Absorbing Aerosol Optical Properties and Radiative Effects on Near-Surface Photochemistry in East Asia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methodology
2.1. Description of AERONET Data
2.2. Description of Radiation Transfer Model TUV and Experimental Setting
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optical Properties of the Aerosols
3.1.1. Spatial Variations in the Aerosol Optical Properties
3.1.2. Seasonal Variations in the Aerosol Optical Properties in BTH and YRD


3.1.3. Interannual Variations in AOD and AAOD in BTH and YRD
3.1.4. Frequency Distribution of the Aerosol Optical Properties BTH and YRD
3.1.5. Brief Discussion
3.2. UV Direct Radiative Forcing of Absorbing Aerosols


3.2.1. Spatial Variations in the DRF

3.2.2. Seasonal Variations in the DRF Induced by Absorbing Aerosols




3.3. Impacts Absorbing Aerosols on Near-Surface Photochemistry of Absorbing Aerosols
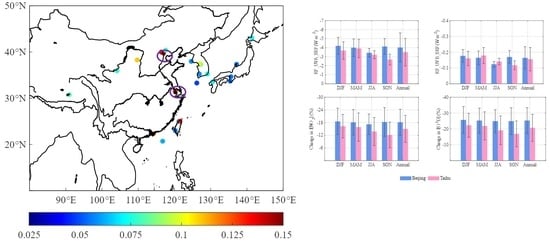
3.3.1. Spatial Variations in the Impacts of Absorbing Aerosols on the Actinic Flux and Photolysis Rates
3.3.2. Seasonal Variations in the Impacts of Absorbing Aerosols on the Actinic Flux and Photolysis Rates
3.3.3. Interannual Variations in the Impacts of Absorbing Aerosols on the in BTH and YRD

4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, X.J.; Zhao, P.S.; Xu, J.; Meng, W.; Pu, W.W.; Dong, F.; He, D.; Shi, Q.F. Analysis of a winter regional haze event and its formation mechanism in the North China Plain. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 5685–5696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Gong, S.; Yu, Y.; Yu, L.; Wu, L.; Mao, H.; Song, C.; Zhao, S.; Liu, H.; Li, X. Air pollution characteristics and their relation to meteorological conditions during 2014–2015 in major Chinese cities. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakamatsu, S.; Morikawa, T.; Ito, A. Air Pollution Trends in Japan between 1970 and 2012 and Impact of Urban Air Pollution Countermeasures. Asian J. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 7, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itahashi, S.; Hayami, H.; Shimadera, H.; Uno, I. The relationships between ground-based PM2.5 observation and space-borne aerosol optical depth. J. Jpn. Soc. Air Pollut. 2014, 49, 149–156. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, W.J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.Y.; Yang, Z.F.; Gao, S.H. Effect of cold wave on winter visibility over eastern China. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2015, 120, 2394–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.P.; Wang, H.J. Haze Days in North China and the associated atmospheric circulations based on daily visibility data from 1960 to 2012. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2015, 120, 5895–5909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Hu, M.; Du, B.; Guo, Q.; Tan, T.; Zheng, J.; Huang, X.; He, L.; Wu, Z.; Guo, S. Temporal and spatial distribution of PM(2.5) chemical composition in a coastal city of Southeast China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 605–606, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Wu, L.; Xie, Y.; He, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, T.; Lin, Y.; Jin, T.; Wang, A.; Liu, Y. Air pollution in China: Status and spatiotemporal variations. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 227, 334–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Ma, Y.L.; Duan, F.K.; He, K.B.; Wang, L.T.; Wei, Z.; Zhu, L.D.; Ma, T.; Li, H.; Ye, S.Q. Characteristics and formation of typical winter haze in Handan, one of the most polluted cities in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613, 1367–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Q.; Qu, W.J.; Li, C.; Zhao, C.H.; Zhong, X. Spatial distribution of wintertime air pollution in major cities over eastern China: Relationship with the evolution of trough, ridge and synoptic system over East Asia. Atmos. Res. 2018, 212, 186–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, S.H.L.; Gu, Y.F.; Shapiro, M.; Stephens, B. Air quality and acid deposition impacts of local emissions and transboundary air pollution in Japan and South Korea. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 13309–13323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Guo, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, D.; Chen, H. The climatology and trend of black carbon in China from 12-year ground observations. Clim. Dynam. 2019, 53, 5881–5892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Tong, D.; Shao, M.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, J.; He, H.; Liu, W.; et al. Drivers of improved PM2.5 air quality in China from 2013 to 2017. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 24463–24469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagami, M.; Ikemori, F.; Nakashima, H.; Hisatsune, K.; Ueda, K.; Wakamatsu, S.; Osada, K. Trends in PM2.5 Concentration in Nagoya, Japan, from 2003 to 2018 and Impacts of PM2.5 Countermeasures. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 590–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, C.A., 3rd; Dockery, D.W. Health effects of fine particulate air pollution: Lines that connect. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2006, 56, 709–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takebayashi, T.; Asakura, K.; Yamada, M. Exposure to PM2.5 and Effects on Human Health: Implications for Health Risk Assessment in Japan. J. Jpn. Soc. Air Pollut. 2011, 46, 70–76. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Mauzerall, D.L. Evaluating impacts of air pollution in China on public health: Implications for future air pollution and energy policies. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 1706–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Wang, S.; Jiang, J.; Fu, Q.; Chen, C.; Xu, B.; Yu, J.; Fu, X.; Hao, J. Long-term trend of haze pollution and impact of particulate matter in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 182, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Chen, Y.; Ye, X. Haze, air pollution, and health in China. Lancet 2013, 382, 2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.B.; Chen, J.; Li, W. An assessment of PM2.5 related health risks and impaired values of Beijing residents in a consecutive high-level exposure during heavy haze days. Environ. Sci. 2014, 35, 1–8, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, P.; Guo, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, W.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Lin, K. PM2.5, PM10 and health risk assessment of heavy metals in a typical printed circuit noards manufacturing workshop. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 2018–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehmood, K.; Wu, Y.; Wang, L.; Yu, S.; Seinfeld, J.H. Relative effects of open biomass burning and open crop straw burning on haze formation over central and eastern China: Modeling study driven by constrained emissions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 2419–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Wang, T.; Yue, X.; Li, S.; Zhuang, B.; Wang, M. Effects of atmospheric aerosols on terrestrial carbon fluxes and CO2 concentrations in China. Atmos. Res. 2020, 237, 104859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chylek, P.; Wong, J. Effect of absorbing aerosols on global radiation budget. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1995, 22, 929–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadhavi, H.; Jayaraman, A. Absorbing aerosols: Contribution of biomass burning and implications for radiative forcing. Ann. Geophys. 2010, 28, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, J.; Tegen, I.; Heinold, B.; Wolke, R. Direct and semi-direct radiative effects of absorbing aerosols in Europe: Results from a regional model. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L0982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C. Impact of anthropogenic absorbing aerosols on clouds and precipitation: A review of recent progresses. Atmos. Res. 2013, 122, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanap, S.D.; Pandithurai, G. The effect of absorbing aerosols on Indian monsoon circulation and rainfall: A review. Atmos. Res. 2015, 164, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, B.L.; Wang, T.J.; Liu, J.N.E.; Che, H.Z.; Han, Y.; Fu, Y.; Li, S.; Xie, M.; Li, M.M.; Chen, P.L.; et al. The optical properties, physical properties and direct radiative forcing of urban columnar aerosols in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 1419–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, B.L.; Chen, H.M.; Li, S.; Wang, T.J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L.J.; Liu, H.N.; Xie, M.; Chen, P.L.; Li, M.M.; et al. The direct effects of black carbon aerosols from different source sectors in East Asia in summer. Clim. Dynam. 2019, 53, 5293–5310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhuang, B.; Liu, J.; Li, S.; Wang, T.; Xie, X.; Xie, M.; Li, M.; Zhao, M. Regional Climate Responses in East Asia to the Black Carbon Aerosol Direct Effects from India and China in Summer. J. Clim. 2020, 33, 9783–9800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, S.E. The whitehouse effect—Shortwave radiative forcing of climate by anthropogenic aerosols: An overview. J. Aerosol Sci. 1996, 27, 359–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myhre, G.; Shindell, D.; Bréon, F.; Collins, W.; Zhang, H. Anthropogenic and Natural Radiative Forcing. In Climate Change 2013—The Physical Science Basis; Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.-K., Tignor, M., Allen, S.K., Boschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Bex, V., Midgley, P.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013; p. 1535. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson, M.Z. Studying the effects of aerosols on vertical photolysis rate coefficient and temperature profiles over an urban airshed. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1998, 103, 10593–10604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Carmichael, G.R. Sensitivity of photolysis rates and ozone production in the troposphere to aerosol properties. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1999, 104, 26307–26324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellouin, N.; Boucher, O.; Tanré, D.; Dubovik, O. Aerosol absorption over the clear-sky oceans deduced from POLDER-1 and AERONET observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 1748–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H. Interactions between tropospheric chemistry and aerosols in a unified general circulation model. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, AAC 1-1–AAC 1-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.F.; Zhang, R.J.; Pu, Y.F.; Zhang, L.M.; Ho, K.F.; Fu, C.B. Aerosol Optical Properties Observed at a Semi-Arid Rural Site in Northeastern China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2012, 12, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.J.; Zhuang, B.L.; Li, S.; Liu, J.; Xie, M.; Yin, C.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, C.; Zhu, J.L.; Ji, L.Q.; et al. The interactions between anthropogenic aerosols and the East Asian summer monsoon using RegCCMS. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 5602–5621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, B.L.; Li, S.; Wang, T.J.; Liu, J.; Chen, H.M.; Chen, P.L.; Li, M.M.; Xie, M. Interaction between the Black Carbon Aerosol Warming Effect and East Asian Monsoon Using RegCM4. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 9367–9388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson-Delmotte, V.; Zhai, P.; Pirani, A.; Connors, S.L.; Péan, C.; Berger, S.; Caud, N.; Chen, Y.; Goldfarb, L.; Gomis, M.I. (Eds.) IPCC, 2021: Summary for Policymakers. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 3–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, T.C.; Doherty, S.J.; Fahey, D.W.; Forster, P.M.; Berntsen, T.; DeAngelo, B.J.; Flanner, M.G.; Ghan, S.; Kärcher, B.; Koch, D.; et al. Bounding the role of black carbon in the climate system: A scientific assessment. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 5380–5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, Y.Q.; Niu, T.; Zhang, X.C.; Gong, S.L.; Zhang, Y.M.; Sun, J.Y. Atmospheric aerosol compositions in China: Spatial/temporal variability, chemical signature, regional haze distribution and comparisons with global aerosols. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 779–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, B.; Liu, Q.; Wang, T.; Yin, C.; Li, S.; Xie, M.; Jiang, F.; Mao, H. Investigation on semi-direct and indirect climate effects of fossil fuel black carbon aerosol over China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2013, 114, 651–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, B.L.; Wang, T.J.; Li, S.; Liu, J.; Talbot, R.; Mao, H.T.; Yang, X.Q.; Fu, C.B.; Yin, C.Q.; Zhu, J.L.; et al. Optical properties and radiative forcing of urban aerosols in Nanjing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 83, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Liao, H.; Mao, Y.; Ridley, D.A. Source sector and region contributions to concentration and direct radiative forcing of black carbon in China. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 124, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golden, D.M.; Manion, J. Applications of chemical kinetics. In Advances in Chemical Kinetics Dynamics; JAI Press: Greenwich, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Fenidel, W.; Matter, D.; Burtscher, H.; Schmidt-Ott, A. Interaction between carbon or iron aerosol particles and ozone. Atmos. Environ. 