Effects of the Gully Land Consolidation Project on Geohazards on a Typical Watershed on the Loess Plateau of China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area
3. Data and Methodologies
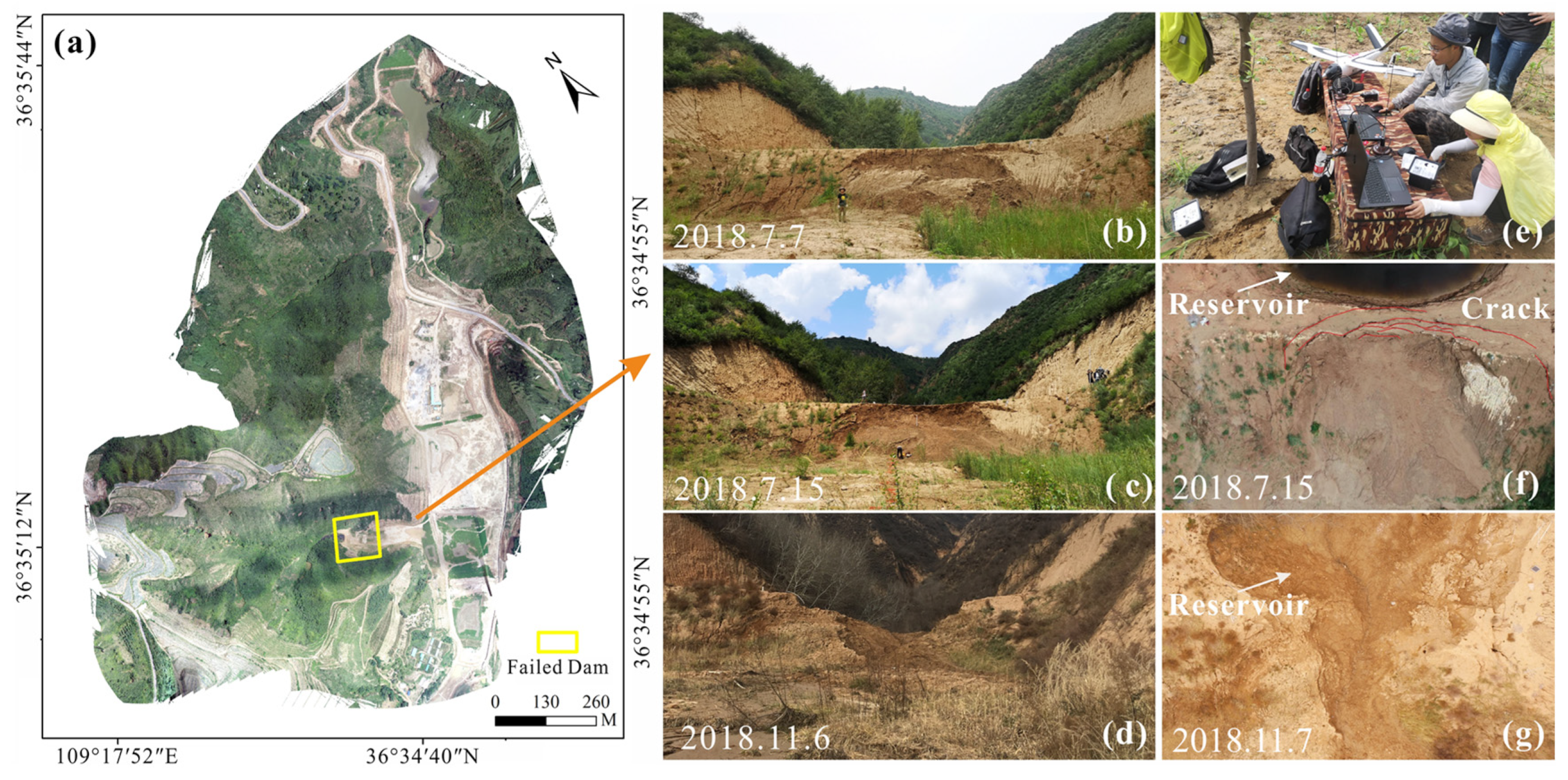
3.1. Interpretation of Remote Sensing Images and Field Surveys
3.2. Erosion
3.3. Salinization
3.4. Dam Failure
4. Results
4.1. Soil Erosion Characteristics
4.2. Regional Salinization
4.3. Distribution Characteristics of Dam Failure
5. Discussion
5.1. Changes in Erosion
5.2. Salinization Formation Mechanism
5.3. Failure Mode of Silt Dams
5.4. Regional Disaster Chain
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Derbyshire, E. Geological hazards in loess terrain, with particular reference to the loess regions of China. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2001, 54, 231–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Dai, F.C.; Tu, X.B.; Javed, I.; Woodard, M.J.; Jin, Y.L.; Tham, L.G. Occurrence of landsliding on slopes where flowsliding had previously occurred: An investigation in a loess platform, North-west China. Catena 2013, 104, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, B.A.; Gao, L.; Ye, Y.; Sun, X.; Connor, J.D.; Crossman, N.D.; Stafford-Smith, M.; Wu, J.; He, C.; Yu, D.; et al. China’s response to a national land-system sustainability emergency. Nature 2018, 559, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, B. Soil erosion and its control in the loess plateau of China. Soil Use Manag. 1989, 5, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhi, L. A Review of Compensation in Convertion of Farmland to Forest Program. World For. Res. 2010, 23, 45–49. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.P.; Shao, M.A.; Wang, Y.Q. Large-scale spatial interpolation of soil pH across the Loess Plateau, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 69, 2731–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.; Zhang, K.; Lei, A. Critical slope gradient for compulsory abandonment of farmland on the hilly Loess Plateau. Chin. Sci. Bull. 1998, 43, 409–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, Y.; Fu, B.; Feng, X.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chang, R.; Sun, G.; Wu, B. A policy-driven large scale ecological restoration: Quantifying ecosystem services changes in the loess plateau of China. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, K.; Lin, Y.; Shi, W.; Song, Y.; He, X. Balancing green and grain trade. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 739–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, N.; Mu, X.M. Analysis on effect of gully control and land reclamation projects on carbon emission in hilly and gully regions of Loess Plateau. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2018, 37, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurui, L.; Yi, L.; Pengcan, F.; Hualou, L. Impacts of land consolidation on rural human–environment system in typical watershed of the Loess Plateau and implications for rural development policy. Land Use Policy 2019, 86, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Guo, L.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Lin, H.; Chen, Y.; Chu, G.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, N. Valley reshaping and damming induce water table rise and soil salinization on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Geoderma 2019, 339, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y. Filling gullies to create farmland on the Loess Plateau. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 7589–7590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Du, G.; Liu, Y. Transforming the Loess Plateau of China. Front. Agric. Sci. Eng. 2016, 3, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pu, C.; Xu, Q.; Zhao, K.; Jiang, Y.; Hao, L.; Liu, J.; Chen, W.; Kou, P. Characterizing the topographic changes and land subsidence associated with the mountain excavation and city construction on the Chinese loess plateau. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, Q.; Zhao, K.; Ye, Z.; Guo, P.; Guo, C. Distribution Rule of Govening Valleys Project in Baota District of Yan’an City. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2019, 39, 141–148. [Google Scholar]
- He, C. How to develop modern agriculture in Yan’an. J. Yanan Univ. Social Sci. 2013, 35, 62–65. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Z. The creation of farmland by gully filling on the Loess Plateau: A double-edged sword. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 883–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Börjesson, P.; Tufvesson, L.M. Agricultural crop-based biofuels—Resource efficiency and environmental performance including direct land use changes. J. Clean. Prod. 2011, 19, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juang, C.H.; Dijkstra, T.; Wasowski, J.; Meng, X. Loess geohazards research in China: Advances and challenges for mega engineering projects. Eng. Geol. 2019, 251, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Y.; Jin, Z.; Lin, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, W.; An, Z. Exploring the role of land restoration in the spatial patterns of deep soil water at watershed scales. Catena 2019, 172, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Chen, W.; Zhao, K.; Zhou, X.; Du, P.; Guo, C.; Ju, Y.; Pu, C. Effects of land-use management on soil erosion: A case study in a typical watershed of the hilly and gully region on the Loess Plateau of China. Catena 2021, 206, 105551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Xu, Q.; Zhao, K.; Zhou, X.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Xu, J. Spatial analysis of land-use management for gully land consolidation on the Loess Plateau in China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacroix, P.; Dehecq, A.; Taipe, E. Irrigation-triggered landslides in a Peruvian desert caused by modern intensive farming. Nat. Geosci. 2020, 13, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karydas, C.G.; Panagos, P.; Gitas, I.Z. A classification of water erosion models according to their geospatial characteristics. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2014, 7, 229–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, K.J.; Kumar, S.; Hole, R.M. Geospatial modelling of soil erosion and risk assessment in Indian Himalayan region—A study of Uttarakhand state. Environ. Adv. 2021, 4, 100039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galdino, S.; Sano, E.E.; Andrade, R.G.; Grego, C.R.; Nogueira, S.F.; Bragantini, C.; Flosi, A.H.G. Large-scale Modeling of Soil Erosion with RUSLE for Conservationist Planning of Degraded Cultivated Brazilian Pastures. Land Degrad. Dev. 2016, 27, 773–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benavidez, R.; Bethanna, J.; Deborah, M.; Kevin, N. A-review-of-the-Revised-Universal-Soil-Loss-Equation-RUSLE-With-a-view-to-increasing-its-global-applicability-and-improving-soil-loss-estimates. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 6059–6086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borrelli, P.; Robinson, D.A.; Fleischer, L.R.; Lugato, E.; Ballabio, C.; Alewell, C.; Meusburger, K.; Modugno, S.; Schütt, B.; Ferro, V.; et al. An assessment of the global impact of 21st century land use change on soil erosion. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alewell, C.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K.; Panagos, P. Using the USLE: Chances, challenges and limitations of soil erosion modelling. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2019, 7, 203–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Zhang, X.; Yan, S.; Chen, H. Estimating soil erosion response to land use/cover change in a catchment of the Loess Plateau, China. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2018, 6, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Kondolf, G.M.; Mu, X.; Han, M.; He, Z.; Rubin, Z.; Wang, F.; Gao, P.; Sun, W. Sediment yield reduction associated with land use changes and check dams in a catchment of the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2017, 148, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Shao, Q.; Liu, J. Soil erosion and its response to the changes of precipitation and vegetation cover on the Loess Plateau. J. Geogr. Sci. 2013, 23, 1091–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lu, P.; Valente, D.; Petrosillo, I.; Babu, S.; Xu, S.; Li, C.; Huang, D.; Liu, M. Analysis of soil erosion characteristics in small watershed of the loess tableland Plateau of China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 137, 108765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, Y. GIS-based effect assessment of soil erosion before and after gully land consolidation: A case study of Wangjiagou project region, Loess Plateau. Chinese Geogr. Sci. 2015, 25, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, X.; Lv, P.; Zhao, S.; Sun, Y.; Yan, S.; Wang, M.; Han, X.; Wang, X. The Effect of the Gully Land Consolidation Project on soil erosion and crop production on a typical Watershed in the Loess Plateau. Land 2018, 7, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Z.; Gao, J.; Sun, P.; Dou, S.; Li, J.; Lou, X.; Wang, H.; Ahmad, R.; Gao, Z. Influence of Gully Land Consolidation on Phreatic Water Transformation in the Loess Hilly and Gully Region. Water 2021, 13, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wei, W.; Bao, H.; Zhang, K.; Lan, H.; Yan, C.; Sun, W. Failure models of a loess stacked dam: A case study in the Ansai Area (China). Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2020, 79, 1009–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Liu, P.; Jiang, L.; Wang, K. The influence of internal erosion in earthen dams on the potential difference response to applied voltage. Water 2021, 13, 3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, T.; Li, Z.; Liu, W.; Han, X. Evolution of potential evapotranspiration in the northern Loess Plateau of China: Recent trends and climatic drivers. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 4019–4028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortina, J.; Amat, B.; Castillo, V.; Fuentes, D.; Maestre, F.T.; Padilla, F.M.; Rojo, L. The restoration of vegetation cover in the semi-arid Iberian southeast. J. Arid Environ. 2011, 75, 1377–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, W.; Zuo, J.; Bi, J.; Shi, J.; Wang, X.; Chang, Z.; Huang, Z.; Yang, S.; Zhang, B.; et al. An overview of the semi-arid climate and environment research observatory over the loess plateau. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2008, 25, 906–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, Y.; Feng, W.; Cao, Z. The Planting Technology and Industrial Development Prospects of Forage Rape in the Loess Hilly Area—A Case Study of Newly-increased Cultivated Land Through Gully Land Consolidation in Yan’an, Shaanxi Province. J. Nat. Resour. 2017, 32, 2065–2074. [Google Scholar]
