Mapping Waterlogging Damage to Winter Wheat Yield Using Downscaling–Merging Satellite Daily Precipitation in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data Processing
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data and Processing
2.2.1. Remote Sensing Data
- (1)
- TRMM 3B42
- (2)
- Soil moisture data
- (3)
- AVHRR NDVI data
- (4)
- Winter wheat map
- (5)
- DEM data
2.2.2. Statistics Datasets
- (1)
- Rain gauge data
- (2)
- Winter wheat yield data
3. Method
3.1. Precipitation Downscaling and Fusion
3.2. Waterlogging Mapping
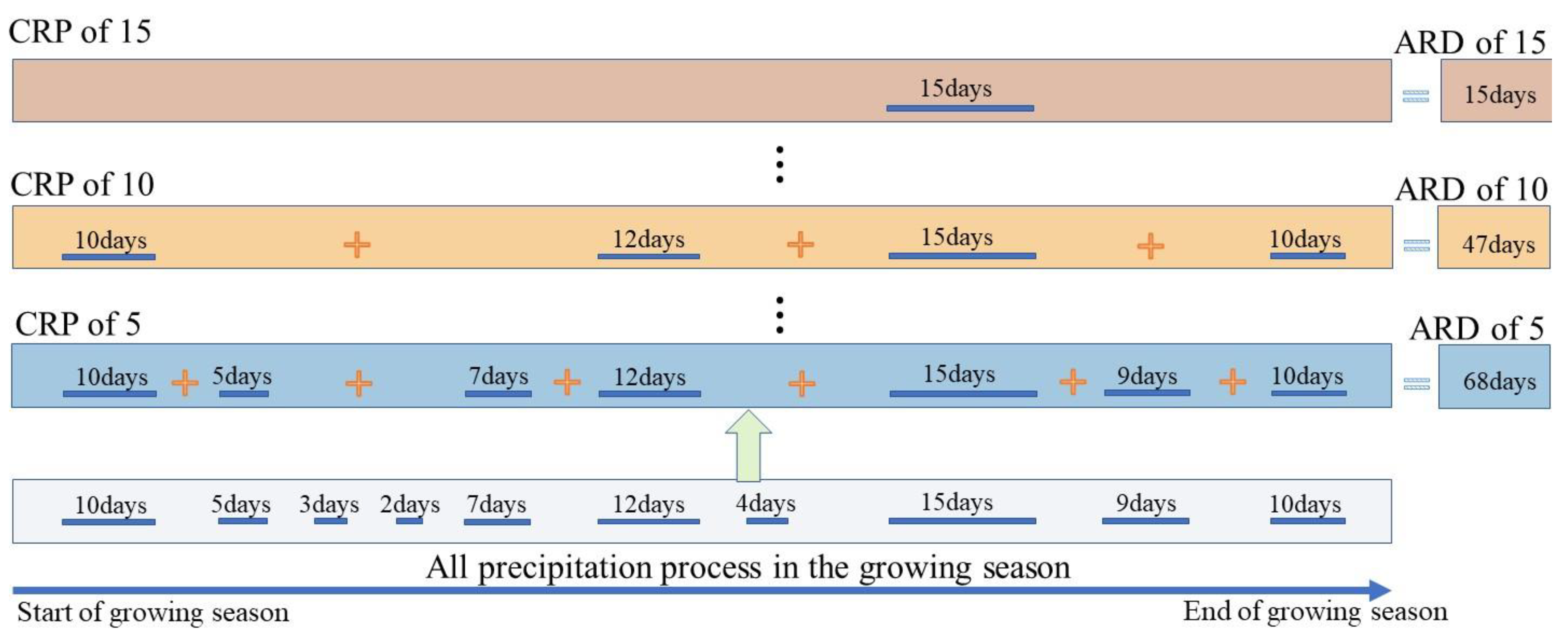
3.2.1. Waterlogging Index (WI) Based on Accumulated Number of Rainy Days
3.2.2. Quantifying Waterlogging Damage to Winter Wheat Yield
3.2.3. Mapping Waterlogging Damage to Winter Wheat Yield Using WI
3.3. Validation
4. Results
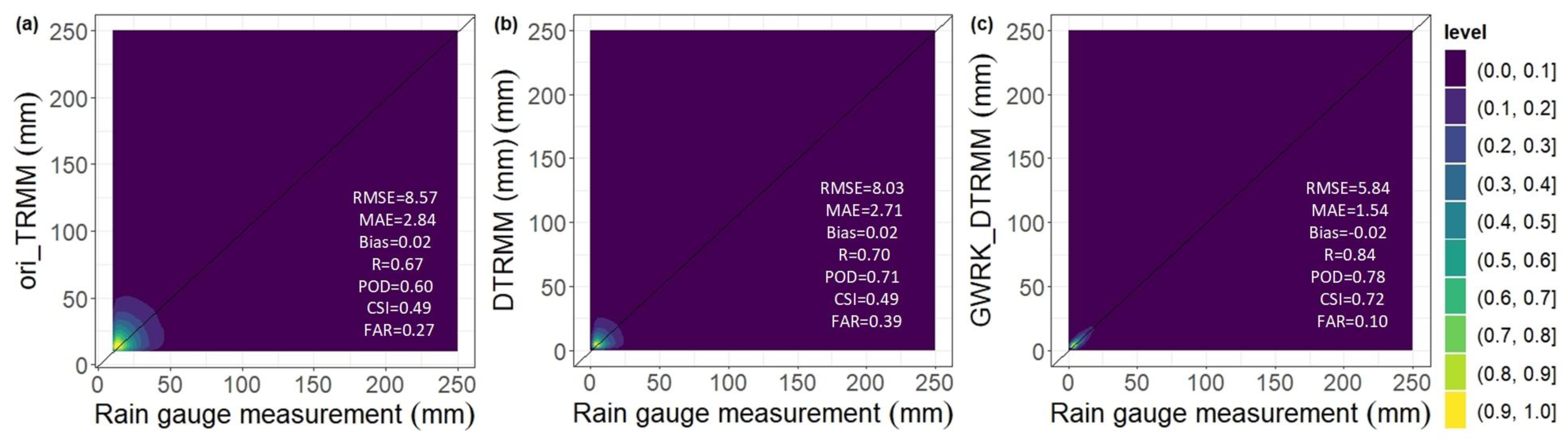
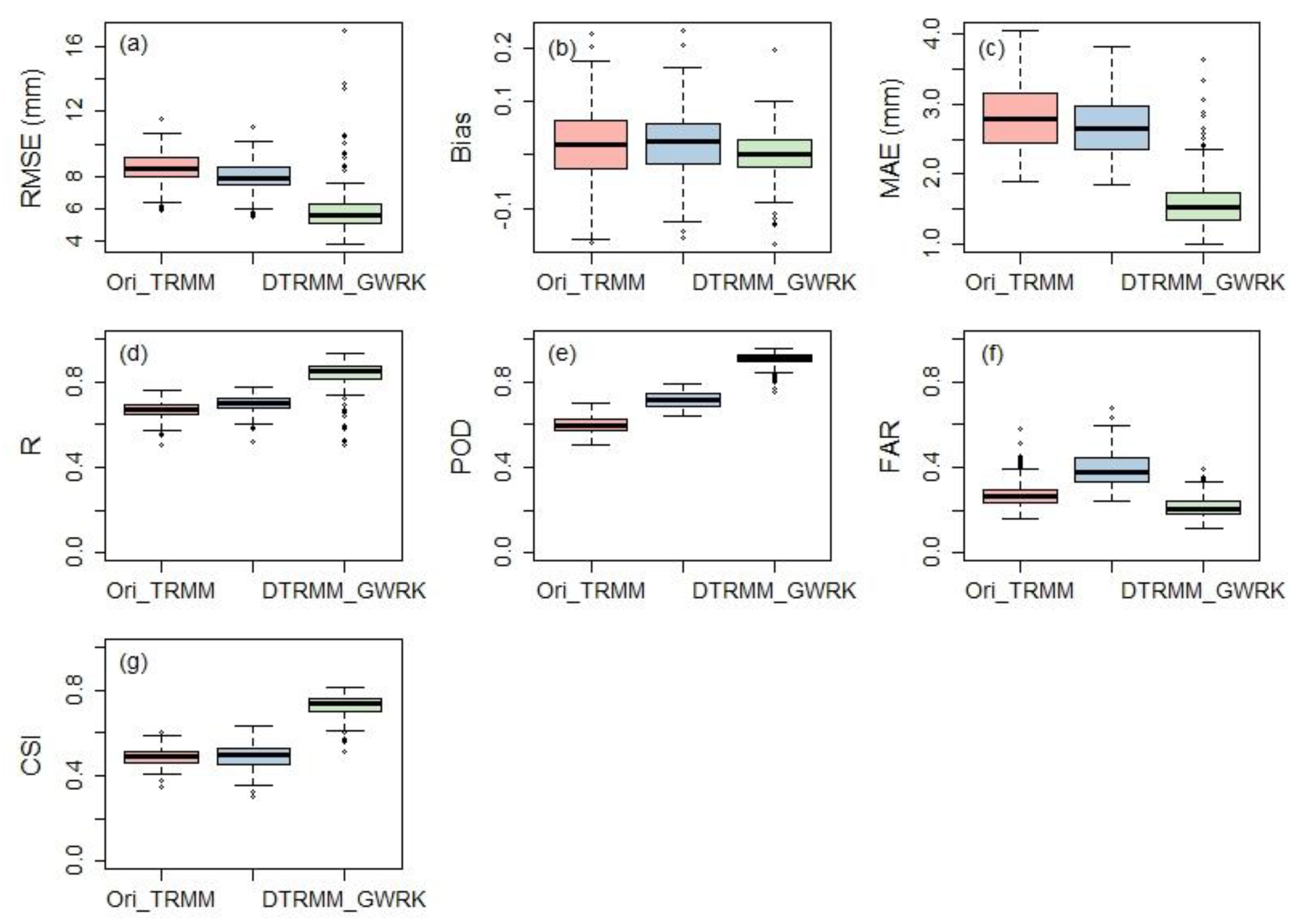
4.1. Performance of Precipitation Estimates
4.1.1. Overall Performance of Precipitation Estimates
4.1.2. Performance of Precipitation Estimates at Station Scale
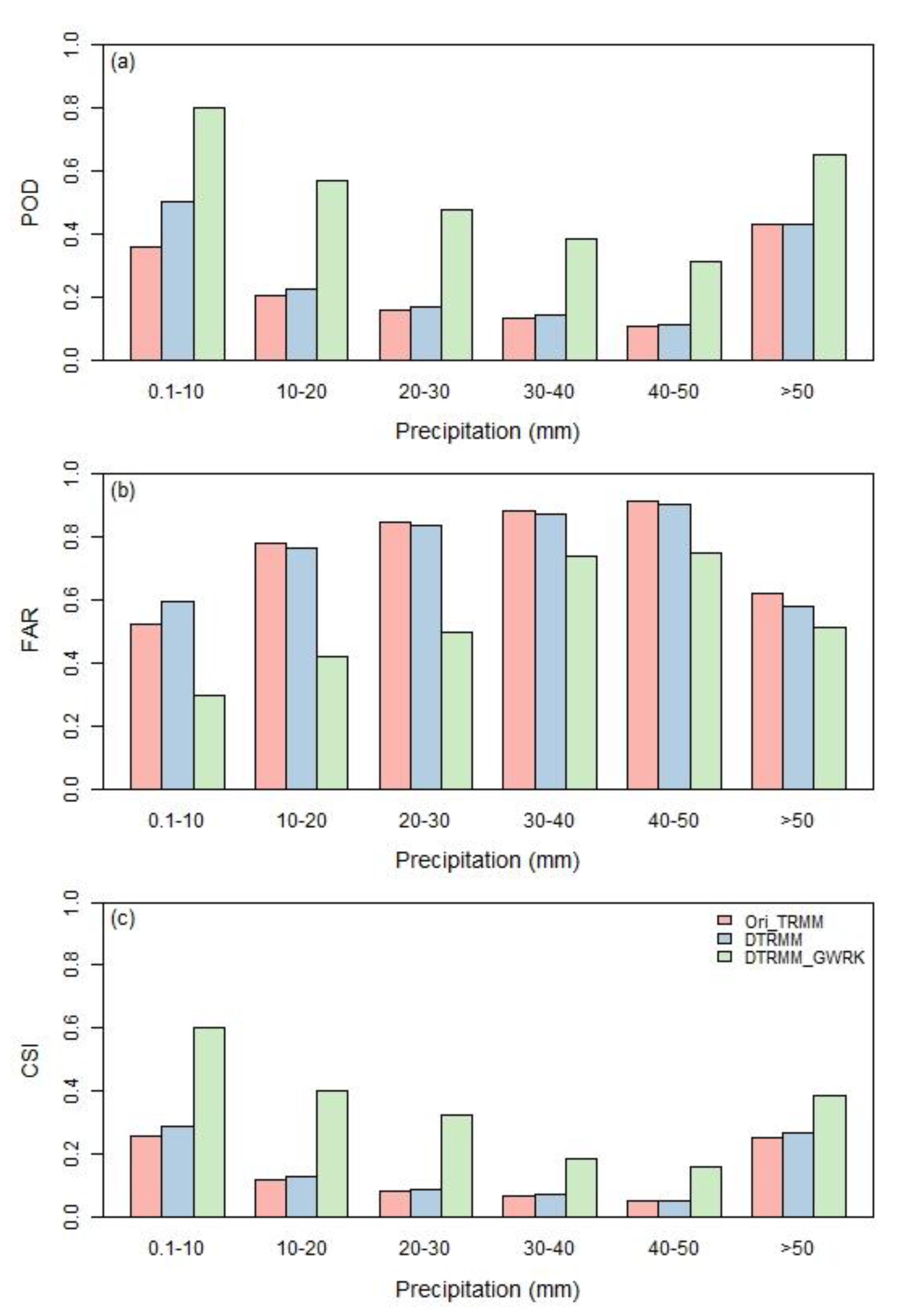
4.1.3. Performance of Precipitation Estimates at Daily Precipitation Level
4.2. The Relationship between Precipitation and YCR
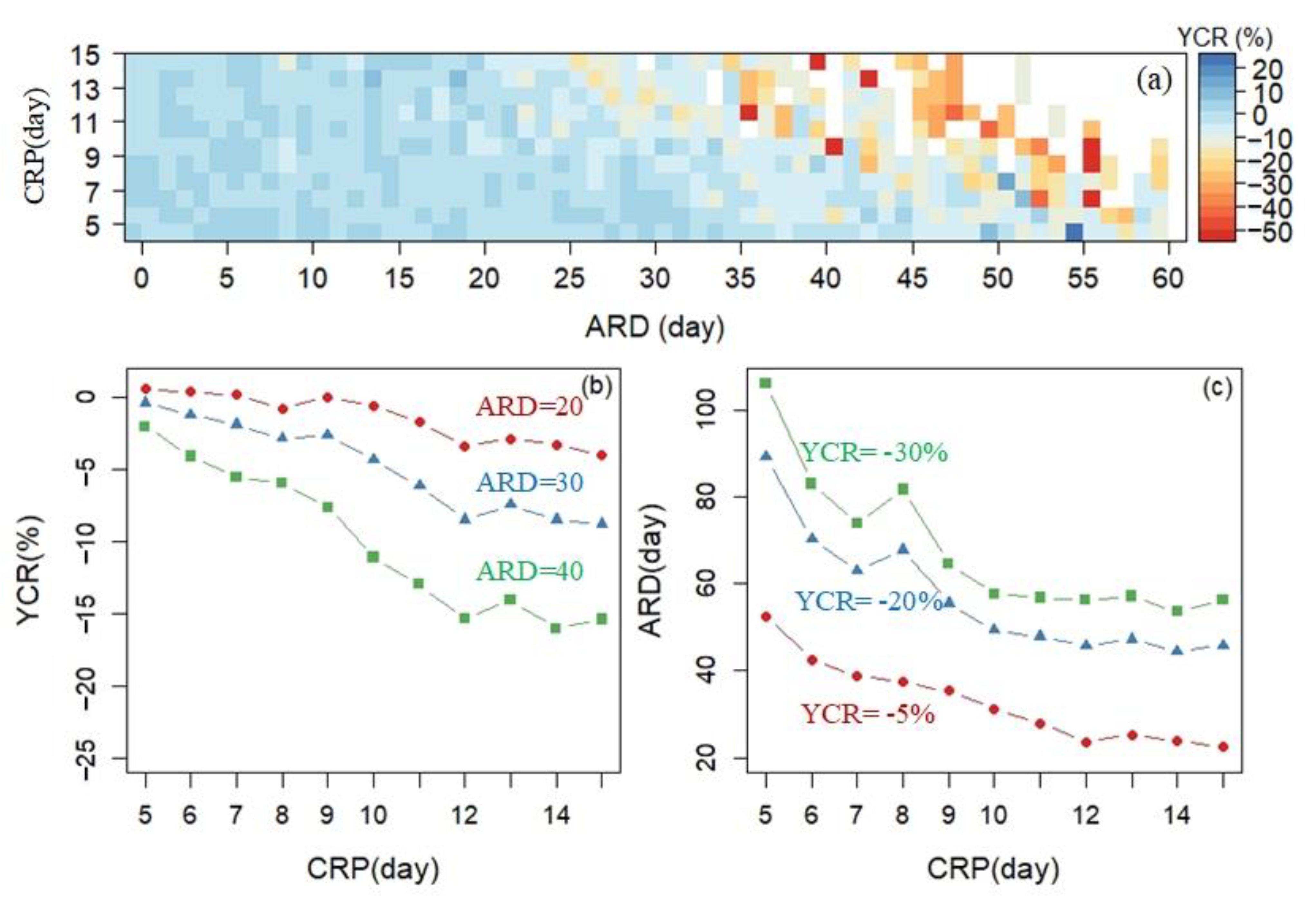
4.2.1. The Relationship between YCR and ARD of Different CRPs
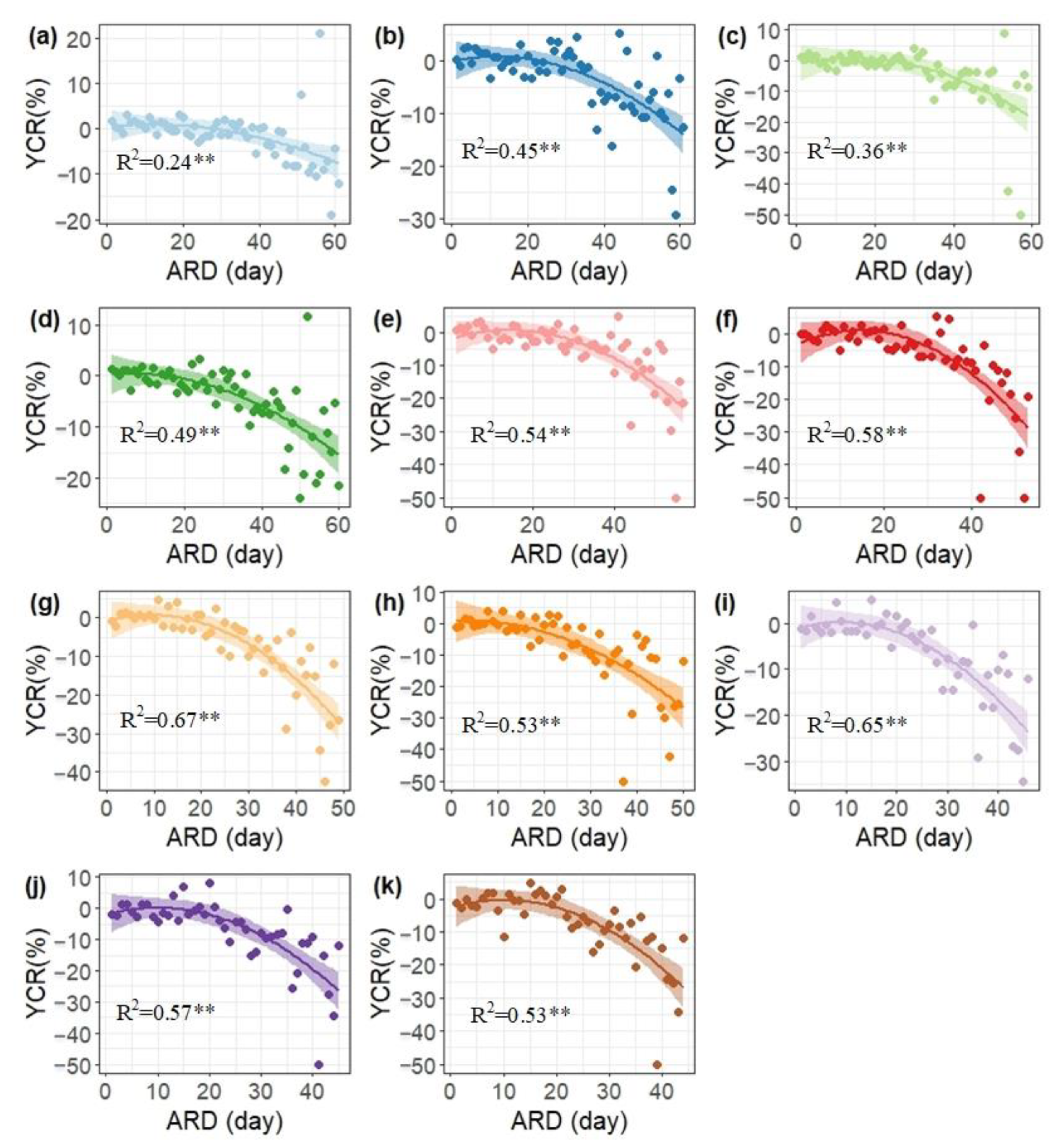
4.2.2. The Relationship between YCR and ARD of CRP of 11 Days for Each Growing Season
4.3. Results of Waterlogging Mapping
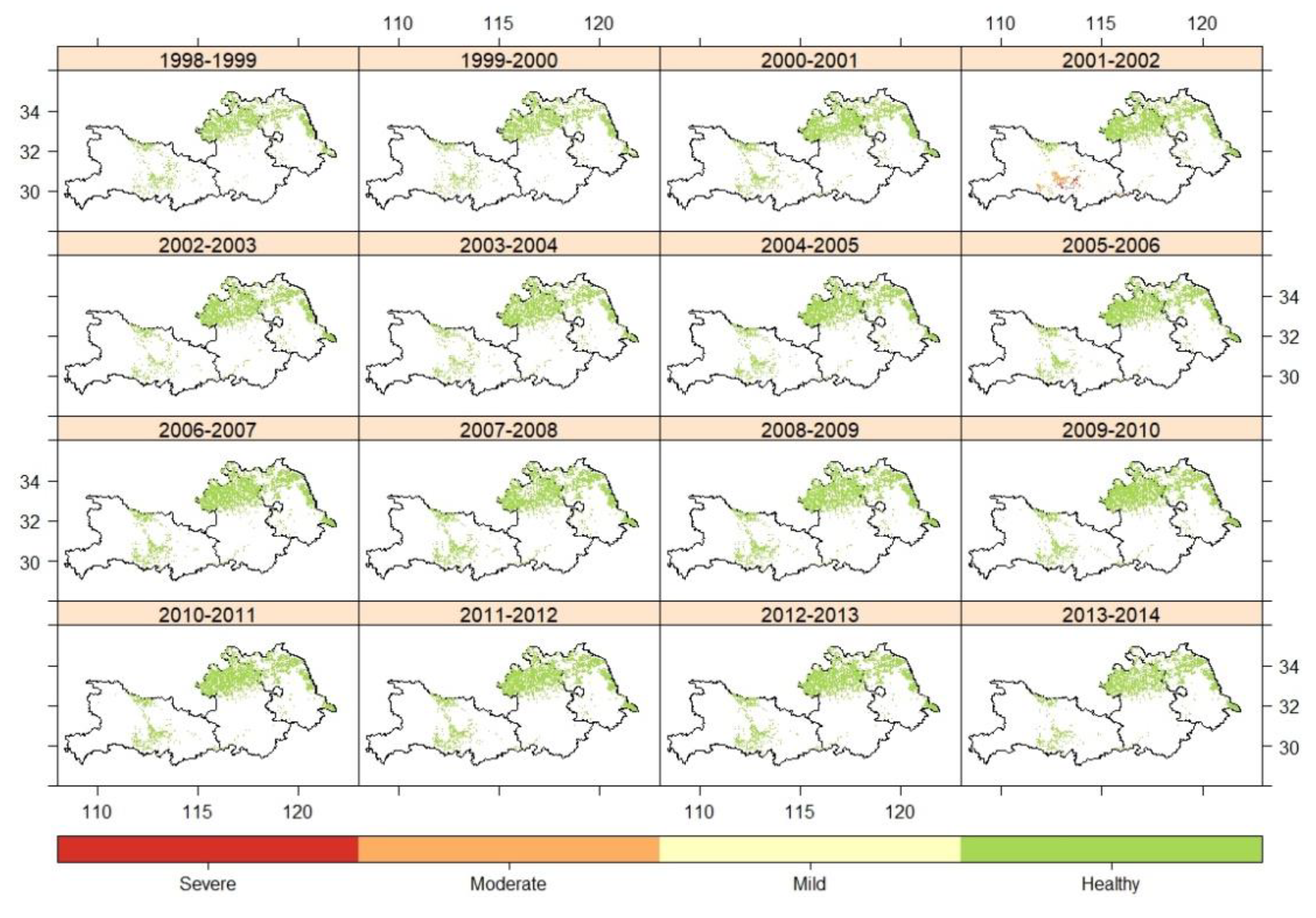
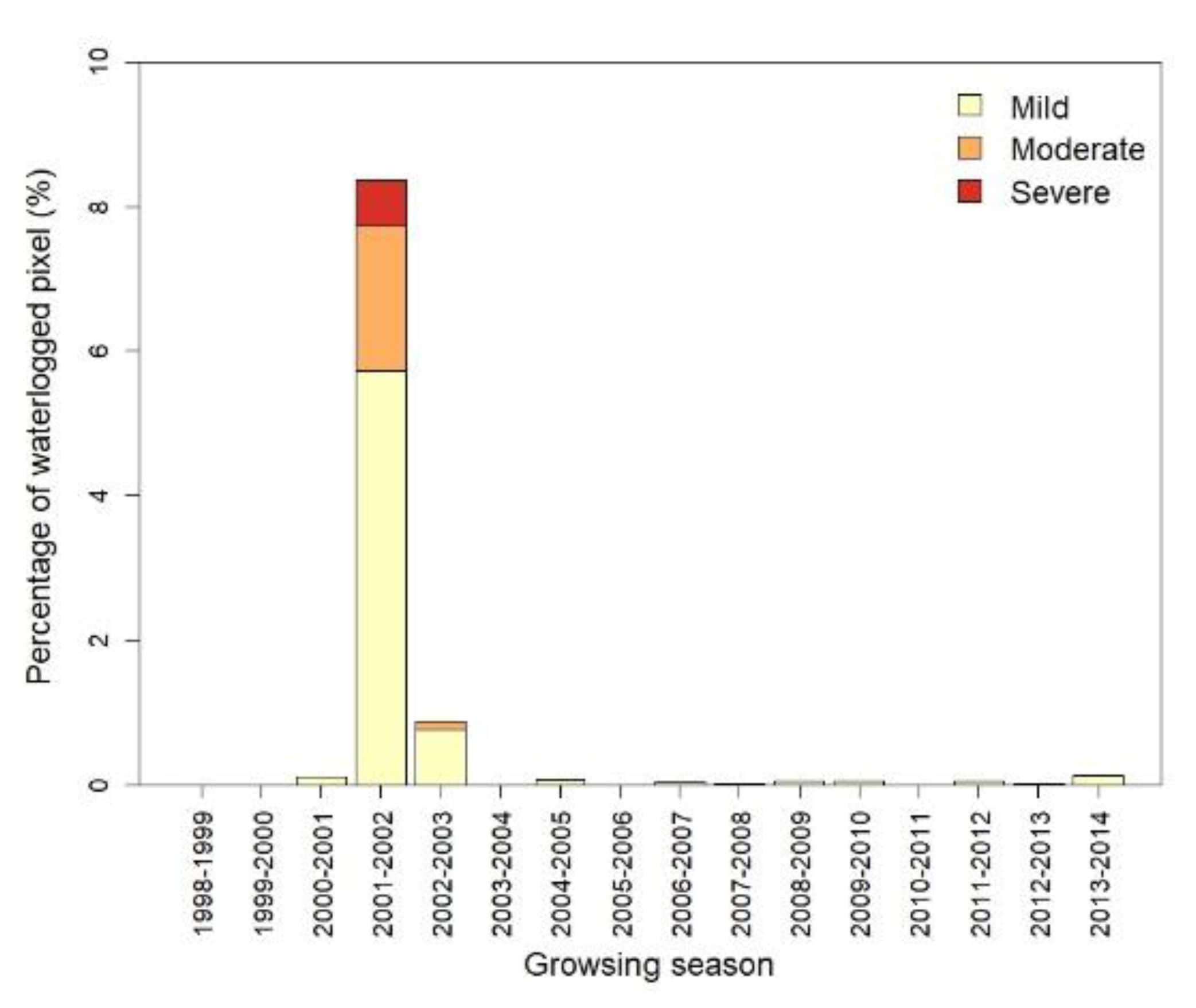
4.3.1. Waterlogging Mapping Results of Winter Wheat from 1998 to 2014
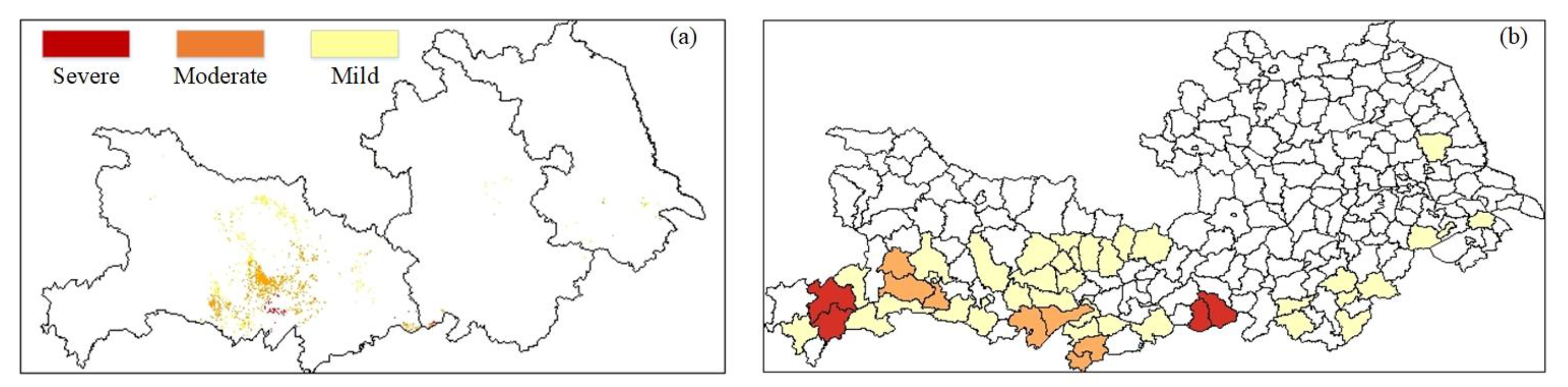
4.3.2. Waterlogging Result Comparison between the TRMM Downscaled–Fusion Estimates and Rain Gauge Measurements for Typical Wet Growing Seasons
4.3.3. Verification of Typical Waterlogging Process Based on Multi-Source Data
5. Discussion
5.1. An Indicator of Extremes Is Important for Quantifiing Their Impact on Crop Yield
5.2. Challenges in Determining the Influence of Extremes on Crop Yield
5.3. Limitations and Future Work
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
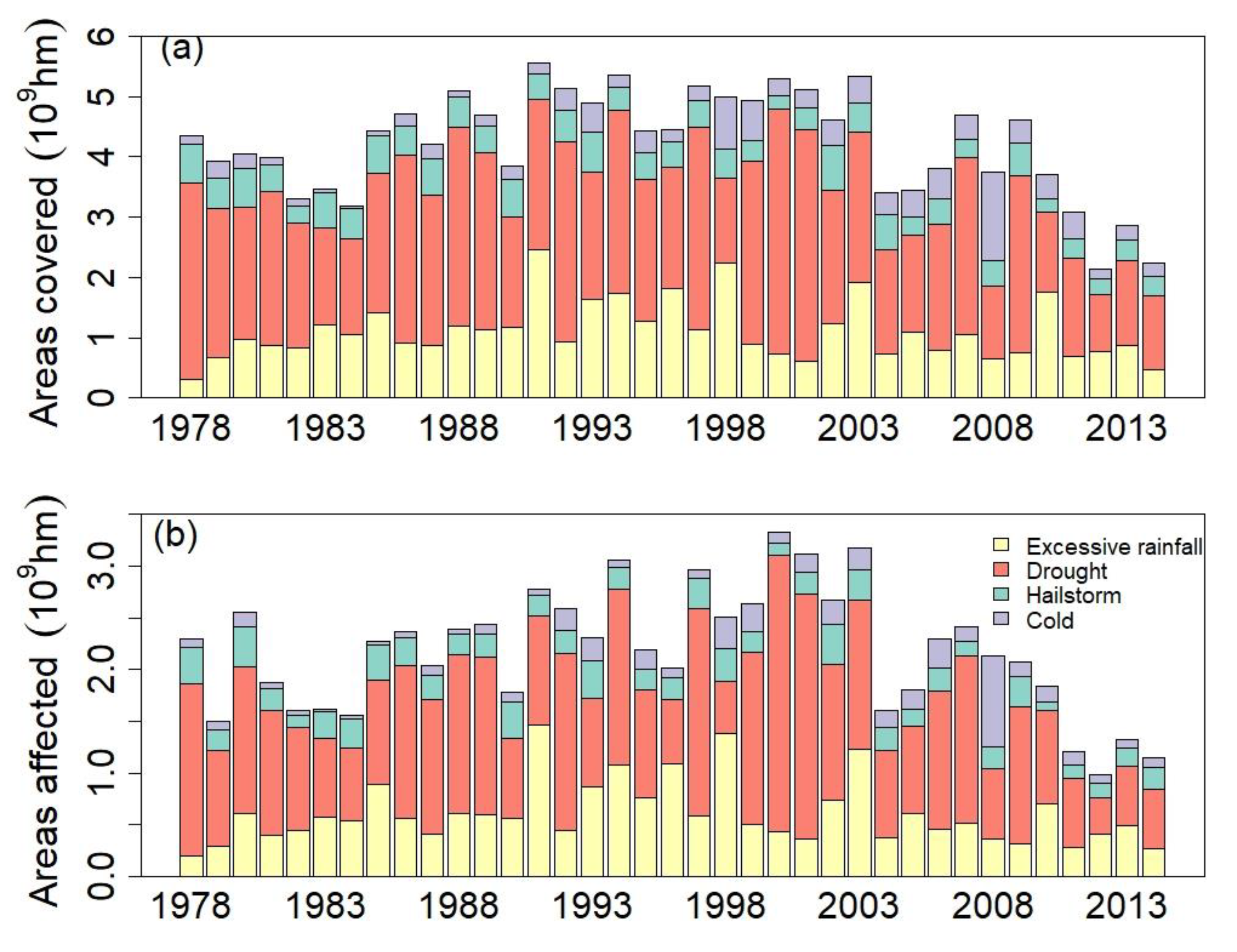
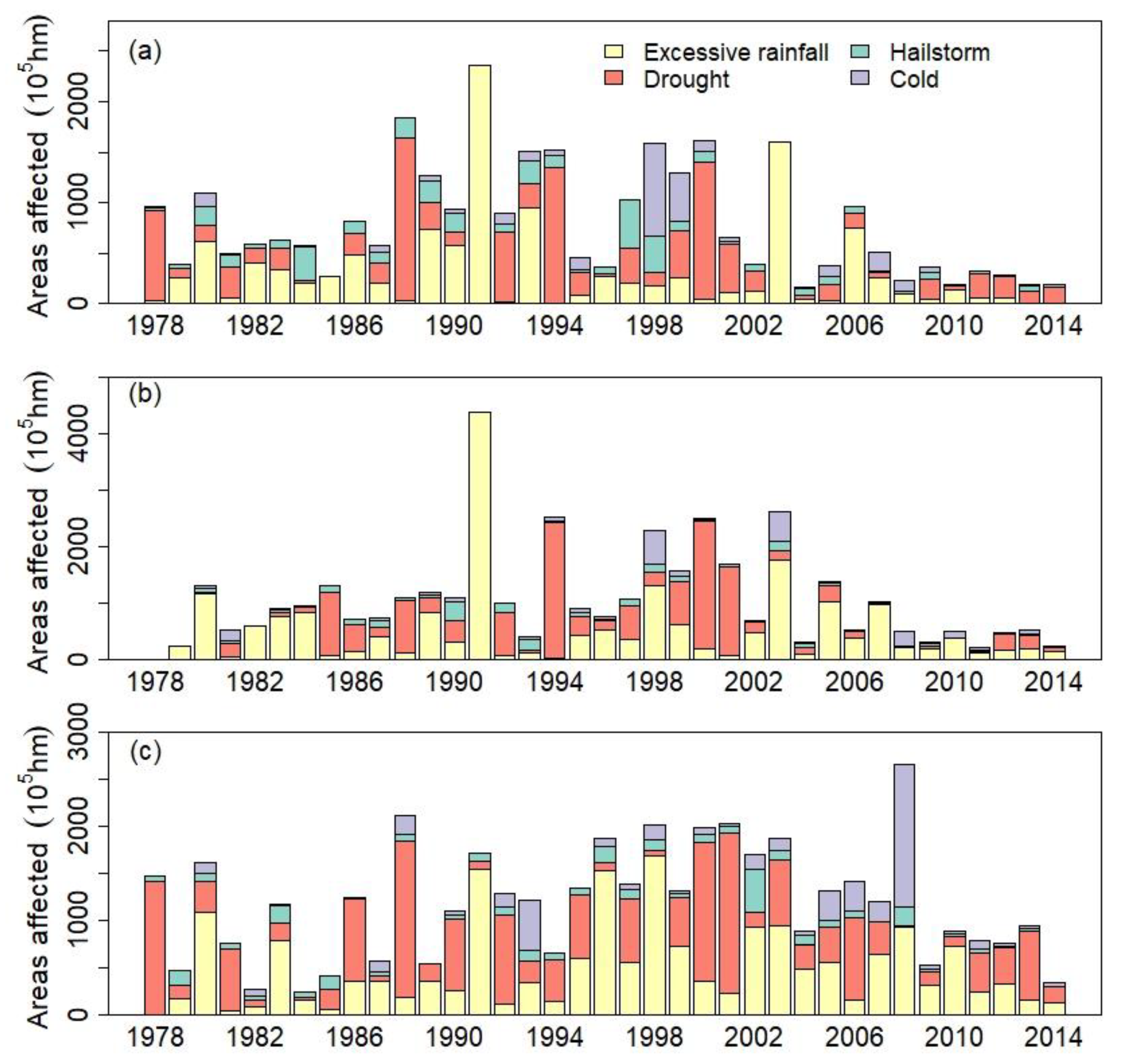
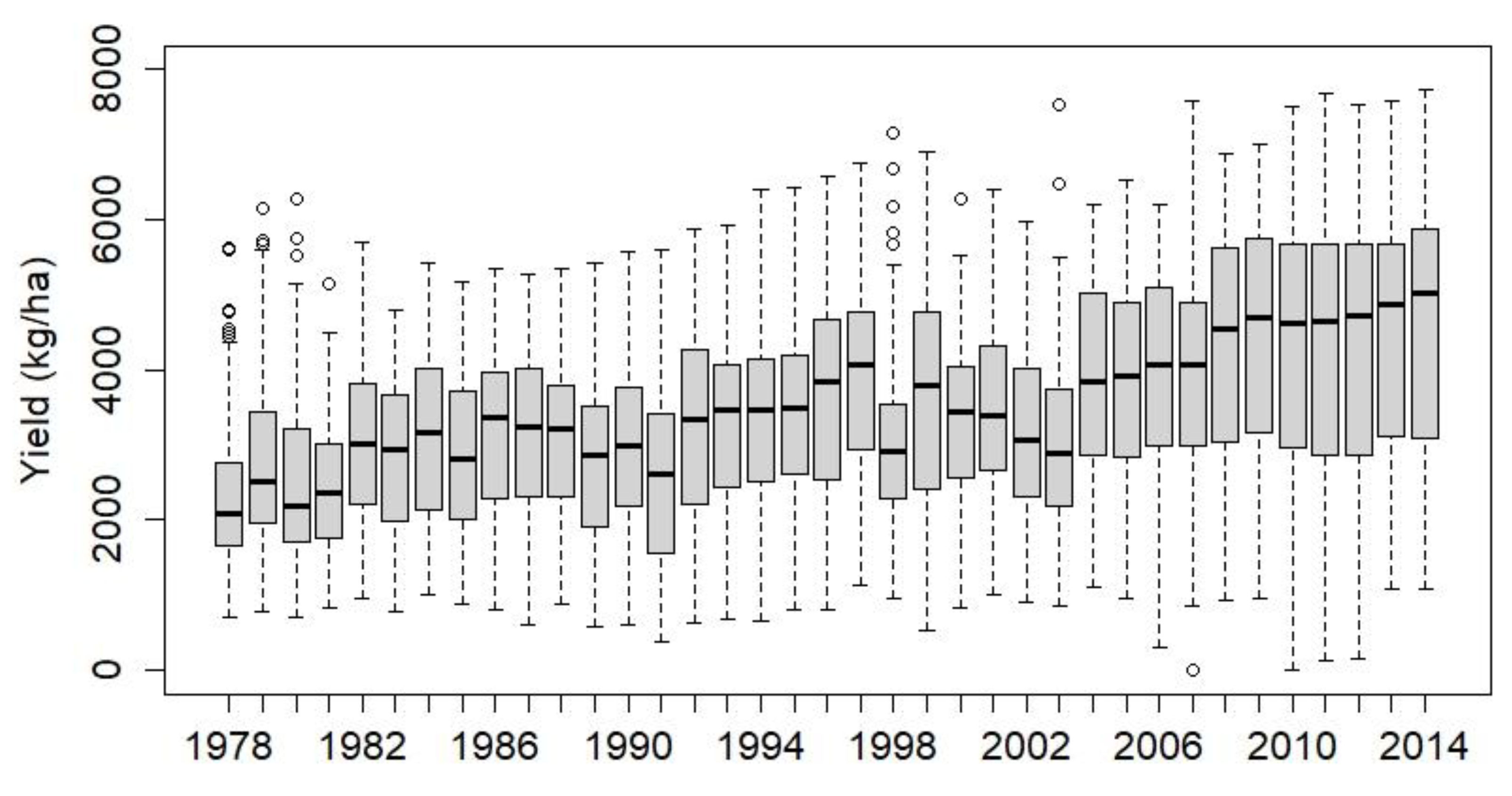
References
