Regional Characteristics of Cloud Properties over the Loess Plateau
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
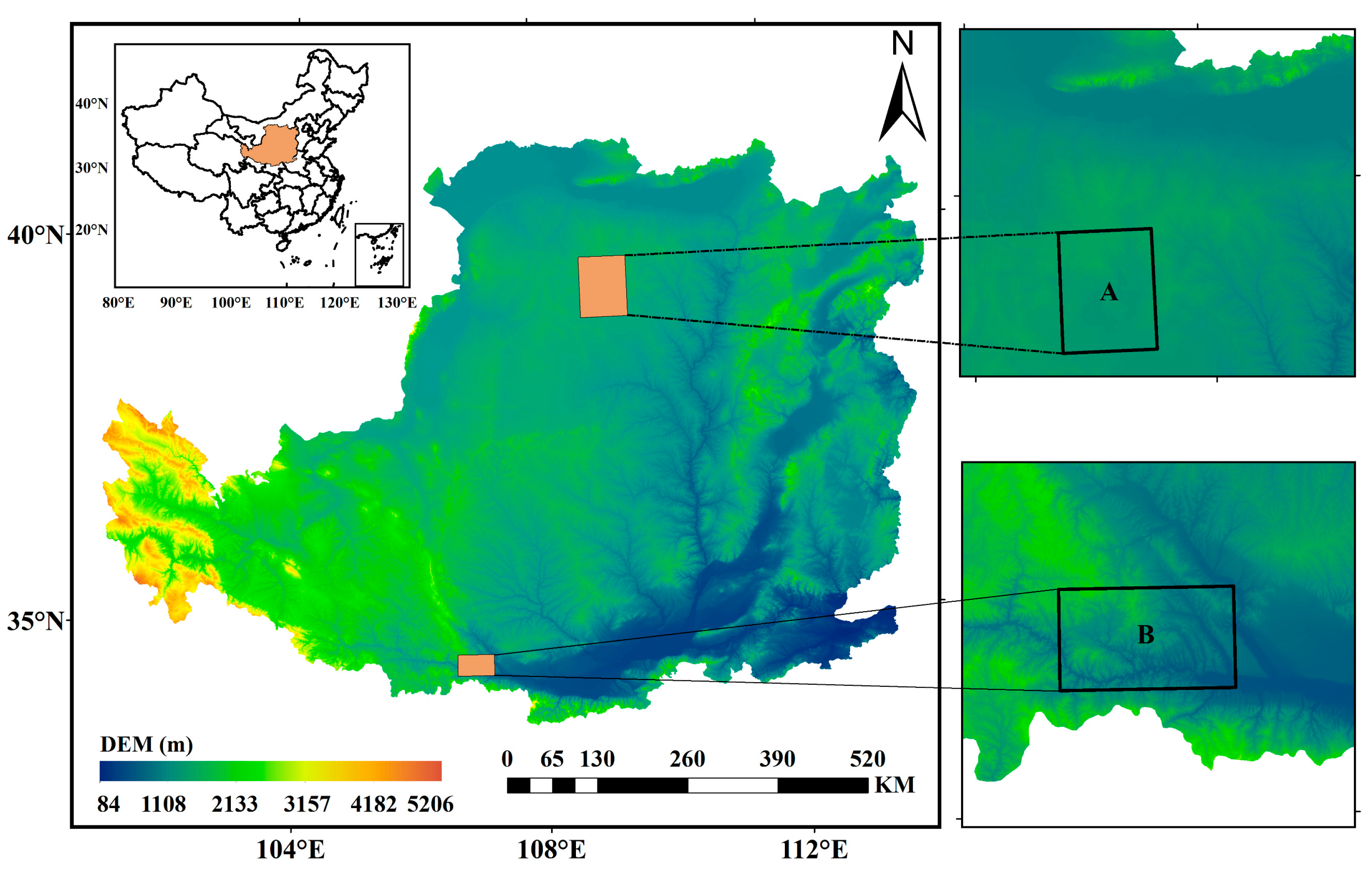
2.1. Research Area
2.2. Himawari-8 Satellite Cloud Products
2.3. Ancillary Datasets
2.4. Methods
3. Results
3.1. Annual and Seasonal Cloud Properties over Loess Plateau
3.2. Diurnal Variation in Cloud Properties over Loess Plateau
3.3. Spatial Characteristics of Diurnal Cloud over Loess Plateau
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stubenrauch, C.J.; Cros, S.; Guignard, A.; Lamquin, N. A 6-year global cloud climatology from the Atmospheric InfraRed Sounder AIRS and a statistical analysis in synergy with CALIPSO and CloudSat. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 7197–7214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, V.; Cess, R.D.; Harrison, E.F.; Minnis, P.; Barkstrom, B.R.; Ahmad, E.; Hartmann, D. Cloud-radiative forcing and climate: Results from the earth radiation budget experiment. Science 1989, 243, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbood, Z.M.; Al-Taai, O.T. Calculation of absorption and emission of thermal radiation by clouds cover. ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2018, 13, 9446–9456. [Google Scholar]
- Gettelman, A.; Sherwood, S.C. Processes responsible for cloud feedback. Curr. Clim. Change Rep. 2016, 2, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Su, J.; Xu, Y.; Han, X.; Peng, N.; Ge, J. Radiative contributions of different cloud types to regional energy budget over the SACOL site. Clim. Dyn. 2023, 60, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yu, R.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, X. Spatial distribution and seasonal variation of cloud over China based on ISCCP data and surface observations. J. Meteorol. Ser. II 2004, 82, 761–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Fan, H. Spatiotemporal distributions of cloud properties over China based on Himawari-8 advanced Himawari imager data. Atmos. Res. 2020, 240, 104927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, J.E.; Karr, M.E.; Johnson, R.W.; Burden, A.R. Day/night whole sky imagers for 24-h cloud and sky assessment: History and overview. Appl. Opt. 2013, 52, 1605–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossow, W.B. History of the International Satellite Cloud Climatology Project; World Climate Research Programme (WCRP): Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wielicki, B.A.; Barkstrom, B.R.; Harrison, E.F.; Lee, R.B.; Louis Smith, G.L.; Cooper, J.E. Clouds and the Earth’s RadiantEnergy System (CERES): An earth observing system experiment. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 1996, 77, 853–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Doelling, D.R.; Loeb, N.G.; Scott, R.C.; Wilkins, J.; Nguyen, L.T.; Mlynczak, P. Clouds and the Earth’s radiant energy system (CERES) FluxByCldTyp edition 4 data product. J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol. 2022, 39, 303–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondragunta, C.R.; Gruber, A. Seasonal and annual variability of the diurnal cycle of clouds. J. Geophys. Res-Atmos. 1996, 101, 21377–21390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cintineo, J.L.; Pavolonis, M.J.; Sieglaff, J.M.; Heidinger, A.K. Evolution of severe and nonsevere convection inferred from GOES-derived cloud properties. J. Appl. Meteor. Climatol. 2013, 52, 2009–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senf, F.; Dietzsch, F.; Hünerbein, A.; Deneke, H. Characterization of initiation and growth of selected severe convective storms over central Europe with MSG-SEVIRI. J. Appl. Meteor. Climatol. 2015, 54, 207–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, H.; Letu, H.; Nakajima, T.Y.; Wang, Z.; Ma, R.; Wang, T.; Lei, Y.; Ji, D.; Li, S.; Shi, J. Diurnal cycle and seasonal variation of cloud cover over the Tibetan Plateau as determined from Himawari-8 new-generation geostationary satellite data. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winker, D.M.; Hunt, W.H.; McGill, M.J. Initial performance assessment of CALIOP. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L19803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mace, G.G.; Zhang, Q.; Vaughan, M.; Marchand, R.; Stephens, G.; Trepte, C.; Winker, D. A description of hydrometeor layer occurrence statistics derived from the first year of merged Cloudsat and CALIPSO data. J. Geophys. 