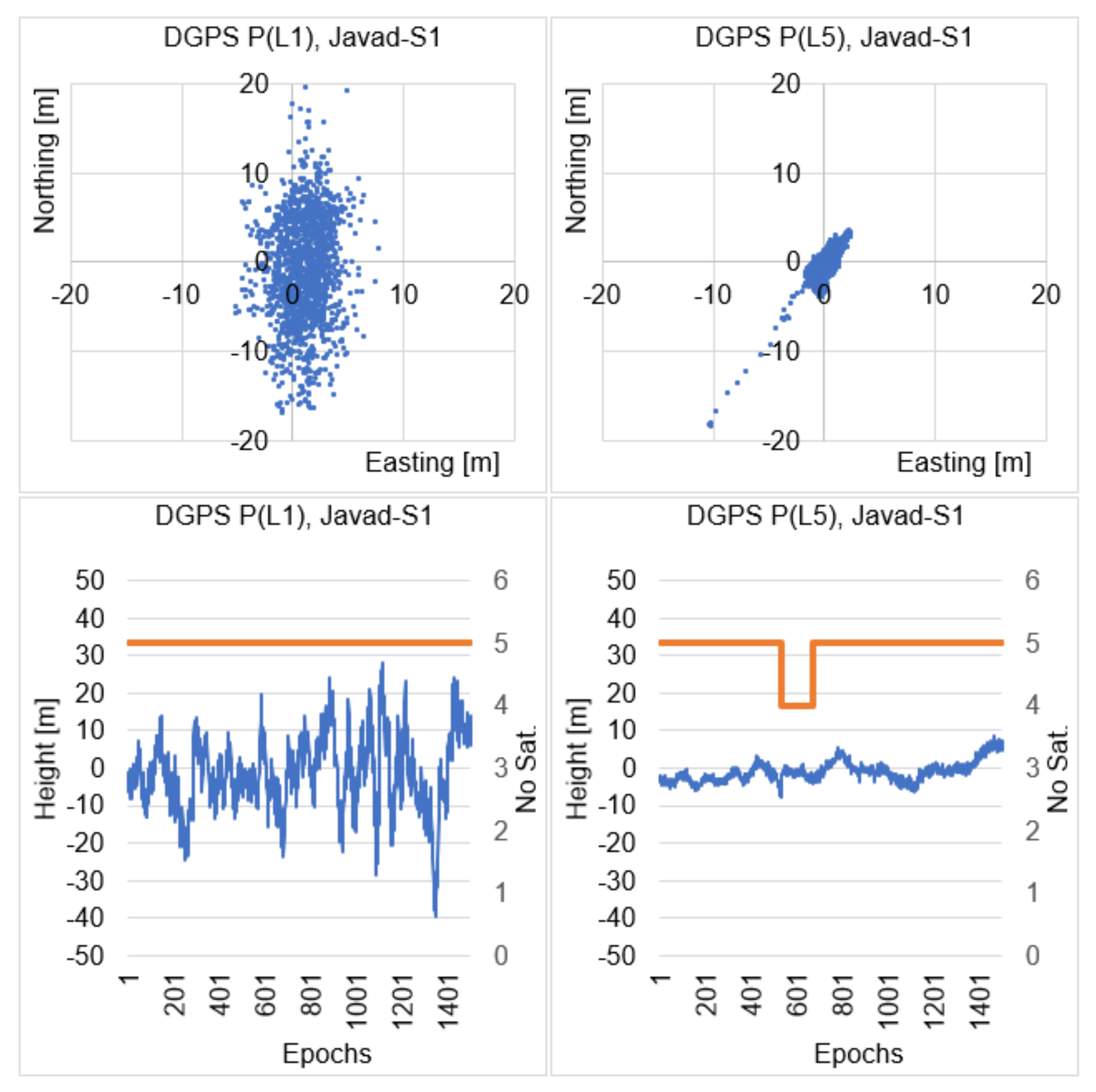
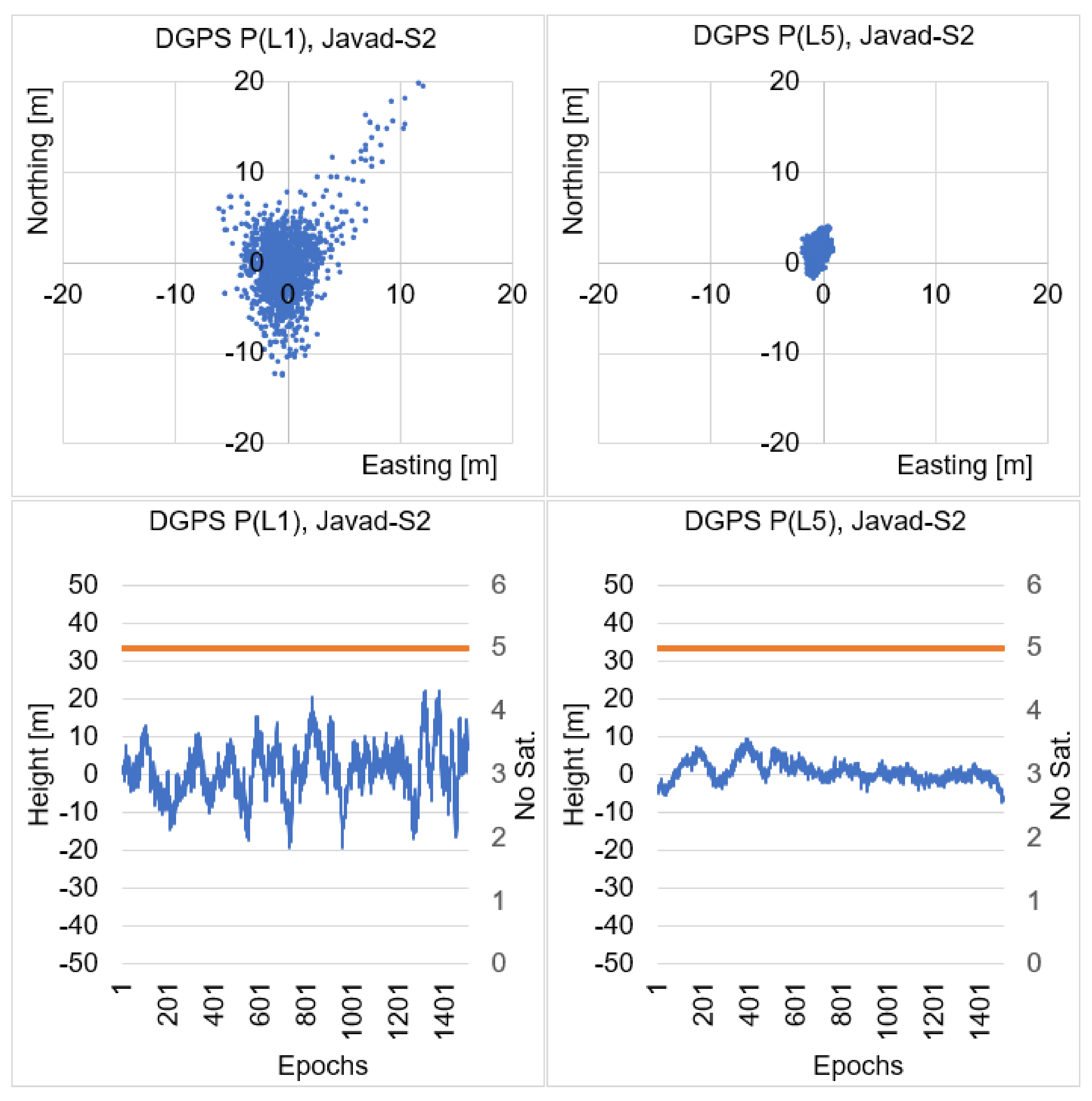
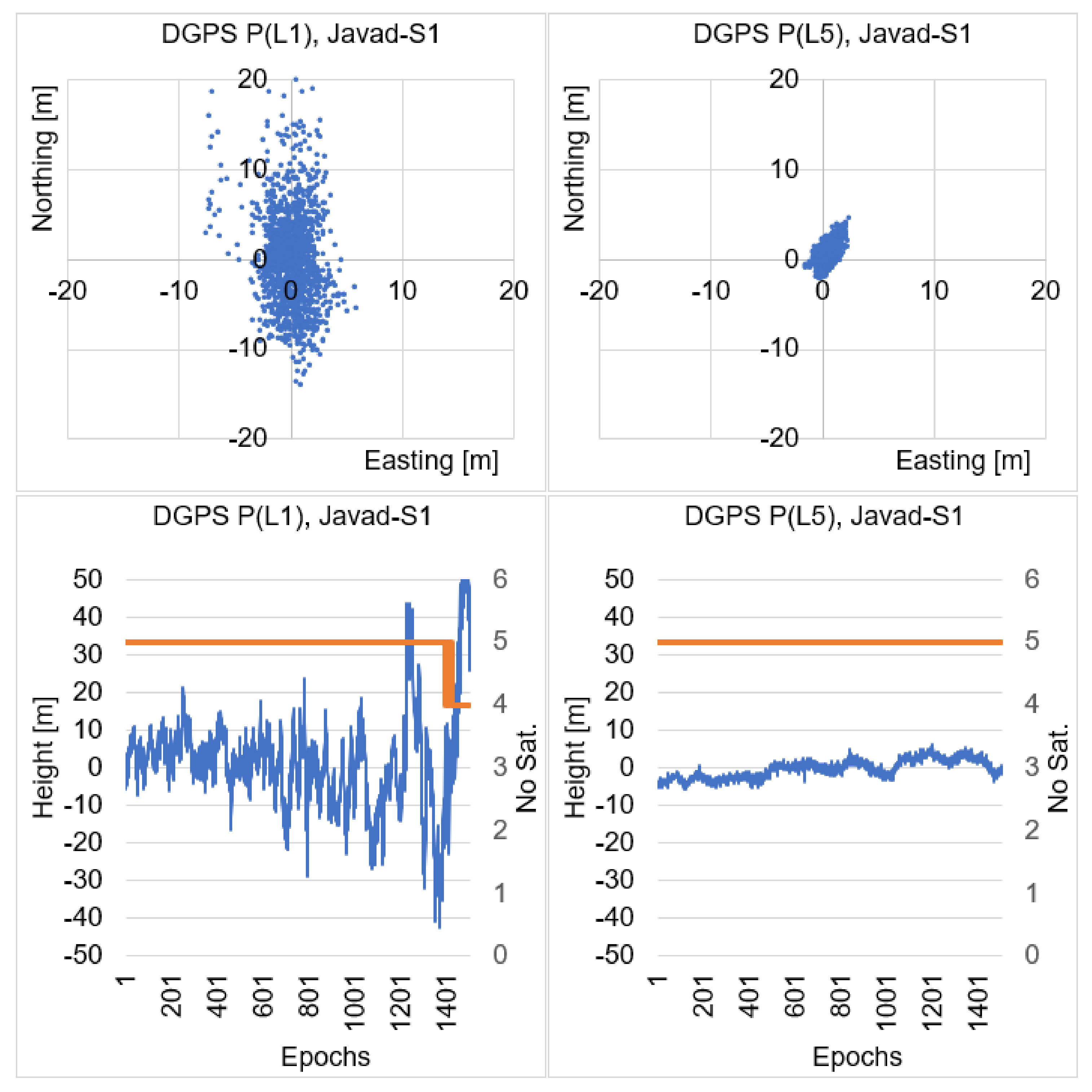

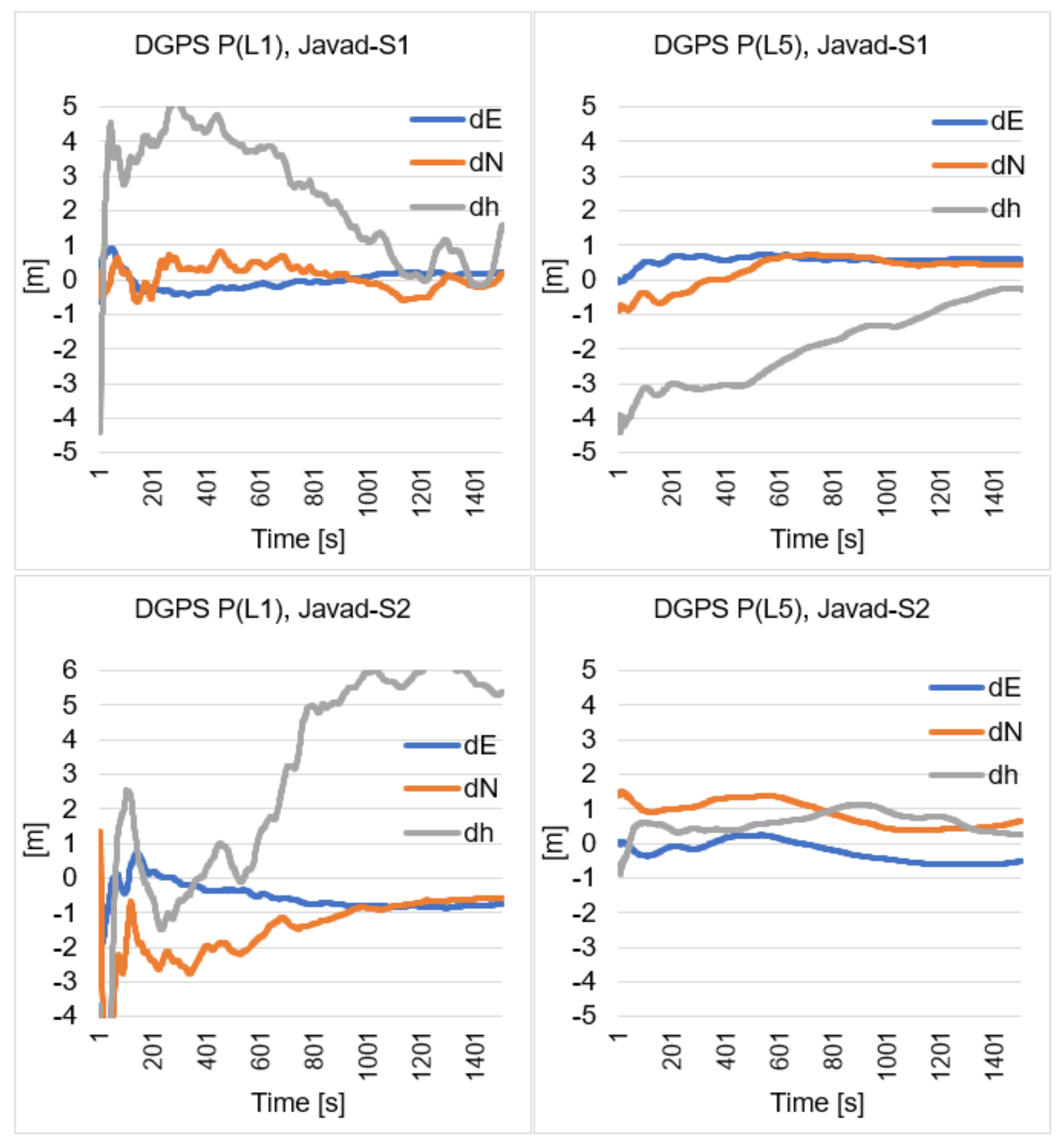
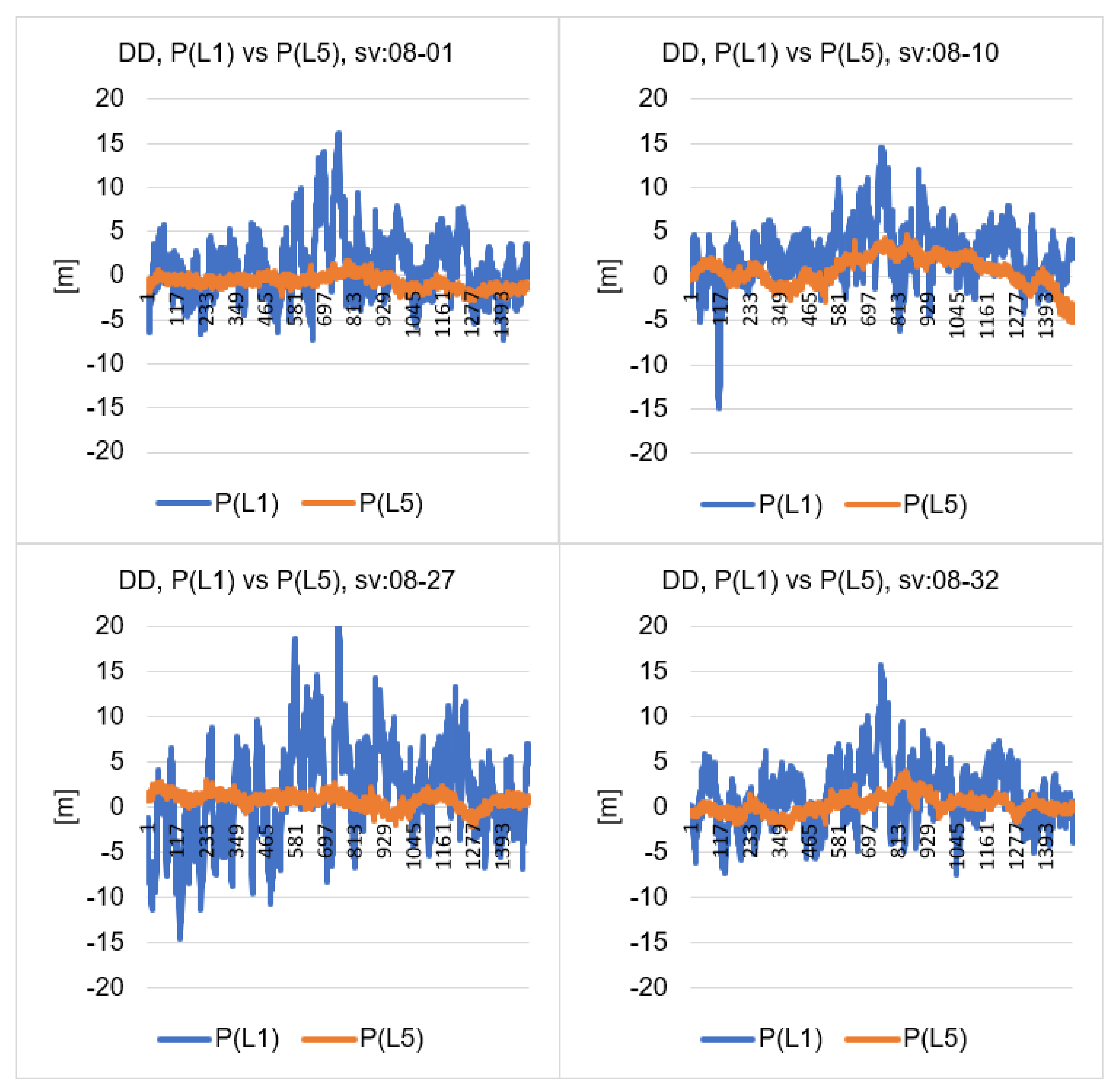

| P(L1) | P(L5) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMS(E) (m) | RMS(N) (m) | RMS(h) (m) | RMS(E) (m) | RMS(N) (m) | RMS(h) (m) | |
| S1 (28.01.21) | 1.88 | 5.94 | 10.05 | 1.03 | 1.71 | 2.66 |
| S2 (28.01.21) | 2.07 | 3.76 | 6.86 | 0.46 | 1.11 | 2.68 |
