Forest Height Inversion Based on Time–Frequency RVoG Model Using Single-Baseline L-Band Sublook-InSAR Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- It considered the path difference of sublook SAR signals and can help to provide detailed interpretation for the impact of the different sublook coherences in the sublook coherent scattering modeling;
- (2)
- It can invert the forest CHM from the single-baseline and single-polarization InSAR data without an a priori CHM, underdetermined parameter inversion, and observation efficiency reduction;
- (3)
- It can alleviate the influence of the 2-D ambiguous error of pure volume coherence by combining the empirical relationship of the and the extinction coefficient [25] with the RVoG + MTD model.
2. Theory and Method
2.1. Sublook Coherent Scattering Modeling
2.2. RME-Induced Phase Error Correction
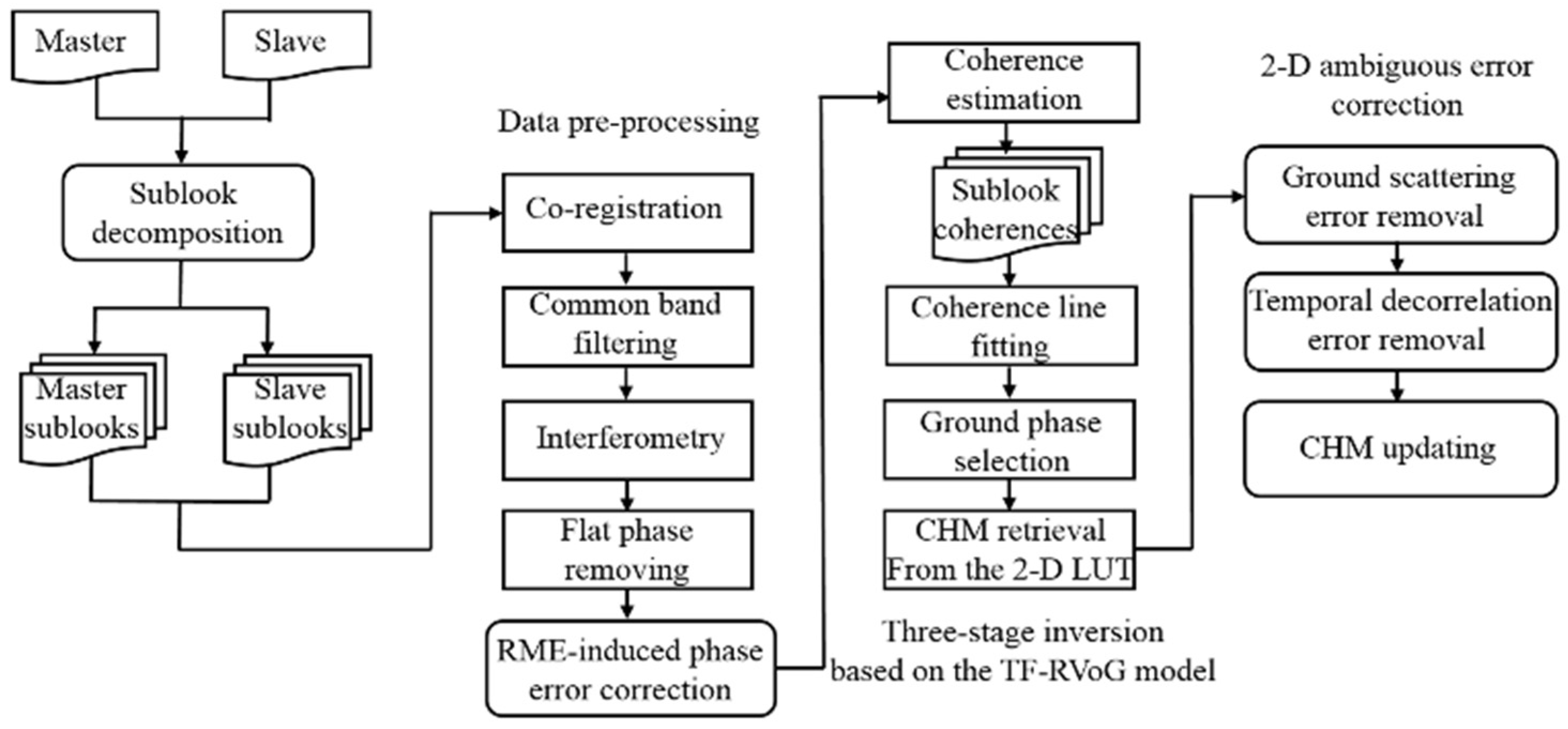
2.3. Three-Stage Inversion Method Based on the TF-RVoG Model
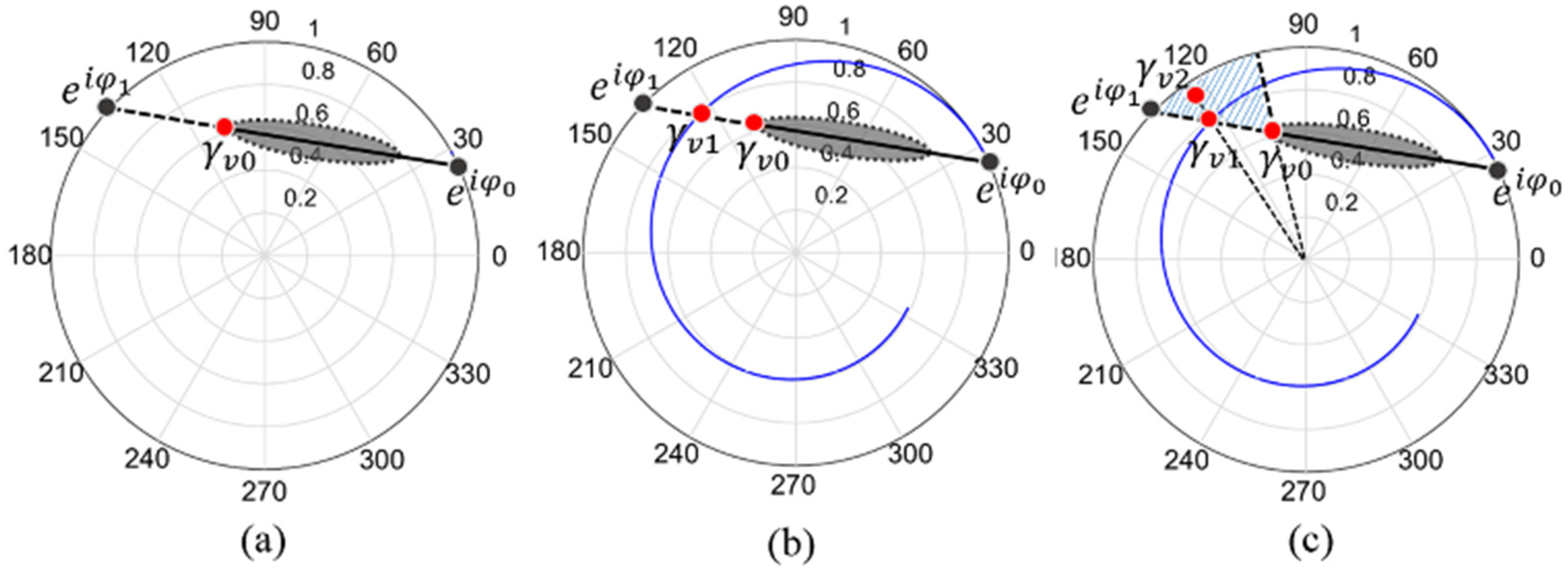
2.4. 2-D Ambiguous Error Correction of the Pure Volume Coherence
3. Experiments and Results
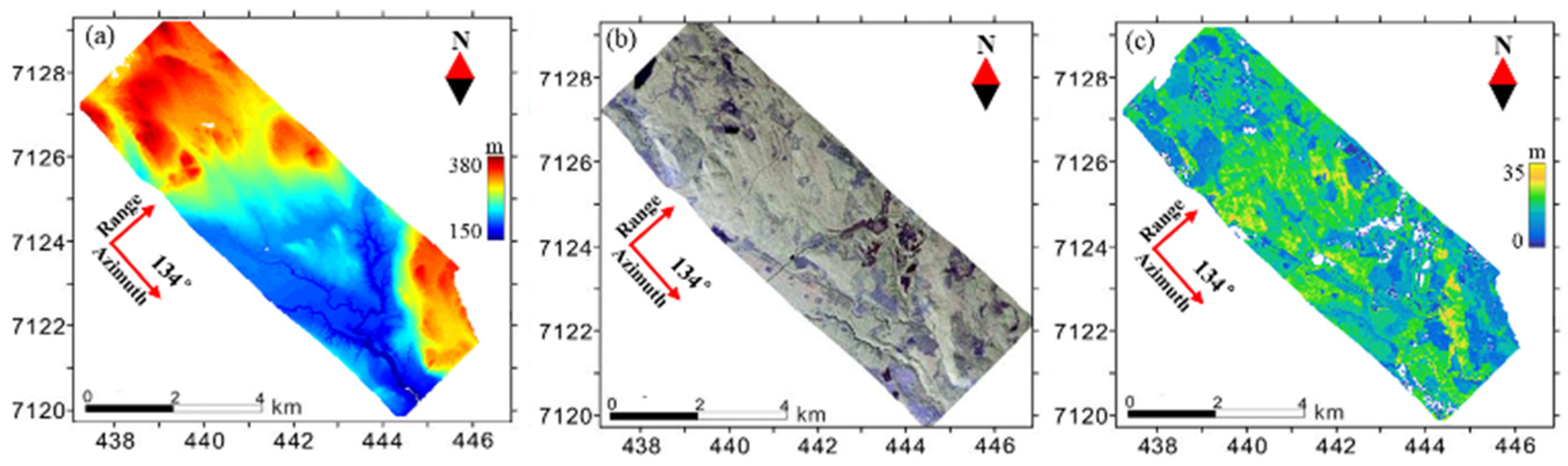
3.1. Experimental Data
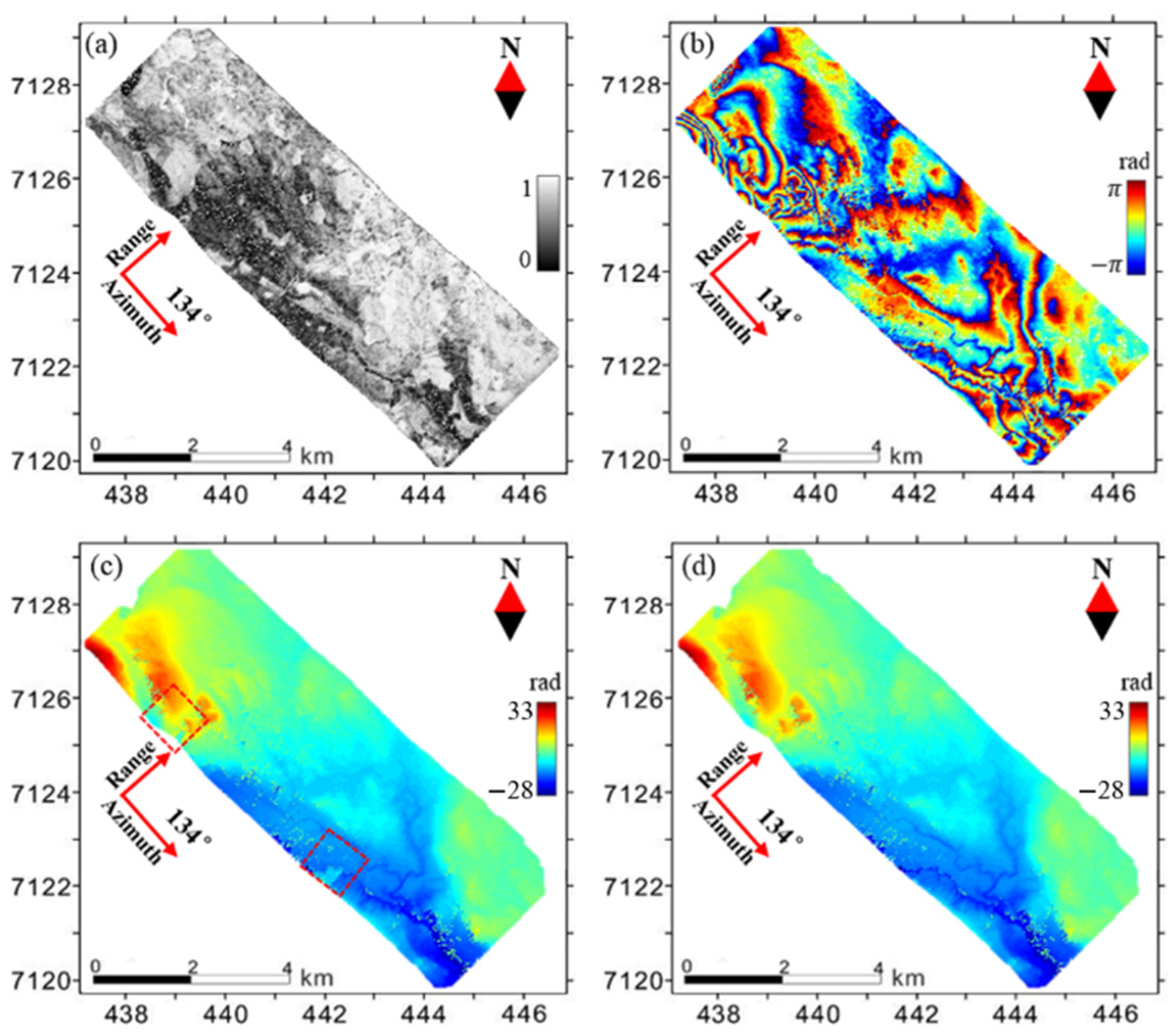
3.2. Processing of the Sublook InSAR Data
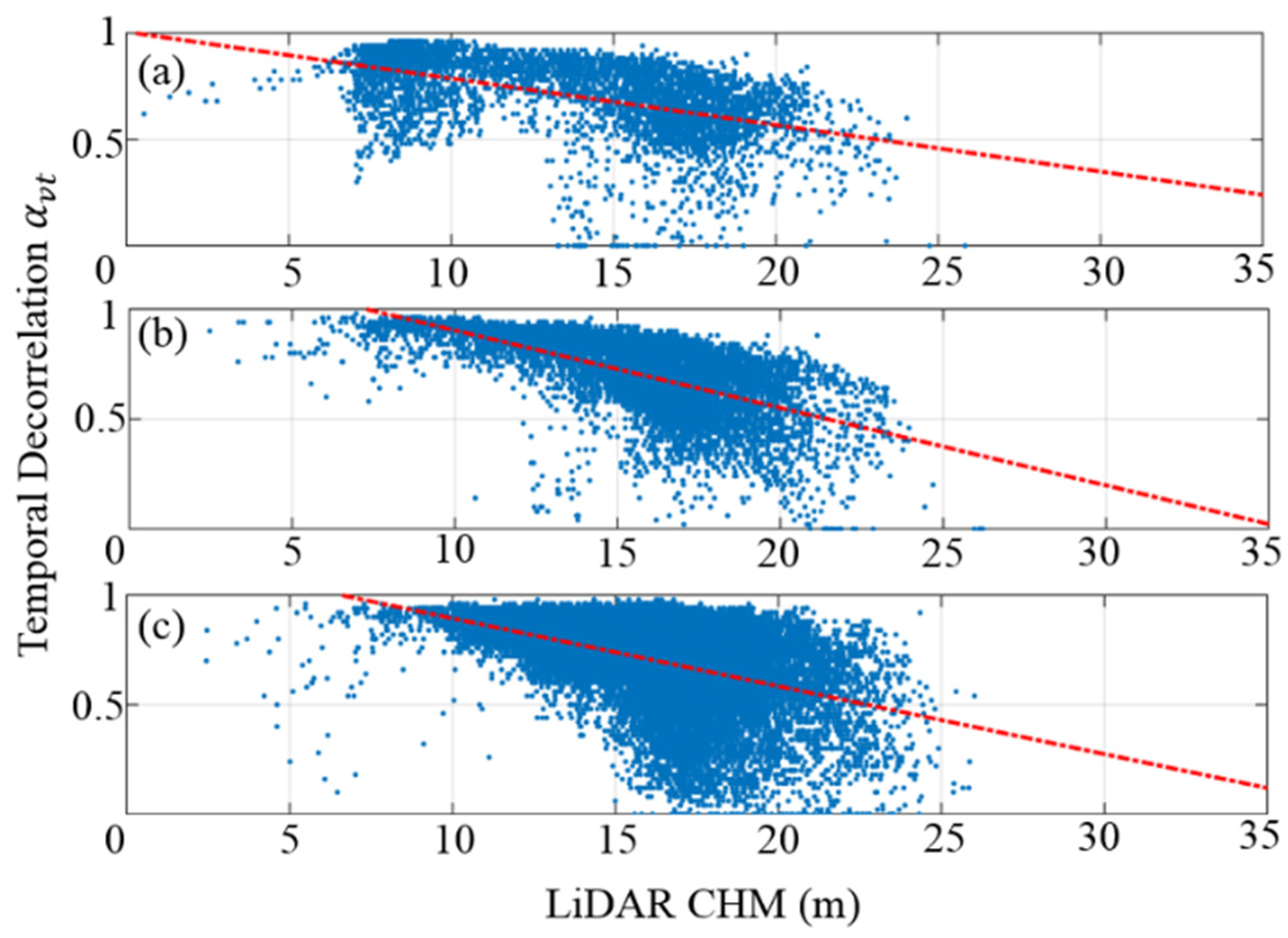
3.3. Results and Analyses
4. Discussion
4.1. The Limitation of the External DEM in the RME Correction
4.2. The Impact of the Rough Ranges of the in the Ground Scattering Error Removal
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rajendran, S.; Nasir, S. Aster capability in mapping of mineral resources of arid region: A review on mapping of mineral resources of the sultanate of oman. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 108, 33–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caicoya, A.T.; Kugler, F.; Hajnsek, I.; Papathanassiou, K.P. Large-scale biomass classification in boreal forests with tandem-x data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 5935–5951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Toan, T.; Quegan, S.; Davidson, M.W.J.; Balzter, H.; Paillou, P.; Papathanassiou, K.; Plummer, S.; Rocca, F.; Saatchi, S.; Shugart, H.; et al. The biomass mission: Mapping global forest biomass to better understand the terrestrial carbon cycle. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2850–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mette, T. Performance of forest biomass estimation from pol-insar and forest allometry over temperate forests. In Proceedings of the POLInSAR 2005, Frascati, Italy, 17–21 January 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Neumann, M.; Saatchi, S.S.; Ulander, L.M.H.; Fransson, J.E.S. Assessing performance of l- and p-band polarimetric interferometric sar data in estimating boreal forest above-ground biomass. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 714–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.Q. Method Development of Insar/Polinsar Sub-Canopy Topography and Forest Height Inversion Taking into Account Trend Error Correction and Observation Information Enhancement; Central South University: Changsha, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.; Kankare, V.; Hyyppä, J.; Wang, Y.; Kukko, A.; Haggrén, H.; Yu, X.; Kaartinen, H.; Jaakkola, A.; Guan, F.; et al. Terrestrial laser scanning in forest inventories. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 115, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltsavias, E.P. Airborne laser scanning: Existing systems and firms and other resources. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 1999, 54, 164–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutz, B.E.; Zwally, H.J.; Shuman, C.A.; Hancock, D.; DiMarzio, J.P. Overview of the icesat mission. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zebker, H.A.; Goldstein, R.M. Topographic mapping from interferometric synthetic aperture radar observations. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1986, 91, 4993–4999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellndorfer, J.; Walker, W.; Pierce, L.; Dobson, C.; Fites, J.A.; Hunsaker, C.; Vona, J.; Clutter, M. Vegetation height estimation from shuttle radar topography mission and national elevation datasets. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 93, 339–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, Y.; St-Onge, B.; Leblon, B.; Simard, M. Canopy height model (chm) derived from a tandem-x insar dsm and an airborne lidar dtm in boreal forest. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 381–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloude, S.R.; Papathanassiou, K.P. Polarimetric sar interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 1551–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papathanassiou, K.P.; Cloude, S.R. Single-baseline polarimetric sar interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 2352–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cloude, S.R.; Papathanassiou, K.P. Three-stage inversion process for polarimetric sar interferometry. IEE Proc.—Radar Sonar Navig. 2003, 150, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.K.; Fatoyinbo, T.E. Tandem-x pol-insar inversion for mangrove canopy height estimation. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 3608–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denbina, M.; Simard, M.; Hawkins, B. Forest height estimation using multibaseline polinsar and sparse lidar data fusion. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 3415–3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yang, J.; Shi, L.; Li, P.; Zhao, L.; Deng, S. Impact of backscatter in pol-insar forest height retrieval based on the multimodel random forest algorithm. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 17, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Wang, C.; Zhu, J.; Xie, Q.; Zhang, B. Estimation of pine forest height and underlying dem using multi-baseline p-band polinsar data. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pardini, M.; Kim, J.S.; Papathanassiou, K.; Hajnsek, I. 3-d structure observation of african tropical forests with multi-baseline sar: Results from the afrisar campaign. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Fort Worth, TX, USA, 23–28 July 2017; pp. 4288–4291. [Google Scholar]
- Dubois-Fernandez, P.C.; Souyris, J.C.; Angelliaume, S.; Garestier, F. The compact polarimetry alternative for spaceborne sar at low frequency. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 3208–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garestier, F.; Dubois-Fernandez, P.C.; Papathanassiou, K.P. Pine forest height inversion using single-pass x-band polinsar data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wang, B.; Xiang, M.; Fu, X.; Zhou, L.; Li, Y. S-rvog model inversion based on time-frequency optimization for p-band polarimetric sar interferometry. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.Q.; Zhu, J.J.; Wang, C.C.; Zhao, R.; Xie, Q.H. Underlying topography estimation over forest areas using single-baseline insar data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 2876–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Managhebi, T.; Maghsoudi, Y.; Valadan