2009, 114, D00A26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jian, B.; Wang, G.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Letu, H.; Zhang, M.; Li, J. Climatology of cloud phase, cloud radiative effects and precipitation properties over the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wu, X.; Yin, Y.; Huang, Q.; Xiao, H. Characteristics of cloud systems over the Tibetan Plateau and East China during boreal summer. J. Climate. 2017, 30, 3117–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Sun, M.; Mei, J. Variation and influencing factors of cloud characteristics over Qinghai lake from 2006 to 2019. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J. Analysis on cloud microphysical property over Qinghai-XizangPlateau using satellite data. Plateau Meteor. 2013, 32, 38–45. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, R.; Wang, G.; Zhaxi, S. Cloud vertical structure measurements from a ground-based cloud radar over the southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Atmos. Res. 2021, 258, 105629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Sang, T. Potential productivity of the Miscanthus energy crop in the Loess Plateau of China under climate change. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 044003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Ma, J.; Han, Z.; Shi, M.; Xu, D.; Sun, Z. Relationship between multi-scale climate factors and performance of ecological engineering on the Loess Plateau, China. J. For. Res. 2021, 33, 789–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liang, W.; Fu, B.; Lu, Y.; Fu, S.; Wang, S.; Su, H. Vegetation changes in recent large-scale ecological restoration projects and subsequent impact on water resources in China’s Loess Plateau. Sci. Total. Environ. 2016, 569–570, 1032–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Song, X.; Mu, X.; Gao, P.; Wang, F.; Zhao, G. Spatiotemporal vegetation cover variations associated with climate change and ecological restoration in the Loess Plateau. Agric. Forest Meteorol. 2015, 209–210, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.; Cheng, M.; Xue, Z.; Ma, R. Current State of Multifunctional Use of Grasslands. In Multifunctional Land-Use Systems for Managing the Nexus of Environmental Resources; Zhang, L., Schwärzel, K., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.J.; He, Q.Y.; Yamanaka, N.; Du, S. Location, Geology and Landforms of the Loess Plateau. In Restoration and Development of the Degraded Loess Plateau, China; Tsunekawa, A., Liu, G., Yamanaka, N., Du, S., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2014; pp. 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zheng, F.; Liu, W.; Flanagan, D.C. Spatial distribution and temporal trends of extreme temperature and precipitation events on the Loess Plateau of China during 1961–2007. Quat. Int. 2010, 226, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Huang, J.; Fu, Q.; Wang, X.; Shi, J.; Zhang, W.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, B. Toward characterization of the aerosol optical properties over Loess Plateau of northwestern China. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Ra. 2011, 112, 346–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Huang, S.; Huang, Q.; Huang, G.; Wang, H.; Leng, G.; Wang, L.; Guo, Y. Probabilistic assessment of remote sensing-based terrestrial vegetation vulnerability to drought stress of the Loess Plateau in China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 232, 111290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letu, H.; Nakajima, T.Y.; Wang, T.; Shang, H.; Ma, R.; Yang, K.; Baran, A.J.; Riedi, J.; Ishimoto, H.; Yoshida, M.; et al. A new benchmark for surface radiation products over the East Asia–Pacific region retrieved from the Himawari-8/AHI next-generation geostationary satellite. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 2022, 103, E873–E888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessho, K.; Date, K.; Hayashi, M.; Ikeda, A.; Imai, T.; Inoue, H.; Kumagai, Y.; Miyakawa, T.; Murata, H.; Ohno, T.; et al. An introduction to Himawari-8/9—Japan’s new-generation geostationary meteorological satellites. J. Meteorol. Ser. II 2016, 94, 151–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Ichii, K.; Higuchi, A.; Takenaka, H. Geolocation accuracy assessment of Himawari-8/AHI imagery for application to terrestrial monitoring. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Xu, C.D. Geodetector: Principles and prospects. Acta Geol. Sin. 2017, 72, 116–134. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Qin, F.; Xu, C.; Li, B.; Guo, L.; Wang, Z. Evaluating the suitability of urban de-velopment land with a Geodetector. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 123, 107339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.J.; Chen, B.D. Cloud occurrence frequency and structure over the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau from CloudSat observation. Plateau Meteor. 2017, 36, 632–642. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; He, H.; Wang, J.; Bai, C.; Zhang, C. Vegetation restoration and its environmental effects on the loess plateau. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Tian, L.; Zhao, X.; Wu, P. Feedbacks between vegetation restoration and local precipitation over the loess plateau in China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2021, 64, 920–931. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Ma, X.; Liang, L.; Yao, W. Spatial–temporal variation characteristics of multiple meteorological variables and vegetation over the Loess Plateau region. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Hao, X. Evapotranspiration trend and its relationship with precipitation over the Loess Plateau during the last three decades. Adv. Meteorol. 2016, 2016, 6809749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Fang, X.; Daryanto, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y. Factors influencing soil moisture in the Loess Plateau, China: A review. Earth Environ. Sci. Trans. R. Soc. Edinb. 2018, 109, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.; Peng, J.; Wang, G.; Javed, I.; Wang, Y.; Li, W. Distribution and characteristics of landslide in Loess Plateau: A case study in Shaanxi province. Eng. Geol. 2018, 236, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, X.; Xue, Q.; Guo, Z. Experimental study on air permeability and microscopic mechanism of intact and remolded Malan loess, Loess Plateau, China. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2020, 79, 3909–3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Duan, W.; Chen, Y.; Dukhovny, V.A.; Sorokin, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. Comprehensive evaluation and sustainable development of water–energy–food–ecology systems in Central Asia. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2022, 157, 112061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; Maskey, S.; Chaffe, P.L.B.; Luo, P.; He, B.; Wu, Y.; Hou, J. Recent advancement in remote sensing technology for hydrology analysis and water resources management. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.X.; Zhang, H.; Jing, X.W. Distribution and variation trends of cloud amount and optical thickness over China. J. Atmos. Environ. Opt. 2016, 11, 1–13. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.X. Optical properties and climatic effects of aerosols in representative regions over China. Ph.D. Thesis, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China, 2018. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Albrecht, B.A. Aerosols, cloud microphysics, and fractional cloudiness. Science. 1989, 245, 1227–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yi, B.; Min, M. Diurnal variations of cloud optical properties during day-time over China based on Himawari-8 satellite retrievals. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 277, 1352–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeckner, E.; Schlese, U.; Biercamp, J.; Loewe, P. Cloud optical depth feedbacks and climate modelling. Nature. 1987, 329, 138–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Che, H.; Wang, H.; Xia, X.; Chen, Q.; Gui, K.; Zhao, H.; An, L.; Zheng, Y.; Sun, T.; et al. Spatial and temporal distribution of the cloud optical depth over China based on MODIS satellite data during 2003–2016. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 80, 66–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, R.G. Cloud formation and the possible significance of charge for atmospheric condensation and ice nuclei. Space Sci. Rev. 2000, 94, 381–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.S.; Wang, P.C. Tempo-spatial distribution characteristics of cloud particle size over china during summer. Clim. Environ. Res. 2012, 17, 433–443, In Chinese. [Google Scholar]