1995, 29, 967–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Zhu, T. Heterogeneous reactions on the surface of fine particles in the atmosphere. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2003, 48, 2005–2013+2267–2276, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.V.; Jacob, D.J.; Yantosca, R.M.; Chin, M.; Ginoux, P. Global and regional decreases in tropospheric oxidants from photochemical effects of aerosols. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, 4097–4115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, M.J.; Jacob, D.J. Impact of New Laboratory Studies of N2O5 Hydrolysis on Global Model Budgets of Tropospheric Nitrogen Oxides, Ozone, and OH. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, 297–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, H.; Han, S.; Tie, X.; Sun, M.; Liu, A. Evidence of impact of aerosols on surface ozone concentration in Tianjin, China. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 4672–4681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfister, G.G.; Wiedinmyer, C.; Emmons, L.K. Impacts of the fall 2007 California wildfires on surface ozone: Integrating local observations with global model simulations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L19814–L19818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Real, E.; Sartelet, K. Modeling of photolysis rates over Europe: Impact on chemical gaseous species and aerosols. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 1711–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, D.A.; Wigder, N.; Downey, N.; Pfister, G.; Boynard, A.; Reid, S.B. Impact of wildfires on ozone exceptional events in the Western U.S. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 11065–11072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, S.R.; Emmons, L.K.; Monks, S.A.; Law, K.S.; Ridley, D.A.; Turquety, S.; Tilmes, S.; Thomas, J.L.; Bouarar, I.; Flemming, J.; et al. Biomass burning influence on high-latitude tropospheric ozone and reactive nitrogen in summer 2008: A multi-model analysis based on POLMIP simulations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 6047–6068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Jacob, D.J.; Liao, H.; Zhu, J.; Shah, V.; Shen, L.; Bates, K.H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhai, S. A two-pollutant strategy for improving ozone and particulate air quality in China. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 906–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickerson, R.R.; Kondragunta, S.; Stenchikov, G.; Civerolo, K.L.; Doddridge, B.G.; Holben, B.N. The impact of aerosols on solar ultraviolet radiation and photochemical smog. Science 1997, 278, 827–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Yung, Y.L.; Seinfeld, J.H. Effects of aerosols on tropospheric photolysis rates in clear and cloudy atmospheres. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1999, 104, 23697–23707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, H.S.; Zender, C.S. Mineral dust and global tropospheric chemistry: Relative roles of photolysis and heterogeneous uptake. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2003, 108, 4672–4685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.H.; Zhang, R.Y.; Fan, J.W.; Tie, X.X. Impacts of black carbon aerosol on photolysis and ozone. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2005, 110, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astitha, M.; Kallos, G. Gas-phase and aerosol chemistry interactions in South Europe and the Mediterranean region. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2008, 9, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, Z.; Tie, X.; Madronich, S.; Li, G.; Massie, S. Simulation of regional dust and its effect on photochemistry in the Mexico City area during MILAGRO experiment. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 2549–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, T.; Han, Y.; Xie, M.; Li, S.; Zhuang, B.; Chen, P. Modeling of a severe dust event and its impacts on ozone photochemistry over the downstream Nanjing megacity of eastern China. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 160, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, W.-C.; Liao, H.; Chang, W. Past and future direct radiative forcing of nitrate aerosol in East Asia. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2014, 121, 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.W.; Tao, J.; Zhang, R.J.; Cheng, T.T.; Leng, C.P.; Chen, J.M.; Huang, G.H.; Li, X.; Zhu, Z.Q. Measurements of surface aerosol optical properties in winter of Shanghai. Atmos. Res. 2012, 109, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, S.; Liao, H.; Zhu, B. Impacts of aerosols on surface-layer ozone concentrations in China through heterogeneous reactions and changes in photolysis rates. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 85, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tie, X. Assessment of the global impact of aerosols on tropospheric oxidants. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, 204–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Han, Y.; Ma, X.; Liu, Z. Elevated heat pump effects of dust aerosol over Northwestern China during summer. Atmos. Res. 2018, 203, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, R.; Ma, X.; Jia, H.; Yu, F.; Sha, T.; Zan, Y. Aerosol radiative effects on tropospheric photochemistry with GEOS-Chem simulations. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 208, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, T.; Madronich, S.; Rivale, S.; Muhlia, A.; Mar, B. The influence of aerosols on photochemical smog in Mexico City. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 1765–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; An, J.L.; Su, X.Q.; Zhu, B.; Shi, S.S. Study on the influence of black carbon aerosol on photolysis coefficient in northern suburb of Nanjing. China Environ. Sci. 2020, 40, 1421–1428, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Bergin, M.H.; Greenwald, R.; Russell, P.B. Direct aerosol radiative forcing in the Yangtze delta region of China: Observation and model estimation. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2003, 108, ACL 4-1–PEM 8-27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergin, M.H.; Cass, G.R.; Xu, J.; Fang, C.; Zeng, L.M.; Yu, T.; Salmon, L.G.; Kiang, C.S.; Tang, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.H.; et al. Aerosol radiative, physical, and chemical properties in Beijing during June 1999. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2001, 106, 17969–17980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Bergin, M.H.; Yu, X.; Liu, G.; Zhao, J.; Carrico, C.M.; Baumann, K. Measurement of aerosol chemical, physical and radiative properties in the Yangtze delta region of China. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Tang, J.; Huang, J.; Mao, J.T.; Zhou, X.J.