Zoej, M.J. An improved three-stage inversion algorithm in forest height estimation using single-baseline polarimetric sar interferometry data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 887–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhu, J.; Fu, H.; Feng, G.; Wang, C. Modeling and robust estimation for the residual motion error in airborne sar interferometry. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 16, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tupin, F.; Tison, C. Sub-aperture decomposition for sar urban area analysis. In Proceedings of the EUSAR 2004, Ulm, Germany, 25–27 May 2004; pp. 431–434. [Google Scholar]
- Souyris, J.C.; Henry, C.; Adragna, F. On the use of complex sar image spectral analysis for target detection: Assessment of polarimetry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 2725–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spigai, M.; Tison, C.; Souyris, J.C. Time-frequency analysis in high-resolution sar imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 2699–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garestier, F.; Dubois-Fernandez, P.C.; Champion, I. Forest height inversion using high-resolution p-band pol-insar data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 3544–3559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.W.; Ding, X.L.; Huang, C.; Zhu, J.J.; Chen, Y.L. Improved filtering parameter determination for the goldstein radar interferogram filter. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2008, 63, 621–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloude, S.R. Polarisation: Applications in Remote Sensing; Oxford Univ. Press: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lavalle, M.; Simard, M.; Hensley, S. A temporal decorrelation model for polarimetric radar interferometers. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 2880–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Sanchez, J.M.; Ballester-Berman, J.D.; Marquez-Moreno, Y. Model limitations and parameter-estimation methods for agricultural applications of polarimetric sar interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 3481–3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stevens, D.R.; Cumming, I.G.; Gray, A.L. Options for airborne interferometric sar motion compensation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1995, 33, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prats, P.; Mallorqui, J.J. Estimation of azimuth phase undulations with multisquint processing in airborne interferometric sar images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 1530–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reigber, A.; Prats, P.; Mallorqui, J.J. Refined estimation of time-varying baseline errors in airborne sar interferometry. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2006, 3, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kugler, F.; Seung-Kuk, L.; Hajnsek, I.; Papathanassiou, K.P. Forest height estimation by means of pol-insar data inversion: The role of the vertical wavenumber. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 5294–5311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.K.; Kugler, F.; Papathanassiou, K.P.; Hajnsek, I. Quantification of temporal decorrelation effects at l-band for polarimetric sar interferometry applications. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 1351–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papathanassiou, K.P.; Cloude, S.R. The effect of temporal decorrelation on the inversion of forest parameters from polinsar data. In Proceedings of the IGARSS, Toulouse, France, 15–21 July 2003; pp. 1429–1431. [Google Scholar]
- Simard, M.; Denbina, M. An assessment of temporal decorrelation compensation methods for forest canopy height estimation using airborne l-band same-day repeat-pass polarimetric sar interferometry. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 95–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, M.; Rosen, P.A. A generalized phase unwrapping approach for sparse data. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 1999, Hamburg, Germany, 28 June–2 July 1999; pp. 267–269. [Google Scholar]
- Tabb, M.; Orrey, J.; Flynn, T.; Carande, R. Phase diversity: A decomposition for vegetation parameter esti-mation using polarimetric sar interferometry. In Proceedings of the EUSAR 2002, Cologne, Germany, 4–6 June 2002; pp. 721–724. [Google Scholar]
- Cloude, S.R.; Papathanassiou, K.P. Coherence optimisation in polarimetric sar interferometry. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 1997, Hamburg, Singapore, 3–8 August 1997; pp. 1932–1934. [Google Scholar]
- Macedo, K.A.C.; Scheiber, R.; Moreira, A. An autofocusapproach for residual motion errors with application to airborne repeatpass SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 10, 3151–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perna, S.; Esposito, C.; Berardino, P.; Pauciullo, A.; Wimmer, C.; Lanari, R. Phase offset calculation for airborne InSAR DEM generationwithout corner reflectors. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 5, 2713–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Fu, H.; Zhu, J.; Feng, G.; Yang, Z.; Wang, C.; Hu, J.; Yu, Y. Correction of time-varying baseline errors based on multibaseline airborne interferometric data without high-precision dems. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 9307–9318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


