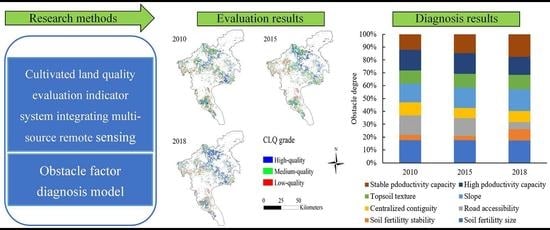
Spatiotemporal Patterns of Cultivated Land Quality Integrated with Multi-Source Remote Sensing: A Case Study of Guangzhou, China
Abstract
Share and Cite
Duan, D.; Sun, X.; Liang, S.; Sun, J.; Fan, L.; Chen, H.; Xia, L.; Zhao, F.; Yang, W.; Yang, P. Spatiotemporal Patterns of Cultivated Land Quality Integrated with Multi-Source Remote Sensing: A Case Study of Guangzhou, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1250. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14051250
Duan D, Sun X, Liang S, Sun J, Fan L, Chen H, Xia L, Zhao F, Yang W, Yang P. Spatiotemporal Patterns of Cultivated Land Quality Integrated with Multi-Source Remote Sensing: A Case Study of Guangzhou, China. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(5):1250. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14051250
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuan, Dingding, Xiao Sun, Shefang Liang, Jing Sun, Lingling Fan, Hao Chen, Lang Xia, Fen Zhao, Wanqing Yang, and Peng Yang. 2022. "Spatiotemporal Patterns of Cultivated Land Quality Integrated with Multi-Source Remote Sensing: A Case Study of Guangzhou, China" Remote Sensing 14, no. 5: 1250. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14051250
APA StyleDuan, D., Sun, X., Liang, S., Sun, J., Fan, L., Chen, H., Xia, L., Zhao, F., Yang, W., & Yang, P. (2022). Spatiotemporal Patterns of Cultivated Land Quality Integrated with Multi-Source Remote Sensing: A Case Study of Guangzhou, China. Remote Sensing, 14(5), 1250. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14051250