- Elnashar, A.; Zeng, H.; Wu, B.; Fenta, A.A.; Nabil, M.; Duerler, R. Soil erosion assessment in the Blue Nile Basin driven by a novel RUSLE-GEE framework. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 793, 148466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getnet, T.; Mulu, A. Assessment of soil erosion rate and hotspot areas using RUSLE and multi-criteria evaluation technique at Jedeb watershed, Upper Blue Nile, Amhara Region, Ethiopia. Environ. Chall. 2021, 4, 100174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaszadeh Shahri, A.; Spross, J.; Johansson, F.; Larsson, S. Landslide susceptibility hazard map in southwest Sweden using artificial neural network. Catena 2019, 183, 104225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, C.W.; Foster, G.R.; Wright, D.A. Estimation of erosion index from daily rainfall amount. Trans. Am. Soc. Agric. Eng. 1983, 26, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.B.; Fu, J.S. Rainfall Erosivity Estimation Under Different Rainfall Amount. Resour. Sci. 2003, 25, 35–41. [Google Scholar]
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K.; Yu, B.; Klik, A.; Lim, K.J.; Yang, J.E.; Ni, J.; Miao, C.; Chattopadhyay, N.; et al. Global rainfall erosivity assessment based on high-temporal resolution rainfall records. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Williams, J.R.; Renard, K.G.; Dyke, P.T. EPIC: A new method for assessing erosion’s effect on soil productivity. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1983, 38, 381–383. [Google Scholar]
- Ghaderi, A.; Abbaszadeh Shahri, A.; Larsson, S. A visualized hybrid intelligent model to delineate Swedish fine-grained soil layers using clay sensitivity. Catena 2022, 214, 106289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Liu, B. Evolution of the Soil Erosion Model. Adv. Earth Sci. 2002, 17, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.Y.; Nearing, M.A.; Risse, L.M. Slope gradient effects on soil loss for steep slopes. Trans. Am. Soc. Agric. Eng. 1994, 37, 1835–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCool, D.K.; Brown, L.C.; Foster, G.R.; Mutchler, C.K.; Meyer, L.D. Revised Slope Steepness Factor for the Universal Soil Loss Equation. Trans. Am. Soc. Agric. Eng. 1987, 30, 1387–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Shao, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhai, J. Assessing the effects of land use and topography on soil erosion on the Loess Plateau in China. Catena 2014, 121, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xie, Z.; Qin, Y.; Sun, Y. Temporal-spatial variation characteristics of soil erosion in the pisha sandstone area, loess plateau, china. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2019, 28, 2205–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Rainfall Energy and Its Relationship to Soil Loss. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1958, 39, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Xing, H.; Zhang, S.; Kang, K.; Qi, X.; Ju, Y.; Zhao, K. Hydrological response of loess slopes with reference to widespread landslide events in the Heifangtai terrace, NW China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2019, 171, 259–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, S.; Chen, G.; Zeng, R.; Meng, X.; Jin, J.; Lin, L.