An Effective Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Approach via Rolling Guidance Filtering and Gradient Saliency Map
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
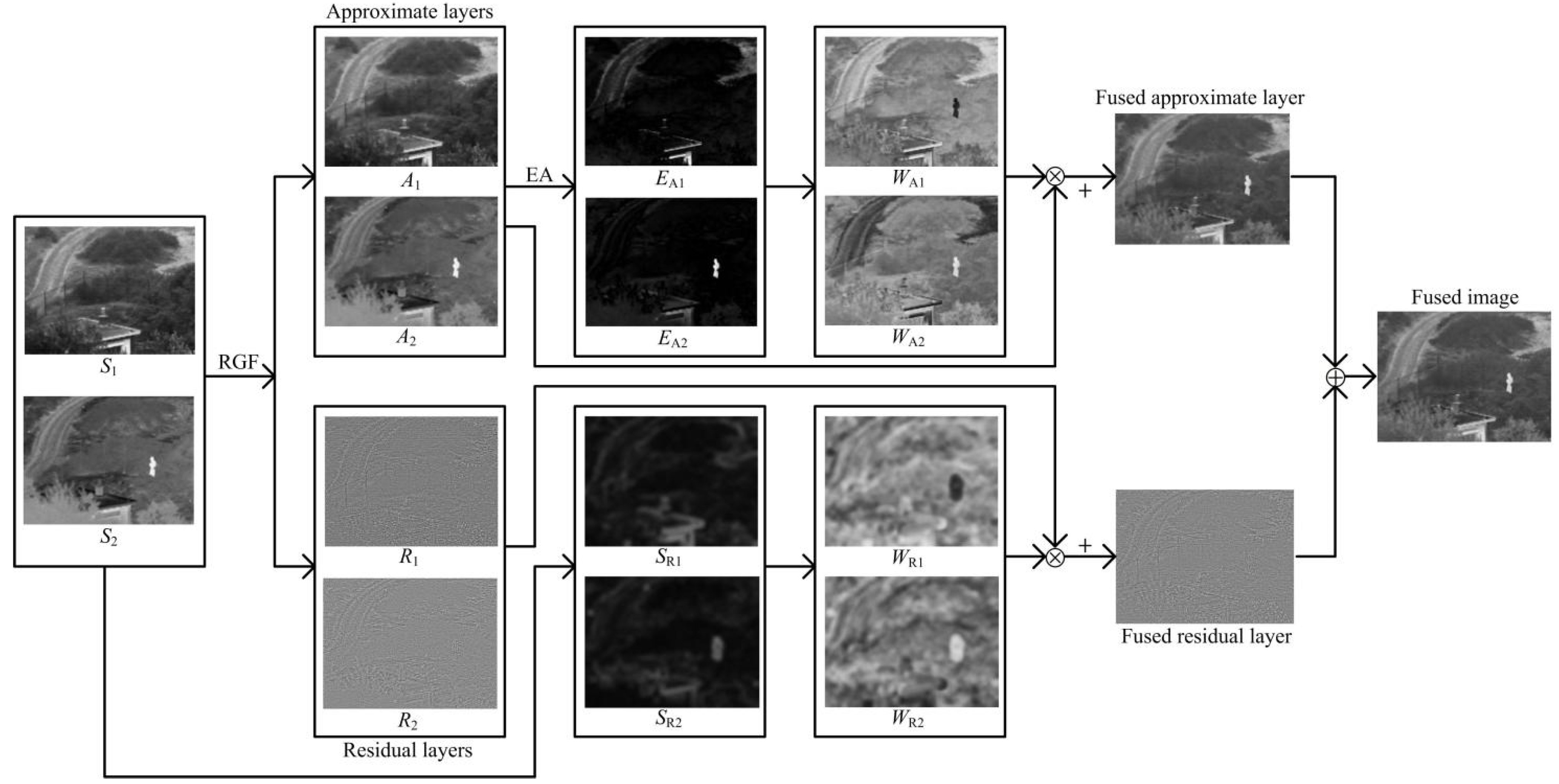
- The rolling guidance filter is introduced as the decomposition structure, and the approximate and residual layers of the source images are generated.
- (2)
- The approximate layers contain most of the background and energy information of the source images, and the energy attribute (EA) fusion strategy is applied to fuse the approximate layers.
- (3)
- The residual layers contain small gradient textures and noise; the gradient saliency map and corresponding weight matrices are constructed to fuse the residual layers.
- (4)
- This method is superior to most fusion algorithms and provides an important approach for assisting target detection.
2. Rolling Guidance Filtering
3. The Proposed Method
- Step 1. Image decomposition
- Step 2. The approximate layer fusion
- Step 3. The residual layer fusion
- Step 4. Image reconstruction
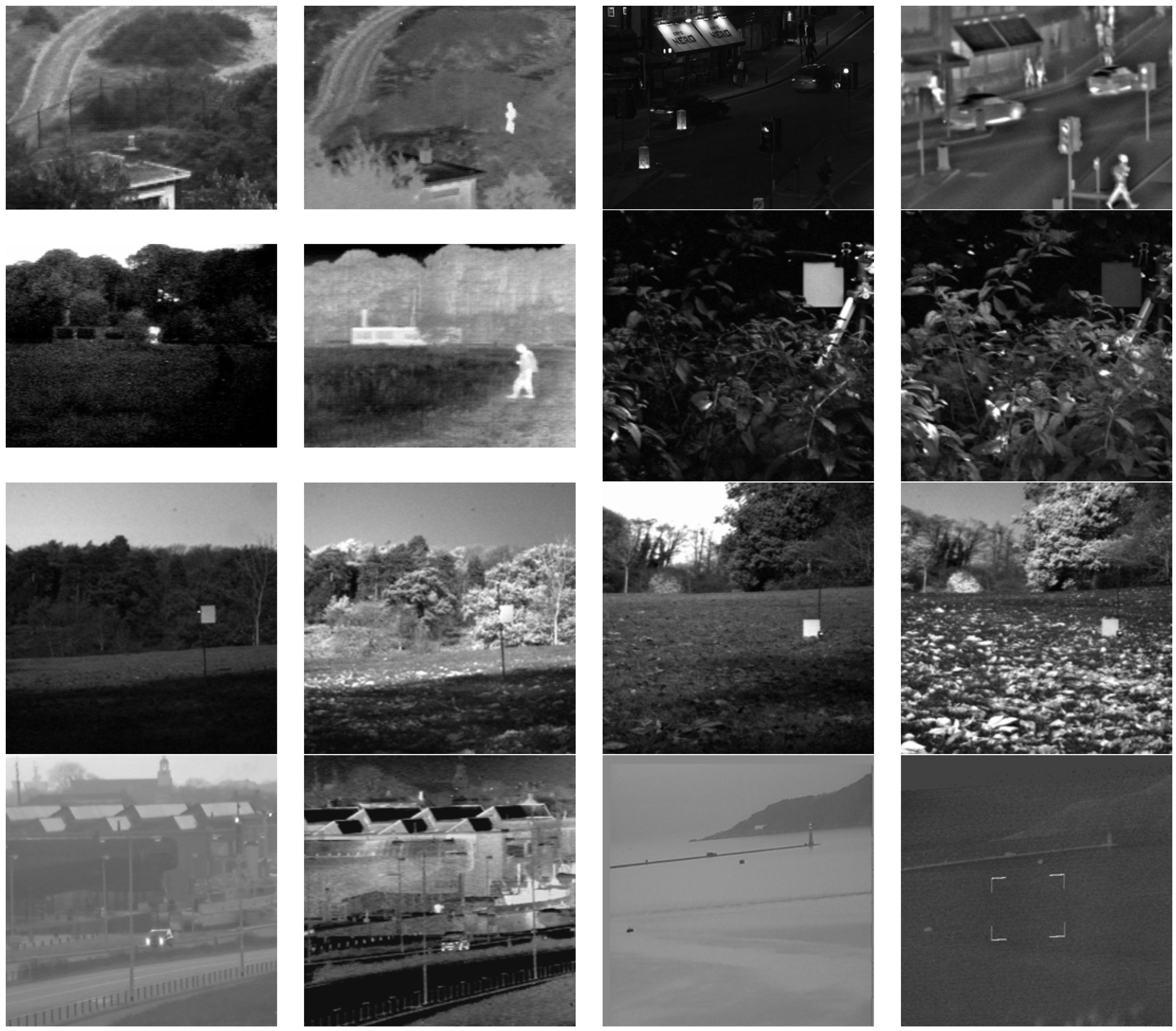
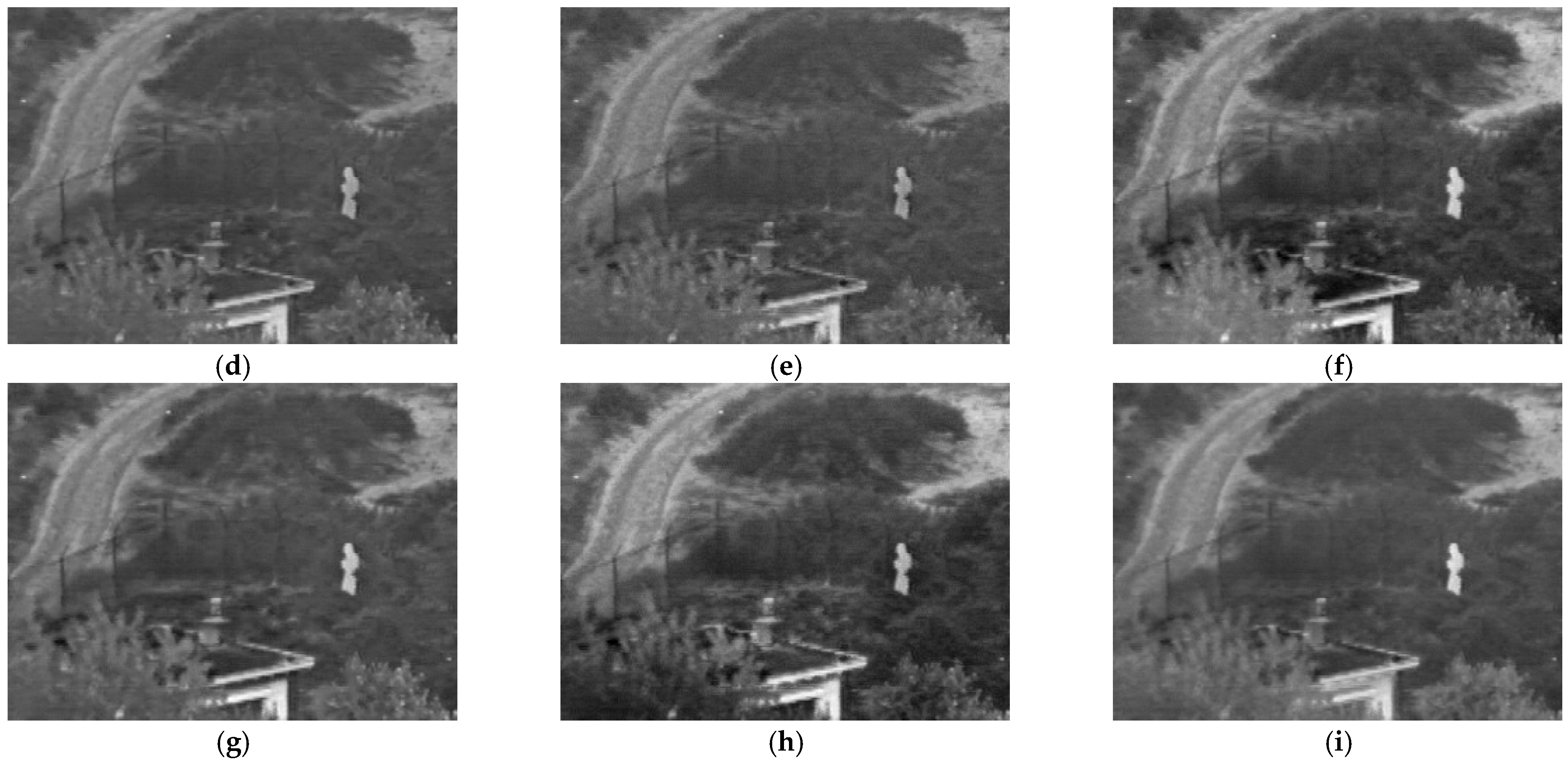
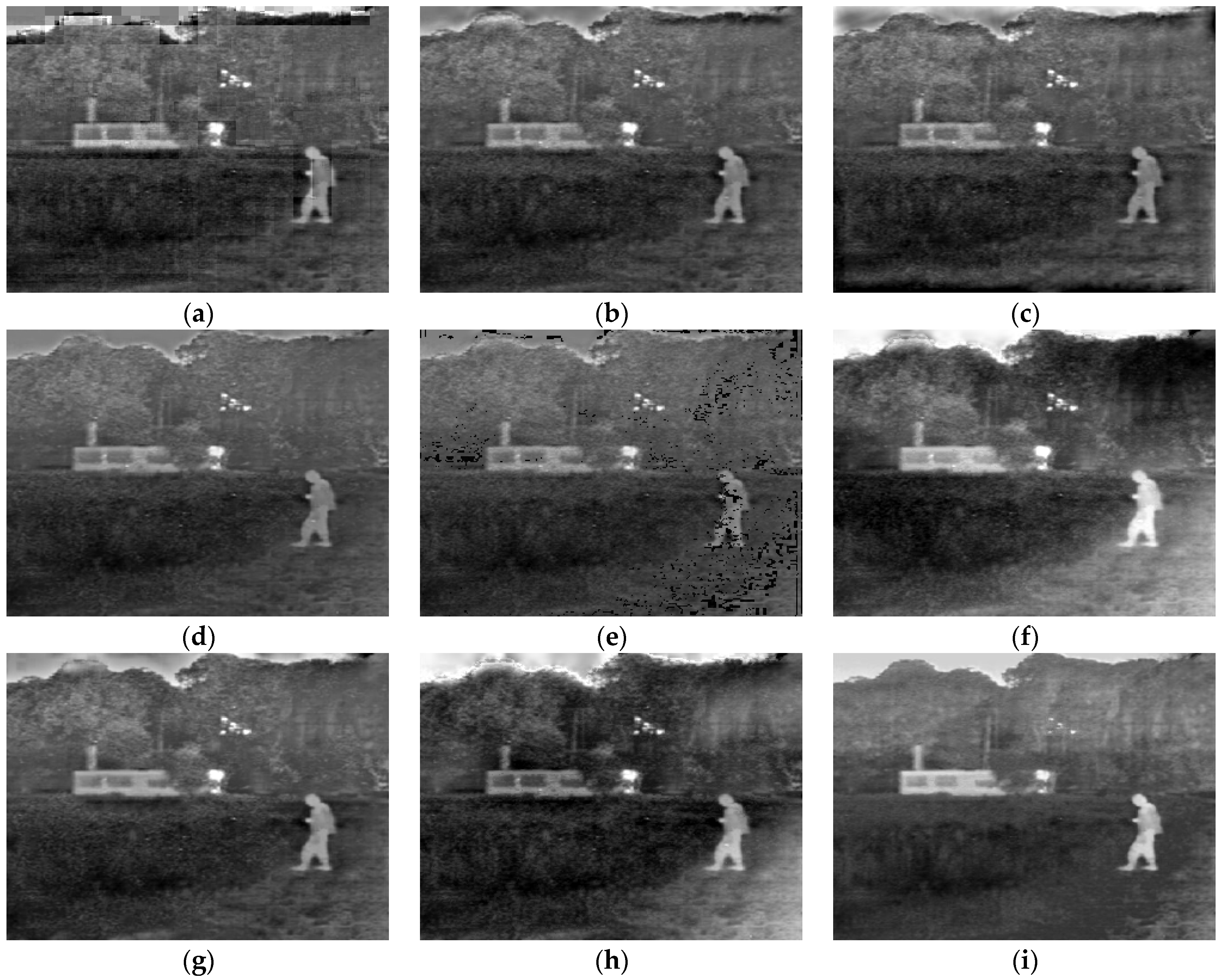
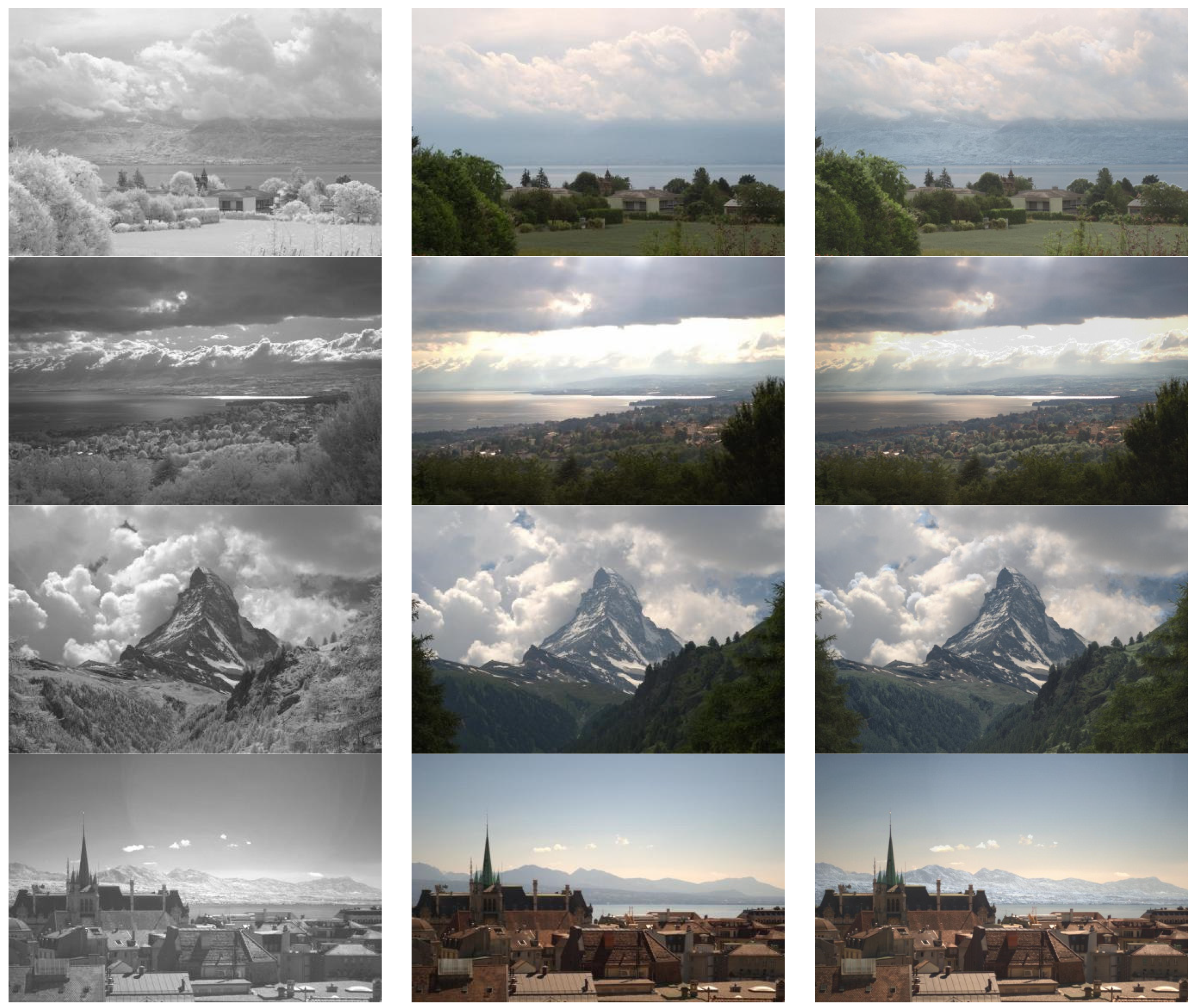
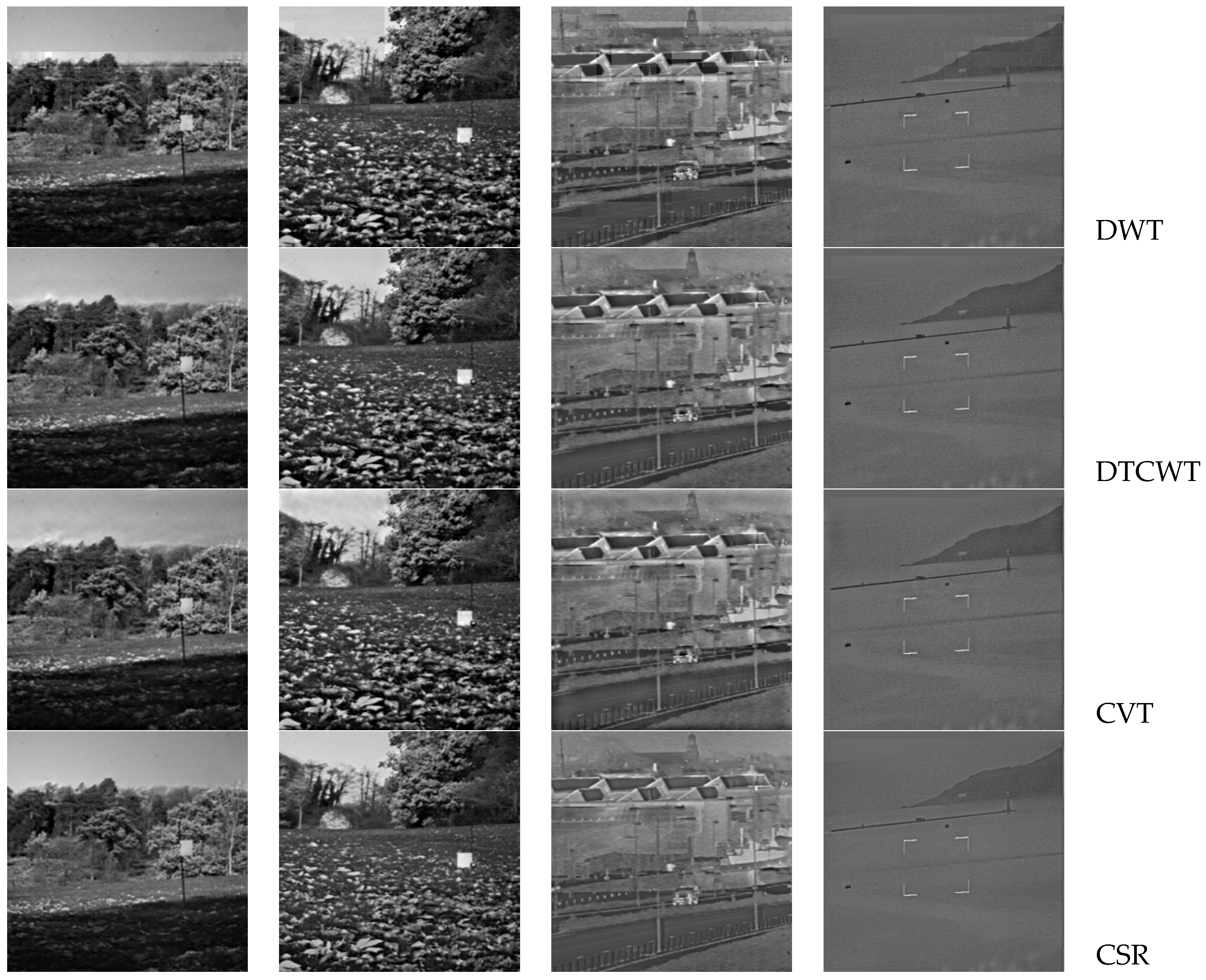
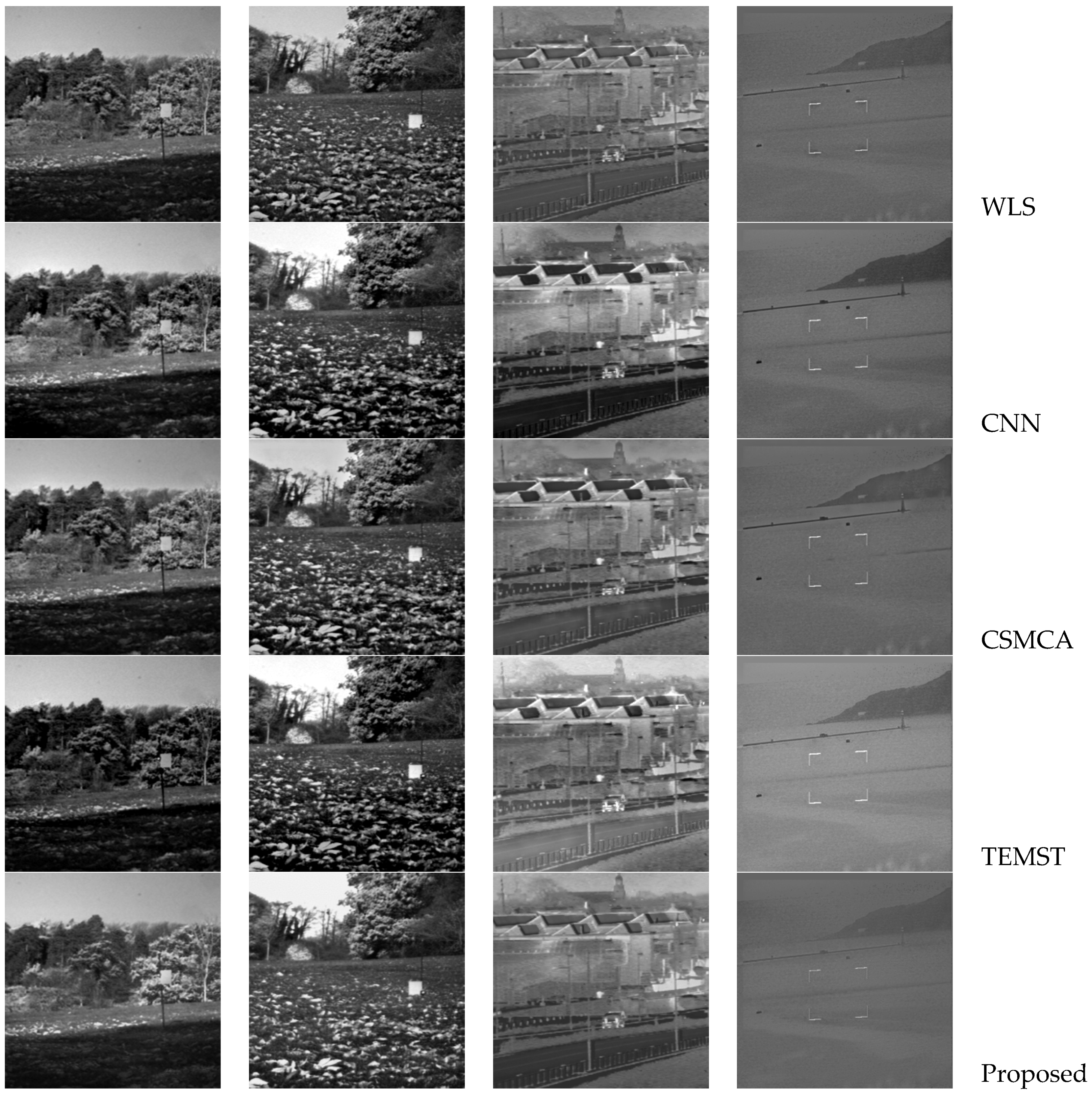
4. Experimental Results and Discussion
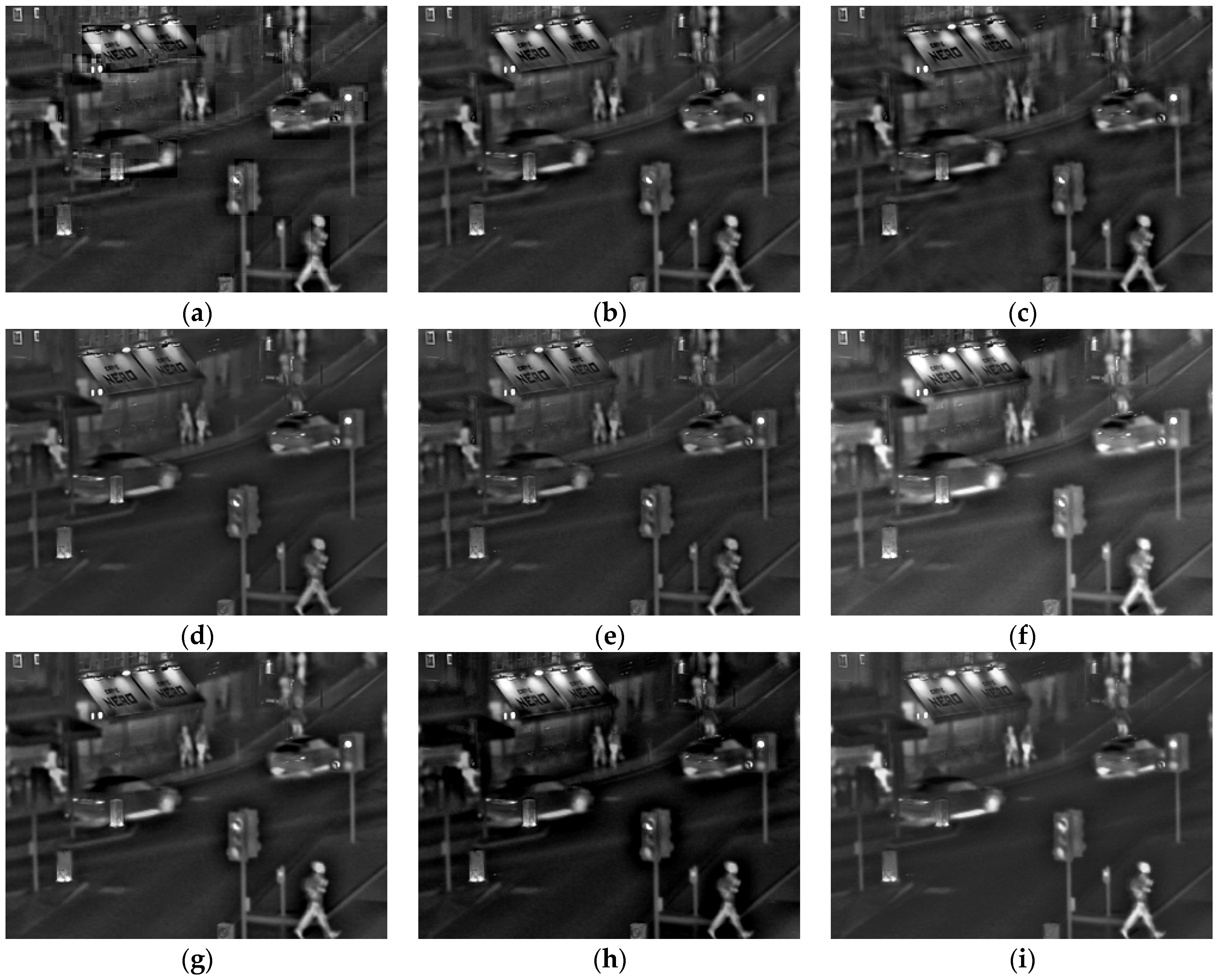
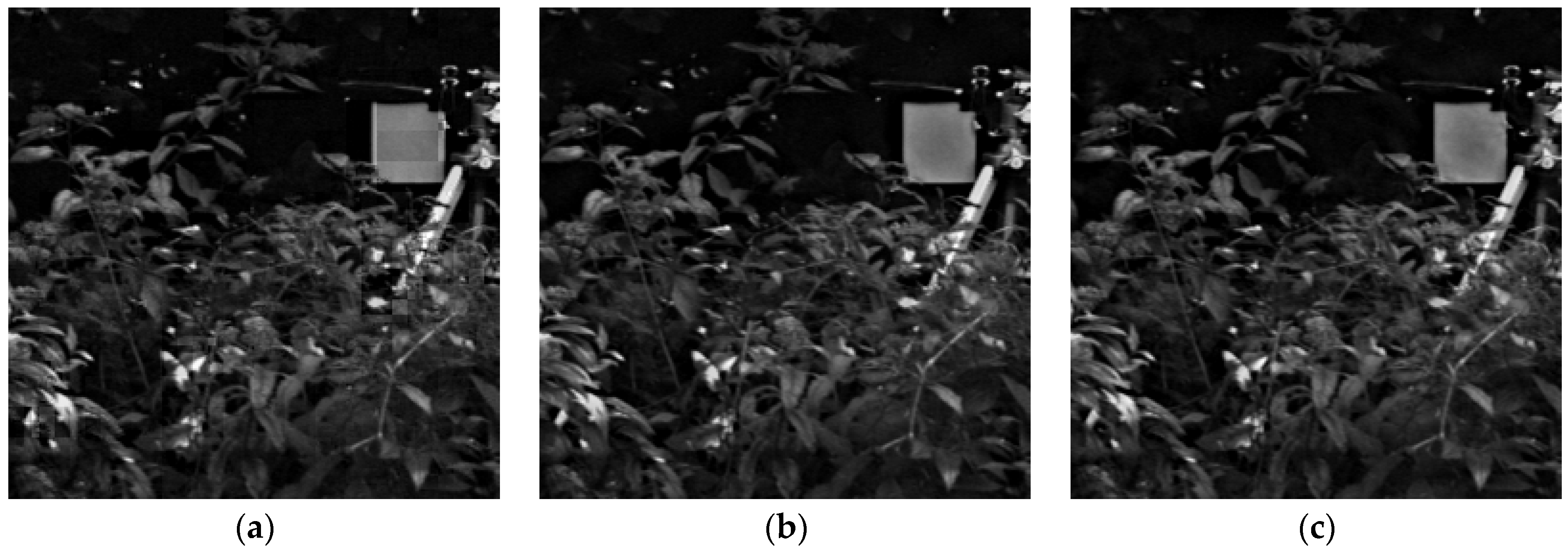
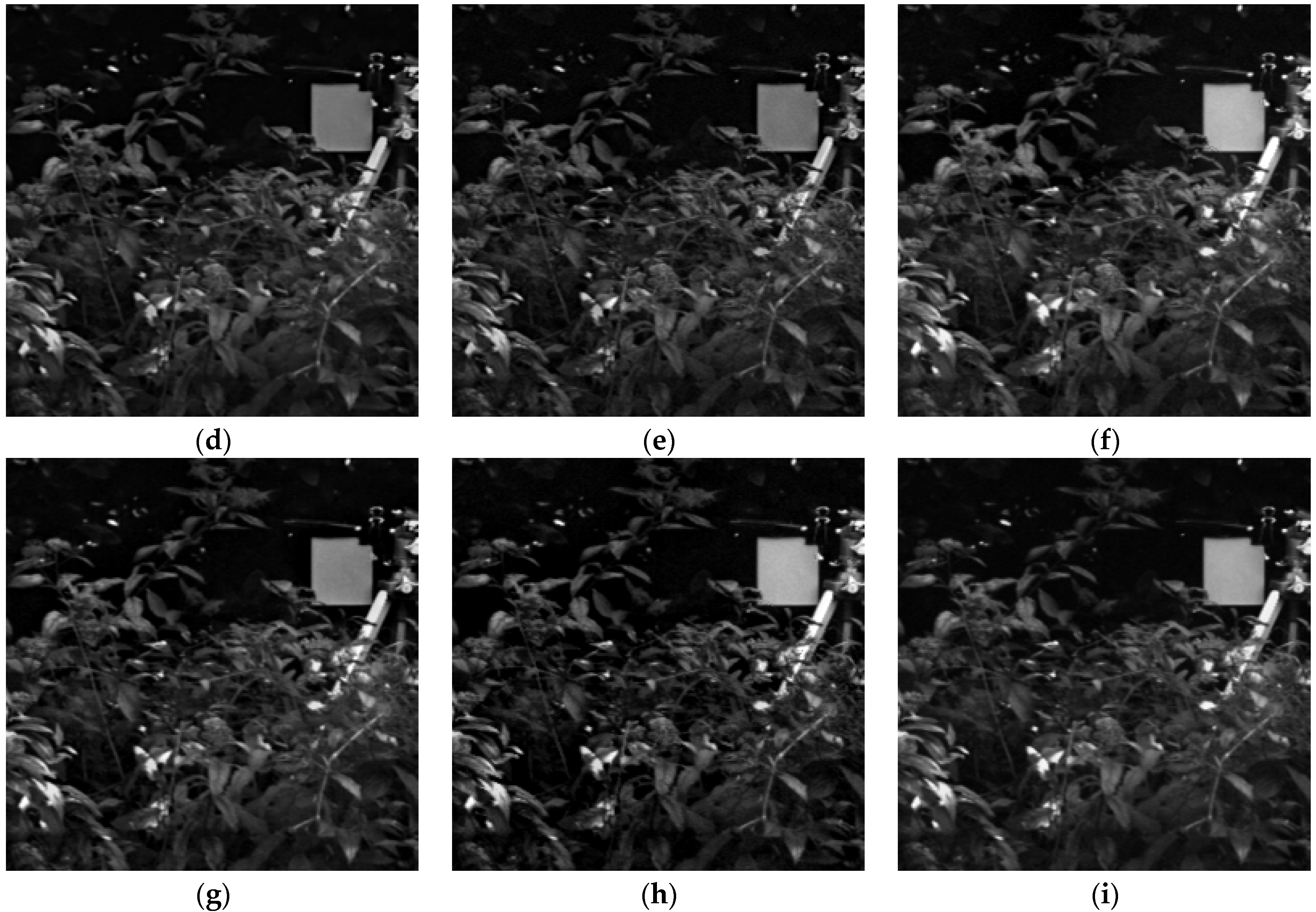
4.1. Subjective Evaluation
4.2. Objective Evaluation
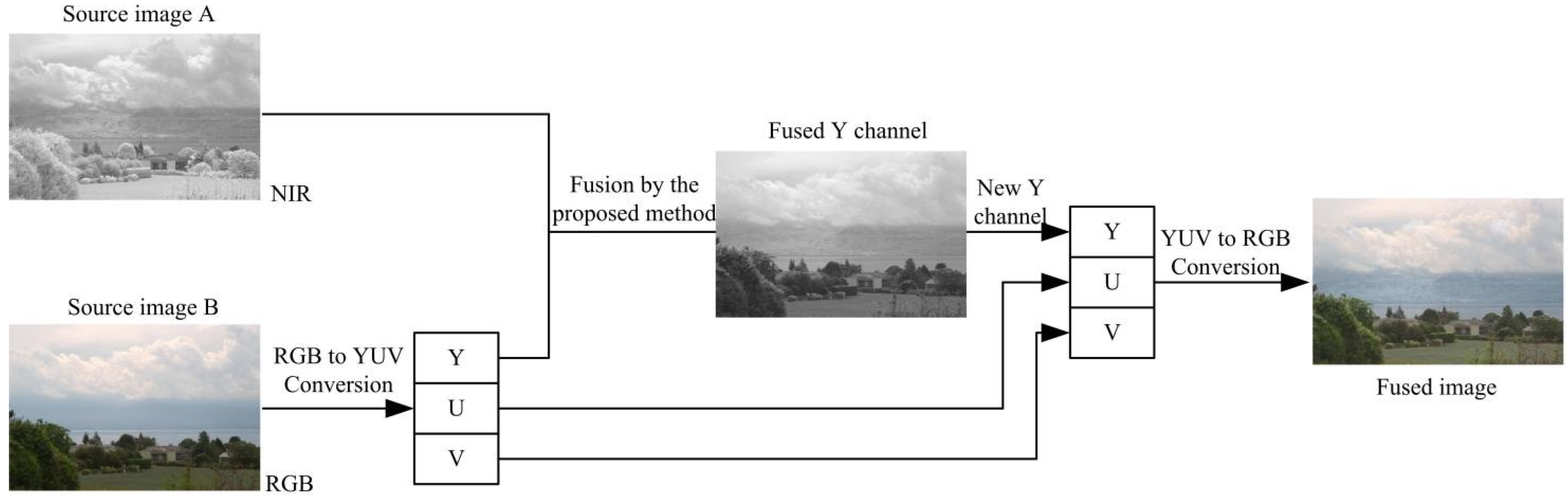
4.3. Application on RGB and Near-Infrared Fusion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, J.; Ma, Y.; Li, C. Infrared and visible image fusion methods and applications: A survey. Inf. Fusion 2019, 45, 153–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Shen, Y.; Han, S. Dense-FG: A fusion GAN model by using densely connected blocks to fuse infrared and visible images. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, J. Multi-focus image fusion: A Survey of the state of the art. Inf. Fusion 2020, 64, 71–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z. Deep learning for pixel-level image fusion: Recent advances and future prospects. Inf. Fusion 2018, 42, 158–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, S.; Tong, G.; Li, J. Current advances and future perspectives of image fusion: A comprehensive review. Inf. Fusion 2023, 90, 185–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Kang, X.; Fang, L. Pixel-level image fusion: A survey of the state of the art. Inf. Fusion 2017, 33, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z. A novel medical image fusion approach based on nonsubsampled shearlet transform. J. Med. Imaging Health Inform. 2019, 9, 1815–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, C.; Chouhan, K.; Rout, R. Improved procedure for multi-focus images using image fusion with qshiftN DTCWT and MPCA in Laplacian pyramid domain. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivone, G.; Marano, S.; Chanussot, J. Pansharpening: Context-based generalized Laplacian pyramids by robust regression. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 6152–6167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Tsukada, K.; Hanasaki, K. Image fusion by using steerable pyramid. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2001, 22, 929–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Chen, J.; Rahardja, S. A new multi-focus image fusion algorithm and its efficient implementation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2020, 30, 1374–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, A.; Elashmawi, W.; Eltaweel, G. IHS-based pan-sharpening technique for visual quality improvement using KPCA and enhanced SML in the NSCT domain. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 42, 537–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Fei, X.; Feng, J. Pan-sharpening via multi-scale and multiple deep neural networks. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2020, 85, 115850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, B.; Jin, L.; Li, G. Infrared and visible image fusion based on co-occurrence analysis shearlet transform. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Gao, H.; Zhang, C. Infrared and visible image fusion using intensity transfer and phase congruency in nonsubsampled shearlet transform domain. Ukr. J. Phys. Opt. 2022, 23, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Lv, M.; Jia, Z.; Ma, H. Sparse representation-based multi-focus image fusion method via local energy in shearlet domain. Sensors 2023, 23, 2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, A. Recent advances in sparse representation based medical image fusion. IEEE Instrum. Meas. Mag. 2021, 24, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejati, M.; Samavi, S.; Shirani, S. Multi-focus image fusion using dictionary-based sparse representation. Inf. Fusion 2015, 25, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, Z. Joint sparse model with coupled dictionary for medical image fusion. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2023, 79, 104030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wu, Y. Joint patch clustering-based adaptive dictionary and sparse representation for multi-modality image fusion. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2022, 33, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Cen, Y.; Liu, Y. Different input resolutions and arbitrary output resolution: A meta learning-based deep framework for infrared and visible image fusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 4070–4083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.; Xu, T.; Wu, X. MUFusion: A general unsupervised image fusion network based on memory unit. Inf. Fusion 2023, 92, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lei, W. Infrared and visible image fusion with entropy-based adaptive fusion module and mask-guided convolutional neural network. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2023, 131, 104629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Li, Y. MCnet: Multiscale visible image and infrared image fusion network. Signal Process. 2023, 208, 108996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Zhang, X. IFormerFusion: Cross-domain frequency information learning for infrared and visible image fusion based on the inception transformer. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ma, H. Saliency-guided nonsubsampled shearlet transform for multisource remote sensing image fusion. Sensors 2021, 21, 1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Si, Y.; Wang, L. A novel approach for multi-focus image fusion based on SF-PAPCNN and ISML in NSST domain. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 24303–24328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X. Injected infrared and visible image fusion via L-1 decomposition model and guided filtering. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging 2022, 8, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Kang, X.; Hu, J. Image fusion with guided filtering. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 22, 2864–2875. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Yin, L.; Miao, S. Multimodal medical image fusion using rolling guidance filter with CNN and nuclear norm minimization. Curr. Med. Imaging 2020, 16, 1243–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, D.; Yang, B. Infrared and low-light visible image fusion based on hybrid multiscale decomposition and adaptive light adjustment. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2023, 160, 107268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Shen, X.; Xu, L. Rolling guidance filter. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2014, 8691, 815–830. [Google Scholar]
- Goyal, B.; Dogra, A. Multi-modality image fusion for medical assistive technology management based on hybrid domain filtering. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 209, 118283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prema, G.; Arivazhagan, S. Infrared and visible image fusion via multi-scale multi-layer rolling guidance filter. Pattern Anal. Appl. 2022, 25, 933–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, L. A novel medical image fusion method based on rolling guidance filtering. Internet Things 2021, 14, 100172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Cao, D.; Zhou, X. Adaptive infrared and visible image fusion method by using rolling guidance filter and saliency detection. Optik 2022, 262, 169218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.; Thitøn, W.; Xiang, P.; Zhou, H. Multi-modal brain image fusion based on multi-level edge-preserving filtering. BioMed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 64, 102280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhou, Y. Infrared and visible image fusion via gradientlet filter. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2020, 197, 103016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Bai, X.; Wang, T. Boundary finding based multi-focus image fusion through multi-scale morphological focus-measure. Inf. Fusion 2017, 35, 81–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z. A general framework for image fusion based on multi-scale transform and sparse representation. Inf. Fusion 2015, 24, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Ward, R.; Wang, Z. Image fusion with convolutional sparse representation. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2016, 23, 1882–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, B. Infrared and visible image fusion based on visual saliency map and weighted least square optimization. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2017, 82, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Cheng, J. Infrared and visible image fusion with convolutional neural networks. Int. J. Wavelets Multiresolution Inf. Process. 2018, 16, 1850018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Ward, R.K. Medical image fusion via convolutional sparsity based morphological component analysis. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2019, 26, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, X.; Luo, L. Infrared and visible image fusion based on target-enhanced multiscale transform decomposition. Inf. Sci. 2020, 508, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Yan, J.; Xiao, H. Image fusion algorithm based on spatial frequency-motivated pulse coupled neural networks in nonsubsampled contourlet transform domain. Acta Autom. Sin. 2008, 34, 1508–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ma, H.; Jia, Z. A novel multiscale transform decomposition based multi-focus image fusion framework. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 12389–12409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Gao, S. Visible-infrared image fusion based on early visual information processing mechanisms. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2021, 31, 4357–4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Blum, R. A new automated quality assessment algorithm for image fusion. Image Vis. Comput. 2009, 27, 1421–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, J. A nonlinear correlation measure for multivariable data set. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 2005, 200, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslantas, V.; Bendes, E. A new image quality metric for image fusion: The sum of the correlations of differences. AEU Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2015, 69, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ma, H. Pulse coupled neural network-based multimodal medical image fusion via guided filtering and WSEML in NSCT domain. Entropy 2021, 23, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shreyamsha, K. Image fusion based on pixel significance using cross bilateral filter. Signal Image Video Process. 2015, 9, 1193–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, J.; Huang, S. Infrared and visible image fusion via texture conditional generative adversarial network. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2021, 31, 4771–4783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanmali, A.; Gadre, V. Visible and NIR image fusion using weight-map-guided Laplacian-Gaussian pyramid for improving scene visibility. Sadhana-Acad. Proc. Eng. Sci. 2017, 42, 1063–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Zhao, W.; Lu, H. Depth-distilled multi-focus image fusion. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2023, 25, 966–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chan, T. Detail-preserving multi-exposure fusion with edge-preserving structural patch decomposition. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2021, 31, 4293–4304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Han, D.; Wang, X.; Yi, P.; Yan, L.; Li, X. Multi-sensor medical-image fusion technique based on embedding bilateral filter in least squares and salient detection. Sensors 2023, 23, 3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xia, Z.; Han, H. Infrared and visible image fusion using a shallow CNN and structural similarity constraint. IET Image Process. 2020, 14, 3562–3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




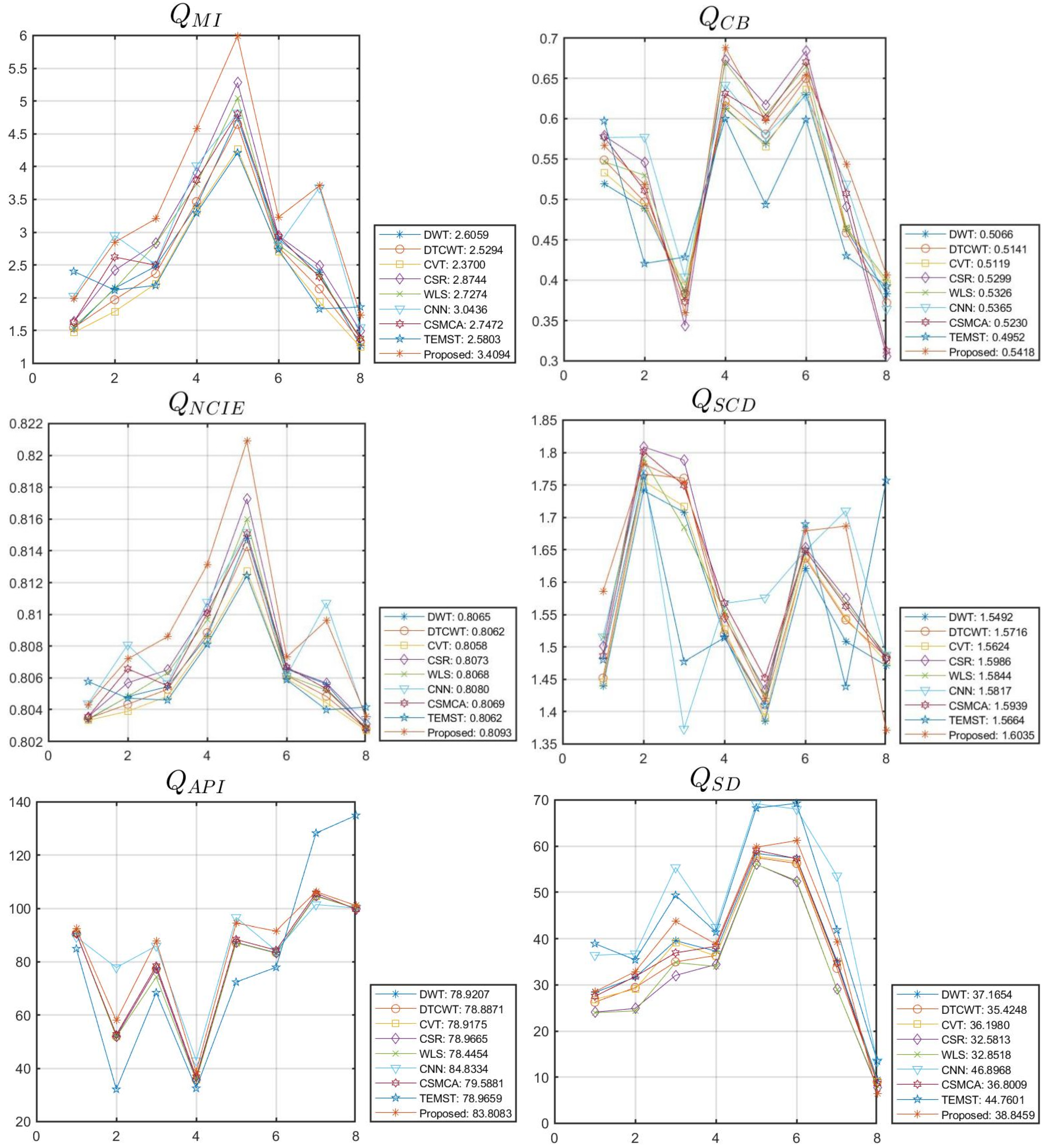


| QMI | QCB | QNCIE | QSCD | QAPI | QSD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DWT | 2.6059 | 0.5066 | 0.8065 | 1.5492 | 78.9207 | 37.1654 |