- Leng, G. Maize yield loss risk under droughts in observations and crop models in the United States. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 024016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.L.; Liang, Z.Y.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, Q.S.; Xie, S.G. Effects of drought and flood on crop production in China across 1949–2015: Spatial heterogeneity analysis with Bayesian hierarchical modeling. Nat. Hazards 2018, 92, 525–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Hao, Z. Quantifying likelihoods of extreme occurrences causing maize yield reduction at the global scale. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 135250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, S.K.; Zhang, X.B.; Zwiers, F.W.; Hegerl, G.C. Human contribution to more-intense precipitation extremes. Nature 2011, 470, 378–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.; Tian, C.; Chang, Q.; Novick, K.A.; Wang, L. A new multi-sensor integrated index for drought monitoring. Agr. Forest. Meteorol. 2019, 268, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couedel, A.; Edreira, J.I.R.; Lollato, R.P.; Archontoulis, S.; Sadras, V.; Grassini, P. Assessing environment types for maize, soybean, and wheat in the United States as determined by spatio-temporal variation in drought and heat stress. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2021, 307, 108513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wu, W.; Yang, X.; Yang, P.; Sun, J. Exploring drought dynamics and its impacts on maize yield in the Huang-Huai-Hai farming region of China. Clim. Chang. 2020, 163, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wu, D.; Piao, X.; Zhang, T.; Yan, Y.; Tian, Y.; Li, Q.; Cui, X. Reduced impacts of heat extremes from limiting global warming to under 1.5 degrees C or 2 degrees C over Mediterranean regions. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 014034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, N.D.; Konar, M.; Debaere, P.; Sheffield, J. Crop-specific exposure to extreme temperature and moisture for the globe for the last half century. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 064006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, E.D.; Yu, J.; Tack, J. Using insurance data to quantify the multidimensional impacts of warming temperatures on yield risk. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Guan, K.Y.; Schnitkey, G.D.; DeLucia, E.; Peng, B. Excessive rainfall leads to maize yield loss of a comparable magnitude to extreme drought in the United States. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2019, 25, 2325–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, D.W.; Roberts, M.J.; Schlenker, W.; Lobell, D.B. The effects of extremely wet planting conditions on maize and soybean yields. Clim. Chang. 2015, 130, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.-Z. Extreme rainfall slows the global economy. Nature 2022, 601, 193–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotz, M.; Levermann, A.; Wenz, L. The effect of rainfall changes on economic production. Nature 2022, 601, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famiglietti, C.A.; Michalak, A.M.; Konings, A.G. Extreme wet events as important as extreme dry events in controlling spatial patterns of vegetation greenness anomalies. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 074014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de San Celedonio, R.P.; Abeledo, L.G.; Mantese, A.I.; Miralles, D.J. Differential root and shoot biomass recovery in wheat and barley with transient waterlogging during preflowering. Plant Soil 2017, 417, 481–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Tang, Y.; Li, C.; Wu, C.; Huang, G. Chlorophyll Fluorescence and Yield Responses of Winter Wheat to Waterlogging at Different Growth Stages. Plant Prod. Sci. 2015, 18, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, Y.; Morinaga, S.; Shibayama, M. Distinctive response of photosynthetic rate and water-use efficiency in 3 soybean varieties to waterlogging and drought-stress. Jpn. J. Crop Sci. 1993, 62, 638–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickin, E.; Wright, D. The effects of winter waterlogging and summer drought on the growth and yield of winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Eur. J. Agron. 2008, 28, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannell, R.Q.; Belford, R.K.; Gales, K.; Dennis, C.W.; Prew, R.D. Effects of waterlogging at different stages of development on the growth and yield of winter wheat. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1980, 31, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.W.; Sun, W.W.; Huang, J.F.; Wen, H.Y.; Huang, R. Excessive Rainfall Is the Key Meteorological Limiting Factor for Winter Wheat Yield in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River. Agronomy 2022, 12, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesk, C.; Coffel, E.; Horton, R. Net benefits to US soy and maize yields from intensifying hourly rainfall. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2020, 10, 819–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontes, F.; Gorst, A.; Palmer, C. Threshold effects of extreme weather events on cereal yields in India. Clim. Change 2021, 165, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troy, T.J.; Kipgen, C.; Pal, I. The impact of climate extremes and irrigation on US crop yields. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 054013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalkuhl, M.; Wenz, L. The impact of climate conditions on economic production. Evidence from a global panel of regions. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2020, 103, 102360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtermann, L. Precipitation anomalies, economic production, and the role of “first-nature” and “second-nature” geographies: A disaggregated analysis in high-income countries. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2020, 65, 102167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Ding, Q.; Wang, L.X.; Wu, D.L.; Hu, Z.H.; Wu, R.J. Effects of Shading and Waterlogging on the Photosynthesis and Yield Performance of Winter Wheat in Jiangsu Province, China. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2019, 21, 472–478. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Yu, W.Z.; Liu, P.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, J.W.; Ren, B.Z. Responses of canopy functionality, crop growth and grain yield of summer maize to shading, waterlogging, and their combination stress at different crop stages. Eur. J. Agron. 2023, 144, 126761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.F.; Zhu, W.B.; Lu, A.F.; Yan, T.T. A statistical spatial downscaling algorithm of TRMM precipitation based on NDVI and DEM in the Qaidam Basin of China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 3069–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhao, S.H.; Duan, Z.; Qin, Z.H. An Improved Spatial Downscaling Procedure for TRMM 3B43 Precipitation Product Using Geographically Weighted Regression. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 4592–4604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, H.F.; Shi, Z.; Ma, Z.Q.; Li, Y. Estimating spatially downscaled rainfall by regression kriging using TRMM precipitation and elevation in Zhejiang Province, southeast China. Int. J Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 7775–7794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Huang, J.F.; Sheng, S.X.; Mansaray, L.R.; Liu, Z.X.; Wu, H.Y.; Wang, X.Z. A new downscaling-integration framework for high-resolution monthly precipitation estimates: Combining rain gauge observations, satellite-derived precipitation data and geographical ancillary data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 214, 154–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.R.; Gao, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.G.; Li, X. A downscaling-merging method for high-resolution daily precipitation estimation. J. Hydrol. 2020, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.Q.; He, K.; Tan, X.; Liu, Y.; Lu, H.Y.; Shi, Z. A new approach for obtaining precipitation estimates with a finer spatial resolution on a daily scale based on TMPA V7 data over the Tibetan Plateau. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 8465–8483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Cao, J.; Tao, F. Identifying the spatiotemporal changes of annual harvesting areas for three staple crops in China by integrating multi-data sources. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 074003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Fu, Y.Y.; Wang, J.J.; Tian, H.F.; Fu, S.; Niu, Z.; Han, W.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, J.X.; Yuan, W.P. Early-season mapping of winter wheat in China based on Landsat and Sentinel images. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2020, 12, 3081–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakidis, P. A geostatistical framework for area-to-point spatial interpolation. Geogr. Anal. 2004, 36, 259–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakidis, P.C.; Yoo, E.H. Geostatistical prediction and simulation of point values from areal data. Geogr. Anal. 2005, 37, 124–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.M.; Shi, W.Z.; Atkinson, P.M. Area-to-point regression kriging for