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, W. Post-failure evolution analysis of an irrigation-induced loess landslide using multiple remote sensing approaches integrated with time-lapse ERT imaging: Lessons from Heifangtai, China. Landslides 2022, 19, 1179–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, R.Q.; Meng, X.M.; Zhang, F.Y.; Wang, S.Y.; Cui, Z.J.; Zhang, M.S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, G. Characterizing hydrological processes on loess slopes using electrical resistivity tomography—A case study of the Heifangtai Terrace, Northwest China. J. Hydrol. 2016, 541, 742–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X. Study on the Influence of Groundwater Level Raising on the Salt Distribution of Surface Loess: A Case Study in Heifangtai and Gutun. Master’s Thesis, Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Gao, Y.; Wang, S.; Lü, Y.; Fu, B. Carbon Sequestration Function of Check-Dams: A Case Study of the Loess Plateau in China. Ambio 2014, 43, 926–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, A. Soil salinization and waterlogging: A threat to environment and agricultural sustainability. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 57, 128–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A. Groundwater modelling for the assessment of water management alternatives. J. Hydrol. 2013, 481, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. Study on Farmland Salinization and Its Mechanism in the Loess Plateau. Ph.D. Thesis, Tottori University, Tottori, Japan, 2012; pp. 95–102. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.; Yue, Z.; Pender, G. Flood hydraulics due to cascade landslide dam failure. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2011, 4, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Pedroli, B.; Liu, G.; Liu, Q.; Liu, H.; Shu, L. Soil salinity development in the yellow river delta in relation to groundwater dynamics. L. Degrad. Dev. 2012, 23, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| Land Use Types | Cropland | Residents, Hardened Pavement | Working Land, Nonhardened Pavement, Water Area, Bare Ground | Grassland | Woodland | Shrubland |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 0.28 | 0.9 | 1 | 0.09 | 0.004 | 0.02 |
| Slope (°) | Cropland | Grassland | Woodland, Nonhardened Pavement, Bare Ground, Working Land, Shrubland | Water Area, Residents, Hardened Pavement |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| >1–9 | 0.3 | 0.8 | ||
| >9–18 | 0.5 | |||
| >18–21 | 0.6 | |||
| >21 | 1 | 1 |
| Erosion Classification | Average Soil Erosion Rate (t·km−2·a−1) | Area (km2) | Average Annual Soil Erosion Rate (t·km−2·a−1) | Erosion Volume (t) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 2020 | Change | 2018 | 2020 | Change | 2018 | 2020 | Change | ||
| Micro-erosion | ≤500 | 14.41 | 12.46 | −1.95 | 185.49 | 230.94 | 45.45 | 2661.41 | 2877.1 | 215.69 |
| Mild erosion | >500–2500 | 15.22 | 15.45 | 0.23 | 928.92 | 955.4 | 26.48 | 14,136.84 | 14,758.6 | 621.76 |
| Moderate erosion | >2500–5000 | 8.3 | 8.46 | 0.16 | 2828.39 | 3137.96 | 309.57 | 23,649.1 | 26,541.55 | 2892.45 |
| Intense erosion | >5000–8000 | 1.5 | 2.61 | 1.11 | 4776.96 | 5140.75 | 363.79 | 7184.79 | 13,439.46 | 6254.67 |
| Extreme erosion | >8000–15,000 | 0.9 | 0.91 | 0.01 | 8972.74 | 9542.76 | 570.02 | 7458.02 | 8746.18 | 1288.16 |