| S1 (29.01.21) | 1.67 | 5.40 | 14.23 | 0.56 | 1.07 | 2.47 |
| S2 (29.01.21) | 1.68 | 3.56 | 10.95 | 0.89 | 1.28 | 1.92 |
| - (%) | - (%) | - (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 (28.01.21) | 45% | 71% | 73% |
| S2 (28.01.21) | 78% | 70% | 61% |
| S1 (29.01.21) | 66% | 80% | 83% |
| S2 (29.01.21) | 47% | 64% | 82% |
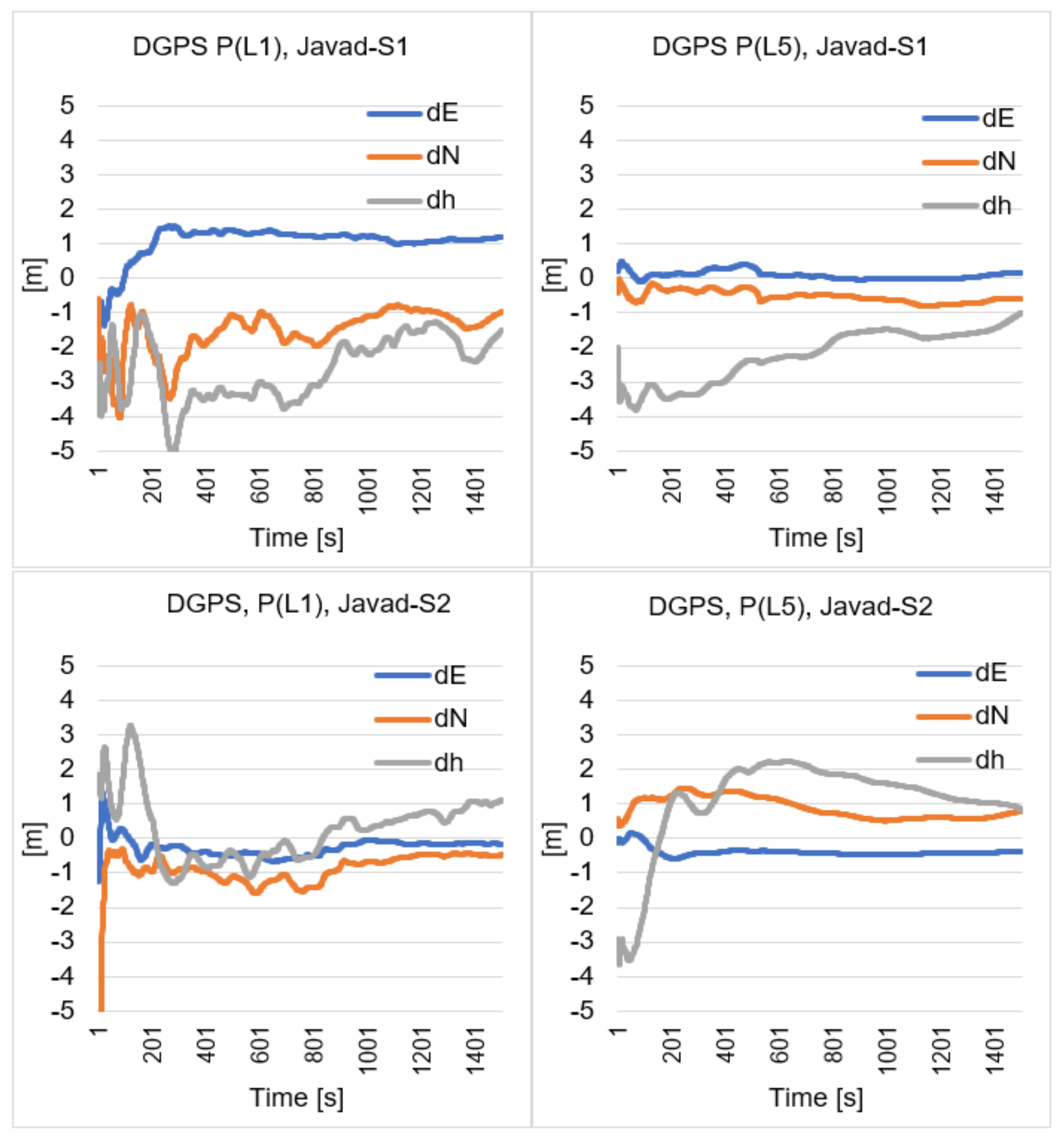
| P(L1) | P(L5) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| dE (m) | dN (m) | dh (m) | dE (m) | dN (m) | dh (m) | |