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Z.F.; Zhou, H.G. The measurement of aerosol optical properties at a rural site in Northern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 2229–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Li, C.C.; Lau, A.K.H.; Deng, Z.Z.; Mao, J.T.; Wang, M.H.; Liu, X.Y. An intensive study of aerosol optical properties in Beijing urban area. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 8903–8915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.H.; Chen, H.B.; Xia, X.G.; Li, Z.Q.; Cribb, M. Aerosol optical properties from the Atmospheric Radiation Measurement Mobile Facility at Shouxian, China. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2010, 115, D00K33–D00K45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Ma, J.; Raghavendra Kumar, K.; Zhu, B.; An, J.; He, J.; Li, M. Measurement and analysis of surface aerosol optical properties over urban Nanjing in the Chinese Yangtze River Delta. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 542, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Hong, Y.; Xu, L.; Chen, Y.; Du, W.; Chen, J. Optical properties of PM2.5 and the impacts of chemical compositions in the coastal city Xiamen in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 557–558, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, B.L.; Wang, T.J.; Liu, J.; Li, S.; Xie, M.; Han, Y.; Chen, P.L.; Hu, Q.D.; Yang, X.Q.; Fu, C.B.; et al. The surface aerosol optical properties in the urban area of Nanjing, west Yangtze River Delta, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 1143–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, C.W.; Chen, W.N.; Liang, W.A.; Das, S.K.; Nee, J.B. Optical properties of tropospheric aerosols based on measurements of lidar, sun-photometer, and visibility at Chung-Li (25°N, 121°E). Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 4128–4137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.A.; Che, H.Z.; Geng, F.H.; Xia, X.G.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhu, C.Z.; Chen, M.; Gao, W.; Guo, J.P. Aerosol optical properties based on ground measurements over the Chinese Yangtze Delta Region. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 2587–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.J.; Che, H.Z.; Zhang, X.Y.; Ma, Y.J.; Wang, Y.F.; Wang, X.X.; Liu, C.; Hou, B.; Che, H.C. Aerosol optical properties over urban and industrial region of Northeast China by using ground-based sun-photometer measurement. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 75, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Che, H.Z.; Xia, X.G.; Chen, H.B.; Goloub, P.; Zhang, W.X. Column-integrated aerosol optical and physical properties at a regional background atmosphere in North China Plain. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 84, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; Zhang, X.Y.; Xia, X.; Goloub, P.; Holben, B.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.C.; Wang, H.; Blarel, L.; et al. Ground-based aerosol climatology of China: Aerosol optical depths from the China Aerosol Remote Sensing Network (CARSNET) 2002–2013. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 7619–7652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.Z.; Qi, B.; Zhao, H.J.; Xia, X.G.; Eck, T.F.; Goloub, P.; Dubovik, O.; Estelles, V.; Cuevas-Agullo, E.; Blarel, L.; et al. Aerosol optical properties and direct radiative forcing based on measurements from the China Aerosol Remote Sensing Network (CARSNET) in eastern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 405–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Che, H.Z.; Chen, Q.L.; Xia, X.G.; Zhao, H.J.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, X.Y.; Shi, G.Y. Investigation of Aerosol Optical Depth (AOD) and Angstrom Exponent over the Desert Region of Northwestern China Based on Measurements from the China Aerosol Remote Sensing Network (CARSNET). Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2015, 15, 2024–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Che, H.; Zhu, J.; Chen, H.; Cong, Z.; Deng, X.; Fan, X.; Fu, Y.; Goloub, P.; Jiang, H.; et al. Ground-based remote sensing of aerosol climatology in China: Aerosol optical properties, direct radiative effect and its parameterization. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 124, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Che, H.Z.; Zhao, T.L.; Xia, X.G.; Gui, K.; An, L.C.; Qi, B.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.Q.; Yu, J.; et al. Aerosol Optical Properties over Beijing during the World Athletics Championships and Victory Day Military Parade in August and September 2015. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, B.; Hu, D.Y.; Che, H.Z.; Du, R.G.; Wu, Y.F.; Xia, X.G.; Zha, B.; Liu, J.; Niu, Y.W.; Wang, H.; et al. Seasonal Variation of Aerosol Optical Properties in an Urban Site of the Yangtze Delta Region of China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2016, 16, 2884–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowicz, K.M.; Flatau, P.J.; Remiszewska, J.; Witek, M.; Reid, E.A.; Reid, J.S.; Bucholtz, Z.; Hilben, B. Observations and modeling of the surface aerosol radiative forcing during UAE. J. Atmos. Sci. 2008, 65, 2877–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhlmann, J.; Quaas, J. How can aerosols affect the Asian summer monsoon? Assessment during three consecutive pre-monsoon seasons from CALIPSO satellite data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 4673–4688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Li, Z.; Holben, B.; Wang, P.; Eck, T.; Chen, H.; Cribb, M.; Zhao, Y. Aerosol optical properties and radiative effects in the Yangtze Delta region of China. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, S12–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Yoon, S.C.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.Y. Seasonal and monthly variations of columnar aerosol optical properties over east Asia determined from multi-year MODIS, LIDAR, and AERONET Sun/sky radiometer measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 1634–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Chung, C.E. Observationally-constrained estimates of global fine-mode AOD. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 2907–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panicker, A.S.; Lee, D.I.; Kumkar, Y.V.; Kim, D.; Maki, M.; Uyeda, H. Decadal climatological trends of aerosol optical parameters over three different environments in South Korea. Int. J. Climatol. 2013, 33, 1909–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, K.; Trautmann, T.; Blaschke, T.; Subhan, F. Changes in aerosol optical properties due to dust storms in the Middle East and Southwest Asia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 143, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.T.; Xu, C.; Duan, J.Y.; Wang, Y.F.; Leng, C.P.; Tao, J.; Che, H.Z.; He, Q.S.; Wu, Y.F.; Zhang, R.J.; et al. Seasonal variation and difference of aerosol optical properties in columnar and surface atmospheres over Shanghai. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 123, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.R.; Huang, J.P.; Holben, B.; Zhang, G.L. Comparison of key absorption and optical properties between pure and transported anthropogenic dust over East and Central Asia. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 15501–15516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Che, H.Z.; Chen, Q.L.; Zhu, J.; Gui, K.; Zheng, Y. Characteristics Analysis of Aerosol on Dust Weather Cases in Northwestern China from 2010 to 2012. Meteorol. Environ. Sci. 2016, 262, 33–40, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Q.; Zhang, H.; Choi, M.; Li, S.; Kondragunta, S.; Kim, J.; Holben, B.; Levy, R.C.; Liu, Y. Evaluation of VIIRS, GOCI, and MODIS Collection 6 AOD retrievals against ground sunphotometer observations over East Asia. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 1255–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, N.; Kumar, K.R.; Yu, X.; Yin, Y. Column-integrated aerosol optical properties and direct radiative forcing over the urban-industrial megacity Nanjing in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 17532–17552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Zheng, Y.; Shen, X.; Xing, L.; Che, H. Global Aerosol Classification Based on Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) and Satellite Observation. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1114–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.X.; Zhang, R.J.; Pu, Y.F. Recent researches on aerosol in China. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2001, 18, 576–586. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.Q. Aerosol and climate: A perspective from East Asia. In Observation, Theory and Modeling of Atmospheric Variability; World Scientific: Hackensack, NJ, USA, 2001; pp. 501–525. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.T.; Li, C.C. Observation study on aerosol radiative properties over China. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2005, 20, 306–321, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Madronich, S. Environmental Effects of UV; Tevini, M., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.; Tanre, D.; Buis, J.P.; Setzer, A.; Vermote, E.; Reagan, J.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Nakajima, T.; et al. AERONET—A federated instrument network and data archive for aerosol characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnov, A.; Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Dubovik, O.; Slutsker, I. Cloud-Screening and Quality Control Algorithms for the AERONET Database. Remote Sens. Environ. 2000, 73, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; King, M.D. A flexible inversion algorithm for retrieval of aerosol optical properties from Sun and sky radiance measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2000, 105, 20673–20696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; Sinyuk, A.; Lapyonok, T.; Holben, B.N.; Mishchenko, M.; Yang, P.; Eck, T.F.; Volten, H.; Muñoz, O.; Veihelmann, B.; et al. Application of spheroid models to account for aerosol particle nonsphericity in remote sensing of desert dust. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, 208–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.N.; Reid, J.S.; Dubovik, O.; Smirnov, A.; O’Neill, N.T.; Slutsker, I.; Kinne, S. Wavelength dependence of the optical depth of biomass burning, urban, and desert dust aerosols. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1999, 104, 31333–31349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, M.; Ginoux, P.; Kinne, S.; Torres, O.; Holben, B.N.; Duncan, B.N.; Martin, R.V.; Logan, J.A.; Higurashi, A.; Nakajima, T. Tropospheric aerosol optical thickness from the GOCART model and comparisons with satellite and Sun photometer measurements. J. Atmos. Sci. 2002, 59, 461–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remer, L.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Tanre, D.; Mattoo, S.; Chu, D.A.; Martins, J.V.; Li, R.R.; Ichoku, C.; Levy, R.C.; Kleidman, R.G.; et al. The MODIS aerosol algorithm, products, and validation. J. Atmos. Sci. 2005, 62, 947–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korras-Carraca, M.B.; Hatzianastassiou, N.; Matsoukas, C.; Gkikas, A.; Papadimas, C.D. The regime of aerosol asymmetry parameter over Europe, the Mediterranean and the Middle East based on MODIS satellite data: Evaluation against surface AERONET measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 13113–13132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angström, A. On the atmospheric transmission of sun radiation and on dust in the air. Geogr. Ann. 1929, 11, 156–166. [Google Scholar]
- D’Allura, A.; Kulkarni, S.; Carmichael, G.R.; Finardi, S.; Adhikary, B.; Wei, C.; Streets, D.; Zhang, Q.; Pierce, R.B.; Al-Saadi, J.A.; et al. Meteorological and air quality forecasting using the WRF–STEM model during the 2008ARCTAS field campaign. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 6901–6910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, Y.H.; Hodzic, A.; Barre, J.; Descombes, G.; Minnis, P. Quantifying errors in surface ozone predictions associated with clouds over the CONUS: A WRF-Chem modeling study using satellite cloud retrievals. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 7509–7525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, A.; Zakey, A.S.; Tawfik, A.B.; Solmon, F.; Giorgi, F.; Stordal, F.; Sillman, S.; Zaveri, R.A.; Steiner, A.L. Implementation and evaluation of online gas-phase chemistry within a regional climate model (RegCM-CHEM4). Geosci. Model Dev. 2012, 5, 741–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Tie, X.; Wu, D.; Bi, X.; Tan, H.; Li, F.; Jiang, C.; Xia, D. Study on the influence of aerosol on actinic flux and ozone in megecities (II)—Analysis of Numerical experiment. Guangdong Meterol. 2006, 28, 5–11, (In Chinese with an English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Palancar, G.G.; Lefer, B.L.; Hall, S.R.; Shaw, W.J.; Corr, C.A.; Herndon, S.C.; Slusser, J.R.; Madronich, S. Effect of aerosols and NO2 concentration on ultraviolet actinic flux near Mexico City during MILAGRO: Measurements and model calculations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 12, 19243–19275. [Google Scholar]