- Coopman, Q.; Riedi, J.; Finch, D.P.; Garrett, T.J. Evidence for changes in arctic cloud phase due to long-range pollution transport. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 10–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Letu, H.; Su, Y.; Chen, T.; Wu, X. Fifteen-year statistical analysis of cloud characteristics over China using Terra and Aqua Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer observations. Int. J. Climatol. 2019, 39, 2612–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.F.; Klein, S.A.; Xie, S.; Liu, X.; Boyle, J.S.; Zhang, Y. Aerosol first indirect effects on non-nrecinitatine low-level liouid cloud nronerties as simulated by CAMs at ARM sites. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L08806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.M.; Zhao, C.F.; Guo, J.P.; Li, J.M. 8-year ground-based observational analysis about the seasonal variation of the aerosol-cloud droplet effective radius relationship at SGP site. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 164, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, W.S.; Panicker, A.; Lee, D.I.; Park, S.H. Estimates of aerosol indirect effect from terra MODIS over Republic of Korea. Adv. Meteorol. 2013, 2013, 976813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, A.R. The Effects of Aerosol-Cloud Interactions on Warm Cloud Properties. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Guo, J.; Zhao, C.; Cribb, M.C.; Dong, X.; Fan, J.; Gong, D.; Huang, J.; Jiang, M.; et al. East Asian study of tropospheric aerosols and their impact on regional clouds, precipitation, and climate (EAST-AIRCPC). J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 13026–13054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Data Source | Datasets/Parameters | Temporal Resolution | Spatial Resolution | Download |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Himawari-8 | Cloud optical thickness (COT); cloud effective radius (CER) | 10 min | 5 km | https://www.eorc.jaxa.jp/ptree/, accessed on 19 June 2022 |
| CloudSat (2B-CLDCLASS-LIDAR) | Cloud phase | 16 d | 2.5 km (along-track) × 1.4 km (cross-track) | http://www.cloudsat.cira.colostate.edu/, accessed on 16 November 2022 |
| ECMWF(ERA5) | Total column water vapor (TCWV) | Hourly | 0.25° × 0.25° | https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu/, accessed on 9 January 2023 |
| NASA(MERRA2) | Aerosol optical thickness (AOT) | Hourly | 0.5° × 0.625° | https://disc.gsfc.nasa.gov/, accessed on 6 January 2023 |
| MODIS (MOD13A3) | Normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) | Monthly | 1 km | https://ladsweb.modaps.eosdis.nasa.gov/, accessed on 27 December 2022 |
| National Tibetan Plateau Data Center | Temperature (TMP) | Monthly | 1 km | http://data.tpdc.ac.cn/, accessed on 26 December 2022 |
| National Tibetan Plateau Data Center | Potential evapotranspiration (PET) | Monthly | 1 km | http://data.tpdc.ac.cn/, accessed on 26 December 2022 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Jin, C.; Tian, Q.; Ding, X.; Ming, G. Regional Characteristics of Cloud Properties over the Loess Plateau. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2603. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102603
Zhang S, Jin C, Tian Q, Ding X, Ming G. Regional Characteristics of Cloud Properties over the Loess Plateau. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(10):2603. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102603
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shuhua, Cunyin Jin, Qianqian Tian, Xueqian Ding, and Guanghui Ming. 2023. "Regional Characteristics of Cloud Properties over the Loess Plateau" Remote Sensing 15, no. 10: 2603. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102603
APA StyleZhang, S., Jin, C., Tian, Q., Ding, X., & Ming, G. (2023). Regional Characteristics of Cloud Properties over the Loess Plateau. Remote Sensing, 15(10), 2603. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102603