| S1 (28.01.21) | 1.20 | −0.97 | −1.50 | 0.17 | −0.59 | −1.00 |
| S2 (28.01.21) | −0.16 | −0.47 | 1.20 | −0.37 | 0.79 | 0.85 |
| S1 (29.01.21) | 0.20 | 0.20 | 1.58 | 0.59 | 0.44 | −0.27 |
| S2 (29.01.21) | −0.75 | −0.56 | 5.37 | −0.51 | 0.67 | 0.26 |
| Baseline: Javad-S1 | Baseline: S1–S2 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| St. Dev. P(L1) (m) | St. Dev. P(L5) (m) | P(L1)/P(L5) | St. Dev. P(L1) (m) | St. Dev. P(L5) (m) | P(L1)/P(L5) | |
| SV: 08-01 | 3.63 | 0.78 | 4.65 | 4.91 | 1.45 | 3.37 |
| SV: 08-10 | 3.32 | 1.69 | 1.96 | 4.25 | 1.80 | 2.36 |
| SV: 08-27 | 5.48 | 0.81 | 6.74 | 13.65 | 1.20 | 11.39 |
| SV: 08-32 | 3.31 | 1.00 | 3.32 | 4.49 | 0.99 | 4.54 |
| Average | 3.94 | 1.07 | 4.17 | 6.83 | 1.36 | 5.42 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bakuła, M.; Uradziński, M.; Krasuski, K. Performance of DGPS Smartphone Positioning with the Use of P(L1) vs. P(L5) Pseudorange Measurements. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14040929
Bakuła M, Uradziński M, Krasuski K. Performance of DGPS Smartphone Positioning with the Use of P(L1) vs. P(L5) Pseudorange Measurements. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(4):929. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14040929
Chicago/Turabian StyleBakuła, Mieczysław, Marcin Uradziński, and Kamil Krasuski. 2022. "Performance of DGPS Smartphone Positioning with the Use of P(L1) vs. P(L5) Pseudorange Measurements" Remote Sensing 14, no. 4: 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14040929
APA StyleBakuła, M., Uradziński, M., & Krasuski, K. (2022). Performance of DGPS Smartphone Positioning with the Use of P(L1) vs. P(L5) Pseudorange Measurements. Remote Sensing, 14(4), 929. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14040929