pan-sharpening. Isprs J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 114, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Atkinson, P.M.; Ling, F.; Foody, G.M.; Wang, Q.; Ge, Y.; Li, X.D.; Du, Y. Object based area to point pegression kriging for pansharpening. IEEE T Geosci. Remote 2021, 59, 8599–8614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.M.; Shi, W.Z.; Li, Z.B.; Atkinson, P.M. Fusion of Sentinel-2 images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 187, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Atkinson, P.M.; Ling, F.; Wang, Q.M.; Li, X.D.; Shi, L.F.; Du, Y. Spectral-spatial adaptive area to point regression kriging for MODIS image downscaling. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 1883–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brus, D.J.; Boogaard, H.; Ceccarelli, T.; Orton, T.G.; Traore, S.; Zhang, M. Geostatistical disaggregation of polygon maps of average crop yields by area-to-point kriging. Eur. J. Agron. 2018, 97, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xang, Y.; Cheng, T.; Wang, K.; Li, J.; Tang, H. The analysis on spatial and temporal distribution features of continuous rain in Jiangsu. J. Meteorol. Sci. 2011, 31, 36–39. [Google Scholar]
- Lesk, C.; Coffel, E.; Winter, J.; Ray, D.; Zscheischler, J.; Seneviratne, S.I.; Horton, R. Stronger temperature-moisture couplings exacerbate the impact of climate warming on global crop yields. Nat. Food 2021, 2, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eck, M.A.; Murray, A.R.; Ward, A.R.; Konrad, C.E. Influence of growing season temperature and precipitation anomalies on crop yield in the southeastern United States. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2020, 291, 108053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Xuan, S.L.; Muneer, M.A.; Sun, B.; Shi, C.L.; Liu, F.S.; Wu, R.Y. Response of dry matter partition and yield components to waterlogging and sunlight shortage in different growth stages of wheat. Nat. Hazards 2022, 110, 1133–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, N.C.; Li, J.Z.; Chen, Z.H.; Niyogi, D. Multi-sensor integrated framework and index for agricultural drought monitoring. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 188, 141–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linkov, I.; Bridges, T.; Creutzig, F.; Decker, J.; Fox-Lent, C.; Kröger, W.; Lambert, J.H.; Levermann, A.; Montreuil, B.; Nathwani, J.; et al. Changing the resilience paradigm. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 407–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atube, F.; Okello, D.M.; Malinga, G.M.; Nyeko, M.; Okello-Uma, I. Farmers’ adaptation to climate change and crop yield: A case of Amuru and Apac districts of Northern Uganda. Int. J. Agric. Sustain. 2022, 20, 967–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marie, M.; Yirga, F.; Haile, M.; Tquabo, F. Farmers’ choices and factors affecting adoption of climate change adaptation strategies: Evidence from northwestern Ethiopia. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.B.; Colmer, T.D. Response and adaptation by plants to flooding stress-Preface. Ann. Bot. 2005, 96, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parent, C.; Capelli, N.; Berger, A.; Crevècoeur, M.; Dat, J. An Overview of Plant Responses to Soil Waterlogging. Plant Stress 2008, 2, 20–27. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Huang, J.; Wei, C.; Wang, X.; Mansaray, L.R.; Han, J.; Zhang, D.; Chen, Y. Mapping water-logging damage on winter wheat at parcel level using high spatial resolution satellite data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 142, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, G.Y.; Hall, J. Crop yield sensitivity of global major agricultural countries to droughts and the projected changes in the future. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 654, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamal, K.; Sharma, S.; Khadka, N.; Haile, G.G.; Joshi, B.B.; Xu, T.L.; Dawadi, B. Assessment of drought impacts on crop yields across Nepal during 1987–2017. Meteorol. Appl. 2020, 27, e1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.E.; Hou, P.; Huang, G.R.; Zhong, X.L.; Li, H.R.; Zhao, J.R.; Li, S.K.; Mei, X.R. Maize grain yield and water use efficiency in relation to climatic factors and plant population in northern China. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 3156–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, E. Determining the start, duration, and strength of flood and drought with daily precipitation: Rationale. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pengcheng, Q.; Zhixiong, L.; Suqin, W.; Min, L.; Rongrui, S. Application and Validation of Weighted Moisture Index in Waterlogging Disaster Monitoring. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2018, 27, 328–334. [Google Scholar]