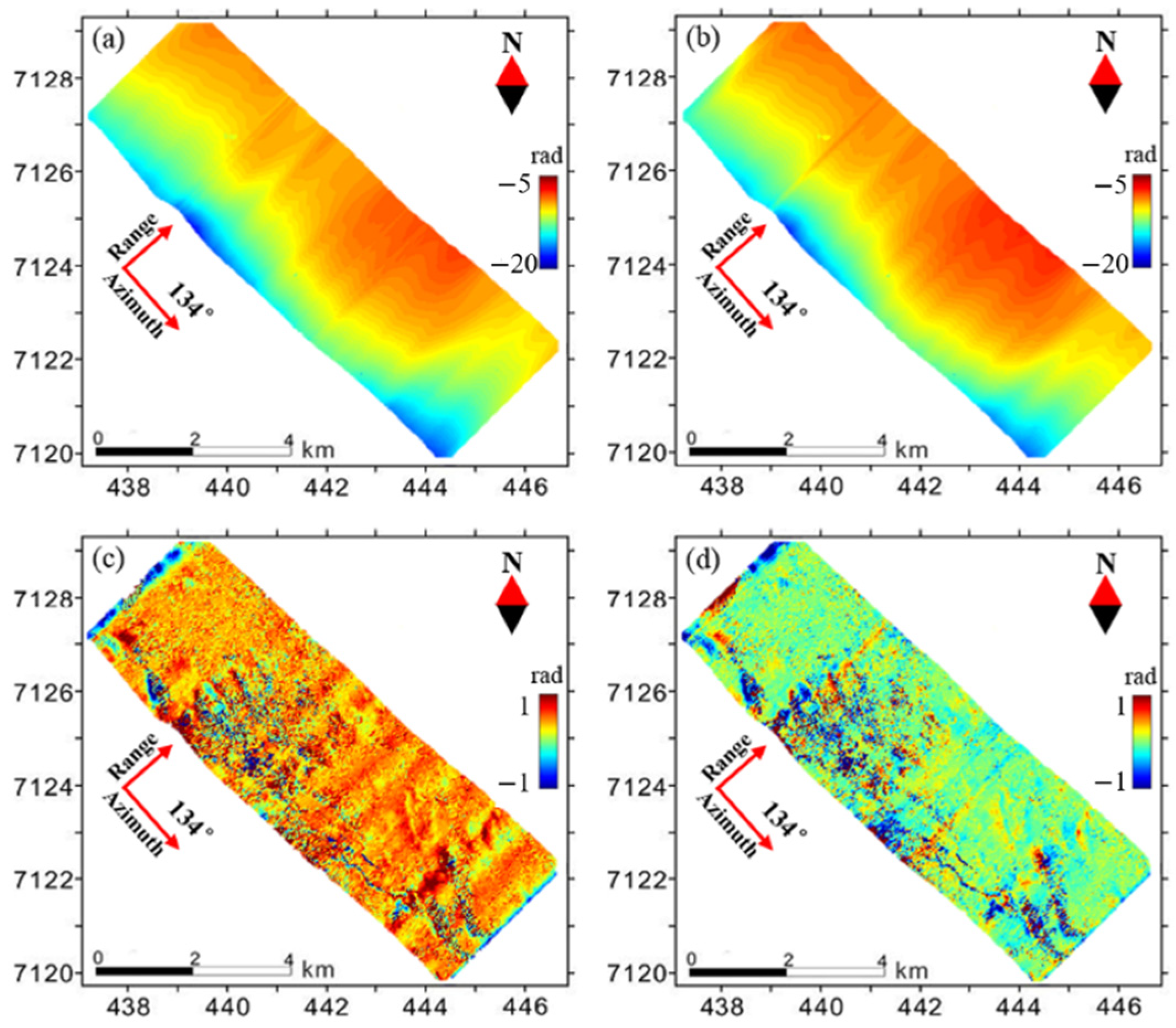

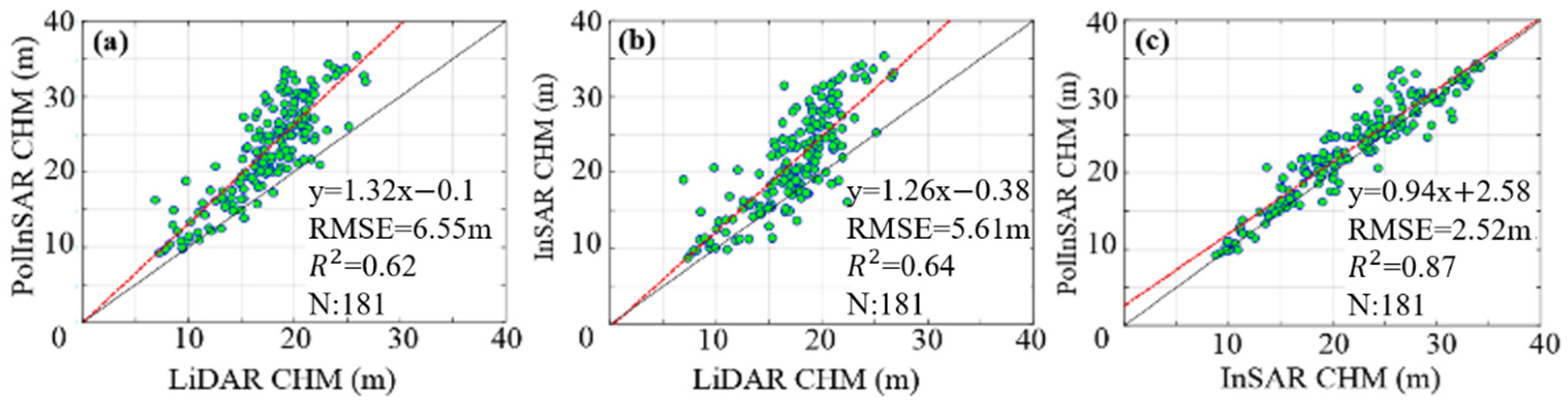

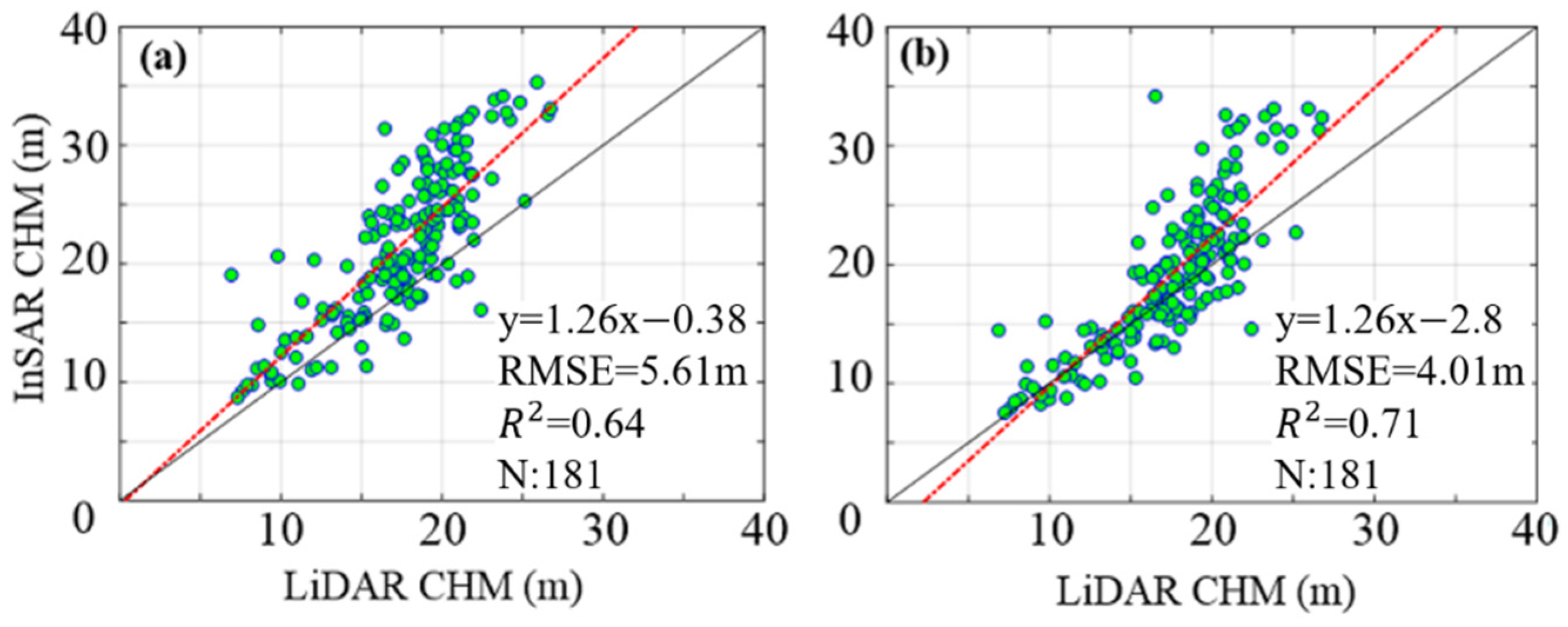

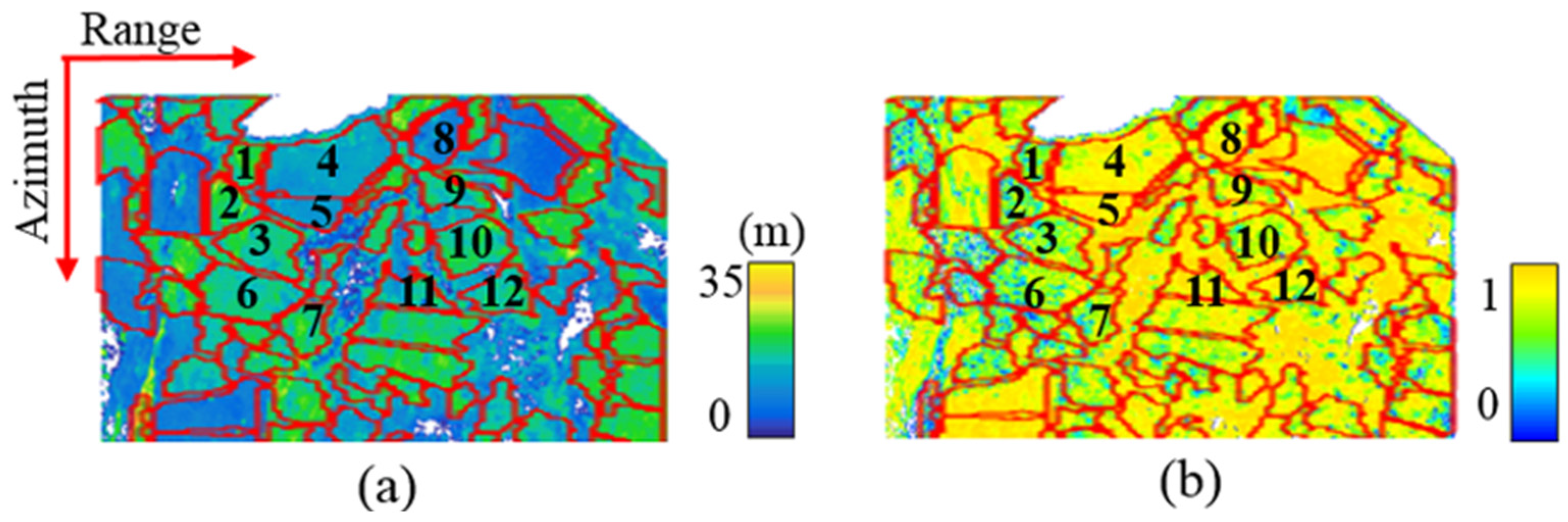

| Index Range | Extinction Coefficient Range (dB/m) |
|---|---|
| 0–0.4 | 0.6–1 |
| 0.4–0.65 | 0.3–0.6 |
| >0.65 | 0–0.3 |
| InSAR CHM (m) | InSAR CHM with a Limited | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.4 | 14.5 | 9.5 | 0.126 |
| 0.32 | 21 | 14.5 | 0.267 |
| 0.43 | 20.5 | 14 | 0.198 |
| 0.71 | 35 | 35 | 0 |
| 0.22 | 17 | 12.5 | 0.055 |
| 0.23 | 22.5 | 15 | 0.054 |
| 2.02 | 6.5 | 6.5 | 0 |
| 0.82 | 32 | 32 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Shen, G.; Xiong, J.; Shi, H. Forest Height Inversion Based on Time–Frequency RVoG Model Using Single-Baseline L-Band Sublook-InSAR Data. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15010166
Wang L, Zhou Y, Shen G, Xiong J, Shi H. Forest Height Inversion Based on Time–Frequency RVoG Model Using Single-Baseline L-Band Sublook-InSAR Data. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(1):166. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15010166
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Lei, Yushan Zhou, Gaoyun Shen, Junnan Xiong, and Hongtao Shi. 2023. "Forest Height Inversion Based on Time–Frequency RVoG Model Using Single-Baseline L-Band Sublook-InSAR Data" Remote Sensing 15, no. 1: 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15010166
APA StyleWang, L., Zhou, Y., Shen, G., Xiong, J., & Shi, H. (2023). Forest Height Inversion Based on Time–Frequency RVoG Model Using Single-Baseline L-Band Sublook-InSAR Data. Remote Sensing, 15(1), 166. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15010166