| Severe erosion | >15,000 | 1.64 | 1.86 | 0.22 | 36,400.7 | 67,766.6 | 31,365.9 | 46,104.12 | 126,018.9 | 79,914.78 |
| Erosion Indicators | Average Annual Soil Erosion Rates (t·km−2·a−1) | Area (km2) | Area Share (%) | Erosion Volume (t) | Percentage of Erosion Volume (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classification | 2018 | 2020 | 2018 | 2020 | Change | Change | 2018 | 2020 | Change | Change | |
| Slope | 0–5° | 968.24 | 1630.73 | 3.41 | 3.25 | −0.16 | −0.38 | 3298.93 | 5296.89 | 1997.96 | −0.51 |
| >5–8° | 2054.55 | 2921.67 | 1.01 | 1.14 | 0.13 | 0.3 | 2084.6 | 3334.55 | 1249.95 | −0.33 | |
| >8–15° | 2378.24 | 7984.44 | 2.9 | 2.05 | −0.85 | −2.03 | 6901.45 | 16,396.04 | 9494.59 | 1.7 | |
| >15–25° | 2472.79 | 6367.48 | 6.99 | 5.08 | −1.91 | −4.56 | 17,283.98 | 32,369.79 | 15,085.81 | −0.25 | |
| >25–35° | 2144.84 | 4145.08 | 9.77 | 8.48 | −1.29 | −3.09 | 20,947.22 | 35,136.19 | 14,188.97 | −2.44 | |
| >35° | 2867.29 | 4591.4 | 17.67 | 21.75 | 4.08 | 9.76 | 50,678.1 | 99,848.3 | 49,170.2 | 1.82 | |
| Aspect | Shady slope | 1499.53 | 3469.26 | 4.33 | 3.16 | −1.17 | −2.8 | 6486.55 | 10,948.89 | 4462.34 | −0.72 |
| Half-shady slope | 2513.13 | 4911.51 | 16.5 | 17.25 | 0.75 | 1.82 | 41,459.3 | 84,747.57 | 43,288.27 | 3.08 | |
| Sunny slope | 2848.51 | 7009.55 | 4.98 | 5.85 | 0.87 | 2.1 | 14,177.32 | 41,023.53 | 26,846.21 | 7.31 | |
| Half-sunny slope | 2448.94 | 3594.19 | 15.95 | 15.49 | −0.46 | −1.12 | 39,071.11 | 55,661.76 | 16,590.65 | −9.68 | |
| Elevation (m) | 900–950 | 2596.21 | 3820.11 | 1.52 | 1.92 | 0.4 | 0.94 | 3956.7 | 7324.52 | 3367.82 | −0.1 |
| >950–1000 | 3617.47 | 4525.71 | 5.94 | 7.99 | 2.05 | 4.9 | 21,493.67 | 36,150.38 | 14,656.71 | −2.45 | |
| >1000–1050 | 2858.49 | 5019.27 | 9.96 | 11.11 | 1.15 | 2.76 | 28,465.95 | 55,753.71 | 27,287.76 | 0.85 | |
| >1050–1100 | 2272.16 | 5758.81 | 10.03 | 9.3 | −0.73 | −1.73 | 22,778.83 | 53,572.28 | 30,793.45 | 5.34 | |
| >1100–1150 | 1750.28 | 4094.1 | 7.47 | 5.43 | −2.04 | −4.9 | 13,074.3 | 22,210.99 | 9136.69 | −1.37 | |
| >1150–1200 | 1509.7 | 2367.02 | 4.77 | 3.983 | −0.787 | −1.89 | 7205.03 | 9426.27 | 2221.24 | −2.23 | |
| >1200–1250 | 2177.38 | 3838.93 | 1.85 | 1.86 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 4027.53 | 7157.83 | 3130.3 | −0.26 | |
| >1250 | 920.96 | 4841.35 | 0.21 | 0.16 | −0.05 | −0.11 | 192.27 | 785.77 | 593.5 | 0.22 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Xu, Q.; Pu, C.; Li, W.; Zhao, K.; Li, Z.; Chen, W.; Xiu, D. Effects of the Gully Land Consolidation Project on Geohazards on a Typical Watershed on the Loess Plateau of China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15010113
Wang X, Xu Q, Pu C, Li W, Zhao K, Li Z, Chen W, Xiu D. Effects of the Gully Land Consolidation Project on Geohazards on a Typical Watershed on the Loess Plateau of China. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(1):113. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15010113
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiaochen, Qiang Xu, Chuanhao Pu, Weile Li, Kuanyao Zhao, Zhigang Li, Wanlin Chen, and Dehao Xiu. 2023. "Effects of the Gully Land Consolidation Project on Geohazards on a Typical Watershed on the Loess Plateau of China" Remote Sensing 15, no. 1: 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15010113
APA StyleWang, X., Xu, Q., Pu, C., Li, W., Zhao, K., Li, Z., Chen, W., & Xiu, D. (2023). Effects of the Gully Land Consolidation Project on Geohazards on a Typical Watershed on the Loess Plateau of China. Remote Sensing, 15(1), 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15010113