- Pengcheng, Q.; Min, L.; Lan, L. Application of Effective Precipitation Index in Rainstorm Flood Disaster Monitoring and Assessment. Chin. J. Agrometeorol. 2016, 37, 84–90. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, R.; Li, Y.; Guan, K.; Zhao, L.; Peng, B.; Miao, C.; Fu, B. Divergent responses of maize yield to precipitation in the United States. Environ. Res. Lett. 2022, 17, 014016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, E.E.; Huybers, P. Adaptation of US maize to temperature variations. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
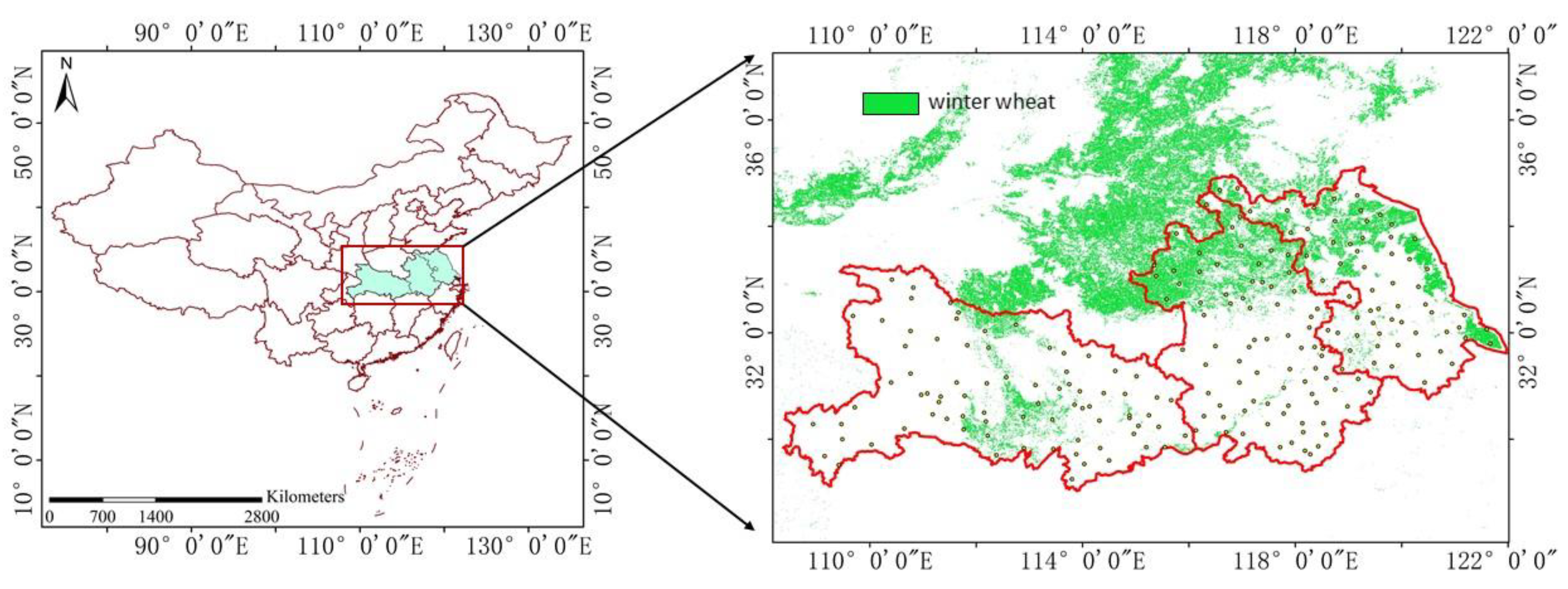



| Study Area | County-Level Yield | Used in This Study | Number of Stations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anhui | 1978–2014 | 1998–2014 | 76 |
| Jiangsu | 1978–2014 | 1998–2014 | 60 |
| Hubei | 1978–2014 | 1998–2014 | 67 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, W.; Chen, Y.; Sun, W.; Huang, R.; Huang, J. Mapping Waterlogging Damage to Winter Wheat Yield Using Downscaling–Merging Satellite Daily Precipitation in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2573. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102573
Liu W, Chen Y, Sun W, Huang R, Huang J. Mapping Waterlogging Damage to Winter Wheat Yield Using Downscaling–Merging Satellite Daily Precipitation in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(10):2573. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102573
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Weiwei, Yuanyuan Chen, Weiwei Sun, Ran Huang, and Jingfeng Huang. 2023. "Mapping Waterlogging Damage to Winter Wheat Yield Using Downscaling–Merging Satellite Daily Precipitation in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River" Remote Sensing 15, no. 10: 2573. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102573
APA StyleLiu, W., Chen, Y., Sun, W., Huang, R., & Huang, J. (2023). Mapping Waterlogging Damage to Winter Wheat Yield Using Downscaling–Merging Satellite Daily Precipitation in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River. Remote Sensing, 15(10), 2573. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102573