- Lingaswamy, A.P.; Arafath, S.M.; Balakrishnaiah, G.; Gopal, K.R.; Siva, K.; Raja, O.; Reddy, R.R.; Rao, T.C. Observations of trace gases, photolysis rate coefficients and model simulations over semi-arid region, India. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 158, 246–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Zhou, X.; Wu, D.; Tie, X.X.; Li, F.; Tan, H.; Bi, X.; Deng, T.; Jiang, D. Characterization of actinic flux and irradiances over Guangzhou region. China Environ. Sci. 2010, 30, 893–899, (In Chinese with an English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Tan, H.; Li, F.; Tie, X.; Wu, D.; Deng, T.; Zhou, X.; Deng, X. Attenuation of atmospheric aerosols to the surface ultraviolet radiation in Guangzhou. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2012, 57, 1684–1691, (In Chinese with an English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, B.; Fischer, C.A.; Madronich, S. Estimation of surface actinic flux from satellite (TOMS) ozone and cloud reflectivity measurements. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 25, 4321–4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palancar, G.G.; Toselli, B.M. Effects of meteorology and tropospheric aerosols on UV-B radiation: A 4-year study. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 118, 2749–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Carlson, B.E.; Lacis, A.A. Using single-scattering albedo spectral curvature to characterize East Asian aerosol mixtures. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2015, 120, 2037–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.N.; Sinyuk, A.; Pinker, R.T.; Goloub, P.; Chen, H.; Chatenet, B.; Li, Z.; Singh, R.P.; Tripathi, S.N.; et al. Climatological aspects of the optical properties of fine/coarse mode aerosol mixtures. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, 205–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, T.; Xie, M.; Han, Y.; Zhuang, B. Observed aerosol optical depth and angstrom exponent in urban area of Nanjing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 123, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, J.Y.; Shen, X.J.; Zhang, Y.M.; Che, H.; Ma, Q.L.; Zhang, Y.W.; Zhang, X.Y.; Ogren, J.A. Observations of relative humidity effects on aerosol light scattering in the Yangtze River Delta of China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 8439–8454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, G.L.; Dubovik, O.; Holben, B.N. Angstrom exponent and bimodal aerosol size distributions. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2006, 111, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnov, A.; Holben, B.N.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Dubovik, O.; Halthore, R.N. Optical Properties of Atmospheric Aerosol in Maritime Environments. J. Atmos. 2002, 59, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, Y.M.; Kim, Y.J.; Müller, D. Seasonal characteristics of lidar ratios measured with a Raman lidar at Gwangju, Korea in spring and autumn. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 2208–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.; Di Girolamo, L. A climatology of aerosol optical and microphysical properties over the Indian subcontinent from 9 years (2000–2008) of Multiangle Imaging Spectroradiometer (MISR) data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D15204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, P.B.; Kacenelenbogen, M.; Livingston, J.M.; Hasekamp, O.P.; Burton, S.P.; Schuster, G.L.; Johnson, M.S.; Knobelspiesse, K.D.; Redemann, J.; Ramachandran, S.; et al. A multiparameter aerosol classification method and its application to retrievals from spaceborne polarimetry. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 9838–9863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.Z.; Zhao, H.J.; Wu, Y.F.; Xia, X.A.; Zhu, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.Q.; Sun, J.Y.; Yu, J.; Zhang, X.Y.; et al. Analyses of aerosol optical properties and direct radiative forcing over urban and industrial regions in Northeast China. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2015, 127, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, M.; Lu, S.; Liu, Y.; Xie, X.; Chang, C.; Huang, S.; Chen, Z. Volatile organic compounds measured in summer in Beijing and their role in ground-level ozone formation. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, D00G06–D00G18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Streets, D.G.; Carmichael, G.R.; He, K.B.; Huo, H.; Kannari, A.; Klimont, Z.; Park, I.S.; Reddy, S.; Fu, J.S.; et al. Asian emissions in 2006 for the NASA INTEX-B mission. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 5131–5153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.J.; Cao, J.J.; Lee, S.C.; Shen, Z.X.; Ho, K.F. Carbonaceous aerosols in PM10 and pollution gases in winter in Beijing. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 19, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, Q.; Kurokawa, J.; Woo, J.H.; He, K.B.; Lu, Z.F.; Ohara, T.; Song, Y.; Streets, D.G.; Carmichael, G.R.; et al. MIX: A mosaic Asian anthropogenic emission inventory under the international collaboration framework of the MICS-Asia and HTAP. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 935–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhuang, B.; Liu, J.; Wang, T.; Li, S.; Xie, M.; Li, M.; Chen, P.; Zhao, M. Characteristics of ozone and particles in the near-surface atmosphere in the urban area of the Yangtze River Delta, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 4153–4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.N.; Dubovik, O.; Smirnov, A.; Goloub, P.; Chen, H.B.; Chatenet, B.; Gomes, L.; Zhang, X.Y.; Tsay, S.C.; et al. Columnar aerosol optical properties at AERONET sites in central eastern Asia and aerosol transport to the tropical mid-Pacific. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, D06202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, H.; Chin, M.; Rodriguez, J.M.; Yu, H.; Penner, J.E.; Strahan, S. Sensitivity of aerosol optical thickness and aerosol direct radiative effect to relative humidity. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 2375–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.J.; Shao, L.Y.; Buseck, P.R. Haze types in Beijing and the influence of agricultural biomass burning. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 8119–8130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Pan, X.L.; Tang, J.; Zhou, X.J.; Zhang, R.J.; Zeng, L.M. Hygroscopic growth of aerosol scattering coefficient: A comparative analysis between urban and suburban sites at winter in Beijing. Particuology 2009, 7, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, A.J.; Fu, C.B.; Yang, X.Q.; Sun, J.N.; Zheng, L.F.; Xie, Y.N.; Herrmann, E.; Nie, W.; Petäjä, T.; Kerminen, V.-M.; et al. Ozone and fine particle in the western Yangtze River Delta: An overview of 1 yr data at the SORPES station. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 5813–5830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.L.; Wang, Z.F.; Du, W.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Q.Q.; Fu, P.Q.; Pan, X.L.; Li, J.; Jayne, J.; Worsnop, D.R. Long-term real-time measurements of aerosol particle composition in Beijing, China: Seasonal variations, meteorological effects, and source analysis. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 10149–10165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, W.X.; Xu, X.Z.; Fang, B.; Zhang, Q.L.; Qian, X.D.; Zhang, W.J.; Chen, W.D.; Pu, W.; Wang, X. Dependence of columnar aerosol size distribution, optical properties, and chemical components on regional transport in Beijing. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 169, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.L.; Zhang, Y.H.; Kan, X.; Wang, J.G. Transport Paths and Identification for Potential Sources of Haze Pollution in the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration from 2014 to 2017. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.L.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zhao, T.L.; McKendry, I.G.; Jaffe, D.A.; Lu, N.M. Characterization of soil dust aerosol in China and its transport and distribution during 2001 ACE-Asia: 2. Model simulation and validation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, ACH4-1–ACH4-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prospero, J.M.; Ginoux, P.; Torres, O.; Nicholson, S.E.; Gill, T.E. Environmental characterization of global sources of atmospheric soil dust identified with the Nimbus 7 Total Ozone Mapping Spectrometer (TOMS) absorbing aerosol product. Rev. Geophys. 2002, 40, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.H.; Shi, S.Y.; Zhang, M.Y.; Li, J. Change Characteristic of Beijing Dust Weather and Its Sand-Dust Source Areas. Plateau Meteorol. 2007, 26, 1039–1044. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Shen, X.; Xing, L.; Che, H.; Holben, B.N. Analysis of Aerosol Type and Fine- and Coarse-mode Aerosol Direct Radiative Forcing over Regions in East and Southeast Asia Based on AERONET Version 3 Data. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2021, 21, 200503–200525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.Y. Analysis of Aerosol Types Based on Global AERONET Ground Observations. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, X.; Chen, H.; Goloub, P.; Zhang, W.; Chatenet, B.; Wang, P. A compilation of aerosol optical properties and calculation of direct radiative forcing over an urban region in northern China. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.M.; Bi, J.R.; Huang, J.P. Analysis on Aerosol Optical Property over Northern China from AERONET and SKYNET Observations. Plateau Meteorol. 2013, 32, 1293–1307, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Che, H.Z.; Zhang, X.Y.; Chen, H.B.; Damiri, B.; Goloub, P.; Li, Z.Q.; Zhang, X.C.; Wei, Y.; Zhou, H.G.; Dong, F.; et al. Instrument calibration and aerosol optical depth validation of the China Aerosol Remote Sensing Network. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2009, 114, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, M. Seasonal variability of aerosol optical properties over Beijing. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 4095–4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.N.; Zhu, B.; Yin, Y.; Fan, S.X.; Chen, A.J. Seasonal Variation of Columnar Aerosol Optical Properties in Yangtze River Delta in China. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2011, 28, 1326–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Che, H.Z.; Yang, L.K.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.Q.; Xia, X.G.; Zhao, H.J.; Wang, H.; Wang, D.Y.; Gui, K.; et al. Optical and Radiative Properties of Aerosols during a Severe Haze Episode over the North China Plain in December 2016. J. Meteorol. Res.-Prc. 2017, 31, 1045–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; Xia, X.; Zhu, J.; Li, Z.; Dubovik, O.; Holben, B.; Goloub, P.; Chen, H.; Estelles, V.; Cuevas-Agulló, E.; et al. Column aerosol optical properties and aerosol radiative forcing during a serious haze-fog month over North China Plain in 2013 based on ground-based sunphotometer measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 2125–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.; Kim, S.; Choi, S.; Choi, I. Regional-scale relationships between aerosol and summer monsoon circulation, and precipitation over Northeast Asia. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2010, 46, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Tao, S. Changes in wind speed over China during 1956–2004. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2010, 99, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, S. Temporal variation of wind speed in China for 1961–2007. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2011, 104, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, T.; Solmon, F.; Zhuang, B.; Wu, H.; Xie, M.; Han, Y.; Wang, X. Impact of aerosols on regional climate in southern and northern China during strong/weak East Asian summer monsoon years. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 4069–4081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, B.L.; Li, S.; Wang, T.J.; Deng, J.J.; Xie, M.; Yin, C.Q.; Zhu, J.L. Direct radiative forcing and climate effects of anthropogenic aerosols with different mixing states over China. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 79, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, P.; Ishizaka, Y.; Takamura, T. A study on aerosol optical properties in an urban atmosphere of Nagoya, Japan. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2009, 87, 19–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Che, H.Z.; Ma, J.Z.; Wang, Q.; Shi, G.Y.; Chen, H.B.; Goloub, P.; Hao, X.J. Aerosol radiative forcing under clear, hazy, foggy, and dusty weather conditions over Beijing, China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L06804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, K.; Trautmann, T.; Blaschke, T. Aerosol optical properties and radiative forcing over mega-city Karachi. Atmos. Res. 2011, 101, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.M.; Su, J.; Ackerman, T.P.; Fu, Q.; Huang, J.P.; Shi, J.S. Dust aerosol optical properties retrieval and radiative forcing over northwestern China during the 2008 China–U.S. joint field experiment. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D00K12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandradewi, J.; Prévôt, A.S.H.; Szidat, S.; Perron, N.; Alfarra, M.R.; Lanz, V.A.; Weingartner, E.; Baltensperger, U. Using aerosol light absorption measurements for the quantitative determination of wood burning and traffic emission contributions to particulate matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 3316–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosmüller, H.; Chakrabarty, R.K.; Ehlers, K.M.; Arnott, W.P. Absorption Ångström coefficient, brown carbon, and aerosols: Basic concepts, bulk matter, and spherical particles. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 1217–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curci, G.; Alyuz, U.; Baro, R.; Bianconi, R.; Bieser, J.; Christensen, J.H.; Colette, A.; Farrow, A.; Francis, X.; Jimenez-Guerrero, P.; et al. Modelling black carbon absorption of solar radiation: Combining external and internal mixing assumptions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 181–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lack, D.A.; Langridge, J.M. On the attribution of black and brown carbon light absorption using the Ångström exponent. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 10535–10543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, M.R.; Victoria Garcia, M.; Robinson, M.A.; Van Rooy, P.; Dietenberger, M.A.; Bergin, M.; Schauer, J.J. Investigation of black and brown carbon multiple-wavelength-dependent light absorption from biomass and fossil fuel combustion source emissions. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2015, 120, 6682–6697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Lei, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Zeng, Y.; Tao, J.; Zhu, C.; Cao, J.; Xu, H.; Liu, S. Methanol Extracted Brown Carbon in PM2.5 Over Xi’an, China: Seasonal Variation of Optical Properties and Sources Identification. Aerosol Sci. Eng. 2017, 1, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, J.; Yin, Y.; Zhu, B.; Feng, Q. Optical properties of black carbon aggregates with non-absorptive coating. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2017, 187, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, P.B.; Bergstrom, R.W.; Shinozuka, Y.; Clarke, A.D.; DeCarlo, P.F.; Jimenez, J.L.; Livingston, J.M.; Redemann, J.; Dubovik, O.; Strawa, A. Absorption Angstrom Exponent in AERONET and related data as an indicator of aerosol composition. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 1155–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadur, R.; Praveen, P.S.; Xu, Y.; Ramanathan, V. Solar absorption by elemental and brown carbon determined from spectral observations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 17366–17371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemura, T. Simulation of climate response to aerosol direct and indirect effects with aerosol transport-radiation model. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, 202–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Heald, C.L.; Sedlacek, A.J.; de Sá, S.S.; Martin, S.T.; Alexander, M.L.; Watson, T.B.; Aiken, A.C.; Springston, S.R.; Artaxo, P. Deriving brown carbon from multiwavelength absorption measurements: Method and application to AERONET and Aethalometer observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 12733–12752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Che, H.; Ma, Y.; Xia, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, P.; Wu, X. Temporal variability of the visibility, particulate matter mass concentration and aerosol optical properties over an urban site in Northeast China. Atmos. Res. 2015, 166, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zan, Y.; Ma, X.; Tian, R. A study on the influencing factors of tropospheric photolysis rate based on TUV model. China Environ. Sci. 2019, 39, 3707–3718, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Deng, X.; Zhou, X.; Wu, D.; Tie, X.; Tan, H.; Li, F.; Bi, X.; Deng, T.; Jiang, D. Effect of atmospheric aerosol on surface ozone variation over the Pearl River Delta region. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2011, 54, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Region | Site | Latitude (°N) | Longitude (°N) | Time Series (Year) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BTH | Beijing | 39.977 | 116.381 | 2005–2016 |
| Xianghe | 39.754 | 116.962 | 2005–2013 | |
| Xinglong | 40.396 | 117.578 | 2006–2012 | |
| Northwest China | SACOL | 35.946 | 104.137 | 2007–2012 |
| Yulin | 38.283 | 109.717 | 2001–2002 | |
| YRD | Taihu | 31.421 | 120.215 | 2006–2012 |
| QTP | NAM_CO | 30.773 | 90.962 | 2009 |
| Hong Kong | Hong_Kong_PolyU | 22.303 | 114.18 | 2006–2012 |
| Taiwan | Chen-Kung Uni | 23 | 120.217 | 2004–2014 |
| EPA-NCU | 24.968 | 121.185 | 2007–2014 | |
| Taipei | 25.03 | 121.5 | 2005–2015 | |
| Southern China | Dongsha_Island | 20.699 | 116.729 | 2010–2015 |
| Japan | Hokkaido_Uni | 43.075 | 141.341 | 2016 |
| Noto | 37.334 | 137.137 | 2008–2015 | |
| Osaka | 34.651 | 135.591 | 2004–2015 | |
| Shirahama | 33.693 | 135.357 | 2003–2014 | |
| Fukuoka | 33.524 | 130.875 | 2013–2015 | |
| Korea | Gangneung | 37.966 | 124.63 | 2015 |
| Seoul_SNU | 37.458 | 126.951 | 2002, 2012–2013 | |
| Hankuk_UFS | 37.339 | 127.266 | 2012–2016 | |
| Pusan_NU | 35.235 | 129.083 | 2015–2016 | |
| Gwangju_GIST | 35.228 | 126.843 | 2012–2016 | |
| Gosan_SNU | 33.292 | 126.162 | 2003–2014 |
| TUV Parameters | Settings |
|---|---|
| Location | All sites |
| Time | Observation period |
| Vertical resolution | 1 km |
| Radiative transfer scheme | δ-Eddington approximation |
| Site | Period | Total | MAM (%) | JJA (%) | SON (%) | DJF (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | 2005–2012 | 1375 | 33 | 12 | 24 | 31 |
| Taihu | 2005–2012 | 1519 | 35 | 9 | 22 | 34 |
| Beijing | Taihu | Beijing | Taihu | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J[NO2]_day (%) | DJF | −16.34 | −16.72 | J[NO2]_noon (%) | DJF | −18.77 | −18.57 |
| MAM | −14.62 | −14.45 | MAM | −16.77 | −18.23 | ||
| JJA | −12.37 | −13.17 | JJA | −14.74 | −13.96 | ||
| SON | −16.11 | −9.32 | SON | −16.88 | −11.26 | ||
| J[O1D] _day (%) | DJF | −22.07 | −22.73 | J[O1D]_noon (%) | DJF | −24.03 | −23.79 |
| MAM | −20.47 | −20.04 | MAM | −21.38 | −22.42 | ||
| JJA | −17.00 | −17.45 | JJA | −18.42 | −17.91 | ||
| SON | −21.74 | −12.54 | SON | −22.00 | −14.75 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, H.; Zhuang, B.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gao, Y.; Wei, W.; Lin, H.; Li, S.; et al. Absorbing Aerosol Optical Properties and Radiative Effects on Near-Surface Photochemistry in East Asia. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2779. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15112779
Chen H, Zhuang B, Liu J, Zhou Y, Hu Y, Chen Y, Gao Y, Wei W, Lin H, Li S, et al. Absorbing Aerosol Optical Properties and Radiative Effects on Near-Surface Photochemistry in East Asia. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(11):2779. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15112779
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Huimin, Bingliang Zhuang, Jane Liu, Yinan Zhou, Yaxin Hu, Yang Chen, Yiman Gao, Wen Wei, Huijuan Lin, Shu Li, and et al. 2023. "Absorbing Aerosol Optical Properties and Radiative Effects on Near-Surface Photochemistry in East Asia" Remote Sensing 15, no. 11: 2779. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15112779
APA StyleChen, H., Zhuang, B., Liu, J., Zhou, Y., Hu, Y., Chen, Y., Gao, Y., Wei, W., Lin, H., Li, S., Wang, T., Xie, M., & Li, M. (2023). Absorbing Aerosol Optical Properties and Radiative Effects on Near-Surface Photochemistry in East Asia. Remote Sensing, 15(11), 2779. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15112779