| DTCWT | 2.5294 | 0.5141 | 0.8062 | 1.5716 | 78.8871 | 35.4248 |
| CVT | 2.3700 | 0.5119 | 0.8058 | 1.5624 | 78.9175 | 36.1980 |
| CSR | 2.8744 | 0.5299 | 0.8073 | 1.5986 | 78.9665 | 32.5813 |
| WLS | 2.7274 | 0.5326 | 0.8068 | 1.5844 | 78.4454 | 32.8518 |
| CNN | 3.0436 | 0.5365 | 0.8080 | 1.5817 | 84.8334 | 46.8968 |
| CSMCA | 2.7472 | 0.5230 | 0.8069 | 1.5939 | 79.5881 | 36.8009 |
| TEMST | 2.5803 | 0.4952 | 0.8062 | 1.5664 | 78.9659 | 44.7601 |
| Proposed | 3.4094 | 0.5418 | 0.8093 | 1.6035 | 83.8083 | 38.8459 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, L.; Lv, M.; Jia, Z.; Jin, Q.; Liu, M.; Chen, L.; Ma, H. An Effective Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Approach via Rolling Guidance Filtering and Gradient Saliency Map. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2486. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102486
Li L, Lv M, Jia Z, Jin Q, Liu M, Chen L, Ma H. An Effective Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Approach via Rolling Guidance Filtering and Gradient Saliency Map. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(10):2486. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102486
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Liangliang, Ming Lv, Zhenhong Jia, Qingxin Jin, Minqin Liu, Liangfu Chen, and Hongbing Ma. 2023. "An Effective Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Approach via Rolling Guidance Filtering and Gradient Saliency Map" Remote Sensing 15, no. 10: 2486. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102486
APA StyleLi, L., Lv, M., Jia, Z., Jin, Q., Liu, M., Chen, L., & Ma, H. (2023). An Effective Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Approach via Rolling Guidance Filtering and Gradient Saliency Map. Remote Sensing, 15(10), 2486. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102486







